Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 41(2); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effect of a Simulation-based Education on Cardio-pulmonary Emergency Care Knowledge, Clinical Performance Ability and Problem Solving Process in New Nurses
- Yun Hee Kim, Keum Seong Jang
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(2):245-255.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.245
Published online: April 30, 2011
1Full-time Lecturer, Department of Nursing, Dong Shin University, Naju, Korea.
2Professor, College of Nursing, Chonnam National University Chonnam Research Institute of Nursing Science, Gwangju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jang, Keum Seong. College of Nursing, Chonnam National University, 5 Hak-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-190, Korea. Tel: +82-62-220-4955, Fax: +82-62-225-3307, jangks@chonnam.ac.kr
© 2011 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was conducted to examine the effects of simulation-based education regarding care in a cardio-pulmonary emergency care as related to knowledge, clinical performance ability, and problem solving process in new nurses.
-
Methods
- An equivalent control group pre-post test experimental design was used. Fifty new nurses were recruited, 26 nurses for the experimental group and 24 nurses for the control group. The simulation-based cardio-pulmonary emergency care education included lecture, skill training, team-based practice, and debriefing, and it was implemented with the experimental group for a week in May, 2009. Data were analyzed using frequency, ratio, chi-square, Fisher's exact probability and t-test with the SPSS program.
-
Results
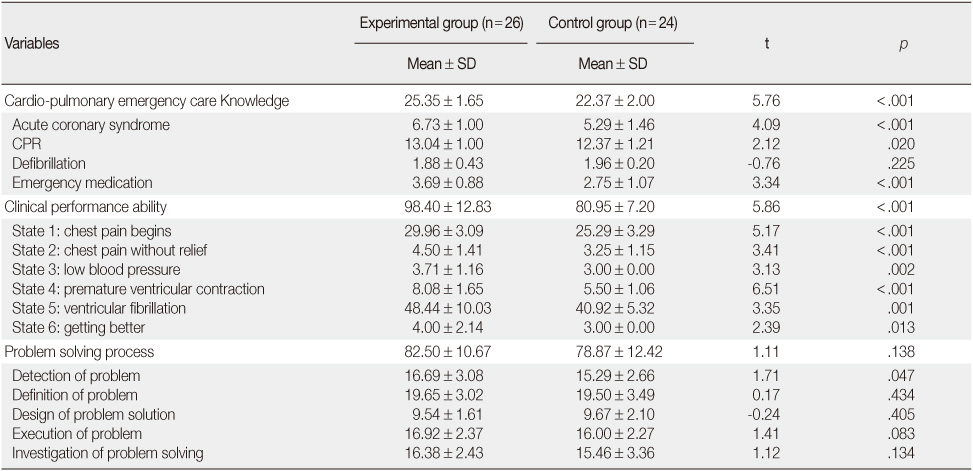
- The experimental group who had the simulation-based education showed significantly higher know-ledge (t=5.76, p<.001) and clinical performance ability (t=5.86, p<.001) for cardio-pulmonary emergency care compared with the control group who had traditional education but problem solving process was not included (t=1.11, p=.138).
-
Conclusion
- The results indicate that a simulation-based education is an effective teaching method to improve knowledge and clinical performance ability in new nurses learning cardio-pulmonary emergency care. Further study is needed to identify the effect of a simulation-based team discussion on cognitive outcome of clinical nurses such as problem solving skills.
This article is based on a part of the first author's doctoral dissertation from Chonnam National University.
- 1. Ackermann AD, Kenny G, Walker C. Simulator programs for new nurses' orientation. Journal for Nurses in Staff Development. 2007;23:136–139.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Alinier G, Hunt WB, Gordon R. Determining the value of simulation in nurse education: Study design and initial results. Nurse Education in Practice. 2004;4:200–207.ArticlePubMed
- 3. American Heart Association. Advanced cardiovascular life support. 2006a;Dallas, TX, American Heart Association.
