Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 38(3); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- A Study on Physical Symptom, Activity of Daily Living, and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) in the Community-Dwelling Older Adults
- Kyung-Rim Shin, Young Soon Byeon, Younhee Kang, Jiwon Oak
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(3):437-444.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.3.437
Published online: June 30, 2008
1Professor, College of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
2Assistant Professor, College of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
3Post-doc fellow, College of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Shin, Kyung-Rim. College of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University, 11-1 Daehyeon-dong, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-750, Korea. Tel: 82-2-3277-2886, Fax: 82-2-3277-2850, krshin@ewha.ac.kr
Copyright © 2008 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study aimed to identify the relationships among physical symptoms, activities of daily living, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in community-dwelling older adults.
-
Methods
- A stratified random sampling method was conducted to recruit participants from May 10 to August 17, 2007. Physical symptoms were measured using the Physical Health Questionnaire (PHQ), activities of daily living using the Late-Life Functional and Disability Instrument (LLFDI), and HRQoL using the Medical Outcomes Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36) in 242 community-dwelling elderly Korean people.
-
Results
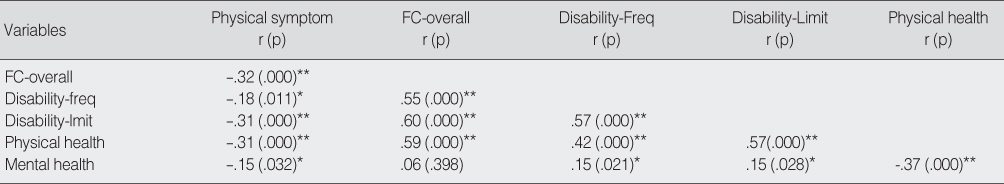
- The HRQoL correlates with the physical symptoms (r=-.31) and the function component (r=.59). Of the two disability parts of the LLFDI, the limitation dimension correlates higher (r=.57) with HRQoL than the frequency dimension (r=.42). The HRQoL is significantly associated with the function component, and disability limitation in capability which explained 44.4% of variance in physical health.
-
Conclusion
- These results may contribute to a better understanding of physical symptoms, activities of daily living, and HRQoL in community-dwelling older adults. Therefore, health programs for prompting older adult's health should be planned based on results of the study.
- 1. Baek HJ. A Study on depression and somatic symptoms in the community-dwelling elderly. 2007;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 2. Borgaonka MR, Irvine EJ. Quality of life measurement in gastrointestinal and liver disorder. Gut. 2000;47:444–454.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Campbell A. Subjective measures of well-being. The American Journal of Psychology. 1977;3:177.
- 4. DeLateur BJ. The 29th Walter J. Zeiter Lecture. Quality of life: A patient-centered outcome. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 1997;78:237–239.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Demyttenaere K, Bonnewyn A, Bruffaerts R, Brugha T, De Graaf R, Alonso J. Comorbid painful physical symptoms and depression: Prevalence, work loss, and help seeking. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2006;92:185–193.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Haley SM, Jette AM, Coster WJ, Kooyoomjian JT, Levenson S, Heeren T, et al. Late life function and disability instrument: II. Development and evaluation of the function component. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2002;57:217–222.
- 7. Jette AM, Haley SM, Coster WJ, Kooyoomjian JT, Levenson S, Heeren T, et al. Late life function and disability instrument: I. Development and evaluation of the disability component. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2002;57:209–216.
- 8. Jun YS. Study on effect of a leisure education program on a leisure awareness and quality of life among elderly persons. 2007;Seoul, Seoul Womans University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 9. Kim SK. Relationships between family support, self-care behavior and perceived health among female patients under the chemotherapy. 2004;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 10. Kim YH, Kim KS. A study on the relationship between self-esteem and quality of life of the elderly. Journal of Welfare for the Aged. 2002;17:157–189.
- 11. Statistics about cause of death in 2005. KNSO. 2006;Retrieved October 1, 2007. Korean National Statistical Office. from http://www.nso.go.kr.
- 12. Koh BS, Yoo YS. A study on the social support and quality of life for the elderly in Jeju. Journal of Welfare for the Aged. 2002;18:49–72.
