Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 38(6); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of a Strengthening Program for Lower Back in Older Women with Chronic Low Back Pain
- Hee-Kyoung Hyoung
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(6):902-913.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.6.902
Published online: December 31, 2008
Full-time Lecturer, College of Nursing, Margaret Pritchard University, Jeonju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Hyoung, Hee-Kyoung. College of Nursing, Margaret Pritchard University, 168-1 Junghwasan-dong 1-ga, Wansan-gu, Jeonju 560-714, Korea. Tel: 82-63-230-7768, Fax: 82-63-231-7790, hhk00@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2008 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify effects of a strengthening program for the lower back in older women with chronic low back pain.
-
Methods
- The research design was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest experiment. The experimental group consisted of 16 older women and the control group, 14, all of whom had experienced low back pain for at least 3 months. The strengthening program for the lower back included lumbar stabilization exercises and education on pain management in daily living. For an 8 week period, exercises were done 3 days a week and on one day education was also given.
-
Results
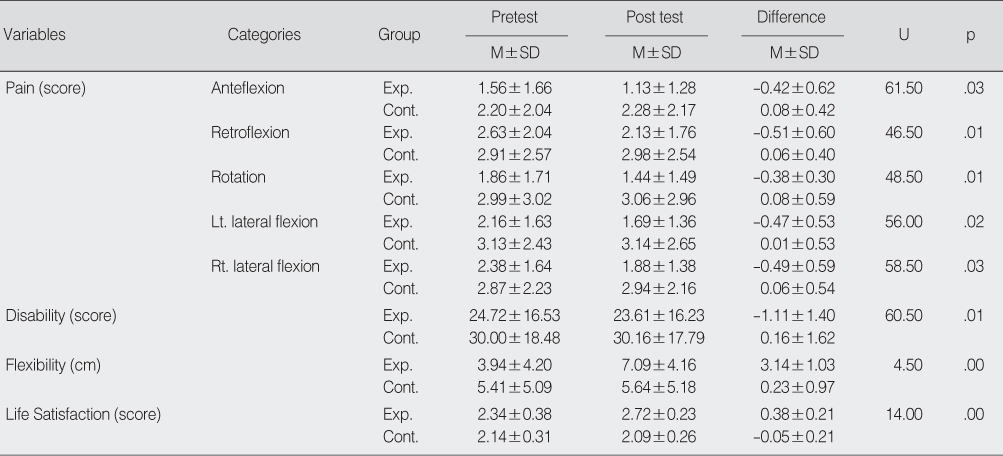
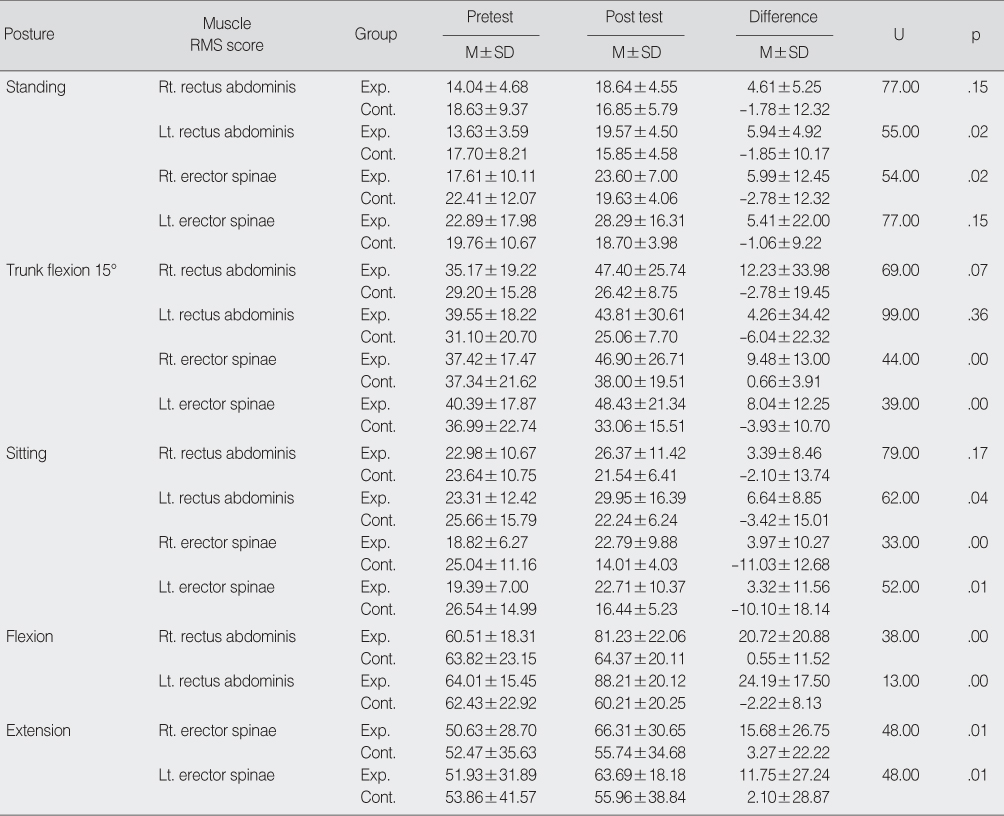
- Pain and disability scores decreased significantly in the experimental group compared to the control group. Flexibility, life satisfaction and lumbar muscle strength scores increased significantly in the experimental group compared to the control group.
-
Conclusion
- Low back pain and disability can be relieved, and flexibility, muscle strength, and life satisfaction increased through a program to strengthen the lower back. It is suggested that a program to strengthen the lower back would be an effective nursing intervention for older women with low back pain.
- 1. Back YH. Effect of lumbago-preventive gymnastics program on female aged lumbago patients. 2000;Seoul, Korea National Sports University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 2. Barnes D, Smith D, Gatchel RJ, Mayer TG. Psychosocioeconomic predictors of treatment success/failure in chronic low-back pain patients. Spine. 1989;14:427–430.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Bingefors K, Isacson D. Epidemiology, co-morbidity, and impact on health-related quality of life of self-reported headache and musculoskeletal pain- A gender perspective. European Journal of Pain. 2004;8:435–450.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Casey KL. Neural mechanisms of pain: An overview. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. Supplementum. 1982;74:13–20.
