Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(6); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Ventilator-associated Pneumonia with Circuit Changes Every 7 Days versus Every 14 Days
- Jeong-Sil Choi, Jeong-haw Yeon
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(6):799-807.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.6.799
Published online: December 31, 2010
1Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Sangji University, Wonju, Korea.
2Infection Control Nurse, Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Choi, Jeong-Sil. Department of Nursing Science, Sangji University, 660 Usan-dong, Wonju 220-702, Korea. Tel: 82-33-738-7627, Fax: 82-33-738-7652, jschoi408@empal.com
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To determine whether the practice of not routinely changing ventilator circuits in patients who require prolonged mechanical ventilation is associated with ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).
-
Methods
- Patients were divided into two groups, ventilator circuits were routinely changed every 7 days for the control group (39) and every 14 days for the experimental group (40) over a period of 1 yr (April 1, 2009-March 31, 2010). Pediatric patients (age 17 yr or less) were not included. VAP was diagnosed by the criteria of the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Incidence of VAP and characteristics of infection were evaluated.
-
Results
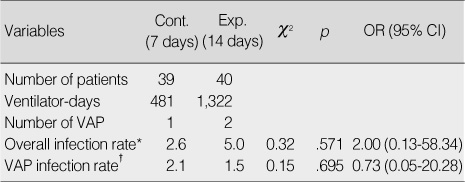
- In the experimental group, 2 episodes of pneumonia were observed in 40 patients and 1,322 ventilator days. The rate of VAP was 1.5 per 1,000 ventilator days. There was 1 episode of pneumonia in 39 patients and 481 ventilator days for the control group. The rate of VAP was 2.1 per 1,000 ventilator days. The difference between both groups was not significant (p=.695).
-
Conclusion
- Extending ventilator circuit change interval from 7 days to 14 days does not increase the risk for VAP.
- 1. Ban KO. The development and effectiveness of a program to prevent ventilator associated pneumonia in the ICU. Journal of Korean Academy of Adult Nursing. 2009;21:155–166.
- 2. Bercault N, Wolf M, Runge I, Fleury JC, Boulain T. Intrahospital transport of critically ill ventilated patients: A risk factor for ventilator-associated pneumonia - a matched cohort study. Critical Care Medicine. 2005;33:2471–2478.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Bonten MJ, Kollef MH, Hall JB. Risk factors for ventilator associated pneumonia: From epidemiology to patient management. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2004;38:1141–1149.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Branson RD. The ventilator circuit and ventilator-associated pneumonia. Respiratory Care. 2005;50:774–787.PubMed
- 5. Chastre J, Fagon JY. Ventilator-associated pneumonia. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2002;165:867–903.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 1988;2nd ed. New Jersey, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- 7. Dodek P, Keenan S, Cook D, Heyland D, Jacka M, Hand L, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline for the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2004;141:305–313.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Dreyfuss D, Djedaini K, Weber P, Brun P, Lanore JJ, Rahmani J, et al. Prospective study of nosocomial pneumonia and of patient and circuit colonization during mechanical ventilation with circuit changes every 48 hours versus no change. The American Review of Respiratory Disease. 1991;143(4 Pt 1):738–743.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Fink JB, Krause SA, Barrett L, Schaaff D, Alex CG. Extending ventilator circuit change interval beyond 2 days reduces the likelihood of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Chest. 1998;113:405–411.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Han J, Liu Y. Effect of ventilator circuit changes on ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Respiratory Care. 2010;55:467–474.PubMed
- 11. Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for preventing health-care-associated pneumonia, 2003 recommendations of the CDC and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Respiratory Care. 2004;49:926–939.PubMed
- 12. Horan TC, Andrus M, Dudeck MA. CDC/NHSN surveillance definition of health care-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. American Journal of Infection Control. 2008;36:309–332.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Kim NC, Kim YR. The incidence rate of ventilator associated pneumonia in relation to the exchange of circuit cycle. Journal of Korean Academy of Adult Nursing. 2003;15:463–471.
- 14. Kollef MH. Ventilator-associated pneumonia. A multivariate analysis. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 1993;270:1965–1970.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Kollef MH, Shapiro SD, Fraser VJ, Silver P, Murphy DM, Trovillion E, et al. Mechanical ventilation with or without 7-day circuit changes. A randomized controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1995;123:168–174.PubMed
- 16. Kwak YG, Cho YK, Kim JY, Leem SO, Kim HY, Kim YK, et al. Korean nosocomial infections surveillance system, intensive care unit module report: Data summary from July 2008 through June 2009 and analysis of 3-year results. Korean Journal of Nosocomial Infection Control. 2010;15(1):14–25.
