Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(3); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Relationship of Peer Relationships, Perceived Parental Rearing Attitudes, Self-reported Attachment Security, to Loneliness in Upper Elementary School-age Children
- So-Hyun Moon
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(3):401-408.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.401
Published online: June 29, 2009
Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Dongshin University, Naju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Moon, So-Hyun. Department of Nursing, Dongshin University, 252 Daeho-dong, Naju 520-714, Korea. Tel: 82-61-330-3587, Fax: 82-61-330-3580, bonjourmsh@dsu.ac.kr
• Received: September 12, 2008 • Accepted: May 28, 2009
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship of peer relationships, self-reported attachment security, perceived parental rearing attitudes, and loneliness in upper elementary school-age children.
-
Methods
- The data were collected from 207 students in grades 5 or 6, and descriptive statistics, t-test, Pearson correlation coefficients and Stepwise multiple regression were used with the SPSS/PC 12.0 program to analyze the data.
-
Results
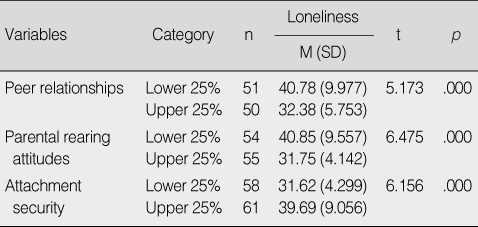
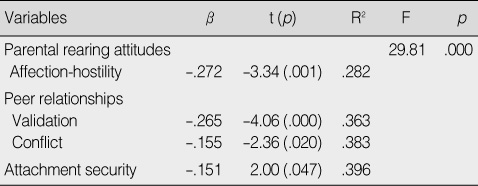
- There was a significant difference in loneliness between the upper 25% and lower 25% groups of peer relationships, perceived parental rearing attitudes, and self-reported attachment security. Stepwise multiple regression analysis showed affection-hostility in parental rearing attitudes, validation and conflict in peer relationships, and attachment security explained 39.6% of the total variance in loneliness.
-
Conclusion
- These results may contribute to a better understanding of loneliness in upper elementary school-age children. The results of the present study indicate a need to develop nursing interventions to prevent and manage children's loneliness.
- 1. Allen JP, Moore C, Kuperminc G, Bell K. Attachment and adolescent psychosocial functioning. Child Development. 1998;69:1406–1419.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Asher SR, Wheeler VA. Children's loneliness: A comparison of rejected and neglected peer status. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1985;53:500–505.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Berlin LJ, Cassidy J, Belsky J. Loneliness in young children and infant-mother attachment: A longitudinal study. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly. 1995;41:91–103.
- 4. Buhrmester D, Furman W. The development of companionship and intimacy. Child Development. 1987;58:1101–1113.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Doh HS. Children's loneliness and parental warmth and control. Korean Home Economics Association. 1996;34(6):1–11.
- 6. Dwyer KM. The meaning and measurement of attachment in middle and late childhood. Human Development. 2005;48:155–182.ArticlePDF
- 7. Hay DF, Payne A, Chadwick A. Peer relations in childhood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 2004;45:84–108.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Kerns KA, Klepac L, Cole A. Peer relationships and preadolescent's perceptions of security in the child-mother relationships. Developmental Psychology. 1996;32:457–466.Article
- 9. Kerns KA, Stevens AC. Parent-child attachment in late adolescence: Links to social relations and personality. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. 1996;25(3):23–49.
- 10. Kim JH. The relationship between children's attachment security, self-esteem, and loneliness. 2006;Seoul, Sookmyung Women's University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 11. Kim OS. Korean version of the revised UCLA loneliness scale: Reliability and validity test. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 1997;27:871–879.ArticlePDF
- 12. Kim OS. Alcohol drinking, smoking, and health perception in college students. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 1999;29:107–116.
- 13. Kim OS, Baik SH. The relationships among loneliness, social support, and family function in elderly Koreans. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2003;33:425–432.PubMed
- 14. Kim SH, Song S. A study on the loneliness of childhood and related variables. Journal of Korean Home Management Association. 2001;19(6):77–93.
- 15. Kim SY. The Effect of Sociodrama on the Children Loneliness and Peer Relations. 2001;Seoul, Hanyang University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 16. Krause-Parello CA. Loneliness in the school setting. The Journal of School Nursing: The Official Publication of the National Association of School Nurs. s. 2008;24(2):66–70.
- 17. Ladd GW, Kochenderfer BJ, Coleman CC. Friendship quality as a predictor of young children's early school adjustment. Child Development. 1996;67:1103–1118.Article
- 18. Lee HS. The impact of peer relationship on child life adjustment. 2001;Daejeon, Chunnam National University Educational Graduate School. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 19. Liberman M, Doyle AB, Markiewicz D. Developmental patterns in security of attachment to mother and father in late childhood and early adolescence: Associations with peer relations. Child Development. 1999;70:201–213.
- 20. Oh SS, Lee JS. Relationship between children's perception and definitional characteristics on parental rearing attitude. 1982;Seoul, Korean Institute for Research in the Behavioral Science.