- 5. Choi SY. The effect of exercise program on chronic low back pain in female teachers of elementary school. 2000;Seoul, Catholic University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 6. Fairbank JC, Couper J, Davies JB, O'Brien JP. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy. 1980;66:271–273.PubMed
- 7. Jacobs JM, Hammerman-Rozenberg R, Stessman J. Longevity and chronic back pain in older people. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2005;53:1636–1637.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Jeon TW. Exercise test and prescription. 1994;Seoul, Teagun Munwhasa.
- 9. Jung YW. The effects of lumbar stabilizing exercise on the functional recovery and the range of motion of low back pain patients. 2003;Daegu, Daegu University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 10. Kim HS. The effect of back pain relieve exercise program on the pain and depression of the elderly with chronic low back pain. 2000;Jinju, Gyeong Sang National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 11. Kim SH. A study on welfare service for the elderly at home and facilities and factors affecting their life satisfaction. 2005;Muan, Chodang University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 12. Kim SJ, Ahn TS, Jung KS, Park JC, Kim CN, Lee SJ. The development of low back exercise program for the elderly. Journal of Ansan College. 2003;21:145–163.
- 13. Kim SS, Jung IG. Exercise physiology. 1995;Seoul, Daekyoung Publishing.
- 14. Ko JK. Comparing the effects of drug therapy, physical therapy, and exercise on pain, disability, and depression in patients with chronic low back pain. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:645–654.ArticlePDF
- 15. Kozma A, Stones MJ. The measurement of happiness: Development of the Memorial University of Newfoundland Scale of Happiness (MUNSH). Journal of Gerontology. 1980;35:906–912.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Lavsky-Shulan M, Wallace RB, Kohout FJ, Lemke JH, Morris MC, Smith IM. Prevalence and functional correlates of low back pain in the elderly: The Iowa 65+ Rural Health Study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1985;33:23–28.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Lee KE. The effect of dance movement program on psychological health in middle aged women. 1998;Seoul, Catholic University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 18. Lee KW. Kim JH, Han TR. Back and neck pain. In: Rehabilitation medicine. 2002;Seoul, Koonja Publishing. 427–444.
