Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(6); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- A Study on Participation in Clinical Decision Making by Home Healthcare Nurses
- Se Young Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(6):892-902.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.6.892
Published online: December 31, 2010
Full-time Lecturer, College of Nursing, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to : Kim, Se Young. College of Nursing, Eulji University, 143-5 Yongdu-dong, Jung-gu, Daejeon 301-746, Korea. Tel: 82-42-259-1718, Fax: 82-42-259-1709, sarakimk@yahoo.co.kr
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to identify participation by home healthcare nurses in clinical decision making and factors influencing clinical decision making.
-
Methods
- A descriptive survey was used to collect data from 68 home healthcare nurses in 22 hospital-based home healthcare services in Korea. To investigate participation, the researcher developed 3 scenarios through interviews with 5 home healthcare nurses. A self-report questionnaire composed of tools for characteristics, factors of clinical decision making, and participation was used.
-
Results
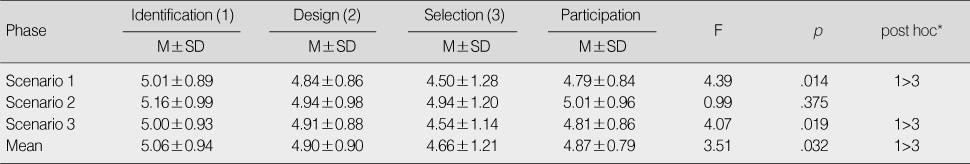
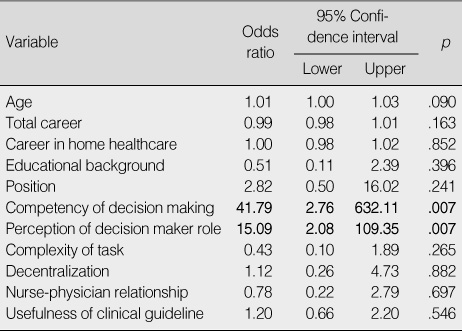
- Participation was relatively high, but significantly lower in the design phase (F=3.51, p=.032). Competency in clinical decision making (r=.45, p<.001), perception of the decision maker role (r=.47, p<.001), and perception of the utility of clinical practice guidelines (r=.25, p=.043) were significantly correlated with participation. Competency in clinical decision making (Odds ratio [OR]=41.79, p=.007) and perception of the decision maker role (OR=15.09, p=.007) were significant factors predicting participation in clinical decision making by home healthcare nurses.
-
Conclusion
- In order to encourage participation in clinical decision making, education programs should be provided to home healthcare nurses. Official clinical practice guidelines should be used to support home healthcare nurses' participation in clinical decision making in cases where they can identify and solve the patient health problems.
*This article is a revision of the first author's doctoral dissertation from Seoul National University.
- 1. Anthony MK. The relationship between decentralization and expertise to participation in decision making: Among staff nurses working in acute care hospitals. 1995;Cleveland, USA, Case Western Reserve University. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation.
- 2. Bakalis N. Clinical decision-making in cardiac nursing: A review of the literature. Nursing Standard. 2006;21(12):39–46.Article
- 3. Bakalis N, Watson R. Nurses's decision-making in clinical practice. Nursing Standard. 2005;19(23):33–39.Article
- 4. Boney J, Baker J. Strategies for teaching clinical decision-making. Nurse Education Today. 1997;17:16–21.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Bucknall T, Thomas S. Nurses' reflections on problems associated with decision making in critical care settings. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997;25:229–237.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Caputo L, Mior S. The role of clinical experience and knowledge in clinical decision making. Topics in Clinical Chiropractic. 1998;5(2):10–18.
- 7. Chi SA, Yoo HS. Concept analysis of professionalnurse autonomy. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2001;31:781–792.ArticlePDF
- 8. Choi HJ. A study on nurse's decision making process and related factors for patient care. 1997;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 9. Chun MH. A study on the decision making process of emergency department nurses. 2005;Jinju, Kyeongsang University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 10. Davies N. Nurse-initiated extubation following cardiac surgery. Intensive and Critical Care Nursing. 1997;13:77–79.ArticlePubMed
- 11. de la Cruz FA. Clinical decision-making styles of home healthcare nurses. Image--the Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 1994;26:222–226.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Hansen AC, Thomas DB. A conceptualization of decision making: Its application to a study of role and situation-related difference in priority decisions. Nursing Research. 1968;17:436–443.PubMed
- 13. Illinois Compiled Statutes. (225 ILCS 65/) Nurse Practice Act. Illinois General Assembly. 2009;04;Retrieved December 17, 2010. from http://ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs5.asp?ActID=1312&ChapterID=24.
- 14. Jenkins HM. A research tool for measuring perceptions of clinical decision making. Journal of Professional Nursing. 1985;1:221–229.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Kim HY. The alternatives for vitalization of home healthcare. Home Healthcare Symposium. 2008;11;In: Symposium conducted at the meeting of the Korean Homecare Nurses Association and Korean Academic Society of Home Care Nurses; Seoul, Korea. Y.S. Kim (Chair).
