Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
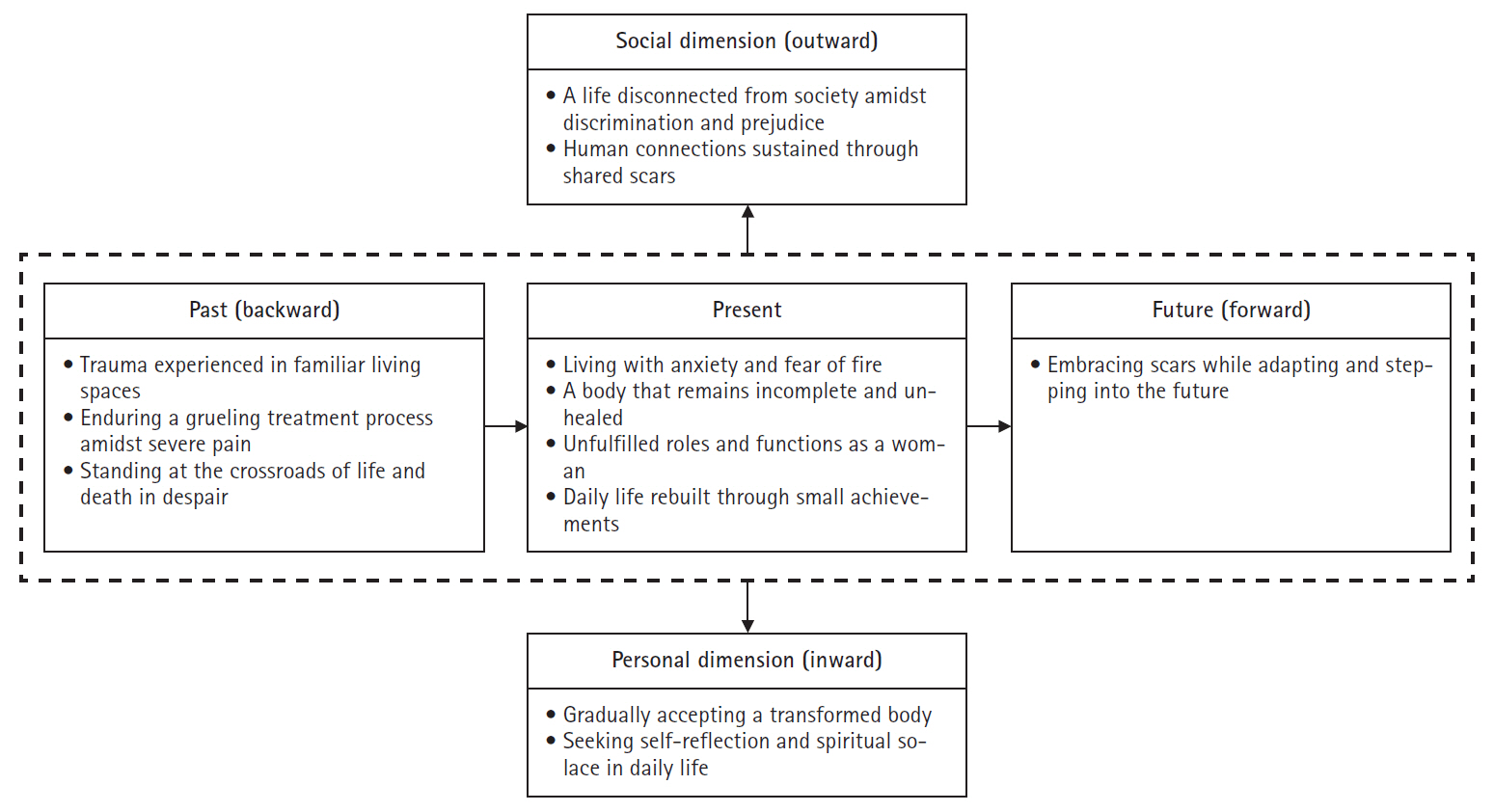
- Life changes following trauma in female burn survivors: a narrative inquiry
- Riah Kim, Inyoung Choe, Ji-Su Yun, Heeseung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):425-439. Published online August 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
Burn survivors endure repeated exposure to intense pain and face recurring trauma throughout social adaptation. This study explored how female burn survivors construct the meaning of their traumatic experience of a burn accident and the subsequent changes in their lives.
Methods
A qualitative study was conducted using narrative inquiry. Participants were recruited through purposive sampling, and each engaged in three in-depth interviews, resulting in a total of 21 interviews between April 18, 2024, and August 1, 2024. Each interview lasted 90 minutes on average and was conducted in a comfortable location preferred by the participants. The collected data were analyzed through Connelly and Clandinin’s approach.
