Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(4); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of Exercise Intervention on Physical Fitness and Health-relalted Quality of Life in Hemodialysis Patients
- Eun-Joung Jang, Hee-Seung Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(4):584-593.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.584
Published online: August 31, 2009
1Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Kyungbok College, Pocheon, Korea.
2Professor, College of Nursing, The Catholic University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Hee-Seung. College of Nursing, The Catholic University, 505 Banpo-dong, Seocho-gu, Seoul 137-010, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2258-7408, Fax: 82-2-2258-7772, hees@catholic.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of stretching, muscle strengthening, and walking exercise on the cardiopulmonary function and health-related quality of life in hemodialysis patients.
-
Methods
- Twenty-one patients in the intervention and the control group participated in the exercise respectively on maintenance hemodialysis at four university hospitals. The exercise was composed of 20 to 60 min per session, 3 sessions a week for 12 weeks. The effect of exercise was assessed by cardiopulmonary function (peak oxygen uptake, peak ventilation, peak respiration rate, maximal heart rate, and exercise duration) using a cycle ergometer. Grip strength was measured by dynamometer, and flexibility was measured by sit and reach measuring instrument. Health-related quality of life was measured using Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36.
-
Results
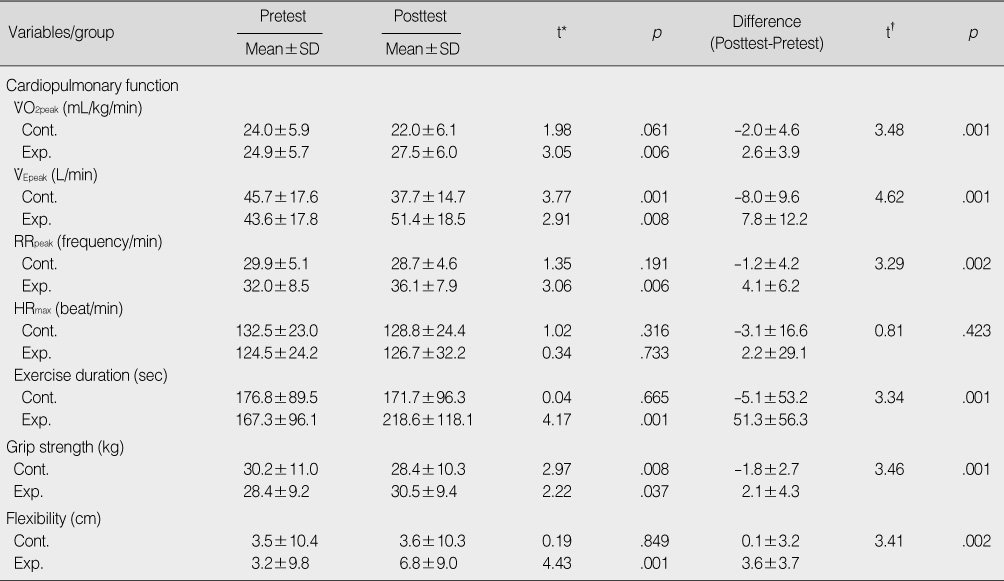
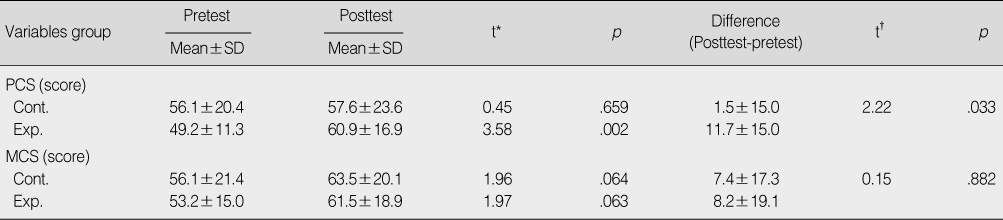
- Peak oxygen uptake, peak ventilation, peak respiration rate, exercise duration, grip strength, flexibility, and physical component scale were significantly improved in the intervention group after 12 week's exercise compared to the control group.
-
Conclusion
- These findings indicate the exercise can improve cardiopulmonary function, grip strength, flexibility, and physical component scale of health-related quality of life in hemodialysis patients.
