Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(5); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Cognitive Impairment, Behavioral Problems, and Mental Health in Institutionalized Korean Elders -An Eligibility Issue for Care Settings-
- Hyun-Sil Kim, Young-Mi Jung, Hung-Sa Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(5):741-750.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.5.741
Published online: October 31, 2009
1Professor, Department of Nursing, Daegu Haany University, Daegu, Korea.
2Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Daegu Haany University, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Hyun-Sil. Department of Nursing, Daegu Haany University, 165 Sang-dong, Suseong-gu, Daegu 706-060, Korea. Tel: 82-53-770-2282, Fax: 82-53-770-2286, hskim@dhu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify the prevalence of cognitive impairment, behavioral problems, and the state of mental health for elderly Korean people who have been institutionalized.
-
Methods
- A cross-sectional, nation-wide survey was performed using an anonymous questionnaire. The participants in this study were 2,521 institutionalized elderly Korean people. A proportional stratified random sampling method was employed.
-
Results
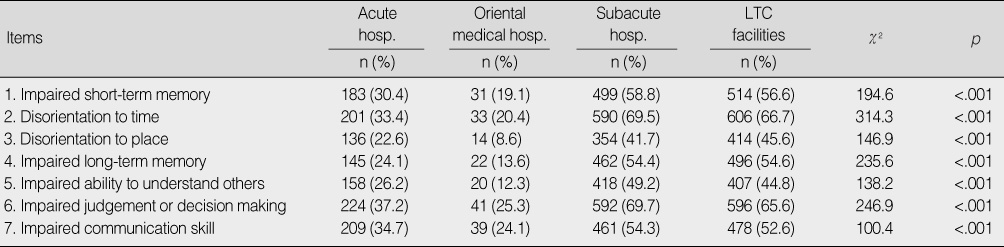
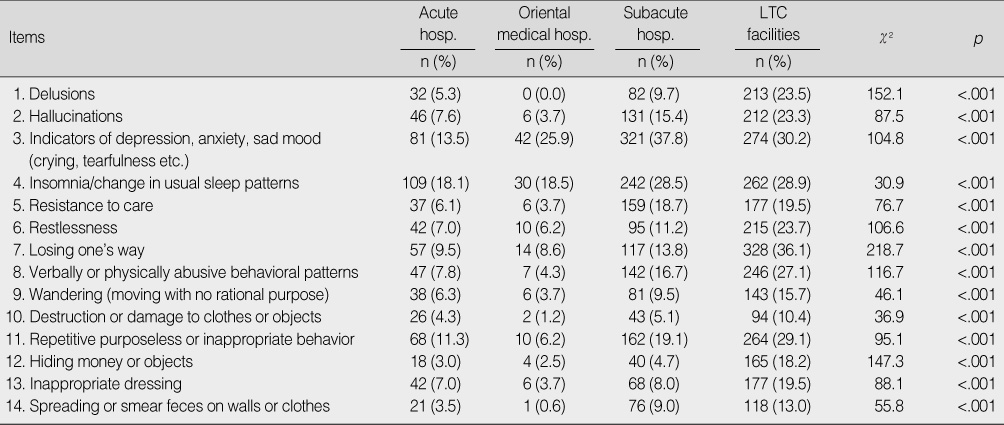
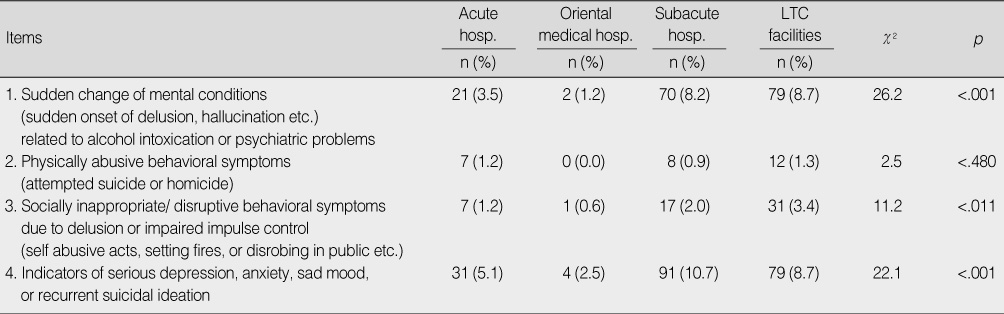
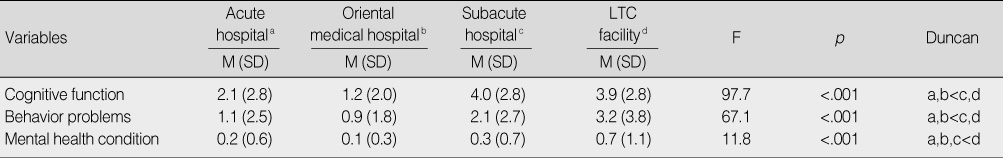
- 1) Elders admitted to subacute hospitals and long term care (LTC) facilities showed a higher level of cognitive impairment compared to elders admitted to acute care hospitals. 2) Elders confined in LTC facilities showed a higher level of behavioral problems compared to elders in acute or subacute hospitals. 3) Elders admitted to subacute hospitals and LTC facilities showed more serious mental health problems, such as depression or suicidal ideation, compared to elders in acute care hospitals.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study indicate that the severity of cognitive-behavioral or mental health problems do not match well with type of care setting. Therefore, health personnel working with elderly people should be provided guidance on detection and management of cognitive-behavioral and mental health problems. The necessity of a decision support system for eligibility and placement in long-term care is also discussed.
