Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development of a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission after kidney transplantation: a retrospective study
- Hye Jin Chong, Ji-hyun Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):528-542. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and validate a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission (EHR) post-kidney transplantation.
Methods
The study was conducted at the organ transplantation center of a university hospital, utilizing data from 470 kidney transplant recipients. We built and trained four machine learning models and tested them to identify the strongest EHR predictors. Predictive performance was evaluated using confusion matrices and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC AUC).
Results
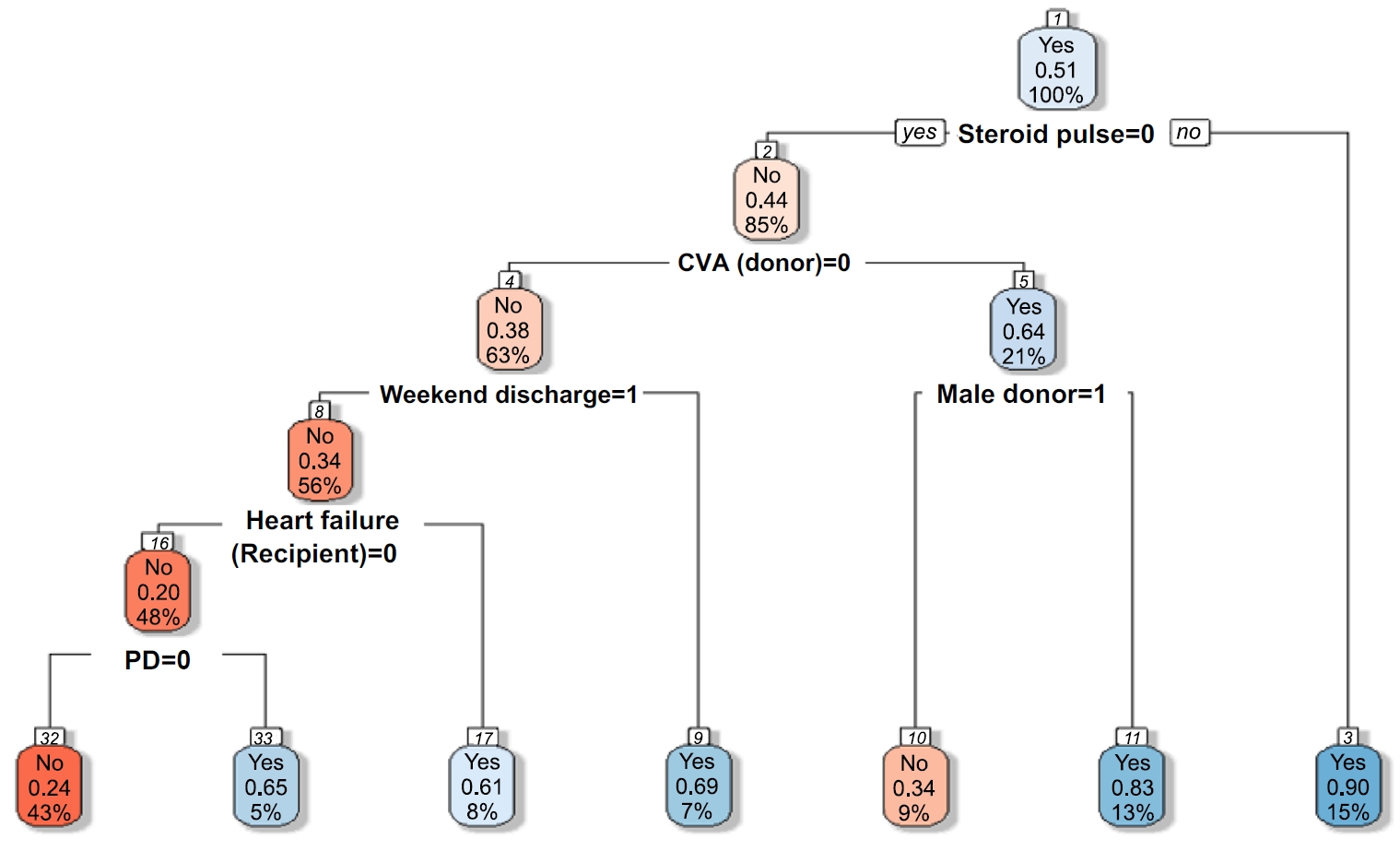
Among the 470 kidney transplant recipients with a mean age of 46.1 ± 12.02 years, 322 (68.5%) were males, and 74 (15.7%) were readmitted within 30 days after kidney transplantation. In total, 241 (51.2%) recipients were found to have experienced EHR after applying the random over-sampling examples method. The random forest model achieved the best performance, with an ROC AUC of .87 (validation set) and .82 (test set). The 15 most important features were steroid pulse therapy (recipient), cerebrovascular accident (recipient), heart failure (recipient), male sex (donor), cardiovascular disease (recipient), weekend discharge (recipient), peritoneal dialysis (recipient) cerebrovascular accident as the cause of brain death (donor), current smoker (recipient), cardiac arrest (donor), previous kidney transplantation (recipient), age (donor), hypertension (donor), male sex (recipient), and dialysis duration (recipient).
Conclusion
Our framework demonstrated strong predictive interpretability. It can support appropriate and effective clinical decision-making by assisting transplant professionals in stratifying recipients based on their risk of EHR. prioritizing post-discharge care and follow-up for high-risk individuals, and allocating targeted interventions such as closer monitoring or education.
- 1,193 View
- 164 Download

- Lived Experience of Kidney Transplant Recipients with Kidney Graft Failure
- Younghui Hwang, Kyoungok Min, Haeng-Mi Son
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):93-105. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The study aimed to understand the semantic structure and nature of the disease experience of kidney transplant recipients with kidney graft failure by applying phenomenological research methods.
Methods
Data were collected between February and September 2021 through individual in-depth interviews with 12 kidney transplant recipients with kidney graft failure. Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis was used to analyze the meaning of the participants’ illness experiences.
Results
5 theme clusters and 15 themes were derived. The five theme clusters are as follows: (1) First transplant giving me a second life; (2) Body and mind becoming sick again; (3) Waiting for a re-transplant with hope and worry; (4) Life supported by gratefulness; (5) Having control over my own life.
Conclusion
This study shows that kidney transplant recipients with kidney graft failure experience physical and psychological difficulties during the long disease period and require help from many people, including family members, friends, colleagues, and health care providers, to overcome their difficulties.
