Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development of a predictive model for exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months using machine learning : a secondary analysis of a cross-sectional survey
- Hyun Kyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):519-527. Published online October 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25086
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
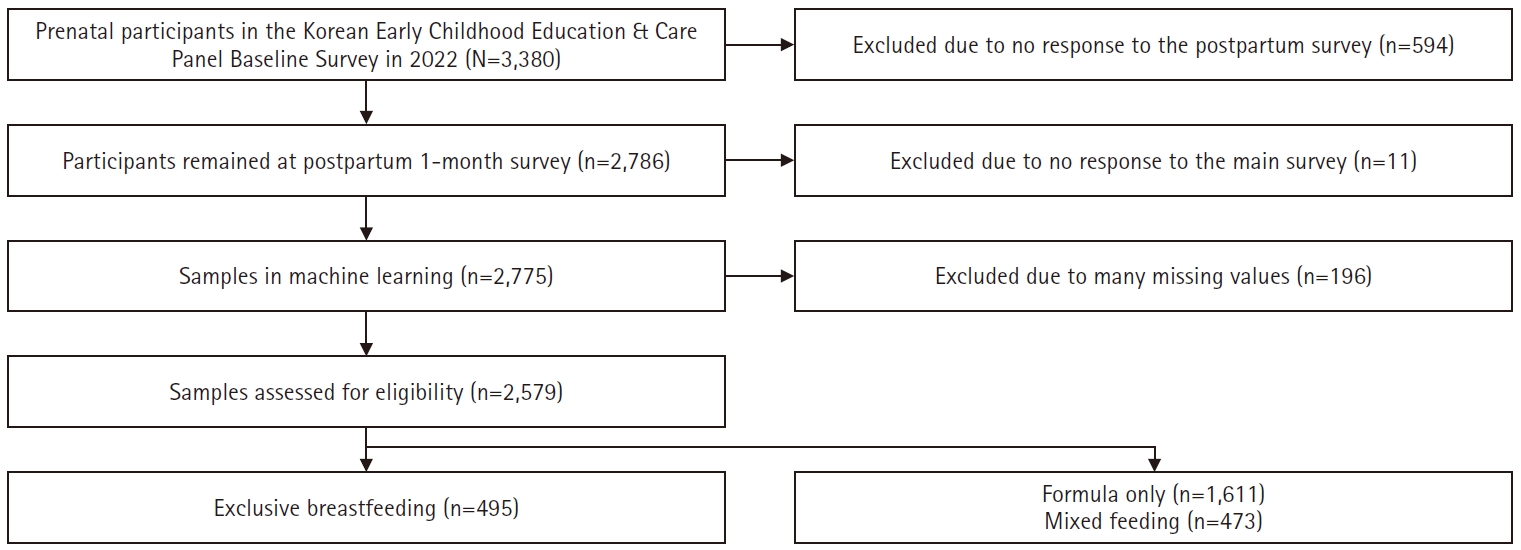
This study aimed to develop a machine learning model to predict exclusive breastfeeding during the first 3 months after birth and to explore factors affecting breastfeeding outcomes.
Methods
Data from 2,579 participants in the Korean Early Childhood Education & Care Panel between March 1 and June 3, 2025 were analyzed using Python version 3.12.8 and Colab. The dataset was split into training and testing sets at an 80:20 ratio, and five classifiers (random forest, logistic regression, decision tree, AdaBoost, and XGBoost) were trained and evaluated using multiple performance metrics and feature importance analysis.
Results
The confusion matrix of the random forest classifier model demonstrated strong performance, with a precision of 86.6%, accuracy of 84.8%, recall of 96.8%, F1-score of 91.9%, and an area under the curve of 86.0%. Twenty-one features were analyzed, from which feeding plan, breastfeeding at 1 month, marriage period, maternal prenatal weight, self-respect, alcohol consumption, grit, value placed on children, maternal age, and depression emerged as important predictors of exclusive breastfeeding in the first 3 months.
Discussion
A robust model was developed to predict exclusive breastfeeding that identified feeding planning and breastfeeding at 1 month as the most influential predictors. The model could be implemented in clinical and community settings to guide tailored breastfeeding support strategies, coupled with the integration of maternal self-respect, grit, and the value placed on children in counseling programs to promote exclusive breastfeeding.
- 1,517 View
- 137 Download

- The experiences of infertile women discontinuing in vitro fertilization treatment: a grounded theory approach
- Eunmi Park, Yeoungsuk Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):440-453. Published online August 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25048
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
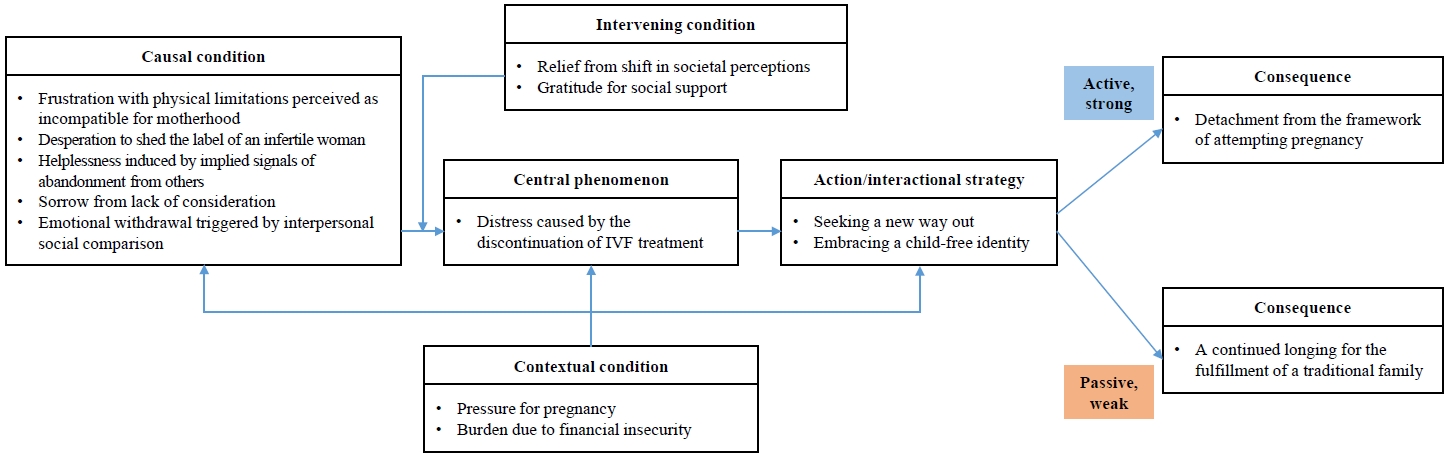
This study aimed to develop a situation-specific theory by gaining an in-depth understanding of the deterrent processes experienced by infertile women who have discontinued in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures, within the socio-cultural context of South Korea.
Methods
The participants were 16 infertile women who discontinued IVF procedures. Data were collected through individual in-depth interviews from February to December 2023. Theoretical sampling was conducted, and the transcribed interview contents were analyzed using Strauss and Corbin’s grounded theory method.
Results
In total, 37 concepts and 14 categories were extracted through the open coding process. The central phenomenon in axial coding was “Distress caused by the discontinuation of IVF treatment.” The core category was “A journey to break free from the identity of infertility toward self-determined womanhood.” The results were categorized into two types: “Detachment from the framework of attempting pregnancy” and “A continued longing for the fulfillment of a traditional family.” The situation-specific theory was the “Theory of reconstructing subjective identity through the acceptance of childfree life,” which illustrates how infertile women actively redefine their life trajectories after discontinuing IVF treatment.
Conclusion
This study highlights the importance of public perceptions about infertile women who discontinue IVF procedures, which are seen as the last resort of assisted reproductive technology, because positive perceptions assists women in living a self-governing life. It may be necessary to develop educational and promotional programs to change negative social perceptions and to establish a psycho-social support system for infertile women who have been deterred from IVF procedures.
- 1,243 View
- 95 Download

- The Effects of Stress Vulnerability and Parental Burnout on Mental Health in Women with Early School-Age Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Mediating Effect of Spirituality
- Mijung Yeom, Min Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):106-117. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the effects of stress vulnerability and parental burnout on the mental health of women with early schoolaged children, with a focus on the mediating role of spirituality.
Methods
A survey was conducted among 171 women with early schoolaged children in Gyeonggi Province, Gangwon Province, and Seoul. Data were collected from September to December 2022 using the Korean-Symptom Check List 95, the Parental Burnout Assessment, and the Spirituality Assessment Scale. The data were analyzed using structural equation modeling with SPSS/WIN 22.0 and AMOS 20.0.
Results
The study model demonstrated a good fit, explaining 40.5% of the variance in mental health through stress vulnerability, parental burnout, and spirituality. Spirituality had a significant direct impact on mental health. Additionally, participants’ spirituality directly influenced their mental health, while stress vulnerability and parental burnout indirectly affected their mental health and were mediated through spirituality.
Conclusion
Stress vulnerability and parental burnout are negatively associated with mental health, while spirituality partially mediates these effects. Implementing a program to promote spirituality is suggested to assist mothers in recognizing the value and meaning of parenting activities during nursing interventions for mental health.
- 2,139 View
- 65 Download

- Factors Influencing the Intention for Continual Fertility Treatments by the Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology Procedures: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Miok Kim, Minkyung Kim, Minkyung Ban
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):59-72. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This cross-sectional study aimed to identify factors influencing the intention for continual fertility treatments among women undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART).
Methods
A total of 197 women were recruited through convenience sample from fertility hospitals in Gyeonggi-do and Busan, South Korea. Data were collected using a self-report questionnaire incorporating measures of uncertainty; Depression Anxiety Stress Scales; Fatigue Severity Scale; Coping Scale for Infertility-Women; spousal support; treatment environment; and intention for continual fertility treatment. Descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, t-tests, and logistic regression analysis were conducted using IBM SPSS 26.0.
Results
As many as 70.6% of the participants expressed an intention for continual fertility treatments. Logistic regression analysis revealed that factors such as uncertainty (odds ratio [OR] = 0.44, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.20~0.95), active coping (OR = 4.04, 95% CI 1.11~14.71), treatment environment (OR = 2.77, 95% CI 1.26~6.07), and the duration of marriage (OR = 2.61, 95% CI 1.24~5.49) were significantly related with this intention.
Conclusion
These findings underscore the significance of uncertainty management, having proactive coping strategies, having supportive treatment environments, and considering the duration of marriage concerning women’s intention for continual fertility treatment in the context of ART. The implications of these results extend to the development of nursing intervention programs aimed at providing crucial support for women undergoing ART and seeking to continue their infertility treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and Safety of Korean Medicine in Treating Female Infertility: A Prospective Multicenter Observational Study
Hyo-Jeong Jung, Dong-Il Kim, Su-Ji Choi, Jang-Kyung Park, Jin-Moo Lee
International Journal of Women's Health.2025; Volume 17: 1771. CrossRef - The experiences of infertile women discontinuing in vitro fertilization treatment: a grounded theory approach
Eunmi Park, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 440. CrossRef - Psychiatric Considerations of Infertility
Yoon Jung Hwang, Junhee Lee, Jihyun Hwang, Hyeonhee Sim, Namwoo Kim, Tae-Suk Kim
Psychiatry Investigation.2024; 21(11): 1175. CrossRef
- Effectiveness and Safety of Korean Medicine in Treating Female Infertility: A Prospective Multicenter Observational Study
- 2,237 View
- 118 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- A Caring Program for Health Promotion among Women Who Have Experienced Trauma: A QuasiExperimental Pilot Study
- Goun Kim, Heejung Kim, Jeongok Park, Hee Sun Kang, Soojin Kim, Sunah Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(5):500-513. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Women are more vulnerable to post-traumatic stress (PTS) than men, causing several health problems. Nurses should understand and work with women who have experienced trauma and provide interventions to promote their physical, social, and mental health.
Methods
This quasi-experimental pilot study used a one-group pre-test/post-test design. Data were collected from 14 women recruited between December 2019 and May 2020 from a self-sufficiency support center in South Korea for sexually-exploited women who had experienced trauma. The program consisted of six one-on-one intervention sessions per week for six weeks. Each session averaged 60~120 minutes. Participants were assessed at pre-test, post-test, and one-month follow-up. Changes in outcome variables over time were analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank and Friedman tests.
Results
The caring program for health promotion was divided into six sessions: understanding the self, sharing traumatic events and negative emotions, reframing the meaning of traumatic events, identifying thoughts and physical and emotional responses, developing health promotion activities, and maintaining a positive attitude during the process of change. As a result of the caring program, PTS (F = 36.33, p < .001), depression (F = 24.45, p < .001), health-promoting behaviors (F = 7.06, p = .004), and self-esteem (F = 19.74, p < .001) among the participants differed significantly at pre-test, post-test, and follow-up.
Conclusion
This study provides foundational information for the implementation of a theory-driven program by nurses in clinical and community settings to provide comprehensive care for women who have experienced trauma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Effectiveness of an Interpersonal Relationship Improvement Program for Inpatients with Chronic Schizophrenia: Quasi-experimental/Non-randomised Evaluation
Jae-Eun Choi, Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(2): 188. CrossRef - Prediction and Feature Selection of Mastectomy-Related Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Using Machine Learning Among Breast Cancer Patients in Bangladesh
Syed Billal Hossain, Md. Mizanoor Rahman, Kapashia Binte Giash, Md. Hazrat Ali, Mst. Asma Akter, A.B.M. Alauddin Chowdhury
Cancer Informatics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Development and Effectiveness of an Interpersonal Relationship Improvement Program for Inpatients with Chronic Schizophrenia: Quasi-experimental/Non-randomised Evaluation
- 2,386 View
- 64 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The Experience of Gynecologic Cancer in Young Women: A Qualitative Study
- Sung-Jin Kim, Hyunjeong Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):115-128. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to understand the experiences of women under 40 years of age with gynecologic cancer.
Methods
Semi-structured individual in-depth interviews were conducted with 14 Korean female patients aged 21~39 years with gynecologic cancer. The data were analyzed using Corbin and Strauss' grounded theory approach, including open coding, context analysis, and integrating categories.