- 4. American Heart Association. Basic life support for healthcare providers. 2006b;Dallas, TX, American Heart Association.
- 5. Back CY. Effects of advanced cardiac life support simulation-based training on nurses' competence in critical care setting. 2006;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 6. Bond WF, Spillane L. The use of simulation for emergency medicine resident assessment. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2002;9:1295–1298.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Brannan JD, White A, Bezanson JL. Simulator effects on cognitive skills and confidence levels. The Journal of Nursing Education. 2008;47:495–500.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Bremner MN, Aduddell K, Bennett DN, VanGeest JB. The use of human patient simulators best practices with novice nursing students. Nurse Educator. 2006;31:170–174.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Chen PT, Cheng HW, Yen CR, Yin IW, Huang YC, Wang CC, et al. Instructor-based real-time multimedia medical simulation to update concepts of difficult airway management for experienced airway practitioners. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association. 2008;71:174–179.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Crofts JF, Draycott TJ, Winter C, Hunt LP, Akande VA. Change in knowledge of midwives and obstericians following obsteric emergency training: A randomized controlled trial of local hospital, simulation centre and teamwork training. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 2007;114:1534–1541.PubMed
- 11. Hoyt P. An international approach to problem solving for better health nursing™(PSBHN). International Nursing Review. 2007;54:100–106.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Jeffries PR. A framework for designing, implementing, and evaluating simulations used as teaching strategies in nursing. Nursing Education Perspectives. 2005;26:96–103.PubMed
- 13. Kang LW, Lee EJ. A Study on new nurse's job analysis for improvement of efficiently nursing educational curriculum. Journal of Gachon. 2001;29:59–73.
- 14. Kim NY. The effects of web-based evidence-based nursing job education on the job knowledge, performance and motivation. 2005;Gwangju, Chonnam National University. Doctoral dissertation.
- 15. Kim YM, Oh YM, Kim HJ, Lee WJ, Im TH, Chung HS, et al. Development and pilot applications of simulation-based comprehensive emergency airway management courses. Journal of The Korean Society of Emergency Medicine. 2007;18:1–9.
- 16. Ko CH. The effect of simulation-based training on the competence of basic life support of the students emergency medical technology. Journal of the Korean Society of Emergency Medical Technology. 2007;11(3):31–45.
- 17. Lee JS. The effects of process behaviors on problem solving performance on various test. 1978;Chicago, USA, University of Chicago. Doctoral dissertation.
- 18. Lim NY, Yun SN, Kim JE, Lee YS, Jung YY, Song JH. Frequency and importance of nurse's job in new graduate nurses working in musculoskeletal ward. Journal of Rheumatology Health. 2003;13:108–118.
- 19. McCausland LL, Curran CC, Cataldi P. Use of human simulator for undergraduate nurse education. International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship. 2004;1:Article23. PubMed
- 20. Medley CF, Horne C. Using simulation technology for undergraduate nursing education. Journal of Nursing Education. 2005;44:31–34.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Nehring WN, Lashley FR. Current use and opinions regarding human patient simulators in nursing education: an international survey. Nursing Education Perspectives. 2004;25:244–248.PubMed
- 22. Oh SH, Jang KS, Choi JY. Protocol development of cardiopulmonary resuscitation nursing tasks targeting patients with ventricular fibrillation generation. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2009;15:203–215.
- 23. Park JW, Woo OK. The effect of PBL (problem-based learning) on problem solving process by learner's metacognitive level. Journal of Educational Technology. 1999;15(3):55–81.
- 24. Ragsdale MA, Mueller J. Plan, do, study, act model to improve an orientation program. Journal of Nursing Care Quality. 2005;20:268–272.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Silvestri LA. Saunders Q & A Review for NCLEX-RN. 2002;Philadelphia, PA, W. B. Saunders Company.