- 1,320 View
- 57 Download

- The Caring Experience of Family Caregivers for Patients of Living Donor Liver Transplantation from the Family Members
- Miseon Bang, Suhye Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):435-450. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22043
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of the study was to understand the care experiences of the family of living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) patients where the donation had occurred within the family.
Methods
Participants were eight family caregivers who cared for recipients and donors of LDLT. Data were collected through individual in-depth interviews from November, 2020 to April, 2021. Data analysis was performed through a cyclical process of data collection and analysis by applying Giorgi’s phenomenological research method.
Results
The five main components extracted from the experiences of the family caregivers were: "A double-edged choice to save the family", "The harsh daily life of liver transplantation care", "The yoke of double care on both shoulders", "The power to withstand the adversity of caring", and "The recovery and growth of life pursued by trusting each other".
Conclusion
The participants tried to do their best in their daily lives, while providing reassurance and care to the LDLT patients in the family; however, they expressed some worry and hardship while doing so. The results of this study provide a deeper understanding of the caring experience of the family caregivers, which may contribute to the development of nursing interventions that will aid these caregivers in providing care to their LDLT family members. Furthermore, the development and application of an integrated management program for LDLT patients in the family is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenges and support needs among family caregivers involved in solid organ transplant care process: a scoping review protocol
Shi He, Ningbin Huang, Meiqi Lai, Wenwen Li, Siting Chen, Guolong Zhang, Danxia Huang, Guilin Peng, Ying Huang, Liang Ruan
BMJ Open.2025; 15(3): e086771. CrossRef
- Challenges and support needs among family caregivers involved in solid organ transplant care process: a scoping review protocol
- 2,209 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Young Adult Donor’s Experiences of Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- Miseon Bang, Haeyun Shin, Min Ryu, Suhye Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):105-118. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to explore young adult donors’ experiences of living donor liver transplantation.
Methods
A phenomenological research method was used. The participants were two women and six men. Data were collected through individual in-depth interviews from November 25th, 2019 to June 10th, 2020 and analyzed using Colaizzi’s phenomenological method.
Results
Five theme clusters extracted from the young adult donors’ experiences were painful decision of a liver donation, the agony of both mind and body that overpowers youth, the bitter and bare face of reality that a young donor encounters, feeling the power of love that fills up the space of the organ removed, and liver donation becoming priming water for maturity.
Conclusion
The results of this study provide a deeper understanding of the lives of young adult donors who have experienced unexpected difficulties as well as self growth from the donation. It is expected that the results can be of use for developing and applying customized nursing interventions for management before and after liver donation among young adult donors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Giving as repaying: towards an embodied ethics of living donor liver transplantation
Ya-Ping Lin, Huei-Ya Chen
Medicine, Health Care and Philosophy.2025; 28(3): 517. CrossRef - Research Trends on Living Donors for Liver Transplantation: A Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Seongmi Choi, Mihui Kim, Won Jin Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(2): 157. CrossRef - Living well or not? Quality of life of parental living liver donors: A cross‐sectional study
Xiaxin Wu, Jing Chen, Yaru Fan, Yuexian Shi, Wei Gao
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(15-16): 5113. CrossRef - The Caring Experience of Family Caregivers for Patients of Living Donor Liver Transplantation from the Family Members
Miseon Bang, Suhye Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(4): 435. CrossRef - The life experiences of living liver donors: A qualitative meta‐synthesis
Hye‐Young Jang, Hyei Yeon Im, Hye Jin Nam
Research in Nursing & Health.2022; 45(6): 693. CrossRef
- Giving as repaying: towards an embodied ethics of living donor liver transplantation
- 1,808 View
- 17 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Nutritional Status of Liver Transplantation Recipients and Factors Influencing Nutritional Status
- SinYoung Hwang, Smi Choi-Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):340-348. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.340
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to investigate the nutritional status of liver transplantation (LT) recipients and explore certain factors that influence nutritional status, including dietary patterns and physical activities.
Methods This was a cross-sectional, descriptive study. The subjects included 211 LT recipients at a medical center outpatient clinic located in Seoul, Korea. The nutritional status, dietary patterns, and physical activities of each subject were measured using the body mass index (BMI), Mini Dietary Assessment (MDA), and Global Physical Activity Questionnaire. Independent t-test, one-way analysis of variance, and multiple linear regression analysis were used to analyze the data.
Results The percentages of living and deceased donor LTs were 81.0% and 19.0%, respectively. The mean BMIs pre- and post-LT were 23.88 and 23.16 kg/m2, respectively, and the average MDA score was 36.55. More than 60.0% of the subjects had a moderate or high level of physical activity. In multivariate analysis, a higher BMI before LT (β=.72,
p <.001), a lower Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (β=-.18,p <.001), and being male (β=-.10,p =.024) contributed to better nutritional status post-LT. Patients within six months of LT were less engaged in muscle exercises than those post six months of LT (p =.020).Conclusion LT recipients in Korea have good nutritional status and a good level of physical activity. To improve recipients’ post-LT nutritional status, the pre-LT nutritional status should be considered, particularly in those with a higher MELD score. In addition, physical activity including muscle-strengthening exercises should be encouraged from an earlier stage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional Intake after Liver Transplant: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Lynsey N. Spillman, Angela M. Madden, Holly Richardson, Fumiaki Imamura, Danielle Jones, Marilyn Nash, Hong Kai Lim, Holly N. Hellawell, Kirsten L. Rennie, Linda M. Oude Griep, Michael Allison, Simon J. Griffin
Nutrients.2023; 15(11): 2487. CrossRef - Impact of Self-esteem and Social support on Self-care Performance in Liver Transplantation Recipients
Hyun Jung Jung, Young-Ju Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 23(2): 132. CrossRef
- Nutritional Intake after Liver Transplant: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,105 View
- 14 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling of Self-Care Behaviors in Kidney Transplant Patients Based on Self-Determination Theory
- Hye Won Jeong, Hyang Sook So
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):731-742. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.731
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to test a hypothesis explaining direct and indirect relationships among the factors affecting self-care behaviors of kidney transplant patients, based on self-determination theory.
Methods Data were collected from 222 outpatients with kidney transplantation. The endogenous and exogenous variables of the hypothetical model consisted of healthcare provider's autonomy support, duration after kidney transplantation, basic psychological need satisfaction, autonomous and controlled motivation, depression, and self-care behaviors. Collected data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 24.0 and AMOS 24.0.
