Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of an integrated healthcare program for postpartum women: a quasi-experimental study
- Eun Suk Hwang, Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):506-518. Published online November 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25076
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
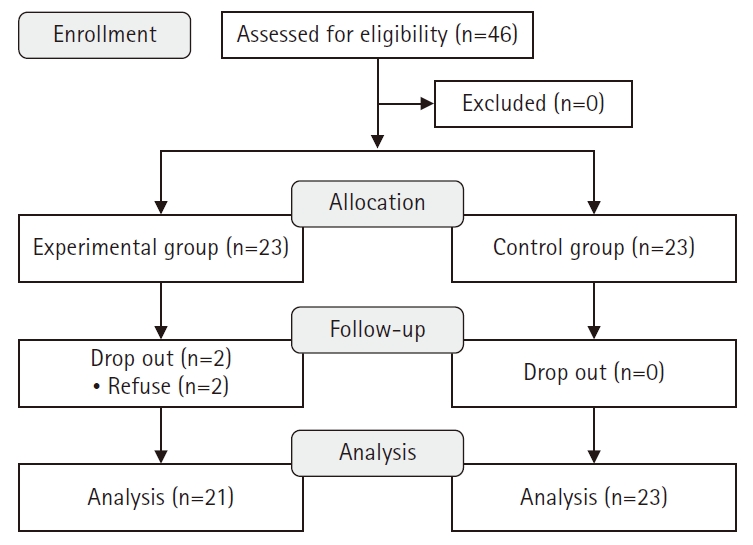
This study aimed to develop and evaluate an integrated healthcare program for postpartum mothers based on Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The integrated healthcare program was administered 6 times over 2 weeks to postpartum mothers in the experimental group (n=21), while the control group (n=23) received standard care. Data were collected from June 3 to July 15, 2024, through structured questionnaires measuring postpartum fatigue, depression, marital intimacy, and mother-infant attachment. Analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0.
Results
The experimental group showed significantly lower postpartum fatigue (Z=–2.00, p=.023), a significantly proportion of improvement in postpartum depression (χ2=10.32, p=.012), and a significant increase in mother-infant attachment (t=1.70, p=.048) compared to the control group. However, there was no significant difference in marital intimacy between groups (Z=–0.46, p=.326).
Conclusion
These results suggest that an integrated health management program including physical health, psychological stability, and relational support can be used as an effective nursing intervention to promote health in postpartum mothers. Therefore, additional research is warranted that expands and applies integrated programs for postpartum mothers in various environments in postpartum care centers and communities.
- 1,627 View
- 227 Download

- Effects of an agro-healing program on depression, stress, and cognitive function in older adults: a quasi-experimental study
- Gyu Yeon Park, Kwang Ok Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):342-352. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
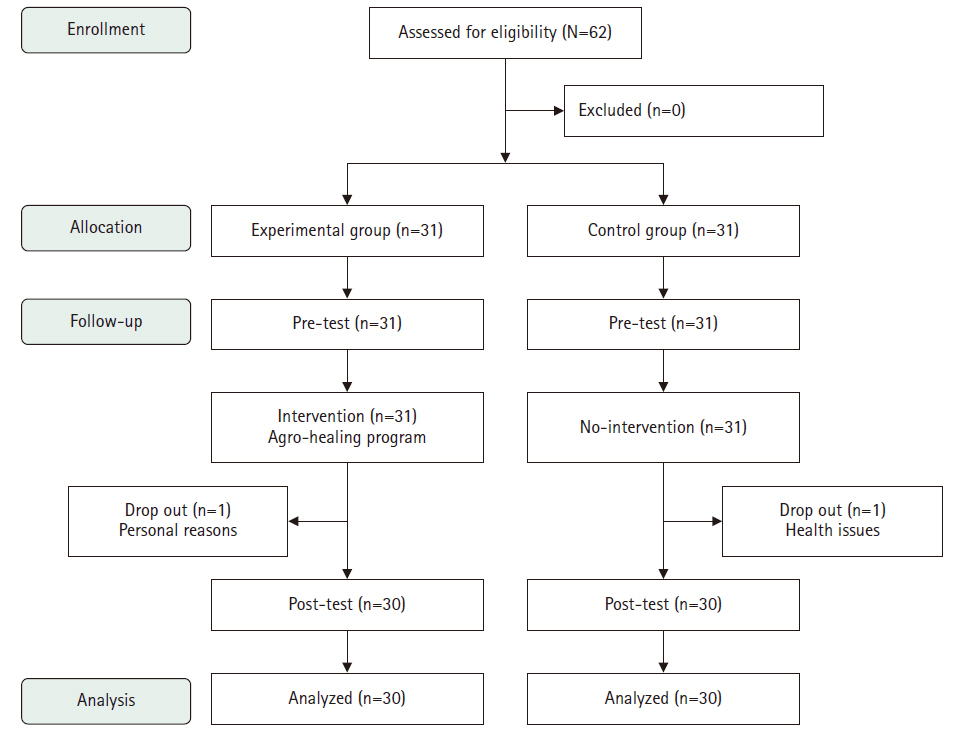
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of an agro-healing program on depression, stress, and cognitive function in older adults.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pretest–posttest design was used. The study was conducted from July 16 to September 6, 2024. Sixty-two individuals aged 65 or older residing in Gimcheon, Gyeongsangbuk-do, were recruited according to the selection criteria (31 in the experimental group and 31 in the control group). The final analysis included 30 participants in each group. The program was delivered by one main instructor (a healing farmer) and three assistants. The pretest assessed general characteristics, the Geriatric Depression Scale Short Form-Korean Version, Stress Response Inventory-Modified Form, and Cognitive Impairment Screening Test. The experimental group participated in the agro-healing program once a week for 90 minutes over 8 weeks. The posttest included the same measurements as the pretest. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0.
Results
The experimental group, which participated in the healing agriculture program, showed reduced depression (F=7.97, p=.007) and stress (F=282.70, p<.001) and improved cognitive function (F=10.12, p=.002) compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that the agro-healing program is an effective intervention for reducing depression and stress and improving cognitive function in older adults. We propose its use to promote health and prevent dementia in this population.
- 2,858 View
- 233 Download

- Impact of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on parental anxiety and depression in severe hypospadias patients in China: a randomized controlled trial
- Ruijuan Wu, Lucai Jia, Biyu Ding, Ying Li, Yaqing Cao, Zhaojun Shi, Yanfang Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):327-341. Published online August 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
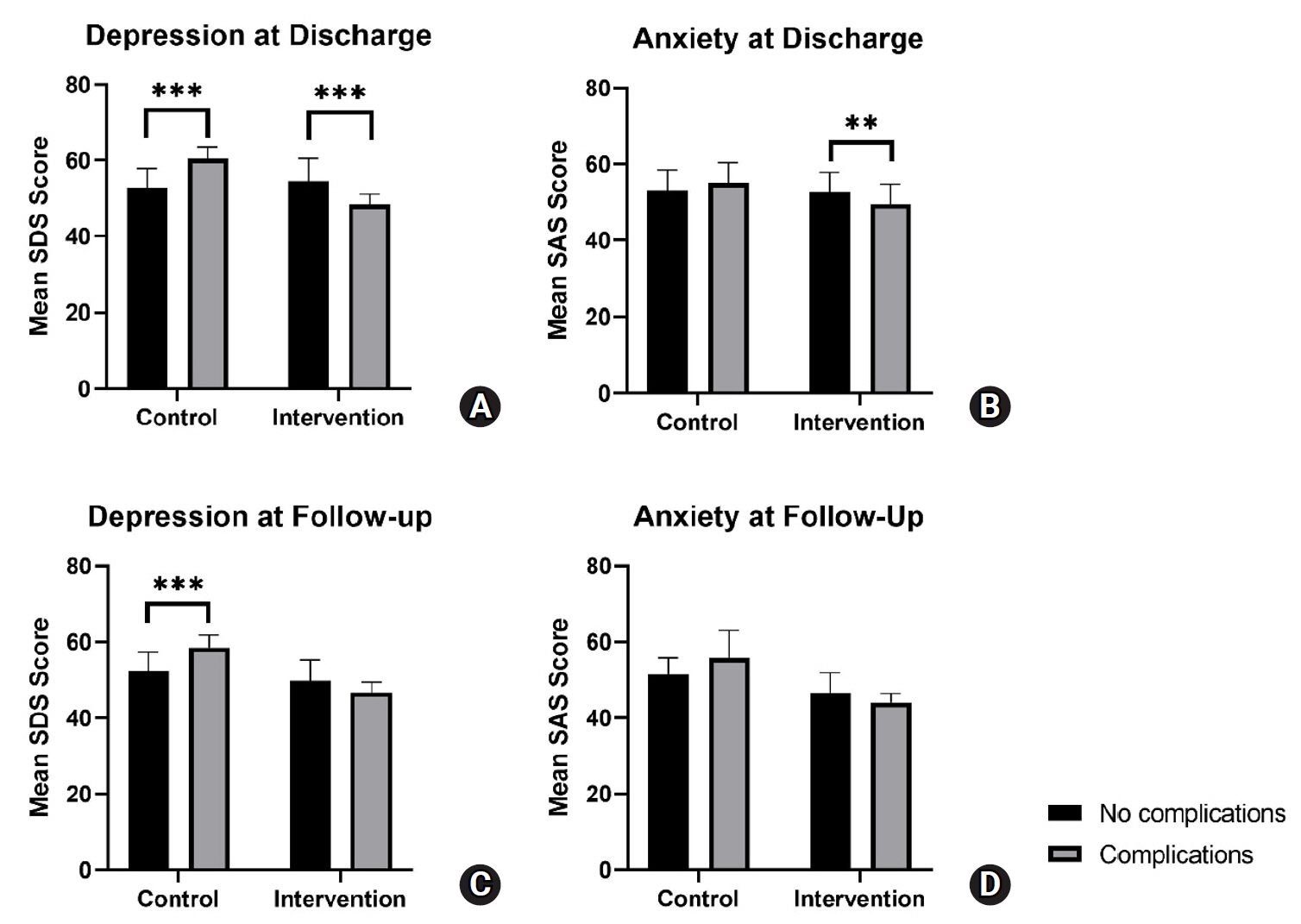
This study aimed to explore the effects of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on alleviating perioperative and post-surgical anxiety and depression in parents of children with severe hypospadias.
Methods
Parents of children with severe hypospadias were recruited and randomly allocated into a control group (n=87), which received standard nursing care, and an intervention group (n=93), which was given an integrated disease-specific nursing intervention in addition to standard care. Parental anxiety and depression were measured using the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) at admission, discharge, and 6-month follow-up post-surgery.
Results
A linear mixed-effects model showed that SAS and SDS scores in the intervention group decreased to a significantly greater extent over time, from admission to follow-up, compared to the control group. Post-hoc analysis showed a trend for increased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up for the control group. Meanwhile, the intervention group exhibited a trend for decreased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up.
Conclusion
The integrated disease-specific nursing model significantly alleviated parental anxiety and depression over time compared to standard care, highlighting its effectiveness in supporting families of children with severe hypospadias. Notably, the intervention appeared to mitigate the negative emotional impact of postoperative and follow-up complications, suggesting its potential as a targeted approach to improve both emotional well-being and overall care outcomes.
- 2,467 View
- 165 Download

- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
- Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):19-33. Published online February 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24070
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
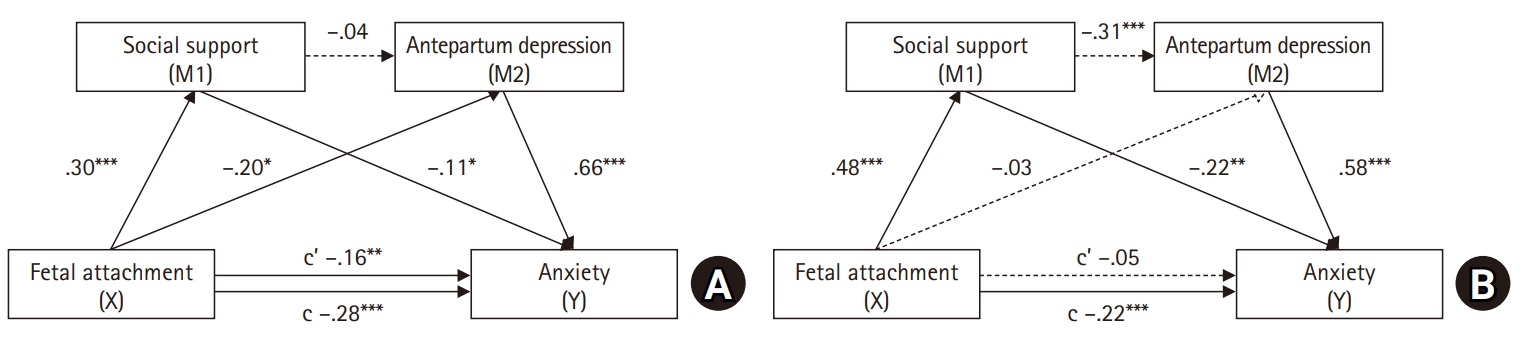
This study examined the direct effects of fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression on anxiety in pregnant women with high-risk pregnancy-related conditions and their husbands. Furthermore, it aimed to explore the serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression in the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety.
Methods
A survey-based study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy conditions at 24–32 weeks and their husbands, recruited from a pregnant women’s online community between January 20, 2021 and July 20, 2022. Data were collected from 294 individuals (147 couples) using self-report questionnaires. Correlations between variables were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.), and the mediation effects were assessed using the PROCESS macro, model 6.
Results
In the maternal model, maternal-fetal attachment directly affected anxiety (p=.005), with antepartum depression partially mediating this relationship (95% confidence interval [CI], –0.26 to –0.01). In the paternal model, paternal-fetal attachment had no direct effect on anxiety (p=.458). However, social support and antepartum depression fully mediated the relationship between paternal-fetal attachment and anxiety (95% CI, –0.14 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that social support in the relationship between fetal attachment and depression in high-risk pregnant women and their partners can have direct or indirect effects on the negative emotions of high-risk pregnant couples. It is necessary to assess the level of anxiety in couples experiencing high-risk pregnancies and provide comprehensive nursing interventions that address fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression in order to reduce anxiety.
- 2,651 View
- 247 Download