- 26. Steinwachs B. How to facilitate a debriefing. Simulation Gaming. 1992;23:186–195.ArticlePDF
- 27. Turcato N, Robertson C, Covert K. Simulation-based education: What's in it for nurse anesthesia educators? AANA Journal. 2008;76:257–262.PubMed
- 28. Wayne DB, Butter J, Viva J, Fudala MJ, Lindquist LA, Feinglass J, et al. Simulation-based training of internal medicine residents in advanced cardiac life support protocols: A randomized trial. Teaching and Learning in Medicine. 2005;17:210–216.PubMed
- 29. Yang JJ. Development and evaluation of a simulation-based education course for nursing students. Journal of Korean Academy of Adult Nursing. 2008;20:548–560.
REFERENCES
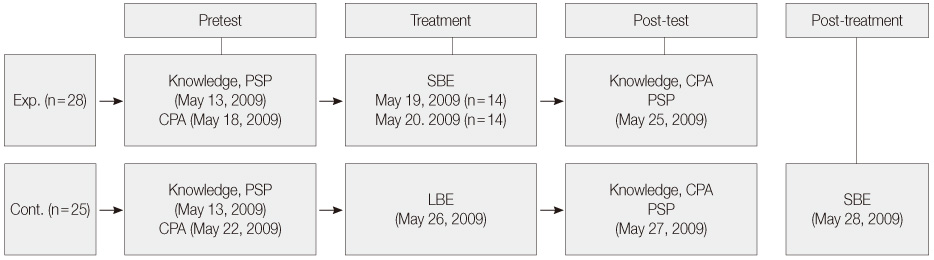
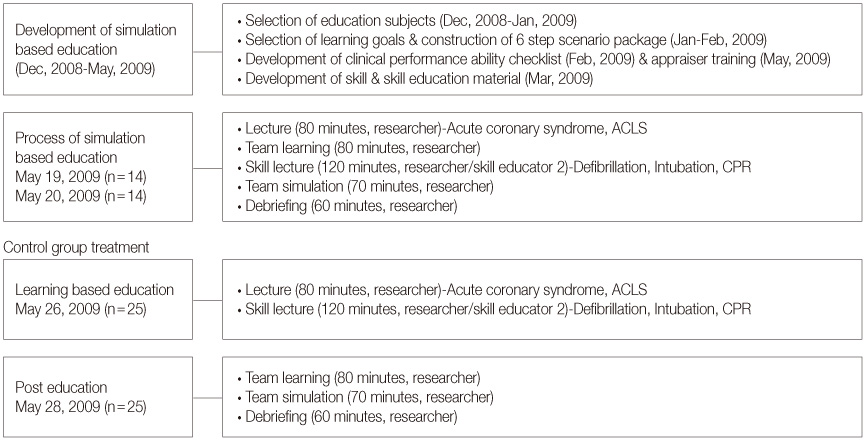
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Assessing the Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Education in Emerging Infectious Disease Management
Sol Yoon, Su Hyun Kim
Simulation in Healthcare: The Journal of the Society for Simulation in Healthcare.2025; 20(2): 118. CrossRef - Effectiveness of room-of-error interventions for healthcare providers: a systematic review
Su Jin Jung, Jiwon Kang, Youngjin Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of “Online–Simulation–Bedside” Three‐Step Teaching Method in Team Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Skills Training of Emergency Department and Critical Care Nursing Interns—An Analysis Based on Kirkpatrick Model
Huan Liu, Hui Huang, Miaoya Li, Ping Mao, Aidi Zhang, Yanting Sun, Zhaoxun Liu, Hong Tao, Sha Zhao, Yuting Xia, Jiandang Zhou, Jinxin Liu, César Leal Costa
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in simulation-based nursing education: Insights from a bibliometric analysis of temporal trends
Minji Mun, Minsung Kim, Kyungmi Woo
Nurse Education Today.2025; 151: 106719. CrossRef - Impact of Educational Intervention on Noninvasive Ventilation (NIV) in Nurses and Students
Elsa Pla‐Canalda, María F. Jiménez‐Herrera, José Fernández‐Sáez, Pablo Concha‐Martínez, Estrella Martínez‐Segura
The Clinical Teacher.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Implementation and Evaluation of an Emergency Response Training Program for Newly Graduated Nurses: A Scoping Review
Jeonghyun Kim, Minjae Lee, Miji Lee
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2024; 12(1): 59. CrossRef - Comparing Simulation Based and Lecture Based Education on Knowledge Acquisition and Long Term Retention in Medical Students
Kh. Ibragimov, A. Axmedov, N. Yarmukhamedova, M. Ravshanova
Virtual Technologies in Medicine.2024; 1(4): 328. CrossRef - A comparison between the effects of simulation of basic CPR training and workshops on firefighters’ knowledge and skills: experimental study
Amir Faghihi, Zeinab Naderi, Mohammad Mehdi Keshtkar, Leila Nikrouz, Mostafa Bijani
BMC Medical Education.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of a Simulation-Based Patient Safety Education Program on Compliance with Patient Safety, Perception of Patient Safety Culture, and Educational Satisfaction of Operating Room Nurses
OkBun Park, MiYang Jeon, MiSeon Kim, ByeolAh Kim, HyeonCheol Jeong
Healthcare.2023; 11(21): 2824. CrossRef - The Effect of Simulation- Based Korean Advanced Life Support on Emergency Management Knowledge, Clinical Performance Ability, Performer Confidence and Learning Ethnicity of New Nurses
Eunmi Nam, Sangsuk Kim, Youngsil Choi
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2023; 11(2): 31. CrossRef - The Effect of Simulation Method on Nursing Students’ Burn Patient Care Planning: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Müjgan Onarıcı, Mevlüde Karadağ