Results
Grounded theory analysis revealed nine categories and a core category of ‘the journey to find my life after losing the life as a typical woman.’ The categories that emerged as the conditions are ‘Unwelcomed guest, cancer,’ ‘Completely devastated life as an ordinary woman,’ ‘Uncertain future,’ ‘Losing my physical characteristics as a woman,’ and ‘Life tied with treatments.’ The actions/interactions were ‘Decrease of interpersonal relationships,’ ‘A lonely battle to overcome alone,’ and ‘The power to overcome hardships.’ The consequence was ‘Live my own life.’ Conclusion: This study contributes to the development of a substantive theory of the experience of gynecologic cancer in young women, which has been on the rise in recent years. The study’s results are expected to be used as a basis for providing nursing care to help young women with gynecologic cancer adapt to their disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mediating Effects of Negative Affect and Cancer Coping in the Relationship between Perceived Stress and Health-Related Quality of Life among Gynecological Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Yeon-woo Kim, Sunki Kim, Hye-Ja Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(3): 266. CrossRef - Exploring the Disease Experience in Women with PCOS: A Qualitative Content Analysis
Miok Kim, Su Jeong Yi
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3243. CrossRef - ORGAN LOSS AS A TRIGGER OF IDENTITY CRISIS IN WOMEN WITH MALIGNANT TUMORS OF THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (literature review)
Valentyn BELYAK, Rostyslav BILOBRYVKA
Ukrains kyi Visnyk Psykhonevrolohii.2025; : 123. CrossRef - Illness Experiences of Young Adult Thyroid Cancer Patients Receiving Radioactive Iodine Treatment
Hyeon Ae Lee, Sue Kyung Sohn
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(4): 195. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 418. CrossRef
- The Mediating Effects of Negative Affect and Cancer Coping in the Relationship between Perceived Stress and Health-Related Quality of Life among Gynecological Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,584 View
- 77 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Healthcare Considerations for Special Populations during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review
- Jeung-Im Kim, YeoJin Im, Ju-Eun Song, Sun Joo Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):511-524. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as a threat to human health and public safety. People of all ages are susceptible to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. However, the clinical manifestations of this infection differ by age. This study purposes to describe healthcare considerations for special populations, such as children, pregnant and lactating women, and older adults, who may have unique healthcare needs, in the pandemic situation. To realize the research purpose, we conducted a review of the practice guidelines of public documents and qualified studies that were published online/offline during a specific period. The review identified current knowledge on care for newborns, children in schools, pregnant women (from antenatal to postpartum care), and older adults suffering from high-risk conditions. Subsequently, we summarize vaccination guidance for special populations and, finally, discuss the issues currently affecting special populations. Therefore, this current knowledge on care for special populations helps nurses to provide accurate information on vaccinations aimed at preventing COVID-19 and protecting the masses from infection. Currently, the scarcity of information on COVID-19 variants necessitates further research on measures to reduce pandemic spread.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global and Regional Burden of Vaccine‐Associated Transverse Myelitis and Potentially Associated With Vaccines From 1967 to 2023: An Analysis of the International Pharmacovigilance Data
Jae E. Lee, Hyesu Jo, Hanseul Cho, Jiyeon Oh, Yi Deun Jeong, Sooji Lee, Jaeyu Park, Hyeon Jin Kim, Yejun Son, Soeun Kim, Hayeon Lee, Louis Jacob, Damiano Pizzol, Ho Geol Woo, Jiyoung Hwang, Dong Keon Yon
Journal of Medical Virology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Preliminary Exploratory Bibliometric Study on COVID-19 and Pregnancy
Fatima Aguirre-Vegas, Jakeline Ramos-Aliaga, Maria E Guerrero, Juan Alvitez, Abigail Temoche, Frank Mayta-Tovalino
Journal of South Asian Federation of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2025; 17(5): 618. CrossRef - The Use of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in the Treatment of a Pregnant Woman with COVID-19 Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Sy Duong-Quy, Duc Huynh-Truong-Anh, Thanh Nguyen-Thi-Kim, Tien Nguyen-Quang, Thanh Nguyen-Chi, Nhi Nguyen-Thi-Y, Van Duong-Thi-Thanh, Carine Ngo, Timothy Craig
Pulmonary Therapy.2022; 8(2): 233. CrossRef
- Global and Regional Burden of Vaccine‐Associated Transverse Myelitis and Potentially Associated With Vaccines From 1967 to 2023: An Analysis of the International Pharmacovigilance Data
- 2,131 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The Lived Experience of Body Alteration and Body Image with Regard to Immediate Breast Reconstruction among Women with Breast Cancer
- Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):245-259. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21028
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to explore the lived experience of body alteration and body image with regard to immediate breast reconstruction among women with breast cancer.
Methods
Data were collected from July to December 2020 through individual in-depth interviews with 15 women who had undergone immediate breast reconstruction due to breast cancer. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis.
Results
The following four theme clusters emerged. First, “revalued meaning of breasts due to cancer” illustrated the fact that cancer removal surgery brought the participants to reconsider the meaning of their breasts. Second, “had no choice but breast reconstruction” demonstrated the participants’ decision-making process of not wanting to lose breasts. Third, “unsatisfied breasts despite reconstruction” portrayed the distress due to the unexpected surgical outcomes. Finally, “restarted everyday routines with the altered body” described the healing process of the participants by accepting their changed body.
Conclusion
In Korea, where family-centeredness and fidelity are highly valued, women perceived their breasts not only as a symbol of femininity but as the mediator connecting the self to family. Despite the distress related to imperfect breasts, the participants were thankful for their reconstructed breasts. Breast reconstruction helped them return to daily life as the psychological trauma of breast cancer was healed. The participants rebuilt their body image by accepting their scarred new body. This may allow health professionals to provide constructive and culturally appropriate counseling in advance by providing insight into women’s perception of their body image with regard to breast reconstruction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
Hyeng Sook Yoon, Eunjung Ryu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100820. CrossRef - Categorising Subjective Perceptions of Middle-Aged Breast Cancer Patients Using Q Methodology
Min-Jeung Shim, Song-Yi Lee, Oh-Sun Ha
Healthcare.2024; 12(18): 1873. CrossRef - Body Acceptance Scale for Women with Breast Cancer: Development and Validation of a Measurement
Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2023; 39(5): 151486. CrossRef - Influence of body image on quality of life in breast cancer patients undergoing breast reconstruction: Mediating of self‐esteem
Yunhee Jang, Mihyeon Seong, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(17-18): 6366. CrossRef - Body acceptance in women with breast cancer: A concept analysis using a hybrid model
Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 62: 102269. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis on the prepectoral single-stage breast reconstruction
Jiameng Liu, Xiaobin Zheng, Shunguo Lin, Hui Han, Chunsen Xu
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(7): 5659. CrossRef
- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
- 2,368 View
- 82 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- A Structural Equation Model of Health-Related Quality of Life among Older Women Following Bilateral Total Knee Replacement
- Hyun Ok Lee, Jae Soon Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):554-570. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19216
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and test a structural equation model of health-related quality of life among older women following bilateral total knee replacement based on a literature review and Wilson and Cleary’s model of health-related quality of life.
Methods
One hundred ninety three women who were diagnosed with osteoarthritis, were older than 65 years, and were between 13 weeks and 12 months of having a bilateral total knee replacement were recruited from an outpatient clinic. Data were collected from July 2017 to April 2018 using a structured questionnaire and medical records. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 22.0, AMOS 22.0, and Smart PLS 3.2.4.
Results
The fitness of the hypothetical model was good, with coefficients of determination (R2 ) ranging between .28 and .75 and predictive relevance (Q2 ) between .26 and .73. The standardized root mean square residual of the model fit indices for the hypothetical model was .04; which explained 64.2% of physical and 62.5% of mental health-related quality of life. Self-efficacy, symptom status, functional status, and general health perceptions had a significant direct effect on physical health-related quality of life, while social support, symptom status, and general health perceptions had a significant direct effect on participants’ mental-health-related quality of life.
Conclusion
To improve the physical and mental quality of life of older women who receive bilateral knee replacement, nursing-based intervention strategies that reduce symptoms, improve functional status, and increase health perceptions, self-efficacy, and social support are needed. The most important factor is the symptom status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life for Community-Dwelling Vulnerable Older Adults with Chronic Diseases in Korea
Hyun-Ju Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 315. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life for older patients with chronic low back pain: A structural equation modeling study
Suin Lee, Eun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(3): 248. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life in female patients with reumatoid arthritis: a structural equation model
Bukyung Kim, Mi-Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 91. CrossRef - Effect of Oral Tranexamic Acid on the Blood Transfusion Rate and the Incidence of Deep Vein Thromboembolism in Patients after TKA
Bingqian Chen, Xiaohong Qu, Xiaowen Fang, Xuesong Wang, Guoxiu Ke, Xiaonan Xi
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Relationship between Uncertainty and Health-related Quality of Life in Elderly Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: The Mediating Effects of Sense of Coherence and Social Support
Min-Yi Song, Min-Jeong Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(3): 284. CrossRef - The Effect of Focusing Manner on Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Pain: The Sequential Mediating Effects of Social Support and Self-efficacy
Song Hee Yoon, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(2): 248. CrossRef
- Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life for Community-Dwelling Vulnerable Older Adults with Chronic Diseases in Korea
- 2,093 View
- 55 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Prevalence of Menstrual Disorders according to Body Mass Index and Lifestyle Factors: The National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort in Korea, 2009~2016
- SoMi Park, Tae Woong Yoon, Dae Ryong Kang, ChaeWeon Chung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):401-410. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was performed to identify the prevalence of menstrual disorders in Korean women based on body mass index (BMI)and lifestyle factors, by utilizing the Korean National Health Insurance Database.
Methods
A retrospective observational study designwas used for the secondary data analysis. Data of women aged 15 to 49 years who were diagnosed with menstrual disorders were extractedfrom The National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort in Korea from 2009 to 2016. The age-standardizedprevalence rate of menstrual disorders was calculated using SAS version 9.4, and a Chi-square test and Cochran-Armitage test were performed.
Results
In total, 2,219,445 cases were extracted from the database. The prevalence of menstrual disorders significantly increasedfrom 8.6% to 11.6% (Z=135.16, p for trend <.001) over the past eight years. In particular, it was higher in underweight womenthan in women with normal weight across all years (Z=-4.18~-14.72, p <.001). Moreover, statistically significant differences in the prevalenceof menstrual disorders were found to be associated with drinking and smoking in all years and with physical activity levels in part(p <.05~.001).
Conclusion
These findings present compelling evidence on the prevalence of menstrual disorders based on a national database.Since the prevalence of menstrual disorders has steadily increased and differs based on BMI and lifestyle factors, educational andclinical interventions are necessary to promote risk awareness and appropriate behavioral changes among Korean women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Menstrual Disorders in Korean Women
Ye-Lin Kim, Jun Young Chang, Suejin Kim, Mira Yoon, Jae-Na Ha, Kang Hyun Um, Boeun Lee, Kyoung Sook Jeong
Healthcare.2025; 13(6): 606. CrossRef - Menstrual Disorders Are Associated With Depressive Symptoms Among Women of Reproductive Age: Findings From the Korean Women’s Health Survey for Sexual and Reproductive Health
Kyunghee Han, Sihan Song, Bo Mi Song, Eunja Park, Joong-Yeon Lim, Hyun-Young Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Disease Experience in Women with PCOS: A Qualitative Content Analysis
Miok Kim, Su Jeong Yi
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3243. CrossRef - Factors associated with regularity and length of menstrual cycle: Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Sihan Song, Hansol Choi, Yanghee Pang, Oksoo Kim, Hyun-Young Park
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Body mass index, menstruation, acne, and hirsutism of polycystic ovary syndrome in women: A cross-sectional study
Jung-Hee Kim, Oksoo Kim, Heeja Jung, Yanghee Pang, Hyunju Dan
Health Care for Women International.2022; 43(1-3): 85. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Menstrual Disorders in Korean Women
- 2,110 View
- 59 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on the Experiences of Employment of Married North Korean Women Defectors Rearing Children
- Hyun Mee Cho, Eun Joung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):39-51. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: This study aimed to understand the experiences of married North Korean women’s child-rearing, working lives, and their home and work environment in depth.
Methods: This study adopted van Manen’s hermeneutic phenomenological method to qualitatively analyze data. The participants were 8 married North Korean women defectors. Data were collected through in-depth interviews and observations from July 4 to August 20, 2018.
Results: Nine essential themes emerged: more personal challenges after overcoming a life-threatening crisis; hopes of firmly settling in this land; the wound from the north, which chased them here; a body that becomes stronger through hardship; being stuck in a past full of anxiety and pain; the present is full of hope; hope for the future; sense of alienation from coworkers that cannot be overcome; and sense of power to endure an exhausting work life.
Conclusion This study provided a broader understanding of the life and experiences of married women from North Korea. It highlights the need for nurses to recognize their importance in nursing care. The study also suggests that academic and practical approaches for nursing, and basic data for a nursing intervention for married women from North Korea be provided. The study findings can be used as a basis for preparing a national policy that will help North Korean defectors to find employment and gain stability.
- 825 View
- 13 Download

- Menstrual Cycle Characteristics and Premenstrual Syndrome Prevalence Based on the Daily Record of Severity of Problems in Korean Young Adult Women
- Yae-Ji Kim, Young-Joo Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):147-157. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: This descriptive study aimed to identify the menstrual cycle characteristics and premenstrual syndrome (PMS) prevalence in Korean young adult women using the retrospective and prospective Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP).
Methods: In the first stage, participants included 151 nursing students studying in a university located in Seoul. Data were collected from April 20 to June 2, 2017, using the questionnaire on menstrual characteristics, pictorial blood assessment chart, and retrospective DRSP. In the second stage, participants included 17 students with PMS, based on the screening conducted in the first stage. Data were collected using the prospective DRSP from May 29 to 2 September 2, 2017.
Results: Of the study sample, 104 participants (68.9%) had regular periods. Those with regular periods had 11.97 periods annually with a menstrual cycle of 29.38 days and a period duration of 5.72 days. Fifty-five participants (37.4%) showed menorrhagia. Sixty-four participants (42.4%) were found to have PMS based on their retrospective DRSP. When the ratio of women (52.9%) with PMS shown in the prospective DRSP was used as a positive predictive value, the estimated PMS prevalence was 22.4%.
Conclusion This study provides clinically significant PMS prevalence among Korean young adult women, positive predictive value of the retrospective DRSP, and valid data to basically understand the menstrual cycle characteristics experienced by these women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Mandala Coloring on Premenstrual Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Experimental Study
Efsun Derin, Ayça Şolt Kirca
Holistic Nursing Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The correlation between personality traits, premenstrual syndrome, body perception and eating behaviours in university students: structural equation model
Merve Işık, Sultan Özkan Şat
Current Psychology.2024; 43(45): 34875. CrossRef - Effects of Yoga for Coping with Premenstrual Symptoms in Taiwan—A Cluster Randomized Study
Hsing-Chi Chang, Yi-Chuan Cheng, Chi-Hsuan Yang, Ya-Ling Tzeng, Chung-Hey Chen
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1193. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a school-based health education program to improve the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome in high school girls in Ilam
Samira Daneshvar, Fereshteh Ahmadi, Mohammad Mehdi Naghizadeh, Ashraf Direckvand-Moghadam, Fathollah Mohammadian, Mohsen Jalilian, Zeinab Ghazanfari
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Daily cortisol awakening response and menstrual symptoms in young females
Tuba Ozgocer, Cihat Ucar, Sedat Yildiz
Stress and Health.2022; 38(1): 57. CrossRef - Depressive symptoms and menstrual distress according to the menstrual phase in nurses: the Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Oksoo Kim, Sue Kim, Hae Ok Jeon, Ahrin Kim, Chiyoung Cha, Bohye Kim
Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics & Gynecology.2022; 43(4): 541. CrossRef - Menstrual Cycle Patterns and the Prevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Korean Young Adult Women
Young-Joo Park, Hyunjeong Shin, Songi Jeon, Inhae Cho, Yae-Ji Kim
Healthcare.2021; 9(1): 56. CrossRef - ÜNİVERSİTE ÖĞRENCİLERİNDE PREMENSTRUAL SENDROM PREVELANSI VE ETKİLEYEN FAKTÖRLER
Nazife Bakır, Nezihe Kızılkaya Beji
İnönü Üniversitesi Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi.2021; 9(1): 264. CrossRef - Are premenstrual syndrome and dysmenorrhea related to the personality structure of women? A descriptive relation‐seeker type study
Rabiye Erenoğlu, Şengül Yaman Sözbir
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2020; 56(4): 979. CrossRef
- The Effect of Mandala Coloring on Premenstrual Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Experimental Study
- 3,344 View
- 47 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Development of an Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle-Aged Women
- Haejin Lee, Mi-Ae You
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):14-25. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This was a methodological study that aimed to develop a measurement scale for aging anxiety among middle-aged women.
Methods In this study, construct factors were extracted, and a conceptual framework was established through an extensive literature review and in-depth interviews with middle-aged women. Under the conceptual framework, 44 preliminary items were constructed, and a preliminary scale of 25 items was completed after two rounds of expert validation and item review. For this study, data were collected from 201 women aged 40∼59 years, and the construct validity and reliability of the preliminary scale were verified.