Results The hypothetical model demonstrated a good fit: RMSEA=.06, SRMR=.04, TLI=.94, CFI=.97. Statistically significant explanatory variables for the self-care behaviors of kidney transplant patients were duration after transplantation and basic psychological need satisfaction. Healthcare provider's autonomy support was indirectly significant, while autonomous motivation, controlled motivation and depression were not statistically significant for self-care behaviors. The variables accounted for 59.5% of the self-care behaviors of kidney transplant patients.
Conclusion It is necessary to develop an autonomy support program for healthcare providers to enhance the self-care behaviors of kidney transplant patients. Preventing the deterioration of self-care behaviors will be possible by conducting this program at one year and six years post-transplantation. In addition, the results suggest the need to developing personalized autonomy support programs for healthcare providers that can meet the basic psychological need satisfaction of kidney transplant patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Sleep Disorder, Depression, and Resilience on Self-care Performance in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Eun-Young Hong, Hun Ha Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(3): 287. CrossRef - Associations between Health Literacy, Autonomy Support, and Health Behavior Adherence in Premature Coronary Artery Disease Patients: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Seong Rae Cho, Yeojin Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 436. CrossRef - Predictors of self-care in kidney transplant patients according to preoperative dialysis: A comparative study
Hyeiyeon Im, Hye-Young Jang
Heliyon.2024; 10(24): e40237. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of the Health Care Climate Questionnaire among Cancer Survivors
Hyun-E Yeom, Jungmin Lee, Young-Joo Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 323. CrossRef - Causal Model of Autonomous Motivation to Modify Dietary Behavior among People with Early-stage Chronic Kidney Disease
Anucha Taiwong, Tipaporn Wonghongkul, Chiraporn Tachaudomdach, Chomphoonut Srirat
Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 28(2): 280. CrossRef - Factors influencing the self-management of kidney transplant patients based on self-determination theory: a cross-sectional study
Mi Kyung Sim, Sun Young Son, Man Ki Ju
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2022; 36(1): 37. CrossRef - Factors associated with health-related quality of life in kidney transplant recipients in Korea
Younghui Hwang, Misook Kim, Kyoungok Min, Frank JMF Dor
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(3): e0247934. CrossRef - A Predictive Model of Sleep Quality of the Older Adults with Low Back Pain
Misoon Lee, Haejung Lee, Sookyung Hyun, Seon-Hwa Ban
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(4): 305. CrossRef - Feasibility and preliminary effects of a theory-based self-management program for kidney transplant recipients: A pilot study
Hye Won Jeong, Chi Eun Song, Minjeong An, Lucy E. Selman
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(6): e0248947. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Self-Care Behaviors of Renal Dialysis Patients
Yoonjung Kim, Sanggeon Park
STRESS.2019; 27(4): 320. CrossRef
- The Influence of Sleep Disorder, Depression, and Resilience on Self-care Performance in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,332 View
- 30 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- The Effects of an Empowerment Education Program for Kidney Transplantation Patients
- Sung Hee Kim, Hye Sook You
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(4):445-455. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.4.445
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop an Empowerment Education Program (EEP) for kidney transplant patients and to test the program's effects on uncertainty, self-care ability, and compliance.
Methods The research was conducted using a nonequivalent control group with a pretest-posttest design. The participants were 53 outpatients (experimental group: 25, control group: 28) who were receiving hospital treatment after kidney transplants. After the pre-test, patients in the experimental group underwent a weekly EEP for six weeks. The post-test was conducted immediately after, and four weeks after the program's completion in the same manner as the pre-test. For the control group, we conducted a post-test six and ten weeks after the pre-test, without and program intervention. A repeated measure ANOVA was performed to compare the change scores on main outcomes.
Results Uncertainty was significantly lower in the experimental group than in the control group, both immediately after (t=-3.84,
p =<.001) and 4 weeks after (t=-4.51p =<.001) the program, whereas self-care ability (t=5.81,p =<.001), (t=5.84,p =<.001) and compliance (t=5.07,p =<.001), (t=5.45,p =<.001) were significantly higher.Conclusion Kidney transplant patients who underwent an EEP showed a decrease in uncertainty and an improvement in self-care ability and compliance. Thus, our findings confirmed that an EEP can be an independent intervention method for improving and maintaining the health of kidney transplant patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-Management Interventions for Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review
Hyejin Lee, Chan Mi Kang
Healthcare.2025; 13(15): 1918. CrossRef - The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on quality of life, medication adherence, anxiety, and depression in kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Seung Yeon Park, Lee Hwa Kwak
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(3): 263. CrossRef - An integrative literature review of kidney transplantation knowledge tools
Chan Mi Kang, Hyejin Lee, Justyna Gołębiewska
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(1): e0281073. CrossRef - Empowering patients to self-control and self-management of anticoagulant therapy
Andreja Hrovat Bukovšek, Bojana Filej
Pielegniarstwo XXI wieku / Nursing in the 21st Century.2023; 22(2): 79. CrossRef - The Effect of Empowering Education Combined With Mindfulness Meditation Training on Negative Emotion and Quality of Life in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Wei-Zhen Xi, Chong-Wu Xu, Ling-Ling Wang
Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcomes of a nurse-led post-discharge education program for heart-transplant recipients: A retrospective cohort study
Ji Hyeon Lee, Seok-Min Kang, Young Ah. Kim, Sang Hui Chu
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 59: 151427. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of the Coronary Artery Disease Empowerment Scale (CADES) in Korea
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin, Kyungmi Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2021; 30(8): 1241. CrossRef - Development of a Mobile App-Based Self-care Health Diary for Heart Transplant Recipients
Hye Jin Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(11): 804. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Self-Care Behaviors in Kidney Transplant Patients Based on Self-Determination Theory
Hye Won Jeong, Hyang Sook So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 731. CrossRef
- Self-Management Interventions for Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review
- 1,461 View
- 19 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Subjectivity on Organ Donation and Transplantation
- Young Mi Kwon, Eun Ja Yeun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1437-1454. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1437
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to identify the attitudes of the people on organ donation and transplantation. The purpose of this study was to provide data to help inspire organ donation, and promote registration yield so donor candidates will have more favorable recipients through Q-methodology. A Q-sample was developed through a review of the literature and interviews. Thirty-three statements made up the final Q-sample. The P-sample consisted of twenty-eight subjects, excluding chronic organic disorder. The Q-sorts by each subject were coded and analyzed with the QUNAL computer program. The results were as follows: This study discovered five different types of organ donation and transplantation of twenty- eight subjects. Type I is 'utilitarian.' The people of this type consider human life very valuable and they recognize that organ transplantation is an affirmative medicine that should be performed to extend human life. They believe that are saving others' lives by donating organs. Type II is 'sardonist.' The people of this type approve of organ transplantation usefulness, but they have no intention of participating in the program because of it may trample on human rights. Type III is 'individualist.' The people of this type consider it proper for the activation of organ transplantation by the legal system. They believe that organ donation a valuable too, but needs support through social benefits to donors. Yet, they have not intention of doing what they propose. Type IV is 'familist.' The people of this type have strong attachments to life but they think that organ donation and transplantation should be done between within a family. Type IV is disposition of family intensive consideration rather than altruistic and utilitarianism. Type V is 'deontologist.' The people of this type recognize the benefits of transplantation, but have a negative opinion of activation. They worry about ethical and social problems occurring in the development of modern medicine. They believe that death is the only natural end to life, so they have strong negative opinions of euthanasia and brain death compared to other types. They regard transplantation to be a non-human behavior, because it involves a removing organs and breaking the boundary of death. The findings of this study are only preliminary and serve as a baseline to understanding the subjectivity of individuals on organ donation and transplantation. Therefore, the subjectivity of the five types will be applied to formulate the educational programs and public relations strategies for organ donation because the public's awareness toward organ donation is closely related to their values, beliefs, and attitudes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of an Organ Donation Education on Undergraduate Students' Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Will to Organ Donation