- 13. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-15: Validity of a new measure for evaluating the severity of somatic symptoms. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2002;64:258–266.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Lee EJ, Han CW. The relationship between the health-related quality of life and home care service needs in the elderly. Journal of Welfare for the Aged. 2005;30:171–190.
- 15. Lee MS. A study on urinary incontinence and sleep disorder, quality of life of elderly women. 2006;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 16. Lee SY, Choi SJ, Na YH. A study on the health-related qualiry of life. The Korean Journal Gastrointestinal Motility. 2001;7:6–17.
- 17. Lim DH. . Effects of regular exercise on stress, coping strategy, and life satisfaction of old ages. 2007;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 18. Moon MJ. A study on the instrumental activities of daily living and quality of life of elderly home residents. Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing. 2001;4:46–57.
- 19. Oh YH, Suk JE, Kwon JD, Kim JS, Park YR, Lim JK. Old person's quality of life and policy implications. 2005;Seoul, Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs.
- 20. Park YH, Kim JH, Kim HJ. Factors influencing regular exercise of the elderly. Journal of Korean Academy of Adult Nursing. 2002;14:348–358.
- 21. Park YR, Kwon HJ, Kim KH, Choi MH, Han SE. A study on relations between self-esteem, self efficacy and quality of life of the elderly. Journal of Welfare for the Aged. 2005;29:237–258.
- 22. Song AR, So HY. An influencing factors on quality of life in the instiutionalized older population. Chungnam Journal of Nursing Academy. 2000;3:29–37.
- 23. Song NW. Infliense of Sexual Life of the Aged on the Quality of Life. 2006;Seoul, Kwangwoon University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 24. Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB. Validation and utility of a self-report version of PRIME-MD: The PHQ primary care study. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;282:1737–1744.PubMed
- 25. Trentini CM, Xavier FM, Chachamovich E, Rocha NS, Hirakata VN, Fleck M.P. The influence of somatic symptoms on the perfomance of elders in the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI). Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria. 2005;27:119–123.PubMed
- 26. Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care. 1992;30:473–483.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Yim ES, Lee KJ. Effect of physical ability, depression and social support on quality of life in low income elders living at home. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2003;5:38–49.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Analysis of the Difference in Nutrient Intake Status by Household Income and Education Level
Min-Young Chong, Inhwa Han
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2025; 36(2): 185. CrossRef - SOCIO-ECONOMIC CONSTRAINTS OF HOME MODIFICATION TO MITIGATE THE RISK OF FALLS AMONG THE ELDERLY IN THE DIVERSE REGIONS OF THAILAND
Sumavalee Chindapol
Journal of Architectural/Planning Research and Studies (JARS).2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Subjective and objective health according to the characteristics of older adults: Using data from a national survey of older Koreans
Nam-Hae Jung, Chun-Yeop Lee
Medicine.2024; 103(47): e40633. CrossRef - Factors associated with the quality of life of Chinese parents who have lost their only child
Hongyan Xu, Hongying Li, Penghao Fan, Chao Rong
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A qualitative study of home-visiting oral health care experience in vulnerable populations
Sang-Eun Moon, Bo-Ram Lee, Min-Sook Jeong, Jae-Ra Lee, Seon-Yeong Kim, Myung-Ok Ha, Il-Shin Kim, Hyeong-Seok Lim, Mi-Ra Lee, Young-Ae Yun, Sun-Hwa Hong
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2024; 24(3): 229. CrossRef - Association between fatigue, pain, digestive problems, and sleep disturbances and individuals’ health-related quality of life: a nationwide survey in South Korea
Younghwa Baek, Kyungsik Jung, Hoseok Kim, Siwoo Lee
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on Effect of Regular Leisure Activities on Health- Related Quality of Life (SF-36) in the Elderly: Physical Leisure Activities
Myonghee Cho, Junsoo Hur
Korean Journal of Lesure, Recreation & Park.2020; 44(4): 77. CrossRef - Feeling good in old age: factors explaining health-related quality of life
Manuela Alcañiz, Aïda Solé-Auró
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the Elderly's Health Statuses, Health Behavior, and Social Relations on Their Health-related Quality of Life: Focusing on Family Types
