Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(2); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- A Comparison of the Effect of Lidocaine or Sodium Bicarbonate Mixed with Rocuronium on Withdrawal Movement, Mean Arterial Pressure and Heart Rate during Rocuronium Injection
- Sung Suk Lee, Haesang Yoon
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(2):270-278.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.270
Published online: April 28, 2009
1Charge Nurse, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University of Medicine & Science, Incheon, Korea.
2Professor, Department of Nursing, Gachon University of Medicine & Science, Incheon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Yoon, Haesang. Department of Nursing, Gachon University of Medicine & Science, 534-2 Yeonsu-dong, Yeonsu-gu, Incheon 406-812, Korea. Tel: 82-32-820-4212, Fax: 82-32-820-4201, hsyoon@gachon.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was performed to find out the effects of lidocaine or 8.4% sodium bicarbonate mixed with rocuronium on mean arterial pressure, heart rate and withdrawal movement.
-
Methods
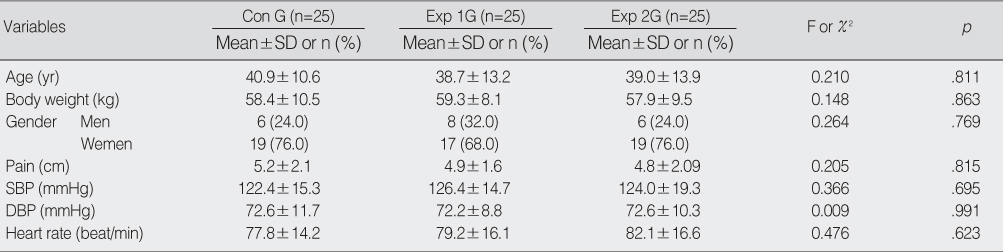
- Data collection was performed from December 15, 2006 through May 31, 2007. Seventy-five patients with American Society Anesthesiologist (ASA) physical status I & II, under general anesthesia, were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 groups: R group (RG) received rocuronium 0.6 mg/kg; RL group (RLG), rocuronium 0.6 mg/kg mixed with 2 mL of 2% lidocaine; RS group (RSG), rocuronium 0.6 mg/kg with the same volume of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate. Mean arterial pressure, heart rate and withdrawal movement were observed from its injection until 5 min after endotracheal intubation.
-
Results
- The incidence of withdrawal movement with its corresponding injections was 72%, 40% and 4% in RG, RLG and RSG, respectively (p<.001). Score of withdrawal movement was the lowest in RSG of all groups (p<.001). While mean arterial pressure (p=.011) in RSG decreased significantly, and heart rate (p=.003) in RG increased more with its injection than before induction of anesthesia.
-
Conclusion
- Administration of the equivalent volume of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate with rocuronium is more effective than that of lidocaine with rocuronium compared with rocuronium only, in preventing withdrawal movement and in stabilizing mean arterial pressure and heart rate.
- 1. Blunk JA, Seifert F, Schmelz M, Reeh PW, Koppert W. Injection pain of rocuronium and vecuronium is evoked by direct activation of nociceptive nerve endings. European Journal of Anaesthesiology. 2003;20:245–253.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Booth MG, Marsh B, Bryden FM, Robertson EN, Baird WL. A comparison of the pharmacodynamics of rocuronium and vecuronium during halothane anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 1992;47:832–834.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Borgeat A, Kwiatkowski D. Spontaneous movements associated with rocuronium: Is pain on injection the cause? British Journal of Anaesthesia. 1997;79:382–383.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Chiarella AB, Jolly DT, Huston CM, Clanachan AS. Comparison of four strategies to reduce the pain associated with intravenous administration of rocuronium. British Journal of Anaesthesia. 2003;90:377–379.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Choi HG, Kim DS, Chang TH, Kim SH, Kim KH, Ryu SJ. Appropriate dosage of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate for preventing injection pain of rocuronium during anesthetic induction. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2006;51:162–166.Article
- 6. Choi JH, Hwang JH, Shin YS. Comparison of the quantitative effect of ketamine on the vascular pain associated with intravenous rocuronium administration. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2005;49:30–34.Article
- 7. Hwang SM, Oh MS, Lim SY. Effect of sodium bicarbonate or lidocaine mixed with rocuronium on withdrawal movement during rocuronium injection. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2004;46:160–163.Article
- 8. Jung SM, Kim SH, Lim YS, Kwon HU, Kang PS, Park CW. The effect of sodium bicarbonate or lidocaine mixed with rocuronium on withdrawal movement in pediatric patients. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2005;48:514–519.Article
- 9. Jung SM, Ko NY, Lim YS, Kang PS, Kwon HU. Comparison of premixed NaHCO3 and lidocaine on rocuronium injection pain. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2005;48:483–488.Article
- 10. Jung SS, Lee JN, Yoon SH. Comparison of prevention effect of lidocaine preagreement on pain and withdrawal associated with injection of rocuronium. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2005;49:131–135.