- 19. Lee SJ. An application effect of rhythmic movement program for the health promotion in the elderly. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2000;30:776–790.ArticlePDF
- 20. Lim HS, Chung MK, Kim SK, Lee JM. A study on the methods evaluation and prevention of occupational low back pain. 1998;Seoul, Korea Occupational Safety & Health Agency, Occupational Safety & Health Research Institute.
- 21. Mailloux J, Finno M, Rainville J. Long-term exercise adherence in the elderly with chronic low back pain. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 2006;85:120–126.Article
- 22. O'Sullivan PB, Phyty GD, Twomey LT, Allison GT. Evaluation of specific stabilizing exercise in the treatment of chronic low back pain with radiologic diagnosis of spondylosis or spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1997;22:2959–2967.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Panjabi M, Abumi K, Duranceau J, Oxland T. Spinal stability and intersegmental muscle forces. A biomechanical model. Spine. 1989;14:194–200.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Park HS, Kang YS, Park KY. A study on health perception and health promoting behavior in chronic back pain patient. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006;36:439–448.PubMed
- 25. Scott J, Huskisson EC. Vertical or horizontal visual analogue scales. Annals of the Rheumatic diseases. 1979;38:560. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Souza GM, Baker LL, Powers CM. Electromyographic activity of selected trunk muscles during dynamic spine stabilization exercises. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2001;82:1551–1557.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Sung PS. Multifidi muscles median frequency before and after spinal stabilization exercise. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2003;84:1313–1318.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Yilmaz F, Yimaz A, Merdol F, Parlar D, Sahin F, Kuran B. Efficacy of dynamic lumbar stabilization exercise in lumbar microdisectomy. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2003;35:163–167.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Yoon G. Development of life satisfaction scale in the Korean elderly. Proceedings from Korean Psychological Symposium. 1982;Seoul. Korean Psychological Association.
- 30. Yun EH. Comparing the effects of lumbar stabilization exercise and McKenzie exercise on the range of motion and pain of the patient with low back pain. 2003;Seoul, Dankook University. Unpublished master's thesis.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Older Chinese adults’ social participation and happiness: the mediating effect of spirituality
Jie Li, Ho-Tang Wu
Journal of Religion, Spirituality & Aging.2025; 37(1): 47. CrossRef - Comparison of Effects of Core Stabilization Exercise according to Mirror Visual Feedback and Video Visual Feedback on Static and Dynamic Balance in College students with Low Back Pain
Kyung Tae Yoo