Jung Sook Kim, In Sun Jang
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2016; 22(2): 104. CrossRef
- The Effect of an Organ Donation Education on Undergraduate Students' Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Will to Organ Donation
- 755 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Learning Needs in Patients undergoing Bone Marrow Transplantation
- So Eun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):514-525. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.514
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The active treatment phase in preparation for bone marrow transplantation(BMT) of che- motherapy regimen and total body irradiation (TBI) containing regimen requires considerable teaching. There have been researches that are related to treatment onto BMT patients and to psychological change during BMT process. However, it was hard to find researches focused on learning needs of patients undergoing BMT. The purpose of this study was to provide the basic data for effective educational program about BMT by investigating the learning needs in patients undergoing BMT. The subjects consisted of 90 BMT patients who have been admitted to the department of BMT at three university hospitals. Data were obtained from October 1998 to March 1999 and analyzed by SAS program for unpaired t-test, ANOVA, Duncan test. The results were as follows : 1. Learning needs related to demographic characteristics was identified as below. That of male was higher than that of female. That of under age 29, unmarried, religious and university graduated group was higher than that of opposite group but it didn't show significant difference. Learning needs of group of patients who were employed was significantly higher then that of unemployed patients. 2. According to types of diagnosis, learning needs of myelodysplastic syndrome(MDS) patients was the higher than that of others, but admission frequency was the least. Learning needs of unrelated matched BMT(UBMT) patients was higher than that of autologous BMT patients. However, it didn't show significant difference. With regard to learning needs according to process of BMT, learning needs of Pre- BMT period or Post-BMT period was significantly higher than that of BMT day. 3. Learning needs related to BMT was relatively high (total mean: 3.11 of 4.0). The order of the mean score of leaning needs was shown as follows : Restricted activities after discharge, Relapse symptom, Complications of BMT, Kinds of available drugs at home. Therefore the learning needs that is related to life after discharge and to relapse and complications after BMT was high. 4. Learning needs related to radiation therapy was high (total mean: 3.35 of 4.0). The highest learning needs in radiation therapy items was the Skin care of radiation therapy and Purpose of radiation therapy. 5. Learning needs related to graft versus host disease(GVHD) therapy was high (total mean: 3.55 of 4.0). The highest learning needs in GVHD therapy items was the Preventive method GVHD. As the result above, individualized educational program is required for MDS patients who have less admission frequency and UBMT patients. It is necessary that education for BMT patients should be focused on life after discharge and on relapse and complications after BMT. Especially education for allogeneic BMT patients should be emphasized on GVHD. For all of these, it is necessary to develop systematic and concrete educational program.
- 445 View
- 0 Download

- Psychosocial Adjustment after Kidney Transplantation
- Myungsun Yi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):291-302. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.291
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this phenomenological study was to understand and describe the essence and the structure of lived experience of people with kidney transplantation. Initially, nine individual interviews were conducted to gather data regarding their subjective experiences. And two focus group interviews were utilized to validate or discard the themes that were emerged from the analysis using Colaizzi's method. Among 17 participants, 13 had living related kidney donations, one living unrelated, and the remaining two cadavor donations. About 130 significant statements were extracted and these were clustered into 11 themes. All participants felt anxiety and fear toward the rejection of transplantation and the complication of immunosuppressive drugs. Although they were initially satisfied with their life after kidney transplantation most of them lost a self-confidence and experienced loneliness, depression, and despair. Most of the participants also felt guilty for not being able to accomplish their appropriate roles in the family. They also had financial difficulties and social restrictions. However, they overcame these psychosocial distress by exercising, working and sharing love with others. They also could overcome it by living a religious life and by working to help others with kidney transplantations. Most of them felt gratitude toward the donor and did not have a psychological rejection toward the kidney transplanted. The results of the study might help nurses who work with people with kidney transplantations in establishing and implementing an effective nursing intervention by understanding their lived experience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on Dispatched Nursing during the Japanese Colonial Era
Sook Young Kim, Eunhyung Cho, Sun ei Joung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 138. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience of Living Kidney Donors after Donation
Da-Hai-Som Kang, Jinhyang Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(2): 271. CrossRef
- A Study on Dispatched Nursing during the Japanese Colonial Era
- 660 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A study of the current ethical situation in organ transplantations in Korea
- Sung Suk Han, Kyung Sig Hwang, Kwang Ho Meng, Dong Ik Lee, Young Rhan Um
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):26-36. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This primary study was done to develop an ethical guideline for organ transplantation, a life-saving treatment which helps improve the quality of life. This study tried to identify the current situation in Korea, in terms of ethical considerations in organ transplantations. This study collected basic data in organ transplantations, in the hope that procedure of organ transplantations could be developed that would be fair to both organ donors and recipients. The immediate goals of this study were : 1)to identify staff in charge of organ transplantations and their jobs in the hospital, 2) to survey whether there exists a Hospital Ethics Committee(HEC), 3) to research what consideration are formally taken in selecting recipients, and 4) to accumulate data on how consent from donors are currently obtained. The study used a survey questionnaire and received responses from 31 hospitals out of 45 hospitals where organ transplantation are being done. Organ transplantation coordinators were found in 16 hospitals, but the job description varied among hospitals. The survey showed that all 16 hospitals with and HEC that health care personnel unnecessarily dominate the committee. The study notes that HECs should be vitalized by recruiting, as members, ethicists, theologians, patients, guardians, as well as the general public outside of the hospital. The study revealed that in selecting recipients the hospital take into account ABO blood type, histocompatibility, age, waiting time, and level of patient compliance. Finally, it was shown that in the cases of living donors the transplanting hospitals seek a formal consent, whereas there are no common consenting practice established for cadaveric donors. The study concludes with three proposals. First, a nationwide institution responsible exclusively for procurement and distribution of cadaveric organs for transplantation should be established. Second, we should rebuild the national health insurance system so that have costly organ transplantation expenses are substantially covered. Last, but certainly not least, there is a need to emphasize the HEC's committment to prepare a proper ethical guideline for organ transplantation in general.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in the Organ Procurement System in South Korea: Effects on Brain-Dead Donor Numbers
S.D. Lee, J.H. Kim
Transplantation Proceedings.2009; 41(9): 3551. CrossRef
- Changes in the Organ Procurement System in South Korea: Effects on Brain-Dead Donor Numbers
- 634 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Experiences of Transplantation Coordinators' Practice
- Haeng Mi Son, Moon Hee Koh, Chun Mi Kim, Myung Sun Yi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(6):1012-1022. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.6.1012
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this phenomenological study was to understand the experiences in the transplantation coordinators' practice.
