Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The experiences of infertile women discontinuing in vitro fertilization treatment: a grounded theory approach
- Eunmi Park, Yeoungsuk Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):440-453. Published online August 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25048
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a situation-specific theory by gaining an in-depth understanding of the deterrent processes experienced by infertile women who have discontinued in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures, within the socio-cultural context of South Korea.
Methods
The participants were 16 infertile women who discontinued IVF procedures. Data were collected through individual in-depth interviews from February to December 2023. Theoretical sampling was conducted, and the transcribed interview contents were analyzed using Strauss and Corbin’s grounded theory method.
Results
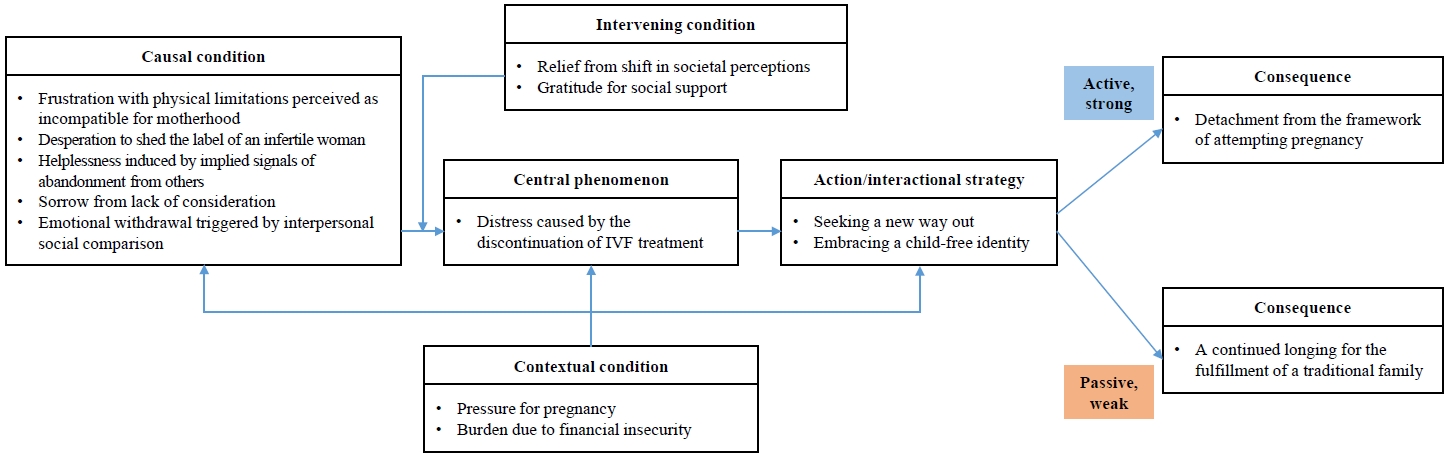
In total, 37 concepts and 14 categories were extracted through the open coding process. The central phenomenon in axial coding was “Distress caused by the discontinuation of IVF treatment.” The core category was “A journey to break free from the identity of infertility toward self-determined womanhood.” The results were categorized into two types: “Detachment from the framework of attempting pregnancy” and “A continued longing for the fulfillment of a traditional family.” The situation-specific theory was the “Theory of reconstructing subjective identity through the acceptance of childfree life,” which illustrates how infertile women actively redefine their life trajectories after discontinuing IVF treatment.
Conclusion
This study highlights the importance of public perceptions about infertile women who discontinue IVF procedures, which are seen as the last resort of assisted reproductive technology, because positive perceptions assists women in living a self-governing life. It may be necessary to develop educational and promotional programs to change negative social perceptions and to establish a psycho-social support system for infertile women who have been deterred from IVF procedures.
- 1,269 View
- 98 Download

- Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Education for Caring Patients with COVID-19
- Min Hye Lee, Eun-Young Noh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):397-411. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The role of medical staff gained immense significance in the context of the prolonged coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. However, few studies had explored the impact of simulation-based education on the ability of nursing students to care for the patients of COVID-19. This study provided nursing students with simulation-based education in caring for the patients of COVID-19 and confirmed its effectiveness.
Methods
This study used a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants were recruited from the nursing departments of two universities in Korea through convenience sampling. A total of 79 participants were included: 37 in the intervention group and 42 in the control group. The intervention group received four sessions of simulation training based on the National League for Nursing Jeffries simulation theory.
Results
The intervention group showed an improvement compared to the control group in terms of knowledge related to coronavirus, confidence in performing infection control skills, and perception of preparedness for caring for the patients of COVID-19, with a high-level of satisfaction and self-confidence in learning. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of anxiety.
Conclusion
This simulation is expected to be a significant strategy for alleviating the global burden in terms of staff safety and patient outcomes by improving the competencies of prospective medical staff in responding to pandemics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Utilization and impact of simulation-based education in prelicensure nurse education; an integrative review
Robyn Cant, Colleen Ryan
Journal of Professional Nursing.2026; 63: 6. CrossRef - Building Skills in Infection Prevention Through Simulation: Insights from Nursing Students in Brazil and Peru
Luciene Muniz Braga, Pedro Paulo do Prado-Junior, Andréia Guerra Siman, Talita Prado Simão Miranda, Mara Rúbia Maciel Cardoso do Prado, Luana Vieira Toledo, Rodrigo Siqueira-Batista, Andréia Patrícia Gomes, Yanet Castro Vargas, Luis Alberto Chihuantito-Ab
Nursing Reports.2026; 16(1): 14. CrossRef - Determinants of Standard Precautions Performance Among Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Se Gyeong Jeon, Eun Jung Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(21): 2803. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of a Novel Education Approach to Prevention and Control of Healthcare-Associated Infections: Insights from PrevInf Pilot Study
Paulo Santos-Costa, Filipe Paiva-Santos, João Graveto
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(2): 1494. CrossRef
- Utilization and impact of simulation-based education in prelicensure nurse education; an integrative review
- 5,719 View
- 98 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Experience of Peer Support Work among People with Mental Illness in the Community: A Grounded Theory Approach
- Myung Sun Hyun, Hyunlye Kim, Kyoung A Nam, Su Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):187-201. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21208
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study discovered a substantive theory of the experience and process of peer support work among people with mental illness.
Methods
The participants were members of community-based mental health facilities and had been working as peer supporters for more than six months. The data were collected through in-depth interviews with twelve participants and analyzed using Corbin and Strauss’s grounded theory approach.
Results
The core category was “becoming a healer going with patients in the journey of recovery,” and the core phenomenon was “identity confusion as a peer supporter.” The causal conditions were “starting peer support work without certainty” and “standing at the boundary between the therapist and patient.” The intervening conditions were “willingness to become a successful peer supporter,” “feeling a sense of homogeneity with the patient,” “accepting the mental illness,” and “support from people around.” The action and interaction strategies were “letting go of greed,” “being open about oneself,” “developing professional skills,” “maintaining wellness in the body and mind,” and “being with the patient.” The consequences were “becoming a useful person,” “changing attitude toward life,” “expansion of the sense of self-existence,” “recovering from mental illness,” and “discovering a role as peer supporter.” Finally, the substantive theory of “becoming a healer going with patients in the journey of recovery” was derived.
Conclusion
This study provides a holistic understanding of peer support work and the implications of interventions to help people with mental illness in a person-centered recovery process. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recovery Identity Formation among Peer Supporters: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Miran Jung, Soo Yeon Lee, Hee Jin Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(4): 370. CrossRef - A model for the involvement of service users as instructors into the psychiatric nursing curriculum in Korea: A qualitative study on participation experience
Suyoun Ahn, Soyoung Shin, Jaewon Joung
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 917. CrossRef - Experience of Mental Health Professionals Collaborating with Peer Supporters in a Community Mental Health Service Team
Sowon Lee, Boyoung Kim, Chung Kil Park
International Journal of Mental Health Promotion.2024; 26(4): 251. CrossRef - Experience of Peer Supporters for Patients with Schizophrenia
Hae Kyung Jo, Se Na Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(3): 280. CrossRef
- Recovery Identity Formation among Peer Supporters: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
- 2,475 View
- 45 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Nurses’ Experiences of the COVID-19 Crisis
- Jung-Hoon Lee, Yeoungsuk Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):689-702. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21160
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a situation-specific theory to explain nurses’ experiences of the COVID-19 crisis.
Methods
The participants were 16 hospital nurses who experienced the COVID-19 crisis. Data were collected through in-depth individual interviews from September 2, 2020 to January 20, 2021. Transcribed interview contents were analyzed using Corbin and Strauss’s grounded theory method.
Results
A total of 38 concepts and 13 categories were identified through an open coding process. The core category found was becoming a pioneering nurse who turns crises into opportunities. The causal conditions were the chaos of being exposed defenselessly to an unexpected pandemic, fear caused by a nursing care field reminiscent of a battlefield, and moral distress from failing to protect patients’ human dignity. The contextual conditions were feeling like the scapegoat of the hospital organization, increasing uncertainty due to the unpredictable state of COVID-19, and relative deprivation due to inappropriate treatment. The central phenomenon was suffering alone while experiencing the dedication of the COVID-19 hero image. The action/interactional strategy were efforts to find a breakthrough and getting the nurse’s mind right, and the intervening conditions were gratitude for those who care for broken hearts and getting used to myself with repetitive work. The Consequences were becoming an independent nurse and frustration with the unchanging reality.
Conclusion
This study provides the foundation for the nurse's situation-specific theory of the COVID-19 crisis by defining the crisis perceived by nurses who cared for COVID-19 patients and suggesting types of coping with the crisis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Moderating Effect of Calling in the Relationship between Post-Traumatic Stress and Turnover Intention of Nurses Who Cared for COVID-19 Patients
Min Ju Woo, Bu Kyung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 75. CrossRef - Experiences of Person‐Centred Care Among Nurses in COVID‐19 Wards: A Qualitative Study
Myoungsuk Kim, Yongmi Lee, Hyun‐Ju Kang
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating and moderating role of recovery experience between occupational stress and turnover intention in nurses caring for patients with COVID‐19
Junghoon Lee, Junekyu Kim, Hong‐A Lim, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2024; 33(4): 1470. CrossRef - Improving Emerging Infectious Disease Control Based on the Experiences of South Korean Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Systematic Review
Ha-Young Park, In-Sun Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression Among Nurses in General Hospitals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Focus on Job Demands, Post-traumatic Stress, and Social and Organizational Support
Si Hyun Baek, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 306. CrossRef - An Integrated Review of Difficulties and Response Strategies
Experienced by Korean Nurses during the COVID-19 Outbreak: Based on
Qualitative Research
Jayoung YOU, Dan Bi CHO
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2024; 27(1): 27. CrossRef - Experience of Clinical Adaptation among Nurses in Intensive Care Unit
Jin Young Hong, Sue Kyung Sohn
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Nurses’ intention to care of COVID-19 patients in hospitals dedicated to infectious disease in South Korea: application of the theory of planned behavior and verification of the moderating effect of ethical nursing competence
Mira Mo, Seongmi Moon, Eun Kyeung Song
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care among Nurses in COVID-19 Special Care Units at Tertiary General Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Kisook Kim, Sunmi Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 127. CrossRef - Perceptions of Healthcare Safety Nets among Tertiary Hospital and Long-Term Care Hospital Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Q-Methodological Approach
Bom-Mi Park, Mi Young Chon, Hyun-Jung Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(20): 2732. CrossRef - Burnout and Its Associated Factors Among COVID-19 Frontline Healthcare Workers
Hyeonseok Oh, Euihyun Kwak, So Yeon Hyun, Songeun Lee, Suk-Hyun Lee, In Mok Oh, Minyoung Sim
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2023; 62(4): 199. CrossRef - Experiences of Psychiatric Nurses Working in a Closed Psychiatric Unit during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 374. CrossRef - Parenting Experience of Shift Nurses With Elementary School-Aged Children During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Phenomenological Study
Jeung-Im Kim, Mi-Youn Jang, A-Ri Song, Jung-Eun Yu, Myung-Sook Baik
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2023; 27(3): 154. CrossRef - Influence of COVID 19 on Nursing Students’ Career Identity: A Cross-sectional Study
Na-geong Kim, Hye-Ryeon Park
The Open Nursing Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Job Stress, Social Support, and Infection Control Fatigue on Professional Quality of Life among Nurses in Designated COVID-19 Hospitals
Minyoung Shin, Woojoung Joung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(5): 603. CrossRef - Burnout among Nurses in COVID-19 Designated Units Compared with Those in General Units Caring for Both COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Patients
Kyung Ah Woo, Eun Kyoung Yun, JiSun Choi, Hye Min Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 374. CrossRef - Effect of Anxiety and Calling on Professional Quality of Life in COVID-19 Dedicated Nurses in Korea
Minjung Moon, Kyoungsan Seo
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1797. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef - Exploring the Experiences of Nurse Managers during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hyunjin Jang, Eun-Mi An, Ki-Eun Kim, Yoounjoong Jung, Youjung Choi, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 460. CrossRef - An Analysis of Tasks of Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in a Nationally-Designated Inpatient Treatment Unit
Minho Jung, Moon-Sook Kim, Joo-Yeon Lee, Kyung Yi Lee, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(4): 391. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Post-traumatic Growth of Nurses at Nationally Designated Infectious Disease Hospital
Ji Eun Oh, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 499. CrossRef
- The Moderating Effect of Calling in the Relationship between Post-Traumatic Stress and Turnover Intention of Nurses Who Cared for COVID-19 Patients
- 2,663 View
- 47 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref

- Job Retention Process among Working People with Mental Illness: A Grounded Theory Approach
- Myung Sun Hyun, Kyoung A Nam, Hyunlye Kim, Su Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):320-333. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The study was conducted to explore the experiences of job retention among working people with mental illness.
Methods
The participants were members with mental illness at the S Community Mental Health Center in Gyeonggi Province and who had been working for more than six months. The data were collected through in-depth interviews with 11 participants between June 27 and August 20, 2018. The data were analyzed through Corbin and Strauss’s grounded theory method.
Results
The core category was struggling to take root in the community as a productive member. The core phenomenon was the desire to be a productive person, and the causal condition was the willingness to change for a purposeful life. The action and interaction strategies included maintaining regular living patterns, maintaining medication, developing one’s tips for self-management, and self-approval. The intervening conditions were difficulties in forming social relationships, presence of symptoms, social resources, and acceptance of one’s mental illness. The consequences were restoration of family relationships, healthy pleasure through work, social inclusion, development of self-worth, and transition to an independent person.
Conclusion
Working people with mental illness are struggling to take root in the community as a productive member. This study suggests that a holistic understanding of the job retention experience among people with mental illness is required. The findings will provide the basis for developing interventions that can improve job retention among working people with mental illness.
- 1,212 View
- 37 Download

- Adaptation to Motherhood in Central Asian-Korean Immigrants to Korea: A Grounded Theory Study
- Su Hyun Kim, Hyang-In Cho Chung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):677-689. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.677
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This qualitative study aimed to develop a substantive theory of the process of adaptation to motherhood in Central Asian-Korean immigrants to Korea.
Methods Individual, in-depth interviews were conducted from July to September 2017, with 18 women who emigrated of Korean ethnicity from Central Asia to Korea, and took care of their baby for at least a year after their first delivery in Korea. The interviews were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim. Data from the transcriptions were analyzed through Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory method, and data analysis was conducted simultaneously with data collection.
Results As a result of categorizing the interview data through the process of open coding, 10 categories, with 31 subcategories and 102 concepts were drawn, and “growth as a Central Asian-Korean mother in an unfamiliar, historical hometown” was found to be the core category of the process of adaptation to motherhood in Central Asian-Korean immigrants to Korea.