Results To verify the construct validity, exploratory factor analysis was conducted. Four factors containing 19 items were extracted. Concurrent validity of the developed scale was verified with Pearson's correlation analysis. The final scale comprised 4 factors (“Social valueless”, “Physical weakness”, “Concern about changes in appearance”, and “Expectations of old age”) and 19 items. The Cronbach's α value was .91.
Conclusion The scale for measuring aging anxiety in middle-aged women developed in this study validly reflected the peculiarities of aging anxiety in middle-aged women, who experience many physical, emotional, and social changes. The scale can be said to reflect the cultural background, as it reflected real experiences gained through in-depth interviews with middle-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gerascophobia or Excessive Fear of Aging Scale (GEFAS): Development, validation, and exploration of psychometric properties of a brief instrument using classical testing theory and item response theory
Waqar Husain, Farrukh Ijaz, Muhammad Ahmad Husain, Ammar Achraf, Hasan M. Isa, Khaled Trabelsi, Seithikurippu R. Pandi-Perumal, Amir H. Pakpour, Haitham Jahrami
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2025; 128: 105599. CrossRef - Family support, social security, commercial insurance, and aging anxiety among Chinese residents: a study based on the 2021 CGSS data
He Gu, Qingli Tan, Yongxing Guo, Han He, Yu Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Determination of the association between aging anxiety and menopausal symptoms in middle-aged women
Seda Hazar, Gülçin Nacar, Furkan Doğan, Sermin Timur Taşhan
Menopause.2025; 32(6): 539. CrossRef - Effects of Physical Activity on Ageism and Aging Anxiety Among Chinese and Korean Adults Aged 55 to 64 Years
Jing Li, Seung-Yong Kim, Cho-Young Yook, Xiao-Long Chen, Woo-Jin An, Ju-Young Oh, Chae-Hee Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(11): 1218. CrossRef - Prevalence of depressive symptoms during the menopausal transition in Türkiye: impact of symptom severity, aging anxiety and health-related quality of life
Banu Aslan, Özgür Önal
Climacteric.2025; 28(5): 607. CrossRef - Orta Yaşlı Kadınlarda Yaşlanma Anksiyetesi, Cinsel Yaşam Kalitesi ve Öznel Mutluluk Arasındaki İlişkinin İncelenmesi Üzerine Kesitsel Bir Çalışma
Ejdane Coşkun, Burcu Çakı Döner
Turkish Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2025; 19(4): 323. CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure selection, optimization, compensation (SOC) strategy in late middle-aged women: a methodological study
Do-Young Lee, Gie Ok Noh
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 216. CrossRef - Association between Menopausal Women’s Quality of Life and Aging Anxiety: The Role of Life Satisfaction and Depression
Seunghee Lee, Mijung Jang, Dohhee Kim, KyooSang Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(8): 1189. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Laughter Therapy Program for Middle-aged Women Hospitalized in Psychiatric Wards
Do Young Lee, Ju Hyun Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(3): 273. CrossRef - Determination of aging anxiety in middle-aged women
Nese Kiskac, Mahruk Rashidi, Muharrem Kiskac
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Informal caregivers’ negative affect: The interplay of caregivers’ resilience, aging anxiety and burden
Yaira Hamama-Raz, Rachel Nissanholtz Gannot, Michal Michaelis, Yichayaou Beloosesky, Adaya Nissanholtz
Aging & Mental Health.2023; 27(7): 1300. CrossRef - Aging anxiety and beliefs about exercise in middle-aged women
Nedim TEKİN, Adeviye AYDIN
Turkish Journal of Kinesiology.2023; 9(3): 214. CrossRef - Experiences Pertaining to Successful Aging in Middle-Aged Women in South Korea
Do-young Lee, Hyun-ju Kim, A-young Jo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(19): 6882. CrossRef - Validity and reliability study of the Turkish version of the Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle‐Aged Women
Zeynep Daşıkan, Selin Paker, Ruken Yağız Altıntaş, Figen Kazankaya, Sümeyye Bakır
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(4): 2918. CrossRef - Turkish Adaptation of the Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle-Age Women: Validity and Reliability Study
Adeviye AYDIN, Esma KABASAKAL
Journal of Basic and Clinical Health Sciences.2022; 6(1): 173. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Life Satisfaction in Middle-Aged Women
Hee Kyung Kim, Hae Kyung Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(3): 326. CrossRef - The health status, aging anxiety, social networking, generativity, and happiness of late middle-aged adults
Hae Kyung Chang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 392. CrossRef - The Effects of Climacteric Symptom Cognition, Self-efficacy on Aging Anxiety in Middle-Aged Couples: Actor and Partner Interdependence Mediation Model
Yeon-Suk Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 247. CrossRef - Verification of the Mediating Effect of Social Support on Physical Activity and Aging Anxiety of Korean Pre-Older Adults
Ahra Oh, Jiyoun Kim, Eunsurk Yi, Jongseob Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 8069. CrossRef
- Gerascophobia or Excessive Fear of Aging Scale (GEFAS): Development, validation, and exploration of psychometric properties of a brief instrument using classical testing theory and item response theory
- 2,073 View
- 49 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

- Comparison of Effects of Oral Health Program and Walking Exercise Program on Health Outcomes for Pregnant Women
- Hae-jin Park, Haejung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):506-520. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.506
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To compare the effects of the Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior (IMCHB)-based oral health program (OHP) and walking exercise program (WEP) on oral health behaviors, periodontal disease, physical activity, and psychological indicators (depression, stress, and quality of life) in pregnant women.
Methods A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design was adopted to compare the effects of a 12-week OHP and WEP on pregnant women (n=65). Pregnant women were randomly assigned to the oral health group (OHG; n=23), walking exercise group (WEG; n=21), or control group (CG; n=21). Data were analyzed by the χ2-test, Fisher's exact test, Scheffe test, and repeated measures ANOVA, using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences for Windows (version 21.0).
Results The OHG and WEG showed significant improvements in oral health behaviors, periodontal disease, and psychological indicators as compared to the CG. The WEG showed significant improvement in physical activity as compared to the OHG and CG.
Conclusion These findings indicate that the IMCHB-based OHP and WEP were effective in improving periodontal disease, physical activity, and psychological indicators. However, further studies are needed to identify the positive effects of the OHP and WEP on birth outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physical Activity as a Mediatior in the Relationship Between Oral Health Status and Prevalence of Diabetes in Older Adults
Min-Jun Kim, Taewan Kim, Youngyun Jin, Donghyun Kim
Exercise Science.2025; 34(1): 35. CrossRef - Physical Activity as a Mediator in the Relationship Between Oral health status and Depression Prevalence in Older Adults
Min-Jun Kim, Taewan Kim, Yoonhwan Kim, Donghyun Kim
Exercise Science.2025; 34(2): 188. CrossRef - Twenty-first century knowledge mapping on oral diseases and physical activity/exercise, trends, gaps, and future perspectives: a bibliometric review
Thamires Campos Gomes, José Lucas Gomes Moura, Daiane Claydes Baia-da-Silva, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Patrícia de Almeida Rodrigues
Frontiers in Sports and Active Living.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Review of domestic and international intervention studies to improve oral health in pregnant women
Jun-Yeong Kwon, Hyoung-Joo Kim, Hanna Gu, Hee-Jung Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2024; 48(3): 155. CrossRef - Secondary prevention of coronary heart disease: The effect of a nursing intervention using Cox's interaction model of client health behaviour
Qianqian Shen, Pingping He, Min Wen, Juping Yu, Yeshi Chen, Junyi Li, Xinping Ouyang
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(10): 4104. CrossRef - Theoretical evaluation of Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior for health promotion in adult
women
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Gi Wook Ryu
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 120. CrossRef
- Physical Activity as a Mediatior in the Relationship Between Oral Health Status and Prevalence of Diabetes in Older Adults
- 1,345 View
- 27 Download
- 6 Crossref

- An Ethnography on the Healthy Life of the Aged Women Participating the Senior Centers
- Eunha Kim, Jinhyang Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):349-361. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.349
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This ethnography was performed to explore patterns and meanings of healthy life among aged women using senior centers.
Methods The informants were 21 individuals aged 65 years and older at 2 community-based senior centers. Data were collected from iterative fieldwork through in-depth interviews and participant observations and analyzed using text analysis and taxonomic methods developed by Spradley. Field notes were used with follow-up interviews and dialogue between authors to enhance interpretation.
Results Patterns of healthy life among aged women using senior centers were categorized by age groups within the context of the four cultural elements of taking care of the body, relationality, temporality, and spatiality: active and passive control, maintenance of interdependence and individuality, expansion and maintenance of the daily routine, unity of peer relations and sustenance of family relations, spending time productively and tediously, and complementary and alternative space of the family relations.
Conclusion The informants in this study demonstrated healthy life by maintaining and strengthening continuous relationships developed in the senior centers without being isolated from the family and society. Patterns of their healthy life differed across age groups within the socio-cultural context. Therefore, interventions should be tailored to address age groups and community needs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Qualitative Study on the Exercise Experiences and Health Perceptions of Older Women
Young Hye Jeong
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2025; 36(4): 645. CrossRef
- Qualitative Study on the Exercise Experiences and Health Perceptions of Older Women
- 1,197 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Life Experiences of Uninfected Women Living with HIV-Infected Husbands: A Phenomenological Study
- Myoung Hee Seo, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):781-793. Published online December 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.781
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to understand the meaning and essence of the life experiences of uninfected women living with HIV-infected husbands.
Methods This qualitative study adopted van Manen's hermeneutic phenomenological method. Study participants were 8 females whose husband had been diagnosed with HIV for longer than 6 months, who had known about their husband's infection for more than 6 months, who were in a legal or common-law marriage and were living with their husbands at the time of interview for this study, and whose HIV antibody test results were negative. Data were collected from in-depth individual interviews with the participants from May to August 2016, and from related idiomatic expressions, literature, artwork, and phenomenological references.
Results The following essential themes were identified regarding the life experiences of uninfected women living with HIV-infected husbands: ‘experiencing an abrupt change that came out of the blue and caused confusion’, ‘accepting one's fate and making desperate efforts to maintain one's family’, ‘dealing with a heavy burden alone’, ‘experiencing the harsh reality and fearful future’, and ‘finding consolation in the ordeal’.
Conclusion This study provided a holistic and in-depth understanding of the meaning and essence of the life experiences of uninfected women living with HIV-infected husbands. Thus, this study recognizes these unnoticed women as new nursing subjects. Further, the present findings can be used as important basic data for the development of nursing interventions and national policy guidelines for uninfected women living with HIV-infected husbands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Using decision tree analysis to understand the influence of social networks on disclosure of HIV infection status
Gwang Suk Kim, Mi-So Shim, Jeongmin Yi
AIDS Care.2022; 34(1): 118. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Initiation of Treatment after the Diagnosis of Korean Patients with HIV
Mi-So Shim, Gwang Suk Kim, Chang Gi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 279. CrossRef
- Using decision tree analysis to understand the influence of social networks on disclosure of HIV infection status
- 1,224 View
- 12 Download
- 2 Crossref

- An Ethnographic Research on the Phenomenon of Women's Utilization of the ZZimzilbang, A Type of Sauna in Korea
- Chung Ja Chun, Eun Kwang Yoo
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):961-974. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.961
-
 Abstract
Abstract
The ZZimzilbang is a room where many women eagerly go due to the special meaning women give to it related to their health. It is a different type of sauna room which maintains low degree of temperature, consisting of an Ondol room(Korean under-floor heating system, hypocaust) built with mineral stone radiating ultrared rays. Even though many women mention that they utilize if for health, there is no precise evidence of the effects of their health. This ethnographic study sought to define the phenomenon from the perspective of the women who experienced the ZZimzilbang. A convenience sample of 27 women was interviewed during a 15 month period from December 1995 to July 1997 in 12 ZZimzilbangs located in Seoul, Korea. The mean ages of the women 57.3 years ; seventeen women were housekeeper and only eight women had job ; twenty women were married and three women among them were widows. The main reasons women patronize the place are : for mitigation and healing of physical signs and symptoms ; composure ; safe lodging and boarding ; control of outward appearance ; control of health ; meeting and fellowship with friends ; and custom. The outcomes of the utilization of the place were : mitigation of physical signs and symptoms ; psychological tranquility ; cosmetic and diet ; good use of spare time ; and utilization of services provided there. Most women who visited ZZimzilbang for relief of physical signs and symptoms strongly mentioned a correlation to inadequate Sanhujori, the traditional postpartal and postabortal care for woman. Some of specific kinds of services provided in that place were alternative therapy such as acupuncture, negative cupping, finger-pressure, mugwort steam and various kinds of massage including massage of blood vessels that are influenced by Oriental medicine ; health education of breathing such as abdominal breathing or Danjeon ; selling of many things including health foods, drugs for osteoporosis, and eutrophics This study suggests that professional caregivers should further study this phenomenon for the development of adequate care of women with a resulting important in their quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Sanhujori and Menopausal Adaptation on Health-related QOL in Middle-aged Women
Moon-Jeong Kim, Kyung-Ja Kang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(1): 62. CrossRef
- Effects of Sanhujori and Menopausal Adaptation on Health-related QOL in Middle-aged Women
- 682 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Conceptual Model for Women's Health
- Kyung Hye Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):933-942. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.933
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF There has recently been an increased interest in women's health from, various disciplines, with different perspectives presented according to each profession's academic background. This has led to many instances of incorrectly defining, or misinterpretation, of the issues even among professionals. Nurse scholars as well as practitioners who work in women's health care need to have a clear conceptual understanding of women's health in order to build a body of knowledge, delineate curricular activities, and set directions for professional nursing interventions. In addition, a conceptual model that may be directly utilized in practice is needed to maintain and promote women's health issues. The purpose of this study was to apply a Hybrid model, analyzing conceptual definitions and discussions related to women's health gathered from review of the literature. Further to compare analyticals the concepts and properties observed from field work, so as to present a final definition of women's health and, build a conceptual framework for a united comprehensive perspective on the concept as well as on nursing practice. Data collection and analysis consisted of a theoretical stage, field work stage, and final analysis. a heterogeneous group of professionals and lay persons, 39 in all, participated in the field work. Study findings include several subconcepts under the concept of women's health : a women's whole life, holistic health, quality of life, awareness of being a woman, individual nursing, self care ability, reproductive health, and family health. Thus, a comprehensive definition was built, i. e., "Women's health care be defined as improvement in the quality of life of women through attainment of holistic health throughout the life span. With reproductive health at the core, the concept is directly related to family and national health, and includes taking care of one's own health based on awareness of being a woman and utilizing self care activities. Women's health care issues are unique and allow various responses, therefore women's health professionals need to apply individual approaches to reach solutions in attaining holistic health and improving quality of life." The constructual factors of women's health were found to be reproductive functions, diseases more common in woman, self actualization, mental health, women's health policies, sexuality, midlife changes, and marital relations, with each factor having more than three properties. Positive factors affecting women's health were found to be a normal childbearing process, a healthy lifestyle, active health management, health information, support and resources, and interpersonal relationships Negative factors were found to be overwhelming role stress, cultural oppression, gender inequality, distorted sexual identity, economic difficulties, misuse and/or abuse of substances, and stress. The model of women's health may be visualized as a balance scale set upon a woman's life, supporting 4 concentric circles. The innermost circle and second circle incorporate conceptual definitions of women's health, and the outer two circles represent the constructional factors and properties of women's health. Each circle has its own color that symbolizes the conceptual meaning. Positive and negative factors are represented as weights at either end of the scale, and are affected by nursing intervention, i. e., health and wellness increase when positive factors are stronger, whereas disease and illness increase when negative factors are stronger. This model is only a preliminary effort and requires much discussion and testing to be further developed. Continuous research is also required.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Participation in Health Check-ups with Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases
Bok Hyun Park, Byung-Kook Lee, Jaeouk Ahn, Nam-Soo Kim, Jungsun Park, Yangho Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of Participation in Health Check-ups with Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases
- 555 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development of Sexual Satisfaction Measurement Tool
- Sook Nam Kim, Soon Bok Chang, Hee Sun Kang
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):753-764. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.753
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to develop a sexual satisfaction tool for married women in Korea. The data was collected from July 19 to Aug 18, 1997 by means of questionnaires developed by researchers. The subject were 417 married women living in Seoul and Pusan. The process of this study was as follows : 1) The concept of sexual satisfaction was defined. 2) A conceptual framework was identified based on the extensive review of relevant literature and interviews with married women. 3) The preliminary question items containing the attributes and elements of the concept of sexual satisfaction were listed. 4) The preliminary items were revised after a pilot study. 5) The Index of Content Validity(CVI) was calculated from the content specialists' rating. 6) The reliability and validity of the sexual satisfaction measurement tool were tested. As a result of the item and factor analysis, 17 out of 30 items were found to be valid, consequently could be used to measure sexual satisfaction for married women. These final 17 items were divided into two factors. These factors were labeled as "situation factor"(10 items) and "response factor"(7 items) according to the attributes of the clustered items. The reliability of the final 17 items was .9118. Further research in needed to confirm the reliability and validity of the tool by applying it to a group of healthy married women and to a group of married women having health-related problem.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Sexual Function Improvement Program for Breast Cancer Survivors on Sexual Distress, Sexual Satisfaction and Marital Intimacy