- 16. Kim SJ, Yi MS, Eun Y, Ko MH, Kim JH, Kim DO, et al. Role-identity of home care nurse practitioners. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006;36:103–113.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Kim SY, Park SA. A study for evaluating the performance of a community-based home care services model. Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing. 2009;19:673–683.
- 18. Kim TS, Choi MK, Lee MH. The relationships of decentralization, expertise and decision-making perceived by clinical nurses. Chungnam Medical Journal. 1997;24:89–100.
- 19. Krairiksh M, Anthony M. Benefit and outcome of staff nurses' participation in decision making. Journal of Nursing Administration. 2001;31:16–23.PubMed
- 20. O'Neill E. An exploratory study of clinical decision makingin home healthcare nursing. Home Healthcare Nurse. 1996;14:362–363.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Park MS. The level of professional autonomy and clinical decision making abilities of advanced practice nurses. 2006;Ulsan, Ulsan University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 22. Suh MJ, Kim SS, Shin KR, Kang HS, Kim KS, Park HR, et al. A study on the lived experiences of home care nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2000;30:84–97.ArticlePDF
- 23. Simon HA. The new science of management decision. 1977;Rev. ed. Englewood Cliffs, N.J., Prentice Hall.
- 24. Tingle J. Wilson J. Clinical guidelines and the law. In: Integrated care management: The path to success?. 1997;Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford. 70–71.
- 25. Yang BM. Mobilizing visiting nurse program in Korea. Korean Journal of Public Health. 1997;34:110–116.
- 26. Yi YJ. The causal relationships of the variables to decision-making of clinical nurses. 2001;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 27. Yu M. A study of nurse manager's decision-making on human resource management. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2007;13:82–97.
REFERENCES
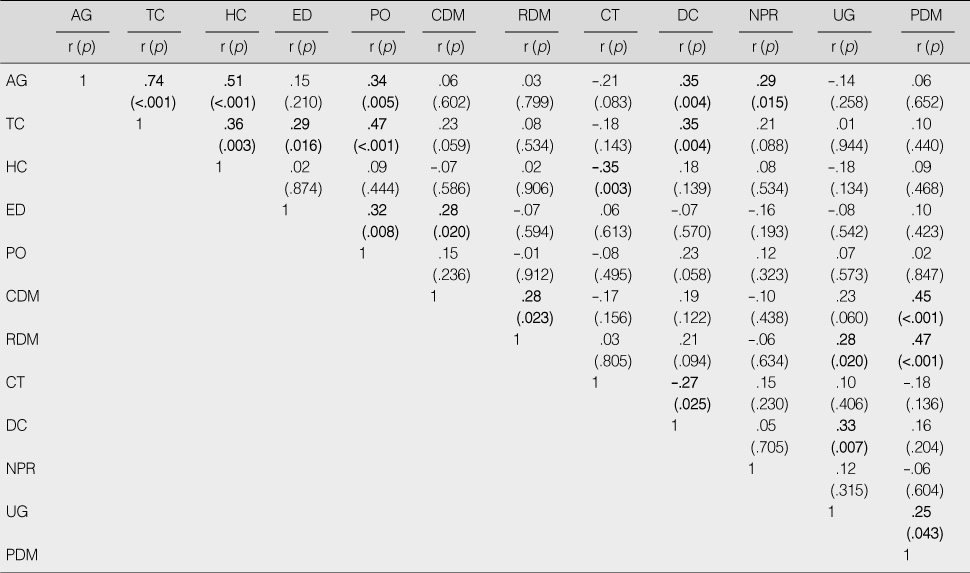
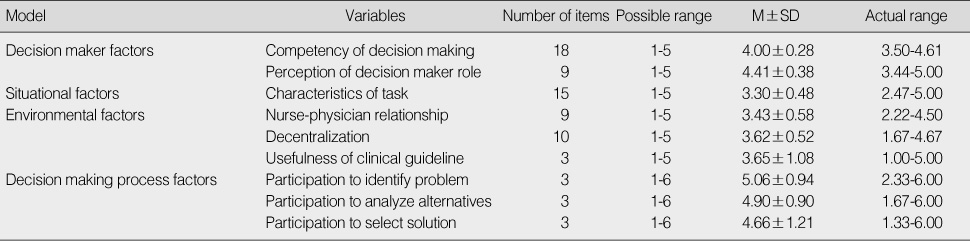
AG=age; TC=total career; HC=Home Healthcare career; ED=education; PO=position; CDM=competency of decision making; RDM=role of clinical decision maker; CT=character of task; DC=decentralization; NPR=nurse-physician relationship; UG=usefulness of clinical guideline; PDM=participation of decision making.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Concept Analysis of Nursing Surveillance Using a Hybrid Model