- An Investigation of the Cumulative Effects of Depressive Symptoms on the Cognitive Function in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging
- Eunmi Kim, Jinkyung Oh, Iksoo Huh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):453-467. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the cumulative effects of depressive symptoms on cognitive function over time in community-dwelling older adults. Methods: Data were investigated from 2,533 community-dwelling older adults who participated in the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA) from the 5th (2014) to the 8th wave (2020). The association between cumulative depressive symptoms and cognitive function was identified through multiple regression analysis. Results: When the multiple regression analysis was conducted from each wave, the current depressive symptoms scores and cognitive function scores were negatively associated, regardless of the waves (B5th = - 0.26, B6th = - 0.26, B7th = - 0.26, and B8th = - 0.27; all p < .001). Further, when all the previous depressive symptoms scores were added as explanatory variables in the 8th wave, the current one (B8th = - 0.09, p < .001) and the previous ones (B5th = - 0.11, B6th = - 0.09, and B7th = - 0.13; all p < .001) were also negatively associated with the cognitive function score. The delta R2 , which indicates the difference between the model’s R2 with and without the depressive symptoms scores, was greater in the model with all the previous and current depressive symptoms scores (6.4%) than in the model with only the current depressive symptoms score (3.6%). Conclusion: Depressive symptoms in older adults have a long-term impact. This results in an accumulated adverse effect on the cognitive function. Therefore, to prevent cognitive decline in older adults, we suggest detecting their depressive symptoms early and providing continuous intervention to reduce exposure to long-term depressive symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic identification and quantification of factors and their interactions with age, sex, and panel wave influencing cognitive function in Korean older adults
Eunmi Kim, Jinkyung Oh, Jungsoo Gim, Iksoo Huh
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Systematic identification and quantification of factors and their interactions with age, sex, and panel wave influencing cognitive function in Korean older adults
- 2,262 View
- 56 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- A Structural Equation Model on Social Re-Adjustment of Stroke Patients: Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
- Jungmi Kim, Hwasoon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):480-495. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22140
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and test a structural equation model on social re-adjustment of individuals with stroke based on a literature review and Roy’s adaptation model.
Methods
This study involved 321 participants who had a stroke and visited the outpatient department after discharge. The hypothetical model was developed based on Roy’s adaptation model and a comprehensive review of previous literature on the topic. The model comprised four exogenous variables (neurological damage, gender [man], age, and social support) and five endogenous variables (activities of daily living, acceptance of disability, depression, rehabilitation motivation, and social re-adjustment). The data were analyzed using SPSS Windows software version 22.0 and AMOS 23.0.
Results
Out of 28 research hypotheses, 18 were supported, and they indicated approximately 64% probability of social re-adjustment. Social re-adjustment is directly and significantly affected by age, social support, activities of daily living, and depression. Social re-adjustment is indirectly affected by neurological impairment, gender (men), age, social support, and rehabilitation motivation.
Conclusion
Continuous assistance and care should be provided for individuals with disabilities caused by sudden neurological damage to facilitate gradual improvement in their social re-adjustment. To enhance social re-adjustment, especially among older adults, newly developed interventions should focus on improving their activities of daily living, preventing depression, and enhancing support from family and healthcare personnel. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Roy Adaptation Model-Based nursing care improves quality of life for elderly burn patients
Yudan Wang
American Journal of Translational Research.2025; 17(6): 4679. CrossRef - The Effects of Aromatherapy on Stroke Symptoms in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
A Reum Lim, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(2): 85. CrossRef
- Roy Adaptation Model-Based nursing care improves quality of life for elderly burn patients
- 3,138 View
- 301 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The Effect of Socioeconomic Status to Depression of Perimenopause Women: Pathway Analysis Using the Reserve Capacity Model
- Mi-Ran Park, Hye Seung Choi, Ju-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):249-259. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Based on the Reserve Capacity Model, this study investigated the effects of pre- and postmenopausal women’s socioeconomic status (SES) on depression, focusing on the mediating effects of self-esteem, happiness, and family relationship satisfaction with social network relationships.
Methods
This cross-sectional study involved secondary analysis of national data on 771 perimenopause women gathered from the 16th Korea Welfare Panel Study (KOWEPS) 2021. A path analysis model was constructed to evaluate the relationship between SES, social network satisfaction, self-esteem, perceived health status, and depression. Data were analyzed using ADANCO 2.3.1 and Mplus 8.4.
Results
Although SES had no direct effect on depression, it did affect depression through self-esteem, happiness, and satisfaction with family relationships.
Conclusion
The findings of this study indicate that perimenopausal women’s personal resources—psychosocial variables such as self-esteem and happiness—had a higher effect on depression than tangible reserves like SES. Therefore, interventions for enhancing self-esteem and happiness may prevent depression in perimenopausal women effectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Socioeconomic Status on the Health of Menopausal Mothers in Multicultural Families in Korea: A Test of the Reserve Capacity Model
Miran Park, Ju-Young Lee
Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health.2025; 27(2): 277. CrossRef
- Effects of Socioeconomic Status on the Health of Menopausal Mothers in Multicultural Families in Korea: A Test of the Reserve Capacity Model
- 1,913 View
- 44 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Affecting the Quality of Life in Low-Income Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Ju-Hee Nho, Eun Jin Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):1-11. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22126
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the factors influencing quality of life (QoL) of low-income older adults (LOAs) with sarcopenia.
Methods
A convenience sample of 125 older adults was recruited from Jeonbuk Province, South Korea. Data were collected using a self-report questionnaire that included nutritional status, the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21, and the World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument-Older Adults Module. Additionally, grip strength and appendicular skeletal muscle mass, were evaluated, along with the short physical performance battery.
Results
Sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia were observed in 43.2% and 56.8% of participants, respectively. Using multiple regression analysis, depression (β = - .40, p < .001), nutritional status (β = .24, p = .003), and anxiety (β = - .15, p = .042) were identified as factors affecting the QoL of the older adults in low-income groups with sarcopenia, the explanatory power of these variables was 44%.
Conclusion
The results of this study can be used to develop a nursing intervention program and establish policies to improve depression, anxiety, and nutritional status to enhance QoL of LOAs with sarcopenia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing health-related quality of life in older adult women with sarcopenia: analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sol Hyun Lee, Ju-Hee Nho, Hye Young Kim, Eun Jee Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(4): 328. CrossRef
- Factors influencing health-related quality of life in older adult women with sarcopenia: analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
- 2,328 View
- 56 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of Fear of Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Social Distancing on Women’s Suicidal Ideation: Mediating Effect of Depression
- Hyo Yeon Kim, Hanjong Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):464-475. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22078
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the mediating effects of depression amid the influence of fear and social distancing arising from Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korean women’s suicidal ideation.
Methods
A descriptive correlation study was conducted. Study participants, recruited by Hankook Research from March 2 to March 5, 2021, included 300 women aged 19 to 49 living in South Korea, and 100 people were randomly allocated and enlisted for each age group out of 700,000 Hankook Research Panels recruited in advance from 17 cities and provinces nationwide. Data were collected through a self-reported questionnaire and analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient and Hayes’ Process Macro Model 4 with 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval via SPSS statistics 27.0.
Results
Suicidal ideation was significantly correlated with fear of COVID-19 (r = .16, p = .006) and depression (r = .65, p < .001). The mediation effect of depression in the relationship between the fear of COVID-19 and suicidal ideation was found to be significant (B = 0.40, boot 95% CI: 0.21~0.61). However, social distancing did not significantly affect suicidal ideation via depression (B = - 0.79, boot 95% CI: - 1.94~0.26).
Conclusion
It is necessary to develop and apply interventions to prevent depression and suicidal behaviors by continuously observing and reducing the negative psychological responses caused by COVID-19. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Secular trend of self-injurious behaviors in PTSD and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic: A quasi-experimental study
Kwanghyun Kim
Journal of Affective Disorders.2026; : 121316. CrossRef
- Secular trend of self-injurious behaviors in PTSD and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic: A quasi-experimental study
- 1,055 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Longitudinal Study of the Reciprocal Relationship between Depression and Income among Korean Older Men and Women
- Jeong Lee, Gyeong-Suk Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):451-463. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the reciprocal relationships between depression and income, and gender differences in these relationships among older adults in South Korea.
Methods
Using 2015 to 2019 of the Korea Welfare Panel Study (KoWePS), we studied 6,070 older adults (2,394 men and 3,676 women) aged 60 years over in 2015. The generalized estimating equation was employed to explore the effect of an individual income on depression and the reverse causal link-that of depression on income.
Results
The study found the reciprocal relationships between income and depression. Income has a significant impact on depression. Higher-income was linked to decreased risks of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D) scores among older adults (B = - 0.121, p < 0.001). Estimates of the reverse causal link show that higher CES-D scores were also linked to income reduction among Korean older adults (B = - 0.007, p < 0.001). In addition, we also observed gender differences in the impact of income on depression but not in the reverse causal link. Income has more detrimental to psychological consequence for older men (B = - 0.108, p < 0.001) than older women (B = - 0.057, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
The finding implies that both psychological and social protection policies for the elderly are needed in view of gender perspective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors of depression among the baby boomer generation: A cross-sectional study using the 2022 Korean Community Health Survey
Kyoung Mi Kim, Hye Jung Jun
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 308. CrossRef
- Risk factors of depression among the baby boomer generation: A cross-sectional study using the 2022 Korean Community Health Survey
- 1,976 View
- 35 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of Social Capital on Depression of Older Adults Living in Rural Area: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the 2019 Korea Community Health Survey
- Minho Jung, Jinhyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):144-156. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21239
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the influence of social capital on the depression of older adults living in rural areas.
Methods
Data sets were obtained from the 2019 Korea Community Health Survey. The participants were 39,390 older adults over 65 years old living in rural areas. Indicators of social capital included trust, reciprocity, network, and social participation. Depression—the dependent variable—was measured using the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). Hierarchical ordinal logistic regression was conducted to identify factors associated with depression after adjusting the data numbers to 102,601 by applying the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE).
Results
The independent variables—indicators of social capital—exhibited significant association with the depression of older adults. The odds ratios of depression were higher in groups without social capital variables.
Conclusion
To reduce depression, we recommend increasing social capital. Factors identified in this study need to be considered in older adult depression intervention programs and policies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Perceived Stress on Depression among Middle-aged Adults with Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Exploring the Mediating Role of Social Capital through a Descriptive Correlational Study
Kyung Ae Kim, Mi Ran Bang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(1): 50. CrossRef - An Observational Study on the Association Between Nutritional Intake and Mental Health Among Older Adults in Rural Areas
Kyeongmin Jang
Nursing & Health Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Modelo de regresión ordinal para pronóstico de la depresión en el adulto mayor peruano
Lilian Roxana Paredes López
UCV Hacer.2025; 14(2): 32. CrossRef - Moderating effects of social capital on the relationship between fear of falling and depressive symptoms among community-dwelling older adults
Yeong-Mi Seo, Eun Sook Lee
Archives of Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction model of weight control experience in men with obesity in their 30 s and 40 s using decision tree analysis
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between human capital and depression among middle-aged rural adults: The multiple-parallel mediating effects of social capital
Soo Mi Jang, Hyung Mi Ha
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(1): 33. CrossRef
- The Effects of Perceived Stress on Depression among Middle-aged Adults with Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Exploring the Mediating Role of Social Capital through a Descriptive Correlational Study
- 2,546 View
- 108 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of a Cognitive Behavior Therapy Program for Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyoung Ran Kong, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):347-362. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21025
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed a cognitive behavioral therapy program aimed at altering the physical condition, emotions, and behaviors of fibromyalgia patients, and confirmed the program’s clinical applicability. The program was developed by analyzing previous studies conducting in-depth interviews with fibromyalgia patients, drawing on cognitive behavior theory to establish the program contents, recruiting experts to test its validity, and conducting a preliminary survey.
Methods
To confirm the program’s effect, this study used a randomized controlled trial design. The participants were outpatients diagnosed with fibromyalgia in Dong-A University Hospital, Busan. The 30 patients in the experimental group took part in the program, which comprised 8 sessions (90 to 120 minutes) based on cognitive behavior theory, delivered over 8 weeks. Hypothesis testing was carried out using the repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
The analysis revealed significant differences between the experimental and control groups in positive automatic thoughts, pain, fatigue, depression, and interpersonal relationships. However, there was no significant difference between the groups in terms of sleep disorders and negative automatic thoughts.
Conclusion
This program is a positive effect on physical condition, emotions, and behaviors. It is thus expected to be used to help fibromyalgia patients improve their disease conditions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How do people with fibromyalgia interpret ambiguous cues in empathy-related healthcare scenarios?
Maria Planes Alias, David J Moore, Nicholas Fallon, Katie Herron, Charlotte Krahé
The Journal of Pain.2026; 40: 106181. CrossRef - Changes in Dental Caries Risk among Middle School Students Using an ICT-Based Caries Management Program
An-Na Yeo, Yu-Min Kang, Su-Young Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for the management of sleep problems in people with fibromyalgia: a multi-methods evidence synthesis
Mari Imamura, Clare Robertson, Jemma Hudson, Daniel Whibley, Lorna Aucott, Katie Gillies, Marcus Beasley, Martin J Stevens, Paul Manson, Debra Dulake, Abhishek Abhishek, Nicole KY Tang, Gary J Macfarlane, Miriam Brazzelli
Health Technology Assessment.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Positive Psychotherapy on Pain Perception, Daily Functioning, and Mental Health in Patients With Fibromyalgia
Hamide Erol, Aysel Karaca
Pain Management Nursing.2025; 26(6): e550. CrossRef - Effects of a Internet-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Program for Adolescents with Diabulimia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Hye-Ryeon Park, Hyeon Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 320. CrossRef - Proposal for a Cognitive Reconstruction Program for Female College Students Experiencing Body Dissatisfaction
Hyun Ju Lee, Helen Ha, Yuan Mei Cui, Jee Hyun Lee, Min Ju Kang
Human Ecology Research.2024; 62(2): 369. CrossRef
- How do people with fibromyalgia interpret ambiguous cues in empathy-related healthcare scenarios?
- 1,679 View
- 79 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of First Assisted Reproductive Technologies on Anxiety and Depression among InfertileWomen: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ju-Young Ha, Seon-Hwa Ban, Hae-Jung Lee, Misoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):369-384. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze anxiety and depression among infertile women at different time points during the firstIn Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) treatment through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
Seven out of 3,011 studies were included for meta-analysis. To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performedusing the RevMan 5.3 program. We compared the measurement outcomes at three time points: before the start of treatment (T0), cancellationof treatment after pregnancy detection (T2), one to six months after treatment (T3). The effect size used was the standardizedmean difference (SMD).
Results
In comparing the different time points of the pregnant women from their cycle, significantly lower levelsof depression were found at T2 than at T0. In non-pregnant women, anxiety at T2 and depression at T2 and T3 were significantly higherthan those at T0. At T2 and T3, the non-pregnant women reported higher levels of anxiety and depression compared with the pregnantwomen.
Conclusion
Anxiety and depression in infertile women undergoing the first IVF or ICSI are associated with the time points andpregnancy status after treatment. These findings suggest that attention should be paid to helping infertile women prepare for and copewith treatment and treatment failure. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Stress on Each of the Stages of the IVF Procedure: A Systematic Review
Anastasia Tsambika Zanettoullis, George Mastorakos, Panagiotis Vakas, Nikolaos Vlahos, Georgios Valsamakis
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 726. CrossRef - An Integrative Review of Psychosocial Intervention Programs for Infertile Females
Youjin Shin, Soo-Hyun Nam
STRESS.2023; 31(4): 158. CrossRef - The dynamics of mental health measures of pre- and postpartum women undergoing assisted reproductive technology
Maria E. Blokh, Varvara O. Anikina, Svetlana S. Savenysheva, Maria I. Levintsova
Journal of obstetrics and women's diseases.2023; 72(1): 17. CrossRef
- Effect of Stress on Each of the Stages of the IVF Procedure: A Systematic Review
- 1,383 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of a Customized Health Promotion Program on Depression, Cognitive Functioning, and Physical Health of Elderly Women Living Alone in Community: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial
- Ye Ri Ja Park, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):515-525. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.515
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a customized health promotion program (CHPP) on depression, cognitive functioning, and physical health of elderly women living alone in the community.
Methods A randomized comparison of pre-and post-test design was used with 62 participants assigned to either an intervention (n=32 in seven clusters) or a control group (n=30 in seven clusters) in 14 areas of a town. The final sample included 30 intervention participants who completed the CHPP for 10 weeks, and 26 control participants. The intervention group participated in the CHPP weekly; they were provided with instructions about coping with their chronic illnesses, lifestyle modification, risk management, providing emotional support to each other, and floor-seated exercise, which they were encouraged to do three times a week in their homes.
Results Significant group differences were found in depression (U=48.50,
p <.001), cognitive functioning (U=2.50,p <.001), left arm flexibility (U=251.50,p =.023), right arm flexibility (U=225.00,p =.007), static balance (U=237.00,p =.012), and gait ability (U=190.50,p =.004). However, there were no significant differences in bothgrip strength and muscle mass between the two groups.Conclusion The findings indicate that CHPP was overall effective at improving depression, cognitive functioning, and physical functioning of elderly women living alone, and could therefore be considered a positive program for community-dwelling elderly women living alone.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcomes of the Together for Life Program in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Living Alone: A Pilot Study
Hye Seung Choi, Younghye Park, Hae-Ra Han, Jong-Eun Lee
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2025; 51(1): 49. CrossRef - Development of core outcome set for healthy aging treatment in primary care settings
Soobin Jang, Hyein Jeong, Jungi Park, Mi Mi Ko, Jeeyoun Jung
Integrative Medicine Research.2025; 14(4): 101205. CrossRef - Development and effects of a customized integrated health management program for older adults living alone: A nonequivalent control-group pre-posttest design
Mooyong Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 295. CrossRef - Primary-level and community worker interventions for the prevention of mental disorders and the promotion of well-being in low- and middle-income countries
Marianna Purgato, Eleonora Prina, Caterina Ceccarelli, Camilla Cadorin, Jibril O Abdulmalik, Francesco Amaddeo, Lyria Arcari, Rachel Churchill, Mark JD Jordans, Crick Lund, Davide Papola, Eleonora Uphoff, Nadja van Ginneken, Wietse Anton Tol, Corrado Barb
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Physical Health Status, Social Support, and Depression on Quality of Life in the Korean Community-Dwelling Elderly
Koung-Oh Chang, Dazhou Li
Advances in Public Health.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Development and application of a self-transcendence enhancement program for the well-being of elderly women living alone in Korea
Sun-Mi Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(2): 128. CrossRef - Effects of a Physical Exercise Program on Physiological, Psychological, and Physical Function of Older Adults in Rural Areas
Sunmi Kim, Eun-Jee Lee, Hyeon-Ok Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8487. CrossRef - The Humanoid Robot Sil-Bot in a Cognitive Training Program for Community-Dwelling Elderly People with Mild Cognitive Impairment during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun-A Park, Ae-Ri Jung, Kyoung-A Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 8198. CrossRef
- Outcomes of the Together for Life Program in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Living Alone: A Pilot Study
- 1,635 View
- 45 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effects of Reminiscence Therapy on Depressive Symptoms in Older Adults with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Kyungsoo Kim, Jia Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):225-240. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.225
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of reminiscence therapy on depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from January 2000 to January 2018 were searched through Research Information Sharing Service (RISS), Korean Studies Information Service System (KISS), Korean Medical Database (KMbase), KoreaMed, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), and Ovid MEDLINE. Two researchers independently performed the search, selection, and coding. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis 3.0 was used for meta-analysis, and Review Manager program 5.3 was used for quality assessment.
Results Out of the 1,250 retrieved articles, 22 RCTs were selected for analysis. The overall effect size of reminiscence therapy for mitigating depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia was -0.62 (95% Cl: -0.92 to -0.31). The effect size was greater in older adults under 80, those with less disease severity, and those for whom the therapy session lasted less than 40 minutes.
Conclusion Reminiscence therapy is an effective non-pharmacological therapy to improve depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia. Because its effectiveness is also influenced by age, disease severity, and application method, it is necessary to consider treatment designs based on individual characteristics as well as methodological approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Group reminiscence therapy interventions in non-clinical older adults: A systematic review
Ali Eryılmaz, Emre Yıldırım, Hacer Yıldırım Kurtulus, Murat Yıldırım
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 63: 35. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Influence of Garden Therapy on Memory Decline and Depression in Older Adults with Cognitive Impairments
Chohye Youn, Minji Kang, Hyejin Kim, Hyeyoon Kim, Jiyun Choi, Suyeon Lee, Juyoung Lee
Journal of Environmental Science International.2025; 34(3): 125. CrossRef - Mental health and treatment challenges in older adults
Ken Laidlaw, Georgina Charlesworth, Sunil Bhar
Nature Reviews Psychology.2025; 4(11): 737. CrossRef - Effects of reminiscence interventions on depression and anxiety: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Martin Pinquart
Aging & Mental Health.2024; 28(5): 717. CrossRef - Effects of reminiscence therapy on quality of life and life satisfaction of the elderly in the community: a systematic review
Eunyoung Shin, Myeongshin Kim, Seyoon Kim, Sohyune Sok
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcultural Pilot Study of the Efficacy of Reminiscence Therapy for Mexican and Spanish Older Adults with Different Levels of Cognitive Decline
Alba Villasán-Rueda, Antonio Sánchez-Cabaco, Manuel Mejía-Ramírez, Rosa Marina Afonso, Eduardo Castillo-Riedel
Journal of Cross-Cultural Gerontology.2023; 38(4): 371. CrossRef - Cross-cultural effects of reminiscence therapy on life satisfaction and autobiographical memory of older adults: a pilot study across Mexico and Spain
Alba Villasán Rueda, Antonio Sánchez Cabaco, Manuel Alejandro Mejía-Ramírez, Rosa Marina Afonso, Eduardo Castillo-Riedel
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of group reminiscence therapy based on Chinese traditional festival activities (CTFA-GRT) on loneliness and perceived stress of rural older adults living alone in China: a randomized controlled trial
Shasha Li, Yanyan Dai, Yuqiu Zhou, Jiayuan Zhang, Chiteng Zhou
Aging & Mental Health.2022; 26(7): 1377. CrossRef - Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms and Associated Factors in Community-Dwelling Persons at the First Time of Dementia Diagnosis
Gijung Jung, Jia Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 7765. CrossRef
- Group reminiscence therapy interventions in non-clinical older adults: A systematic review
- 2,553 View
- 57 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- The Longitudinal Relationships between Depression and Smoking in Hardcore Smokers Using Autoregressive Cross-Lagged Modeling
- Jeong Won Han, Hanna Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):69-79. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.69
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to identify the directionality of the causal relationship and interaction between depression and amount of smoking over time in hardcore smokers using longitudinal descriptive analysis.
Methods Secondary data from the Korean Welfare Panel Study were analyzed using autoregressive cross-lagged modeling. Participants included 342 hardcore smokers who participated in the 8th to 11th waves of the panel study.
Results Analyses revealed that change(s) in depression levels according to time had a significant positive relationship with the total amount of smoking per day (β=.29, β=.19, β=.17,
p <.001), while change(s) in total amount of smoking per day according to time had a significant positive relationship with depression (β=.43, β=.50, β=.38,p <.001). Analysis of the cross-lagged effect between depression and total amount of smoking per day showed that depression at one time point had a significantly positive relationship with the total amount of smoking per day at the next time point (β=.14, β=.13, β=.13,p =.021), and that the total amount of smoking per day at one time point had a significant positive relationship with depression at the next time point (β=.04, β=.04, β=.03,p =.044).Conclusion The findings in the present study confirmed a cross-interaction between depression and total amount of smoking per day in hardcore smokers. The present findings could be used to develop appropriate smoking-related interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlations among nicotine dependence, health-related quality of life, and depression in current smokers: a cross-sectional study with a mediation model
Huali Xiong, Fengxun Ma, Dayi Tang, Daiqiang Liu
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A study on related factors of hardcore smokers
Hanna Lee, Jeong‐Won Han
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Correlations among nicotine dependence, health-related quality of life, and depression in current smokers: a cross-sectional study with a mediation model
- 1,269 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Effect of the Intergenerational Exchange Program for Older Adults and Young Children in the Community Using the Traditional Play
- Min-Jung Choi, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):743-753. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.743
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to explore the effects of a community-based first and third Intergenerational Exchange Program (IGEP) on older adults’ health-related quality of life (HRQoL), loneliness, depression, and walking speed, and on 4~5-year-old preschool children's learning-related social skills.
Methods This study employed a non-equivalent control group pre-post-test design. The experimental group included 42 older adults and 42 children who participated in the IGEP for 8 weeks, and the control group included 39 older adults. The experimental group participated in the IGEP once a week for 8 weeks. It comprised a traditional play program based on the intergroup contact theory.
Results Compared to the control group, there was a significant increase in scores on the HRQoL-Visual analogue scale (VAS) and a decrease in loneliness and depression in older adults in the experimental group (
p <.05). Children who participated in the IGEP showed an improvement in their learning-related social skills (p <.001).Conclusion These results confirm that the IGEP is an effective intervention to improve HRQoL-VAS, loneliness, and depression among older adults and learning-related social skills among preschool children in the community.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Intergenerational Interaction on Older Adults Depends on Children’s Developmental Stages; Observational Evaluation in Facilities for Geriatric Health Service
Rie Fukuoka, Shinji Kimura, Toru Nabika
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(1): 836. CrossRef - Intergenerational Taekwondo Program: A Narrative Review and Practical Intervention Proposal
Yongseop Kim, Junhyoung Kim, Jung-Min Lee, Dong-Chul Seo, Hyun Chul Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5247. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study Exploring Negative Affect in Older Adults Residing in Long-Term Care Facilities
Zhen Chen, Hongxia Zhang, Jinhua Zhang, Suqing Li, Yanmei Zhao
Research and Theory for Nursing Practice.2022; 36(3): 301. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Intergenerational Interaction on Older Adults Depends on Children’s Developmental Stages; Observational Evaluation in Facilities for Geriatric Health Service
- 1,597 View
- 47 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Impact of Parents’ Problem Drinking on Suicidal Ideation of Their University Student Children : The Multiple Mediating Effects of Childhood Trauma, Experiential Avoidance and Depression
- Eun Sook Lee, Eun Ju Bong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):565-577. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.565
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct and test a hypothetical model about impact of parents’ problem drinking on suicidal ideation of their children who are university students and the multiple mediating effects of childhood trauma, experiential avoidance, and depression based on stress-vulnerability model.
Methods A purposive sample of 400 university students was recruited from three universities in provincial areas and the data were collected between October and November 2016. The collected data were then analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 programs. For data analysis, descriptive statistics, factor analysis, and structural equation modeling were performed. Multiple mediating effects analysis using phantom variable and bootstrapping were implemented to verify the mediating effect of the research model.
Results We found no significant direct effect on depression and suicidal ideation of parents’ problem drinking, but multiple mediating effects of childhood trauma and experiential avoidance between parents’ problem drinking and depression (B=.38,
p =.001). The path from parents’ problem drinking to suicidal ideation was significantly mediated by childhood trauma and depression (B=.02,p =.016) and by childhood trauma, experiential avoidance, and depression (B=.05,p =.011), but experiential avoidance did not have a significant direct effect on suicidal ideation (B=.02,p =.616). Conclusions: Based on the results of this study, it can be suggested that in order to decrease depression and prevent suicide of university students, considering of parents’ problem drinking and childhood trauma, intervention methods that decreased chronic use of experiential avoidance and strengthen acceptance should be developed and made available to them.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unraveling the Complex Pathways: A Conditional Process Analysis of Adverse Childhood Experiences and Internalizing Problems in Late Adolescence
Nooshin Majlesi, Shahram Mohammadkhani, Jafar Hasani, Maryam Moghadasin
Adversity and Resilience Science.2025; 6(4): 579. CrossRef - Psychological Trauma Predicts Obesity in Welsh Secure Mental Health Inpatients
Joseph Lloyd Davies, Daniel Lawrence, Ruth Bagshaw, Andrew Watt, Shane Mills, Catherine Heidi Seage
International Journal of Forensic Mental Health.2024; 23(3): 241. CrossRef - Associations between Suicidal Ideation and Relatives’ Physical and Mental Health among Community Residents: Differences between Family Members and Lineal Consanguinity
Caifeng Li, Zhen Wei, Yifan Wang, Long Sun
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15997. CrossRef
- Unraveling the Complex Pathways: A Conditional Process Analysis of Adverse Childhood Experiences and Internalizing Problems in Late Adolescence
- 1,572 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Differences in Factors Associated with Depressive Symptoms between Urban and Rural Female Adolescents in Korea
- Gyuyoung Lee, Ok Kyung Ham, Bo Gyeong Lee, Abuan Micah Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):475-484. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.475
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose To examine the prevalence of depressive symptoms and differentiate factors associated with them in urban and rural areas by applying the Ecological Models of Health Behavior.
Methods We employed a cross-sectional design and convenience sample of 460 female adolescents. The instruments included the Adolescent Mental-Health Problem-Behavior Questionnaire (AMPQ-II) and the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI).
Results Depressive symptoms were confirmed in 15.7% of urban adolescents and 22.9% of rural adolescents (
p <.05). In the urban group, perception of health and stress associated with school performance were significantly associated with depressive symptoms. In the rural group, aca-demic/internet related problems and rule violations were significantly associated with depressive symptoms (p <.05). General life happiness, worry/ anxiety, and mood/suicidal ideation were common factors in both urban and rural areas (p <.05).Conclusion Multiple factors were associated with depressive symptoms, and those significant factors differed between urban and rural female youths. Accordingly, tailored approaches are required considering urban and rural differences. The approaches should include intrapersonal, interpersonal, and organizational levels of interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rural Suicide: A Systematic Review and Recommendations
Tyler R. Pritchard, Jennifer L. Buckle, Kristel Thomassin, Stephen P. Lewis
Clinical Psychological Science.2025; 13(1): 3. CrossRef - Urban-Rural Differences in the Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms in Korean Adults
Ji-An Jeong, Sun A Kim, Jung Ho Yang, Min-Ho Shin
Chonnam Medical Journal.2023; 59(2): 128. CrossRef - Urbanicity and depression: A global meta-analysis
Colin Xu, Lucille Miao, Devon Turner, Robert DeRubeis
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 340: 299. CrossRef - Short Video-Based Mental Health Intervention for Depressive Symptoms in Junior High School Students: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial
Yuting Yang, Hao Wang, Wen Sha, Xiaoqin Guo, Wei Deng, Jingyi Wang, Chaowei Fu
Psychology Research and Behavior Management.2023; Volume 16: 4169. CrossRef - Association between mental health and executive dysfunction and the moderating effect of urban–rural subpopulation in general adolescents from Shangrao, China: a population-based cross-sectional study
Qingmin Lin, Cody Abbey, Yunting Zhang, Guanghai Wang, Jinkui Lu, Sarah-Eve Dill, Qi Jiang, M K Singh, Xinshu She, Huan Wang, Scott Rozelle, Fan Jiang
BMJ Open.2022; 12(8): e060270. CrossRef - Measuring Happiness in Adolescent Samples: A Systematic Review
Justė Lukoševičiūtė, Gita Argustaitė-Zailskienė, Kastytis Šmigelskas
Children.2022; 9(2): 227. CrossRef - Effects of Life Skill Training on the School Violence Attitudes and Behavior Among Elementary School Children
Jae Yeon Lee, Ok Kyung Ham, Hyun Soo Oh, Eun Jin Lee, Young Ko, Bongjeong Kim
The Journal of School Nursing.2022; 38(4): 336. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Obesity in Urban and Rural Adolescents: Demographic, Socioeconomic Characteristics, Health Behavior and Health Education
Gyu-Young Lee, Youn-Joo Um
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2405. CrossRef - Sociodemographic characteristics associated with adolescent depression in urban and rural areas of Hubei province: a cross-sectional analysis
Guo Li, Junhua Mei, Jing You, Jinfeng Miao, Xiaoyan Song, Wenzhe Sun, Yan Lan, Xiuli Qiu, Zhou Zhu
BMC Psychiatry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Rural Suicide: A Systematic Review and Recommendations
- 2,087 View
- 10 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of a Memory and Visual-Motor Integration Program for Older Adults Based on Self-Efficacy Theory
- Eun-Hwi Kim, Soon-Rim Suh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):431-444. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.431
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to verify the effects of a memory and visual-motor integration program for older adults based on self-efficacy theory.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest–posttest design was implemented in this quasi-experimental study. The participants were 62 older adults from senior centers and older adult welfare facilities in D and G city (Experimental group=30, Control group=32). The experimental group took part in a 12-session memory and visual-motor integration program over 6 weeks. Data regarding memory self-efficacy, memory, visual-motor integration, and depression were collected from July to October of 2014 and analyzed with independent t-test and Mann-Whitney U test using PASW Statistics (SPSS) 18.0 to determine the effects of the interventions.
Results Memory self-efficacy (t=2.20,
p =.031), memory (Z=-2.92,p =.004), and visual-motor integration (Z=-2.49,p =.013) increased significantly in the experimental group as compared to the control group. However, depression (Z=-0.90,p =.367) did not decrease significantly.Conclusion This program is effective for increasing memory, visual-motor integration, and memory self-efficacy in older adults. Therefore, it can be used to improve cognition and prevent dementia in older adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the Association Between Physical Fitness Components and Cognitive Function in Older Korean Adults: The SUPERBRAIN Exploratory Sub-study
Da Ae Kim, Buongo Chun, Muncheong Choi, Kyunghwa Sun, Jee Hyang Jeong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Chang Hyung Hong, Hae Ri Na, Seong Hye Choi, So Young Moon, Hong-sun Song, Sun Min Lee
Dementia and Neurocognitive Disorders.2026; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - Health beliefs model to explore older adults’ dementia prevention and health promotion from 2021 to 2022 in Taiwan: A cross-sectional survey study
Fu-Ju Tsai, Sheng-Wei Shen, Yih-Jin Hu, Chie-Chien Tseng
Medicine.2024; 103(42): e39744. CrossRef - Investigating predictors of self‐care behavior among homebound older adults: The role of self‐efficacy, eHealth literacy, and perceived social support
Arkers Kwan Ching Wong, Jonathan Bayuo, Frances Kam Yuet Wong
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2022; 54(3): 278. CrossRef - Avaliação da Autoeficácia e da Memória em Idosos: Uma Análise Exploratória
Angela Maria Sacramento, Isabelle Patriciá Freitas Soares Chariglione, Gislane Ferreira de Melo, Carmen Jansen de Cárdenas
Psicologia: Teoria e Pesquisa.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving Cognitive Visual-Motor Abilities in Individuals with Down Syndrome
Pablo V. Torres-Carrión, Carina S. González-González, Pedro A. Toledo-Delgado, Vanesa Muñoz-Cruz, Rosa Gil-Iranzo, Nuria Reyes-Alonso, Selene Hernández-Morales
Sensors.2019; 19(18): 3984. CrossRef - Effect of interactive cognitive-motor training on eye-hand coordination and cognitive function in older adults
Pi-Tuan Chan, Wen-Chi Chang, Huei-Ling Chiu, Ching-Chiu Kao, Doresses Liu, Hsin Chu, Kuei-Ru Chou
BMC Geriatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring the Association Between Physical Fitness Components and Cognitive Function in Older Korean Adults: The SUPERBRAIN Exploratory Sub-study
- 1,731 View
- 14 Download
- 6 Crossref