Duck Hee Moon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(1): 30. CrossRef
- Effect of Sexual Function Improvement Program for Breast Cancer Survivors on Sexual Distress, Sexual Satisfaction and Marital Intimacy
- 575 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Incidence and Correlates of Urinary Incontinence in Women
- Hae Sang Yoon, You Za Ro
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):683-693. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.683
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary and inappropriate loss of urine to failure to emit normal responses as the bladder fills, or inability to reach the bathroom in sufficient time. This study was undertaken to estimate the incidence of urinary incontinence and to determine the correlates of urinary incontinence among women. Subjects of this survey consisted of 408 women, 26 to 83 years old in Incheon. The results of this study are follows. 1. Of the subjects 50.7% reported urine loss once or twice per year and 28.5% reported incontinence on a regular basis at least once per month. 2. 40.5% of women reported small volume accidents of only 1 to 2drops, 31.4% ; 1t-spoon, 16.9% ; 1T-spoon, while 10.1% of women couldn't estimate the volume of urine loss. 3. The volume of urine loss was great enough to require a change of garment(undergarments or outer garments) in 73%. But only 3.8% of those used some type of pads. 4. 56.5% of incontinent women didn't talk about their urinary incontinence with other persons because they felt that urinary incontinence was shameful(38.4%), was not a disease(31.6%), was incurable in spite of treatment(27.4%) and was fearful of being uncured(2.6%). 5. Only 15.5% of urinary incontinent women had sought treatment. 6. The incidence of urinary incontinence was significantly higher in women who had more pariety and uterine-ovarian disease, older age, worrying about where toilets were when they visited new places or voiding anxiety, nocturia and frequency, but was significantly lower in women who had coffee intake. The incidence of urinary incontinence was not related to smoking and enuresis. The results indicate that urinary incontinence is common among young and middle-aged women. That few seek treatment for urinary incontinence suggests a need for more information about women's attitudes toward urinary incontinence and more attention to this problem by health care providers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Product Analysis for the Development of Functionality Underwear for Seniors:Based on the Male Urinary Incontinence Brief on Sale in the United States
Mi-ran Koo
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2020; 31(3): 353. CrossRef - Prevalence of urinary incontinence in older Korean women
Aeyoung So, Jennie C De Gagné, Mary H Palmer
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2012; 6(2): 51. CrossRef
- Product Analysis for the Development of Functionality Underwear for Seniors:Based on the Male Urinary Incontinence Brief on Sale in the United States
- 636 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Study of Primiparous Womens' Breastfeeding Experience
- Shin Jeong Kim, Sook Ja Yang
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):477-488. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to understand the subjective breastfeeding experience of primiparous women to identify how breastfeeding was started and to explore the process of breastfeeding. The Grounded theory methodology was used. Data was collected from 6 primiparous women who had breastfeed their infants for at least over 8 weeks, recently breastfeeding or having breatfeed their infants within the last 6 months. With the permission of the subjects, the interviews were recorded and transcribed. The data were analysed in the framework of grounded theory method as mapped out by Strauss and Corbin(1990). 105 concepts and 21 subcategories were of data analysis. In the process of data analysis, "Identity as a mother" was found to be the core phenomenon. The 21 sub-categories were as follows : natural food, neighbour inducement, self purpose, good feeling, tenderness, breast pain, change of breast shape, physical discomfort, loss of physical energy, confirmation of adhesion, one body through coupling, tie, capacity, role performance, mental comfort, healthy mother, healthy infant, confidence of breast milk, feeling of satisfaction. The sub-categories were again grouped into 14 categories including infant nutritious food, formation of breastfeeding opportunity, feeling of satisfaction, injury of the breast, physical suffering, awareness of mothering, formation of maternal affection, connecting, coupling, acceptance, effort, emotional stability, mother and child health and feeling of achievement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Breastfeeding Success Experience of Primiparas
Sun Ok Lee, Sung Soon Na, Hee Sook Kim, Kyung Eui Bae, Mi Sun Youn, Eun Ju Oh
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(4): 254. CrossRef
- Breastfeeding Success Experience of Primiparas
- 608 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Study of Smoking Behavior in College Women: A Grounded Theory Approach
- Moon Sil Kim, Ae Kyoung Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):315-328. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.315
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to explore the process of smoking behavior of college women with a history of smoking. The subject were 48 female students selected by theoretical sampling from a women's university in Korea. The data were collected by in-depth interviews using audiotape recordings done over a period of seven months. The data were analyzed simultaneously by a constant comparative method in which new data were continuously coded in to categories and properties according to strauss and corbin's methodology. Analysis of the data resulted in identification of 15 categories representing 34 concepts. The results of this study were as follows : 1. Smoking in college women is caused by either curiosity or antagonism toward male smokers. 2. The meaning(phenomena) of smoking behavior in college women is justifiable or regretable. 3. Smoking occurs in connection with eating, during period of psychological conflict or as an habitual practice. 4. Smoking behavior is related to the perception of harmfulness to health, influence of others and the accessability of cigarettes. 5. College women experienced a change in their state of health, emotional relaxation, change in their social relationships. It is suggested that the results of this study may contribute to the development of strategies for the purpose of decreasing smoking behavior among female college students.
- 395 View
- 1 Download

- Effect of Korean Traditional Dance Movement Training on Psychophysiological Variables in Korean Elderly Women
- Mi Yang Jeon, Myoung Ae Choe
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(4):833-852. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.4.833
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Regular long term dance movement could be one of ways to induce improvement of psychophysiological variables, resulting in improvement of quality of life. However, there have been few studies to evaluate the effect of dance movement training on both physiological and psychological variables in the elderly. This study was focused to determine the effect of Korean traditional dance movement training on psychophysiological variables-body weight, body fat, lean body mass, muscle strength, muscle endurance, flexibility, agility, resting heart rate and blood pressure, depression and life satisfaction-in Korean elderly women. Thirty four subjects, aged between 65 and 75years who have normal cognition, sensory function, cerebellum function, cardiovascular function, participated in this study. Seventeen experimental group subjects were selected from E-elderly university in Kyung Gi province, and Seventeen control group subjects were selected from N -welfare facility in Seoul City. Seventeen experimental group subjects participated for 12weeks dance movement program. Korean traditional dance movement program was developed on the basis of Korean traditional dance and music by the author. The program consisted of approximately 50minutes of dance, 3times a week for 12weeks. During 50minutes workout, there were 15minutes of warm-up dancing, 25minutes of conditioning dance and 10minutes of cool-down dancing. The intensity for the conditioning phase was at between 60% and 65% of age-adjusted maximum heart rates. The body weight, body fat, lean body mass, muscle strength(grip strength, leg strength), muscle endurance, flexibility, agility, resting heart rate and blood pressure, depression and life satisfaction were measured prior to and following the experimental treatment. The participants in dance movement were interviewed focusing on subjective feeling following 12 week's regular dance movement. Data were analyzed with mean, standard deviation, percentage of change, X2-test, t-test, and ANCOVA test using SPSS PC+ program. Subjec tive feeling was categorized into cognitopsy-chological and physiological responses. Results were obtained as follows: 1) The body weight(F=15.52, p=.000), body fat (F=18.33, p=.000) and lean body mass(F=7.28, p=.011) of the experimental group were significantly lower than those Of the control group following the dance movement training. 2) The leg strength (F=30.96, p=.000), muscle endurance (F=9.06, p=.005), agility(F=44.92, 000), flexibility(F=6.84, p=.014) of the experimental group were significantly higher than those of the control group following the dance movement training. There was no significant difference of grip strength (F=. 43, p=.515) between experimental and control groups. 3) The heart rate(F=26.96, p=.000), systolic (F=10.40, p=.000) and diastolic(F=3.99, p= .005) blood pressure at rest of the experimental group were significantly lower than those of the control group following the dance movement training. 4) No significant difference of score of depression (F=3.49, p=.071) was observed between experimental and control groups. 5) Score of life satisfaction of experimental group was remarkably higher than that of control group following 12weeks of dance movement training (p<0.05). 6) Thematic responses about the dance movement following the training were positive. "I feel good" was the most frequent among cognitopsychol-ogical responses and "I feel lightness of body" was the most frequent among physiological responses. The results suggest that Korean traditional dance movement training can improve psychophysiological variables of Korean elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Dance Sports Program on Physical Function, Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life in Rural Elderly Women
Yun-Hee An, Nam-Soo Hong, Hee-Jung Yoon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2020; 45(4): 385. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Therapy on Physical Functions in the Elderly
Sook Hee Jung, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 252. CrossRef - Retracted:Effects of Exercise Program on Physical Fitness, Depression, and Self‐Efficacy of Low‐Income Elderly Women in South Korea
Kyung Rim Shin, Younhee Kang, Hyo Jung Park, Margaret Heitkemper
Public Health Nursing.2009; 26(6): 523. CrossRef
- The Effect of Dance Sports Program on Physical Function, Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life in Rural Elderly Women
- 639 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Development of a Maternal Identity Scale for Pregnant Women
- Hae Won Kim, Kyung Ja Hong
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(3):531-543. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.3.531
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to develop a Maternal Identity Scale for Pregnant Women and to test the validity and reliability of the scale. A convenience sample of 161 pregnant women were asked to complete the MISP questionnaire which consisted of 45 item, this was done from December 20, 1995 to January 15, 1996. The research procedure were as follows. The first step was to identify a conceptual definition of maternal identity using Rubin(1984)'s maternal identity and maternal experience during pregnancy. The second step was to operationalize the maternal identity, that is, perception of image possible of selves as mother, maternal role play by imagination, and the experiences of various emotional responses which are embedded in the mother-fetus dyad. The third step was item development which resulted in 45 items as appropriate measurement of maternal identity are except for the perception of image possible of selves as mother. The result findings were as follows: 1) Four factors for MISP(finally 40 items) were extracted through the principal component analysis and varimax rotation, and these contributed 49.3% of the variance in the total score. All 40 items in the scale loaded above .43 on one of 4 factors. 2) Each factor was named: factor 1 was named maternal role imagery and has 10 items, factor 2 was named happiness and has 11 items, factor 3 was named maternal fetal interaction and has 10 items, and the last factor 4 was named negative emotion and has 9 items. 3) Cronbach's -alpha coefficient for internal consistsncy was .92 for the total 40 items and .89, . 90, .86, .78 for the four subscales in that order. Recommendations are suggested below: 1) The developed MISP be used to assess maternal readiness in pregnancy. 2) Replication study be done to test validity and relaibility. 3) For the overall measure of Maternal Identity in Pregnancy, scale for the perception of image possible of selves as mother, and cognitive domain be reorganized for the maternal identity in pregnancy. 4) It is necessary to identify variables that influences maternal pregnancy. 5) It is necessary to identify that maternal identity in pregnancy is a reliable index of motherhood, to do correlation studies on maternal identity and major maternal variables in maternal transition period, to reoperationalize the maternal identity in postpartum, and finally to designate a longitudinal study of the maternal identity changes or stabilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal identity measurement based on the experiences of mothers with infants: a methodological study
Sun jung Park, Eun young Choi
Women's Health Nursing.2025; 31(1): 46. CrossRef - Factors influencing happiness and depression in high-risk pregnant women: a cross-sectional study using the ecological systems approach
Hyunkyung Choi
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 203. CrossRef - An explanatory model of quality of life in high-risk pregnant women in Korea: a structural equation model
Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(4): 302. CrossRef - Effects of stress, depression, and spousal and familial support on maternal identity in pregnant women
Hye-Jung Seo, Ju-Eun Song, Youngjin Lee, Jeong-Ah Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 84. CrossRef - Effects of Music Therapy and Phone Counseling on Postpartum Depression and Maternal Identity in High Risk Women
Hae Won Kim, Sun OK Kim, Hye Gyung Kim, Hyang Ran Jeon
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(1): 63. CrossRef - Factors associated with Postpartum Depression and Its Influence on Maternal Identity
Yoen Yi Jung, Hae Won Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(1): 29. CrossRef - Effects of an Integrated Self-Management Program on Self-Management, Glycemic Control, and Maternal Identity in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
HeeSook Kim, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 69. CrossRef
- Maternal identity measurement based on the experiences of mothers with infants: a methodological study
- 1,065 View
- 26 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Factors of the 'Taegyo' of Korean Pregnant Women: Self Care of Pregnant Women Based on Oriental Folk Behavior
- Soon Bok Chang, Young Joo Park, Youn Soon Choi, Chae Won Chung
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(2):345-358. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.2.345
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF All human health behavior is deeply rooted one's beliefs or value system usually encompassed within the culture in which they live. The Taegyo, based on Oriental folk medicine, is defined as the behavior and self care of pregnant women administered for herself and her fetus(unborn child). Taegyo is believed to be desirable, effective, and healthy behavior by most of Korean pregnant women. It is essential in our contemporary culture, to ascertain what the components of Taegyo are and to integrate them into current, western nursing care, particularly in the area of prenatal care. 910 Korean women were the subjects of this study, who were in a gestation period of pregnancy between 10 weeks to three months postpartum. The subjects were selected by clustered sampling from 10 representative cities in Korea. Data was collected from February 10 to March 30 1995 by a constructed questionnaire which consisted of 95 items. The questionnaire was developed through three steps such as content analysis, calculation of content validity index, and pretest. Data was analyzed by descriptive statistics and rotated matrix factor analysis with pc-SAS. The mean age of the subjects was 28.9 years; 36.5% of them were employed and the mean income per month was about 2000 dollars. The component of Taegyo was clustered into five factors such as fetus psychological stability(equity), fetus personality development, maternal-fetal interaction, fetus intellectual development and physical health promotion. The variance of each factor were 23.7%, 8.3%, 4. 7%, 4.1%, and 3.3% respectively in that order. The Eigen value of each factor was 13.03, 4.57, 2.60, 2.23, and 1.83 respectively. It was found that the Taegyo is an unique and holistic self care behavior of Korean pregnant women. Therefore it has been concluded that this study has broadened the understandability of the implications the Taegyo. It is suggested that further studies on the effects of the Taegyo are needed to provide a scientific basis for professional maternity nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influencing Factors and Consequences of Maternal-Fetal Attachment among Pregnant Women in East Asia: A Scoping Review
Eungil Ko, Yaelim Lee
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2026; 37(1): 110. CrossRef - Correlations among Perceptions and Practice of Taegyo and Maternal-Fetal Attachment in Pregnant Women
Sang-Youn Jang, Kyung-Sook Bang
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(4): 398. CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Practice of Traditional Prenatal Education (Taegyo) among Pregnant Korean Women
Young Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(5): 491. CrossRef
- Influencing Factors and Consequences of Maternal-Fetal Attachment among Pregnant Women in East Asia: A Scoping Review
- 1,067 View
- 12 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Determinants of Health Promoting Behavior of Middle Aged Women in Korea
- Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Young Joo Park
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(2):320-336. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.2.320
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Health promoting behaviors of an individual are affected by various variables. Recently, there has been a growing concern over important health problems of the middle aged women. Physiological changes in the middle aged women and their responsibility for family care can result in physical and psychological burden experienced by middle aged women. This study was designed to test Pender's model and thus purpose a model that explains health promoting behaviors among middle-aged women in Korea. The hypothetical model was developed based on the Pender's health promoting model and the findings from past studies on women's health. Data were collected by self-reported questionnaires from 863 women living in Seoul, between 20th, April and 15th, July 1995. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis. The Linear Structural Relationship (LISREL) modeling process was used to find the best fit model which assumes causal relationships among variables. The results are as follows; 1. The overall fit of the hypothetical model to the data was good expect chi -square value (GFI=.96, AGFI=.91, RMR=.04). 2. Paths of the model were modified by considering both its theoretical implication and statistical significance of the parameter estimates. Compared to the hypothetical model, the revised model has become parsimonious and had a better fit to the data expect chi-square value (GFI=. 95, AFGI=.92, RMR=.04). 3. Some of modifying factors, especially age, occupation, educational levels and body mass index (BMI) are revealed significant effects on health promoting behaviors. 4. Some of cognitive -perceptual factors, especially internal health locus of control, self-efficacy and perceptive health status are revealed significant effects on health promoting behaviors. 5. All predictive variables of health promoting behaviors, especially age, occupation, educational levels, body mass index(BMI), internal health locus of control, self-efficacy and perceptive health status are explained 20.0% of the total variance in the model.