Journal of Burn Care & Research.2021; 42(5): 1011. CrossRef - Infection Control Education Programs for Nursing Students: A Systematic Review
Hayoung Park, Yoojin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(2): 237. CrossRef - The Effect of a Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Simulation Program on General Ward Nurses’ Knowledge and Self-Efficacy
Moon-Sook Kim, Mi-Hee Seo, Jin-Young Jung, Jinhyun Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(6): 2877. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study to Develop a Virtual Reality Based Simulation Training Program for Hypovolemic Shock Nursing Care: A Qualitative Study Using Focus Group Interview
Jaehee Jeon, Sihyun Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(4): 417. CrossRef - The Relationship between Self-Directed Learning and Problem-Solving Ability: The Mediating Role of Academic Self-Efficacy and Self-Regulated Learning among Nursing Students
Younghui Hwang, Jihyun Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1738. CrossRef - Effects of case-based confusion assessment methods for intensive care unit training on delirium knowledge and delirium assessment accuracy of intensive care units: A quasi-experimental study
Young-Nam Kim, Dong-Hee Kim
Nurse Education Today.2021; 103: 104954. CrossRef - Effects of Virtual Reality Simulation Program Regarding High-risk Neonatal Infection Control on Nursing Students
Mi Yu, Miran Yang, Boram Ku, Jon S. Mann
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(3): 189. CrossRef - The effects of a maternal nursing competency reinforcement program on nursing students’ problem-solving ability, emotional intelligence, self-directed learning ability, and maternal nursing performance in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Sun-Hee Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 230. CrossRef - Correlation between Sedation Knowledge, Clinical Decision Making and Nursing Competence in Sedation Practice among ICU Nurses
Gyoo-Yeong CHO, Yeon-A KIM
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(1): 204. CrossRef - The Effects of Simulation-Based Advanced Life Support Education for Nursing Students
Sung Hwan Kim, Barry Issenberg, Young Sook Roh
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2020; 38(5): 240. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Effects of Virtual Reality Simulation on Nursing Students Caring for Children with Asthma
Kyung-Ah Kang, Shin-Jeong Kim, Myung-Nam Lee, Mikang Kim, Sunghee Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(22): 8417. CrossRef - Education Programs for Newly Graduated Nurses in Hospitals: A Scoping Review
Mijung Kim, Sujin Shin, Inyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(5): 440. CrossRef - The Effect and Development of a Simulation Learning Module based on Schizophrenic Patients Care of Nursing Students
Dong Hee Seo, Soo Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2020; 29(2): 106. CrossRef - Educational Simulation Program Based on Korean Triage and Acuity Scale
Jae-Hyuk Jang, Sang Suk Kim, Sunghee Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 9018. CrossRef - The Effects of Simulation Education for New Nurses on Emergency Management Using Low-fidelity Simulator
Young Hee Lee, Hye Young Ahn
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 331. CrossRef - The Effects of Jigsaw Cooperation Learning on Communication Ability, Problem Solving Ability, Critical Thinking Disposition, Self-directed Learning Ability and Cooperation of Nursing Students
Myo Gyeong Kim, Hye Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(4): 508. CrossRef - Nursing competency and educational needs for clinical practice of Korean nurses