- A Study on the Development of a Postrartum Depression Scale
- Jeung Iee Bai
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):588-600. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.588
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Postpartum depression is one of the most serious problems in maternal health because it affects not only the mother but also her family. Postpartum depression disturbs the maternal-infant interaction and attachment. However, most postpartum depression patients ignore this problem and do not seek treatment. Many clinicians and researchers realize there is a need to develop a postpartum depression scale. Thus, this study has been designed to development of a postpartum depression scale. Data were collected through a survey over a period of three months. Subjects who participated in the study were 167 Korean mothers in their postpartum period. The author used a convenience sampling method. The analysis of the data was done with SPSS PC+ for descriptive statistics, item analysis and factor analysis. Initially 62 items were generated from the interview data of eight postpartum depression patients and from a literature review. This preliminary scale was analyzed for reliability and validity. The results of this analysis are as follows. 1. Initially 62 items were analyzed through the index of Content Validity(CVI)and 48 items were selected. 2. Seven factors were extracted through the principal component analysis, and these contributed 61% of the variance in the total score. Finally 46 items in the scale loaded .41~.84 on one of seven factors. 3. Each factor was labeled. Factor 1 was labeled 'emotional phenomena-emotional upset' and included 13 items, factor 2 was labeled 'cognitive phenomena-self concept disturbance' and included seven items, factor 3 was labeled 'relationship to baby-negative feeling' and included six items, factor 4 was labeled 'relationship to baby-overload' and included eight items, factor 5 was labeled 'negative maternal identity' and included five items, factor 6 was labeled 'biophysiological phenomena-disturbance of physical functioning' and included four items, and factor 7 was labeled 'interpersonal relationship phenomena-blamed others' and included three items. 4. Cronbach Coefficient Alpha for internal consistency was .95 for the total 46 items. Finally, the author suggests that this scale could be adequately applied in assessing the postpartum depression of mothers during the postpartum period. The results of this study can contribute to designing an appropriate postpartum depression prevention strategy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Trends in Postpartum Depression in Korea: A Systematic Review
Jungha Lim, Eunkyung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(4): 383. CrossRef
- Research Trends in Postpartum Depression in Korea: A Systematic Review
- 411 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study on the Postpartum Depression Experience: Q-Methodological Approach
- Hye Sook Jang, Su Jin Kim, Jeong Sun Kim, Hung Kyu Kim, Euy Soon Choi
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(4):917-929. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.4.917
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to explore types of postpartum depression and to understand the nature and structure of the postpartum depression by using Q-methodological approach. As a way of research, 55 statements concerning postpartum depression were selected through individual interviews with postpartum mothers and literature review. 30 women were chosen as a subject group for the study, with opinions shown in 55 statements divided into 9 scales by forced distribution. PC QUANL Program was used for analysis and Q-factors were analyzed by using principal component analysis. As a result, postpartum depression experience was classified into 5 types. There are "Role -Strain Type", "Unattributional Depression Type", "Psychosomatic Symptoms Type", "Self-Compassion Type", and "Role-Crisis Type". Type I was named "Role-Strain Type", referring to the strain generally experienced by mothers with regard to the new role as a mother and as a social member. Type II was named "Unattributional Depression Type", referring to the symptom experienced by people who were in a state of vanity and a sense of loss. They often break into tears for no specific reasons. In case of Type III, people in a state of "Psychosomatic Symptoms Type" develop physical symptoms after suffering from inherent emotional conflict. Type IV was named "Self-Compassion Type" refers to the symptom shown by those who feel pity for their children and for themselves. And they show inability to cope with the reality properly. Type V was named "Role-Crisis Type", which is experienced by people who have a burden and a severe fear of their own job and their children in their mind, also showing serious conflict with maternal role. Futhermore, it was carried out to examine structure of postpartum depression in terms of degree of depression and adjustment ability. Type I showed mild degree of depression and relatively good adjustment ability. Type II showed broad range of degree in depression and moderate adjustment ability. Type III showed moderate depression and relatively low adjustment ability. Type IV revealed relatively serious degree of depression and the lowest adjustment ability. Type V revealed very serious degree of depression and the lowest adjustment ability. As a result, considering the structure of postpartum depression, Type I is considered to be a normal depression sympton which most mothers generally experience, followed by Type II, Type III, Type IV and Type V, each of which show increasingly worse degree of depression and lower adjustment ability. In conclusion, it seems to be it is necessary to understand distinct symptoms of postpartum depression and to examine the characteristics and structure of those types, so that it could lead to more individual nursing approach.
- 372 View
- 0 Download