- 411 View
- 1 Download

- The Effect of Circumvaginal Muscle Exercise on Sexual Function in Married Women
- Young Sook Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(1):148-164. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.1.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effect of circumvaginal muscle (CVM) exercises to improve sexual function in married women has not been investigated by currently acceptable research methods, nor have appropriate instruments and techniques to carry out such investigation been available. The purpose of this research was to study the effect of CVM exercise on sexual function, and of measuring CVM function after CVM exercises. The research tools used were a modified Derogatis Sexual Function Inventory questionnare and a pressure sensitive intravaginal balloon device. This research was conducted in Kwangju-city and Chonnam province, Korea from July, 1994 to July, 1995. The research used a non-equivalent control pre-post test quasi-experimental design. Forty-five healthy married female volunteers, aged 30?8, and were randomly assigned by age using the matching fixed-length blocks to two groups. The experimental group consisted of 21 women who were assigned a 25 -minute per day CVM home exercise program for six weeks. The control group of 24 women did not do the CVM home exercises. The CVM home exercise was developed by Dougherty (1989a) and adopted to Korea by Lee (1993). Data were analyzed by x2-test, Paired t-test, Spearman product-moment correlation using SAS/PC+. The results are summarized as follows: 1. There were no significant differences in the characteristics of the subjects between the exper imental and control groups before the CVM home exercises. 2. Hypothesis 1 that married women who participated in CVM home exercises would have higher mean scores on the sexual function (SF) than in those who did not participate in home exercise was supported. 3. Hypothesis 2 that married women who participated in CVM home exercises would have higher vaginal pressure on SF than in those who did not participate in home exercises was supported (mean maximum pressure, t= -7.338, P<.0001, peak maximum pressure, t=-11.164, P<.0001). 4. Hypothesis 3 that the more often (number of days) and the more frequent (numbers of times per day) that married women do CVM home exercise, the higher their mean scores on SF and vaginal pressures was supported (r =0.233, P<.01; r=0.352, P<.05). A six week CVM home exercise program using a tape recording showed that SF can be improved. Results of this study showed that married women who exercise on a regular basis for six weeks improve their sexual function and increase the mean vaginal pressure and peak maximum pressure (tested by electronic monitor). In conclusion, CVM exercise is effective in increasing SF.
- 368 View
- 0 Download

- A phenomenological perspective and discovery of meaning in mid-aged women's experience of mastectomy
- Kyung Rim Shin
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1995;25(2):295-315. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1995.25.2.295
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This qualitative nursing research used a hermeneutic phenomenological approach to discover meaning in mid-aged women's experience of mastectomy. The ultimate aim of the inquiry was to discover the essence of mid-aged women's experience and promote understanding. The study was guided by Van Manen's method for doing research. The method of inquiry included: turning to phenomenon of interest; inquiring and investigating experience as it was lived rather than as conceptualized; reflecting and analyzing essential themes which characterize phenomenon; and describing phenomenon through art of writing and rewriting. Multiple strategies for data collecting were needed: in depth face-to-face interview; analysis of women's writings; artistic works; and analysis of examples of phenomenon in art, literature, and drama. Although the experience was different for all of the women interviewd, essential themes of experience emerged; Self-discovering of vicious disease, Divining punishment-unfortunate women, loss of self though the scar, a nightmare, change of life values and attitudes, rediscovering living alone, living through with fearing of death. Findings from artistic and creative inquiry further validated findings and meaning descovered. The study illuminated meaning and simultaneously validated the phenomenological research process. Essential themes for understanding women's experience, implications for education, research, and practice, direction and need for continuing inquiry were identified.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Survey of Brassiere Related Clothing Tendency for Mastectomy Patients
Youn Joo Kim, Da Som Koo, Yun Ja Nam, Kwan Sik Seo, Eun Shin Lee, Dong Young Noh, Kyu Jin Cho
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2019; 21(6): 800. CrossRef - Life Experience of Inpatients with Recurrent Breast Cancer
Young Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(2): 214. CrossRef
- Survey of Brassiere Related Clothing Tendency for Mastectomy Patients
- 681 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Experience of Women Living with Lymphedema
- Myoung Ok Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):1049-1053. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.1049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The object of this study was to explore and describe the experience of women living with lymphedema within a socio-medical context in Korea.
METHODS
Research data was collected through interviews and participant observation with 9 informants between February 2000 and July 2002. Data was examined using Spradley's taxonomy analyzing techniques.
RESULTS
5 themes were identified; 'overwhelming and despair over the ailment condition', 'distrust and abandonment of conventional medicine' 'shaming of losing maternity and femineity', 'returning to the permanent safe shelter', and 'struggling for reconstruction of one's self'. The 'chaotic' state of knowledge and health care system for lymphedmea patient affected the experiences of informants.
CONCLUSIONS
This result will be a basic understanding of psychosocial impact of lymphedema for the women and to develop the comprehensive nursing program including counseling program.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- “Just live with it”: Having to live with breast cancer related lymphedema
Johanna E. Maree, Dalene Beckmann
Health SA Gesondheid.2016; 21: 77. CrossRef
- “Just live with it”: Having to live with breast cancer related lymphedema
- 626 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Age at Menopause and Related Factors in Korean Women
- Young Joo Park, Hesook Suzie Kim, Hyun Choel Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):1024-1031. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.1024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This cross-sectional design was to identify the age at menopause of Korean women using a national sample, and to examine relationships between age at menopause and the anthropometric, sociodemographic, biological and life style behavioral factors. Two thousand eight hundred seven naturally postmenopausal women aged between 41-65 years were recruited by self-selection from 7 metropolitans and 6 provinces in Korea from Dec. 20, 1998 to April 30, 1999. The age at menopause of Korean women was 49.2 years (mean) and 50.0 years (median). The range of age at menopause was 33.0 to 61.0 years. The significant influencing factors on age at menopause were body mass index, mother's and sister's age at menopause, alcohol use, physical activity, coffee preference, and residential area. The menopausal age of Korean women has slightly increased compared to a previous study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exposure to the one-child policy and fertility among chinese immigrants to the US
Siyuan Lin, Laura Argys, Susan Averett
Review of Economics of the Household.2025; 23(3): 969. CrossRef - Menopause Across Asia: A Comprehensive Meta-analysis of Age and Influencing Factors
Prabhat Kumar Agrawal, Amit Varshney, Siddhant Dev, Ruchika Garg, Ashish Gautam, Nikhil Pursnani, Sandipta Kumar Panda, Nidhi Agastya
Journal of Mid-life Health.2025; 16(3): 257. CrossRef - Functional Effects of Sericin on Bone Health and D-Serine Regulation in Estrogen-Deficient Rats
Hyun-Seung Kim, Xiangguo Che, Shihyun Kim, Jongho Choi, Joon Ha Lee, You-Young Jo, Seong-Gon Kim, Je-Yong Choi, Ji-Hyeon Oh
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(18): 10247. CrossRef - Nonpharmacological Intervention Effects on Middle-Aged Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ji-Hyun Kim, Hea-Jin Yu
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3206. CrossRef - Longitudinal patterns and group heterogeneity of depressive symptoms during menopausal transition in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Junhee Park, Sang Won Jeon, Byungtae Seo, Jae Ho Park, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Regular Use of Analgesics before Cancer Diagnosis and Occurrence of Mood Disorders
Hyun Sook Oh, Subin Noh, Hwa Jeong Seo
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(3): 1828. CrossRef - Study on depletion of ovarian function and late‐life chronic diseases in India
Sampurna Kundu, Sanghmitra Sheel Acharya
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2023; 162(3): 1057. CrossRef - Exposure to the One-Child Policy and Fertility Among Chinese Immigrants to the Us
Siyuan Lin, Laura Argys, Susan Averett
SSRN Electronic Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Iron Deficiency in Korean Patients With Heart Failure
Jin Joo Park, Minjae Yoon, Hyoung-Won Cho, Sang-Eun Lee, Jin-Oh Choi, Byung-Su Yoo, Seok-Min Kang, Dong-Ju Choi
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of early age at menopause on disease outcomes in postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis: a large observational cohort study of Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Eun Hye Park, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, You-Jung Ha
RMD Open.2023; 9(1): e002722. CrossRef - Osteoporosis Associated with Breast Cancer Treatments Based on Types of Hormonal Therapy: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Korean National Sample Data
Yen Min Wang, Yu-Cheol Lim, Deok-Sang Hwang, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Ye-Seul Lee
Medicina.2023; 59(9): 1505. CrossRef - Measured sodium excretion is associated with cardiovascular outcomes in non-dialysis CKD patients: results from the KNOW-CKD study
Seong Cheol Kang, Minjung Kang, Hyunjin Ryu, Seonmi Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Eunjeong Kang, Yujin Jeong, Jayoun Kim, Yong-Soo Kim, Soo Wan Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Kook-Hwan Oh
Frontiers in Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of tiotropium on the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with COPD: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyoung Shin, Jin Hwa Lee
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Effects of Unhealthy Lifestyle Behaviors on Metabolic Syndrome among Postmenopausal Women
Jin-Suk Ra, Hyesun Kim
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 848. CrossRef - Ovarian Function Preservation in Patients With Cervical Cancer Undergoing Hysterectomy and Ovarian Transposition Before Pelvic Radiotherapy
Wonguen Jung, Yun H. Kim, Kyung S. Kim
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Impact of Body Mass Index on Breast Cancer in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Jae Hwan Jeong, Hak Min Lee, Hai Young Son, Ilkyun Lee
Journal of Breast Disease.2020; 8(1): 51. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Breastfeeding on the Prevention of Metabolic Syndrome Among Postmenopausal Women
Jin Suk Ra, Soon Ok Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2020; 14(3): 173. CrossRef - Neck Circumference and Cerebral Gray Matter Volume
Chol Shin, Regina E.Y. Kim, Robert J. Thomas, Chang-Ho Yun, Seung Ku Lee, Robert D. Abbott
Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders.2020; 34(4): 306. CrossRef - Inhaled corticosteroids in COPD and the risk for coronary heart disease: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyoung Shin, Hee-Young Yoon, Yu Min Lee, Eunhee Ha, Jin Hwa Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends of Premature and Early Menopause: a Comparative Study of the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Seung-Ah Choe, Joohon Sung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary bisphenol A, phthalate metabolites, and obesity: do gender and menopausal status matter?