- 21. Park EJ. Relationships between parenting efficacy, children's self-perceived competence and loneliness. 2003;Gyeongsan, Yeungnam University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 22. Park HJ. Effects of attachment security and self-image on depression in middle childhood. 2001;Seoul, Ewha Woman's University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 23. Radke-Yarrow M, Richters J, Wilson WE. Hinde R, Stevenson-Hinde J. Child development in network of relationship. In: Relationships within families: mutual influences. 1988;Oxford, Oxford University Press.
- 24. Richaud de Minzi MC. Loneliness and depression in middle and late childhood: The relationship to attachment and parental styles. The Journal of Genetic Psychology. 2006;167:189–210.ArticlePubMed
- 25. ohner RP, Pettengill SM. Perceived parental acceptance- rejection and parental control among Korean adolescents. Child Development. 1985;56:524–528.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Rubin KH, Ross HS. Peer relationships and social skills in childhood in peer rejection in childhood. 1990;New York, NY, Cambridge University Press.
- 27. Shin YL. Peer relationships, social behaviors, academic performance and loneliness in Korean primary school children. School Psychology International. 2007;28:220–236.ArticlePDF
- 28. Song MH. Effects of Parent's love versus hostility child-rearing attitude on the juvenile's loneliness. 2007;Seoul, Sookmyung Women's University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 29. Tak KS. A study on parental rearing patterns and stress perceived by elementary school students in urban and rural communities. 2005;Seoul, Konkuk University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 30. Yang KM. The link between body-esteem and self-esteem during adolescence. 1993;Cheongju, Chungbuk National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Commentary-Culture and Attachment During Middle Childhood
Bin-Bin Chen
New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development.2015; 2015(148): 93. CrossRef - Grounded Theory Approach to Transition Process of Parenting Experience among Mothers Defecting from North Korean
Hyun-Jeong Park, Yun-Soo Kim, Ho-Ran Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(1): 48. CrossRef - Relationship between Quality of Life and Parenting Attitude and Parent-Child Communication Patterns of School Age Children
Hee Geon Shin, Il Young Yoo, Eui Geum Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(3): 220. CrossRef
Relationship of Peer Relationships, Perceived Parental Rearing Attitudes, Self-reported Attachment Security, to Loneliness in Upper Elementary School-age Children
Relationship of Peer Relationships, Perceived Parental Rearing Attitudes, Self-reported Attachment Security, to Loneliness in Upper Elementary School-age Children
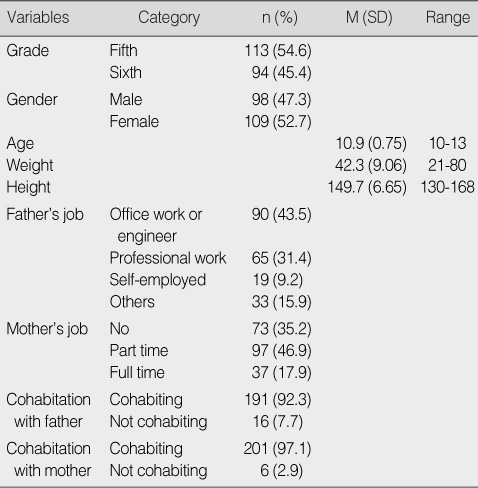
General Characteristics of the Participants (N=207)
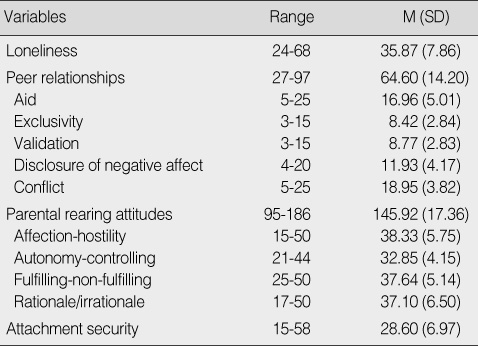
Level of Loneliness, Peer Relationships, Parental Rearing Attitudes, Attachment Security
Difference in Mean Scores for Loneliness by the Level of Peer Relationships, Parental Rearing Attitudes, and Attachment Security (N=207)
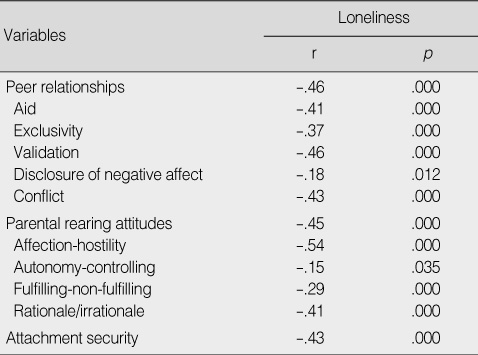
Correlation among Major Variables
Predictive Variables for Loneliness (N=207)
Table 1
General Characteristics of the Participants (N=207)
Table 2
Level of Loneliness, Peer Relationships, Parental Rearing Attitudes, Attachment Security
Table 3
Difference in Mean Scores for Loneliness by the Level of Peer Relationships, Parental Rearing Attitudes, and Attachment Security (N=207)
Table 4
Correlation among Major Variables
Table 5
Predictive Variables for Loneliness (N=207)
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