The Journal of Korean Academy of Physical Therapy Science.2025; 32(4): 95. CrossRef - Effects of hand-press pellet on pain and daily life of elders with chronic lower back pain: randomized controlled trial
Hyojung Park, Hyejin Lee
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Lumbar Stabilization Exercise on Pain, Disability and Functional Performance among Older People with Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review
Zarina Zahari, Siti Aishah Shaiful Azan, Naim Faiz Ahmad Imran
Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences.2023; 19(4): 307. CrossRef - The Effects of Lumbar Stabilization Exercises Using A Traction Force Sensor on The Flexibility of The Spine, Dynamic Balance, Pain Intensity, and ODI(Oswestry Disability Index) in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain
Sung il Ahn, Se Yun Kim, Tae Woo Kang, Seo Yoon Park, Hee jin Cho, Soung Kyun Hong
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2023; 12(4): 547. CrossRef - Effectiveness of strengthening exercise plus activities of daily living instructions in reducing pain in patients with lumbar disc herniation: a randomized controlled trial
Shabbir Ahmed Sany, MD Imam Shahriar, Zannatun Nyme, Taukir Tanjim
F1000Research.2021; 10: 1163. CrossRef - Effects of an Individualized Educational Program for Korean Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Seong-Kyong KIM, Hee-Seung KIM, Sung-Soo CHUNG
Journal of Nursing Research.2021; 29(6): e177. CrossRef - The Effects of Stretching and Strengthening Exercise on the Pain, Pelvic Tilt, Functional Disability Index, and Balance Ability of Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain
Tae Woo Kang, Beom Ryong Kim
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2019; 31(1): 7. CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Stage-Matched Intervention for Elderly Women with Chronic Back Pain in the Contemplation and Preparation Stage
Hyun-Ju Oh, Soon-Rim Suh, Mihan Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(4): 414. CrossRef - The Effects of Combined Training Applying Dance Sports and Elastic Band Exercise on Disability Indexes and Daily Living Fitness in Aged Women with Chronic Backache
Lee, Hyang-Beum
The Journal of Korean Dance.2018; 36(4): 213. CrossRef - Effects of the application of ankle functional rehabilitation exercise on the ankle joint functional movement screen and isokinetic muscular function in patients with chronic ankle sprain
Sung-Bum Ju, Gi Duck Park
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2017; 29(2): 278. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Strengthening Exercises for the Elderly with Low Back Pain to Improve Symptoms and Functions: A Systematic Review
Nor Azizah Ishak, Zarina Zahari, Maria Justine
Scientifica.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Korean Medical Treatment with Postural Yinyang Correction of Temporomandibular Joint on Chronic Low Back Pain
Shin Young Kim, Jong Cheol Seo, Yeon Ju Seo, Jong Hyeon Park, Yoon Joo Lee, Cheol Hong Kim, Chun Ho Song, Kyung Jeon Jang, Young Jun Lee, Hyun Min Yoon