Jung-eun Lim, BongKyoo Choi, Sun Ha Jee
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2020; 27(27): 34300. CrossRef - Association between lower urinary tract symptoms and cardiovascular risk scores in ostensibly healthy women
Hyun Young Lee, Ji Eun Moon, Hwa Yeon Sun, Seung Whan Doo, Won Jae Yang, Yun Seob Song, So‐Ryoung Lee, Byoung‐Won Park, Jae Heon Kim
BJU International.2019; 123(4): 669. CrossRef - Higher Pro-Inflammatory Dietary Score is Associated with Higher Hyperuricemia Risk: Results from the Case-Controlled Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study_Cardiovascular Disease Association Study
Hye Sun Kim, Minji Kwon, Hyun Yi Lee, Nitin Shivappa, James R. Hébert, Cheongmin Sohn, Woori Na, Mi Kyung Kim
Nutrients.2019; 11(8): 1803. CrossRef - Association between obesity type and obstructive coronary artery disease in stable symptomatic postmenopausal women: data from the KoRean wOmen'S chest pain rEgistry (KoROSE)
Jun Hwan Cho, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Myung-A Kim, Sohee Oh, Mina Kim, Seong Mi Park, Hyun Ju Yoon, Mi Seung Shin, Kyung-Soon Hong, Gil Ja Shin, Wan-Joo Shim
Menopause.2019; 26(11): 1272. CrossRef - Obesity and colorectal adenomatous polyps: A cross-sectional study in Korean adults
Ji Young Lee, Sang Mi Kwak, Seung-Kwon Myung, Sun Ha Jee
Obesity.2014; 22(2): 518. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Risk Factors for Intracranial Cerebral Atherosclerosis Among Asymptomatic Subjects
Young-Suk Kim, Jin-Woo Hong, Woo-Sang Jung, Seong-Uk Park, Jung-Mi Park, Sung-Il Cho, Young-min Bu, Sang-Kwan Moon
Gender Medicine.2011; 8(1): 14. CrossRef - Cortisol, estradiol-17β, and progesterone secretion within the first hour after awakening in women with regular menstrual cycles
Ryun S Ahn, Jee H Choi, Bum C Choi, Jung H Kim, Sung H Lee, Simon S Sung
Journal of Endocrinology.2011; 211(3): 285. CrossRef
- Exposure to the one-child policy and fertility among chinese immigrants to the US
- 3,061 View
- 24 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Relationship Between Postpartum Depression and Body Image in Postpartum Women
- Boon Han Kim, Hye Won Jeon, Yun Jung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):906-916. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.906
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to identify the change and difference and relationship of postpartum depression and physical image. METHOD: The subjects consisted of 86 postpartum women at one general hospital in Seoul. The data was collected from September to November 2001. The instrument used for this study were SRD (Self-Rating Depression Scale) and Norris' Body Image Scale to evaluate depression and body image. The collected data was analyzed with frequency, mean, t-test, paired t-test, ANOVA and Pearson's correlation coefficient. RESULT: The result of this study were as follows: 1.The mean score of D2 was significantly higher than D1(p=.003). There was no difference significantly B1 and B2(p=310). 2. There was significant correlation between the two, D1-D2(r=.381, p<.01), B1-B2(r=.364, p<.01), D1-B1(r=.579, p<.01), D2-B2(r= .567, p<.01). (D1: depression of postpartum 1-3days, D2: depression of postpartum 6-8weeks, B1: body image of postpartum 1-3days, B2: body image of postpartum 6-8weeks) CONCLUSION: There was very high postpartum depression in postpartum women, but body image was positive. Also, there was correlated to postpartum depression and body image. Thus it is necessary to implement nursing intervention focused on to decrease the postpartum depression and to enhance the body image of the postpartum women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Self Efficacy, Body Image and Family Support on Postpartum Depression in Early Postpartum Mothers
Ji-Won Lee, Yong-Sook Eo, Eun-Hye Moon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 4011. CrossRef
- Effects of Self Efficacy, Body Image and Family Support on Postpartum Depression in Early Postpartum Mothers
- 757 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Influencing on Quality of Life in Aged Women with Chronic Pain
- Jung Tae Son, Sun Rim Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):735-742. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.735
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was conducted to identify the pain characteristics, family support and physical functioning and to determine predictors of the quality of life in aged women with chronic pain. METHOD: The questionnaires were collected through direct interview by a trained research assistant from July 2 to August 24, 2001. Subjects were 108 women clients with chronic pain over 65 years of age. Data analyzed frequency, percentage, mean, Pearson's correlation, ANOVA and stepwise multiple regression by SAS. RESULT: Care providers were mostly spouses and daughters in law. Care providers who took care of elderly for a few hours a day had the highest percentile. Aged women had persistently had chronic pain of moderate intensity and was moderately satisfied with pain management. The mean score of disability due to pain was 3 on a 10 point scale. The mean scores of physical function and quality of life were moderate and there were negative correlations between pain characteristics, physical functioning, and quality of life at the range from r=-.46 to r=-.83. Satisfaction with care, duration of pain, disability due to pain, and physical functioning accounted for 56% of the variance in perceived quality of life for aged women with chronic pain. Disability due to pain was the most predictable variable of quality of life and physical function was the second . CONCLUSION: The results suggest that care by family, education in pain control, prevention of disability, and maintenance of physical function are important to improve and maintain quality of life in aged women with chronic pain. Therefore, there is a need for program development that enhance family support and nursing intervention that focuses on active pain control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Liquid Soap Manufactured with Vegetable Fatty Acid and Essential Oil by Hand on the Foot Skin of the Elderly
Mi-Young Gu, Soo-Yean Oh, Hwa-Jung Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Cosmetology.2022; 28(2): 233. CrossRef - Pain, Wisdom and Health Conservation in Older Adults with Chronic Diseases
Kiwol Sung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2014; 16(1): 85. CrossRef - Effects of Tai Chi Exercise on Physical Fitness and Quality of Life in Elderly Women
Jung Ah Park, Sook Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2014; 17(1): 38. CrossRef - Factors contributing to the use of complementary and alternative medicine in rural older women with chronic pain in South Korea
Saunjoo L. Yoon, Jeong-Hee Kim
Applied Nursing Research.2013; 26(4): 186. CrossRef - Relationship between Low Back Pain and Health-Related Quality of Life among Some Elderly
Kyeong-Ae Oh, Jong Park, Dae-Jung Jeon, Mi-Ah Han, Seong-Woo Choi
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2012; 37(3): 156. CrossRef - Relationships among the Pain Belief, Pain Coping, and Pain Disability of Patients with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
Sung-Nam Choi, Jeong-Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 30. CrossRef - Alternative View of Health Behavior: The Experience of Older Korean Women
Jin Hyang Yang, Bok Sun Yang
Qualitative Health Research.2011; 21(3): 324. CrossRef - EFFICACY OF QI-THERAPY (EXTERNAL QIGONG) FOR ELDERLY PEOPLE WITH CHRONIC PAIN
KYUNG HEE YANG, YOUNG HEE KIM, MYEONG SOO LEE
International Journal of Neuroscience.2005; 115(7): 949. CrossRef
- Effects of Liquid Soap Manufactured with Vegetable Fatty Acid and Essential Oil by Hand on the Foot Skin of the Elderly
- 630 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Study on Health Behavior Experience of Middle-aged Women in Rural Area
- Jin Hyang Yang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):694-705. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.694
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study is to describe the health behavior experience of middle-aged Korean women in rural areas, and to help understand their health practice, perceive their nursing needs and provide guidelines to developing appropriate nursing interventions. METHOD: The participants were 18 healthy middle-aged women living in rural areas, with no serious illness that require hospitalization. The data was collected through interviews and participant observation, analyzed by the grounded theory methodology of Strauss and Corbin(1997). The data collection period was from April to November of 2001. RESULT: Depending on the paradigm model, the central phenomenon was family-oriented pursuing of yangsaeng. The causal condition was less confidence on one's own health, responsibilities in caring for family. The contexts were cultural system. The intervening condition was information system, support system, limitation of approaching a medical institution. The action/ interaction strategies were yangsaeng through dietary practice, yangsaeng through promoting clothing and housing, yangsaeng through exercise, practice of folk therapy, yangsaeng through mental hygiene, and use of medical institution. The consequences were stabilization of body and mind, and stabilization of family. CONCLUSION: It is recommended for nurses to understand health behavior experience of middle-aged women, and provide nursing intervention with theoretical scheme and practical principles so that these women can pursue the family-oriented process of yangsaeng.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Ethnographic Study on the Health related Lifestyles for Sea Women of Jeju
김필환, Kim,Yeong-Kyeong
Qualitative Research.2017; 18(1): 114. CrossRef - Evaluation of Anthropometric Characteristics, Bone Density, Food Intake Frequency, Nutrient Intakes, and Diet Quality of Preand Postmenopausal Women : Based on 2008∼2011 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soon Nam Choi, Kwang Hyun Jho, Nam Yong Chung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(5): 500. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Hwa-byung Awareness in Middle-Aged Women
Sun-Jung Park, Eun-Young Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(2): 1304. CrossRef - A Korean Version of the Appraisal of Diabetes Scale (ADS-K)
Eun-Hyun Lee, Young Whee Lee, Kwan-Woo Lee, Moonsuk Nam, Yong Seong Kim, Seung Jin Han
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2015; 26(3): 270. CrossRef - The relationship between Intake of Health Foods and Dietary Behavior in Middle-Aged Women
Mi-Hee Kim, Hye-Jin Lee, Mi-Jeong Kim, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(5): 436. CrossRef - Evaluation of Diet Quality according to Self-Rated Health Status of Korean Middle-Aged Women -Based on 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(9): 1395. CrossRef - The Related Factors Influencing on Self-rated Health Level of Middle-aged Women
Hyejin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee, Eunkyung Kim, Mi-Jung Kim, Suk-Man Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(3): 290. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Self-Foot Reflexology Massage on Stress and Immune Responses and Fatigue in Middle-Aged Women in Rural Areas
Ja Ok Kim, In Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(5): 709. CrossRef - Climacteric and Menopausal Women's Beliefs on Daily Meals and Food Supplements - A Focus Group Interview Study -
Jeong-Soon Pyun, Mi Jeong Kim, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(2): 239. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Efficacy Promotion Program on Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
Hea-Kyoung Ko, Geum Ja Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Do the determinants of physical activity change by physical activity level?
Hyun Kyung Kim, Mi Ja Kim, Chang Gi Park, Hyeon Ok Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2009; 65(4): 836. CrossRef
- An Ethnographic Study on the Health related Lifestyles for Sea Women of Jeju
- 653 View
- 0 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The Effect of the Dan-Jun Breathing Exercise Program on pulmonary function and psychological Health of Women in Midlife
- Kyung Sun Hyun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(4):459-469. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.4.459
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was to examine the effects of the Dan-Jun Breathing Exercise Program on pulmonary function and psychological health promotion of women in midlife. METHOD: Experimental group(20) was matched to control group(20) according to age, education, religion and marital status. The Dan-Jun Breathing Exercise Program was carried out for 80 minutes a day, 3 times a week for 12 weeks. FVC and FEV1.0/FVC(%) were measured by using the Health Management System developed by the Korean Physical Science Institution. The scores of depression, anxiety and hostility were measured by the Korean Manual of Symptoms-Checklist -90 revision. RESULT: 1) FVC of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group, FEV1.0/FVC(%) was not higher than that of the control group. 2) The scores for depression, anxiety and hostility in the experimental group were lower than those of the control group. 3) FVC of 6 weeks and 12 weeks experiment in the experimental group was higher than that of pre-experimental group. CONCLUSION: The Dan-Jun Breathing Exercise Program promotes the Pulmonary function and psychological health of women in midlife.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Trend on Aromatherapy for Korean Middle-aged Women
Hee-Jung Yong, Hyun Hee Jang, Sung Nae Lee, Soo-Yeon Kim, Young-Sam Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2017; 15(1): 113. CrossRef
- Research Trend on Aromatherapy for Korean Middle-aged Women
- 686 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Subjectivity on Stressful Life Events of Middle-aged Women: A Q Methodology Approach
- Hye Sook Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(3):406-415. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.3.406
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study measures the subjectivity on stressful life events of middle- aged women. METHOD: Q-Methodological method was used for that purpose. As for the research method, Q-statements were collected reliminary to the study of through in-depth interviews and a literature review. For the study 38 Q-statements were selected. There were 28 middle aged women as subjects for the research. Q-Factor Analysis by using PC Quanl Program to supply the material. RESULT: Through the result of this study, the stressful life events of middle-aged women could be identified by 4 types. The type I is called the conflict in relationship with husband's family members. The type II is called lack of marital intimacy. The type III is called low self-esteem. The type IV is called changing life cycle itself. CONCLUSION: Therefore, identifing the subjectivity on the stressful life events of middle-aged women would be a basic step for the understanding of middle aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of transformative tourism activity on the mitigation of menopause symptoms and life satisfaction
Bomi Hazel Kim, Haeok Liz Kim
International Journal of Tourism Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Perception of Aging Symptoms as a Mediator and Moderator on the Relationship between Family Function and Stress in Middle-Aged Adults
Hyun-E Yeom, Kyoung Ok Ju
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(2): 175. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Mid-Life Crisis
Hae Kyung Chang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 98. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Adaptation to Menopause in Middle-aged Women
Eun Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 336. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression in Middle Aged Women: Focused on Quality of life on Menopause
Jung Nam Sohn
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(2): 148. CrossRef - Factors Related to Obesity of Mid-year Korean American Women and Their Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
Sukyong Seo
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(1): 8. CrossRef
- Effects of transformative tourism activity on the mitigation of menopause symptoms and life satisfaction
- 744 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- The Experiences of the Middle: Aged Women's Crisis
- Kwuy Bun Kim, Jae Hee Yoo, Eun Ja Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(3):305-316. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.3.305
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study examined the crisis experiencing by middle - aged women and tried to understand their lived experiences also explored the nature of their crisis. METHOD: The data was collected from 7 participants living in Incheon and Seoul from Sep. 2000 to Feb. 2001. The analysis of the data was made the phenomenological analytic method suggested by Giorgi. RESULT: The meanings of the lived experiences of the middle - aged women's crisis ; Impatience about decreased physical function : an attack of a disease, decreased strength, decreased quickness, decreased desire, increased concern of health, poor memory, easy fatigue, change of appearance, change of conjugal relations, sense of loss. Psychological, emotional disturbances : sense of emptiness, regret, sharpness, feeling gloomy, fear of dying, loneliness, feeling the want, loss of confidence. Attitude of active life : reinforcement of self experience, enrichment of understanding, search of self satisfaction, search of self development, development of support system, management of independent life. Envy feeling from relative comparison : feeling of comfort, unsatisfaction to the husband, yearning for youth. CONCLUSION: Therefore, the program should be developed for the program of physical, psychological, and emotional health and expansion of social role of the middle - aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Subjectivity on Experience of Middle-aged Women Who Attend Self-help Group to Overcome Midlife Crisis: Q Methodology Approach
Hyun Jung Doo
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 78. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Foot Reflexology on Stress, Fatigue and Blood Circulation in Premenopausal Middle-Aged Women
Soo Hyun Jang, Kye Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 662. CrossRef - A Study on Exercise Behavior, Exercise Environment and Social Support of Middle-Aged Women
Myoung-Ae Choe, Yang Sook Hah, Keum Soon Kim, Myungsun Yi, Jung-An Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 101. CrossRef
- Subjectivity on Experience of Middle-aged Women Who Attend Self-help Group to Overcome Midlife Crisis: Q Methodology Approach
- 696 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A Study on the Relationships between Osteoporosis Knowledge, Self-efficacy and Health Belief of Women in an Island
- Kyung Rim Shin, Young Mi Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(1):89-99. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.1.89
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was to examine the relationships between knowledge, health belief and self-efficacy of osteoporosis with the women residents in an island. METHOD: The subjects were 64 women who lived in an island located in Incheon metropolitan city. Data collection was performed by using questionnaire that included Osteoporosis Knowledge Test, Osteoporosis Self-Efficacy Scale and Osteoporosis Health Belief Scale by Kim, Horan & Gendler (1991). The Data were analyzed using SAS computer program that included descriptive statistics, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient. RESULT: 1) The mean of osteoporosis knowledge was 10.03 in the range of 0 to 24, shows the relatively lower score than mean score. The mean of osteoporosis health belief variables were susceptibility 18.95, seriousness 19.05, benefits of exercise 22.35, benefits of calcium 21.81, barriers to exercise 16.95, barriers to calcium 13.13, and health motivation 19.75 in every range of 6 to 30. The mean of osteoporosis self-efficacy was 37.95 in the range of 12 to 60, shows a relatively higher score than mean score. 2) There were statistically significant differences in the degree of osteoporosis knowledge according to age, education. But There was no significant difference in the degree of osteoporosis and self-efficacy according to general characteristics. There were statistically significant differences in the degree of susceptibility according to religion, family income. There were statistically significant differences in the degree of seriousness, health motivation according to family income. There was statistically significant difference in the degree of barriers to exercise according to education. 3) There were statistically significant positive correlations between osteoporosis knowledge and benefits to exercise, benefits of calcium intake. There was statistically no significant correlation between osteoporosis knowledge and osteoporosis self-efficacy. There was statistically a significant positive correlation between osteoporosis self-efficacy and barriers to exercise. There was statistically a significant negative correlation between osteoporosis self-efficacy and health motivation. CONCLUSION: According to the result, osteoporosis education program including exercise, calcium intake should be operated to increase benefits to exercise and calcium intake for osteoporosis prevention. In addition, the program of improving self-efficacy should be designed and operated to decrease the perception of barriers to exercise and to increase the perception of health motivation of women in island.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Home visit-based baby tailored support program for infants
Hyeji Shin, Yoonjung Kim, Jeonghyun Choi
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 80: 1. CrossRef - The Development of Picture Comprehension Across Early Environments: Evidence From Urban and Rural Toddlers in Western Kenya
Rebecca Zhu, Helen O. Pitchik, Tabitha Nduku Kilonzo, Jan Engelmann, Lia C. Fernald, Alison Gopnik
Developmental Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A preliminary study on the effects of an osteoporosis prevention program based on an Information-Motivation-Behavioral skill model in older adult women: A cluster randomized controlled trial
Yeongsuk Lee, Dong-Hee Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 45: 55. CrossRef - Influencing Factors of Behavior for Reducing Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Demand for Related Education
Chae-Min Yoon, Hye-Jin Kim
European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education.2022; 12(3): 295. CrossRef - Comparison of Factors Related to Health Behavior for Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Prevention in Middle-Aged Women with and without Depression
Eun Ko, Hyukjoon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(4): 543. CrossRef - Related Factors and Osteoporosis Health Beliefs and Self-Efficacy of Women
Nülüfer ERBİL
Middle Black Sea Journal of Health Science.2019; 5(1): 16. CrossRef - A Validation Study of the Gross Motor Scale of Korean Version of Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, Third Edition
So-Hyun Ahn, Eun-Young Yoo, Soon-Hang Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2018; 26(2): 81. CrossRef - General Characteristics, Self-Efficacy, and Diet Control of Hypertension Patients at a Diabetes Admission Control Center in the Jeollanma-do Area
Su Jeong Yeo, In Woo Shin, Bok Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(4): 731. CrossRef - A Study of the Practical Knowledge Regarding Osteoporosis and Health Promoting Behavior Among University Students
Hyun Sook Hwang
Journal of International Academy of Physical Therapy Research.2014; 5(2): 772. CrossRef - Relationship of dietary self-efficacy and illness beliefs, perceived benefits and perceived barriers for the reduction of sodium intake in the elderly
Yoonsuk Suh, Yun-Hee Seok, Young-Jin Chung
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(4): 324. CrossRef - A Study on Osteoporosis Knowledge, Health Beliefs and Health Behaviors among Female College Students
Hyejin Min, Hee Young Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(2): 111. CrossRef - A Study on the Level of Awareness and Self-Efficacy of Osteoporosis in Young Women
Euysoon Choi, Ju Young Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 204. CrossRef - The Relationship between Knowledge, Health Beliefs, and Prevention Behaviors of Osteoporotic Fracture in Patients receiving Osteoporosis Treatment
Eun-Suk Moon, Eun Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 147. CrossRef - Development & Validation of a Checklist for Infant and Child Developmental Screening
Hyeon-Ok Ju, Nae-Young Lee, In-Sook Park, Sun-Ok Lee, So-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2009; 15(1): 34. CrossRef - Development of an Osteoporosis Awareness Scale for Women
Euysoon Choi, Juhu Kim, Miyoung Chung, Kyunghye Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 813. CrossRef
- Home visit-based baby tailored support program for infants
- 820 View
- 2 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Assessing Decisional Balance toward Mammography Screening in Korean Women
- Young Joo Park, Sung Ok Chang, Hyun Cheol Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(7):1174-1180. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.7.1174
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This cross-sectional survey was carried out to assess the decisional balance of Korean women toward mammography screening. A sample of 1, 903 naturally postmenopausal women was selected from the community-based social groups in town or city hall auxiliaries in seven metropolitan areas and six provinces in Korea. The classification of women according to the stage of adoption of mammography was 54.9% in pre-contemplation, 31.9% in contemplation, 7.8% in action, and 5.5% in maintenance. The mean differences of pros, cons, and the decisional balance by the stage of mammography adoption were statistically significant. There were significant mean differences between the stages of adoption according to a woman's experience with and intention for mammography and the pros score, the cons score, and the decisional balance score. Results provide the empirical evidence for the Transtheoretical model. An association between stages of mammography adoption and decisional balance exists.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analyzing paths from online health information seeking to colorectal cancer screening using health literacy skills frame and cognitive mediation model
Seok Won Jin, Yeonggeul Lee, David A. Dia
Patient Education and Counseling.2019; 102(3): 416. CrossRef
- Analyzing paths from online health information seeking to colorectal cancer screening using health literacy skills frame and cognitive mediation model
- 606 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Attitudinal Type on Delivery for College Women
- Jung Hee Yeo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(6):1088-1097. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.1088
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was formed to propose a theoretical background trying to create a positive delivery experience by understanding college women's subjective accounts (their view and attitude) on delivery.