- 11. Kim SJ, Lee HY, An TH. Comparison of withdrawal responses associated with temperature and gender on the injection of rocuronium. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2004;47:331–335.Article
- 12. Klement W, Arndt JO. Pain on intravenous injection of some anaesthetic agents is evoked by the unphysiological osmolality or pH of their formulations. British Journal of Anaesthesia. 1991;66:189–195.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Kwak HJ, Lee WK, Kim DY, Kwak HS. Pain on injection of rocuronium: Influence of two methods of lidocaine injection. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2004;46:675–678.Article
- 14. Lee SK, Lee JM, Kim YM, Moon HS. Pain on injection of rocuronium: The effect of pretreatment of lidocaine, fentanyl, and ondansetron. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2004;46:151–154.Article
- 15. Lui JT, Huang SJ, Yang CY, Hsu JC, Lui PW. Rocuronium induced generalized spontaneous movements cause pulmonary aspiration. Chang Gung Medical Journal. 2002;25:617–620.PubMed
- 16. Martin R, Carrier J, Pirlet M, Claprood Y, Tetrault JP. Rocuronium is the best nondepolarizing relaxant to prevent succinylcholine fasciculations and myalgia. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia. 1998;45:521–525.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. McCoy EP, Maddineni VR, Elliott P, Mirakhur RK, Carson IW, Cooper RA. Haemodynamic effects of rocuronium during fentanyl anaesthesia: Comparison with vecuronium. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia. 1993;40:703–708.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Memis D, Turan A, Karamanloglu B, Sut N, Pamukcu Z. The prevention of pain from injection of rocuronium by ondansetron, lidocaine, tramadol, and fentanyl. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2002;94:1517–1520.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Mencke T, Beerhalter U, Fuchs-Buder T. Spontaneous movements, local reactions and pain on injection of rocuronium. A comparison between female and male patients. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 2001;45:1002–1005.PubMed
- 20. Moorthy SS, Dierdorf SF. Pain on injection of rocuronium bromide. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 1995;80:1067. Article
- 21. Robertson EN. Pain on administration of rocuronium. Anaesthesia. 1996;51:93. ArticlePDF
- 22. Robertson EN, Hull JM, Verbeek AM, Booij LH. A comparison of rocuronium and vecuronium: The pharmacodynamic, cardiovascular and intra-ocular effects. European Journal of Anaesthesiology. 1994;11:Suppl 9. 116–121.
- 23. Ryoo HJ. Specific practice of nurse anesthetist. 2008;04;In: Paper presented at the meeting of the Korean Nurse Anesthetists Association; Incheon.