- A Study on the Degree of Burden and Depression in Family Caregivers of Patients with Stroke
- Kang Yi Lee, Kyeong Yae Sohng
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(4):853-867. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.4.853
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed and undertaken to identify the degree of burden and depression in family caregivers of patients with stroke and to determine whether burden was directly related to depression. The data were collected from October 23th to November 20th, 1995. The subjects in this study were 80 caregivers, that is, one family member and 80 patients with stroke who were hospitalized in one oriental medicine hospital located in Taejon City. The questionnaires consisted of questions regarding burden(13 item, 6 point scale) and depression(20 item, 4 point scale). Data were analyzed using percentages, means, t-test, ANOVA and Peason-correlation coefficients, done with the SAS program. The results of this study are as follows; 1. The score for family caregiver's burden was higher than the mid level for the 13 items. 2. The score for of family caregiver's depression was relatively low. 3. The relationship between burden and depression showed a significant inverse correlation. 4. In the relationships between total burden and general characteristics of the family caregivers; there were no significant differences. But, in the relationship between objective burden and general characteristics of the family caregivers; age and education had statistically significant differences. That is, the 40's group felt more objective burden than any other age group and the high education group more than the illiterate group. 5. In the relationship between depression and general characteristics of the family caregivers; sex, education and monthly income had statistically significant differences. That is, female caregivers felt more depression than males, and the lower the level of education and the lower the monthly income, the higher the degree of depression. 6. In the relationships between burden and general charateristics of the stroke patients, only subjective burden according to the patients' sex was significantly different. That is, caregivers felt more subjective burden when caring for male patients than for female patients. 7. In the relationships between depression and general charateristics of the stroke patients, only the patients' economic status showed a statistically significant difference. That is, caregivers felt more depression in case of patients' low economic status.
- 572 View
- 7 Download

- An Effect of Muscle Strengthening Exercise Program on Muscle Strength, Pain, Depression, Self-efficacy, and Quality of Life of Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis
- Mi Ra Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(3):556-575. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.3.556
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In an attempt to investigate the effect of a muscle strengthening exercise program on muscle strength, pain, depression, self-efficacy and quality of life of patients with knee osteoarthritis, a pre-experiment, one group pre-test and post-test design, was planned. Muscle strengthening exercise was carried out from May 22 through August 14, 1995 at isokinetic exercise room in rehabilitation department of University Hospital in Taejon. The subjects were seven female clients conveniently sampled from University Hospital located in Taejon, between 39 and 61 years of age, who had a osteoarthritis in knee. Muscle strengthening exercise program was composed of three sessions per week, one isokinetic exercise at angular velocity of 60degrees and 180degrees with Cybex isokinetic dynamometer and two resistance home exercise sessions with elastic band. Data were analyzed with frequency, percentage of change, Friedman test, Duncan test using SAS program. Results were obtained as follows: 1) Flexion and extension muscle strength at angular velocity of 60degrees and 180degrees were increased after 12weeks' exercise than those of before experiment. But exept flexion muscle strength at angular velocity of 180degrees (F=3.34, P=0.0261), there was no statistically significant difference among muscle strengths, which is measured every 3 weeks. 2) Pain was decreased after 6weeks' exercise than that of before experiment, and after 12weeks' exercise than that of 6weeks' exercise. There was statistically significant difference(F=4.28, P= 0.0396). 3) Depression was increased after 6weeks' exercise than that of before experiment, and after 12weeks' execise than that of 6weeks' exercise. There was no statistically significant difference between before experiment and after 6weeks' exercise. But, there was statistically significant difference between after 6weeks' exercise and 12weeks' exercise (F=9.38, P=0.0035). 4) Self-efficacy was decreased after 6weeks' exercise than that of before exercise. But, it was increased after 12weeks' exercise than that of before exercise and after 6weeks' exercise. But there was no statistically significant difference (F=1.46, P=0.2706). 5) Quality of life was increased after Gweeks' exercise than that of before exercise, and after 6weeks' exercise than that of 12weeks' exercise. But there was no statistically significant differ-ence(F=1.06, P=0.3816). Thus, the significant of muscle strengthening exercise for the improvement of muscle strength, pain, depression, is verified. But, this study was a preexperiment with small size subjects. So, controlled experimental study is necessary to determine the effect of this muscle strengthening exercise program on muscle strength, pain, depression, self-efficacy, and quality of life of patients with knee osteoarthritis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of elastic band exercises and nutritional education on frailty, strength, and nutritional intake in elderly women
Yena Bong, Wook Song
Physical Activity and Nutrition.2020; 24(1): 37. CrossRef - The Relationship between Job Stress and Depression in Opticians in Seoul, Korea
Semi Kim, Jihye Ahn, Moonsung Choi
Journal of Korean Ophthalmic Optics Society.2019; 24(3): 223. CrossRef - Retracted:Effects of Exercise Program on Physical Fitness, Depression, and Self‐Efficacy of Low‐Income Elderly Women in South Korea
Kyung Rim Shin, Younhee Kang, Hyo Jung Park, Margaret Heitkemper
Public Health Nursing.2009; 26(6): 523. CrossRef
- The effects of elastic band exercises and nutritional education on frailty, strength, and nutritional intake in elderly women
- 791 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Experience of the Postpartum Depression: A Grounded Theory Approach
- Jeung Lee Bai
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(1):107-236. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.1.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Purpose of this study was to build a substan tive theory about the experience of postpartum depression. The qualitative research method used was grounded theory. The interviewees were eight mothers who had experienced postpartum depression. The data were collected through in-depth interviews with audiotape recording done by the investigator over a period of twelve months. The data were analyzed simultaniously by a constant comparative method in which new data were continuously coded into categories and properties according to Strauss and Corbin's methodology. Analysis the grounded data resulted in 28 concepts being identified. Eight categories emerged from the analysis. The categories were regret, loss of freedom, isolation of oneself, heartache, loss, emotional upset, avoidance, recovery. These substantive categories are consistant with preious research results. Causal conditions included: regret, loss of freedom. Phenomena: heartache, loss, emotional upset. Context: isolation oneself. Intervention condition: avoidance. Action/interaction strategies: desire for recovery. Consequences: recovery. These categories were synthesized into the core concept-The process of filling the empty loss of self The process of the experienced postpartum depression was (1) change after delivery, (2) searching for a reason for depression, (3) effort to recover from postpartum depression, (4) recovery from postpartum depression and return to previous life. The process of recovery from postpartum depression was proceeded by (1) support from others, especially husband, (2) resolution of stressful life events, (3) reconstructing of life goals and resolution strategies, (4) acceptance of depression and seeking psychiatric treatment. Seven hypotheses were derived from the analysis. (1) Mothers who experienced stressful life event and economic problem are more depressive. (2) Mothers who have conflict with parents are more depressive. (3) The more somatic symptoms, the more depression. (4) Social support faciliates recovery from postpartum depression. (5) Mothers who have lower self-esteem are more depressive. (6) Mother's role overload disturbs recovery from postpartum depression. (7) Ideal maternal identity faciliates recovery from postpartum depression. Through this substantive theory, nurses can understand the importance of postpartum depression management.
- 627 View
- 2 Download

- Relationship Between Postpartum Depression and Body Image in Postpartum Women
- Boon Han Kim, Hye Won Jeon, Yun Jung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):906-916. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.906
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to identify the change and difference and relationship of postpartum depression and physical image. METHOD: The subjects consisted of 86 postpartum women at one general hospital in Seoul. The data was collected from September to November 2001. The instrument used for this study were SRD (Self-Rating Depression Scale) and Norris' Body Image Scale to evaluate depression and body image. The collected data was analyzed with frequency, mean, t-test, paired t-test, ANOVA and Pearson's correlation coefficient. RESULT: The result of this study were as follows: 1.The mean score of D2 was significantly higher than D1(p=.003). There was no difference significantly B1 and B2(p=310). 2. There was significant correlation between the two, D1-D2(r=.381, p<.01), B1-B2(r=.364, p<.01), D1-B1(r=.579, p<.01), D2-B2(r= .567, p<.01). (D1: depression of postpartum 1-3days, D2: depression of postpartum 6-8weeks, B1: body image of postpartum 1-3days, B2: body image of postpartum 6-8weeks) CONCLUSION: There was very high postpartum depression in postpartum women, but body image was positive. Also, there was correlated to postpartum depression and body image. Thus it is necessary to implement nursing intervention focused on to decrease the postpartum depression and to enhance the body image of the postpartum women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Self Efficacy, Body Image and Family Support on Postpartum Depression in Early Postpartum Mothers
Ji-Won Lee, Yong-Sook Eo, Eun-Hye Moon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 4011. CrossRef
- Effects of Self Efficacy, Body Image and Family Support on Postpartum Depression in Early Postpartum Mothers
- 815 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Discriminating Nurses' Depression among Personal and Environmental Characteristics
- Hae Jung Lee, Yong Sook Eo, Nam Hee Park, Gil Za Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):867-877. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.867
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine the levels of depression experienced by Korean hospital nurses (N=198) and to identify discriminating factors of their depression experience among personal and environmental characteristics. METHOD: A cross-sectional survey design was used to answer the research questions. A sample consisted of 198 hospital nurses in Korea. The data were collected from May 1999 to March 2000. Descriptive and discriminant analyses were utilized. RESULT: Korean nurses experienced low levels of depression. Twenty nine percent of nurses in the study experienced depression based on the cut-point suggested by Radloff. Role ambiguity, working in the tertiary hospital, work satisfaction in autonomy, professional status and interaction within nurses were significant discriminating factors for nurses' depression. These factors correctly discriminated 71% of the sample (Hit ratio= .71). CONCLUSION: Based on the findings of this study, developing managemental intervention programs and examining the effects of the program for nurses to reduce their depression experience are suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a mobile simulation program for nursing delegation: A randomised controlled trial
Haena Lim, Yeojin Yi
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 83: 104283. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Depression among Workers by Socio-economic Factors, Health Behaviors, and Characteristics of Work Environment
Hyunkyung Lee, Minsung Sohn, Mankyu Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(5): 125. CrossRef - A Study on the Uncertainty and Depression in Mothers of Hospitalized Children
Kyung Hee Yoo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(2): 265. CrossRef - The Relationships between Emotional Labour and Depressive Symptoms Among Nurses in University Hospitals
Kyung-Ok Kim, Young-Chae Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(8): 3794. CrossRef
- Effects of a mobile simulation program for nursing delegation: A randomised controlled trial
- 691 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Affecting Factors of Homebound Bedridden Elderly's Depression
- In Ja Kim, Keum Soon Kim, Moon Ja Suh, Nam Ok Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):665-672. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.665
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: It was identified that how many homebound bedridden elderlies and their primary caregivers were depressed, and which factors affected the bedridden elderly's depression. METHOD: The subjects were 191 homebound bedridden elderlies and their primary caregivers. The affecting factors were classified into two categories: bedridden elderly and their primary caregiver related factors. Then bedridden elderly's factors were classified demographic and disease-related factors again. The stepwise regression was used to identify significant factors. RESULT: The prevalence of bedridden elderly's and caregiver's depression was 77.8% and 67.0%, respectively. And the model explained 33.3% of variance of bedridden elderly's depression. Cognitively-impaired female elderlies who had depressed caregivers were found to be more depressed. And caregivers who perceived burden were identified to be more depressed. CONCLUSION: It is recommended that the health professionals need to identify bedridden elderlies and caregivers at risk of depression. Especially elderlies who is in poor cognition, those who are female, and those whose caregivers were depressed might be considered carefully in all counseling or follow-up. Also the primary caregivers must be helped to access already available formal and informal support.
- 494 View
- 2 Download