Conclusion A characteristic of the process of adaptation to motherhood in Central Asian-Korean immigrants to Korea, drawn from this study, is that it differs according to the level of initiative to carry out interaction strategies, and the use of various supportive social resources. The findings indicate the need for Medicare eligibility adjustment for antenatal care, the extension of the visa renewal period during childbirth, the development of web- or mobile application-based educational programs in Russian language, and the establishment of integrated visiting healthcare services, community service resources, and policy support to enable these women to utilize various supportive social resources.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Web-based program for sexual and reproductive health education of immigrant women: A scoping review protocol
Suhyun Kim, Aeri Jang, Ileana B. Heredia-Pi
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(5): e0298551. CrossRef - Effects of Maternal Adjustment Enhancement Program Using Mobile-Based Education for Chinese Immigrant Women in Korea: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Ju-Eun Song, Eun Ha Roh, Youn-Jeong Kim, Jeong-Ah Ahn
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2022; 33(6): 685. CrossRef - Adaptation in pregnant women: a descriptive phenomenological study using Giorgi’s approach
Minseon Koh, Jisoon Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(4): 346. CrossRef - Influence of Stress and Anxiety on Depression in Central Asian Koreans in Korea
Hyun-Bok Lee, Myeong-Suk Cho, Hyo-Ja An, Jeong-A Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2020; 29(4): 339. CrossRef
- Web-based program for sexual and reproductive health education of immigrant women: A scoping review protocol
- 1,512 View
- 19 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Changes in Strauss & Corbin's Grounded Theory
- Ji Eun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):505-514. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.505
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to introduce and elucidate changes in Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory and discuss its application to the field of nursing in South Korea.
Methods The changes in grounded theory by Strauss and Corbin were examined through a literature review of grounded theory from its inception.
Results Strauss and Corbin acknowledged their philosophical backgrounds of symbolic interactionism and pragmatism; however, their methodology based on positivism overwhelmed their epistemology and ontology. This inconsistency has been represented by the coding paradigm and the premise of “emergent from the data.” In the revised version of
Basics , Strauss and Corbin modified their theory to weaken the coding paradigm and strengthen the strategies for the development of substantive theory.Conclusion Strauss and Corbin's revised grounded theory did not fully address the inconsistency of their epistemology and ontology between their acknowledgement and methodology. However, these changes constitute a meaningful step toward resolving inconsistencies and highlight the development of substantive theory. This has implications for Korean nursing researchers who have utilized methodologies in grounded theory with dogmatic approaches; grounded theory, with its evolving nature, is not a finalized method and calls for open approaches for the development of a grounded theory that fits Korean nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emergency Nurses’ Comprehensive process of surrogate decision Support: Reanalysis of qualitative data Using a grounded theory
Sadami Momiyama, Hayato Katayanagi, Makoto Nakabayashi, Tomoko Fujino, Noriko Sakoda, Yoshiko Sato, Takafumi Noguchi, Hiroko Susaka, Hidekazu Hishinuma, Tomoya Tozawa, Tomomi Muraoka
International Emergency Nursing.2026; 84: 101749. CrossRef - From Perception to Practice: Identifying and Ranking Human Factors Driving Unsafe Industrial Behaviors
Azim Karimi, Esmaeil Zarei, Ehsanollah Habibi
Safety.2026; 12(1): 14. CrossRef - Exploration of Family-Centered Care in NICUs: A Grounded Theory Methodology
Young Ah Park, YeoJin Im
Qualitative Health Research.2025; 35(10-11): 1231. CrossRef - Breaking boundaries: integration of sports and medicine in the community elderly service model
Yuanli Chen, Mohd Firdaus Bin Abdullah, Nor Eeza Zainal Abidin, Fanghui Li
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expert school nurses' experiences of reopening schools during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study
Ji Eun Kim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Jaehee Yoon
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 76: 16. CrossRef - Digital textbooks for undergraduate nursing education: a scoping review protocol
Aeri Jang, Hyunyoung Park
BMJ Open.2024; 14(7): e071147. CrossRef - Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
Dasom Im, Jeehye Pyo, Haneul Lee, Hyeran Jung, Minsu Ock
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(2): 100. CrossRef - Efeitos da intervenção terapêutica de enfermagem em pacientes com doença cardíaca coronária
Bifei Yan, Jing Chen, Juanhua Tu, Yan Wang
Acta Paulista de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing and Validating Educational Strategies for Couples to Enhance Family Bonds: A Qualitative Expert Analysis
Seyed Amin Saadat, Mohammad Hosein Fallah, Saeid Vaziri Yazdi
Thrita.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Illness Experiences of Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Ji Eun Kim, Ilaria Campesi
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Internet of things platform technology used in undergraduate nursing student education: a scoping review protocol
A Jang, CE Song
BMJ Open.2022; 12(4): e058556. CrossRef - The Health Management Experience of Vietnamese Married Immigrant Women Living in the City
Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(4): 506. CrossRef
- Emergency Nurses’ Comprehensive process of surrogate decision Support: Reanalysis of qualitative data Using a grounded theory
- 3,341 View
- 79 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Experiences of Ego Integrity Recovery in Elderly Cancer Patients: Grounded Theory Approach
- Han-Gyo Choi, Hye-Ah Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):349-360. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.349
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to derive a substantive theory on lived experiences of elderly cancer patients.
Methods The data were collected from February to March 2018 through in-depth personal interviews with 14 elderly cancer patients. The collected data were analyzed based on Corbin and Strauss's grounded theory.
Results The core category was “the journey to find balance in daily lives as a cancer patient by recovering disturbed ego integrity.” The core phenomenon was “shattered by suffering from cancer,” and the causal conditions were “physical change” and “limitations in daily life.” The contextual conditions were “decreased self-esteem,” “feelings of guilt toward the family,” and the sense of “economic burden.” The participants’ action and interaction strategies were “maintaining or avoiding social relations,” “seeking meaning of the illness,” “falling into despair,” and “strengthening the willingness to battle the cancer.” The intervening conditions were “support from health care providers and family,” “dissatisfaction with health care providers,” “spiritual help from religion,” and “the improvement or worsening of health conditions.” The consequences were “having a new insight for life,” “living positively along with cancer illness,” and “the loss of willingness to live.” A summary of the series of processes includes the “crisis stage,” “reorganizing stage,” and the “ego integration stage.”
Conclusion This study explored the holistic process of ego integrity impairment and the recovery experience of elderly cancer patients. This study is expected to be used as a basis for the development of nursing interventions that can support patients when coping with all stages of their cancer illness trajectory.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decision-making experiences regarding kidney transplant among older adults in South Korea: A qualitative descriptive study
Hye Jin Chong, Min Kyeong Jang, Hyun Kyung Kim
Patient Education and Counseling.2024; 119: 108044. CrossRef - Living experiences of older patients with cancer amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A phenomenological study
Yong Hwan Hyeon, Kyoung Ja Moon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 54. CrossRef - Relationship between Communication Competence, Empathy and Geriatric Nursing Practice of Nurses Caring for Elderly Cancer Patients at a General Hospital: Focusing on Veterans Hospital
Eun Sil Park, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 94. CrossRef - Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
Dasom Im, Jeehye Pyo, Haneul Lee, Hyeran Jung, Minsu Ock
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(2): 100. CrossRef - Decision-Making Experience of Older Patients with Cancer in Choosing Treatment: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Se Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 418. CrossRef - Identifying optimal care coordination strategies for older adults with cancer
Han-Gyo Choi, Hye-Ah Yeom
Geriatric Nursing.2021; 42(6): 1349. CrossRef - Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on the Lived Experience of Illness among Older Females with Cancer in South Korea
Miseon Bang, Suhye Kwon, Seonnyeo Kim, Haeyun Shin, Eunyoung Seo
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(2): 110. CrossRef - Experiences of Inpatients Living with Lung Cancer in South Korea
Hae Ok Kim, Hyeon Jeong Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Good Nursing Experience of Patients with Cancer in a Korean Cancer Hospital
Eunyoung E. Suh, Hye Jin Yoo, Jeong Hee Hong, In Gak Kwon, Hyunju Song
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(3): 51. CrossRef
- Decision-making experiences regarding kidney transplant among older adults in South Korea: A qualitative descriptive study
- 1,372 View
- 23 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Testing a Middle-Range Theory of Self-Care of Chronic Illness: A Validation for Korean Adult Patients with Severe Hypertension
- Eunha Gil, Heeyoung Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):521-533. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.521
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aims of this study are to provide a theoretical framework for improving the self-care of adults with severe hypertension and to examine the practical suitability of a middle-range theory of self-care for chronic illness by validating the structural model.
Methods Data were collected at a university hospital in D metropolitan city from July 1 to August 14, 2015. A total of 224 Korean adult patients with severe hypertension were recruited. Data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 and AMOS 22.0.
Results The results show that the fit index of the hypothetical model meets the recommended level; 7 out of 8 hypothetical model paths were statistically significant. Motivation, self-efficacy, support from others, and accessibility to care showed statistical significance and explained 67.3% of the self-care process. The self-care process explained 45.3%, 63.6%, and 26.5% of quality of life, health, and illness stability, respectively.
Conclusion This model can be used as a theoretical framework for improving self-care among adult Korean patients with severe hypertension. Moreover, the practical suitability and validity of the middle-range theory of self-care for chronic illness is secured.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a self-care scale for women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a methodological approach
Miok Kim
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Self Care Education on Knowledge and Behavior Among Android-based Hypertension Patients at Yogyakarta Health Center
Tatik Pujiastuti, Musheer A. Aljaberi, Tukimin Sansuwito, Bibi Florina Abdullah, Ruma Poddar
Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences.2023; 19(s9): 1. CrossRef - Linking Health Literacy to Self-Care in Hypertensive Patients with Physical Disabilities: A Path Analysis Using a Multi-Mediation Model
Hye Jin Nam, Ju Young Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3363. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance in Adult Moyamoya Patients
Bo Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 80. CrossRef - Self-care Efficacy and Health-related Quality of Life among Patients on Primary Treatment for Pulmonary Tuberculosis: The Mediating Effects of Self-Care Performance
Hyun Ju Lee, Jiyoung Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(3): 305. CrossRef
- Development of a self-care scale for women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a methodological approach
- 4,236 View
- 194 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Threats to Identity: A Grounded Theory Approach on Student Nurses’ Experience of Incivility during Clinical Placement
- Jiyeon Kang, Yeon Jin Jeong, Kyoung Ran Kong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):85-95. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.85
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This qualitative study aimed to explore the experience of incivility among nursing students.
Methods Sixteen nursing students who had experienced incivility during their clinical placement were invited for one-on-one interviews until the point of theoretical saturation. The grounded theory approach of Corbin and Strauss was adopted to analyze transcribed interview contents.
Results Incivility occurred in the context of a hierarchical organizational culture, due to nursing students’ position as outsiders, non-systematic clinical education, and poor nursing work environment. The experience of incivility was identified as “being mistreated as a marginal person,” and nursing students responded to this phenomenon in the following three steps: reality shock, passive action, and submissive acceptance. This process caused students to lose self-esteem and undergo role conflict. Furthermore, nursing students’ experience of incivility could eventually lead to workplace bullying in nurses.
Conclusion The results of this study suggest that nursing students’ experience of incivility can be a process that threatens their identity. It is necessary to develop educational programs and provide appropriate counseling services so that nursing students can actively cope with the incivility. In addition, institutional plans are needed to ensure safe and supportive clinical learning environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Turkish Validity and Reliability of the Nursing Students' Rights Awareness Scale in Clinical Practice
Elif Sözeri Öztürk, Tuğba Karataş
Journal of Nursology.2025; 28(1): 20. CrossRef - Exploring relationships among workplace incivility, organizational commitment, work engagement and job burnout in Vietnamese primary schools
Quan H.N. Tran
Industrial and Commercial Training.2025; 57(4): 345. CrossRef - Systemic antecedents of academic incivility in nursing: An integrative review
Justin Fontenot, Michael Hebert, Robbie Stefanski, Dawn Morris
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2024; 19(2): 192. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perception of Injustice in Clinical Practice
Hye Young Cho, Kyoung Ah Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 433. CrossRef - A structural model of nursing students’ performing communication skills
Cho Rong Gil, Kyung Mi Sung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 148. CrossRef - The effect of verbal violence, clinical practice stress, and coping with stress on nursing students’ major satisfaction during clinical practice
Heejung Heo, Yeoungsuk Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 190. CrossRef - Nursing students' rights in clinical practice in South Korea: a hybrid concept-analysis study
Sunghee Park, Mi-Young Choi
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(4): 260. CrossRef - Effects of a Nonviolent Communication-Based Empathy Education Program for Nursing Students: A Quasi-Experimental Pilot Study
Jieun Sung, Youngran Kweon
Nursing Reports.2022; 12(4): 824. CrossRef - Impact of incivility and psychological capital on nursing students’ transition shock
Chung Hee Woo, Chanhee Kim
Collegian.2022; 29(5): 621. CrossRef - The influence of nursing students’ perfectionism tendency and perception of instructor caring on incivility experienced by nursing students
Eun Nam Lee, Na Geong Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 436. CrossRef - The influence of experienced violence and the clinical learning environment on vocational identity in nursing students
Mira Lee, Hee Ok Park, Insook Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 321. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Nursing Students’ Rights Awareness Scale in Clinical Practice: A Scale Development Study
Sung-Hee Park, Mi-Young Choi
Healthcare.2021; 9(10): 1323. CrossRef - Effects of clinical practice stress and moral sensitivity on clinical competency in nursing students
Yeoungsuk Song, Joon-Young Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(2): 157. CrossRef - Radiotherapy students’ perceptions of support provided by clinical supervisors
L. Armstrong-James, R. N. M. Khine, R. J. Thorne, M. J. E. Tuckey, C. Bennett
Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice.2020; 19(1): 15. CrossRef - Experiences of Perception of Nursing Students' Rights in Clinical Practice
Sunghee Park, Hyeyoung Cho
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(4): 471. CrossRef - Interventions for coping with bullying need further investigation and should be built into nursing curricula
Jiyeon Kang
Evidence Based Nursing.2018; 21(3): 70. CrossRef - Educating our future generation-The role of nurse managers in encouraging civility
Annamaria Bagnasco, Giuseppe Aleo, Fiona Timmins, Gianluca Catania, Milko Zanini, Loredana Sasso
Journal of Nursing Management.2018; 26(8): 899. CrossRef - “Loving Nursing” and “Taking Responsibility”: Strategies for Transitioning to Practice in Lebanon
Michael Clinton, Sawsan Ezzeddine, Myrna Doumit, Ursula Rizk, Murielle Madi
Sage Open.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Turkish Validity and Reliability of the Nursing Students' Rights Awareness Scale in Clinical Practice
- 2,081 View
- 58 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Bridging the Gap Between Research, Practice and Theory in Nursing
- Ketefian Shake
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1994;24(2):303-312. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1994.24.2.303
- 371 View
- 1 Download

- Prediction of Breastfeeding Intentions and Behavior: An Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior
- Hea Sook Kim, Eun Sook Nam
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):796-806. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.796
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The majority of studies on breastfeeding consists of descriptive correlational studies identifying the incidence and correlates of breastfeeding. The theory of planned behavior has been shown to yield great predictive power for behavioral goals over which individuals have only limited control such as improving school grades and weight loss. The purpose of this study was to test the "theory of planned behavior" in the prediction of breastfeeding of mothers who delivered vaginally. One hundred mothers who delivered vaginally in one general hospital in Seoul and one general hospital and three private hospitals in Taejeon participated in this study. The instruments used for data collection in this study were developed by the researchers following the guidelines suggested by Ajzen and Fishbein(1980) and Ajzen and Madden(1986). The instruments included measurement of attitude, subjective norm, perceived behavioral control and intention. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson product moment correlation, hierachical multiple regression and logistic regression. The results are as follows : 1. Intention to breastfeed correlated significantly with attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioral control. Both attitude and subjective norm did not make a significant contribution to the prediction of intention, but the addition of perceived behavioral control to the regression equation greatly improved the model's predictive power, increasing the R(2) from .05 to .52. 2. Intention to breastfeed alone had a significant predictive effect on actual breastfeeding, resulting in a regression coefficient of .16(x2=8.60, p<.01), but when perceived behavioral control was added to the equation, intention was not a significant predictive variable and only perceived behavioral control showed significant predictive power on actual breastfeeding, resulting in a regression coefficient of .12(x2=4.68, p<.05). In sum, breastfeeding behavior lent only partial support to the second version of the theory of planned to the second version of the theory of planned behavior, and because perceived behavioral control had a strong effect on intention to breastfeed and actual breastfeeding, it would be desirable to develop nursing intervention programs which focus on strengthening the perceived behavioral control for the promotion of breastfeeding.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Examination of Predicting Factors for COVID-19 Vaccination Behaviors of University Students Utilizing the Theory of Planned Behavior
Yeon Jeong Heo, Hye-Jin Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 178. CrossRef - The Factors related to Mothers' Intention to Vaccinate against Hepatitis A: Applying the Theory of Planned Behavior
Kyeong-Sook Cha, Kyung Mi Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors associated with Maternal Attachment of Breastfeeding Mothers
Sun-Hee Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(1): 65. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Primiparas' Breastfeeding Behavior
Hyun-Joo Yang, Ji-Min Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(3): 399. CrossRef
- Examination of Predicting Factors for COVID-19 Vaccination Behaviors of University Students Utilizing the Theory of Planned Behavior
- 792 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Lived Experience of the Family Members of Gastric Cancer Patients
- Myung Sun Yi
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):275-288. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.275
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of the study is to explore and describe the lived experience of family members with gastric cancer patients using the grounded theory methodology. The participants were ten spouses of gastric cancer patients who had some kind of treatment at the hospital. They were asked open-ended and descriptive questions in order for them to talk about their experiences in their owl terms. As the interview progressed the questions became more specific to discuss themes and working hypotheses that emerged from the analysis of previous interviews. All interviews were tape-recorded and transcribed for the analysis. Constant the core category that was emerged from the comparative analysis is "magmaggam" which can be described as a psychological distress due to a high level of uncertainty regarding the health of the patient and the future of the caregivers. Psychological distress includes several emotional feelings such as frustration, anxiety, fear, guilty, and self depreciation. Subcategories or strategies related to the core category are 1) managing illness, 2) using folk medicine, 3) giving the patient a reason to live, 4) being patient, 5) losing reality, 6) anticipatory experience on the patient's death and parting, and 7) changing interpersonal relationships. The results of this study would help clinical nurses to develop nursing intervention to help spouses of gastric cancer patients establish efficient coping strategies in dealing with the problems they face.