- 17. Lee MH. The effect of ventilator associates respiratory infection control education on perception, performance and nosocomial infection for critical care nurse. 2003;Daejeon, Dae-Jeon University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 18. Lien TC, Lin MY, Chu CC, Kuo BI, Wang ED, Wang JH. Ventilator-associated pneumonia with circuit changes every 2 days versus every week. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 2001;64:161–167.PubMed
- 19. Long MN, Wickstrom G, Grimes A, Benton CF, Belcher B, Stamm AM. Prospective, randomized study of ventilator-associated pneumonia in patients with one versus 3 ventilator circuit changes per week. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 1996;17(1):14–19.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Oh HS, Choi YK, Lee BN, Shim MY, Choi HS, Kim EC, et al. A prospective study on the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia in patients with circuit changes every 3 days versus weekly changes. Korean Journal of Nosocomial Infection Control. 2000;5(1):9–21.
- 21. Song JH. A meta analysis of the ventilator circuit change period on ventilator associated pneumonia. 2010;Seoul, Chung-Ang University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 22. Thomachot L, Leone M, Razzouk K, Antonini F, Vialet R, Martin C. Randomized clinical trial of extended use of a hydrophobic condenser humidifier: 1 vs. 7 days. Critical Care Medicine. 2002;30:232–237.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Thompson RE. Incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) with 4-day circuit change in a subacute environment. Respiratory Care. 1996;41:601–606.
- 24. Zack JE, Garrison T, Trovillion E, Clinkscale D, Coopersmith CM, Fraser VJ, et al. Effect of an education program aimed at reducing the occurrence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Critical Care Medicine. 2002;30:2407–2412.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
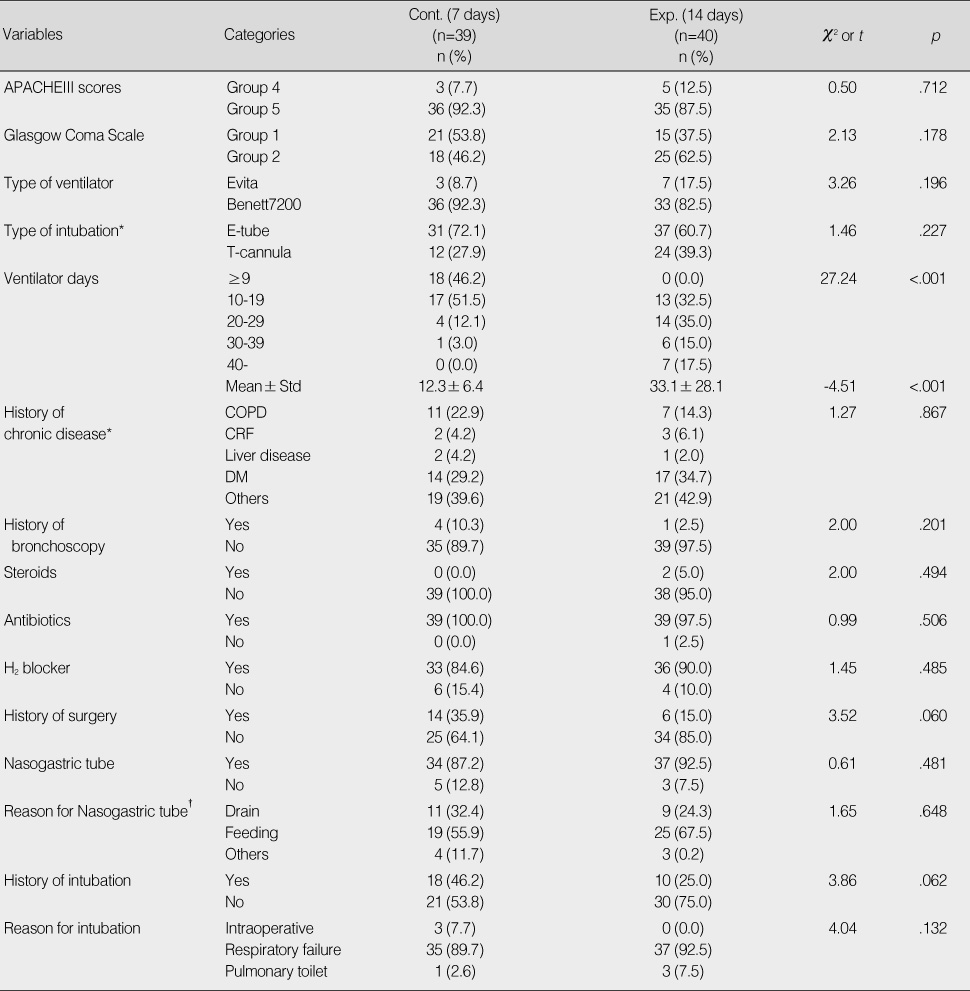
*Multiple choice; †Number of case "yes" in nasogastric tube insertion.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; APACHE=Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; E-tube=Endotracheal tube; T-cannula=Tracheostomy cannula; COPD=Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CRF=Chronic renal failure; DM=Diabetes mellitus.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Efficacy of compliance with ventilator-associated pneumonia care bundle: A 24-month longitudinal study at Bach Mai Hospital, Vietnam
Hoan Minh Hoang, Co Xuan Dao, Hoang Huy Ngo, Tatsuya Okamoto, Chieko Matsubara, Son Ngoc Do, Giang Thi-Huong Bui, Han Quang Bui, Nguỵen Thi Duong, Ngoan Thi Nguyen, Toan Xuan Vuong, Kham Van Vu, Thach The Phạm, Cuong Van Bui