Young Bum Kim, Seung-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 310. CrossRef - Somatic Symptoms Mediate the Relationship Between Health Anxiety and Health-Related Quality of Life over Eight Weeks
Karly M. Murphy, Adam P. McGuire, Thane M. Erickson, Amy H. Mezulis
Stress and Health.2017; 33(3): 244. CrossRef - The Effects of a Functional Game (Rejuvenescent Village) for Older Koreans' Cognitive Function, Instrumental Activities of Daily Living, Depression, and Life Satisfaction
Kyung Choon Lim, Min Ho Chun
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2016; 18(4): 296. CrossRef - Effects of Health Status and Health Management on Activities of Daily Living among Urban-Dwelling Older Koreans
Myung Sill Chung, Kyung-Choon Lim, Yeon Ha Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(1): 72. CrossRef - Prediction of Quality of Life among the Elderly at Care Facilities for the Elderly according to Health States, Physical and Cognitive Functions, and Social Supports-Focused on D Metropolitan City
Jong-Im Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(7): 4656. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life according to breakfast in elderly
Ji-Yeon Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(7): 4668. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Influencing Factors of Health Related Quality of Life of the Elderly in Senior Center by Region : Focus on Urban and Rural Areas
Soon-Ok Yang, Hae-Ryun Cho, Seung-Hee Lee
The Journal of Digital Policy and Management.2014; 12(1): 501. CrossRef - Factors associated with Health-related Quality of Life in Vulnerable Elderly Women
Gyeyoung Shin, Eun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 419. CrossRef - Gender Difference in Factors Related to Depression in Vulnerable Elderly
Eun-Kyung Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2014; 8(3): 169. CrossRef - Effect of Health status and Health Behavior on the Diabetes Mellitus Prevalence
Ji-Yeon Hong, Jin-Ah Park
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(10): 198. CrossRef - Self-reported function and disability in late life – cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Swedish version of the late-life function and disability instrument
Kirsti Skavberg Roaldsen, Alexandra Halvarsson, Belinda Sarlija, Erika Franzen, Agneta Ståhle
Disability and Rehabilitation.2014; 36(10): 813. CrossRef - Subjective health status and relative factors of old-old elderly of more than 75-year-old -Based on 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Eun-Seok Kim, Sung-Kook Lee, Hee-Jung Yoon, Hang-Me Nam, Kyung-Hee Kim, Gi-Hong Kwon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(7): 4279. CrossRef - The Study on Functional State, Self Efficacy, and Life Satisfaction in the Elderly with Decreased Visual Acuity
Ki Jung Cha, Young Eun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(3): 225. CrossRef - Influence of Malnutrition and Social Network on Health-related Quality of Life in Elders
Hee Kyung Kim, Hae Kyung Chang, Mi-Ra Lee, Youn-Jung Son, Su Jeong Han, Nam Young Yang, Myoung-Ran Yoo, Seon Young Choi, Youn Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2013; 20(2): 98. CrossRef - Effects of Art Therapy on Cognition, Depression, and Quality of Life in Elderly
Yeon Hee Choi, En Young Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(3): 323. CrossRef - Gender Difference in Influencing Factors on Health related Quality of Life among the Elderly in Community
Seung-Hee Lee
The Journal of Digital Policy and Management.2013; 11(12): 523. CrossRef - Reliability and validity of the French-Canadian Late Life Function and Disability Instrument in community-living wheelchair-users
Brodie M. Sakakibara, François Routhier, Marie-Pier Lavoie, William C. Miller
Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy.2013; 20(5): 365. CrossRef - Relationship between Low Back Pain and Health-Related Quality of Life among Some Elderly
Kyeong-Ae Oh, Jong Park, Dae-Jung Jeon, Mi-Ah Han, Seong-Woo Choi
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2012; 37(3): 156. CrossRef - Comparison of Comprehensive Health Status and Health-related Quality of Life between Institutionalized Older Adults and Community Dwelling Older Adults
Hye-Jin Hyun, Aekyung Chang, Su Jeong Yu, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(1): 40. CrossRef - Association of Health Risk Behaviors with Mental Health among Elderly Koreans
Ki Dong Ko M.D., Young Tae Cho Ph.D., Sung Il Cho M.D., PhD., Joo Hon Sung M.D., PhD., Be Long Cho M.D., PhD., Ki Young Son M.D., Ho Chun Choi M.D.