Se Young Kim, Mi-Kyoung Cho
Healthcare.2023; 11(11): 1613. CrossRef - Path model on decision‐making ability of clinical nurses
Minsook Park, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(7-8): 1343. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Role Clarity between Clinical Decision-Making Abilities and Job Stress for Advanced Practice Nurses at Tertiary Hospitals
Min Young Kim, Jeong Hye Kim, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(2): 27. CrossRef - Difficulties and Coping Experienced by Advanced Practice Nurses in Home Health Nursing Field
Moon-Sook Hwang, Hak Young Park, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 143. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Clinical Decision Making Ability of Nurses
Min Kyoung Park, Soukyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 601. CrossRef
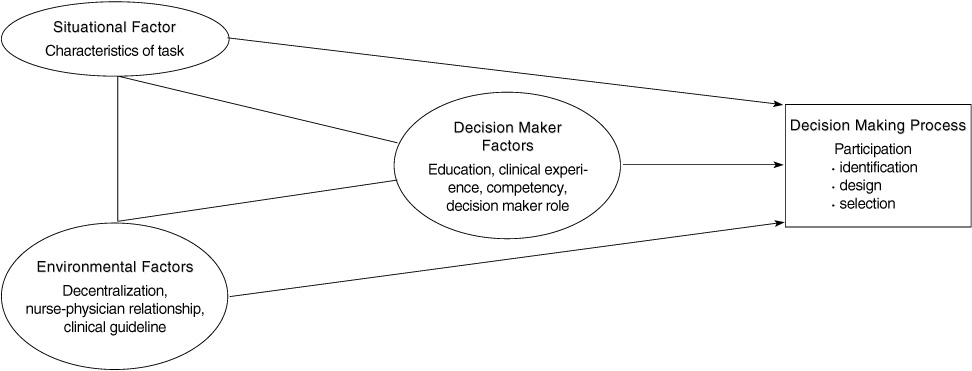
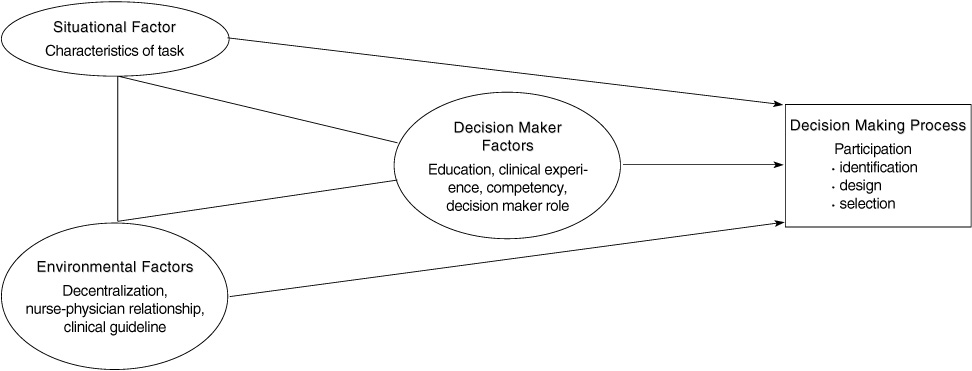
Figure 1
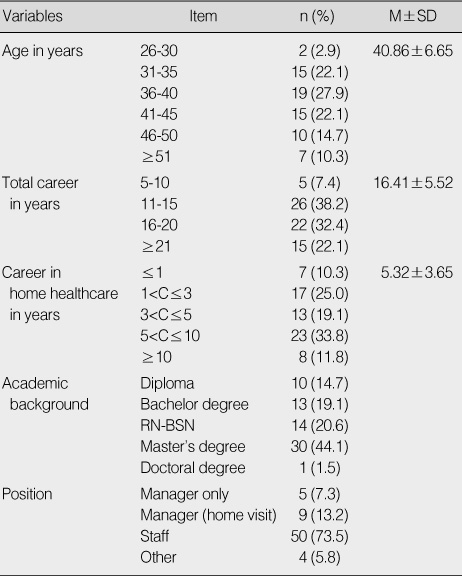
General Characteristics (N=68)
Descriptive Statistics of Observed Variables (N=68)
Differences in Participation in 3 Phases of Decision Making Process (N=68)
*Scheffe test.
Correlation between Variables in Clinical Decision Making Process (N=68)
AG=age; TC=total career; HC=Home Healthcare career; ED=education; PO=position; CDM=competency of decision making; RDM=role of clinical decision maker; CT=character of task; DC=decentralization; NPR=nurse-physician relationship; UG=usefulness of clinical guideline; PDM=participation of decision making.
5. Factors Affecting Participation in Clinical Decision Making in Multivariate Logistic Regression (N=68)
-2 Log likelihood=62.01 (p<.001); Cox & Snell R2=.38; Nagelkerke R2=.50.
*Scheffe test.
AG=age; TC=total career; HC=Home Healthcare career; ED=education; PO=position; CDM=competency of decision making; RDM=role of clinical decision maker; CT=character of task; DC=decentralization; NPR=nurse-physician relationship; UG=usefulness of clinical guideline; PDM=participation of decision making.
-2 Log likelihood=62.01 (
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