- Physical Health Status and Depression of a Community-Dwelling Elderly Group
- Nam Cho Kim, Soo Yang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(6):1012-1020. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.1012
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to describe physical health and depression status, as well as to assessing factors that influence the physical health status.
METHOD
The data was collected from July to August 2000. Study participants were 252 community-dwelling elderly who were recruited from 10 senior centers located in Seoul, Korea. Their physical health status was measured using the Physical Health Status Measurement Scale developed by Choi and Jung (1991), and depression was measured using BDI-II developed by Beck et al. (1996).
RESULTS
1) The physical health status score was 4.00 +/-0.68 (range :1-5). The sub-dimension that showed the highest score was personal hygiene ability at 4.62+/-0.95, and the lowest score was sexual function at 2.20+/-1.38. 2. The depression score was 17.99+9.79 (range : 0-63). Regarding the sub-dimensions, the depression scores were higher in the domain of interest with sexuality, general weakness, difficulty in concentration, and fatigue. 3. Deeper levels of depression were correlated with a declining physical health status. 4. The most influential factor on physical health was depression, and the explaining variance was 31.68%.
CONCLUSION
It is concluded that elder subjects in senior centers had fairly good physical health and self-care ability. Also, they did not have significantly high levels of depression. Therefor, health promotion of elderly, it is recommended that elder individuals should be regarded as a respectful and useful segment of our society. Along with this basic concept, there should be a social milieu that does not snow prejudice. Moreover, health care professionals should give more attention to helping the elderly achieve a minimal level of ALD, and, particularly, to raise sexuality and help energize the lives of elder individuals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing a Predictive Model for Depressive Disorders Using Stacking Ensemble and Naive Bayesian Nomogram: Using Samples Representing South Korea
Haewon Byeon
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Perception and Family Support as Influencing Factors on Depression in Hospitalized Elderly Patients
Sun-Ok Lee, Moon-Jeong Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(4): 145. CrossRef - The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
Young Rye Park, Yang Gyeong Yoo
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(1): 71. CrossRef - A comparison of the factors influencing life satisfaction between Korean older people living with family and living alone
S.H. Shin, S.R. Sok
International Nursing Review.2012; 59(2): 252. CrossRef - Gender Differences in the Relationships between Physical Activity and the Psychological and Physical Self-Reported Conditionof the Elderly in a Residential Care Facility
Emanuela Rabaglietti, Monica Emma Liubicich, Silvia Ciairano
Psychology.2011; 02(01): 35. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Life Satisfaction of Korean Older Adults Living with Family
Sohyune R. Sok
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2010; 36(3): 32. CrossRef - Residential status and depression among Korean elderly people: a comparison between residents of nursing home and those based in the community
Soondool Chung
Health & Social Care in the Community.2008; 16(4): 370. CrossRef - 10.5932/JKPHN.2012.26.1.072
CrossRef Listing of Deleted DOIs.2000;[Epub] CrossRef
- Developing a Predictive Model for Depressive Disorders Using Stacking Ensemble and Naive Bayesian Nomogram: Using Samples Representing South Korea
- 685 View
- 1 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Depression Among Korean Women
- Kyung Rim Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):391-400. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.391
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine depression in order to identify and improve health care policies promoting health among Korean women. METHOD: There were 329 participants, all older than 18 years old, and staying in Kyungki-Do, city. The data was collected from July to September 1999. The instrument used for this study was the CES-D (Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale) to evaluate depression. The collected data was analyzed with frequency, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, X2-test and Multiple logistic Analysis. RESULT: The result of this study are as follows: 1. Among the participants, 90.6% had normal to mild depression and 9.4% had severe depression. 2. For general characteristics, there were significant difference in the degree of depression according to age(P=0.0001), and marital status(P=0.0001). As for health related characteristics, the depression scores were affected by health perception(P= 0.0001), menopause(P=0.0005), stress (P= 0.0001) and sexual activity (P=0.0001). 3. There was a significant relationship between marital status and stress. CONCLUSION: This study suggests that a replicate study is needed. The results are also is useful in developing various nursing intervention programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Work–Family Conflict on Depression Among Korean Women During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Moderated Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction
Hyo Sung Cha, Jin Pyo Lee
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 923. CrossRef - The Impact of Sleep Quality and Education Level on the Relationship between Depression and Suicidal Ideation in Parents of Adolescents
Ji Yeon Shim, Sook Lee, Il Hyun Lee, Yoo Mi Jeong
Healthcare.2021; 9(9): 1171. CrossRef - Efficacy of Cognitive Behavioral Treatment for Insomnia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Ok Kyung Ham, Bo Gyeong Lee, Eunju Choi, Su Jung Choi
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 42(12): 1104. CrossRef - Black Tea Intake in Relation to BMI and Depression in Adult Women
You-Mi Jung, Mi-Ja Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(5): 436. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire to Estimate the Intake of Fatty Acids
Seon-Joo Park, Changho Lee, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(3): 239. CrossRef - Behavioral Characteristics and Cardiovascular Disease Risks Associated With Insomnia and Sleep Quality Among Middle‐Aged Women in South Korea
Ok Kyung Ham, Jinyoung Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee, Eunju Choi
Research in Nursing & Health.2017; 40(3): 206. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-esteem and Family Stress on Depression of Middle-aged Couples: Analysis of Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Yu Jeong Yang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 60. CrossRef - Influence of Spiritual Wellbeing and Social Support on Depression in Middle-aged Women
Je Eun Heo, Young Sook Tae
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 181. CrossRef - Comparison of Stress, Depression and Suicidal Ideation between Nursing Students and Students of Other Majors
Sun Kyung Cha, Eun Mi Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(4): 650. CrossRef - The Effects of Job Stress with Depression and Fatigue of Firemen
Kwang-Seok Kim, Jong Park, Bu-Yeon Park, Sung-Gil Kim, Eun-Yeong Hwang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(3): 223. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Self-Identity and Menopausal Symptoms on Level of Depression in Middle Aged Women
Mi-Jeong Han, Ji-Hyun Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2013; 19(4): 275. CrossRef - Beliefs and Attitudes toward Intimate Partner Violence and Depression in Victims of Intimate Partner Violence Dwelling in the Community
Young Ran Han
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(3): 532. CrossRef - A Path Analysis: A Model of Depression in Korean Women With Breast Cancer-Mediating Effects of Self-Esteem and Hope
Young Sook Tae, Margaret Heitkemper, Mi Yea Kim
Oncology Nursing Forum.2012; 39(1): E49. CrossRef - A comparison of the health and related quality of life between middle‐aged Korean and Chinese women
K.‐B. Kim, S.R. Sok
International Nursing Review.2010; 57(4): 463. CrossRef
- The Impact of Work–Family Conflict on Depression Among Korean Women During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Moderated Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction
- 798 View
- 1 Download
- 14 Crossref

- A Correlational Study on Uncertainty, Coping and Depression of Cancer Patients
- Yun Jung Lee, Eun Mi Ham, Kum Sun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(2):244-256. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.2.244
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coping mechanisms on uncertainty and depression. The subjects were 71 cancer patients selected from Junbook National University Hospital, and the data collection period was from June 21 to October 19 of 2000. Uncertainty was measured by using Mishel's Uncertainty Scale, problem- focused coping, and emotional-focused coping. The data was collected by a questionnaire developed by Lee (1984), and then depression measured by using Beck's depression scale. Data was analyzed with SPSS/WIN 7.5 program by Pearson Correlation Coefficients, and Path analysis. The results were as follows : 1. The mean uncertainty score was 59.17, the mean problem-focused coping score was 48.78, the mean emotional-focused coping score was 42.52. 2. The mean depression score was 15.77. 3. Uncertainty in illness was significantly related to depression (p=0.003) and emotional-focused coping (p=0.028), but uncertainty was not associated with coping mechanisms. 4. When analyzed multiple regression between uncertainty, problem-focused coping, emotional- focused coping, and depression, more specifically emotional-focused coping showed a stronger association with depression than problem-focused coping. 5. Depression was highly correlated with economic status (p=0.015), educational background (p=0.005), duration of disease (p=0.045). 6. Problem-focused coping and emotional-focused coping appeared to function as moderators instead mediators on the relation between uncertainty and depression. In addition, as a whole, uncertainty showed a significant moderating effect on depression, while problem-focused coping did on depression. Finally, limitation of present findings were discussed and implications for future studies are suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Duration of Prophylactic Antibiotics Therapy on Uncertainty of Recovery in Elective Laparoscopic Uterine Myomectomy Patients
Mi Young Jung, Kyung-Yeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(4): 240. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the quality of life in thyroid cancer patients after thyroidectomy
Jeong-Sook Jeong, In-Sook Kim, Eun-Seon Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(8): 5442. CrossRef - Uncertainty in Elderly Women with Osteoarthritis: Relationship to Pain, Self-care Agency and Health Conservation
Jiran Nam, Kiwol Sung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2014; 16(3): 201. CrossRef - A Study on the Uncertainty and Depression in Mothers of Hospitalized Children
Kyung Hee Yoo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(2): 265. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Psychosocial Adjustment in Patients with Early Breast Cancer
Hye Young Kim, Hyang Sook So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 105. CrossRef - The Influence of Uncertainty and Social Support on General Well-being among Hemodialysis Patients
Youn-Jin Kim, Hee-Jung Choi
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 20. CrossRef - Level and Correlation Factors of Uncertainty in Members of Families of a Patient with Mental Illness
In-Ohg Oh, Eui Geum Oh, Sunah Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(2): 158. CrossRef
- Influence of Duration of Prophylactic Antibiotics Therapy on Uncertainty of Recovery in Elective Laparoscopic Uterine Myomectomy Patients
- 789 View
- 7 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Depression of Stroke Patient's Family Caregivers and the Relating Factors
- Hee Jung Choi, Moon Ja Suh, Kum Soon Kim, In Ja Kim, Nam Ok Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1531-1542. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1531
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this paper, we examined the depression of stroke patient's caregivers and analyzed influencing factors of the depression. The subjects were 215 caregivers who have takencare of stroke survivors in their home. The conceptual model of this study consisted of the caregiver's depression, perceived burden, illness intrusiveness, and patient's ADL. Modified Korean CES-D, modified subjective and objective Burden Scale, Illness intrusiveness(II), and Instrumental Activity of Daily Living(IADL) were used to measure concepts. Path analysis was used to test the model of this study. The results were as follows: 1. The mean depression score was 11.6 which was below the cut-off score of the CES-D. This score indicates that the subjects were higher than normal adults' mean score but not depressive. Eighty-six out of 215 caregivers(40%) were above the cut-off score. This finding was different from previous research results, and the reason might be the patients' capability of ADL. In a group of low capability patient's activities of daily living, caregiver's depression score was 15.5. 2. Caregiver's depression was positively related to caregiver's burden and illness intrusiveness, but negatively related to patient's activities of daily living. 3. The caregiver's perceived burden and illness intrusiveness directly influenced on their depression. Furthermore, the and caregiver's illness intrusiveness led to depression indirectly through their burden. A patient's activities of daily living didn't influence directly on depression but indirectly through caregiver's illness intrusiveness and burden.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spirituality and Quality of Life Model of Family Caregivers Caring for Patients with Stroke: Path Analysis
Jiyeong Lee, Jinsun Yong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(6): 619. CrossRef - Needs of Family Caregivers Caring for Stroke Patients
Jae Won Kim, Sung Seek Moon
Social Work in Health Care.2007; 45(1): 81. CrossRef
- Spirituality and Quality of Life Model of Family Caregivers Caring for Patients with Stroke: Path Analysis
- 816 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Comparative Study of Depression and Stress Related Life Events among Women in the Menopausal Stage
- Eun Soon Chung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):956-966. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.956
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to examine the comparative between depression and stress related to life events among women in the menopausal stage. Menopausal stages were divided into two groups: Pre and post- menopausal stages. The degree of depression and stress related to life events between pre and post menopausal women were compared to each other. Women, aged between 41 and 59 years, answered self-reported questionnaires which included Zung's depression scale and life events scale modified by Lee (1984). Findings were as follows; 1) The mean score of premenopausal women who experienced depression was 39.66, and for post-menopausal women the score was 41.45. There was no significant differences in depression levels between pre and post menopausal group.s (t=-1.55, p=.122). 2) Menopausal women experienced low levels of stress related to life events. There were no significant differences between pre and post menopausal groups(t=.527, p>.05). Both pre and post menopausal groups were highly concerned about education issues of their children and disharmony between couples. 3) There was a significant relationship between depression and stress related to life events among post-menopausal groups (r=.22, p<.01). Based on the findings of this study, the menopausal depression was associated with stress related to life events, especially among post-menopausal women. Feelings of lost fertility and feminine attributies result in menopausal depression, which is significantly correlated with women's negative perception of their life events. Therefore, nursing intervention needs to develop to help reduce the levels of depression and overcome their negative perception of the menopausal experience. Nurses should develop nursing strategies to help menopausal women to have positive perceptions and enhance quality of life by assisting their adaptability to physiological and psychological changes related to menopause.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting suicidal ideation among premenopausal and postmenopausal women
Go‐Un Kim, Hae Kyoung Son, Mi‐Young Kim
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 28(3): 356. CrossRef
- Factors affecting suicidal ideation among premenopausal and postmenopausal women
- 582 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of Group Imago Psychotherapy on Comfort and Depression of Patients with Hemodialysis
- Gui Yun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):791-798. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.791
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The hemodialysis patients with chronic renal disease have experienced negative emotions, especially depression among with physical, social, and psychological changes. Based upon a stress-coping theory, group imago psychotherapy which can induce effective coping through self awareness and positive emotional responses is implemented to the hemodialysis patients. The effects of the imago psychotherapy in regards to comfort and depression are studied here. Group imago psychotherapy was performed on forty-three subjects(twenty subjects in the experimental group and twenty-three subjects in the control group). The results of the study were as follows. After being given group imago psychotherapy, the comfort scores of the experimental group were significantly higher than those of the control group (F=15.33, p= .003). Moreover, after being given treatment, the depression scores of the experimental group were significantly lower than those of the control group (F=9.14. p=.0044). Specifically, the scores on comfort in the experimental group under emotion-focused coping style were significantly higher than those of the control group (F=18.59, p= .0002). The mean difference on comfort scores in the experimental group under problem - focused coping style was higher than that of the control group. But their scores were not significant (F=0.19, p= .6729). The scores on depression in the experimental group under emotion-focused coping style were significantly lower than those of the control group (F=14.62, p= .0006). The mean difference on depression scores in the experimental group under problem - focused coping style was much lower than that of the control group. But their scores were not significant (F=0.31, p=.5947). There was a significant positive correlation between comfort and depression variables. After group imago psychotherapy the hemodialysis patients recognized positive changes in emotional reponses, self awareness, self control, ease of mind, and felt overall more relaxed. Imago psychotherapy is a nursing intervention which as this study has shown can improve to comfort. The
results
of this study can be applied to general nursing practices. In the view of holistic nursing, the development of the nursing practice combined with imago psychotherapy will contribute to the enlargement of the nursing field with conventional nursing practices.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of the comfort level of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease within the scope of Kolcaba's comfort theory
Aylin Bilgin, Goncagul Aldan, Leyla Ozdemir, Sibel Gunay
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 83: 151964. CrossRef
- Investigation of the comfort level of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease within the scope of Kolcaba's comfort theory
- 601 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- An Application Effect of Rhythmic Movement Program for the Health Promotion in the Elderly
- Sook Ja Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):776-790. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.776
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Every year the number of the elderly increases in Korea thanks to the improvement of social and economical levels and the development of medicine. However, many problems such as insufficent care and the isolation of the elderly have been commonplace. This trend exists not only because of increased lifespan but also the changing social structure of the nuclear family. Accordingly, inspite of the development of medicine, geriatric diseases including circulatory diseases are increasing in proportion of elderly population, as well as the severity. Therefore, it is important to emphasize that health care programs provide the best possible health care and functional capacities in terms of healthy elderly lifestyles. Especially, the phenomena of aging and geriatric diseases taking place with the elderly naturally are affected by lifestyle and the drastic changes in exercise patterns. This study aims to improve geriatric health by introducing a rhythmic movement program for the elderly to estabilish a health-promoting self-care system and by developing quality of life, perceived health status, their physical and physiological functions and emotional state. The theoretical framework used in this dissertation is derived from the Health-Promoting Self-Care System Model (Simmons, 1990), which integrates the Self-Care Deficit Nursing Theory (Orem, 1985), the interaction model of Client Health Behavior (Cox, 1982) and the Health Promotion Model (Pender, 1987). As a quasi-experimental design, the nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design is utilized for this study. The subjects of this study consist of 64 people, over 65 years old who live in 2 nursing homes for the aged located in S city , Kyong-gi province and volunteered for this study from July, 12, 1999 to September, 17, 1999. They are divided into two groups: 33 in the experimental group and 31 in the control group. The experimental group particpated in the Rhythmic Movement Program at the nursing home, which was comprised of 45 minutes a session, 5 sessions a week during 9 weeks. In order to measure the results of the Rhythmic Movement Program, aspects of perceived health status, balance, flexibility, grip strength, leg strength, heart rate, blood pressure, depression, anxiety and the quality of life were measured before and after participating in the Rhythimic Movement Program for the experimental group after 9 weeks, as well as the control group. The collected data were processed by SPSS PC+ and analyzed by the X2 test, t-test, ANCOVA and the Pearson Correlation Coefficient. The results of this study are as follows: 1. The perceived health status conditions in the experimental group show statistically significant improvement when compared to the control group (F=17.51, p=.000). 2. The physical and physiological functions, that is, balance (F=17.51, p=.000), flexibility (F=8.01, p=.006), grip strength (F=3.21, p=.018) and leg strength (F=25.78, p=.000) in the experimental group are higher than the control group. The vital signs, that is, the number of heart rate (F=.022, p=.884), systolic pressure (F=1.73 p=.193), and diastolic pressure (F=2.74, p=.103) in the experimental group compared to the control group decreased, but doesn't show statistically significant differences. Immune responses (F=5.13, p=.003) showed statistically significant increases in the experimental group when compared to the control group. 3. The emotional state are improved, that is, degree of depression (F=11.56, p=.001) and degree of anxiety (F=9.14, p=.004) in the experimental group showed statistically significant decreases. 4. The quality of life in the experimental group (F=3.03, p=.037) showed statistically significant differences compared to the control group. 5. The observations of the relationships among the perceived health status, emotional state , the quality of life, the relationships between the perceived health status, the degree of depression (r=-.653, p=.000) and the degree of anxiety (r=-.786, p=.000) were in contrary propotions, while the relationships between the perceived health status and the quality of life (r=.234, p=.008) were in direct propotion. In conclusion, the Rhythmic Movement Program used in this study for geriatric nursing care is simple and safe for application to the elderly and shows significant effects by implementing 5 sessions a week for 9 weeks. The Rhythmic Movement Program improves the quality of life, maintains as well as improves the physical and physiological fuctions and emotional state, therefore this program is strongly recommended for positive applications for independant geriatric nursing health care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Dance Sports Program on Physical Function, Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life in Rural Elderly Women
Yun-Hee An, Nam-Soo Hong, Hee-Jung Yoon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2020; 45(4): 385. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-Care Intervention Programs for Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Myung-Suk Kim, Moonhee Gang, Jihye Lee, Eunyoung Park
Issues in Mental Health Nursing.2019; 40(11): 973. CrossRef - The Effects of Qi-gong Exercise on the Health of the Elderly - With Respect to the Physical Health Status, the Fear of Falling, Balance Efficacy, and Hwa-Byung -
Kum-Sook Park, Heon-Young Jeong, Young-Hee Kim
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2016; 27(4): 207. CrossRef - Impact Factors for Health of Family Caregivers of Hospice Patients
Bok Yae Chung, Hyeon Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(2): 75. CrossRef - The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
Young Rye Park, Yang Gyeong Yoo
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(1): 71. CrossRef - The Effects of an Aerobic Exercise Program on Mobility, Fall Efficacy, Balance, and Stress in the Elderly at Senior Centers
Su Kyung Chu, Chung Yul Lee, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(1): 22. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Therapy on Physical Functions in the Elderly
Sook Hee Jung, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 252. CrossRef - Relations among Depression, Life Satisfaction and Health Promoting Behavior in the Elderly
Ji-Hye Seo, Hyun-Sook Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 169. CrossRef - Effects of Music Therapy and Rhythmic Exercise on Quality of Life, Blood Pressure and Upper Extremity Muscle Strength in Institution-Dwelling Elderly Women
Eun Young Jeon, Sook Young Kim, Hyun Suk Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 829. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Hand Massage On Sleep, Depression and Quality of Life in the Institutionalized Elderly Women
Soon Yi Seo, So Young Chang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 372. CrossRef - The effect of modified jazz dance on balance, cognition, and mood in older adults
Patricia T Alpert, Sally K Miller, Harvey Wallmann, Richard Havey, Chad Cross, Theresa Chevalia, Carrie B Gillis, Keshavan Kodandapari
Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners.2009; 21(2): 108. CrossRef - Effects of a Strengthening Program for Lower Back in Older Women with Chronic Low Back Pain
Hee-Kyoung Hyoung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 902. CrossRef - Comparisons of Motivation, Health Behaviors, and Functional Status Among Elders in Residential Homes in Korea
Rhayun Song, Kyung Ja June, Chun Gill Kim, Mi Yang Jeon
Public Health Nursing.2004; 21(4): 361. CrossRef
- The Effect of Dance Sports Program on Physical Function, Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life in Rural Elderly Women
- 751 View
- 5 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Depression of Women after a Hysterectomy
- Young Sook Park, Young Lan Ahn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):709-719. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.709
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purposes of the study was to identify the depression of women after a hysterectomy and to clarify the factors related to depression. This was a cross-sectional descriptive study. The data was collected by a mailed questionnaire that was composed of the Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale(SDS), support scale of husband and socio-demographic variables from 255 women undergoing hysterectomies for any nonmalignant condition in S. University Hospital. They also must have lived with their spouses from 3 months to 2 years after the operation. The results were as follows: 1. The SDS mean was 42.25 and range was 21 to 67. The incidence of clinical depression (over SDS 50) was 20.8% from 3 months to 2 years after a hysterectomy. 2. The depression of women in 18-24 months after surgery (39.80) was lower than that of any other periods such as 3-5 months, 6-12 months, and 13-17 months (p<0.01). 3. The support form husband was negatively correlated with the depression of women after a hysterectomy. 4. Depression among women had hysterectomies were associated with lower income, less sexual satisfaction, the feeling of being asexual, and the bias of concept the uterus controlling general health.
- 486 View
- 1 Download