Sun-Ok Kim, Yun-Jung Choi
Nurse Education in Practice.2019; 34: 43. CrossRef - A meta-analysis for comparing effective teaching in clinical education
Pin-Hsiang Huang, Matthew Haywood, Anthony O’Sullivan, Boaz Shulruf
Medical Teacher.2019; 41(10): 1129. CrossRef - Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA) to Improve Emergency Care for Novice Nurses
Hayoung Park, Yoojin Kim, Sang Hui Chu
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(3): 155. CrossRef - Development and Effects a Simulation-based Emergency Airway Management Education Program for Nurses in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Minjung Kim, Sunghee Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(4): 518. CrossRef - Simulation scenarios in Korea according to the learning objectives of adult health nursing: A literature review
Ae Ri Jang, In Kyoung Lee, Hang Nan Cho, Piotr Mikiewicz
Cogent Education.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A Structural Model on the Nursing Competencies of Nursing Simulation Learners
Soo Jin Park, Eun Sun Ji
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 588. CrossRef - Effect of Practical Delivery-nursing Simulation Education on Team-based Learning on the Nursing Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Clinical Competence of Nursing Students
Sun Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(2): 150. CrossRef - Psikiyatride ve İletişim Eğitiminde Simüle Hasta Uygulamaları
Neşe Mercan, Celale Tangül Özcan, Mehmet Sinan Aydın
Psikiyatride Guncel Yaklasimlar - Current Approaches in Psychiatry.2018; 10(3): 292. CrossRef - Effects of a simulated emergency airway management education program on the self‐efficacy and clinical performance of intensive care unit nurses
Myong‐Ja Han, Ju‐Ry Lee, Yu‐Jung Shin, Jeong‐Suk Son, Eun‐Joo Choi, Yun‐Hee Oh, Soon‐Haeng Lee, Hye‐Ran Choi
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2018; 15(3): 258. CrossRef - The Factor Influencing Problem Solving Ability of Nursing Students in Nursing Simulation Learning
Gyoo-Yeong CHO
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2017; 29(4): 1083. CrossRef - Effect of Team Debriefing in Simulation-based Cardiac Arrest Emergency Nursing Education
SangJin Ko, Eun-Hee Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(6): 667. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Simulation Practice Program about Family centered Delivery Care
Seung Hee Yang, Sehoon Hong
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(1): 52. CrossRef - Effects of Maternity Nursing Simulation using High-fidelity Patient Simulator for Undergraduate Nursing Students
Ahrin Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(3): 177. CrossRef - Standard instruction versus simulation: Educating registered nurses in the early recognition of patient deterioration in paediatric critical care
Jessica O'Leary, Robyn Nash, Peter Lewis
Nurse Education Today.2016; 36: 287. CrossRef - Nurses' Perception of Accreditation, Awareness and Performance of Infection Control in an Accredited Healthcare System
Moon-Hee Hong, Ju-Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(2): 167. CrossRef - Persistence of Integrated Nursing Simulation Program Effectiveness*
Sun-Kyoung Lee, Sun-Hee Kim, Sun-Nam Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(3): 283. CrossRef - Effects of Blended Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Defibrillation E-learning on Nursing Students’ Self-efficacy, Problem Solving, and Psychomotor Skills
Ju Young Park, Chung Hee Woo, Jae Yong Yoo