- 384 View
- 4 Download

- A Study for the Development of Korean Nursing Theory: A Humanistic Approach based on Shinhyung, Naekyungpyun in Dongeuibogam
- Kyung Rim Shin
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):141-155. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.141
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The universe had its order of yang and yin ; all creation are continuously generated, grow and die, which is the results of the harmonious operation by yang and yin. Among all creation, the human is one of the samjae(three bases of the world, which are heaven, earth, and man) and he is from the combined sukhi(a superior khi) of yang and yin. And human life itself is basically a condensed jonghyul(life blood) and at the same time it is only a transient joining of sadae(the four elements of earth, air, fire and water). Yang and yin, the two axes of the world, therefore, are the most crucial and fundamental concept to explain the generation and extinction of all creation, to understand people in time and space, to find out the reality of human life as an organism, and at last, to observe the state of human health. If so, what is the most essential idea in yang and yin? It is taegeuk(chungkhi) or tao(of one yang and one yin). If the property of heaven and earth is kongon, taegeuk is a khi and tao a principle. And it can be sid that a human body is merely a union of hyung and khi, that human life is an essence of sambo, jeongkhishin, that human health is a harmonized coordination of yang and yin because it is from the combined sukhi of yang and yin because it is from the combined sukhi of yang and yin. Hyung, a vessel for smbo, jeongkhishin, is at the bottom and shin is on the top ; the personality and the disposition of individuals differ according to their working. Thus, on the basis of the above discussion, the following can be offered as some suggestions for Korean Nursing Theory. Though human beings are part of Nature, they are the most eminent microcosm among all creation. So, as a subject for nursing, a person should be understood with khijok kyoryu rather than with logical thinking, then mutual trust between the patient and the nurse can be established. The health of a person on the harmony of yang and yin. To be healthy, a person should consider harmonization with Nature(including his surroundings) as well as a balanced human relationships in society. Moreover, it is crucial for each person to obtain hoshim as a method of mind control rather than to only treat the symptoms of disease.
- 468 View
- 2 Download

- A Study on Health Behavior Experience of Middle-aged Women in Rural Area
- Jin Hyang Yang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):694-705. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.694
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study is to describe the health behavior experience of middle-aged Korean women in rural areas, and to help understand their health practice, perceive their nursing needs and provide guidelines to developing appropriate nursing interventions. METHOD: The participants were 18 healthy middle-aged women living in rural areas, with no serious illness that require hospitalization. The data was collected through interviews and participant observation, analyzed by the grounded theory methodology of Strauss and Corbin(1997). The data collection period was from April to November of 2001. RESULT: Depending on the paradigm model, the central phenomenon was family-oriented pursuing of yangsaeng. The causal condition was less confidence on one's own health, responsibilities in caring for family. The contexts were cultural system. The intervening condition was information system, support system, limitation of approaching a medical institution. The action/ interaction strategies were yangsaeng through dietary practice, yangsaeng through promoting clothing and housing, yangsaeng through exercise, practice of folk therapy, yangsaeng through mental hygiene, and use of medical institution. The consequences were stabilization of body and mind, and stabilization of family. CONCLUSION: It is recommended for nurses to understand health behavior experience of middle-aged women, and provide nursing intervention with theoretical scheme and practical principles so that these women can pursue the family-oriented process of yangsaeng.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Ethnographic Study on the Health related Lifestyles for Sea Women of Jeju
김필환, Kim,Yeong-Kyeong
Qualitative Research.2017; 18(1): 114. CrossRef - Evaluation of Anthropometric Characteristics, Bone Density, Food Intake Frequency, Nutrient Intakes, and Diet Quality of Preand Postmenopausal Women : Based on 2008∼2011 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soon Nam Choi, Kwang Hyun Jho, Nam Yong Chung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(5): 500. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Hwa-byung Awareness in Middle-Aged Women
Sun-Jung Park, Eun-Young Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(2): 1304. CrossRef - A Korean Version of the Appraisal of Diabetes Scale (ADS-K)
Eun-Hyun Lee, Young Whee Lee, Kwan-Woo Lee, Moonsuk Nam, Yong Seong Kim, Seung Jin Han
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2015; 26(3): 270. CrossRef - The relationship between Intake of Health Foods and Dietary Behavior in Middle-Aged Women
Mi-Hee Kim, Hye-Jin Lee, Mi-Jeong Kim, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(5): 436. CrossRef - Evaluation of Diet Quality according to Self-Rated Health Status of Korean Middle-Aged Women -Based on 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(9): 1395. CrossRef - The Related Factors Influencing on Self-rated Health Level of Middle-aged Women
Hyejin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee, Eunkyung Kim, Mi-Jung Kim, Suk-Man Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(3): 290. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Self-Foot Reflexology Massage on Stress and Immune Responses and Fatigue in Middle-Aged Women in Rural Areas
Ja Ok Kim, In Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(5): 709. CrossRef - Climacteric and Menopausal Women's Beliefs on Daily Meals and Food Supplements - A Focus Group Interview Study -
Jeong-Soon Pyun, Mi Jeong Kim, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(2): 239. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Efficacy Promotion Program on Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
Hea-Kyoung Ko, Geum Ja Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Do the determinants of physical activity change by physical activity level?
Hyun Kyung Kim, Mi Ja Kim, Chang Gi Park, Hyeon Ok Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2009; 65(4): 836. CrossRef
- An Ethnographic Study on the Health related Lifestyles for Sea Women of Jeju
- 663 View
- 0 Download
- 11 Crossref

- A Grounded Theory Approach to the Adjustment Process of the Institutionalized Elderly: The Control of Reluctance
- Ga Eon Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):624-632. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.624
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The number of residents in elderly institution has been increasing due to the change of the family support system. This study was focused on understanding the process of adjustment of the institutionalized elderly using the Grounded Theory approach. METHOD: There were seven participants, 4 men and 3 women living in 3 different elderly facilities. The data was collected through in-depth interviews and participant observation from June 20, 1999 to January 10, 2000 and analyzed by the Strauss and Corbin's analysis method. RESULT: 125 concepts were found and grouped into 30 sub-categories and then grouped into 13 categories. These categories are <humiliation>, <fear>, <reluctance>, <difficulty of economic status>, <health problem>, <process of entrance>, <loss of family support>, <facility support>, <personality disposition>, <positive self mind-control>, <negative self mind-control>, <adjustment> and <maladjustment>, which were synthesized into the process of adjustment. <The Control of Reluctance (to live in facility)> being the core category. The adjustment process of the facility elderly consisted of: 1. expressive phase of 'reluctance' 2. control phase of 'reluctance' 3. latent phase of 'reluctance' CONCLUSION: This study offers better understandings on the adjustment process of the institutionalized elderly and provides more appropriate nursing care to the New Comers of these facilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded byFeasibility of a Mobile Meal Assistance Program for Direct Care Workers in Long-Term Care Facilities in South Korea
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C De Gagne, Minkyung Lee, Hyesoon Lee, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi, Juyoun Chung
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2020; Volume 15: 2019. CrossRef- Influence of Nursing Satisfaction, Self-Esteem and Depression on Adjustment of the Elderly in Long-term Care Hospital
Kyoung-Mi Lee, Eun-Joo Jo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(5): 441. CrossRef - Factors influencing the adaptation to skilled nursing facilities among older Korean adults
Jin Yi Choi, Sohyune R Sok
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2015; 21(2): 184. CrossRef - Effect of the Facility Satisfaction, Anxiety, Self-esteem, Stress, and Depression of the Elderly in Care Facilities on Their Life Satisfaction
Young-Haw Sa, Sung-Je Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(12): 6998. CrossRef - Effects of Upper Meridian Massage on Cerebral Blood flow, Emotions, and Sleep of the Institutionalized Elderly
Dong Choon Uhm, Mi Jung Nam
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 171. CrossRef - The Experiences of Family Caregivers under the Long-term Care Insurance
Eun-Young Kim, Ga Eon Lee, Sam-Sook Kim, Chun Yee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(4): 347. CrossRef - Predictors of adjustment to nursing home life of elderly residents: A cross-sectional survey
Ga Eon Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2010; 47(8): 957. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Hand Massage On Sleep, Depression and Quality of Life in the Institutionalized Elderly Women
Soon Yi Seo, So Young Chang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 372. CrossRef - Predictors of Facility Adaptation in Nursing Home Residents
Hyekyung Lee, Hyang-Yeon Lee, Jia Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(2): 177. CrossRef
- 700 View
- 6 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Development and Test of the Hypothetical Model to Explain Smoking Cessation Behaviors Based on Triandis' Interpersonal Behavior Theory
- Hyun Soo Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(1):16-27. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was conducted to develop and test the hypothetical model which explains smoking cessation behavior was established based on the Triandis' interpersonal behavior theory.
METHOD
The data were collected from the 400 university student smokers enrolled in the universities located in Seoul and Kyung-In province. The study was analyzed by path analysis with LIESREL 8 program.
RESULTS
All of the fit statistics, except the Chi-square value, it showed the hypothetical model was well fitted to the data. Benefit, affect, and social influences related to smoking cessation behavior had significant direct effect on intention to smoking cessation as shown in the study of the hypothetical model. Perceived barrier and the physiologic arousal related to smoking cessation had significant direct effects on performing smoking cessation behavior, whereas numbers of previous attempts to quit smoking and intention to smoking cessation did not.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of an Aging Management Program for Middle-aged Women on Resilience and Successful Aging
Hyeyun Jung, Kyung Mi Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 392. CrossRef
- Effects of an Aging Management Program for Middle-aged Women on Resilience and Successful Aging
- 686 View
- 11 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Clinical Experiences of Adaptation as a New Nursing Staff
- Haeng Mi Son, Moon Hee Koh, Chun Mi Kim, Jin Ha Moon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(6):988-997. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.988
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study aimed at uncovering the experience of adaptation of the new nursing staff in hospital setting.
METHODS
For this study, 15 new graduate nurses participated. The data was collected through the in-dept interviews and analysed in terms of Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory methodology.
RESULTS
The core category was identified with "entering orbit". The new graduate nurses, who experienced the taeoom because of their unskilled professions, tried to enter orbit by overcoming difficult situations through reducing stress, maintaining good interpersonal relationship, grasping, compensating, persisting, and introspecting. Noticeably, in the process of adaptation, negative image of nursing, conflict of interpersonal relationship and the educational program for the new nursing staff had effect on the intervening factors. Finally, this study confirmed that the processes of new nurses' adaptation are confusing, confrontating, becoming a member and settling in hospital setting.