- 1. Brodaty H, Peters K, Boyce P, Hickie I, Parker G, Mitchell P, et al. Age and depression. Journal of Affective Disorders. 1991;23:137–149.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Chu SK, Yoo JH, Lee CY. The effects of a cognitive behavior program on cognition, depression, and activities of daily living in elderly with cognitive impairment. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:1049–1060.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Doble SE, Fisher AG. The dimensionality and validity of the older Americans resources and services (OARS) activities of daily living (ADL) scale. Journal of Outcome Measurement. 1998;2:4–24.PubMed
- 4. Fox P, Maslow K, Zhang X. Long-term care eligibility criteria for people with Alzheimer's disease. Health care and Financing Review. 1999;20:67–85.PubMed
- 8. Hambletone RK, Robin F, Xing D. Tinsley H, Brown S. Item Response Models for the analysis of educational and psychological test data. In: Handbook of applied multivariate statistics and mathematic modeling. 2000;San Diego, CA, Academic Press. 553–585.
- 8. Hirdes JP, Tjam EY, Fries BE. . Eligibility for community, hospital and institutional services in Canada: A preliminary study of case managers in seven provinces. 2001;Toronto, National Evaluation of the Cost-Effectiveness of Home Care, Canada, Department of Health Studies & Gerontology, University of Waterloo, Canadian Collaborating Centre -inter RAI, Province Centre, Toronto, St.Mary's Hospital, Kitchener, Institute of Gerontology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Ann Arbor VA Medical Centre.
- 7. Ito H, Miyamoto Y. Impact of long-term care insurance on institutional dementia care in Japan. Health Policy. 2003;64:325–333.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Ito H, Tachimori H, Miyamoto Y, Morimura Y. Are the care levels of people with dementia correctly assessed for eligibility of the Japanese long-term care insurance? International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2001;16:1–7.PubMed
- 9. Kim B, Hong S. A psychometric revision of the Asian values scale using the Rasch model. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development. 2004;37:15–27.Article
- 10. Kim HS, Hwang JY, Jung YM, Lee HS, Park YE, Cho YH, et al. A Study on eligibility and placement for the elderly in the Korea longterm care insurance. 2008;Seoul, National Health Insurance Corporation, Daegu Haany University, & Korea Health Industry Development Institute.
- 11. Kim JS, Jung JS. The effects of a folk play program on cognition, ADL, and problematic behavior in the elderly with dementia. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:1163–1173.PubMed
- 12. Kim KA. Development of an assessment tool of problematic behaviors for institutionalized old people with dementia. 2003;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 13. Korea Alzheimer's Association. Suicide in the elderly. 2008;12 30 Retrieved December 30, 2008. from http://www.alzza.or.kr/sub/dementia/sub_01.asp.
- 14. Lenze EJ, Mulsant BH, Shear MK, Alexopoulos GS, Frank E, Reynolds CF II. Comorbidity of depression and anxiety disorders in later life. Depression and Anxiety. 2001;14(2):86–93.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Mazure CM, Maciejewski PK. A model of risk for major depression: Effects of life stress and cognitive style vary by age. Depression and Anxiety. 2003;17:26–33.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Mental Health Foundation. Mental health problems. 2009;01 20 Retrieved March 16, 2009. from http://www.mentalhealth.org.uk.