METHOD
Q- methodology was used to appreciate the highly abstract concept in an objective manner, since delivery can be assessed differently with each experience.
RESULT
There were three types of opinions about the delivery in college women. The first type (matured type) understood delivery to be a precious experience that enables women to gain the value of life through labor pain, and granted then more appreciation to their own mothers. The second type (will type) recognizes delivery as an option rather than an obligation for women. They think women chooses whether or not to experience the process, especially since delivery requires a great deal of responsibility. The third type (positive type) takes delivery as a valuable, worthwhile, and marvelous process that they wish to experience. They are not even afraid of giving birth multiple times.
CONCLUSION
The study explains and allows us to understand college women's overall opinion and attitudes about delivery. Thus this study aids the seizure of an opportunity to build a theoretical base for delivery management.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences of Nursing College Students attended to Delivery Practice at Midwifery Clinic
Chaisoon Park, Hyejin Kim, Soongyo Yeoum
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(2): 115. CrossRef
- Experiences of Nursing College Students attended to Delivery Practice at Midwifery Clinic
- 508 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Elderly Women's Grief
- Kwuy Bun Kim, Kyung Ho Lee, Hye Kyung Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(6):1021-1033. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.1021
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study sought to find a nursing intervention tool for enhancing elderly women's lives by investigating the causes and the meaning of their grief.
METHOD
This research was derived from a phenomenological tool such as qualitative research design. The data collection took place from December of 2000 until April of 2001 Through systematic interviews and participatory observations of five elderly women attending C welfare center located in downtown Seoul the data was collected. Each interview lasted an hour and a half and was arranged five times. The analysis of this research was conducted using the Giorgi method.
RESULTS
(1) There was obvious physical and physiological decline caused by aging old; as well as there being spouse health problems, additional physical suffering, signs of senility, adn insomnia, (2) Further grief was imposed by unpleasant memories of the spouse; infidelity, incapability, and even disregard of her own well-being, (3) Then there was pity for children; unfaithful children, uncertain futures of the children, and early death of a child, (4) Also, regrettable fate, painful daily acttrities, unreliable factors, bad circumstances, and feelings emptiness were reported, (5) Finally, anxiety for the future; ac sense of despair, loneliness, economic hardship, and the fear of imminent death increased grief levels.
CONCLUSION
A variety of programs and social meetings for the elderly to overcome their physiological or psychological crisis should be substantially developed and supported by the government. In order to implement the social welfare for the elderly women, special consideration whether on the governmental level or the personal level, should be devoted to the elderly who live without any financial support or social concern.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incidence and related factors of traffic accidents among the older population in a rapidly aging society
Kimyong Hong, Kyoung-Mu Lee, Soong-nang Jang
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2015; 60(3): 471. CrossRef - Grieving among Adolescent Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Situational Analysis.
Juhye Jin
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(1): 49. CrossRef - Ageing Experiences of Nurses with Overseas Employment: Focusing on the Korean Nurses Dispatched to Germany in the 1960s and 1970s
Hack-Sun Kim, Sun-Woo Hong, Kyung-Sook Choi, Ae-Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(2): 185. CrossRef
- Incidence and related factors of traffic accidents among the older population in a rapidly aging society
- 675 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A Model for Community Based Mother Infant Care Center: TMIC (transitional mother infant care center) using a Sanhujoriwon
- Eun Kwang Yoo, Young Mee Ahn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(5):932-947. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.5.932
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was 1) analyze the current state of Sanhojoriwon; and 2) to suggest the new model for the community based mother infants health care delivery system: strategies of TMIC are related to Public Health policy, cost-effectiveness, mother infant care provision of medical professionalism, and so on.
METHOD
Forty-seven workers from seventeen Sanhojoriwon participated to analyze several aspects of Sanhojoriwon. Using a questionnaire developed at Korean Sanhojori Research Forum (KSARF), such as the traditional and medical concept of the Sanhojori, postpartum care, Korean traditional postpartum care, job description on women and infant care at Sanhojoriwon, professional management, health care policy and the educational need.
RESULTS
Based on the descriptive study results, the TMIC, the community based transitional mother infants care center was suggested as a new model for the cyclic public health care system related on the reproductive health, using an already existing related center, Sanhojoriwon. Also, several strategies were presented on the TMIC.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Operational Status of Postpartum Care Centers and Application of Family-Centered Care in South Korea’s Era of Ultralow Birth Rates
Ju-Eun Song
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(3): 101. CrossRef - Mothers’ Experiences of Childbirth and Perspectives on Korean Medicine-Based Postpartum Care in Korea: A Qualitative Study
Do-Eun Lee, Hyo-Weon Suh, Han-Song Park, Inae Youn, Minjung Park, Joohee Seo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5332. CrossRef - The Review and Future Perspectives of the Postpartum Care Service System for the Improvement of the Private-Postpartum Care Center’s Publicity
Hee-Sun Kim, Jae Hee Lee, Jeong Rim Lee, Ji-Won Eom, Ja Yeun Koo, Byoung Lok Park, Hyun Soo Park, In Sook Sohn
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2021; 25(3): 153. CrossRef - Efficacy of a footbath for post‐partum fatigue in South Korea: A quasi‐experimental study
Eunsun Choi, Eunju Song
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2017; 14(2): 126. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promoting Behavior in Postpartum Women at Sanhujoriwon
Hyekyung Choi, Namok Jung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(2): 135. CrossRef - Patterns and Factors associated with Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use among Korean Postpartum Women
Ju Hee Kim, Hye Sook Shin, So Young Kim, Hye Kyung Lee, So Hee Lim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Perceptions and Challenges
Juyeon Son
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2016; 27(3): 241. CrossRef - A qualitative review of immigrant women's experiences of maternal adaptation in South Korea
Ju-Eun Song, Jeong-Ah Ahn, Tiffany Kim, Eun Ha Roh
Midwifery.2016; 39: 35. CrossRef - Effects of Laughter Therapy on Immune Responses in Postpartum Women
Kyung Hee Ryu, Hye Sook Shin, Eun Young Yang
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine.2015; 21(12): 781. CrossRef - Effects of a Newborn Care Education Program using infant model
Hyemin Hwang, Juok Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(6): 3805. CrossRef - Effect of Intervention Programs for Improving Maternal Adaptation in Korea: Systematic Review
Ju Eun Song, Jeong Ah Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2013; 19(3): 129. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Postpartum Stress, Postpartum Depression, Postpartum Discomfort and Postpartum Activity, Between Women who Used and those Women did not Used Sanhujori Facilities
김민아, Choi so young
JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY OF MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH.2013; 17(2): 184. CrossRef - The Changing Pattern of Physical and Psychological Health, and Maternal Adjustment Between Primiparas Who Used and Those Who did Not Use Sanhujori Facilities
Ju-Eun Song, Bo-Lim Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 503. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Neonatal Infections in Full-term Babies in South Korea
Hye Sun Yoon, Youn Jeong Shin, Moran Ki
Yonsei Medical Journal.2008; 49(4): 530. CrossRef
- The Operational Status of Postpartum Care Centers and Application of Family-Centered Care in South Korea’s Era of Ultralow Birth Rates
- 755 View
- 2 Download
- 14 Crossref

- A Comparative Study on Climacteric Symptoms of Natural Menopausal Women and Artificial Menopausal Women
- Hyun Sook Jo, Kun Ja Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(4):692-702. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.4.692
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: To extend the understanding on climacteric symptoms, and to improve women's health and the quality of life by providing the basic data relating to the climacteric symptoms of natural menopausal women and artificial menopausal women.
METHOD
The subjects of this study were 149 women selected conviniently (89 natural menopausal women and 60 total hystrectomy women) who have visited the climacteric clinic of G. hospital in Inchon, the MENSI questionnaire which was developed by Sarrel (1995)was modified considering Korean culture for the measuring tool of this study with 20 items of question(Cronbach'salpa =.76), duration of data collection with the questionnaire was 5 months from Sept. 1, 2000 to Jan. 30, 2001.
Result
Artificial meanopausal women showed statistically significant higher menopausal symptoms than the natural menopausal women in the most of the items, and psychiatric and urogenital symtoms of artificial menopausal women were significantly higher than those of the natural menopausal women.
CONCLUSION
Nursing intervention for psychological support upon artificial menopausal women and their spouses is recommended more than natural menpause women.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing quality of life in post-menopausal women
Hyunsook Shin, Eunjoo Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(4): 336. CrossRef - Regular Leisure-Time Physical Activity is Effective in Boosting Neurotrophic Factors and Alleviating Menopause Symptoms
Boram Kim, Sunghwun Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(22): 8624. CrossRef - Effects of an Aging Management Program for Middle-aged Women on Resilience and Successful Aging
Hyeyun Jung, Kyung Mi Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 392. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Adaptation to Menopause in Middle-aged Women
Eun Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 336. CrossRef - The Effect of Emotional Freedom Technique(EFT) as Forest Therapy Program on the Menopause Symptoms and the Quality of Life of the Middle - aged Women
김홍규, 구창덕, 연평식, 이연희
The Journal of Korean institute of Forest Recreation.2016; 20(3): 83. CrossRef - Effect of Light Therapy on Sleep Disturbance and Depression in Climacteric Women
Yun Ah Kim, Mi Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(3): 197. CrossRef - Impact of Climacteric Symptoms and Fatigue on the Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: The Mediating Effect of Cognitive Dysfunction
Gyung Duck Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(2): 58. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Cognitive Function on Climacteric Symptoms and Quality of Life in the Middle-aged Women
Jeong-Hwa Lee, Kyung-Hae Kim, Gyung-Duck Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(7): 4439. CrossRef - Comparison of Climacteric Symptoms and Cognitive Impairment in Breast Cancer Survivors and Healthy Women
Gyung Duck Kim, Bok Yae Chung, Kyung Hae Kim, Hye Sun Byun, Eun Hee Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2013; 13(1): 11. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Self-Identity and Menopausal Symptoms on Level of Depression in Middle Aged Women
Mi-Jeong Han, Ji-Hyun Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2013; 19(4): 275. CrossRef
- Factors influencing quality of life in post-menopausal women
- 734 View
- 22 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Depression Among Korean Women
- Kyung Rim Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):391-400. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.391
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine depression in order to identify and improve health care policies promoting health among Korean women. METHOD: There were 329 participants, all older than 18 years old, and staying in Kyungki-Do, city. The data was collected from July to September 1999. The instrument used for this study was the CES-D (Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale) to evaluate depression. The collected data was analyzed with frequency, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, X2-test and Multiple logistic Analysis. RESULT: The result of this study are as follows: 1. Among the participants, 90.6% had normal to mild depression and 9.4% had severe depression. 2. For general characteristics, there were significant difference in the degree of depression according to age(P=0.0001), and marital status(P=0.0001). As for health related characteristics, the depression scores were affected by health perception(P= 0.0001), menopause(P=0.0005), stress (P= 0.0001) and sexual activity (P=0.0001). 3. There was a significant relationship between marital status and stress. CONCLUSION: This study suggests that a replicate study is needed. The results are also is useful in developing various nursing intervention programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Work–Family Conflict on Depression Among Korean Women During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Moderated Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction
Hyo Sung Cha, Jin Pyo Lee
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 923. CrossRef - The Impact of Sleep Quality and Education Level on the Relationship between Depression and Suicidal Ideation in Parents of Adolescents
Ji Yeon Shim, Sook Lee, Il Hyun Lee, Yoo Mi Jeong
Healthcare.2021; 9(9): 1171. CrossRef - Efficacy of Cognitive Behavioral Treatment for Insomnia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Ok Kyung Ham, Bo Gyeong Lee, Eunju Choi, Su Jung Choi
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 42(12): 1104. CrossRef - Black Tea Intake in Relation to BMI and Depression in Adult Women
You-Mi Jung, Mi-Ja Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(5): 436. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire to Estimate the Intake of Fatty Acids
Seon-Joo Park, Changho Lee, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(3): 239. CrossRef - Behavioral Characteristics and Cardiovascular Disease Risks Associated With Insomnia and Sleep Quality Among Middle‐Aged Women in South Korea
Ok Kyung Ham, Jinyoung Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee, Eunju Choi
Research in Nursing & Health.2017; 40(3): 206. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-esteem and Family Stress on Depression of Middle-aged Couples: Analysis of Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Yu Jeong Yang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 60. CrossRef - Influence of Spiritual Wellbeing and Social Support on Depression in Middle-aged Women
Je Eun Heo, Young Sook Tae
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 181. CrossRef - Comparison of Stress, Depression and Suicidal Ideation between Nursing Students and Students of Other Majors
Sun Kyung Cha, Eun Mi Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(4): 650. CrossRef - The Effects of Job Stress with Depression and Fatigue of Firemen
Kwang-Seok Kim, Jong Park, Bu-Yeon Park, Sung-Gil Kim, Eun-Yeong Hwang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(3): 223. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Self-Identity and Menopausal Symptoms on Level of Depression in Middle Aged Women
Mi-Jeong Han, Ji-Hyun Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2013; 19(4): 275. CrossRef - Beliefs and Attitudes toward Intimate Partner Violence and Depression in Victims of Intimate Partner Violence Dwelling in the Community
Young Ran Han
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(3): 532. CrossRef - A Path Analysis: A Model of Depression in Korean Women With Breast Cancer-Mediating Effects of Self-Esteem and Hope
Young Sook Tae, Margaret Heitkemper, Mi Yea Kim
Oncology Nursing Forum.2012; 39(1): E49. CrossRef - A comparison of the health and related quality of life between middle‐aged Korean and Chinese women
K.‐B. Kim, S.R. Sok
International Nursing Review.2010; 57(4): 463. CrossRef
- The Impact of Work–Family Conflict on Depression Among Korean Women During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Moderated Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction
- 734 View
- 1 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Pain of Elderly Women with Osteoarthritis
- Jae Shin Shin, Hye Gyung An, Hyang Mi Kim, Youn Ja Yoo, Kyung Hee Kim, In Kyung Chong, Yun Mi Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(2):180-193. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.2.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to determine the meaning of the pain and experiences of elderly women with osteoarthritis, by adopting Colaizzi's phenomenological method. The participants were 7 elderly women over the age of 65. They were selected using a theoretical sampling technique. The Data was collected by in-depth and open-ended interviews from Dec. 1. 1999. to Feb, 28. 2000. The length of the interviews varied from 120 minutes to 180 minutes. Data was recorded and analyzed by a constant comparative
method
. From the data, significant statements were extracted and then organized into 48 themes, which resulted in 15 clusters of themes and 6 categories. The final descriptions turned out to be valid through the interviewee' validation process. Essential themes of the pain experiences emerged : "physical discomfortness(disturbances)", "negative state of mind", "influence of the death", "positive change in life", "Cause of pain perceived", and "change of their personal relationships". From these results, it was found that elderly women need nursing care based on a deep understanding of pain, and a reflection on their past is imperative to overcome their given situations. In conclusion, it is suggested that the care givers provide more support to solve the problems experienced by the elderly. Thus the researchers expect to provide understanding of older people and give basic data of holistic care for them.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors related to Life Satisfaction in Young-Old, Old, and Oldest-Old Women
Kae-Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 21. CrossRef - Reconstructing a Meaning of Pain: Older Korean American Women's Experiences with the Pain of Osteoarthritis
Geri L. Dickson, Jong Im Kim
Qualitative Health Research.2003; 13(5): 675. CrossRef
- Factors related to Life Satisfaction in Young-Old, Old, and Oldest-Old Women
- 616 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Influencing Factors on the Quality of Job Role of Married, Working Women in Korea
- Eun Ok Park, Kyung Ja June
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(7):1697-1708. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.7.1697
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The labor participation rate of women are increasing, especially for married and 30 and over aged women in Korea. The employment of married women occurs dual-role problems. But recent empirical evidences suggest that employment yields a net gain of benefits over costs with respect to both physical and mental health for women as well as men. Previous researches suggested that the quality of the role or role satisfaction, not the occupancy of the role, is one of the predictors of psychological health. The purpose of this study is to investigate influencing factors on quality of job role for Korean women with children and husband. Data were collected from 323 mothers of students at 3 kindergartens, 2 elementary schools, 3 middle schools, 4 high schools in metropolitan area, during 1998.8 - 1998.12. they were dual-earner couples, and were employed over one year. Response rate is 62.3%. Quality of role was measured using Role Quality Scale developed by Park, June & Kim(1999). This instrument is based on Role Rewards and Concerns Scale of Barnett et al.(1993) for quality of job role. Quality of job role is made of 27 items and the subfactors are interpersonal relationship, job stress, pride, payment, and autonomy. Scales have good internal consistency(Cronbach ??= 0.86). The findings of this study show that personal income, occupation, husband's attitude for wife's employment, and the perceived equity for labor division between couples are significant variables for quality of job role. But age, education, career years, working hours per week are not significant. 24.83% of the variance in quality of job role were accounted for by these variables.