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2016; 34(6): 272. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Student Learning with a Simulation Program focusing on Cardiac Arrest in Knowledge, Self-confidence, Critical Thinking, and Clinical Performance Ability
Min-Jeong Chae, Soon-Hee Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(4): 447. CrossRef - The Effects of Trauma-patient Training Education Using Simulation on Knowledge, Satisfaction and Problem-solving in Emergency medical Students
Tae-Young Moon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(4): 710. CrossRef - Relationships among Information Resources Use, Problem Solving Ability, Nursing Information Literacy Competency in General Hospital Nurses
Yeong-Mi Ha, Jeong-Eui Cho, Seung-Kyoung Yang
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(7): 289. CrossRef - First experiences of high‐fidelity simulation training in junior nursing students inKorea
Suk Jeong Lee, Sang Suk Kim, Young‐Mi Park
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2015; 12(3): 222. CrossRef - Comparison of the Problem Solving Abilities as Simulation Learning Stage -Focused on Care for Patients with Asthma in Emergency Units
Young-Hee Kim, Kyung-Ah Kang, Myung-Nam Lee, Yun-Kyung Kim, Ye-Jean Kim, Jung-Jae Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Jeong
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2015; 15(1): 495. CrossRef - The Development and Effects of a Tailored Simulation Learning Program for New Nursing Staffs in Intensive Care Units and Emergency Rooms
Eun Jung Kim, Hee-Young Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 95. CrossRef - The Effects of Video-based Peer assisted Learning in Standardized Patients Simulation: Pre and Post Operative Care
In-Hee Park, Sujin Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(1): 73. CrossRef - The Effect of High-Fidelity Simulation Practice Related with Classical Education of Medical Surgical Nursing
Yeol-eo Chyn, Kyoung-Mi Kim, Hye-Young Hwang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(12): 8176. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Integrated Simulation Program (Maternal-Child) for Nursing Students
Hyun Jung Park, Sun Hee Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2015; 21(4): 293. CrossRef - Effect of Simulation-based Advanced Cardiopulmonary Life Support Education for Nursing Students Hospitals
Hyo-Ju Jung, Min-Jeong Chae
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(3): 127. CrossRef - Effects of High-fidelity Simulation-based Education on Nursing Care for Patients with Acute Chest Pain
Sang-Young Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(3): 1515. CrossRef - Effect of a simulation-based program for post-operative care of emergency patients
Min-Jeong Chae, Soon-Hee Choi, Jeoung-Suk Kim
The Korean Journal of Emergency Medical Services.2014; 18(3): 91. CrossRef - Effects of Basic Clinical Practice Program in Academic Motivation, Critical Thinking and Clinical Nursing Competence of Nursing Students
In-Soon Seo, Su-Min Oh, Dongwon Choi, Hee-Ok Park, Rye-Won Ma
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(4): 2276. CrossRef - Effect of Simulation-based Practice by applying Problem based Learning on Problem Solving Process, Self-confidence in Clinical Performance and Nursing Competence
Young A Song
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(4): 246. CrossRef - Effects of Multi-mode Simulation Learning on Nursing Students' Critical Thinking Disposition, Problem Solving Process, and Clinical Competence
Eun Ko, Hye Young Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(1): 107. CrossRef - Critical Thinking Disposition, Problem Solving Process, and Simulation-Based Assessment of Clinical Competence of Nursing Students in Pediatric Nursing.