- 1. American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM's resource mannual for guides for exercise testing and prescription. 2001;4th ed. Philadelphia, PA, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- 2. DeOreo PB. Hemodialysis patient-assessed functional health status predicts continued survival, hospitalization, and dialysis-attendance compliance. American Journal of Kidney Disease. 1997;30:204–212.Article
- 3. Diesel W, Novakes TD, Swanepoel C, Lambert M. Isokinetics muscle strength predicts maximal exercise tolerance in renal patients on chronic hemodialysis. American Journal of Kidney Disease. 1990;16:109–114.
- 4. End Stage Renal Disease Registry Committee. Current renal replacement therapy in Korea -Insan memorial dialysis registry 2007-. Korean Journal of Nephrology. 2008;27:Suppl. 2. 437–465.
- 5. Fuhrmann I, Krause R. Principles of exercising in patients with chronic kidney disease, on dialysis and for kidney transplant recipients. Journal of Clinical Nephrology. 2004;61:Suppl. 1. 14–25.
- 6. Grumann MM, Noack EM, Hoffmann IA. Comparison of quality of life in patients undergoing abdominoperitoneal extirpation or anterior resection for rectal cancer. Annals of Surgery. 2001;233:149–156.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Jun TW, Woo JH, Kim YS. Effect of basic military training on cardiopulmonary function of midshipmen. Journal of Korean Exercise Academy. 2000;9:347–354.
- 8. Kim JS. The effect of exercise program on depression and anxiety in hemodialysis. 1997;Seoul, Korea University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 9. Konstantinidou E, Koukouvou G, Kouidi E, Deligiannis A, Tourkantonis A. Exercise training in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis: Comparison of three rehabilitation programs. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2002;34:40–45.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Kopple JD, Storer T, Casaburi R. Impaired exercise capacity and exercise training in maintenance on hemodialysis patients. Journal of Renal Nutrition. 2005;15:44–48.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Kouidi E. Exercise training in dialysis patients: Why, when, and how? Artificial Organs. 2002;26:1009–1013.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Kouidi E, Grekas D, Deligiannis A, Tourkantonis A. Outcomes of long-term exercise training in dialysis patients: Comparison of two training programs. Journal of Clinical Nephrology. 2004;61:Suppl. 1. 31–38.
- 13. Lee SJ, Yoo JS. The effects of a physical activity reinforcement program on exercise compliance, depression, and anxiety in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2004;34:440–448.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Lee YK, Kim C, Pyo JH, Kim CH, Ji JW. Endurance exercise training before hemodialysis: An effective therapeutic modality for end stage renal disease patients. Korean Journal of Nephrology. 2001;20:290–297.
- 15. Moinuddin I, Leehey DJ. A comparison of aerobic exercise and resistance training in patients with and without chronic kidney disease. Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease. 2008;15:83–96.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Molsted S, Eidemak I, Sorensen HT, Kristensen JH. Five months of physical exercise in hemodialysis patients: Effects on aerobic capacity, physical function and self-rated health. Nephron Clinical Practice. 2004;96(3):76–81.
- 17. Oh SH, Yoo EK. Comparison of quality of life between kidney transplant and hemodialysis patients. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006;36:1145–1153.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Painter P, Carlson L, Carey S, Paul SM, Myll J. Low functioning hemodialysis patients improve with exercise training. American Journal of Kidney Disease. 2000;36:600–608.Article
- 20. Painter P, Moore G, Carlson L, Paul S, Myll J, Phillips W, et al. Effects of exercise training plus normalization of hematocrit on exercise capacity and health-related quality of life. American Journal of Kidney Disease. 2002;39:257–265.Article
- 20. Park OM, Fast S, Lynn R, Frei G, Drenth R, Zohman L. Exercise for the dialyzed: Aerobic and strength training during hemodialysis. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 2002;81:814–821.Article
- 21. Shankar K. Exercise prescription. 1999;Philadelphia, PA, Hanley & Belfus Inc.