Method Data was collected through a tape-recorded in-depth interview from nine participants who were transplantation coordinators of their hospitals. It was analyzed using the phenomenological method proposed by Colaizzi(1978).
Results From significant statements, six categories of themes were integrated into the essential structure of the experiences of transplantation coordinators. Six categories of themes were ‘ continue to be professional during dash this way and rush that’, ‘ burden due to persistent heavy work’, ‘ the uniqueness in family care of the brain-dead patients’, ‘ support of family and a professional group’, ‘ worthiness and achievement of the patients' recovery’, and ‘ establishment of self-confidence as a coordinator’.
Conclusion Although the transplantation coordinators played various roles, they had a conflict in role identity due to poor working environments. The results of this study suggested that development of an educational program, an increase in understanding for the coordinators' role, and institutional support for better working conditions are needed to get professional acknowledgement for transplantation coordinators.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Organ Donation and Transplantation Coordinators' Experience and needs for ethics education
Jayoung You, Myoungsoo Kim, Sunyoung Son, Ilhak Lee
Nursing Ethics.2025; 32(2): 588. CrossRef - Effects of intolerance of uncertainty on turnover intention in transplantation coordinators: the roles of burnout and grit
Suran Lee, Kyung Ock Jeon, HyungSook Kim, Eun Kyoung Chung
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2020; 34(4): 265. CrossRef - The Mediating and Moderating Effect of Professional Self-concept in Relationship between Emotional Labor and Burnout of Organ Transplantation Coordinators
Ya-Ki Yang, Hye-Sook You
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(2): 158. CrossRef
- Organ Donation and Transplantation Coordinators' Experience and needs for ethics education
- 772 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Health Related Quality of Life among Organ Transplant Recipients
- Keum Soon Kim, Ji Yeon Kang, Ihn Sook Jeong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(3):365-375. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.3.365
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was aimed to investigate the health related quality of life and related factors of organ transplant recipients.
Method The participants were 188 people who had liver(86), kidney(81), or heart(24) transplanted. Data on the demographic characteristics, transplantation-related characteristics, symptom frequency or discomfort measured by Transplant Symptom Frequency and Symptom Distress Scale by Lough et al(1987), and health related quality of life measured by SF-36(version 2) were collected.
Result Overall health related quality of life score was 492.1 for 100scoring and, 344.9 for norm based. Physical functioning showed the highest quality of life score (77.5) and vitality showed the lowest(51.1). The kidney transplanted showed the highest quality of life (504.4) and the heart transplanted showed the lowest(426.7) Quality of life was related with occupation(p=.016) and symtom discomfort(p<.0001).
Conclusion The health related quality of life of transplated patients was lower than the norm of American. Further studies need to be done to identify the norm of Korean and to investigate the effect of releving symptom discomfort on the increasing the health related quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the quality of life of lung transplant patients
Byung Hee Hwang, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(3): 73. CrossRef - Microangiopathy is associated with bone loss in female type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
Ni Zhong, Youyang Zhang, Xiangling Pu, Bei Xu, Mingxin Xu, Haidong Cai, Ge Zhang, Ran Cui, Hui Sheng, Shen Qu
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2018; 15(5): 433. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Self-Management of Liver Transplant Recipients
Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 663. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Pre-dialysis patients with Chronic Kidney Disease at Glomerular Filtration Rates
Hye Won Kim, Smi Choi-Kwon
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(2): 82. CrossRef - The Quality of Life for Living Donors after Kidney Transplantation
Myoung Hee Kim, Oh Jung Kwon, Chong Myung Kang
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2012; 26(1): 15. CrossRef - Comparison of Anxiety, Depression, and Quality of Life between Organ Transplant Candidates and Recipients
Ji-Eun Cha, Myung-Sun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(3): 284. CrossRef - A Prediction Model Development on Quality of Life in Kidney Transplant Recipients
Hye Sook Kim, Hyang Sook So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 518. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the quality of life of lung transplant patients
- 761 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Task Analysis of Korean Transplantation Nurse Practitioner
- Soo Ja Byun, Hee Kyung Kim, Ae Ri Kim, Hee Sun Ha, Kyung Ok Joen
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(2):179-188. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.2.179
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to create the job description of Korean transplantation nurse practitioner and examine performance frequencies, criticality, and difficulties of task elements.
Method The sample consisted of 63 nurses and coordinators who performed duties related to transplantation at medical center in Korea. A survey method was used, and the questionnaire included frequencies, criticality, and difficulties of task elements in job description by the DACUM method. Using SPSS WIN 10.0, descriptive statistics such as frequency distribution, means, and standard deviations were conducted to examine the subject's general characteristics, the frequencies, criticality, and difficulties of task performance.
