Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(4); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effectiveness of Public Health Center Smoking Cessation Counseling Program using the Transtheoretical Model
- Yun Hee Kim, Jung Soon Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(4):469-479.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.469
Published online: August 31, 2009
1Public Health Nurse, Health Promotion Division, Busan Metropolitan City, Busan, Korea.
2Professor, College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
3Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Ulsan College, Ulsan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Myoung Soo. Department of Nursing, Ulsan College, San 160-1 Hwajeong-dong, Dong-gu, Ulsan 682-715, Korea. Tel: 82-52-230-0737, Fax: 82-52-230-0730, kanosa@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify the effectiveness of public health center smoking cessation counseling program using the transtheoretical model on the process of change, smoking temptation, decisional balance and stage change transition.
-
Methods
- A nonequivalent control group non-synchronized design was used for this study. The study population was 115 adult smokers. The counseling program was administered to the experimental group and a smoking cessation program from the Korean Ministry of Health & Welfare was administered to the control group. Descriptive analysis, χ2-test, t-test, and ANCOVA were used with the SPSS 12.0 program to analyze the data.
-
Results
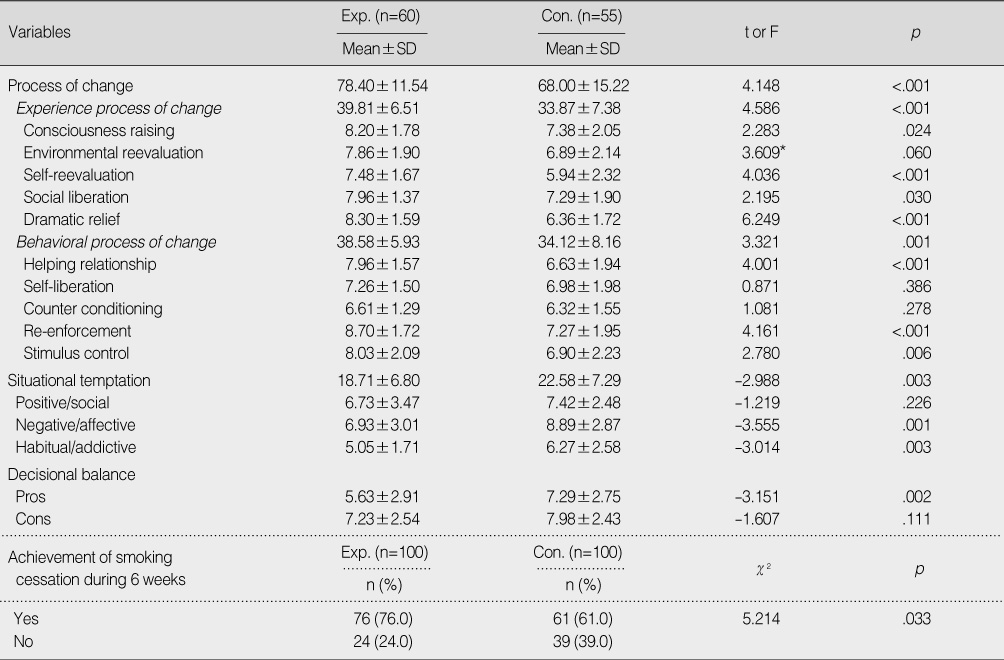
- After treatment with this program, the experimental group showed significantly higher scores for process of change (t=4.148, p<.001), smoking temptation (t=-2.988, p=.003), and stage change transition (χ2=5.871, p=.031) compared to the control group. Experimental group members also showed significantly lower score for Pros of smoking (t=-3.151, p=.002).
-
Conclusion
- The findings indicate that this program could have positive effect on process of change, smoking temptation, decisional balance and stage transition for adult smokers. Based on these findings, the authors suggest additional counseling program focusing on smokers in specific stages.
This article is based on a part of the first author's doctoral thesis from Pusan National University.