- Stressful Life Event., Close Relationship, Self-Esteem, and Depression in College Women
- Sun Ah Kim, In Ohg Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(5):1021-1029. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.5.1021
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Koreans rarely complain of depression or other psychological problems because mental illness is viewed as a stigmatizing and threatening experience. This study examined the relationships among stressful life events, close relationships, self-esteem, and depression in 400 college women aged 18 to 30 years. Depression was positively related to stressful life events(r=.21 p=<.01). Depression and stressful life events were negatively associated with self-esteem(r=-.67: r=-.11, p<.01; p<.05 respectively). Close relationships with women and men friends were each negatively associated with depression (r=-.24; r=-.16, p<.05). Close relationships with women and men friends were positively associated with self-esteem (r=.23; r=.20, p<.01). Forty nine percent of variance in depression rates in this sample was explained. After adjustment for degrees of freedom, a total of 49% of the variance in depression was explained by self-esteem and stressful life event. This investigation into the relationships among the variables influencing depression for college women is a critical issue as health professional interventions are those designed for specific populations to meet unique care needs and since young Korean women may be at considerable risk for depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of Interrole Conflict and Role-related Stress among Registered Nurses Pursuing Advanced Nursing Degrees
Taesook Kim, Lijuan Xu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(1): 5. CrossRef - Employed women with depression in Korea
K. A. NAM, S. KIM, H. LEE, H. L. KIM
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 18(2): 139. CrossRef
- Relationship of Interrole Conflict and Role-related Stress among Registered Nurses Pursuing Advanced Nursing Degrees
- 781 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Predictive Model of Adolescent Women's Depression
- Young Joo Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Jung Nam Sohn, Suk Hee Cheon, Hyun Jung Shin, Young Nam Chung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):829-840. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.829
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was condicted to construct a hypothetical model of depression in Korean adolescent women and validate the fit of the model to the empiricla data. The data were collected from 345 high school girls in Seoul, from May 1 to June 30, 1998. The instruments were the Body Mass Index, Physical Satisfaction Scale, Family Adaptatibility and Cohesion Evaluation Scale III, Family Satisfaction Scale, CES-D and School Adaptation Scale. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics with the pc-SAS program. The Linear Structural Relationship(LISREL) modeling process was used to find the best fit model which would predict the causal relationships among the variables. The overall fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate [X2=69.6(df=17, p=.000), GFI=0.95, AGFI=0.90, RMR=0.087, NNFI=0.86, NFI=0.90]. The predictable variables, especially menstrual symptoms, physical symptoms and family function, had a significant direct effect on depression, but school life adaptation did not have a significant direct effect. These variables explained 18.1% of the total variance.
- 532 View
- 0 Download

- A Study on the Burdens and Depressive Reactions on Families who Cared for Patients Suffering from Senile Dementia
- Young Ja Kim, Pyoung Sook Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):766-779. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.766
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between the burdent on families who live with an elderly person suffering from senile dementia, and the degree of their depression. There were 400 participants in this study, staying in the Seoul and Kyonggi areas from August, 1, 1997 to February 28, 1998. Among the group, 100 participants took care of their patients at home, and another 300 participants left 100 patients at a day-care center, 100 sanatorium for senile dementia(asylum for helpless elderly people), 100 an infirmary for elderly people. Eventually 242 subjects out of the 400 were selected for the data analysis. The Zarit(1980) tool was employed to measure the degree of burden and Zung's(1965) "Self-Rating Depression Scale" was employed for the data analysis. The data was analyzed, and the percentage, t-test, ANOVA, and Pearson's Correlation Coefficient were calculated. The results are as follows. 1. The average degree of burden that care-giving families felt was 49.13, which is somewhat high. 2. The average degree of depression that-giving families felt was 51.95, which is relatively high. 3. The degree of burden was directly affected by the relation with the patient(F=2.48, P<.05), and the socio-economic status of the family(F=5.17, P<.05). It's also affected by the patient's educational status(F=2.17, P<.05). 4. The degree of depression of the family was significantly dependent on sex(t=-2.05, P<.05), age(F=2.99, P<.05), the relationship with the patient(F=3.65, P<.01), socio-economic status(F=7.74, P<.001), occupation(t=2.82, P<.01), health status(F=4.42, P<.01), and the place of residence(F=4.30, P<.01). The patient characteristics was significantly dependent on his/her educational status(F=3.85, P<.01), the period of suffering from senile dementia(F=2.47, P<.05), and smoking habit(F=6.17, P<.001). 5. The relationship between the degree of burden and that of depression reads r=0.43, which is statistically positive correlation in the high significant level. Upon analyzing the entire summation, most care-giver for elderly patients suffering from senile dementia lack time in caring for themselves. They also experience chronic fatigue and mental discomfort caused by the isolation from society, curtailment of certain activities, a sense of responsibility of certain activities, a sense of responsibility for their patients, and limits of their endurance in taking care of their patients over time. In conclusion, this study emphasizes the necessity for the following propositions : 1. In order to measure the degree of burden that Korean care-giving families undergo, a new tool must be developed on the basis of Korean culture. 2. An educational program based on the demands that care-giving families undergo must e developed, and its clinical effect also has to be examined.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the Quality of Life among Family Caregivers of the Elderly with Dementia
Hwasoon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 500. CrossRef - Review of studies on spousal caregivers of frail spouses in South Korea
Youngsam Oh, Eunyoung Han
International Social Work.2019; 62(2): 529. CrossRef - The Burden of Aged Parents Caring for Adult Children with Disabilities
Min-Hyun Suk, Eunhye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 439. CrossRef - Comparison in Care Burden, Fatigue, and Life Contentment of Caregivers by Gender Relationship with Demented Elders
Young Whee Lee, In Sook Cho, Hwa Soon Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(3): 196. CrossRef - Family Caregiver Burden by Relationship to Care Recipient with Dementia in Korea
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Hyojeong Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2008; 29(4): 267. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Burden of Family Caregivers of Community-Dwelling Ambulatory Elders with Dementia in Korea
Young Mi Lim, Gwi-Ryung Son, Jun-Ah Song, Elizabeth Beattie
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2008; 22(4): 226. CrossRef - A thematic analysis of Korean family caregivers' experiences in making the decision to place a family member with dementia in a long‐term care facility
Myonghwa Park, Howard Karl Butcher, Meridean L. Maas
Research in Nursing & Health.2004; 27(5): 345. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the Quality of Life among Family Caregivers of the Elderly with Dementia
- 757 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The Effect of Dance Therapy on Physical and Psychological Characteristics in The Elderly
- Young Ran Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):429-444. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.429
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to explore the effects of a dance therapy on physical and psychological characteristics in the elderly. The design of this study was a non-equivalent pre-post test experiment. The subjects consisted of elderly persons living in a facility located in Suweon and Bucheon. Fifty eight subjects, aged between 65 and 93 years who had normal cognition, sensory function, balance, and resting blood pressure. They underwent tests of balance, flexibility, muscle strength, depression, and anxiety as baseline data before dance therapy, and at 6 th week and at the end of the 12nd week after following dance therapy. Twenty seven elderly persons were assigned to the experimental group and participated with the dance therapy between April and July, 1998. The dance therapy was developed by the author with the help of a dance therapist and a physiatrist. This therapy was based on the Marian Chace's dance therapy and Korean traditional dance with music. The dance therapy was developed by the author with the help of a dance therapist and a physiatrist. This therapy was based on the Marian Chace's dance therapy and Korean traditional dance with music. The dance therapy consists of 50 minutes session, 3 times a week for 12 weeks. One session was consisted of warming-up, expression, catharsis, sharing, and closing stage. The intensity of the dance therapy was at the 40% of age-adjusted maximum heart rates. Data were analyzed with mean, standard deviation, Chi-square test, unpaired t-test, repeated measures ANOVA, and Bonferroni multiple regression using SAS program. 1. The results related to the physical characteristics were as follows : 1) The balance (standing on one leg, walking on the balancing bar), flexibility and muscle strength (knee extensor, knee flexor, ankle plantarflexor and dorsiflexor) of the experimental subjects significantly increased over time more than that of the control subjects. 2) The experimental group had significantly higher score for balance, flexibility, muscle strength of knee extensor, and knee flexor than the control group at the 12nd week after dance therapy. 3) The experimental group had significantly higher score for muscle strength of ankle dorsiflexor and plantarflexor than the control group at the 6th week and the 12nd week after dance therapy. 2. The results related to psychological characteristics were as follows : 1) Scores of Geriatric Depression Scale, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, and Zung's Self-rating Anxiety Scale of the experimental group were significantly decreased over time more than that of the control group. 2) The experimental group had significantly lower score for depression than the control group at the 12nd week after dance therapy. 3) The experimental group had significantly lower score for anxiety than the control group at eh 6th week and the 12nd week after dance therapy. The findings showed that the dance therapy could be effective in improving the balances, flexibility, and muscle strength of lower limb, and effective in decreasing the depression and anxiety of the elderly. Additional merits of the dance therapy would be inexpensiveness, easy accessibility, and increasing interpersonal relationship. It can be suggested that the dance therapy is effective in the health promotion of the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
Young Rye Park, Yang Gyeong Yoo
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(1): 71. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
- 571 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of Exercise Therapy on Joint Mobility, Daily Activity, pain and Depression in patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hyun Ja Lim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):328-335. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.328
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to investigate the effects of exercise therapy on joint mobility, daily activity, pain and depression of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. 25 persons with the experimental group and 25 persons with the control group were conveniently sampled among out-patients diagnosed with ankylosing spondylitis at the rheumatism center of H University Medical Center. The control patients were matched to the experimental group and they were selected considering sex and age. The exercise therapy was developed by the author with the assistance of exercise specialists. The program includes muscle relaxation, flexibility, muscle strengths, breathing strengths and straight posture exercises. The 20-minute exercise therapy was carried out to the experimental group once a day for eight weeks from October, 1997 to February, 1998. Before and after the experiments, joint mobility, daily activity, pain and depression were measured respectively. Data were analyzed by x2-test, t-test, paired t-test and unpaired t-test. The results were as follows : Joint mobility(cervical flexion, extension, shoulder flexion, abduction, hip abduction, knee flexion and fingertip to floor distance) and daily activity in the experimental group after the exercise were significantly increased than that in the control group. The pain and depression score in the experimental group after the exercise were significantly decreased than that in the control group. These findings may indicate that the exercise therapy is effective in increasing the joint mobility and daily activity, and also effective in decreasing pain and depression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Accordingly, the exercise therapy can be adopted as an effective nursing intervention for ankylosing spondylitis.
- 459 View
- 0 Download