- 24. Shevchenko Y, Jocson JC, McRae VA, Stayer SA, Schwartz RE, Rehman M, et al. The use of lidocaine for preventing the withdrawal associated with the injection of rocuronium in children and adolescents. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 1999;88:746–748.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Steegers M, Robertson EF. Pain on injection of rocuronium bromide. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 1997;84:228. Article
- 26. Steegers MA, Robertson EF. Pain on injection of rocuronium bromide. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 1996;83:203. Article
- 27. Wee SY, Lee Y, An TH, So GY, Lim KJ, Jung JD, et al. The dose-dependent analgesic effect of lidocaine for pain on injecting rocuronium. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2004;47:327–330.Article
REFERENCES
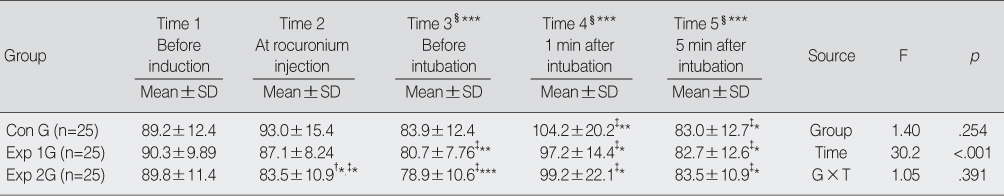
*p<.05; **p<.01; ***p<.001.
†comparison between Con and Exp 2G; ‡comparison between Time 1 and each Time in each group; §comparison between Time 1 and each Time in total group.
Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate); G×T=Group×Time.
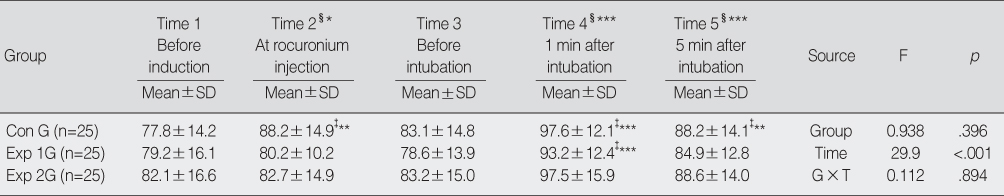
*p<.05; **p<.01; ***p<.001.
‡comparison between Time 1 and each Time in each group; §comparison between Time 1 and each Time in total group.
Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate); G×T=Group×Time.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for reducing rocuronium bromide induced pain on injection in children and adults
Hemanshu Prabhakar, Gyaninder Pal Singh, Zulfiqar Ali, Mani Kalaivani, Martha A Smith
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacological and non-pharmacological intervention for rocuronium-induced withdrawal movement in the Korean population: a meta-analysis of 41 studies including 4,742 subjects
Geun Joo Choi, Sangseok Lee, Jeoung Hyuk Lee, Seul Gi Park, Hyun Kang
Korean Journal of Anesthesiology.2014; 66(6): 419. CrossRef - Bolus Effective Dose of Ketamine for Preventing Withdrawal Movement on Injection of Rocuronium in Paediatric Patients
SK Min, SY Lee, KS Park, J Yoo, YJ Chae
Journal of International Medical Research.2011; 39(4): 1408. CrossRef

Figure 1
Homogeneity Test for Physiologic Characteristics (N=75)
SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate).
Frequency and Level of Withdrawal Movement (N=75)
Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate); *Kruskal Wallis test.
Mean Arterial Pressure (N=75)
*p<.05; **p<.01; ***p<.001.
†comparison between Con and Exp 2G; ‡comparison between Time 1 and each Time in each group; §comparison between Time 1 and each Time in total group.
Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate); G×T=Group×Time.
Heart Rate (N=75)
*p<.05; **p<.01; ***p<.001.
‡comparison between Time 1 and each Time in each group; §comparison between Time 1 and each Time in total group.
Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate); G×T=Group×Time.
SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate).
Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate); *Kruskal Wallis test.
* †comparison between Con and Exp 2G; ‡comparison between Time 1 and each Time in each group; §comparison between Time 1 and each Time in total group. Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate); G×T=Group×Time.
* ‡comparison between Time 1 and each Time in each group; §comparison between Time 1 and each Time in total group. Con G=control group (administration of rocuronium); Exp 1G=experimental 1 group (administration of rocuronium & lidocaine); Exp 2G=experimental 2 group (administration of rocuronium & 8.4% sodium bicarbonate); G×T=Group×Time.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION


 Cite
Cite