CONCLUSION
Therefore, the educational programs reflecting new nursing staffs' experiences should be developed.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- New Graduate Nurses' Experiences by Generation in South Korea: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Heejin CHUNG, Mihyun PARK
Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 32(2): e325. CrossRef - Influence of Musical Activity on the Embitterment and Psychological Well-Being of Nurses
Jin Ho Choi, Sang Hee Choo
Sage Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing burnout among Korean nurses caring for patients with COVID-19: a cross-sectional study
Seon Yeong Lee, Mi-Ae You, Jeong Ah Ahn, Eun Ji Seo
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(4): 276. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Practice for Physical Restraints among Nurses in the Intensive Care Unit
Da Eun Kim, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 62. CrossRef - Effects of Head Nurses' Authentic Leadership, Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment Perceived by Newly Licenced Nurses on Turnover Intention
Eun Min An, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 428. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Critical Care Nurses based on Lazarus & Folkman's Stress, Appraisal-Coping Model
Hye Gyeong Kim, Ja Yun Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(1): 88. CrossRef - The Effect of Appreciative Inquiry on Positive Psychological Capital and Organizational Commitment of New Nurses
Hyunju Kim, Young Hee Yi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 13. CrossRef - Win-Win Partnership in the Clinical Setting: Female Nurses' Adaptive Experience to Male Nurses
Hyunsu Kim, Eun Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 423. CrossRef - The Clinical Experience of Adaptation as Novice Psychiatric Nurses In Hospital
김미영, SeongSook Jun, 하수정
Global Health and Nursing (글로벌 건강과 간호).2018; 8(1): 17. CrossRef - Role Adaptation Process of Hospice Nurses
Su Young Kwak, Byoung Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(2): 149. CrossRef - Turnover Experience of Male Nurses
Hyunsu Kim, Jeongseop Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(1): 25. CrossRef - Development of the Transition Shock Scale for Newly Graduated Nurses
Eun-Young Kim, Jung Hee Yeo, Kyeong Im Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 589. CrossRef - A study on the Moderating Effect of Social Support in Line with the Effect of the Organizational Socialization Perceived by Hotel Employees on the Turnover Intention
방기석, Katelyn H. Kim
Tourism Research.2017; 42(4): 149. CrossRef - Development of the Developmental Support Competency Scale for Nurses Caring for Preterm Infants
Jeong Soon Kim, Hee Sun Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(6): 793. CrossRef - A Grounded Theory Approach on Nurses' Experience with Workplace Bullying
Jiyeon Kang, Seonyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(2): 226. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience of Sleep in New Nurses
Hyoung-Sook Park, Jae-Hyun Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(1): 21. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Turnover Intention for New Graduate Nurses in Three Transition Periods for Job and Work Environment Satisfaction
Mi Yu, Kyung Ja Kang
The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing.2016; 47(3): 120. CrossRef - The Coping Experience of Nursing Students in Clinical Practice: Trying to be a Meaningful Presence
Doo Nam Oh, Young-Rhan Um, Chunmi Kim, Sejin Ju, Jung Hyun Choi, Myung Sook Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(4): 430. CrossRef - Qualitative Research on Nurses Experiencing Taeoom
SunHwa Choeng, InSook Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 238. CrossRef - The Development and Effects of a Tailored Simulation Learning Program for New Nursing Staffs in Intensive Care Units and Emergency Rooms
Eun Jung Kim, Hee-Young Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 95. CrossRef - Impact of DISC Behavioral Styles on Job Satisfaction and Clinical Competencies among Newly Hired Nurses
Mi Yeong Mun, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 43. CrossRef - Influence of Workplace Bullying and Resilience on Organizational Socialization in New Graduate Nurses
Eun Ah Jo, Jiyeon Kang
Journal of muscle and joint health.2015; 22(2): 78. CrossRef - Role Adaptation Process of Elementary School Health Teachers: Establishing Their Own Positions
Jeong Hee Lee, Byoung Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(3): 305. CrossRef - Experience of Turnover in New Nurses
Sun Ae Kim, Hye Won Jeon
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 644. CrossRef - The Experiences of Night Duty among Clinical Nurses Who are Considering Job Transfer
Kaehwa Jo, 김연자
Qualitative Research.2014; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on Happiness Experienced by Career Nurses
Kyungwoo Lee, Yeonok Suh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(5): 492. CrossRef - The Job Experience of Oncology Nurse Specialists
Young Sook Tae, Suhye Kwon, Young Sook Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(4): 236. CrossRef - Conceptual Development of Workplace Bullying: Focusing on Hospital Nurses
Younju Lee, Eun Jin Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(1): 57. CrossRef - A Study on Type of Clinical Experience of Adaptation of New Nursing Staffs in a General Hospital
Yun-Jeong Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(4): 443. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Professionalism in the Relationship between Clinical Competence and Field Adaptation in Newly Graduated Nurses
Young-Soon Kim, Kyung-Yeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 536. CrossRef - Lived Experiences of New Graduate Nurses
Yeonok Suh, Kyungwoo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(2): 227. CrossRef - The Experiences of Turnover Intention in Early Stage Nurses
Se Young Lee, Eun Jin Oh, Kyung Mi Sung
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 168. CrossRef - Perception of Patient Safety Culture and Safety Care Activity of Entry-level Nurses
Seong-Suk Cho, Moon Hee Gang
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(1): 24. CrossRef - Job Stress, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Commitment according to Life Organization (LIFO) Behavior Type of Novice Nurses
Hye Jin Yang, Sun Im Im, Eun Young Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(5): 636. CrossRef - A Study on Experience of Transition from New Clinical Nurse to Competent Step
Kwang-Ok Park, Jong Kyung Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 594. CrossRef - Psychological Well-being, Perceived Health Status, and Health Promoting Behavior of Clinical Nurses
Yune-Jung Choi, Young-Hee Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(5): 589. CrossRef - The Experience of Turnover Decision Making in New Graduate Nurses
김근령, Cho YoungSuk, Kim,Myung-Hee, Haejung Lee
Qualitative Research.2013; 14(1): 23. CrossRef - Process of Overcoming Turnover Intention in Career Nurses
Ha Yoon Cheong, Sun Hee Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(3): 414. CrossRef - Role Transition from Clinical Nurse to Case Manager for Medical-aid Beneficiaries: Taking Root in a Barren Land
Eun-Jun Park, Chunmi Kim, Seung Joo Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(2): 149. CrossRef - Predictors of the Clinical Competence in New Graduate Nurses
Youn-Wha Shin, Haejung Lee, Yeonjung Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(1): 37. CrossRef - Re-employment Experience of Nurses Who Have Left the Profession
Young Soon Byeon, Miyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 768. CrossRef
- New Graduate Nurses' Experiences by Generation in South Korea: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
- 1,274 View
- 22 Download
- 41 Crossref

- Experience of Patients Living with Chronic Renal Failure
- Sung Ye Kang, Byung Sook Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(4):525-537. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.4.525
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Purpose of the study was to understand the experience of chronic renal failure patients for the qualified individual care for them. The purpose of this study was to explore the experience of patients living with chronic renal failure and to identify the meaning and structure of their experience. The subjects were four patients, two females and two males. The age range was from 21 to 54. Data was collected with a few in-depth interviews by the authors until the data was fully saturated. The framework and methodology of this study was based on Parse's "Human Becoming methodology," an existential phenomenological research
method
ology. The findings of this study were as follows. Three experience structures of chronic renal failure patients were : 1. Sufferings and conflicts originated in the frustration caused by uncurable disease. 2. Dependence upon God and significant others with complex emotions. 3. Acceptance of sufferings, emerging hope for serving people, and gratitude for living. In conclusion the experience of chronic renal failure patients could be described from the findings (three structures) as "Experiencing the sufferings, conflicts originated in the frustration caused by uncurable disease, dependence upon God and significant others with complex emotion, acceptance of the suffering and hope for serving people, and gratitude for living." The three structures of the lived experience of patients with chronic renal failure, the findings of this study, could be explained by the three concepts of "Theory of Human Becoming," the first structure could be explained with values, the second with revealing-concealing, and the third with transforming.
- 516 View
- 1 Download

- Literature Review of HIV-Positive Patient Care Studies which used Concepts from Theory of Reasoned Action
- Hyera Yoo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(7):1645-1657. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.7.1645
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Twenty-three research studies regarding nurses or nursing students intention to care for HIV disease patients were reviewed. Studies on this issue were sporadic and not systematic. A majority of the studies were limited to one institution at one point in time. Convenience sampling was prevalent. Only 5 studies used random sampling (Jemmott III et al., 1992; Kelly et al., 1988; Planter & Foster, 1993; Scherer et al., 1989; Van Servellen et al., 1988). Consequently the findings of most studies can not be generalized to the population at large. In addition, between 1985 and 1994, the emphasis on descriptive studies continued even though correlational and experimental studies were being conducted. The development of the body of knowledge on this issue is still in a primitive stage. Correlational or comparative studies reviewed rarely had a theoretical basis for the study questions. Only two studies were found that cited a theoretical basis (Laschinger & Goldenberg, 1993; Goldenberg & Laschinger, 1991). A variety of attitude instruments were developed by investigators and used in their own studies. The constructs of the instruments were quite varied. For example, some studies identified fear as the attitude to be measured, while others measured opinion or intention as the attitude. None of the studies reviewed reported content, construct or convergent validity of the instruments. Reliability data for most instruments used in the studies were either not reported or low. Such a lack of information limits the interpretation of the findings. Study findings were inconclusive. Some descriptive studies indicated that nurses or nursing students were willing to care for HIV disease patients, while others revealed they were not willing to do so. Three correlational studies examining the relationship between attitude and intention obtained inconsistent findings. Findings from one study (Jemmott et al., 1992) indicated a positive relationship, while others found no relationship between them (Cole & Slocumb, 1994; Jemmott et al., 1992). Descriptive studies identified that families or friends stigmatization were the important factors. Only two correlational studies on this issue were found, but study findings were inconsistent (Laschinger & Goldenberg, 1993; Glodenberg & Laschinger, 1991). Studies focusing on nursing students intentions or attitude were limited. Only 7 of the 23 research reviewed were conducted using nursing students (Lawrence & Lawrence, 1989; Lester & Beard, 1988; Mueller et al., 1992; Oerman & Gignac, 1991; Jemmott et al., 1992; Jemmott III et al., 1992; Wiely et al., 1988). This review leads to the conclusion that there is a need for study of this issue with nursing students as the target population. Studies with questions based upon a theoretical framework provide a basis for linking findings. In addition, reliable instruments and sophisticated statistical analysis are also needed when studying this topic.
- 459 View
- 0 Download

- Analysis and Evaluation of the Theory of Unpleasant Symptoms
- Eun Hyun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(7):1627-1635. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.7.1627
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The theory of unpleasant symptoms is a middle-range theory proposed by Lenz and her colleagues (1997). Analysis and evaluation of this theory was performed using Fawcett (1999) and Fawcett and Downs's (1992) guidelines. Results of the theory analysis and evaluation suggest that the theory of unpleasant symptoms has theoretical and social significance and parsimony. However, a lack of internal consistency was evident. For empirical adequacy of the theory, it is recommended that research be conducted examining the complexities of the interaction effects, reciprocal relationships, and medication effects among physiological, psychologic, and situational factors, symptoms, and performance. The knowledge derived from the research findings should be used in practice for patients experiencing symptoms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Analysis and Evaluation of the Theory of Unpleasant Symptoms
Seung Eun Lee, Catherine Vincent, Lorna Finnegan
Advances in Nursing Science.2017; 40(1): E16. CrossRef - Relationships of mood disturbance and social support to symptom experience in Korean women with breast cancer
Eun-Hyun Lee, Bok Yae Chung, Hee Boog Park, Ki Hong Chun
Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.2004; 27(5): 425. CrossRef
- An Analysis and Evaluation of the Theory of Unpleasant Symptoms
- 1,239 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Predicting Exercise Behavior in Middle-aged Women: An Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior
- Mi La Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):537-548. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.537
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The objectives of this study were to verify the effectiveness of the Theory of Planned Behavior in predicting exercise intention and exercise behavior, and to examine the determinants of exercise intention and exercise behavior in the sample of middle-aged women. The subjects who participated in this study were 263 middle-aged women. The instruments used for this study was a survey of general characteristics, attitude (18 items), subjective norm (2 items), perceived behavioral control (19 items), intention (3 items), and exercise behavior (7 items and 23 items for each). Analysis of data was done by use of descriptive statistics and correlation analysis with SAS PC program. The hypothetical model based on the Theory of Planned Behavior was tested by use of LISREL 8.12a program. 1) The overall fit of the hypothetical model to the data was good(chi-square=11.76, p=0.03, RMSEA=0.07, standardized RMR= 0.03, GFI=0.99, AGFI=0.94, NFI=0.97, NNFI=0.95). 2) Perceived behavioral control, attitude, and subjective norm were significant determinants of exercise intention, and these variables explained 35% of the total variance of exercise intention. 3) Perceived behavioral control, intention, and attitude were significant determinants of exercise behavior. But, subjective norm was not a significant determinants. These four variables explained 69% of the total variance of exercise behavior. In conclusion, this study shows the applicability of the Theory of Planned Behavior in explaining exercise behavior of middle-aged women, and suggests that health care providers should focus on perceived behavioral control and attitude rather than subjective norm to improve exercise behavior of middle-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Performance of Exercise Behavior of Middle-Aged Men with Chronic Disease Based on the Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skill-Revealed-Related Variables (IMBR) Model
Hee-Kyung Kim, Hyoungtae Kim, Jeong-Hyo Seo
Healthcare.2022; 11(1): 100. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Nurses' Nursing Intention toward COVID-19 Patients
Do Eun Kyung, Yong Soon Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(4): 376. CrossRef - Verification of Predictive Model of Mutual Cooperative Behavior of Disabilities without Disability for Students with Disability in Inclusive Physical Education Setting Using the Theory of Planned Behavior
박수경, Lee Hyun Su
Journal of adapted physical activity and exercise.2012; 20(1): 15. CrossRef - A Study on the Effect of Adult Female's Personality Type on Health Control Behavior and Obesity Stress
In Kyung Han
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2009; 42(4): 358. CrossRef - The Stages of Physical Activity and Exercise Behavior: An Integrated Approach to the Theory of Planned Behavior
Byung-Ha Park, Moo-Sik Lee, Jee-Young Hong, Seok-Hwan Bae, Eun-Young Kim, Kwang-Kee Kim, Dae-Kyoung Kim
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2009; 21(1): 71. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Performance of Exercise Behavior of Middle-Aged Men with Chronic Disease Based on the Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skill-Revealed-Related Variables (IMBR) Model
- 751 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Traditional Concept of Health in Korea
- Jin Hyang Yang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(1):72-83. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.1.72
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study purports to review traditional health concepts of Korea by age, and to compare them to health concepts defined in western societies. Furthermore the study offers these results as the basis of construction for Korean nursing theory. Literature for the review were traditional health books published in Korea. These books are Euibangyoochui, Hyangyakjibsungbang, Dongeuibogam, Eiyangpyun, Dongeuisoosebowon, & Hwangjaenaekyung. In addition, articles that studied traditional literature or Korean medical history were reviewed when no publication of a primary source was available. In ancient Korean society, health was viewed as a 'good relationship or harmony with a supernatural subject', 'harmony of earth, water, fire, and air', and a 'long life with no illness'. The treatment aspect of medicine was emphasized in the middle-aged society. The health concepts in the pre-modern society included such concepts as 'jeongkhibojeon', 'adjustment to the nature', 'harmony between yang and yin', 'strengthening of jeongkhishin', 'circulation of owoonyookchi', 'kyungjok mind-body state' and 'jeongshimjeonghang'. Major health concepts in western literature were 'adaptation', 'role performance', 'actualization of human potential', 'adaptation and actualization of potential', and 'comfort'. Traditional health concepts of Korea focus on principles. They deliver abstract meanings, which make their measures uneasy. They believe in holism and unity with nature and especially emphasize the mental aspect. On the other hand, health concepts of western societies focus on phenomena. Their meanings are somewhat concrete, which make their measurements relatively easy. They see a person adapts positively to the environment as an independent being from the environment. These concepts have biopsychosocial aspects with no partial emphasis in the mental aspects. These traditional concepts of health were classified into two main perspectives. One is the unity of heaven & man, and the other is the unity of mind and body. The former perspective is based on the main concept of Chi. The latter has the main concept of ruling of the mind. The two main concepts discussed above need further examination for development of a nursing theory for Korean society. The application of circulation of Chi needs balance and harmony, and the application of ruling of mind needs temperance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health Concept and Health Promotion Process Among Korean Migrant Women
Chiyoung Cha
Health Care for Women International.2013; 34(8): 628. CrossRef - Asian Medicine and Holistic Aging
Kwang-hee Park
Pastoral Psychology.2011; 60(1): 73. CrossRef - A Study of Yangsaeng and Dietary Practices Among Korean Women
Jin Hyang Yang, Kyung Rim Shin
Nursing Science Quarterly.2003; 16(1): 83. CrossRef
- Health Concept and Health Promotion Process Among Korean Migrant Women
- 681 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Pattern of Decision Making to Donate a Living Kidney
- Myung Sun Yi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(1):47-59. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.1.47
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to explore decision making phenomenon of living kidney donation experienced by kidney donors. Data were collected through semi-structured indepth interviews from 12 kidney donors. All interviewes were audiotaped and transcribed verbatim. Constant comparative analysis was used to analyze the data with NUDIST4.0 software program. The core category emerged was "wish to give (a kidney)". "Wish to give" in the deliberation process have effects on the execution of kidney donation. Based on the degree of "wish to give", three distinct patterns were identified: Voluntary, compromising, and passive. The voluntary decision making was the most frequent one, while the passive the least. The degree of "wish to give" was influenced by intimacy between the donor and the receipient, geographical locations, economical efficiency of kidney transplantation, and religion. Each pattern was explained by describing interfering and facilitating factors as well as other issues occured in the decision making process. The results of this study will help nurses make effective nursing intervention by understanding the characteristics of decision- making patterns and decision-making process to donate a living kidney.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Barriers to the donation of living kidneys for kidney transplantation
Kyungok Min, Tai Yeon Koo, Young Hui Hwang, Jaeseok Yang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Barriers to the donation of living kidneys for kidney transplantation
- 607 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Psychosocial Adjustment in Families with Kidney Donor or Recipient
- Myung Sun Yi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):790-801. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.790
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to generated a grounded theory of how families with kidney donor or recipient copel with kidney transplantations. Interview data from twelve familes involved in didney transplants was analyzed using the grounded theory method. Data analysis revealed that "protecting the family" was the main theme that represented family member experiences. In order to maintain family function and to protect the family from breaking up, family members had to adjust the family structure from the traditional style of a husband-centered family, to one that was patient health-centered. the process of this adjustment was a very long and difficult one, taking several years from the recognition of the kidney disease to the kidney transplants. Family members, especially spouses, employed nine different strategies to deal with various problems and conflicts which occurred during the process : 1) paying attention to the patient's illness and complications ; 2) accepting the patients's illness as the family's illness as well ; 3) managing the patient's illness and complications that occurred ; 4) being thrifty ; 5) supporting the kidney donor ; 6) accepting and replacing the lost roles of the patient ; 7) keeping composure and encouraging the patient ; 8) sustaining the patient's independence ; 9) self-restraining sexual desires.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decision‐Making Process for Living Kidney Donors
Myungsun Yi
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2003; 35(1): 61. CrossRef
- Decision‐Making Process for Living Kidney Donors
- 561 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Lived Experience of Mothers Mentally Handicapped Daughters Having Menarche at Puberty
- Myung Sook Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(3):494-506. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.3.494
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to understand the structure of mothers of mentally handicapped daughters' lived experience, to apprehend the connectedness of the structure of the experience with concept of Parse's human becoming theory, and to provide a foundation for nursing research and education. Data collection was conducted from October 1995 to April 1996. Research participants were eight mothers of mentally handicapped daughters whose ages ranged from 12 to 18 attending special schools located in either Inchon or Seoul. The researcher had interviews with them over their lived experience conducted tape recorded, and made an analysis according to Parse's "human becoming research methodology." The data were collected using the dialogical engagement process "I and You," the participant researcher and the participant subject. The data were analyzed using the extraction-synthesis and heuristic interpretation. The structural integration is illustrated in the following: 1) Realizing the mother's role of mentally handicapped daughters and admitting situation. 2) Concealing a part of their relationship with others is interpreted as revealing-concealing. 3) Their fight back voluntarily to improve the situation is interpreted as powering. The conceptual integration which emerged was the lived experience of mothers is powering through the revealing-concealing and connection-separating of valuing.