Result The job description of transplantation nurse practitioners revealed 5 duties, 22 tasks, and 85 task elements. On the all five duties, the averages of the performance frequency, criticality, and difficulty were 2.41, 3.38, and 2.78, meaning that the respondents rarely perform the 5 duties, but consider them critical and easy to perform.
Conclusion The job description of the transplantation nurse practitioner included duty, task, and task element and definition of job completed. Thus we recommended a data based trial to confirm and validate the information gathered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Workforce, task performance, and analysis of organ transplant coordinators in Korea: a survey study
Suhee Kim, Sun Young Son, Man Ki Ju, Seungheui Hong, Ji Yeon Park, Hyung Sook Kim
Clinical Transplantation and Research.2024; 38(3): 222. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Visiting Nurses in the Process of Change Using FGI and DACUM
Jieun Kim, Insook Lee, Jina Choo, Songwhi Noh, Hannah Park, Sohyeon Gweon, kyunghee Lee, Kyoungok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(1): 13. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Nurse Care Coordinators for Chronic Illness Management in Primary Care Settings: Using Developing a Curriculum Process
Ju-Hee Hwang, Yong-Jun Choi, Mi-Sook Kim, Seng-Eun Yi, Yong-Soon Park, Ji-Hyang Kim, Ju-Young Yoon, Dong-Soo Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 758. CrossRef - Job Analysis and Curriculum Development for Gambling Addiction Prevention Counselors based on DACUM
Sungjae Kim, Soo Mi Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(1): 34. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Clinical Research Coordinators Using the DACUM Process
Hyun-Sook Kang, Haeng-Mi Son, Nan-Young Lim, Kyung-Sook Cho, Sung-Bok Kwon, Yeo-Jin Yi, Young-Sook Park, Eun-Hee Lee, Joo-Hyun Kim, Hye-Ja Han, Jung-Mi Baik, Younhee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 1027. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Medical Care Client Managers based on DACUM
Jeong-Myung Choi
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 299. CrossRef - Task Analysis of the Job Description of Gerontological Nurse Practitioners based on DACUM
Keum Soon Kim, Yeon-Hwan Park, Nan Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 853. CrossRef
- Workforce, task performance, and analysis of organ transplant coordinators in Korea: a survey study
- 833 View
- 5 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The Lived Experience of Patients with Heart Transplantation: A Phenomenological Study
- Younghui Hwang, Myungsun Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(1):110-120. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to describe the lived experience of patients with heart transplantation in Korea.
Methods Individual indepth interviews and a focus group interview were used to collect the data from nine patients who had heart transplantations in 2015. All interviews were audio-taped and verbatim transcripts were made for the analysis. Data were analyzed using Colaizzi's phenomenological method.
Results Among the nine participants, eight were men. Mean age was 57.30 years. Six theme clusters emerged from the analysis. ‘Joy of rebirth obtained by good luck’ describes the pleasure and expectation of new life after narrow survival. ‘Suffering from adverse drug effects’ illustrates various psychosocial difficulties, such as low self-esteem, helplessness, alienation, and burnout, arising from the side effects of medications. ‘Body and mind of being bewildered’ illustrates disintegrated health and haunting fear of death. ‘Alienation disconnected with society’ describes isolated feeling of existence due to misunderstandings from society. ‘Suffering overcome with gratitude and responsibility’ includes overcoming experience through various social supports and suitable jobs. Finally, ‘acceptance of suffering accompanied with new heart’ illustrate changed perspective of life itself.
Conclusion The findings in this study provide deep understanding and insights of the lived experience of heart related illness for these patients and should help in the development of tailored-interventions for patients with heart transplantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Outcomes of Fears in Advanced Heart Failure: Differences Across Disease Stages
Mats Westas, Semyon Melnikov
Current Heart Failure Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceptions of Health-Related Quality of Life Among Heart Transplant Recipients: A Qualitative Study
Redouane Mahmoudi, Pascal Battistella, Laurent Sebbag, Latame Komla Adoli, Francis Guillemin, Cécile Couchoud
Transplantation Proceedings.2025; 57(10): 2010. CrossRef - An educational design and development project for pediatric heart transplant recipients and their families
Go-Eun Kim, Eun Kyoung Choi, HyeJung Lee, Yu-Mi Im
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2022; 66: e152. CrossRef - Clinical outcomes of a nurse-led post-discharge education program for heart-transplant recipients: A retrospective cohort study
Ji Hyeon Lee, Seok-Min Kang, Young Ah. Kim, Sang Hui Chu
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 59: 151427. CrossRef - Lived Experiences of Korean Young Adults After Heart Transplantation: A Phenomenological Approach
Hye Jin Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(2): 89. CrossRef - Life experiences of adult heart transplant recipients: a new life, challenges, and coping
CEBECİ Fatma, CETİN Cigdem, CATAL Emine, BAYEZİD Omer
Quality of Life Research.2021; 30(6): 1619. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Outcomes of Fears in Advanced Heart Failure: Differences Across Disease Stages
- 1,485 View
- 24 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling of Self-Management of Liver Transplant Recipients
- Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Yeon-Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):663-675. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.663
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct and test a structural equation model of self-management of liver transplant recipients based on self-determination theory.
Methods Participants were 275 outpatients who received liver transplantation. A structured self-report questionnaire was used to assess health care providers’ autonomy support, transplant-related characteristics, illness consequence perception, autonomy, competence, family relatedness, depression and self-management. Collected data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 24.0 and AMOS 24.0 program.
Results The modified model showed a good fitness with the data: GFI=.96, RMSEA=.06, CFI=.96, NFI=.93, TLI=.93, PGFI=.43, PNFI=.49. The health care providers’ autonomy support, competence, family relatedness and depression were factors with a direct influence on the self-management of liver transplant recipients. The health care providers’ autonomy support and illness consequence perception had an indirect influence through competence, family relatedness and depression. However, the transplant-related characteristics and autonomy did not have a significant effect on self-management. This model explained 59.4% of the variance in self-management.