- 22. Sietsema KE, Hiatt WR, Enne E, Adler S, Amato A, Brass EP. Clinical and demographic predictors of exercise capacity in end-stage renal disease. American Journal of Kidney Disease. 2002;39:76–85.Article
- 23. Suh MR, Jung HH, Kim SB, Park JS, Yang WS. Effects of regular exercise on anxiety, depression, and quality of life in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Renal Failure. 2002;24:337–345.ArticlePubMed
- 24. The Life Options Rehabilitation Advisory Council. Exercise: A prescribing guide. 1995;Madison, WI, Amgen Inc.
- 25. The Life Options Rehabilitation Advisory Council. Exercise: A guide for the people on dialysis. 2000;Madison, WI, Amgen Inc.
- 26. The Society of Korean Language and Literature. Korean Language Dictionary. 2004;Seoul, Minjungeogwan.
- 27. Tsuyuki K, Kimura Y, Chiashi K, Matsushita C, Ninomiya K, Choh K, et al. Oxygen uptake efficiency slope as monitoring tool for physical training in chronic hemodialysis patients. Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis. 2003;7:461–467.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Ware JE, Snow KK, Kosinski M, Gandek B. SF-36 health survey manual and interpretation guide. 1993;Boston, MA, New England Medical Center, The Health Institute.
- 29. Yang JS. A trial for development of health profile (KHP1.0) to measure the self-perceived health status of Korean. 2001;Gimhae, Inje University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 30. Yurtkuran M, Alp A, Yurtkuran M, Dilek K. A Modified yoga-based exercise program on hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled study. Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 2007;15:164–171.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
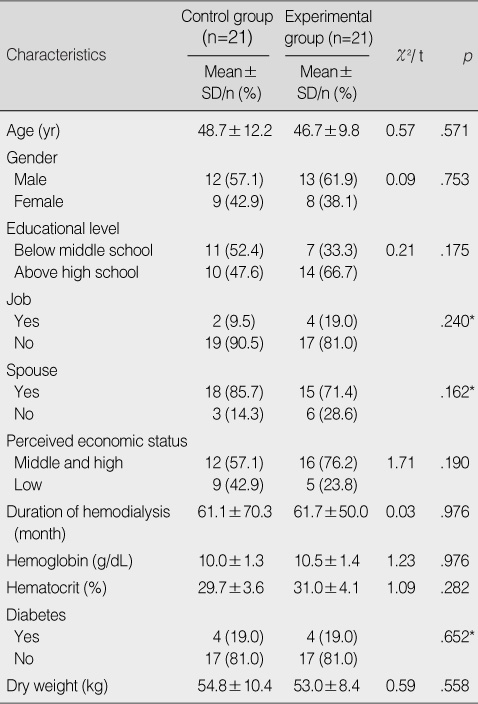
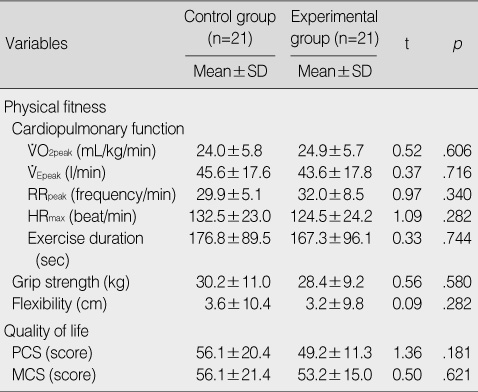
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Efficacy of resistance exercise during hemodialysis on improving lower limb muscle strength in patients with chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Monaline Nascimento Alves, Aenoan Souza Soares, Patrícia Melo Marinho
Physiotherapy Theory and Practice.2024; 40(6): 1351. CrossRef - Effect of Exercise on Fatigue in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis Treatment
Xianying Lu, Jing Yang, Dingxi Bai, Chenxi Wu, Mingjin Cai, Wei Wang, Jiali He, Xiaoyan Gong, Jing Gao, Chaoming Hou
American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation.2024; 103(4): 293. CrossRef - The effectiveness of structured educational programs for hemodialysis patients in Korea: an integrated literature review
Young Ran Chae, Jeong-Joo Choi, Min Sub Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(3): 143. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Smartphone App-Based Exercise Program for Hemodialysis Patients
Eun Jeong Ki, Hyang Sook So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(1): 52. CrossRef - Application of Wearables to Facilitate Virtually Supervised Intradialytic Exercise for Reducing Depression Symptoms
He Zhou, Fadwa Al-Ali, Gu Eon Kang, Abdullah I. Hamad, Rania A. Ibrahim, Talal K. Talal, Bijan Najafi
Sensors.2020; 20(6): 1571. CrossRef - Influences on the Performance based Frailty of Physical Performance, Exercise Self-efficacy, Decisional Balance, and Health related Quality of Life in Adults Undergoing Hemodialysis
Sun-Ki Kim, Hye-Ja Park, Dong Ho Yang, Hye Yun Jeong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(2): 149. CrossRef - Effects of a Muscle Strength Reinforcement Exercise Program for Older Adult Patients on Hemodialysis