- 17. Min SG, Go KB, Kim KH, Kim BH, Kim I, Kim HS, et al. Modern psychiatry. 1998;3rd ed.Seoul, Iljogak.
- 18. Ministry of Health and Welfare & National Health Insurance Corporation. Manual for long term care eligibility system & service provision. 2007;05;Seoul, Author.
- 19. Morris J, Murphy K, Nonemaker S. Long term care Resident Assessment Instrument user's manual for version 2.0. U.S. 1995;Retrieved December 30, 2008. from http://chfs.ky.gov/NR/rdonlyres/C3215FE3-A99B-4C41-878C-A2AC8CB4BF26/0/1775a.pdf.
- 20. Ownby RL, Harwood DG, Barker WW, Duara R. Predictors of anxiety in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Depression and Anxiety. 2000;11:38–42.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Parashos IA, Stamouli S, Rogakou E, Theodotou R, Nikas I, Mougias A, et al. Recognition of depressive symptoms in the elderly: What can help the patient and the doctor. Depression and Anxiety. 2002;15:111–116.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Rovner BW, Broadhead J, Spencer M, Carson K, Folstein MF. Depression and Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Psychiatry. 1989;146:350–353.ArticlePubMed
- 23. van Campen C, van Gameren E. Eligibility for long-term care in the Netherlands: Development of a decision support system. Health & Social Care in the Community. 2005;13:287–296.Article
- 24. Weeks JW, Heimberg RG. Evaluation of the psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory in a non-elderly adult sample of patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Depression and Anxiety. 2005;22:41–44.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Won JS, Kim KH. Evaluation of cognitive functions, depression, life satisfaction among the elderly receiving visiting nursing services. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:1–10.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Prevalence of Suicidal Behaviors in Residents of Long-Term Care Facilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Syeda Beenish Bareeqa, Syeda Sana Samar, Yasir Masood, Mustafa M. Husain
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2025; 92(1): 83. CrossRef - Longitudinal trends in schizophrenia among older adults: a 12-year analysis of prevalence and healthcare utilization in South Korea
Jung Su Park, Sangwan Kim, Jeong Pil Choi, Mi-Sook Kim, Yu Sang Lee, Eun-Jeong Joo, Yong Sik Kim, Joongyub Lee, Se Hyun Kim