Conclusion The result suggests that continuous education must be done to promote the competence of liver transplant recipients and to encourage the patient to positively perceive their current health condition with a view that enhances one's self-management. Additionally, the liver transplant recipients should be screened for depression, which would affect self-management. Most of all, health care providers, who have the most influence on self-management, should improve therapeutic communication and try to form a therapeutic relationship with the liver transplant recipients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of self-care in kidney transplant patients according to preoperative dialysis: A comparative study
Hyeiyeon Im, Hye-Young Jang
Heliyon.2024; 10(24): e40237. CrossRef - Structural equation modeling for associated factors with self-care behavior among young and middle-aged hypertensive patients: a cross-sectional study
Nam Jo Kim, Myung Kyung Lee
Contemporary Nurse.2023; 59(2): 99. CrossRef - Mediating Role of Hope Between Social Support and Self-Management Among Chinese Liver Transplant Recipients: A Multi-Center Cross-Sectional Study
Dan Zhang, Nannan Zhang, Hui Chang, Ying Shi, Zijun Tao, Xu Zhang, Qi Miao, Xiaofei Li
Clinical Nursing Research.2023; 32(4): 776. CrossRef - Factors associated with self‐management after hybrid revascularization in patients with peripheral artery disease: A structural equations model
So‐Young Kim, Yun Mi Lee, Youn‐Jung Son
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2023; 79(1): 170. CrossRef - Type D personality, cognitive illness perception, depression, approach coping, and self-management among older adults in long-term care hospitals: Structural equation modeling
Sunki Kim, Mona Choi, JuHee Lee, Heejung Kim, Kijun Song, Hye-Ja Park
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 48: 150. CrossRef - Factors influencing the self-management of kidney transplant patients based on self-determination theory: a cross-sectional study
Mi Kyung Sim, Sun Young Son, Man Ki Ju
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2022; 36(1): 37. CrossRef - Feasibility and preliminary effects of a theory-based self-management program for kidney transplant recipients: A pilot study
Hye Won Jeong, Chi Eun Song, Minjeong An, Lucy E. Selman
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(6): e0248947. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Chinese Version of the Readiness for Hospital Discharge Scale for people living with HIV
Chen Chen, Xiaoxia Zhang, Chulei Tang, Xueling Xiao, Zirong Tao, Honghong Wang
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2020; 7(2): 220. CrossRef - Mediation Effects of Basic Psychological Needs Between Autonomy Support from Healthcare Providers and Self-Management Among Cancer Survivors
Eun-Jung Bae, Yun-Hee Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2019; 10(6): 385. CrossRef - Analysis of mortality prognostic factors using model for end-stage liver disease with incorporation of serum-sodium classification for liver cirrhosis complications
Yuna Kim, Kyunghee Kim, Insil Jang
Medicine.2019; 98(45): e17862. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Self-Care Behaviors in Kidney Transplant Patients Based on Self-Determination Theory
Hye Won Jeong, Hyang Sook So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 731. CrossRef
- Predictors of self-care in kidney transplant patients according to preoperative dialysis: A comparative study
- 1,352 View
- 24 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Adaptation Experience of Living Kidney Donors after Donation
- Da-Hai-Som Kang, Jinhyang Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(2):271-282. Published online April 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to explore adaptation experience of living kidney donors after donation. Specific aims were to identify challenges donors face in the process of adaptation following surgery and how they interact with recipients and other people.
Methods Grounded theory methodology was utilized. Participants were 13 living kidney donors at six months or more after donation. Data were collected by in-depth interviews with individual participants. Data were analyzed using constants comparative method with theoretical saturation.
Results A core category emerged as 'keeping the fences of my family in spite of vulnerability'. The adaptation process after donation was manifested in four phases: exploration, balance, maintenance, and acclimatization. Phenomenon was perception of vulnerability. Strategies to manage the vulnerability were assessing changes of body awareness, tailoring regimen to one's own body condition, coping with health problems, keeping restoration of health, and ruminating on the meaning of one's kidney donation. Consequences were reestablishing family well-being, realizing the values of one's kidney donation, and living with uncertainty.
Conclusion Findings of the study indicate that there is a need for health professionals to understand the vulnerability of living kidney donors and help their family system maintain a healthy and productive life. The results of this study can be used to develop phase-specific, patient-centered, and tailored interventions for living kidney donors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with the quality of life of living kidney donors in Korea: A cross-sectional study
Kyungok Min, Younghui Hwang
Medicine.2024; 103(19): e38068. CrossRef - An Alternative View of a Hemodialysis–Life Balance: Life Reorganization of Korean Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Songsoon Kim, Jinhyang Yang
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2021; 32(6): 664. CrossRef - Young Adult Donor's Experiences of Living Donor Liver Transplantation
Miseon Bang, Haeyun Shin, Min Ryu, Suhye Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 105. CrossRef - Living Donors: Altruism and Feeling Forgotten
Abdel-Hadi Al Breizat, Momen Tawfiq Abunaser, Zain Al Breizat
Experimental and Clinical Transplantation.2020; 18(Suppl 1): 22. CrossRef - Experiences of physical complications and sequelae among living liver donors
Sun Ju Jeong, Han Na Kim
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2019; 33(2): 36. CrossRef
- Factors associated with the quality of life of living kidney donors in Korea: A cross-sectional study
- 1,724 View
- 11 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Changes in Quality of Life in Patients undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Longitudinal and Multilevel Analysis
- Chi Eun Song, Hyang Sook So
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):694-703. Published online October 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.694
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was a prospective longitudinal study to identify changes in quality of life in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). It was based on Roy's adaptation model.
Methods The questionnaires were administered before HSCT, 30 and 100 days after HSCT. Of the 48 potentially eligible patients, 44 (91.7%) participated in the study and 40 (90.9%) completed the questionnaires at 100 days after HSCT. Multilevel analysis was applied to analyze changes in quality of life.