- A Study of the Relationship Among Health Promoting Behaviors, Climacteric Symptoms and Depression of Middle-Aged Women
- Eun Kwang Yoo, Myoung Hee Kim, Tae Kyung Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):225-237. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.225
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to analyze the relationship among the health promoting behaviors, self-reported climacteric symptoms and depression on a cross-sectional survey design. The subjects were 108 middle-aged women who were non-hystrectomized and ranged in age from 40 to 60. They were selected in Seoul and Kyoung-ki province, Korea. Data were collected from Oct. 25 to Nov. 10, 1997 by a structured questionnaire. The instrument used for this study was the revised Health Promotion Lifestyle Profile(HPLP) developed by Walker, Sechrist and Pender, revised Climacteric Symptoms Scale developed by Chi, Sung Ai, and the Beck's Depression Inventory(BID). The data were analyzed by the SPSS/PC+ program using t-test, ANOVA and Scheffe test as a post hoc and Pearson Correlation Coefficient. The results of the study were as follows ; 1. The mean score of health promoting behaviors was low(2.42+/-0.35). There were statistically significant difference in the score of health promoting behaviors according to the educational background, family income, marital satisfaction, and whether or not taking a restorative food(t=-2.07, F=2.60~7.57, p<0.05). 2. The mean score of self-reported climacteric symptoms was 1.69 ; 99% of middle-aged women had symptoms. There were statistically significant difference in the score of middle-aged women's self-reported climacteric symptoms according to the age, number of children, educational background, occupation, family income, marital satisfaction, whether or not receiving hormone replacement therapy(HRT) or consultation experience with a professional, and perceived health status(t=-2.04~3.69, F=2.87~11.63, p<0.05). 3. The mean score of depression was 10.84. There were statistically significant differences in the score of the depression according to the age, number of children, educational background, occupation, marital satisfaction, whether or not receiving menopausal treatment of consultation by a professional, and perceived health status(t=-2.25~3.00, F=3.50~9.24, p<0.05). 4. Women's degree of health promoting behaviors was a negative correlation with the degree of climacteric symptoms(r=-0.19, p=0.03) and the degree of depression(r=-0.23, p=0.01). The degree of climacteric symptoms was a positive correlation with the degree of depression(r=0.64, p=0.01). In conclusion, health promoting behavior should be considered when developing nursing strategies for middle-aged women, especially when dealing with climacteric symptoms and depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the Relationship between Depression on Menopausal Symptoms and Personality Trails
Niloufar Ahmadi, Mouloud Agajani Delavar, Sepideh Mashayekh-Amiri, Sedighe Esmaeilzadeh
Community Health Equity Research & Policy.2023; 43(2): 125. CrossRef - Mediating effect of a health-promoting lifestyle in the relationship between menopausal symptoms, resilience, and depression in middle-aged women
Sungwon Park
Health Care for Women International.2020; 41(9): 967. CrossRef - The Relationships between Body Mass Index, Nutrition Knowledge and the Health Promotion Behavior of Nursing Students
Su Ol Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2016; 18(2): 87. CrossRef - The Effect of 12 - Week Forest Walking on Functional Fitness, Self - Efficacy, and Stress in the Middle - Aged Women
Jonghwan Choi, 이재순, 연평식, 김현주, Changseob Shin
The Journal of Korean institute of Forest Recreation.2016; 20(3): 27. CrossRef - A Study on Heart Rate Variability (HRV) of Women with Atrophic Vaginitis
Min-Young Kim, Eun-Sil Yoo, Deok-Sang Hwang, Jin-Moo Lee, Jun-Bock Jang, Kyung-Sub Lee, Chang-Hoon Lee
The Journal of Oriental Obstetrics and Gynecology.2015; 28(3): 11. CrossRef - A Predictive Model of Health Promotion Behavior in Nursing Students
Jae-Woo Oh, Young-Sook Moon
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(10): 391. CrossRef - A study relationship between dental health perception and practice of college students
Kyeong-Hee Lee, Soo-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2013; 13(5): 845. CrossRef - The Mediating Effects of Self-efficacy on the relationship between Job-stress and Depression
Hye-Sook Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(10): 5069. CrossRef - Factors influencing health-promoting behaviors in Korean breast cancer survivors
Myungsun Yi, Jeongeun Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2013; 17(2): 138. CrossRef - Depression and Health Promoting Behavior Depending on the Climacteric Symptoms of Middle-aged Male Workers
Myoung Lyun Heo, Sook Bin Im
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2012; 21(3): 239. CrossRef - The effects of participation in a combined exercise program on the metabolic syndrome indices and physical fitness in the obese middle-aged women
Sung-Min Ban, Kyung-Jun Lee, Jeong-Ok Yang
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2012; 23(4): 703. CrossRef - A Predictive Model on Health Promotion Behavior in Women who Immigrate for Marriage
Namok Jeong, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 695. CrossRef - Relationships between menopausal symptoms, depression, and exercise in middle-aged women: A cross-sectional survey
Youngwhee Lee, Hwasoon Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2008; 45(12): 1816. CrossRef
- Exploring the Relationship between Depression on Menopausal Symptoms and Personality Trails
- 735 View
- 1 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Development of a Home-Based Multimedia Tutoring System for Postpartum Depression Management
- Jeung Iee Bai
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(1):9-20. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Postpartu depression is one of the most serious problems in maternal health because it affects not only the mother but also her family. Postpartum depression disturbs maternal-infant interaction and attachment. However, most postpartum depression patients ignore this problem and do not seek treatment. Thus this study in conducted to development of a Home-Based Multimedia Tutoring System for postpartum depression management. With this computerized system, mothers in the postpartum periods can check the level of postpartum depression using a personal computer. This system will go through each mother's data and screen those who have abnormal values. In addition this system includes intervention programs-education for nutrition, hygiene care, sleep, postpartum exercise, methods of relaxation, deep breathing, visualization, music therapy and family therapy-to relieve postpartum depression. Using this system, a mother who has a minor level of depression can manage it by herself. Computer language used in this study were html 3.2 OS used was Microsoftware Ni Server 4.0, the graphic tool was Adobe Photoshop 4.0, and the Webpage tool was Notepade. The results of this study are show at internet "URL : Http://203.241.225.42/". Finally, the author suggests that this system could be adequately applied to assessing postpartum depression and as a intervention strategy for mothers during the postpartum period. Further this study contributes to designing an appropriate postpartum depression prevention strategy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Music Therapy on Postpartum Blues and Maternal Attachment of Puerperal Women
Sun Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 60. CrossRef
- The Effects of Music Therapy on Postpartum Blues and Maternal Attachment of Puerperal Women
- 675 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of the Group Commuication Program on the Dysfunctional Communication, Self-Esteem and Depression : In the Group of Mothers with Children of Mental Disorder
- Gil Za Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):801-809. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.801
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was carried out the group communication program which I had composed of using the Satir's communication family theory and skills. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects on the dysfunctional communication self-esteem and depression, executed this program for the mothers group with caring the mental disorders, and then for the test of some hypotheses it was divided two groups ; the experimental group(n= 20) and control group(n=25). In the control group they were learned two session family education program in the psychiatric of Pusan National University Hospital and it the experimental group they had experienced during the 10 session by the group communication program. In the methods of the statistics on this data, it was to statistics x2-test for the comparison between the experimental group and control group with general characteristics. The effect of the Group Communication Program was analyse ANCOVA between pre-post test on the dysfunctional communication, self-esteem and depression in the control group and experimental group. The conclusions were derived from the results and test of hypothesis as followings : 1) The results were tested the differentiation between the experimental and control group, and the pre-post test in the experimental group with dysfunctional communication self-esteem and depression. Some hypothesis were tested and supported as following: It was supported that the level of dysfunctional communication of the experimental group would be lower than the control group(hypothesis 1). It was supported that the level of self-esteem of the experimental group would be lower than the control group(Hypothesis 2) It was supported that the level of depression of the experimental group would be lower than the control group(Hypothesis 3) 2) The relation of the dysfunctional communication with the self-esteem was presented negative correlation and with the depression was not correlation. The relation of the dysfunctional communication with the self-esteem was presented negative correlation. The relation of the sacrificuny pattern of dysfunctional communication with the self-esteem was presented negative correlation and with the depression positive correlation.
- 383 View
- 1 Download

- A Study on the Depression, Somatic Symptom, Activities of Daily Living for the Elderly Women in an Urban Area
- Kyung Rim Shin, Younhee Kang, Dukyoo Jung, Kyung Ae Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(7):1131-1138. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.7.1131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationships among depression, somatic symptoms, and activities of daily living of elderly women in urban areas. METHOD: After obtaining participant's consent forms, a one-time, face-to-face, and private interview was conducted with each participant from Sep, 2006 to Jan, 2007 by trained graduate-level students. The questionnaire consisted of K-GDS, PHQ-15, Barthel Index, and Instrumental Activity of Daily Living. The collected data was analyzed with the SPSS/PC 12.0 program, which was used for frequency, percentage, mean, standard deviation, Pearson correlation coefficients, and multiple regression. RESULTS: The major findings of this study were as follows 1) 34.1% of participants belonged to the depression group. 2) There were significant relationships between depression and monthly income, somatic symptoms, ADL, IADL, and number of chronic disease. 3) Significant factors influencing depression were somatic symptoms, ADL, and monthly income. CONCLUSION: The results of this study give useful information for designing interventions and program development for appropriate depression management and care for elderly women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Association between Internet Use and Depression Risk among Chinese Adults, Middle-Aged and Older, with Disabilities
Xiaodong Zhang, Anqi Li, Niuniu Cui, Bin Guo, Hafiz T. A. Khan, Lei Zhang
Systems.2023; 11(5): 264. CrossRef - Quality of Life and Its Factors in Korean Elderly With Mild Cognitive Impairment
Younhee Kang, Eliza Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2018; 27(7): 871. CrossRef - Depression Is a Mediator for the Relationship between Physical Symptom and Psychological Well-being in Obese People
Eun Kyoung Goh, Oh Yoen Kim, Hyo Jeong Jeon
Clinical Nutrition Research.2017; 6(2): 89. CrossRef - Depression and Cognitive Function of the Community-dwelling Elderly
Seong Ok Seo, Ae Young So
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - The Association between Family Support, Activities of Daily Living and Depression among Hospitalized Older Patients with Chronic Diseases
Jeong Yi Kim, So Yeon Ryu, Mi Ah Han, Seong Woo Choi
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2016; 41(1): 13. CrossRef - Prevalence of Depression and its Risk Factors among Aged at Social Service Centers in One Urban Community
Hye-Ryoung Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(2): 79. CrossRef - Symptoms, aging-stereotyped beliefs, and health-promoting behaviors of older women with and without osteoarthritis
Hyun-E Yeom
Geriatric Nursing.2013; 34(4): 307. CrossRef - Prevalence and Its Influencing Factors on Depression among Elderly Vulnerable People in Urban Community
Hye-Ryoung Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2013; 7(3): 275. CrossRef - Gender Difference in Influencing Factors on Health related Quality of Life among the Elderly in Community
Seung-Hee Lee
The Journal of Digital Policy and Management.2013; 11(12): 523. CrossRef - Computer and Internet Interventions for Loneliness and Depression in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis
Mona Choi, Saelom Kong, Dukyoo Jung
Healthcare Informatics Research.2012; 18(3): 191. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression Among Patients with Chronic Degenerative Arthritis after Total Knee Arthroplasty
Yeong-Ju Ju, Hee-Kyung Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(2): 161. CrossRef - Prediction of Depression among Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment Living in the Community
Kyung-Rim Shin, Youn-Hee Kang, Mi-Young Kim, Duk-Yoo Jung, Eliza Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(2): 171. CrossRef - Depression Health Literacy and Help-seeking Intention of the Aged Receiving Customized Home Visiting Health Care Services
Doo-Nam Oh, Ji Yun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(3): 276. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression of Elderly Women in a Metropolitan City
Seung-Ae Yang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(1): 158. CrossRef - The Effects of Health Behavior-related Characteristics, Self-esteem, Activities of Daily Living, and Family Support on Depression in the Community-dwelling Elderly
So Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 489. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression in Elderly People Living at Home
Myeong Ja Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 542. CrossRef - The Effects of Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain and Depression on Health-related Quality of Life by Gender in Community-dwelling Older Adults
Seung-Hee Lee, Soon-Ok Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 21. CrossRef - Depression Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults in Korea: A Prediction Model of Depression
Kyung-Rim Shin, Dukyoo Jung, Inho Jo, Younhee Kang
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2009; 23(1): 50. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Status of Korean-Chinese Elderly People Living in Yanbian, China
Chun Yu Li, Ogcheol Lee, Gi Soo Shin, Xian Wen Li
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 386. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Depression in the Relationship between Muscle Strength of Extremities and Falls among Community-Dwelling Elderly
Hyoung-Sook Park, Kyung-Yeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 730. CrossRef
- The Association between Internet Use and Depression Risk among Chinese Adults, Middle-Aged and Older, with Disabilities
- 920 View
- 2 Download
- 20 Crossref