- 408 View
- 0 Download

- Testing the Theory of Planned Behavior in the Prediction of Contraceptive Behavior among Married Women
- Myoung Hee Kim, Kyung Shin Paek
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):550-562. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.550
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to test the Theory of planned Behavior in the prediction of contraceptive behavior among married women. This study used a descriptive correlational design to examine the relationships among the study variables. Eighty married women in Seoul and Kyungki-do participated in this study. Research instruments used were the tool for measuring TPB variables search as attitude toward contraception , subjective norm, perceived behavior control, and intention: and the tool for measuring contraceptive behavior . The former was modified by the researcher according to Ajzen and Fishbein(1980)'s guidelines for tool development and Jee(1993)'s tool. The latter was developed by the research. Data was collected from July 20, 1996 to October 25, 1996. The results are as follows: The three factors, attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioral control of contraception can explain 30% of the variance in contraceptive intention. Inspection of path coefficient for each of the three predictor variables revealed that subjective norm and perceived behavior control were the predictor variables on intention, while attitude was not ; and intention and perceived behavior control factors can explain 42% of the variance in contraceptive behavior. Inspection of path coefficient for each of the two predictor variables revealed that intention and perceived behavior control were the predictor variables on behavior. In conclusion, this study identified that Theory of Planned Behavior was a useful model in the prediction of contraceptive behavior, and the contraceptive service program based on the TPB variables would be an effective nursing intervention for the change in contraceptive behavior.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Examination of Predicting Factors for COVID-19 Vaccination Behaviors of University Students Utilizing the Theory of Planned Behavior
Yeon Jeong Heo, Hye-Jin Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 178. CrossRef - Effects of a Customized Birth Control Program for Married Immigrant Postpartum Mothers
So Young Kim, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(6): 780. CrossRef - A Study on Health Promotion Behavior and Contraception in Married Immigrant Women
Mi Jong Kim, Tae Im Kim, Yun Jung Kwon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2008; 14(4): 323. CrossRef
- Examination of Predicting Factors for COVID-19 Vaccination Behaviors of University Students Utilizing the Theory of Planned Behavior
- 732 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Study of the Process of Smoking Cessation in Adults
- Ae Kyoung Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):319-328. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.319
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to explore the process of smoking cessation behavior in adults with a history of smoking cessation. The subjects were 17 adults selected by theoretical sampling. The data were collected by in-depth interviews using audiotape recording over a period of six months. The data were analyzed simultaneously by a constant comparative method in which new data were continuously coded in categories and properties according to Strauss and Corbin' methodology. Analysis of the data resulted in the identification of 12 categories. The result of this study are as follows : 1. Smoking cessation in adults is caused by fear about health, environmental pressure of smoking cessation, and intention of smoking cessation. 2. Smoking cessation occurs in connection with situations of limited smoking. 3. Maintenance of smoking cessation is related to psychological stress, and environmental cues to smoking. 4. In the smoking cessation process, adults experienced either health promotion or relapse. It is suggested that the result of this study may contributed to the development of a strategy for decreasing smoking behavior among adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Factors Implicated When an Individual Starts to Smoke Again After a 6 Month Cessation
Hyo-Kyung Son, Un-Young Jung, Ki-Soo Park, Sin Kam, Sun-Kyun Park, Won-Kee Lee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2009; 42(1): 42. CrossRef
- The Factors Implicated When an Individual Starts to Smoke Again After a 6 Month Cessation
- 619 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Caring Experience of Mothers with IDDM Children
- Mi Hye Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):81-92. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study is to define the caring experience of mothers with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus children, by finding core category, contextual factors, intervening factors, and the patterns of caring, and to develop a practice theory on it. Research method followed grounded theory methodology by Strauss and Corbin. Subjects were six mothers, whose children have had insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus for 4 months to 14 years by the interview time. They were selected by theoretical sampling. Data were collected from September, 1995 to January, 1996. Interview were done by long interview took 50 minutes to 2 hours. Content of interview was recorded and transcribed later. Based on the results of previous interview, content of next interview was planned until data reached to the saturation point. Results were as follows : One hundred and forty concepts were found. These concepts were grouped into thirty-three categories, and then to ten categories. Mothers with diabetic child were revealed to face "being overwhelmed by burden". Overwhelming by burden is found to be progressed through the cycle production-coping-decrease or in crease process. Mothers showed four patterns of adaptation in caring the diabetic children. 1) If mothers felt large amount of overwhelming by burden because of difficulty of caring and unsympathizing but they had sufficient support, no condition of the child, and their coping mechanism was positive, most of them overcome with strong will, but some fell into burnout. 2) If mothers felt large amount of overwhelming by burden because of difficulty of caring, unsympathizing, insufficient support, serious condition of the child, and their coping mechanism was negative, they fell into burnout by coping with feeling. 3) In mothers felt small amount of overwhelming by burden because of little difficulty of caring and sympathizing, sufficient support, no serious condition of the child, but their coping was negative, most of them fell into burnout by coping with feeling, but some overcome. 4) If mothers felt small amount of overwhelming by burden because of little difficulty of caring and unsympathizing, sufficient support, no serious condition of the child, and their coping was positive, they overcome with strong will. On the basis of the above result, in order to help mothers take good care of their children, nursing assesment and intervention on life readjustment, and getting support should be required. Especially, through understanding mothers' personalities, individual support consistent with each of them should be required. Therefore education, counseling, mutual support and exchange of information will have to be accomplished.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role Adaptation Processes of Family Caregivers with Patients Transferred from Intensive Care Unit to General Ward: Becoming almost a Nurse with Hope and Fear
Heui-Kyeong Kwon, Misoon Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(6): 603. CrossRef
- Role Adaptation Processes of Family Caregivers with Patients Transferred from Intensive Care Unit to General Ward: Becoming almost a Nurse with Hope and Fear
- 654 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Family Caregivers' Experiences Utilizing a Nursing Home for Their Elderly Family Members
- Sun Woo Hong, Haeng Mi Son
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):724-735. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.724
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore and describe the experiences of the family caregivers using a nursing home for their elderly family members.
Method Participants for this study were 1 man and 9 women caregivers. Data was collected through in-depth interviews from October, 2005 to April, 2006 and analyzed using Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory methodology.
Results “Finding a way to live together” emerged as a core category and it reflected expanding consciousness allowing them to see each other in a more positive view. The basic social process of “finding a way to live together” includes 3 phases: 1) recognizing the problems, 2) finding solutions to the problems, and 3) accepting the changes in their surrounding. Lack of privacy, family troubles, extreme distress, and unavailable caregivers are reflected in the process of recognizing the problems. The process of finding solutions was making a decision, obtaining family agreement, choosing the best nursing home, and enduring the financial burden. Possible outcomes of the last phase include recovering peace of mind and continuing conflict.
Conclusion Findings from this study offer suggestions for developing a strategy to help not only the elderly but also the family caregivers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of the Care Burden Scale for Family of Elderly in Nursing Facilities
Eun Jeong Kim, Kyung Mi Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(1): 80. CrossRef - Useful lessons for the provision of services in long-term care facilities in South Korea: operators’ experiences illuminate the phenomenon of working with the elderly in the field
Young Ran Tak, Hae Young Woo, Lee Han Yi, Ah Rim Kim
International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Hospice care education needs of nursing home staff in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Mihyun Park, Hye-Ah Yeom, Sr Jinsun Yong
BMC Palliative Care.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prise en charge d’un proche âgé dépendant à domicile en Corée du Sud : recherche sur les aidantes principales de la génération du baby-boom
Yoonji Oh
Enfances, Familles, Générations.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Barriers and Solution of Providing Long-term Care Services at Home for the Beneficiaries with Mild Dementia: A Focus Group Interview
Mi Sook Song, Kyung Sook Lim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 259. CrossRef - Assessment of Long-Term Care Service Needs in the Baby Boom Generation
Song Yi Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(1): 21. CrossRef - Feelings of Guilt and Depression in Family Caregivers after Nursing Home Placement of Older Adults
Sun Young You, Young Ran Tak
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2014; 16(3): 276. CrossRef - Grounded Theory Approach on the Adaptation Process in Facility of Long-Term Care Elderly
신용석, Jung-Woo Kim, 김수정
Korean Journal of Social Welfare.2013; 65(3): 155. CrossRef - A Study on the conflict among Siblings Regarding the Long-term Care of Older Parents
Yoo,Hi-Jung
Korean Journal of Family Social Work.2013; null(40): 63. CrossRef - A Study of Determinants of Caregivers’ Attitudes towards Utilization of Residential Care in the UK: Focused on Scottish Family Caregiver in Edinburgh City
이현숙
Health and Social Welfare Review.2013; 33(1): 260. CrossRef - Knowledge regarding Advance Directives among Community-dwelling Elderly
Sun Woo Hong, Shin Mi Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(3): 330. CrossRef - Nursing Home Placement: The Process of Decision Making and Adaptation among Adult Children Caregivers of Demented Parents in Korea
Su-Hye Kwon, Young-Sook Tae
Asian Nursing Research.2012; 6(4): 143. CrossRef - The Study on commodification of filial piety through Long term care service
홍세영, 서종희
Korean Journal of Gerontological Social Welfare.2012; null(57): 51. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Observable Indicators of Nursing Home Care Quality Evaluation Instrument
Jia Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 474. CrossRef
- Development of the Care Burden Scale for Family of Elderly in Nursing Facilities
- 742 View
- 6 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Effects of Programmed Information on Coping Behavior and Emotions of Mothers of Young Children Undergoing IV Procedures
- Daeyoung Won
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(8):1301-1307. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.8.1301
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To determine the effects of provision of information on mother's problem focused coping ability during their child's intravenous procedure.
Methods Data were collected from 56 mothers whose children have admitted to pediatric ward in the hospital. The participants included 27 intervention group mothers and 29 control group mothers. For the information intervention, “Programmed Information for Parental Coping before Intravenous Procedure (PIPC-IP)”, video program was made based on self-regulation theory for the experimental group mothers. Mother's coping ability was measured by parental supportive behavior, parental beliefs and Profile of Mood State (POMS).
Results Mothers who received PIPC-IP showed significantly higher levels of supportive behavior (t = 3.55, p = .005) and Parental Beliefs (t = 2.95, p = .005), but no significant difference in negative mood on POMS (t = .15, p = .87) compared to mothers in the control group.
Conclusions These results demonstrate that PIPC-IP is an effective intervention to increase the supportive behaviors and beliefs of mothers' problem focused coping ability but not the negative mood.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Voices of Korean Young Adults on Climate Change : Emotions and Communication Attempts Driven by Climate Change
Hye-Sun Lee, Gyuhyun Ho
Korean Journal of Journalism & Communication Studies.2024; 68(5): 5. CrossRef - Validação de cartilha sobre cateterização intravenosa periférica para famílias
Cleonara Sousa Gomes e Silva, Luciano Marques dos Santos, Manuela De Jesus Souza, Silvia Da Silva Santos Passos, Silvone Santa Barbara da Silva Santos
Avances en Enfermería.2020; 38(1): 28. CrossRef - Parent Coping Support Interventions During Acute Pediatric Hospitalizations: A Meta-Analysis
Stephanie K. Doupnik, Douglas Hill, Deepak Palakshappa, Diana Worsley, Hanah Bae, Aleesha Shaik, Maylene (Kefeng) Qiu, Meghan Marsac, Chris Feudtner
Pediatrics.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Family-centred care for hospitalised children aged 0-12 years
Linda Shields, Huaqiong Zhou, Jan Pratt, Marjory Taylor, Judith Hunter, Elaine Pascoe
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2012;[Epub] CrossRef
- Voices of Korean Young Adults on Climate Change : Emotions and Communication Attempts Driven by Climate Change
- 646 View
- 4 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Attitude, Beliefs, and Intentions to Care for SARS Patients among Korean Clinical Nurses: An Application of Theory of Planned Behavior
- Cho Ja Kim, Hye Ra Yoo, Myung Sook Yoo, Bo Eun Kwon, Kyung Ja Hwang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(4):596-603. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.4.596
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study examined Korean clinical nurses' intentions to care for SARS patients and identify determinants of the intentions. Theory of planned behavior was the framework to explain the intentions of Korean nurses for SARS patients care.
Methods A convenient sample of six hundreds and seventy nine clinical nurses from four university-affiliated hospitals located in Seoul and in Kyung-gi province was used. Self-administered (83-items) questionnaire was used to collect data. Intentions, attitude, subjective norm, perceive behavioral control, behavioral beliefs, normative beliefs, and control beliefs were the study variables. All items were measured using 7-point Likert scale (−3 to +3). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation method, and stepwise multiple regression methods.
Results Intentions and attitudes toward SARS patient care among Korean clinical nurses were moderate, but their subjective norm and perceive behavioral control of SARS patients care were negative. Stepwise multiple regression analysis indicated that attitude toward SARS patient care, perceived behavioral control, subjective norm were the determinants of the intentions for SARS patients care as theory proposed. Among the behavioral beliefs, “SARS-patient caring would be a new experience”, “during SARS-patient caring, I should be apart from my family”, “after completing SARS-patient caring, I would be proud of myself being able to cope with a stressful event” and “with my SARS-patient caring, patients could recover from SARS” were the significant determinants. Among the normative beliefs, colleague approval, spouse approval, and physician approval were significant determinants of the intentions. Among the control beliefs, “SARS-patient caring would be a challenge” “SARS-patient caring is a professional responsibility”, “tension during the care of SARS patients” and “support from team members” were the significant determinants of the intentions.
