Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Paper
- Triglyceride-glucose parameters as predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults: a secondary analysis of a Prospective Cohort Study
- Yu Jin Park, Miseon Shin, Hyun Seon Jeon, Eun Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):205-221. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the association between triglyceride-glucose (TyG)–related parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus in Korean adults. Data were obtained from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES).
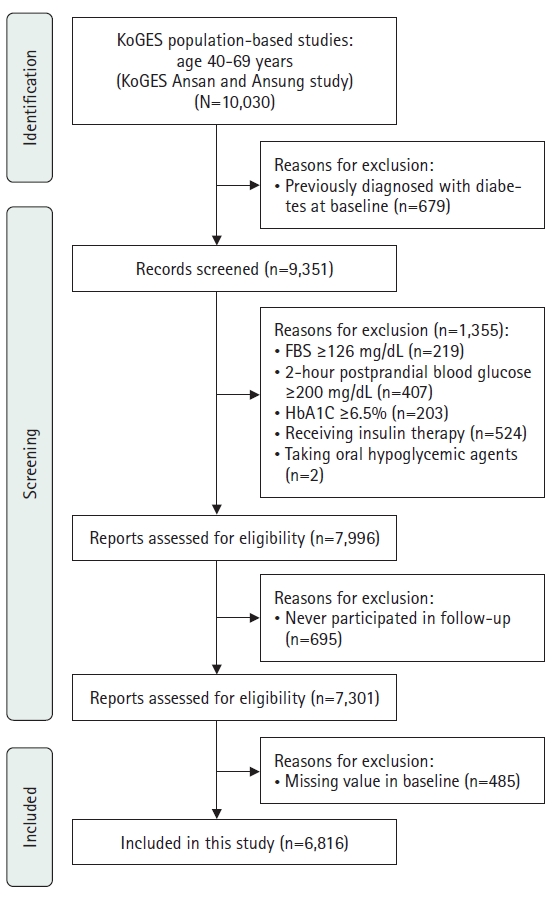
Methods
This secondary analysis examined data from 6,816 adults aged 40–69 years who participated in the KoGES from 2001 to 2020. TyG–related parameters, including the TyG index, TyG–body mass index (TyG–BMI), TyG–waist circumference (TyG–WC), and TyG–waist-to-height ratio (TyG–WHtR), were assessed. Cox proportional hazards models were employed to determine the association between these parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus, with adjustments made for demographic, lifestyle, and health-related characteristics.
Results
Higher levels of all TyG–related parameters were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus. Specifically, participants in the highest quartile of the TyG index, TyG–BMI, TyG–WC, and TyG–WHtR exhibited significantly higher hazard ratios for diabetes mellitus incidence compared with those in the lowest quartile (p<.001 for all). Notably, the TyG index demonstrated a stronger predictive value for diabetes mellitus than traditional measures such as the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance.
Conclusion
TyG–related parameters are robust predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults. These findings support the incorporation of TyG–related measures into clinical settings for the early identification and intervention of high-risk populations. Utilizing these parameters for early diagnosis and preventive strategies may significantly enhance diabetes mellitus management.
- 2,439 View
- 154 Download

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 First
First Prev
Prev