- 1. Ahn OH, Yeun EJ, Kwon SB, Chung HK, Ryu EJ. Predictive factors of aspects of the transtheoretical model on smoking cessation in a rural community. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:1285–1294.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Aveyard P, Lawrence T, Cheng KK, Griffin C, Croghan E, Johnson C. A randomized controlled trial of smoking cessation for pregnant women to test the effect of a transtheoretical model-based intervention on movement in stage and interaction with baseline stage. British Journal of Health Psychology. 2006;11:263–278.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Chang SO. The concept development of smoking temptation. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2004;34:160–171.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Chang SO, Kim EJ, Kil SY, Seomun GA, Lee SJ. Influential variables on intention and action to quit smoking between adolescent smokers and adults smokers- based on the transtheoreticalmodel. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:1410–1419.PubMed
- 5. Cho KS, Song TM. Analysis of key factors in smoking cessation and cost effectiveness at public health centers. Health and Welfare Forum. 2007;121:65–77.
- 6. DiClemente CC, Fava JL. Measuring processes of change: Applications to the cessation of smoking. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1988;56:520–528.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Fava JL, Velicer WF, Prochaska JO. Applying the transtheoretical model to representative sample of smokers. Addictive Behaviors. 1995;20:189–203.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Fiore MC, Bailey WC, Cohen SJ. Treating tobacco use and dependence, clinical practice guideline. 2000;Rockville, MD, U.S. Department of Health and Human Service, Public Health Service.
- 9. Hall SM, Humfleet GL, Reus VI, Munoz RF, Cullen J. Extended nortriptyline and psychological treatmentfor cigarette smoking. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2004;161:2001–2007.
- 10. Kim MR. Recent options of smoking cessation program. Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2005;10:259–276.
- 11. Korean Association of Smoking Health. The report of smoking report. 2007;10 02 Retrieved December 10, 2008. http://www.kash.or.kr/user_new/pds_list.asp?.
- 12. Lee HS. A study on evaluation of effects of juvenile smoking cessation program applied by transtheoretical model. 2004;Busan, Inje University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 13. Ministry of Health Welfare and Family Affairs. National tobacco control and smoking cessation program guideline. 2006;Seoul, Author.
- 14. Moore L, Campbell R, Whelan A, Mills N, Lupton P, Misselbrook E, et al. Self help smoking cessation in pregnancy: Cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2002;325:1383. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Nam JJ. Guide for education of smoking cessation and moderation in drink. 2001;Seoul, Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs.
- 16. O'Connell KA, Gerkovich MM, Cook MR. Reversal theory's mastery and sympathy states in smoking cessation. Image-Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 1995;27:311–316.Article
- 17. Prochaska JO. Strong and weak principles for progressing from precontemplation to action on the basis of twelve problem behaviors. Health Psychology. 1994;13:47–51.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Prochaska JO, Diclemente CC, Velicer WF, Rossi JS. Standardized, individualized, interactive, and personalized self-help programs for smoking cessation. Health Psychology. 1993;12:399–405.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Prochaska JO, Velicer WF. The transtheoretical model of health behavior change. American Journal of Health Promotion. 1997;12:38–48.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Prochaska JO, Velicer WF, Diclemente CC, Fava JL. Measuring processes of change: Applications to the cessation of smoking. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1988;56:520–528.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Prochaska JO, Velicer WF, Fava JL, Rossi JS, Tsoh YT. Evaluating a population-based recruitment approach and a stage-based expert system intervention for smoking cessation. Addictive Behaviors. 2001;26:583–602.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Prochaka JO, Velicer WF, Redding C, Rossi JS, Goldsein M, DePue J, et al. Stage-based expert systems to guide a population of primary care patients to quit smoking, eat healthier, prevent skin cancer, and receive regular mammograms. Preventive Medicine. 2005;41:406–416.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Rovina N, Nikoloutsou I, Dima E, Michailidou M, Roussos C, Gratziou C. Smoking cessation treatment in a real-life setting: The Greek experience. Therapeutic Advances in Respiratory Disease. 2007;1:93–104.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Song TM. Smoking cessation clinics at public health centers in Korea. Health and Welfare Forum. 2007;129:50–65.
- 25. Song YH, Lee KS. Effects of a tailored smoking cessation program in high school girls. Journal of Korean Society for Health Education and Promotion. 2006;23(2):11–27.