Conclusion Korean clinical nurses in this study were not willing to care for SARS patients and showed negative attitude toward the care. They believed their friends and family were not approved their care for SARS patients. Nurses were in conflicts between professional responsibilities to care for SARS patients and personal safety. This study was the first to understand stress and burden of Korean clinical nurses who are in front line to care for newly developed communicable disease such as SARS. Under the circumstance where several fatal communicable diseases are predictable, conflicts between professional responsibility and their personal risks should be taken into considerations by nurses themselves and by nursing administrators in order to improve quality of care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Nursing Intention among Korean Clinical Nurses for COVID-19 Patient Care: a Cross-Sectional Study
Ji Hyun Kim, Sung Hee Shin, Soojung Jo, Vicki Simpson
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2026; 32(1): 39. CrossRef - Caring behaviors and associated predictive factors in nurses caring for Covid-19 patients: An application of the theory of planned behavior
Reyhaneh Maleki, Afsaneh Raiesifar, Nasibeh Sharifi, Elham Shafiei, Fatemeh Darabi
Heliyon.2025; 11(4): e42683. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of Factors Influencing Nursing Intentions toward COVID-19 Patients
Nari Lee, Hae Ran Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 285. CrossRef - Psychometric validation of the nursing care behavior questionnaire during emerging disease epidemics: A theory of planned behavior approach
Afsaneh Raiesifar, Reyhaneh Maleki, Nasibeh Sharifi, Fatemeh Darabi, Sayyadi Hojjat
Heliyon.2024; 10(4): e25900. CrossRef - Factors influencing nurses' intent to provide care involved in coronavirus disease 2019: Theory of planned behaviour perspectives
Areum Hwang, Donghee Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2024; 33(1): 333. CrossRef - Predictors of nurses’ reporting for work at the time of epidemics and natural disasters; solutions for hospital surge capacity
Vahid Ghavami, Fatemeh Kokabi Saghi, Ali Asghari, Hamidreza Shabanikiya
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2022; 54(4): 470. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nursing Intention for Patients with Emerging Infectious Diseases among Nurses in Hospitals Dedicated to COVID-19: A Focus on the Mediating Effects of Job Crafting
Yu Na Lim, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 105. CrossRef - Examining Primary Care Physicians' Intention to Perform Cervical Cancer Screening Services Using a Theory of Planned Behavior: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach
Zhiqing Hu, Yanjun Sun, Yuhao Ma, Kejin Chen, Ling Lv, Lingling Wang, Yuan He
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioral Intentions and Factors Influencing Nurses' Care of COVID-19 Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Feifei Cui, Yundan Jin, Haiying Wu, Rongting Wang, Xinling Pan, Shuainan Chen, Yanyan Jin, Meiqi Yao, Huiqiang Fan, Jing Xu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing nursing students’ care intentions toward emerging infectious diseases patients: A descriptive-predictive study
Seungmi Park, Insun Jang, Soo-Young Yu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - Intention to Care for COVID-19 Patients Among Nurses Working at Health Care Institutions of Debre Tabor Town, North Central Ethiopia
Binyam Minuye, Wubet Alebachew, Melese Kebede, Sintayehu Asnakew, Demeke Mesfin Belay
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2021; Volume 14: 2475. CrossRef - Identifying Occupational and Non-Occupational Factors Affecting the Retention of Health Care Employees in the Covid-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review Study
Masoud Khosravipour, Payam Khanlari, Mohammad Reza Jafari
Journal of Ergonomics.2021; 9(1): 15. CrossRef - Latent Profile Analysis of Perceptions and Attitudes Towards COVID-19 in a Sample of Chinese People
Zhimin Niu, Li Li, Hongying Li, Songli Mei, Hui Jiang, Zhiyong Deng, Jun Xin
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Providing care to patients with COVID-19 in a reference hospital: health care staff intentional behavior and factors that affect it
Theodoros Pesiridis, Petros Galanis, Eleni Anagnostopoulou, Athena Kalokerinou, Panayota Sourtzi
AIMS Public Health.2021; 8(3): 456. CrossRef - Factors influencing nurses’ behavioral intention toward caring for COVID-19 patients on mechanical ventilation: A cross-sectional study
Jingxia Cheng, Jinbo Cui, Wenwen Yu, Hua Kang, Yongming Tian, Xiaolian Jiang, Khatijah Lim Abdullah
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(11): e0259658. CrossRef - Factors Associated With the Intention to Participate in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Frontline Prevention Activities Among Nursing Students in Vietnam: An Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior
Quynh Anh Tran, Huong Thi Thanh Nguyen, Tung Van Bui, Nguyet Thi Tran, Nguyet Thi Nguyen, Tham Thi Nguyen, Hien Thu Nguyen, Son Hoang Nguyen
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of Workforce Preparedness during Pandemics Among Healthcare Workers at the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs
Michelle D. Balut, Claudia Der-Martirosian, Aram Dobalian
Journal of Primary Care & Community Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Intentions to Care For Emerging Infectious Disease Patients among National and Public Hospitals Nurses
Hea-Jin Moon, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(1): 11. CrossRef - Intention to response, emergency preparedness and intention to leave among nurses during COVID‐19
Jiaying Li, Pingdong Li, Jieya Chen, Liang Ruan, Qiuxuan Zeng, Yucui Gong
Nursing Open.2020; 7(6): 1867. CrossRef - Review of possible psychological impacts of COVID-19 on frontline medical staff and reduction strategies
Xiao-Wei Fu, Li-Na Wu, Ling Shan
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(15): 3188. CrossRef - Factors influencing nurses' intention to care for patients with emerging infectious diseases: Application of the theory of planned behavior
Jiyeon Lee, Sook Jung Kang
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(1): 82. CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Nursing Intention among Korean Clinical Nurses for COVID-19 Patient Care: a Cross-Sectional Study
- 877 View
- 8 Download
- 21 Crossref

- A Paradigm Analysis Related to Spiritual Experiences Focused on Christian of Patients with Terminal Cancer
- Hiun Ju Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(2):299-309. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.2.299
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The main purpose of this study was to develop a substantive theory on the process of the spiritual experience in Christian terminal cancer patients in the context of Korean society and culture. The question for the study was ‘ What is the spiritual process in Christian terminal cancer patients?’.
Method The research method used was the Grounded Theory Method developed by Strauss and Corbin (1998). Participants for this study in total were 9 Christian terminal cancer patients. Data was collected using in-depth interviews during April 2003 to March. 2004. Data collection and analysis were carried out at the same time.
Result From the analysis 58 concepts and 20 categories emerged. The categories were presented into a paradigm, which consisted of condition-actions/ interactions-consequences. The theoretical scheme was described by organizing categories. In total, 4 stages were developed from the condition-actions/ interactions-consequences. Throughout these stages, the ‘ overcoming process of unbalanced interconnectedness’ was the core category discovered.
Conclusion This study provides a framework for the development of individualized care interventions in the ‘ overcoming process of unbalanced interconnectedness’ for Christian terminal cancer patients.
- 490 View
- 0 Download

- Experience of Gastric Cancer Survivors and their Spouses in Korea: Secondary Analysis
- Myungsun Yi, David Kahn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(4):625-635. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.4.625
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the experiences of gastric cancer couples in Korea and to generate a substantive theory integrating the experiences of gastric cancer survivors and their spouses as a whole. The specific aims of this study were to explore major problems gastric cancer couples faced and how they resolved these problems, focusing on inter-relational dynamics within the couples and on similarities and differences between the couples.
Methods This was a secondary analysis study using grounded theory techniques. The study used the data of 11 married couples which was collected from in-depth interviews from two primary studies. The unit of analysis was dyads of gastric cancer survivors and their spouses.
Results The basic social psychological process that emerged from the analysis was “taking charge of their health.” Major categories involved in this process were identified as 1) adjusting to new diets, 2) reinforcing physical strength, 3) seeking information, 4) strengthening Ki, 5) lowering life-expectations, and 6) going their separate ways. These six categories represent major strategies in overcoming critical problems that occurred in day-to-day experiences. In terms of the process, the first five categories characterize the earlier stage of the process of “taking charge of their health,” while “going their separate ways” indicates the later stage and also the beginning of their separate ways: “pursuing spiritual life” for the survivors, and “preparing for the future” for the spouses.
Conclusions The results of this study will help design family care for the people with gastric cancer by providing in-depth understanding and insight on the lives of gastric cancer couples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences of informal caregivers supporting individuals with upper gastrointestinal cancers: a systematic review
Melinda Furtado, Dawn Davis, Jenny M. Groarke, Lisa Graham-Wisener
BMC Health Services Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient, nursing and medical staff experiences and perceptions of the care of people with palliative esophagogastric cancer: a systematic review of the qualitative evidence
Alison Cowley, Catrin Evans, Fiona Bath-Hextall, Joanne Cooper
JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports.2016; 14(10): 134. CrossRef - A meta-analysis of qualitative studies on living with oesophageal and clinically similar forms of cancer, seen from the perspective of patients and family members
Sissel Andreassen, Ingrid Randers, Kerstin Ternulf Nyhlin, Anne-Cathrine Mattiasson
International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being.2007; 2(2): 114. CrossRef
- Experiences of informal caregivers supporting individuals with upper gastrointestinal cancers: a systematic review
- 750 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Adjustment Patterns of Illness Process of People with Hemophilia in Korea
- Won Ock Kim, Hyun Sook Kang, Myung Sun Yi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(1):5-14. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.1.5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore adjustment pattern of illness process of people with hemophilia in Korea.
Method 23 people with hemophilia had participated for this study. The data were collected through in-depth interviews and analyzed using Strauss & Corbin's grounded theory method.
Result “would be free from” was emerged as a core category and it reflects that all participants wanted to be free from the constraints of the disease. The adjustment process was categorized into two stage, the ‘ unstable stage’ and the ‘ stable stage’. In the process of “would be free from” four different patterns were identified: hopelessness type; appreciation type; challenge type; and transcendence type. These types were identified based on the degree of pursuing normal life and managing the disease, and social support. The most frequently occurring type was hopelessness type but the participants of this type suffered the most. The transcendence type was the most ideal type, but it occurred the least.
Conclusion The results of this study indicate that people with hemophilia in Korea still suffer from the disease and they need supports. The results would be useful for health care professionals in establishing education and counseling program for the people with hemophilia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Foot-Reflexology Massage on Fatigue, Stress and Postpartum Depression in Postpartum Women
Mi Son Choi, Eun Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 587. CrossRef - Comparative Study on Parenting Stress, Guilt, Parenting Attitude, and Parenting Satisfaction Between Mothers with a Hemophilic Child and a Healthy Child
Won Ok Kim, Hyun Sook Kang, Kyoul Ja Cho, Young A Song, Eun Sun Ji
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2008; 14(4): 270. CrossRef
- Effects of Foot-Reflexology Massage on Fatigue, Stress and Postpartum Depression in Postpartum Women
- 784 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Turnover Experience of Male Nurses
- Hyunsu Kim, Jeongseop Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(1):25-38. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to identify turnover experiences of men in nursing and to derive a substantive theory on the turnover experience of men who are nurses.
Methods Data were collected through in-depth interviews with 13 men who had worked as a nurse for 1 year or more, and had a turnover experience during that period. Collected data were analyzed on the basis of Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory.
Results The core category in the turnover experiences of the respondents was ‘seeking a stable place for me’. In the analysis of the core category, types of ‘contentment’, ‘seeking’, ‘survival’ and ‘confusion’ were identified. The sequential stages of these nurses’ turnover experience were ‘confrontation’, ‘incertitude’, ‘retrying’ and ‘realization’. However, when a problem arose in the process, they returned to the stage of confusion. Thus, these stages could occur in a circular fashion.
Conclusion These findings provide a deep understanding of the turnover experience of men in nursing and offers new information about how they adapt to nursing practice. The findings should be useful as foundational data for men who hope to become nurses and also for managers responsible for nurses who are men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Male nurses’ adaptation experiences after turnover to community institutions in Korea: A grounded theory methodology
Ja-Sook Kim, Suhyun Kim, Hyang-In Cho Chung, Sally Mohammed Farghaly
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(5): e0302819. CrossRef - Turnover Rates and Factors Associated With Turnover: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Retention Period of Clinical Nurses in Korea Using National Data
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice.2024; 25(2): 83. CrossRef - A survival analysis approach to determine factors associated with non-retention of newly hired health workers in Iran
Vahid Ghavami, Seyed Saeed Tabatabaee
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing work engagement among male nurses: A structural equation model
Chao Wu, Si‐zhe Cheng, Jing Wu, Yin‐juan Zhang, Ya‐wei Lin, Lu Li, Juan Du, Yu‐hai Zhang, Hong‐juan Lang
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7749. CrossRef - Turnover intention and retention of newly licensed nurses in their first job: A longitudinal study
Hyoung Eun Chang, Sung‐Hyun Cho
International Nursing Review.2023; 70(3): 338. CrossRef - Clinical Work and Life of Mid-Career Male Nurses: A Qualitative Study
Soo-Yong Shin, Eun-Ju Lim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(12): 6224. CrossRef - Analysis of Male and Female Nurses’ Attitudes toward Nurse Uniforms in South Korea: The Functional, Expressive, and Aesthetic (FEA) Framework
Seon Mi Jang, Sae Eun Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo
International Journal of Costume and Fashion.2021; 21(1): 25. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Turnover Intention among Male Nurses in Korea
Su Ol Kim, Sun-Hee Moon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(18): 9862. CrossRef - Factors associated with the nurses’ intent to stay in China, Japan, and Korea: an integrative review
Ting Xue, Wen-Bin Jiang, Meng-Di Ma, Jie Zhang, Ming-Hui Lu, Yong-Mei Jiang
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(3): 269. CrossRef - Why newly graduated nurses in South Korea leave their first job in a short time? A survival analysis
Eunhee Lee
Human Resources for Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Subjectivity About Turnover Intention Among Male Nurses in South Korea: A Q-Methodological Study
Ick-Jee Kim, Hyung-Wha Shim
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(2): 113. CrossRef - Win-Win Partnership in the Clinical Setting: Female Nurses' Adaptive Experience to Male Nurses
Hyunsu Kim, Eun Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 423. CrossRef
- Male nurses’ adaptation experiences after turnover to community institutions in Korea: A grounded theory methodology
- 2,149 View
- 21 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Adaptation Process to Group Home Living by Older Adults
- Hee Sook Yoon, Sohyune Sok
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(6):858-870. Published online December 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.858
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to explore and describe the adaptation process of older people to group homes.
Methods Participants were twenty older adults aged 65 or older who were living in group homes. Data were collected from January to April, 2015. In-depth unstructured interviews were conducted with individual participants. Data were analyzed using Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory method.
Results From open coding, 100 concepts, 38 sub-categories, and 14 categories were identified. Analysis showed that the central phenomenon of the adaptation process of older people to group homes was ‘gradually giving up’. Causal conditions were ‘good-for-nothing body’, contextual conditions were ‘pushed’, ‘beleaguered’. Intervening conditions were ‘reliable pillar: children’, ‘having affection (情) more than having it from family: facility workers’, ‘comfort - like feeling at home’, ‘relieved: system’. Action/interaction strategies were ‘facing the unfamiliar reality’, ‘building relationships with other people’, ‘accepting reality’. Consequences were ‘a good place, more than expected’, ‘hope for the remaining days’, ‘waiting for a peaceful death’.
Conclusion The results of this study provide an in-depth understanding of the experience of the adaptation process of older people to group homes. The findings from this study can be used as basic data to establish policies to increase the number of small scale facilities which can help older adults adapt easily to the facilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recovery experience of older adults with COVID-19: A grounded-theory study
Hee-Sook Kim, Jae Wan Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 66. CrossRef
- Recovery experience of older adults with COVID-19: A grounded-theory study
- 1,038 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Grounded Theory Approach on Nurses’ Experience with Workplace Bullying
- Jiyeon Kang, Seonyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(2):226-237. Published online April 17, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: The purpose of this qualitative study was to explore the workplace bullying experience of Korean nurses.
Methods: Participants were twenty current or former hospital nurses who had experienced workplace bullying. Data were collected through focus group and individual in-depth interviews from February to May, 2015. Theoretical sampling method was applied to the point of theoretical saturation. Transcribed interview contents were analyzed using Corbin and Strauss’s grounded theory method.
Results: A total of 110 concepts, 48 sub-categories, and 17 categories were identified through the open coding process. As a result of axial coding based on the paradigm model, the central phenomenon of nurses’ workplace bullying experience was revealed as ‘teaching that has become bullying’, and the core category was extracted as ‘surviving in love-hate teaching’ consisting of a four-step process: confronting reality, trial and error, relationship formation, and settlement. The relationship formation was considered to be the key phase to proceed to the positive settlement phase, and the participants utilized various strategies such as having an open mind, developing human relationships, understanding each other in this phase.