Korean Journal of Acupuncture.2016; 33(4): 157. CrossRef - Effects of a Muscle Energy Technique on Pain and Functionality in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain
Yeong-Taek Oh
Journal of the Korean Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation Association.2016; 14(2): 139. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Behavior in Elderly Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain
Sukhee Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2015; 17(1): 20. CrossRef - The Effects of Balance Ability by Selective Core Exercise on the Elderly
박장성, 김양호, 유원종, 이상호, 서삼기
Journal of Advanced Engineering and Technology.2015; 8(3): 231. CrossRef - Musculoskeletal Changes before and after High-Frequency Management - Females in their 20s and 40s as Subjects -
김현옥, 김명우
Journal of Investigative Cosmetology.2015; 11(4): 341. CrossRef - The comparative effectiveness of advice/education compared to active physiotherapy (manual therapy and exercise) in the management of chronic non-specific low back pain
Samuel Kweku Wie Otoo, Paul Hendrick, Daniel Cury Ribeiro
Physical Therapy Reviews.2015; 20(1): 16. CrossRef - Effects of the Hand Acupressure and Lumbar Strengthening Exercise on Women with Lower Back Pain
Eun Young Jeon
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 63. CrossRef - Effect of flexibility exercise on lumbar angle: A study among non-specific low back pain patients
Nithima Purepong, Anusorn Jitvimonrat, Sujitra Boonyong, Premtip Thaveeratitham, Praneet Pensri
Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies.2012; 16(2): 236. CrossRef - Physical Functions of Industrial Workers with Chronic Low Back Pain and Changes in Health-related Quality of Life according to Virtual Reality Exercise Program
Dae-Sik Ko, Dae-In Jung, Sang-Heon Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(10): 4564. CrossRef - The Effects of Stabilization Exercise on Muscle Performance according to Bearing Surface
Jae-Cheol Park, Jong-Man Han, Yong-Seong Kim, Yong-Nam Kim
Journal of the Korean Academy of Clinical Electrophysiology.2012; 10(1): 39. CrossRef
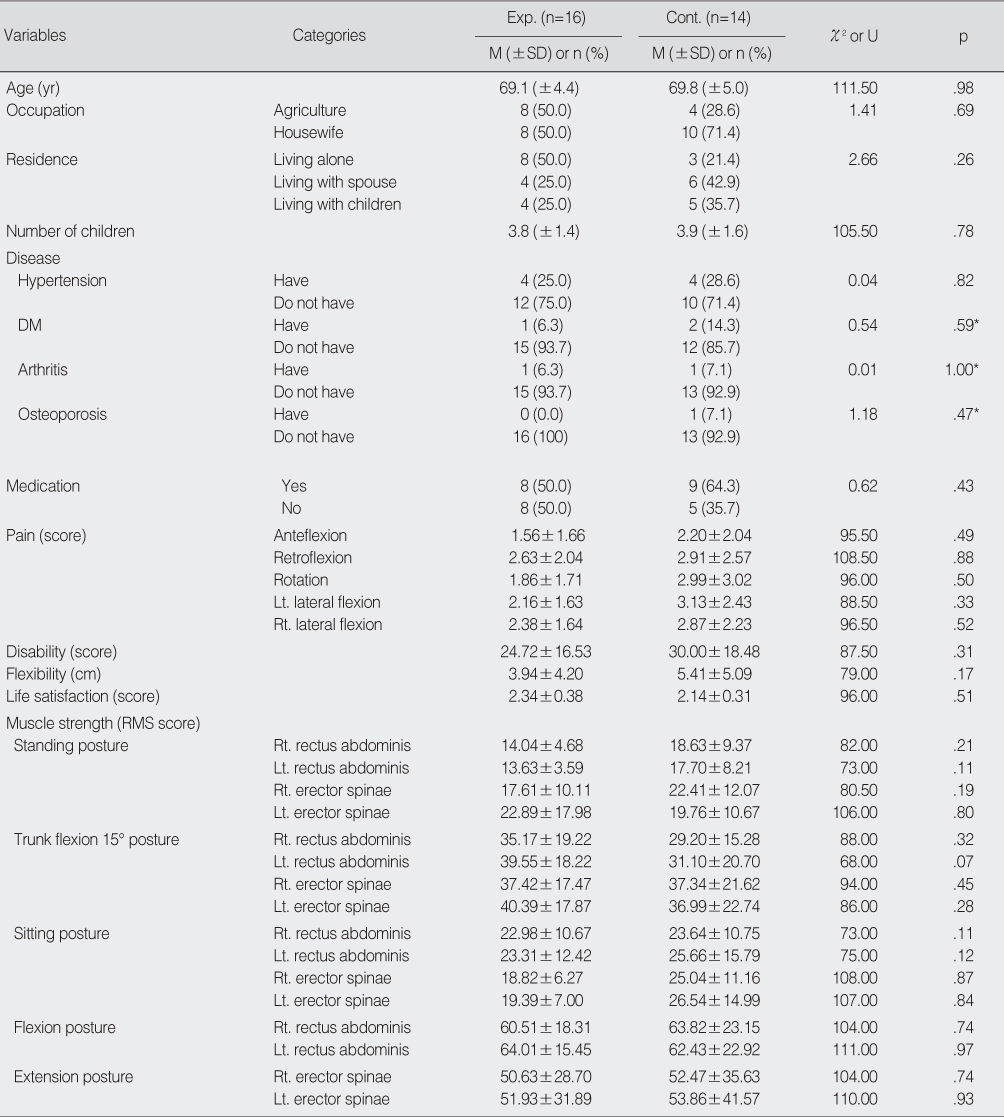
Test for Homogeneity of Participants (N=30)
*Fisher's exact test (2-tailed test).
Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group; DM=Diabetes Mellitus; Lt.=left; Rt=right; RMS=root mean square.
Effect of Strengthening Program on Pain, Disability, Flexibility and Life Satisfaction between Experimental and Control Group (N=30)
Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group; Lt.=left; Rt=right.
Effect of Strengthening Program on Muscle Strength between Experimental and Control Group (N=30)
RMS=root mean square; Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group; Lt.=left; Rt=right.
*Fisher's exact test (2-tailed test). Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group; DM=Diabetes Mellitus; Lt.=left; Rt=right; RMS=root mean square.
Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group; Lt.=left; Rt=right.
RMS=root mean square; Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group; Lt.=left; Rt=right.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