Results Overall, quality of life showed a decreasing tendency from pre-HSCT to 100 days after HSCT. The adaptation level of participants was compensatory. Type of conditioning was the significant factor influencing quality of life before HSCT (β00=79.92,
p <.001; β01= - 12.64,p <.001) and the change rate of quality of life (β10= - 1.66,p =.020; β11=2.88,p =.014). Symptom severity (β20= - 1.81,p =.004), depression (β30= - 0.58,p =.001), social dependency (β40= - 0.35,p =.165), and loneliness (β50= - 0.23,p =.065) had a negative effect on changes in quality of life. Symptom severity and depression were statistically significant factors influencing changes in quality of life.Conclusion According to the results of this study, the development of nursing intervention is needed to improve quality of life in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the early immune reconstruction period. The interventions should include programs to enhance coping capacity and programs to help control symptom severity and depression. Also these interventions need to be started from the beginning of HSCT and a multidisciplinary approach would be helpful.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting post-traumatic growth in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients in South Korea: a descriptive survey study
Karyeong Bae, Eunjin Jo
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimating the Incidence-Based Cost of Illness Due to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Using One-Year Insurance Claim Data in Korea
Sol Kwon, Hye-Young Kang
PharmacoEconomics - Open.2023; 7(2): 189. CrossRef - Determining the symptoms and coping methods of patients at home after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Kader Caliskan, Gulbeyaz Can
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(7): 5881. CrossRef - Effect of Acculturative Stress on Multicultural Adolescents’ Life Satisfaction: Sequential Multiple Mediating Effects of Bicultural Acceptance Attitude, Self-Esteem, and Social Withdrawal -Using the 2016 Multicultural Adolescents Panel Study-
Soo Mi Kim, Hyeon Ok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 324. CrossRef - Changes in Fatigue, Psychological Distress, and Quality of Life After Chemotherapy in Women with Breast Cancer
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung-Ran Cho
Cancer Nursing.2020; 43(1): E54. CrossRef - Experiences of Unrelated Hematopoietic Stem-cell Donors and Experts of Relevant Institutions
Soyoung Yu, Miok Kim, Tai-Gyu Kim, Su-Hee Beom
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(5): 522. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Related Quality of Life in Adult Survivors of Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hyunjin Kwon, Eunjung Ryu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(4): 220. CrossRef - The Symptom Management of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
晓婧 李
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2017; 07(02): 59. CrossRef - A Multilevel Analysis of the Effect of Individual and Family Personalities on Depressive Symptoms in Families with College Students
김석선, 길민지
Health and Social Welfare Review.2016; 36(3): 34. CrossRef - Evaluation of Quality of Life and Care Needs of Turkish Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Neslisah Yasar, Semiha Akin
Nursing Research and Practice.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- Factors affecting post-traumatic growth in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients in South Korea: a descriptive survey study
- 1,275 View
- 27 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Incidence and Factors Influencing Oral Mucositis in Patients with Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Kwan Suk Jo, Nam Cho Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(5):542-551. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.542
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to examine the incidence of oral mucositis in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients and to identify factors influencing oral mucositis and patient outcomes according to severity.
Methods In this retrospective study, data were collected from electronic medical records of 222 patients who had received hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Oral mucositis was evaluated using WHO's assessment scale. Data were analyzed using Chi-square test, Fisher exact test, Spearman's correlation, Ordinal logistic regression, ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis test.
Results A total of 69.8% of the patients evaluated developed oral mucositis (grade II and over). As a results of ordinal regression, factors influencing oral mucositis severity were found to be diagnosis, type of transplantation, oxygen inhalation and the number of antiemetics administration before transplantation. The severity of oral mucositis was found to increase the days of hospitalization, days of TPN administration, days of using antibiotics and the number and dosage of analgesics.
Conclusion The results would help predict severity of oral mucositis in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients and suggest that provision of appropriate nursing assessment and oral care would improve patient outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Two Kinds of Gargles on Oral Mucositis in Patients After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
Wei Hu, Hua Jiang, Ting Wang, Xiu-Juan Guo, Bei-Bei Zhang, Yan Song, Ce Shi, Xiao-Dong Xu, Lin-Nan Wang, Xin-Xin He, Bo-ning Liu, Jun-xiu Zhou, Ze-yu Xue
Transplantation Proceedings.2024; 56(9): 2027. CrossRef - Nutritional status as a predictor of adverse events and survival in pediatric autologous stem cell transplant
Izabela Kranjčec, Nuša Matijašić, Mario Mašić, Alen Švigir, Gordana Jakovljević, Ante Bolanča
Pediatric Hematology and Oncology.2020; 37(8): 717. CrossRef - Kemoterapi ve Radyoterapi Alan Hastalarda Oral Mukozit: Bir Gözden Geçirme
Seher ÇAKMAK, Nesrin NURAL
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektronik Dergisi.2020; 13(3): 185. CrossRef - Experiences of Unrelated Hematopoietic Stem-cell Donors and Experts of Relevant Institutions
Soyoung Yu, Miok Kim, Tai-Gyu Kim, Su-Hee Beom
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(5): 522. CrossRef - Effect of Oral Cryotherapy for Reducing Oral Mucositis in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Seong-Hi Park, Su Ha Han
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(4): 362. CrossRef - Elimination of unplanned treatment breaks and dose reductions caused by mucositis: Positive implications for survival outcomes and cost reductions using high potency polymerized cross-linked sucralfate in 55 patients undergoing radiation for head and neck
Ricky Wayne McCullough
Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology.2017; 13(1): 10. CrossRef
- The Effects of Two Kinds of Gargles on Oral Mucositis in Patients After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
- 1,270 View
- 10 Download
- 6 Crossref

- The Life of Patients with a Heart Transplant
- Yeoungsuk Song
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(1):64-71. Published online February 28, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.1.64
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The main purpose of this study was to develop a substantive theory on the life of patients with heart transplantation in the context of Korean society and culture. The question for the study was “What is the life of patients like with a heart transplant?”.
Method A grounded theory method guided the data collection and analysis. Participants for this study were 12 adults who regularly visited a Cardiovascular ambulatorium in a medical center. The data was collected through an in-depth interview and analyses were performed simultaneously.
Result ‘Developing a new life to live on borrowed time’ was the core category in this study. It revealed two types of life, one is living in peace and another is thinking positive.
Conclusion This study provides a framework for the development of individualized nursing interventions to care for patients with Heart Transplantation. The findings may provide pointers for health professionals about ways to improve support for heart transplant recipients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Lived Experience of Patients with Heart Transplantation: A Phenomenological Study
Younghui Hwang, Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(1): 110. CrossRef - Experiences of Pregnancy and Childbirth in Women after Liver Transplantation
Hea Seon Ha, Kyung Choon Lim, Jung Ja Hong, In Ok Kim, Mi Kyeong Jeon, Jae Sim Jeong, Soon Haeng Lee, Haeng Mi Son, Myungsun Yi, Sung Gyu Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 690. CrossRef
- The Lived Experience of Patients with Heart Transplantation: A Phenomenological Study
- 791 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