Sunghee Kim, Hyuna Nam, Miok Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(4): 294. CrossRef - The Impact of a Simulation-based Education Program for Emergency Airway Management on Self-efficacy and Clinical Performance among Nurses
Mi-Ja Lee, Dukyoo Jung
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Simulation on Knowledge of Advanced Cardiac Life Support, Knowledge Retention, and Confidence of Nursing Students in Jordan
Loai I. Tawalbeh, Ahmad Tubaishat
Journal of Nursing Education.2014; 53(1): 38. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Scenario for Simulation Learning of Care for Children with Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Neonatal Intensive Care Units.
Myung Nam Lee, Hee Soon Kim, Hyun Chul Jung, Young Hee Kim, Kyung Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of a Simulation-based Training for Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support on the Knowledge and Competence for Nursing Students
Seung-Hwa Shin, Mal-Suk Kwon, Sang-Min Kwon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(11): 5819. CrossRef - Development and Applicability Evaluation of an Emergent Care Management Simulation Practicum for Nursing Students
Hea Kung Hur, SoMi Park, Yoon Hee Shin, Young Mi Lim, GiYon Kim, Ki Kyong Kim, Hyang Ok Choi, Ji Hea Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(2): 228. CrossRef - Achievements of Nursing Students among Simulation and Traditional Education of Bleeding Patients
Eun Hee Choi, Kyung Nam Kwon, Eun Ju Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(1): 52. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Simulation-based Education Program for Newborn Emergency Care
So Young Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(4): 468. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Korean Studies on Simulation within Nursing Education
Jung-Hee Kim, In-Hee Park, Sujin Shin