- 26. Velicer WF, Diclemente CC, Prochaska JO, Brandenberg N. A decisional balance measure for assessing and predicting smoking status. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1985;48:1279–1289.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Velicer WF, Prochaska JO, Rossi JS, Snow MG. Assessing outcome in smoking cessation studies. Psychological Bulletin. 1992;111:23–41.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Velicer WF, Rossi JS, Prochaska JO, Diclemente CC. A criterion measurement model for health behavior change. Addictive Behaviors. 1996;21:555–584.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
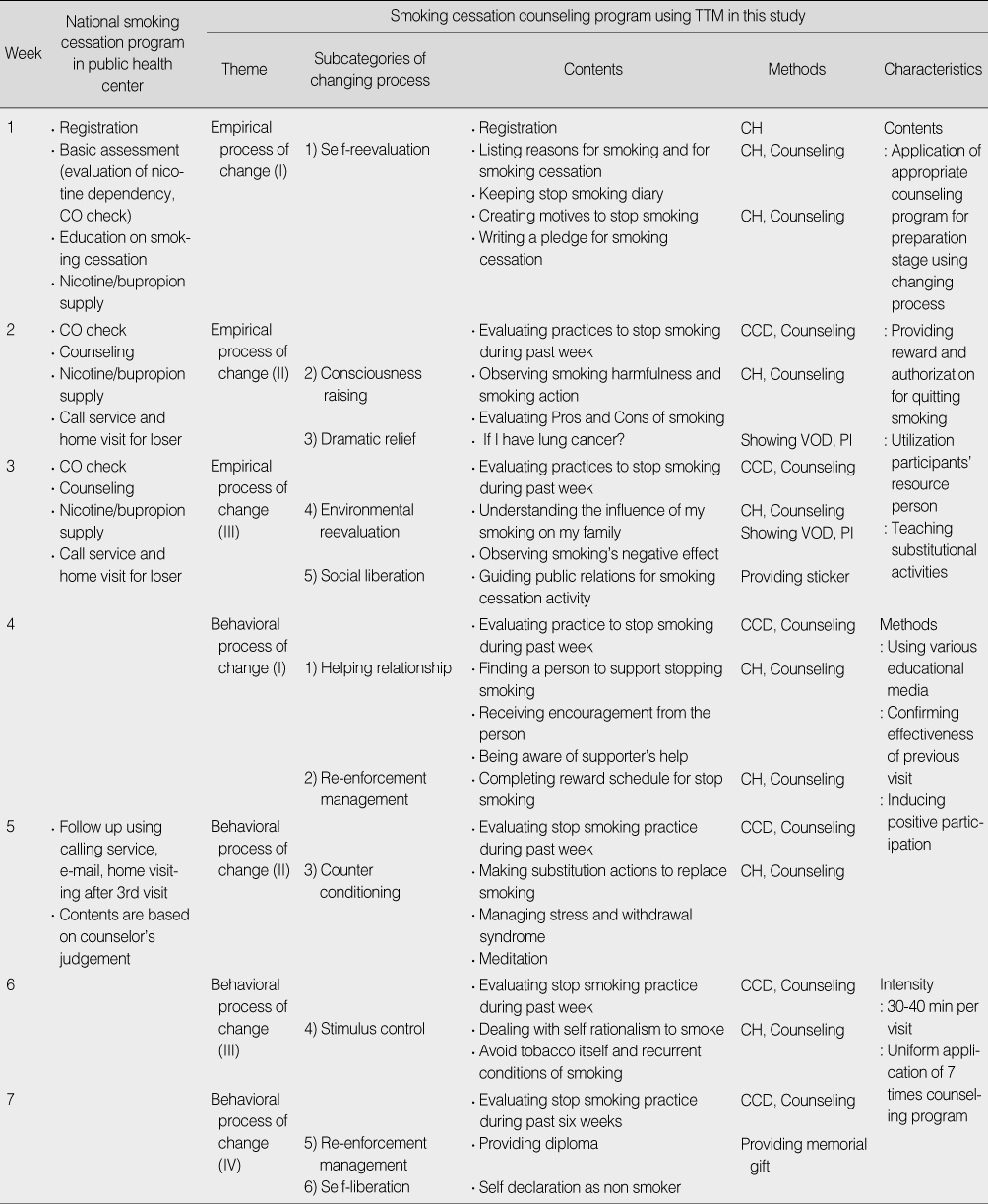
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis on Drug Addicts Recovery Based on a Transtheoretical Model
Riah Kim, Youngeun Park, Jieun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(3): 238. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a smoking cessation program on self-esteem, attitude, perception, and practice regarding control over smoking among male high school
Niyom Junnual, Chulaporn Sota, Anun Chaikoolvatana
Journal of Health Research.2019; 33(5): 366. CrossRef - Factors associated with the satisfaction of smoking cessation programs in clinics among Korean military personnel: An application of Transtheoretical model
Eunjoo Kwon, Eun-Hee Nah
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(5): 1. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Smoking Cessation Success during 4-week Smoking Cessation Program for University Students