Conclusion: The in-depth understanding of the workplace bullying experience has highlighted the importance of effective communication for cultivating desirable human relationships between nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Organizational Silence and Related Factors Among Shift Work Nurses in Korea: A Cross‐Sectional Study
Sung Eon Sim, Hye-Young Jang, De-Chih Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Social status mediates the propagation of unfairness
Hyeran Kang, JuYoung Kim, Daeeun Kim, Hackjin Kim
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of cognitive rehearsal programs for the prevention of workplace bullying among hospital nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yulliana Jeong, Hye Sun Jung, Eun Mi Baek
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Moderating Role of Perceived Social Support in the Relation between Type D Personality and PTSD Symptoms among ICU and ER Nurses
Sohyeon Kim, Myung-Ho Hyun
STRESS.2023; 31(4): 197. CrossRef - Intervention types and their effects on workplace bullying among nurses: A systematic review
Sun Joo Jang, Youn‐Jung Son, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1788. CrossRef - ICU nurses’ experiences of feeling hurt by medical personnel
Jung-Hoon Lee, Yeoungsuk Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 347. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Bullying Measurement in Korean Nurses' Workplace
Hyo-Suk Song, So-Hee Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 478. CrossRef - Traumatic Events and Factors Affecting Post-traumatic Growth of Nurses in General Hospitals
Haesook Kim, Eunsook Kim, Younghee Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(3): 218. CrossRef - Nurses’ Workplace Bullying Experiences, Responses, and Ways of Coping
Sun Yee Yoo, Hye Young Ahn
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(19): 7052. CrossRef - A Grounded Theory Approach on Experiences of Citizen Participation in Urban Regeneration
Jaeun Lee
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2019; 54(7): 24. CrossRef - The Effects of Nursing Organizational Culture, Work Performance and Workplace Bullying Type on Workplace Bullying Consequence of Nurses
Ga Yeon Jeong, Hyun Jung Jang
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(4): 424. CrossRef - A Topic Modeling Analysis for Online News Article Comments on Nurses' Workplace Bullying
Jiyeon Kang, Soogyeong Kim, Seungkook Roh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(6): 736. CrossRef - Response Patterns of Nursing Unit Managers regarding Workplace Bullying: A Q Methodology Approach
Jin Kyu Choi, Byoungsook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 562. CrossRef - The Influence of Lateral Violence on Burnout and Empathy with Patients among Nurses: The Moderating Effect of Communication
Soohyun Nam, Boyoung Hwang
Stress.2019; 27(3): 224. CrossRef - Threats to Identity: A Grounded Theory Approach on Student Nurses' Experience of Incivility during Clinical Placement
Jiyeon Kang, Yeon Jin Jeong, Kyoung Ran Kong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(1): 85. CrossRef - Effects of a Cognitive Rehearsal Program on Interpersonal Relationships, Workplace Bullying, Symptom Experience, and Turnover Intention among Nurses: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Jiyeon Kang, Jeung-Im Kim, Seonyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 689. CrossRef - The Related Factors to Workplace Bullying in Nursing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jiyeon Kang, Minju Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(4): 399. CrossRef - Qualitative Research on Nurses Experiencing Taeoom
SunHwa Choeng, InSook Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 238. CrossRef
- Organizational Silence and Related Factors Among Shift Work Nurses in Korea: A Cross‐Sectional Study
- 1,425 View
- 28 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Transitional Care for Older Adults with Chronic Illnesses as a Vulnerable Population: Theoretical Framework and Future Directions in Nursing
- Youn-Jung Son, Mi-Ae You
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):919-927. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.919
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Effective transitional care is needed to improve the quality of life in older adult patients with chronic illness and avoid discontinuity of care and adverse events. The aim of this article is to provide an overview of the key features, broader implications, and the utility of Meleis' transition theory intended for the transitional care of older adults with chronic illnesses. We present the role of nurse in the context of transitional care and propose future directions to increase the quality of nursing care.
Methods The online databases Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature, MEDLINE, and Science Direct were searched for relevant literature published since 1970 along with textbooks regarding nursing theory.
Results An evaluation of the usefulness of transition theory based on transitional care in older adult patients with chronic illnesses is provided. Healthy transition should be the expected standard of nursing care for older adults across all healthcare settings.
Conclusion Nurses need to contribute to the development of transitional care for vulnerable populations; however, transition theory needs to be enhanced through additional theoretical work and repeated evaluations of the applicability in areas of transitional care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-Management Support (SMS) in Transition: The Case of Osteoporosis Management Support in a Chinese Hospital
Jinling Huang, Xianghua Ding
Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW).2025; 34(1): 1. CrossRef - Critical evaluation of Afaf Meleis´s Transition Theory: strengths, limitations and applications in nursing education
Daniella Cancino-Jiménez, Naldy Febré, Ximena Cea-Netting, Jorge Cancino-Jiménez, Salomé Olguín, Katherine Olguín
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Evolving Roles of Nurses Providing Care at Home: A Qualitative Case Study Research of a Transitional Care Team
Wei Ting Chen, Hong-Gu He, Yeow Leng Chow
International Journal of Integrated Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID‐19 and hospice community palliative care in New Zealand: A qualitative study
Rosemary Frey, Deborah Balmer
Health & Social Care in the Community.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Transitional care interventions to reduce emergency department visits in older adults: A systematic review
Latifah Jehloh, Praneed Songwathana, Wipa Sae-Sia
Belitung Nursing Journal.2022; 8(3): 187. CrossRef - Measurement tools that assess the quality of transitional care from patients' perspective: A literature review
Mai Yoshimura, Naomi Sumi
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Components of hospital-to-home care interventions for patients with heart failure in Japan: An integrative review
Mai Yoshimura, Naomi Sumi
Journal of International Nursing Research.2022; 1(1): e2021-0001. CrossRef - Discharge teaching, readiness for hospital discharge and post‐discharge outcomes in cataract patients: A structural equation model analysis
Aihua Zhang, Xianqiong Feng, Chujin Qiu, Lopez Violeta
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(3): 543. CrossRef - A Theory on the Components of Depression Self-Management in Older Adults
Meg Polacsek, Gayelene H. Boardman, Terence V. McCann
Qualitative Health Research.2021; 31(1): 160. CrossRef - The Influence of a Successful Wellness-Illness Transition on the Experience of Depression in Older Adults
Meg Polacsek, Gayelene H. Boardman, Terence V. McCann
Issues in Mental Health Nursing.2020; 41(1): 31. CrossRef - Effects of Multidisciplinary Team-Based Nurse-led Transitional Care on Clinical Outcomes and Quality of Life in Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis
Limin Liang, Yinghua Pan, Danchun Wu, Yongli Pang, Yuanyuan Xie, Hengying Fang
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(2): 107. CrossRef
- Self-Management Support (SMS) in Transition: The Case of Osteoporosis Management Support in a Chinese Hospital
- 2,644 View
- 55 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The Process of Acceptance of Complementary and Alternative Therapies (CATs) among Nurses: Grounded Theory Approach
- Ae-Kyung Kim, Young-Shin Lee, Hyun-Jung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(5):669-680. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.669
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to explore the process of accepting CATs among nurses who experienced CATs in Korea.
Methods Grounded theory methodology was utilized. Data were collected from 10 nurses during individual in-depth interviews. Theoretical sampling was used until the data reached saturation. Data were analyzed using the constant comparative analysis method.
Results The core category emerged as "resolving the doubt and integrating" explaining the process of accepting CATs. The nurses engaged in three stages: need awareness, look for solution and integration. Causal conditions were interest as a nursing intervention and orthodox medical limitations. Context was lack of basis for application and increase in social interest. Strategies were new knowledge acquisition, having a strong will, combined with existing knowledge, and individualized intervention. Intervening conditions were others' eye, exhaustion for nurses and physical environment. Consequences were expanding of the nursing role and improved nurse satisfaction.
Conclusion The results of the study should facilitate application of CATs in nursing practice. To help nurses who are interested in CATs, there is a need for education programs, and further research on CATs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends in Korean intervention studies on complementary and alternative therapies in rehabilitation nursing
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2024; 20(5): 158. CrossRef - Clinical nurses' perceptions of the opportunities for using complementary therapies in Iranian clinical settings: A qualitative study
Zahra Tagharrobi, Sima Mohammadkhan Kermanshahi, Eesa Mohammadi
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2016; 24: 11. CrossRef
- Trends in Korean intervention studies on complementary and alternative therapies in rehabilitation nursing
- 969 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Analysis of Trends and Contents of Nursing Doctoral Dissertations in Korea
- Kwang-Ja Lee, Younhee Kang, Mee Ock Gu, Kyunghee Kim, Oksoo Kim, Yeon-Ok Suh, Eunyoung Suh, Soo Yang, Eun-Hyun Lee, Ja Hyung Lee, Myoung-Ae Choe, Yang Sook Hah
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(2):302-309. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.2.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to identify contents and trends of Korean nursing doctoral dissertations in terms of research methodology and theoretical characteristics.
Methods The design of the study was descriptive study and a total of 1,089 quantitative studies completed between 1982 and 2010 were reviewed using the analytical framework developed by the researchers.
Results The majority of studies utilized the experimental design (51.5%) and the others were survey design (38.8%) and methodological design (5.0%). Study subjects were shown as patients (45%), care givers (11.2%), ordinary persons (40.6%) and others (3.2%). There were growing trends in experimental design and patients as subjects. The prevailing data collection settings were hospitals (45.8%) and community (27.8%). The theoretical frameworks that studies were based on were the existing theories (37%) and a newly developed theoretical framework by a researcher (25.2%). a framework derived from other studies by the researcher (25.2%). Majority of studies (78.5%) employed a single theory as a theoretical framework. However, 31.8% of studies had no theoretical framework based on.
Conclusion Findings of this study provided the opportunities to shed new light on the current status of Korean doctoral dissertation and to deliberate on the future direction of nursing studies in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Integrative Review of Korean Nursing Studies on Pediatric Tonsillectomy
Kyoung Eun Yu, Jin Sun Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(4): 416. CrossRef - Trend Analysis of Research in the Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing (2010~2015)
Yerin Cha, Joeun Kwon, Sunhye Kwon, Kyung Hee Lee, Jiyun An
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(2): 92. CrossRef - Analysis of Trends and Contents of Ancestral Ritual Foods of Korean Jong-ga
Changhyeon Lee, Young Kim, Young Hwang, Hyeonmi Kim
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2016; 31(4): 286. CrossRef - A Historical Trends of Doctoral Nursing Education in Korea
Kasil Oh, Young Sook Park, Ja Hyung Lee, Kyong-Ok Oh, Yang Heui Ahn, Jiyoung Lim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 93. CrossRef - An Analysis of Nursing Research on Child Rearing in Korea.
Dong Won Lee, In Soo Kwon
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(4): 264. CrossRef
- An Integrative Review of Korean Nursing Studies on Pediatric Tonsillectomy
- 913 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Experiences of Family Caregivers of Patients with Terminal Cancer
- Eun Sook Choi, Keum Soon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(2):280-290. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.2.280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study done to identify the experiences of families caring for patients with terminal cancer. The question was, "What is the caregiving experience of a family who has a member with terminal cancer?"
Methods Grounded Theory was applied and in-depth interviews were done with 11 family members. Interviews were recorded with the interviewees' consent and were transcribed and analyzed. Participants' relationships to patients were 6 spouses, 4 daughters, and 1 mother. The ages of the participants were between 32 and 62, with an average of 47.5.
Results The study showed "enduring with bonds" as the main category and the main factor affecting this category was the "patients' diagnosis of terminal cancer." The caregiving experience was divided into four stages: shock, confusion, struggle, and acceptance. Mediating factors were relationship with the patient, intimacy with the patient, social support, communication, and trust. Conclusively, participants underwent internal maturity, and changes occurred in family and social and personal life.
Conclusion The families took care of the patients with responsibility and love. The study results should help with the understanding of a family with a member with terminal cancer and should be used to develop nursing, mediating, and consulting programs for these caregivers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenges and Proposed Improvements in Advance Care Planning: Insights from a Real Clinical Case of a Terminally Ill Patient in Korea
Hongyeul Lee
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2025; 28(1): 41. CrossRef - The End-of-Life Experiences of Cancer Patients’ Families in a Tertiary Hospital Providing Palliative Care Consultation During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hyoung Suk Han, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2025; 28(2): 40. CrossRef - Do spouse burden of care, family resilience, and coping affect family function in gynecologic cancer in Korea?: a cross-sectional study
Minkyung Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 197. CrossRef - Caregiving experiences of Korean family caregivers of cancer patients: An integrative literature review
Eunice E. Lee, Shin‐Young Lee
Psycho-Oncology.2020; 29(10): 1486. CrossRef - Validation of the Nurses’ Involvement in Dying Patients and Family Care-Korean Version
Mi Yeon Kim, Hanna Lee, Inyoung Lee, Mirim Lee, Haeryun Cho
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2020; 23(4): 228. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis of Posttraumatic Growth in Family Caregivers of Cancer Patients
Kyoung Hee Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(1): 9. CrossRef - Experiences of Distress among Family Caregivers of Hospitalized Cancer Patients
Juhye Jin, Jin-Hee Yoo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(5): 451. CrossRef - Unmet Needs and Caregiver Burden Among Family Caregivers of Hospice Patients in South Korea
Jihyeon Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2017; 19(4): 323. CrossRef - The Lived Experience of Suffering of Family with Cancer Patients: Parse’s Human Becoming Research Method
Ye-Sook Choi
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(2): 127. CrossRef - Experiences of Spouses of Patients with Hematologic Malignancies: Finding a Way to Get Out of the Endless Tunnel
Youngshin Lee, Youngran Tak
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(1): 46. CrossRef - Family Caregivers’ Quality of Life, Depression and Anxiety according to Symptom Control in Hospice Patients
Yun Hee Kim, Seung Hun Lee, Ho Seop Lim, Young Jin Choi, Yun Jin Kim, Sang Yeoup Lee, Jeong Gyu Lee, Dong Wook Jeong, Kyoung Hwa Yu
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2015; 18(4): 314. CrossRef - Impact Factors for Health of Family Caregivers of Hospice Patients
Bok Yae Chung, Hyeon Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(2): 75. CrossRef - Effect of Supportive Education Program for Hospice Patients's Family
Tae Yeon Lee, Yunhee Kwon
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(2): 175. CrossRef - Recognition of Patients, Families, Nurses, and Physicians about Clinical Decision-making and Biomedical Ethics
Ae Ran Park, Hyang Sook So, Myeong Cheong Chae
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(1): 23. CrossRef
- Challenges and Proposed Improvements in Advance Care Planning: Insights from a Real Clinical Case of a Terminally Ill Patient in Korea
- 1,469 View
- 9 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Life Experience of Inpatients with Recurrent Breast Cancer
- Young Ju Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(2):214-224. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.214
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Understanding daily life experiences of patients admitted to hospital with recurrent breast cancer.
Methods The grounded theory method was used for this study.
Results Consistent comparative analysis was used throughout the study to obtain the results. Results showed that inpatients with recurrent breast cancer experience 'a co-existence of life suffering and fear of death'. The causal condition of this result was determined to be 'patient's response to cancer recurrence (acceptance/despair)', including contextual conditions such as, 'previous experience with cancer treatment', 'patient's current physical condition', and 'treatment methods for recurrent cancer'. Intervening conditions, such as 'a strong will to live', 'family support', 'moral support providers', and action/interaction strategies were found to provide patients with 'a strength to live'. Shown in these results, inpatients with recurrent breast cancer were seen to have a simultaneous 'hope for life and fear of death'.
Conclusion When providing nursing services to inpatients with recurrent breast cancer, people must recognize there is a notable difference between individual patients' contextual conditions and interactive strategies. Henceforth, proper cognitive nursing must be provided which encourages patients to maintain a strong will to overcome the many hardships of treatment as well as physical nursing, such as management of side effects caused by chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Post-traumatic Growth Experiences of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Grounded Theory Approach
Seung-Kyoung Yang, Young-Suk Park, Eun-Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(2): 79. CrossRef - Journey through the Fight against Ovarian Cancer: Finding the Existence Value with being Tied to the Bridle of Death
Young-Suk Park, Jeong Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(6): 656. CrossRef - The Illness Adaptation Process of Patients Suffering from Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS): Doing My Best in Uncertainty
Ae-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(5): 472. CrossRef - Decision-making process related to treatment and management in Korean women with breast cancer: Finding the right individualized healthcare trajectory
Kkotbong Kim, Jinhyang Yang
Applied Nursing Research.2017; 35: 99. CrossRef - The Experience of Illness in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients
Hye Sook Kim, Myungsun Yi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(3): 121. CrossRef - A comparison of the effectiveness of complex decongestive physiotherapy and stellate ganglion block with triamcinolone administration in breast cancer-related lymphedema patients
Jeong-Gil Kim, Soon Ook Bae, Kwan Sik Seo
Supportive Care in Cancer.2015; 23(8): 2305. CrossRef - An Ethnographic Research on Psychological Experiences of Mothers Caring for their Children with Recurent Cancer
Seong-Heui Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(2): 75. CrossRef
- Post-traumatic Growth Experiences of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Grounded Theory Approach
- 926 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The Life of Adolescent Patients with Complex Congenital Heart Disease
- Sunhee Lee, So-Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(3):411-422. Published online June 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.411
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose In the present study, an analysis of the life of adolescents with complex congenital heart disease (CHD) was done using grounded theory. Consideration was given to the socio-cultural context of Korea.