Schizophrenia.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudo das publicações científicas (2002-2017) sobre ideação suicida, tentativas de suicídio e autonegligência de idosos internados em Instituições de Longa Permanência
Maria Cecília de Souza Minayo, Ana Elisa Bastos Figueiredo, Raimunda Matilde do Nascimento Mangas
Ciência & Saúde Coletiva.2019; 24(4): 1393. CrossRef - Life experiences of elderly people with suicide ideation at the long‐term care hospitals in South Korea
Ok Sun Kim, Sohyune R. Sok
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive Factors associated with Death of Elderly in Nursing Homes
Kiwol Sung
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(2): 143. CrossRef - The Influences of Swallowing Function on Swallowing-Quality of Life and Activity of Daily Living of Inpatients in Geriatric Hospital
Ji-Young Baek, Keun-Bae Oh
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2013; 7(1): 167. CrossRef - The Long-term Care Utilization of the Elderly with Dementia, Stroke, and Multimorbidity in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Soonman Kwon, Hongsoo Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(1): 90. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Dysphagia Assessment Tool and an Intervention Program for the Elderly in the Long-Term Care Facilities
Chi-Young Kim, Young-Mi Lee, Eun-Ho Ha
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(2): 685. CrossRef - Cognitive Function and Activity of Daily Living of Older Adults Using Long-term Care Service
Hyun-Sook Chang, Hung Sa Lee
Korean Journal of Health Policy and Administration.2012; 22(4): 522. CrossRef
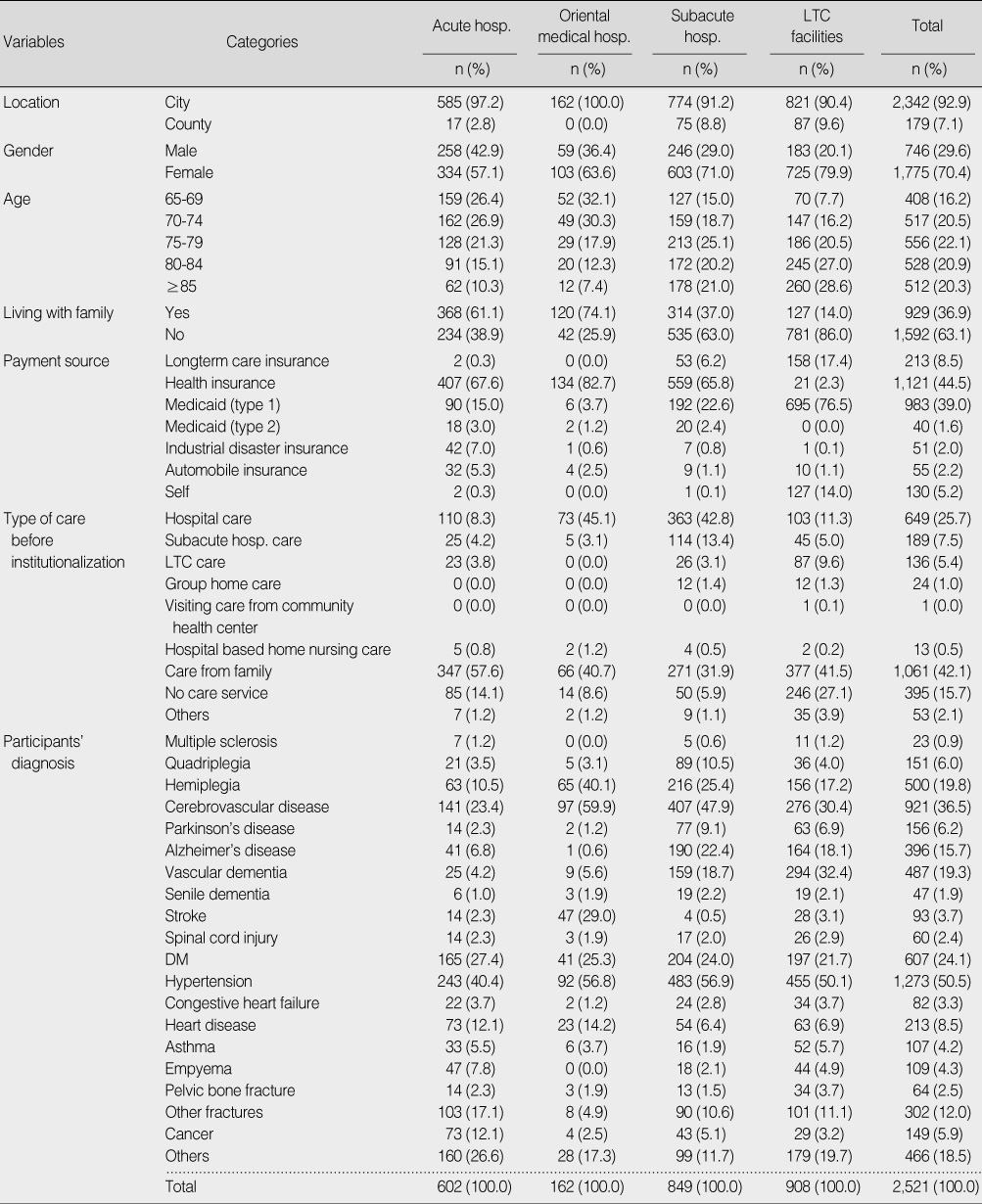
Demographic Characteristics of the Participants (N=2,521)
hosp.=hospital; LTC=long term care; DM=diabetes mellitus.
Comparison of Cognitive Function by Care Settings (N=2,521)
hosp.=hospital; LTC=long term care.
Comparison of Behavioral Problems by Care Settings (N=2,521)
hosp.=hospital; LTC=long term care.
Comparison of Mental Health Conditions by Care Settings (N=2,521)
hosp.=hospital; LTC=long term care.
Differences in Cognitive Function, Behavioral Problems, & Mental Health by Care Settings
LTC=long term care.
hosp.=hospital; LTC=long term care; DM=diabetes mellitus.
hosp.=hospital; LTC=long term care.
hosp.=hospital; LTC=long term care.
hosp.=hospital; LTC=long term care.
LTC=long term care.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