SAGE Open Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Actualización de las recomendaciones del proyecto Neumonía Zero
S. Arias-Rivera, R. Jam-Gatell, X. Nuvials-Casals, M. Vázquez-Calatayud
Enfermería Intensiva.2022; 33: S17. CrossRef - Survey on Self Care, Respiratory Difficulty, Sleep Impediment, Anxiety and Depression among Patients with Neuromuscular Disease dependent on Home Mechanical Ventilator
Moon Sook Hwang, Mi Kyung Lee, Jong Rye Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(5): 595. CrossRef
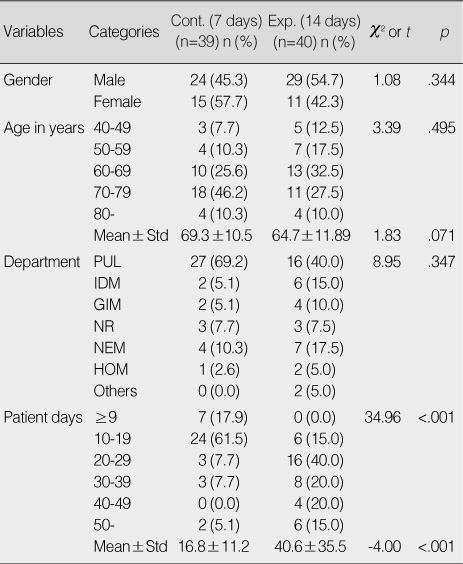
Homogeneity Test of General Characteristics between Control and Experimental Group (N=79)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; PUL=Pulmonology; IDM=Infectious disease medicine; GIM=Gastroenterology; NR=Neurology; NEM=Nephrology; HOM=Hemato-oncology.
Homogeneity Test of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia Risk Factor between Control and Experimental Group (N=79)
*Multiple choice; †Number of case "yes" in nasogastric tube insertion.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; APACHE=Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; E-tube=Endotracheal tube; T-cannula=Tracheostomy cannula; COPD=Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CRF=Chronic renal failure; DM=Diabetes mellitus.
Incidences of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia (N=79)
*Number of VAP/Number of patients×100; †Number of VAP/Ventialtor-days×1,000.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; VAP=Ventilator associated pneumonia; OR=Odds ratio; CI=Confidence interval.
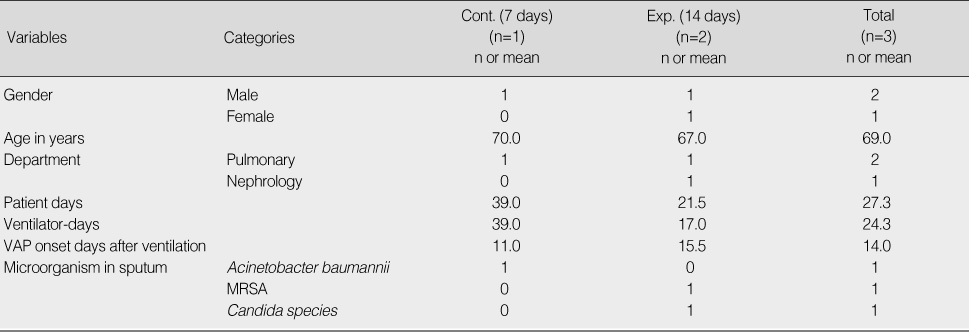
Characteristics of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia Patients (N=3)
VAP=Ventilator associated pneumonia; MRSA=Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; PUL=Pulmonology; IDM=Infectious disease medicine; GIM=Gastroenterology; NR=Neurology; NEM=Nephrology; HOM=Hemato-oncology.
*Multiple choice; †Number of case "yes" in nasogastric tube insertion. Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; APACHE=Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; E-tube=Endotracheal tube; T-cannula=Tracheostomy cannula; COPD=Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CRF=Chronic renal failure; DM=Diabetes mellitus.
*Number of VAP/Number of patients×100; †Number of VAP/Ventialtor-days×1,000. Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; VAP=Ventilator associated pneumonia; OR=Odds ratio; CI=Confidence interval.
VAP=Ventilator associated pneumonia; MRSA=Methicillin-resistant
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