Methods After approval from the institutional review board of Y hospital, 12 patients ranging in age from 14 to 35 were recruited. Data were gathered using in-depth interviews. Theoretical sampling was performed until the concepts were saturated.
Results The results confirmed the life of adolescents with complex CHD as a 'journey to finding uniqueness of oneself as a person with CHD'. The life consisted of 3 stages. In the crisis stage, participants had a feeling of threat to self-existence, and made an effort to be the same as others. In the self-recognition stage, participants who had sufficient role-performance built self-esteem while those who did not fell into self-accusation. In the self-establishment stage, participants who reached sufficiency in independence and knowledge planned the future, whereas those who did not conformed to the realities of life.
Conclusion The results of present study provide help in understanding the experiences of adolescents with CHD and provide a basis for developing nursing intervention strategies for these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Workplace Harassment in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease
Efrén Martínez-Quintana, Beatriz Déniz-Alvarado, Carlos Gallego-Sosa, Javier Pardo-Maiza, Jesús María González-Martín, Fayna Rodríguez-González
International Journal of Bullying Prevention.2025; 7(1): 36. CrossRef - Multifaceted Assessment of Quality of Life in Hospitalized Adolescents Aged 11–18 with Cardiological Problems
Agnieszka Pluta, Alicja Marzec, Monika Chojnowska, Mariola Głowacka
Children.2025; 12(12): 1661. CrossRef - Management of Caustic Esophageal Injury: A Survey Study in Türkiye and Review of the Literature
Sümeyye Sözduyar, Denizcan İnal, Ergun Ergün, Gülnur Göllü, Ahmet Murat Çakmak, Ufuk Ateş
Journal of Ankara University Faculty of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Familial Relationships on School Adjustment of Adolescents and Young Adults With Congenital Heart Disease
Youngji Moon, Jo Won Jung, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2023; 38(1): 52. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Congenital Heart Disease Patients According to Their Anatomical and Physiological Classification
Efr閚 Mart韓ez-Quintana, Hiurma Estupi襻n-Le髇, Ana Beatriz Rojas-Brito, Liuva D閚iz-D閚iz, Alejandro Barreto-Mart韓, Fayna Rodr韌uez-Gonz醠ez
Congenital Heart Disease.2023; 18(2): 197. CrossRef - La intervención psicocardiológica en la rehabilitación cardiovascular de niños escolares con cardiopatías congénitas: una revisión sistemática
T. Rodríguez Rodríguez, A. Nohaya Alonso, N. González Vales
Rehabilitación.2022; 56(4): 353. CrossRef - Factor analysis of the Korean version of the Illness Cognition Questionnaire for adolescents with chronic illness
Dasuel Lee, Dae‐Chul Jeong, Nack‐Gyun Chung, Sunhee Lee
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of rational emotive behavior therapy for depressive symptoms in adults with congenital heart disease
Ju Ryoung Moon, June Huh, Jinyoung Song, I-Seok Kang, Seung Woo Park, Sung-A Chang, Ji-Hyuk Yang, Tae-Gook Jun, Jong-Sook Han
Heart & Lung.2021; 50(6): 906. CrossRef - The adaptation process of mothers raising a child with complex congenital heart disease
Jeong-Ah Ahn, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Child Health Care.2018; 22(4): 520. CrossRef - The Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale is an adequate screening instrument for depression and anxiety disorder in adults with congential heart disease
Ju Ryoung Moon, June Huh, Jinyoung Song, I-Seok Kang, Seung Woo Park, Sung-A Chang, Ji-Hyuk Yang, Tae-Gook Jun
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between perceived parental rearing behaviors and school adjustment of adolescent cancer survivors in Korea
Sunhee Lee, Dong Hee Kim
Medicine.2017; 96(32): e7758. CrossRef - The effect of a resilience improvement program for adolescents with complex congenital heart disease
Sunhee Lee, Junga Lee, Jae Young Choi
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2017; 16(4): 290. CrossRef - Comparison of Physical Activity and Health-related Quality of Life in Adolescents with and without Congenital Heart Disease: A Propensity Matched Comparison
Hyun Jeong Kim, Eun Sun Yoon, Soo Jung Lee, Jina Choo, Seong-Ho Kim, Sae Young Jae
The Korean Journal of Sports Medicine.2017; 35(1): 40. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life in adolescents with congenital heart disease
Juliana Bertoletti, Giovana C. Marx, Sérgio P. Hattge, Lúcia C. Pellanda
Cardiology in the Young.2015; 25(3): 526. CrossRef - Comparison of Coping Strategy and Disease Knowledge in Dyads of Parents and Their Adolescent With Congenital Heart Disease
Jeong-Ah Ahn, Sunhee Lee, Jae Young Choi
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2014; 29(6): 508. CrossRef - Coping and Resilience of Adolescents With Congenital Heart Disease
Sunhee Lee, Sue Kim, Jae Young Choi
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2014; 29(4): 340. CrossRef
- Workplace Harassment in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease
- 1,096 View
- 4 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Health Experience of Depressive Adolescents: Reflected from Newman's Praxis Methodology
- Young-Ran Kweon, Chung-Sook Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(2):217-228. Published online April 28, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.217
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Guided by Newman's theory of health as expanding consciousness, this study was done to explore the health experience of adolescents having depression.
Methods The researcher engaged in six to eight in-depth interviews with six adolescents. To begin the dialog, the researcher asked each participant to recount the first important memory he/she had. All the narrative and diagram sharing between the researcher and participants were summarized according to recognized patterns and later elaborated in following interviews based on Newman's praxis methodology.
Results The significant individual pattern of early health experience was during the binding stage. At the turning point, individual patterns for participants revealed a personal journey of self-discovery and then emergence of reflecting behaviors. After the turning point, the participants changed as they evolved from the initial period of disruption and disorganization to organization at a higher level. The results suggest that adolescents who are depressive find new ways of relating to friends, family, healthcare providers, and the community by expanding their consciousness.
Conclusion Newman's praxis methodology is a good way of helping and studying adolescents with depression because it emphasizes participant-nurse/researcher partnership and pattern recognition as nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- 947 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Parenting Experiences of Parents of Children with ADHD: Approaching the Normal
- Won Oak Oh, Eun Sook Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(1):91-104. Published online February 28, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.1.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the experiences of parenting from the parents of children with ADHD and to develop a grounded theory about their experiences.
Method This study was a qualitative research study that used a grounded theory to understand and discuss the parenting experiences of parents of children with ADHD in a greater depth. Grounded data was collected through an in-depth interview from twelve participants with ADHD children. The data was analyzed using the grounded theory method.
Results “Approaching the normal” emerged as the core phenomenone. Parenting experiences for parents of children with ADHD referred to a process of bringing the children, back on track of normal growth development, and their functioning in the family at a normal level and establishing a new normalcy. The process of approaching the normal involved a basic social-psychological process, such as ‘living a day in hell’, ‘accepting’, ‘confronting the conflicts’, ‘lowering expectations’, and ‘making a new normalcy’.
Conclusion The outcomes of this study, which observed the parenting process of parents of children with ADHD, could enhance nurses' understanding of ADHD and help nurses become major mental health service providers for the mental health of children with ADHD and their families.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Burnout in Primary Family Caregivers of Hospital-based Home Care Patients
Ju Ok Yang, Hye Kyung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(1): 54. CrossRef - The Differences between ADHD and Normal Preschoolers in Narrative Representation
Hyewon Shin
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2017; 26(6): 559. CrossRef - Treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder with acupuncture: A randomized controlled trial
Soon-Sang Hong, Seung-Hun Cho
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2016; 8(3): 150. CrossRef - Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder among School-aged Children in Korea: A Meta-Analysis
Wan-Ju Park, Shin-Jeong Park, Sung-Dong Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(2): 169. CrossRef - Factors related to Medication Adherence according to Severity of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children
Youn Kyoung Kwag
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(4): 321. CrossRef - Parenting of children with ADHD in South Korea: the role of socio‐emotional development of children with ADHD
Won‐Oak Oh, Eun Sook Park, Min Hyun Suk, Dong Ho Song, Yeojin Im
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2012; 21(13-14): 1932. CrossRef - Teaching Status and Knowledge of Elementary School Teachers of Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Kyoung-Rim Kang, Young-Hae Kim, Young-Ok Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 136. CrossRef - Consumer-based Apparel Design Elements and Evaluation Criteria -Focus on F/W Outer-
Ji-Hyun Lee, Sun-Woo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Clothing and Textiles.2011; 35(9): 1015. CrossRef - Life Transition of Mothers of Children with Autism
Ae Ran Lee, Sun Woo Hong, Ji Soo Kim, Se Jin Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 808. CrossRef - Analysis of Relationships between Parenting Stress, Maternal Depression, and Behavioral Problems in Children at Risk for Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder
Hee Sun Shin, Jeong Mee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(3): 453. CrossRef - Patterns of Parenting in Korean Mothers of Children With ADHD
Won-Oak Oh, Judy Kendall
Journal of Family Nursing.2009; 15(3): 318. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Burnout in Primary Family Caregivers of Hospital-based Home Care Patients
- 796 View
- 11 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of an Instrument for Predictive Nursing Intention for SARS Patient Care
- Hye Ra Yoo, Bo Eun Kwon, Yon Soo Jang, Heun Keung Youn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(6):1063-1071. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.6.1063
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop and test validity and reliability of on instrument for predicting nursing intention for SARS patient care.
Method The psychometric properties of a SARS patient care attrition prediction tool, based on the Theory of Planned Behavior, were examined in this study. The Three-phase design involved a) salient beliefs generated from clinical nurses (n=43) b) content validation by expert panel evaluations(n=5) c) face validation by plot testing (n=10) d) and instrument validation in a cross sectional survey (n=299). Psychometric analysis of survey data provided empirical evidence of the construct validity and reliability of the instrument.
Result Principal component analysis verified the hypothesized 6-factor solution, explaining 68.2% of variance, and Alpha coefficients of .7538 to .9389 indicated a high internal consistency of the instrument.
Conclusion The instrument can be used by nurse administrators and researcher to assess clinical nurses' salient beliefs about caring for SARS patients, guide tailored intervention strategies to effective caring, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between nursing professionalism and nursing intention for patients with emerging infectious diseases of nursing students who had experienced COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating effect of e-Health literacy
Hee Jung Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(1): 71. CrossRef - Nurses’ intention to care of COVID-19 patients in hospitals dedicated to infectious disease in South Korea: application of the theory of planned behavior and verification of the moderating effect of ethical nursing competence
Mira Mo, Seongmi Moon, Eun Kyeung Song
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and psychometric evaluation of nurse’s intention to care for patients with infectious disease scale: an exploratory sequential mixed method study
Esmaeil Hoseinzadeh, Hamid Sharif-Nia, Tahereh Ashktorab, Abbas Ebadi
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Graduate Nurses’ Intention to Care for Emerging Infectious Disease Patients Based on Theory of Reasoned Action
Seonhye Jeong, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 60. CrossRef - The Influence of Long-term Care Hospital Nurses' Nursing Professionalism and Knowledge of COVID-19 on Nursing Intentions for COVID-19 Patients
Mi Aie Lee, Hyun Ju Park, Bonghwa Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 35. CrossRef - Development and testing effectiveness of a simulation program to control COVID-19 infections in nursing students
Kino Kang, Mihae Im, Miyoung Jang, Jaewoon Lee, Okjong Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(2): 54. CrossRef - Influences of Nursing Professionalism and Nursing Intention on Disaster Nursing Competency among Nurses when a Disaster Occurs in a Community: Response to COVID-19
Hyun-Jung JANG, Yoon-Jung KOO, Sun-Yeon HONG, Jeong-Eon PARK, Soo-Jin BAE, Suk-Jin PARK
THE JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2023; 35(2): 276. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Preparedness to Care for Patients with Highly Infectious Diseases among Nursing Staff in Long-term Care Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Ye Seul Lee, Min Hye Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(1): 35. CrossRef - Effects of Fatigue, Nursing Professionalism, and Nursing Work Environment on Nursing Intention for COVID-19 Patients among Nurses in a Designated COVID-19 Hospital
Hyeon Jeong Park, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 223. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nursing Intention for Patients with Emerging Infectious Diseases among Nurses in Hospitals Dedicated to COVID-19: A Focus on the Mediating Effects of Job Crafting
Yu Na Lim, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 105. CrossRef - Factors influencing nursing students’ care intentions toward emerging infectious diseases patients: A descriptive-predictive study
Seungmi Park, Insun Jang, Soo-Young Yu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - The Influencing Factor of Motivation to Transfer, Work Value, Social Responsibility on Nursing Intention for Patients with Emerging Communicable Diseases among Nursing Students
Da-Hye Park, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(3): 339. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Educational Needs and Nursing Intention Regarding COVID-19 Patient Care among Undergraduate Nursing Students
Eun-Joo Ji, Eun-Kyung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15671. CrossRef - Factors influencing nurses’ intention to care for patients with COVID-19: Focusing on positive psychological capital and nursing professionalism
Sun-a Jeong, Jinhee Kim, César Leal-Costa
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(1): e0262786. CrossRef - Pediatric nurses' grit and nursing intention during the COVID-19 pandemic: Mediating and moderating effects of mindset and psychological collectivism
Young Soo Chu, Won-Oak Oh, Il Tae Park, Anna Lee, Myung-Jin Jung
Child Health Nursing Research.2021; 27(4): 395. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Nurses' Nursing Intention toward COVID-19 Patients
Do Eun Kyung, Yong Soon Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(4): 376. CrossRef - Nursing work intention, stress, and professionalism in response to the COVID-19 outbreak in Iran: A cross-sectional study
Hamed Zandian, Minoo Alipouri Sakha, Elhameh Nasiri, Telma Zahirian Moghadam
Work.2021; 68(4): 969. CrossRef - Intentions of frontline nurses regarding COVID‐19 patient care: A cross‐sectional study in Korea
Yu‐Mi Heo, Miyoung Lee, Sun Joo Jang
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(6): 1880. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Intentions to Care For Emerging Infectious Disease Patients among National and Public Hospitals Nurses
Hea-Jin Moon, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(1): 11. CrossRef - Understanding Factors Contributing to Nurses’ Intention to Care for COVID-19 Patients Using the Theory of Planned Behavior
Khalid A. Aljohani, Mohammad S. Aljohani, Maria Jocelyn B. Natividad, Paul Reinald B. Gracia, Ibtehal I. Qazanli
Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 16(4): 546. CrossRef - Factors influencing nurses' intention to care for patients with emerging infectious diseases: Application of the theory of planned behavior
Jiyeon Lee, Sook Jung Kang
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(1): 82. CrossRef Psychometric Evaluation of Persian Version of Nurses’ Intention to Care Scale (P-NICS) for Patients with COVID-19
Pardis Rahmatpour, Hamid Sharif Nia, Erika Sivarajan Froelicher, Omolhoda Kaveh, Saeed Pahlevan Sharif, Behzad Taghipour
International Journal of General Medicine.2020; Volume 13: 515. CrossRef- Exploring Nursing Intention, Stress, and Professionalism in Response to Infectious Disease Emergencies: The Experience of Local Public Hospital Nurses During the 2015 MERS Outbreak in South Korea
Namhee Oh, NamSoo Hong, Dong Hee Ryu, Sang Geun Bae, Sin Kam, Keon-Yeop Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(3): 230. CrossRef
- The relationship between nursing professionalism and nursing intention for patients with emerging infectious diseases of nursing students who had experienced COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating effect of e-Health literacy
- 980 View
- 13 Download
- 23 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