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2012; 16(2): 66. CrossRef - Effects on Salivation, Xerostomia and Halitosis in Elders after Oral Function Improvement Exercises
Young Jin Kim, Kyung Min Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(6): 898. CrossRef - Influence of Korean Traditional Dance Exercise upon Mental Health and Life Satisfaction in Elderly Women
Young-Hee Kim, Jin-Sook Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(7): 3082. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression and Quality of Life in Elderly Customized Home Visiting Health Services
Yunhee Kwon, Chungnam Kim, Oh-Gye Kwag
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(3): 262. CrossRef - Validation of the Spanish Version of the Short‐Form Late‐Life Function and Disability Instrument
Pedro Abizanda, Mercedes López‐Jiménez, Jesús López‐Torres, Pilar Atienzar‐Núñez, Juan M. Naranjo, Edward McAuley
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2011; 59(5): 893. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Health-Promoting Behaviors of Community-Dwelling Korean Older Women
Young Mi Lim, Mi Hae Sung, Kyung Sook Joo
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2010; 36(10): 42. CrossRef - The Effects of a Cognitive Enhancement Group Training Program for Community-dwelling Elders
Young Ran Han, Mi Sook Song, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 724. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health-related Quality of Life in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Jeong Sun Kim, Vit Na Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 287. CrossRef - The Effects of Related Factors on Health-related Quality of Life for the Frail Elderly
Eun Shil Yim, Kyoung Hee No
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 12. CrossRef - The Effects of Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain and Depression on Health-related Quality of Life by Gender in Community-dwelling Older Adults