- The Effects of a Cognitive Behavior Program on Cognition, Depression, and Activities of Daily Living in Elderly with Cognitive Impairment
- Su Kyong Chu, Jang Hak Yoo, Chung Yul Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(7):1049-1060. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.7.1049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was conducted to investigate the effects of a cognitive behavior program on cognition, depression, and activities of daily living in elderly with Cognitive Impairment. METHOD: The research design was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. There were 21 subjects in the experimental group and 19 in the control group among 40 senior residents in a Hall for the elderly in the city of S. The subjects scores ranged from 15 to 23 on the MMSE-K(Korean Version of Mini-Mental State Examination) over age 65. The length of time for data collection and intervention was from Jun 26 to September 1, 2006. The cognitive behavior program consisted of 'Facing problem behavior', 'Searching for a coping skill', and 'Training in the coping skill'. It was applied to the experimental group twice a week, fifty minutes per session for six weeks. RESULT: Cognition(t=-4.232, p< .001) and IADL(t=-2.939, p< .01) in the experimental group were significantly higher than those of the control group. Depression in the experimental group was significantly less than the control group(t=3.870, p< .01). However, ADL in the experimental group was not significantly higher than the control group. CONCLUSION: These findings confirmed that a cognitive behavior program contributed to improving cognition and IADL, and to reducing depression in the elderly with Cognitive Impairment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of walking exercise on cognitive and physical functions: meta-analysis of older adults
Mi Jin Lee, Hee Ju Ro, Jung Kee Choi, So Yeon Kim
Forest Science and Technology.2024; 20(2): 201. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of an AI Chatbot-Based Mobile Cognitive Screening and Customized Training Application for Preventing Dementia: Older Adults Living in Rural Areas of South Korea
Byung Hun Yun, Whani Kim, Hyun Jeong Ko, So Yoon Park, Jin Sung Kim, Geon Ha Kim, Bori Kim, Jee Hang Lee, Jin Woo Kim
Archives of Design Research.2024; 37(5): 77. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Community based Multifaceted Cognitive Training Program for the Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Yeonhee Park, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(2): 119. CrossRef - Effects of Silver-Care-Robot Program on Cognitive Function, Depression, and Activities of Daily Living for Institutionalized Elderly People
Jin-Hwan Oh, Yeo-Jin Yi, Chul-Jin Shin, Cheonshu Park, Sangseung Kang, Jaehong Kim, In-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(3): 388. CrossRef - The Effects of an Individual Cognitive Improvement Program on the Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairments
Inhyae Park, In-Hee Choi, Seo Young Kang, Younkyoung Kim, Chong Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of the Laughter Therapy Combined with Cognitive Reinforcement Program for the Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Eunjoo Ji, Oksoo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Effects of Art Therapy on Cognition, Depression, and Quality of Life in Elderly
Yeon Hee Choi, En Young Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(3): 323. CrossRef - The Effects of a Cognitive Enhancement Group Training Program for Community-dwelling Elders
Young Ran Han, Mi Sook Song, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 724. CrossRef - Cognitive Impairment, Behavioral Problems, and Mental Health in Institutionalized Korean Elders -An Eligibility Issue for Care Settings-
Hyun-Sil Kim, Young-Mi Jung, Hung-Sa Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 741. CrossRef - Depressive Symptoms and Related Risk Factors in Old and Oldest-old Elderly People with Arthritis
Ji-Yeon An, Young-Ran Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 72. CrossRef - Power Analysis in Experimental Designs with t test Analysis
Jeong-Hee Kang, Kyung-Sook Bang, Sung-Hee Ko
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2009; 15(1): 120. CrossRef
- Effects of walking exercise on cognitive and physical functions: meta-analysis of older adults
- 1,081 View
- 9 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The Effects of Hope Intervention on Hope and Depression of Cancer Patients Staying at Home
- A Mi Shin, Jeong Sook Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):994-1002. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.994
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was to identify the effects of hope intervention on hope and depression of cancer patients staying at home. METHODS: The study design was a randomized control group design. The subjects consisted of forty cancer patients randomly selected who were registered at S-Gu Public Health Center. Hope intervention, which was composed of hope assessment, hope objective setting, positive self identity formation, therapeutic relationships, spiritual & transcendental process improvement, positive environmental formation and hope evaluation, was provided from November 20, 2006 to January 26, 2007. RESULTS: The 1-1 hypothesis, "The experimental group which received hope intervention will have a higher score of hope than the control group", was supported(t=-3.253, p= .003). The 1-2 hypothesis, "The experimental group which received hope intervention will have a higher level of hope index than the control group", was supported (t=-4.001, p= .000). Therefore the 1st hypothesis, "The experimental group which received hope intervention will have a higher level of hope than the control group" was supported. The 2nd hypothesis, "The experimental group which received hope intervention will have a lower level of depression than the control group", was not supported (t=1.872, p= .070). CONCLUSION: Hope intervention is an effective nursing intervention to enhance hope for patient with cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Culturalizing theory and research on cognitive models of hope
Allan B. I. Bernardo, Sixtus Dane A. Ramos
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - EFFECT OF GROUP-BASED HOPE INTERVENTION ON DEPRESSION IN FEMALE INMATES
Mei Rianita Elfrida Sinaga, Megah Andriany, Artika Nurrahima
Belitung Nursing Journal.2020; 6(4): 116. CrossRef - Effects of a Group Coaching Program on Depression, Anxiety and Hope in Women with Breast Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
So Ryoung Seong, Moon-kyung Cho, Jeeyoon Kim, Yeo Ok Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(3): 188. CrossRef - Effects of Horticultural Therapy Program on State-Anxiety, Fatigue and Quality of Life among Women Cancer Survivors
Kyong Ok Oh, Moon Hee Gang, Kwon Sook Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(2): 125. CrossRef
- Culturalizing theory and research on cognitive models of hope
- 756 View
- 16 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Risk of Malnutrition, Depression, and the Perceived Health Status of Older Adults
- Yeon Hwan Park, Eunyoung E Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):941-948. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.941
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to investigate the risk of malnutrition and its relationship with depression and perceived health status. METHODS: A total number of 154 elderly over 60 years participated in the study through a community elderly center. The risk of malnutrition was measured by NSI (Nutritional Screening Initiative), depression by CES-D, and health status by a self-rated Likert scale. RESULTS: About one fourth (22.7%) of the subjects had a high risk, and 31.2% had a moderate risk of getting malnutrition. Regarding depression, 34.4% (53 elderly) of the subjects had a high risk. Overall health status had a mean of 3.46 within the range of 1 to 5. In relation to demographic factors, female elderly (chi-square=6.68, p= .04), aged younger than 75 years old (chi-square=8.60, p= .01), and having co-morbidity (F=9.81, p= .001) were significantly related to a high risk of malnutrition. Having a higher depression score, higher number of co-morbidity, and lower perceived health status were significantly related to a higher risk of becoming malnourished. CONCLUSION: The elderly's risk of getting malnutrition was significantly related to their depression and perceived health status. With these findings nursing interventions focusing on these factors should be developed in order to improve the elderly's multidimensional well-being.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The bidirectional association of malnutrition with depression and anxiety in patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence
Agnieszka Micek, Ewa Błaszczyk-Bębenek, Aneta Cebula, Justyna Godos, Kamil Konopka, Anna Wąż, Giuseppe Grosso
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of nutritional status using anthropometric index among older adult and elderly population in India
Junaid Khan, Aparajita Chattopadhyay, Subhojit Shaw
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The longitudinal reciprocal relationship between food insecurity and depressive symptoms among Korean elderly who live in poverty: application of auto-regressive cross-lagged model
Jayoung Cho
Asia Pacific Journal of Social Work and Development.2023; 33(2): 86. CrossRef - Comparison of Coronary Risk Factor and Nutrient Intake Status of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Normal Subjects : Data Obtained from the 2015-2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun Kyung Oh, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(2): 189. CrossRef - Physical Function Monitoring Systems for Community-Dwelling Elderly Living Alone: A Comprehensive Review
Sungbae Jo, Changho Song
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2022; 11(1): 49. CrossRef - Malnutrition and other risk factors of geriatric depression: a community-based comparative cross-sectional study in older adults in rural Bangladesh
Md. Ziaul Islam, Tasnim Rahman Disu, Sharmin Farjana, Mohammad Meshbahur Rahman
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Malnutrition and its determinants among older adults people in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Tadele Abate, Berhanu Mengistu, Asmamaw Atnafu, Terefe Derso
BMC Geriatrics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Food and nutrient intake status of Korean elderly by perceived anxiety and depressive condition: data from Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 ~ 2015
Da-Mee Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(1): 58. CrossRef - Malnutrition and its association with functional, cognitive and psychological status among Palestinian older adults in long-term care houses
Manal Badrasawi, Kamal Badrasawi, May Hamdan, Alma A. Irshaid
Educational Gerontology.2019; 45(12): 708. CrossRef - Nutritional Risk of the Elderly Receiving a Home-Delivered Meal Service Program and the Factors for Nutritional Risk
Na-Young Yi, Jung-Hwa Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 197. CrossRef - Depression and Cognitive Function of the Community-dwelling Elderly
Seong Ok Seo, Ae Young So
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Depression Symptom, Anthropometric Assessment, and Nutrient Intake of Elderly Females Who Eat Congregate Meals at Lunch in Rural Area
Sujung Lee, Hyunsuk Ryu, Kyunghee Song, Hongmie Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(4): 517. CrossRef - The Effects of Korean DASH Diet Education with Calcium/Vitamin D Supplements on Nutrient Intakes, Food Consumption, Bone Turnover Markers and Bone Mineral Density among Korean Elderly Women
Haeyoung Lee, Smi Choi-Kwon, Seung-Hye Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(1): 94. CrossRef - A study on dietary habits and food intakes in adults aged 50 or older according to depression status
Seungjae Lee, Yuri Kim, Sunhee Seo, Mi Sook Cho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(1): 67. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health-Promoting Behaviors in People Living with HIV
Young Mi Park, Gisoo Shin, Jiyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 234. CrossRef - The Effect of a Community-Based Nutrition Intervention Program on Dietary Behavior and Nutritional Status of Low-Income Elderly Women in Gwangju City
Bok Hee Kim, Ji-Suk Yang, Seung-Hee Kye, Yoonna Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(3): 495. CrossRef - Prevalence and Its Influencing Factors on Depression among Elderly Vulnerable People in Urban Community
Hye-Ryoung Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2013; 7(3): 275. CrossRef - Prevalence of Depression and its Risk Factors among Aged at Social Service Centers in One Urban Community
Hye-Ryoung Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(2): 79. CrossRef - Analysis of the Characteristics of the Older Adults with Depression Using Data Mining Decision Tree Analysis
Myonghwa Park, Sora Choi, A Mi Shin, Chul Hoi Koo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 1. CrossRef - Influence of Malnutrition and Social Network on Health-related Quality of Life in Elders
Hee Kyung Kim, Hae Kyung Chang, Mi-Ra Lee, Youn-Jung Son, Su Jeong Han, Nam Young Yang, Myoung-Ran Yoo, Seon Young Choi, Youn Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2013; 20(2): 98. CrossRef - Depression Health Literacy and Help-seeking Intention of the Aged Receiving Customized Home Visiting Health Care Services
Doo-Nam Oh, Ji Yun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(3): 276. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Exercise Compliance among Older Adults
Young-Ji Ko, Ju-Hee Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(2): 223. CrossRef - Nutritional Risk, Perceived Health Status, and Depression of the Young-Old and the Old-Old in Low-Income Elderly Women
Myung-Suk Lee
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2012; 37(1): 12. CrossRef - Characteristics of Eating Behavior in Elders with Dementia residing in Long-Term Care Facilities
Kyoung Min Lee, Jun-Ah Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(4): 466. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression and Quality of Life in Elderly Customized Home Visiting Health Services
Yunhee Kwon, Chungnam Kim, Oh-Gye Kwag
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(3): 262. CrossRef - The Effects of Foot Reflexology on Sleep, Depression and Skin Temperature of the Female Elderly at Home
Chung Soon Kim, Se Hwa Hong, Se Ryeong Kim, Yeo Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(4): 409. CrossRef - Impact of Body Mass Index and Perceived Health Status on Depression in Elderly Women Living Alone in the Community
Eun Kyeung Song, Youn-Jung Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(4): 376. CrossRef - The Effects of Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain and Depression on Health-related Quality of Life by Gender in Community-dwelling Older Adults
Seung-Hee Lee, Soon-Ok Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 21. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Hand Massage On Sleep, Depression and Quality of Life in the Institutionalized Elderly Women
Soon Yi Seo, So Young Chang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 372. CrossRef - The Relationship of Quality of Sleep, Depression, Late-Life Function and Disability (LLFDI) in Community-Dwelling Older Women with Urinary Incontinence
Kyung Rim Shin, Younhee Kang, Jiwon Oak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(4): 573. CrossRef
- The bidirectional association of malnutrition with depression and anxiety in patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence
- 946 View
- 5 Download
- 30 Crossref

- The Study on Predictors of Depression for Korean Female Adolescents
- Hyun Sook Park, Hyun Young Koo, Eun Hee Jang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):715-723. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.715
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were 1) to compare the contribution of demographic-behavioral variables and psychological variables in explaining the variance of depression, 2) identify the most important predictors of depression for Korean female adolescents.
Method The participants were 840 female adolescents. Data was collected through self-report questionnaires, which were constructed to include demographicbehavioral factors, self-esteem, hostility, hopelessness, and depression. Data was analyzed using the SPSS program.
Result Female adolescents' demographicbehavioral variables explained 17% of the variance in depression, and perceived physical health status, history of physical abuse, smoking, satisfaction of body weight, parental alcohol abuse, parental divorce, and history of suicidal attempt were the significant predictors of depression for female adolescents. Psychological variables explained 50% of the variance in depression, and self-esteem, hostility, and hopelessness were the significant predictors of depression for female adolescents. The significant predictors of depression among female adolescents' demographicbehavioral variables and psychological variables were self-esteem, hostility, hopelessness, perceived physical health status, parental alcohol problem, and history of physical abuse, explaining 52% of the variance in depression.
Conclusion In order to reduce depression in female adolescents, it is necessary to design an intervention program that emphasizes improving self-esteem while reducing hostility and hopelessness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validity and Reliability of the Sense of Coherence Scale among Korean Adolescents with Chronic Diseases
Sung-Hyun Lim, Won-Oak Oh, In Sun Yeom
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2021; 61: e22. CrossRef - Body Mass Index, Body Weight Perception, and Depressed Mood in Korean Adolescents
Yooli Lim, Bongseog Kim
Journal of the Korean Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.2017; 28(1): 31. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Suicidal Ideation in Girls' High School Students
Gab-Yeon Kim, Hee-Sook Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(3): 366. CrossRef - A Study on Perceived Entrapment, Anger and Depression in Adolescent Women
Suk-Hee Cheon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2008; 14(4): 239. CrossRef
- Validity and Reliability of the Sense of Coherence Scale among Korean Adolescents with Chronic Diseases
- 719 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Comparing the Effects of Drug Therapy, Physical Therapy, and Exercise on Pain, Disability, and Depression in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain
- Ja Kyung Ko
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):645-654. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.645
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This research was conducted to compare the effects of drug therapy, physical therapy, and exercise on pain, disability, and depression in patients with chronic low back pain.
Methods The research design of this study was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The subjects of this study were 28 patients for the drug therapy & physical therapy, 24 patients for the drug therapy & exercise, and 22 patients for the physical therapy & exercise. Data was collected by MVAS, Oswestry disability questionnaires, and questionnaires of depression. It was analyzed by paired t-test for effectiveness, ANOVA, and Scheffe for comparison of the effects of the 3 experimental treatments, using SPSS/WIN 12.0.
Results There were no effects of drug therapy & physical therapy on pain, disability, and depression. However, there were effects of drug therapy & exercise and the physical therapy & exercise on pain, disability, and depression. The effects of physical therapy & exercise on pain, disability, and depression were the greatest, but there was no statistically significant differences between the drug therapy & exercise and the physical therapy & exercise.
Conclusions Exercise is regarded as a more effective and easily accessible nursing intervention to apply alone than drug therapy or physical therapy simultaneously in reducing pain, disability and depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Stretching on Lumbar Muscle Flexibility, Isokinetic Parameters and Lower Extremity Function
Ye-Won Lee, Jun-Ho Yoo, Dong Yeop Lee, Jae Ho Yu, Jin Seop Kim, Seung Gil Kim, Yeon-Gyo Nam, Jihoen Hong
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(4): 145. CrossRef - Analysis of Recent Research Trends in Thread Embedding Acupuncture for Low Back Pain
Yae Gi Min, Hyang Gi Lim, Hyun Jong Lee, Jung Hee Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Yun Kyu Lee, Jae Soo Kim
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2024; 41(2): 96. CrossRef - Effects of Breathing Exercise of Pilates on Dysfunction and Lumbar Flexibility in Patients with Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain
Sooyong Lee, Yusik Choi
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2023; 12(3): 268. CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Stage-Matched Intervention for Elderly Women with Chronic Back Pain in the Contemplation and Preparation Stage
Hyun-Ju Oh, Soon-Rim Suh, Mihan Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(4): 414. CrossRef - The effect of abdominal drawing-in exercise and myofascial release on pain, flexibility, and balance of elderly females
Seong Hun Yu, Yong Hyeon Sim, Myung Hoon Kim, Ju Hee Bang, Kyung Hyun Son, Jae Woong Kim, Hyun Jin Kim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2016; 28(10): 2812. CrossRef - Effect of Spinal Stabilization Exercise and Manual Therapy on Visual Analogue Scale and Oswestry Disability Index in Acute or Subacute Patients with Low Back Pain
Eun-Young Park, Won-Ho Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(4): 1792. CrossRef - Effects of the Hand Acupressure and Lumbar Strengthening Exercise on Women with Lower Back Pain
Eun Young Jeon
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 63. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience to Work of Nurses with Low Back Pain
Jin-Hyang Yang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 597. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience to Work of Nurses with Low Back Pain
Jin Hyang Yang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 597. CrossRef - A Study of Pain, Depression, and Adjustment to Military Life of Soldiers with Low Back Pain
Ji-Hyun Lee, Jong-Im Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(2): 173. CrossRef - Effects of a Strengthening Program for Lower Back in Older Women with Chronic Low Back Pain
Hee-Kyoung Hyoung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 902. CrossRef
- The Effect of Stretching on Lumbar Muscle Flexibility, Isokinetic Parameters and Lower Extremity Function
- 961 View
- 9 Download
- 11 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