Sang Mee Koo, Jeong Hee Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2017; 28(2): 165. CrossRef - Development of tailored nutrition information messages based on the transtheoretical model for smartphone application of an obesity prevention and management program for elementary-school students
Ji Eun Lee, Da Eun Lee, Kirang Kim, Jae Eun Shim, Eunju Sung, Jae-Heon Kang, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(3): 247. CrossRef - Exploring socio-contextual factors associated with male smoker’s intention to quit smoking
Minsoo Jung
BMC Public Health.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Smoking Cession Program Using Telephone Counselling and Text Messaging for Patients after Ischemic Heart Disease
Eun-Shim Kim, Hye-Ok Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(12): 7248. CrossRef - Effects of a Smoking Cessation Program including Telephone Counseling and Text Messaging using Stages of Change for Outpatients after a Myocardial Infarction
Jung-Hyeon Kong, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(4): 557. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Preparation Stage to Quit Smoking in Men
Jeong-Woon Yeon, Hyeongsu Kim, Kunsei Lee, Sounghoon Chang, Heejung Choi, Eunmi Ham, Jun Pyo Myong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 377. CrossRef - Stage-based interventions for smoking cessation
Kate Cahill, Tim Lancaster, Natasha Green
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2010;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Smoking Cessation Program on Processes of Change, Situational Temptation and Decisional Balance in Male University Student Smokers
Ju-Sung Kim, Sun-Ok Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(2): 113. CrossRef
Comparison of National Smoking Cessation Program and Smoking Cessation Counseling Program using Transtheoretical Model
CH=completing handout; CCD=check counseling documentation; VOD=video on demand; PI=presentation of impressions.
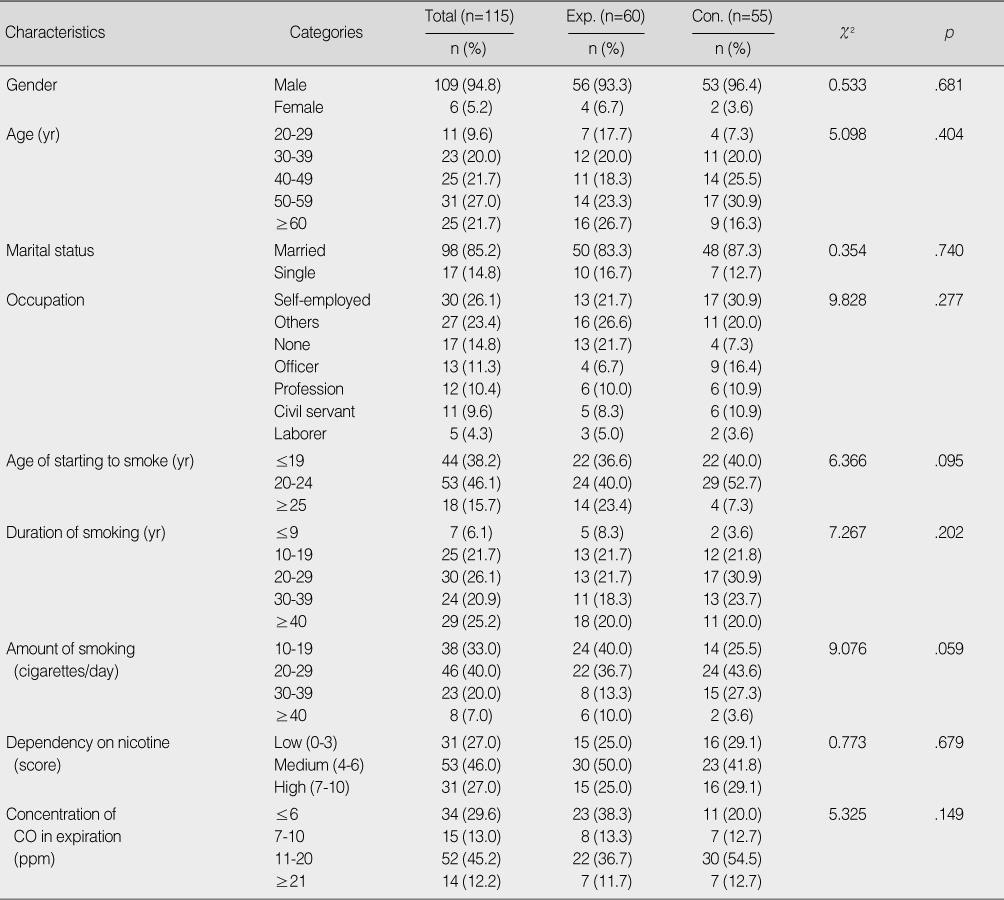
Homogeneity Test for Smoking related Characteristics between the Two Groups
Exp.=experimental group; Con.=control group.
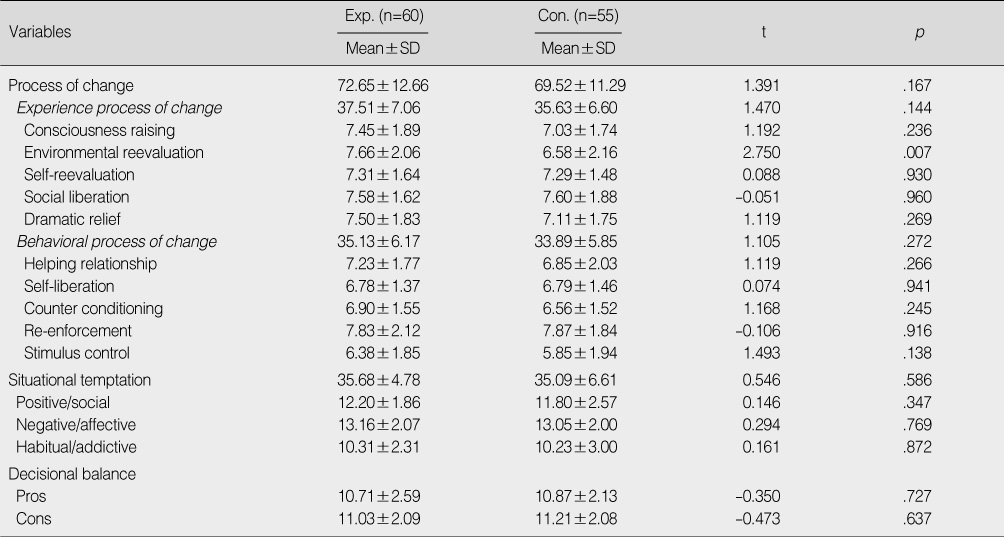
Homogeneity Test for Process of Change, Situational Temptation and Decisional Balance between the Two Groups
Exp.=experimental group; Con.=control group.
Post-test Score between the Two Groups for Process of Change, Situational Temptation, Decisional Balance and Achievement of Smoking Cessation during 6 weeks
*ANCOVA. Exp.=experimental group; Con.=control group.
CH=completing handout; CCD=check counseling documentation; VOD=video on demand; PI=presentation of impressions.
Exp.=experimental group; Con.=control group.
Exp.=experimental group; Con.=control group.
*ANCOVA. Exp.=experimental group; Con.=control group.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