Seung-Hee Lee, Soon-Ok Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 21. CrossRef - Factors Related to the Health Related Quality of Life in Elderly Women
Shinyoung Sohn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(2): 99. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Factors Influencing the Life Satisfaction of the Elderly According to their Cognitive Impairment Level
Rah Il Hwang, Ji Young Lim, Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 622. CrossRef - Factors influencing Health-related Quality of Life in Korean Medicaid Beneficiaries
Sun-Woo Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 480. CrossRef
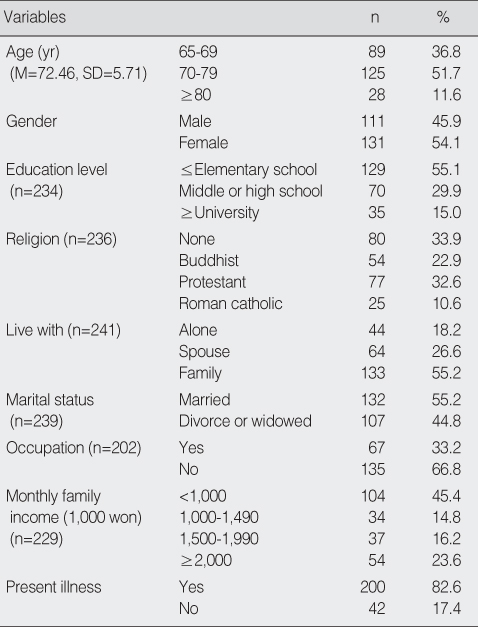
General Characteristic of Participants (N=242)
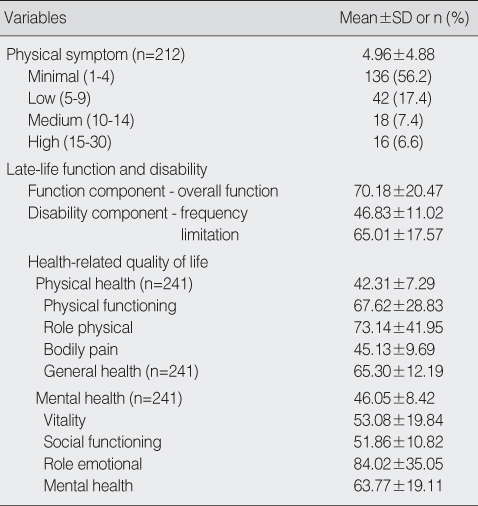
Summary of Descriptive Statistics for Study Variables (N=242)
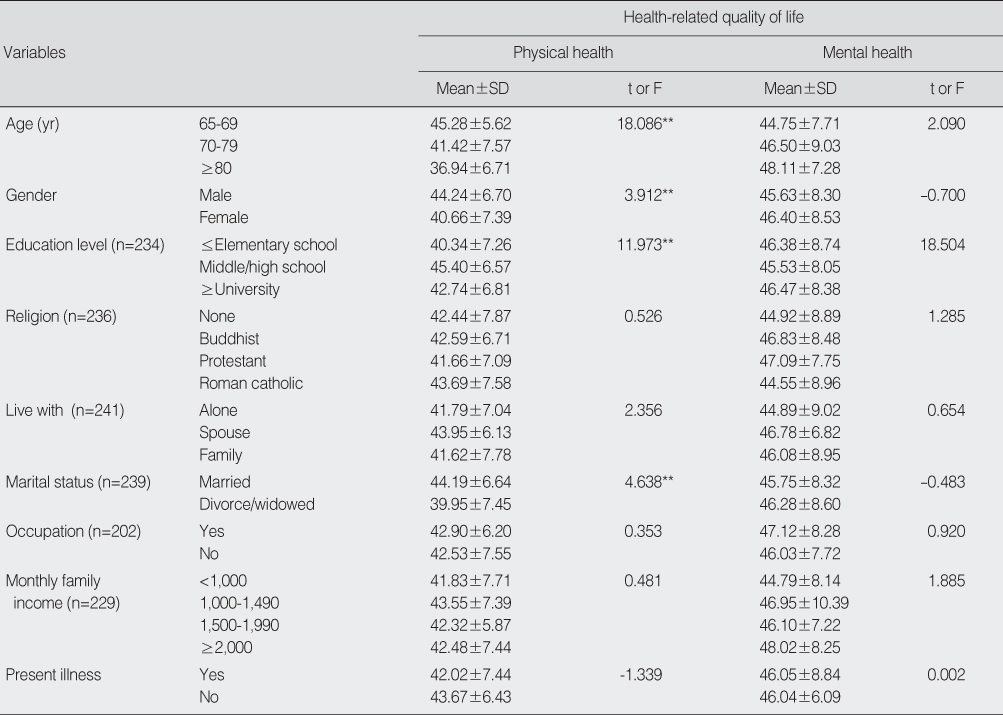
The Health-Related Quality of Life according to General Characteristics (N=242)
*p<.05; **p<.01.
Relationships among the Characteristics (N=242)
*p<.05; **p<.01. FC-Overall=Function Component-Overall function; Disability-Freq=Disability-Frequency; Disability-Limit=Disability-Limitation.
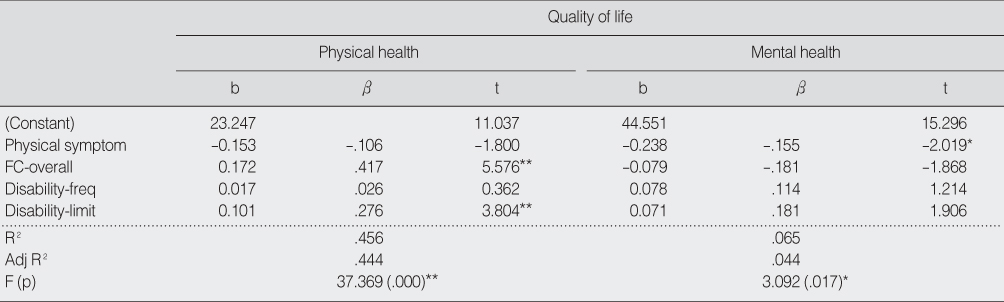
Influencing Factors on Health-Related Quality of Life (N=242)
*p<.05; **p<.01. FC-overall=Function component-overall function; Disability-Freq=Disability-Frequency; Disability-Limit=Disability-Limitation.
*p<.05; **p<.01.
*p<.05; **p<.01. FC-Overall=Function Component-Overall function; Disability-Freq=Disability-Frequency; Disability-Limit=Disability-Limitation.
*p<.05; **p<.01. FC-overall=Function component-overall function; Disability-Freq=Disability-Frequency; Disability-Limit=Disability-Limitation.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