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(3): 307. CrossRef - Lived Experiences of New Graduate Nurses
Yeonok Suh, Kyungwoo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(2): 227. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Practice and Simulation-Based Practice for Obstetrical Nursing
Sun-Ae Kim, Sun-Kyung Lee, Hyun Ju Chae
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(3): 180. CrossRef - Educational Needs in the Development of a Simulation Based Program on Neonatal Emergency Care for Nursing Students
So-Young Yoo, Sung-Hee Kim, Ja-Hyung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(4): 170. CrossRef - Nurses' Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Performance during the First 5 minutes in In-Situ Simulated Cardiac Arrest
Eun Jung Kim, Kyeong Ryong Lee, Myung Hyun Lee, Jiyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 361. CrossRef - The Development and Evaluation of a New Educational Program, Introduction to Clinical Nursing, for Third Year Nursing Students
Kyung-Ae Song, Hyun-Jung Park, Hye-A Yeom, Jong-Eun Lee, Ga-Eul Joo, Hee-Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(3): 322. CrossRef
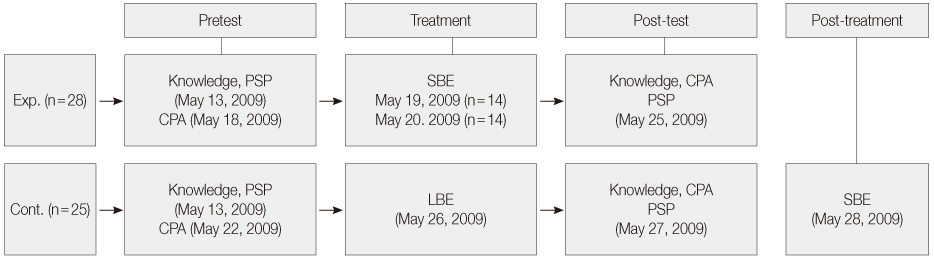
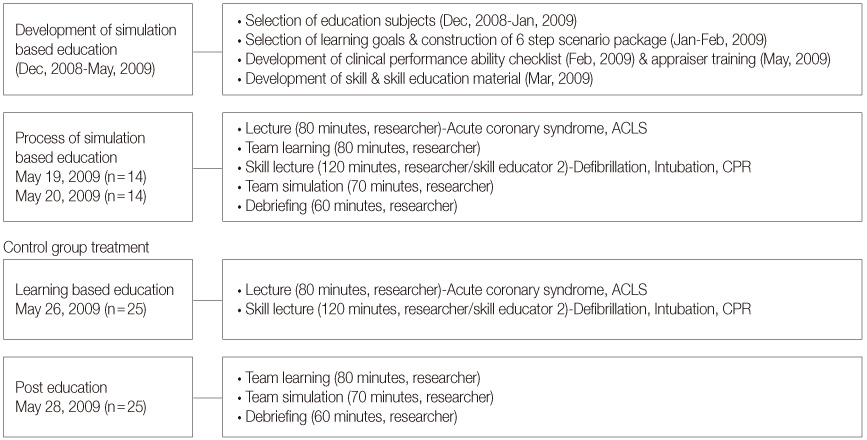
Figure 1
Figure 2
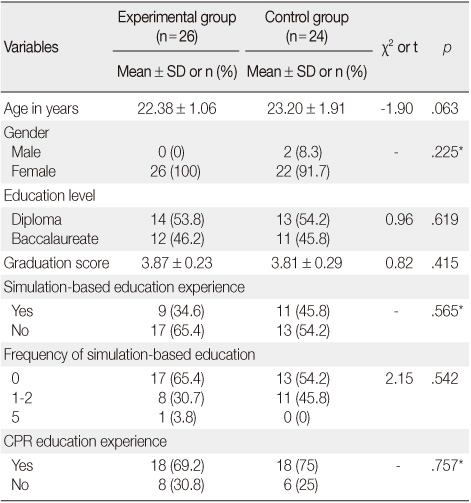
Homogeneity Test for General Characteristics between Experimental and Control Group (N=50)
*Fisher exact test.
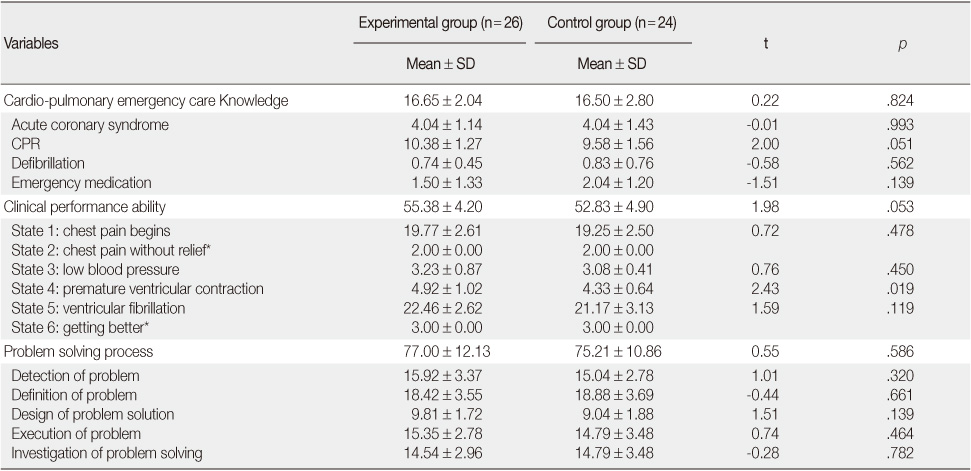
Homogeneity Test of Cardio-pulmonary Emergency Care Knowledge, Clinical Performance Ability, Problem Solving Process between Experimental and Control Group (N=50)
*Did not analyze with t-test as standard deviation is zero; CPR=cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Comparison of Dependent Variables between Experimental and Control Group (N=50)
*Fisher exact test.
*Did not analyze with t-test as standard deviation is zero; CPR=cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