- 429 View
- 0 Download

- Influencing Factors on Symptoms of Stress of Middle Aged Women
- Kuem Sun Han, Pyoung Sook Lee, Yong Mi Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1427-1436. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1427
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify the influencing factor on Symptoms of Stress of Middle Aged Women. The subjects of this study were 35 middle aged women who lives in Seattle, Washington in U.S, and 74 middle aged women who lives in Seoul. Data collection was performed at the University of Washington and Seoul from Oct. 1998 to May. 1999. Data collected through 4 types of questionnaires : SOS, Ways of Coping, Mood Status, Perceived Stress. The results of this study are as follows: 1. The stress symptoms showed positive correlation with emotion-oriented coping, mood status, and perceives stress. 2. Stepwised multiple regression analysis revealed that most powerful predictor of Stress Symptoms was mood status. A combination of perceived stress, mood status and ways of coping account for 64% of the variance in Symptoms of stress in Middle aged women. From the results of the study, the following recommendations are presented as follow: 1. It is necessary to replicate this study with a larger sample. 2. It is necessary to develop a stress management program focused on ways of coping, mood status, perceived stress for middle aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Menopausal stage transitions and associations with overall and domain-specific perceived stress in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Sang Won Jeon, Junhee Park, Byungtae Seo, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Maturitas.2025; 200: 108660. CrossRef - The relationship between psychological distress, depressive symptoms, emotional eating behaviors and the health-related quality of life of middle-aged korean females: a serial mediation model
Jihyun Oh, Sunghee Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Forest Therapy on Health Promotion among Middle-Aged Women: Focusing on Physiological Indicators
Bum-Jin Park, Chang-Seob Shin, Won-Sop Shin, Chung-Yeub Chung, Si-Hyung Lee, Dong-Jun Kim, Youn-Hee Kim, Chang-Eun Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4348. CrossRef - The Effect of walking exercise on the improvement of housewives' Self-esteem, Stress, Depression in terms of convergence
Hae-Mi Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(12): 453. CrossRef - Development of the Perceived Stress Inventory: A New Questionnaire for Korean Population Surveys
Eon Sook Lee, Ho Cheol Shin, Jun Hyung Lee, Yun Jun Yang, Jung Jin Cho, Gwiyeoroo Ahn, Yeong Sook Yoon, Eunju Sung
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2015; 36(6): 286. CrossRef - Study of on Academic Stress Responses According to Sasang Constitutions of Oriental Medicine College Students
Jun-Yong Chang, Kyoung-Shin Kim, Byoung-Soo Kim
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2012; 23(3): 77. CrossRef
- Menopausal stage transitions and associations with overall and domain-specific perceived stress in middle-aged Korean women
- 750 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- The Psychological Effect of Hand and Arm Massage on Middle-Aged Women
- Hee Jung Jang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1389-1399. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1389
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Massage therapy is a traditional, alternative and nonphamacological means of promoting rest and relaxation. However, nursing intervention by massage for middle-aged women is rarely practiced by nurses. The purpose of this research was to examine the effects of the hand and arm massage as an independent nursing intervention tool for middle- aged women. The data used in this research were collected from forty-nine subjects using a nonequivalent control group non- synchronized design. Twenty-four persons for the experimental group and Twenty-five persons for the control group were selected from D city and C city from July 1997 to September 2000. Subjects' ages were between forty and fifty-six years old with mean the age of 45.6. Hand and arm massage developed by Cayce and Reilly was applied to the experimental group for a session of 15 minutes two or three times a week for four weeks. The instruments used for the measurement of the subjects' stress, anxiety, depression and the middle-life crisis were Langners's 22-item Screening Score, Spielberger's State Anxiety Inventory, Zung's Self-rating Depression Scale, and Kim's Middle Life Crisis Scale(1988). These psychological factors were measured before and after the implementation of hand and arm massage. The data were analyzed with mean+/-s.d, percent, t-test, and a paired t-test. The results were summarized as follows; 1. Before the treatment, there were no significant differences between the two groups. 2. After the treatment, there were significant differences in the stress and the occurrence of mid life crisis between the two groups. The findings suggest that the use of the hand and arm massage for middle-aged women made significant changes in the level of stress and middle life crisis. Therefore, it is recommended that hand and arm massage be used as an independent nursing intervention tool for middle-aged women. For further research, is needed replication of this concept of research with different subjects in a larger population. Also, it is recommended to investigate the effects of massage with aroma therapy for the berefit of decreasing womens' stress level further.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Sorusangzi Massage on Stress, Fatigue, and Depression in Middle-aged Working Women
Ji On Park, Yun Hee Son, Eun-Hwa Ju
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2017; 15(1): 55. CrossRef - Research Trend on Aromatherapy for Korean Middle-aged Women
Hee-Jung Yong, Hyun Hee Jang, Sung Nae Lee, Soo-Yeon Kim, Young-Sam Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2017; 15(1): 113. CrossRef - Analysis of Studies on Hand Massage Published in Korea: On the Effects of Sleep, Pain, Anxiety and Depression
In-Ja Kim, Yu-Na Cho
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Effects of Hand Holding on Self-esteem and Assertiveness in Women Patients with Depression
Mi-Hae Sung, Mi Young Choi, Ok Bong Eum
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 154. CrossRef
- Effects of Sorusangzi Massage on Stress, Fatigue, and Depression in Middle-aged Working Women
- 986 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Pregnant Women's Attitude and Satisfaction for Sexuality
- Young Pyo Lee, Shin Jeong Kim, Geum Hee Jeong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(5):1292-1302. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.5.1292
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The relationship between the attitude and satisfaction for sexuality of pregnant women was observed to provide rationales of nursing intervention to help promote healthy sexual lifestyles. Questionnaires were collected from 211 obstetric outpatients of H university hospital in C city, Korea from February to May 1999. The research tools were D.S.F.I (Derogatis Sexual Function Inventory in Korean, Chronbach's alpha= 0.710) and Sexuality Satisfaction Method (Kim, 1997, Chronbach's alpha =0.864). Data was analyzed for frequency, mean, standard deviation, Pearson correlation, t-test and ANOVA by Windows SAS. The results of this study were as follows: Mean age of the subjects were 29.8; the average score of attitude to sex was moderate (27.60), and that of satisfaction sex was high (54.11); the positive relationship was shown between attitude and satisfaction for sexuality (r=0.51, p=.000); the higher educational and income levels of pregnant women and their husbands, were the better the attitude and satisfaction for was; professional women had better attitude than housewives. According to the results, it is suggested that the study is necessary to develop an effective nursing intervention related with the sexuality of pregnant women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of pregnant couples’ attitudes towards sex during pregnancy on sexual function
Moon Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 161. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Sexual Function of Pregnant Women
Eun Jung Oh, Moon Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(1): 73. CrossRef - Impact of Sexual Attitude and Marital Intimacy on Sexual Satisfaction in Pregnant Couples: An Application of the Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Hee Eun Kim, Jung Hee Yeo
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(3): 201. CrossRef - Factors Related to Female Sexual Dysfunction of North Korean Women Defectors
Young Sun Rhee, Hye Wan Ku, In Young Han
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(2): 55. CrossRef
- Influence of pregnant couples’ attitudes towards sex during pregnancy on sexual function
- 717 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Model Development a Womens' Health Care Center in the Community
- Eun Hee Lee, Ae Young So, Sang Soon Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(5):1195-1206. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.5.1195
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to analyze womens' health problems using Green & Kreuter's 1991 PRECEDE model and to develop a model for a womens' health care center located in the community. The subjects were recruited from Wonju City. 1. The results showed that 23% of the sample population felt there was a need for a womens' health care center. The mean number of health problems was 3.1. The prevalence rate, was 44.4%, and the rate for an artificial abortion, was 36.4%. Also 30.5% did not have a health examination in the past year. Women using the hospital for medical care accounted for 45% of the sample, while 40% used the drugstore. The average score on the HPLP was 2.41, and this was influenced by self-efficacy, family support, sexual role, and health locus of control. There are a few educational programs in the city provided by the Wonju Health Center and by community health nurse practitioners. 2. The nursing center, as defined in North America, is a nurse-anchored system of primary health care delivery or neighborhood health center. Centers offer various services ranging from primary care to the more traditional such as education, health promotion, wellness screening, and coordination of services by advanced practice nurses. For examples in Sweden MCH centers provide total services for childbearing women and their families, sexual counseling and education for adolescents, and screening by midwives for cervical cancer. 3. The developed model combines purpose, target population, organization, and services, and is related to health resources. The purpose is primary health care and promotion of the quality of life. The target population can be grouped according to the life cycle, (premarriaged age group, the childbearing/child rearing age group, and middle aged and elderly women) and focuses on self-help. The organization of the center includes an advisory committee to plan and evaluate, and a health services team that will be multidisciplinary to provide health care, counseling education, and research. The model development suggested that a variety of women's health care centers are needed to insure adequate management of women's health. Follow-up research using PROCEED is needed to analyze health outcomes. Also a health nursing specialist system is required to develop health promotion, and improve the quality of life of women.
- 465 View
- 0 Download

- Lived Experience of Women's Urinary Incontinence in Small Island
- Myung Hee Lee, Kyoung Rim Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):799-812. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.799
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study adopts the phenomenological approach in order to explore the experience of urinary felt by the small island women and to find the meaning and structure of their experience, for the further understanding of them. This study succeeded in detecting five topics and three basic structure from eight participants, and followings are the comprehensive statement of them. The five topics include neglect of care after childbirth, unavoidable life in the tidal flat, shame which cannot be expressed even to their husbands, endless anxiety toward the expected future, and sad(dilemmatic) lived experience. The basic structure is that small island women who have urinary incontinence are apt to regard their disease as a natural destiny of women who fail to get adequate care after childbirth, and something to be endured to live in the seashore. They think of urinary incontinence as something so shameful that they cannot reveal it even to their husband and family. They believe that it even changes their personality since they must always stay alert in order to cope with the situation; for example, when it takes place unexpectedly, like too often to go to toilet, to change the underwears, to wake up in the middle of the night to go to toilet, to try not to laugh loudly, or to have showers. In addition, they accept it as a natural process of aging and incurable disease, and they consider themselves already ruined on the way of becoming uglier. They show dilemmatic abandonment: give it up unwillingly but at the same time think it is natural for others too. The unique experience of small island women with urinary incontinence implied in those statement are inseparable with the specific conditions for survival in the island. Unlike other diseases, it is considered the result of traditionally poor care after childbirth. However this misunderstanding that it is a natural phenomena for all the women who experience childbirth and aging and thereby incurable leads to an undesirable attitude toward urinary incontinence. According to the analysis, environmental conditions specific for small islands make the women there have distinct and unique experience concerned with urinary incontinence. Consequently, the future nursing plan for urinary incontinence in the small island area must be made and enforced with the consideration of these specific phenomenological meanings. Modern Korean nursing has basically been centered to hospital or urban areas. Besides, nursing intervention has long depended upon the research of western countries. This research, however, shows how greatly the regional and cultural characteristics influence the understanding of a certain disease, and is expected to make more specific and in-depth nursing approach enable for those who have urinary incontinence in small islands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experience of Urinary Incontinence in Elderly Women in Urban Areas
Min Ryu, Haeyun Shin, Miseon Bang, Suhye Kwon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(3): 213. CrossRef - Effect of Moxibustion at Junggeuk(CV3), Singwol(CV8) on Women's Urinary Incontinence and Quality of Life
Eun-Sook Lee, Yi-Soon Kim, Jeong-Won Lee, Mi-Jung Oh, Gyeong-Cheol Kim
Korean Journal of Acupuncture.2013; 30(3): 193. CrossRef - Prevalence of urinary incontinence in older Korean women
Aeyoung So, Jennie C De Gagné, Mary H Palmer
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2012; 6(2): 51. CrossRef - Effects of an Incontinence Prevention Program on Postpartum Women
Nam Ok Jeong
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(3): 177. CrossRef
- Experience of Urinary Incontinence in Elderly Women in Urban Areas
- 712 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