Jena Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(3): 204. CrossRef - Effects of Pilates exercise on general health of hemodialysis patients
Zahra Rahimimoghadam, Zahra Rahemi, Neda Mirbagher Ajorpaz, Zohre Sadat
Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies.2017; 21(1): 86. CrossRef - Effects of Aerobic Exercise During Hemodialysis on Physical Functional Performance and Depression
Yueh-Min Liu, Yu-Chu Chung, Jung-San Chang, Mei-Ling Yeh
Biological Research For Nursing.2015; 17(2): 214. CrossRef - Effects of Self-motivated Virtual Reality Exercise Program on Heart Rate Variability and Quality of Life in the Hemodialysis Patients
Hye-Young Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(9): 5578. CrossRef - The Effect of a Virtual Reality Exercise Program on Physical Fitness, Body Composition, and Fatigue in Hemodialysis Patients
Hyeyoung Cho, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2014; 26(10): 1661. CrossRef - The Attitude on Exercise, Physical Activity and Quality of Life in Hemodialysis Patients
Hyun Sook Sohn, Mi Jin Lee, Seon Mi Kang, Young Ok Han, Kyung Hee Moon, Dong Il Kim, Yun Joo Lee, Justin Y. Jeon, Sang Hui Chu
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(1): 15. CrossRef - Effects of Progressive Resistance Training on Body Composition, Physical Fitness and Quality of Life of Patients on Hemodialysis
Woo-Jung Song, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 947. CrossRef - Effects of Structured Arm Exercise on Arteriovenous Fistula Stenosis in Hemodialysis Patient
Aee Lee Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2012; 14(4): 300. CrossRef - Exercise training for adults with chronic kidney disease
Susanne Heiwe, Stefan H Jacobson
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2011;[Epub] CrossRef
Homogeneity Test for Demographic and Clinical Characteristics in the Control and Experimental Groups
*Fisher's exact test.
Homogeneity Test for Physical Fitness and Health-related Quality of Life in the Control and Experimental Groups
VO2peak=peak oxygen uptake; VEpeak=peak minute ventilation; RRpeak=peak respiration rate; HRmax=maximal heart rate; PCS=physical component scale; MCS=mental component scale.
Changes of the Cardiopulmonary Function, Grip Strength, and Flexibility in Control and Experimental groups
*Paired t-test; †Independent t-test.
Cont.=control group (n=21); Exp.=experimental group (n=21); VO2peak=peak oxygen uptake; VEpeak=peak minute ventilation; RRpeak=peak respiration rate; HRmax=maximal heart rate.
Changes of the Quality of Life in Control and Experimental Groups
*Paired t-test; †Independent t-test.
Cont.=control group (n=21); Exp.=experimental group (n=21); PCS=physical component scale; MCS=mental component scale.
*Fisher's exact test.
VO2peak=peak oxygen uptake; VEpeak=peak minute ventilation; RRpeak=peak respiration rate; HRmax=maximal heart rate; PCS=physical component scale; MCS=mental component scale.
*Paired t-test; †Independent t-test. Cont.=control group (n=21); Exp.=experimental group (n=21); VO2peak=peak oxygen uptake; VEpeak=peak minute ventilation; RRpeak=peak respiration rate; HRmax=maximal heart rate.
*Paired t-test; †Independent t-test. Cont.=control group (n=21); Exp.=experimental group (n=21); PCS=physical component scale; MCS=mental component scale.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