Results
The participants were seven women with burns on the full body, face-upper limbs, or face-torso. All burns were third- to fourth-degree, and most participants had lived with these injuries for over 10 years. From the significant statements, five themes and 12 subthemes were extracted. The five themes were “unforeseen catastrophe,” “burn scars encroaching upon daily life,” “navigating life as an incomplete woman,” “exclusion from social integration,” and “the meaning of life deepened by suppressed pain.”
Conclusion
Female burn survivors experienced immense hardships following their accidents. However, through their recovery efforts, they found new meaning in life, experienced a renewed sense of being alive, and achieved inner growth and maturity. This study highlights the need for social support and underscores the importance of providing various opportunities and policy assistance for female burn survivors dealing with trauma.
- 1,874 View
- 111 Download

- Development and Evaluation of an App-Based Self-Management Program for Exercise Practice of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Suyoun Maeng, Jungok Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):250-265. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an app-based self-management program based on the transtheoretical model (TTM) for breast cancer survivors’ exercise practice, as well as to investigate the program’s effects on the stage of change for exercise, exercise self-efficacy, exercise decisional balance, exercise amount, and body composition.
Methods
This non-randomized controlled study included 52 participants (26 in each of the experimental and control groups, respectively). An app-based self-management program based on the TTM was conducted with the experimental group for a 12-week period. The program comprised three components: individual coaching for each stage of change for exercise based on TTM, amount of exercise and body composition monitoring, and online self-help meetings.
Results
Compared with the control group, the experimental group had significantly higher stages of change for exercise (p < .001), exercise self-efficacy (p < .001), exercise decisional balance (p = .002), exercise amount (p < .001), and body composition (body weight [p = .006], body mass index [p = .005], and body fat percentage [p = .010]) immediately and four weeks after the intervention.
Conclusion
An appbased self-management program based on the TTM improves exercise behaviors in breast cancer survivors and provides physical benefits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a mobile health coaching intervention on symptom experience, self-management, and quality of life in breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Ji Young Kim, Su Jin Jung
Medicine.2025; 104(12): e41894. CrossRef
- Effects of a mobile health coaching intervention on symptom experience, self-management, and quality of life in breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
- 4,122 View
- 210 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
- Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):245-260. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the effects of an advanced practice nurse-led psychoeducational program on distress, anxiety, depression, coping with cancer (CWC), health promotion behavior (HPB), and quality of life (QOL) among colorectal cancer survivors.
Methods
This study was designed as a quasi-experimental study with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest. The participants were survivors of colorectal cancer who underwent follow-up care. There were 39 survivors: 19 in the experimental group and 20 in the control group. The experimental group performed a psychoeducational program for 120 minutes per session, once a week for a total of six weeks, while the control group received routine education and counseling. Distress, anxiety, depression, CWC, HPB, and QOL were investigated before, immediately after, and 4 weeks after the intervention. The data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN ver. 24.0, using repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
There were significant interactions between time and group for distress and anxiety. In addition, CWC interacted with the total of CWC and interpersonal coping, and QOL interacted with the total of QOL and functional status. However, there were no significant differences in the depression or HPB scores.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, we expect that this program can be used as an effective intervention for colorectal cancer survivors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tailored psychoeducation for multiple myeloma patients: a step toward enhancing quality of life and health outcomes
Yoorin Cho, Yang Sook Yoo
Health Education Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a mobile-based return to work program for decent return to work, fatigue, stress, and quality of working life among cancer survivors
Kisook Kim, Hyohyeon Yoon
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2025; 19(2): 713. CrossRef - Elevating Elderly Cancer Care: A Systematic Review of Advanced Practice Nursing’s Role in Senior Oncology Patients’ Quality of Life
Cristian-David Useche-Guerrero, María-de-los-Ángeles Merino-Godoy, Eva-María Barroso-Márquez, Emilia Isabel Martins Teixeira da Costa, Rafaela Camacho Bejarano, Francisco-Javier Gago-Valiente, Rizal Angelo Grande
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Psycho-education Interventions on Colorectal Cancer Patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
XiaoYing Zhang, HuangQin Liu, LiYing Lin, Huimin Xiao
Journal of Cancer Education.2023; 38(5): 1413. CrossRef - How should the healthcare system support cancer survivors? Survivors’ and health professionals’ expectations and perception on comprehensive cancer survivorship care in Korea: a qualitative study
Su Jung Lee, Dal-Lae Jin, Young Ae Kim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Seok-Jun Yoon
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Survivorship Care and Roles of Oncology Nurses
Eun Young Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 121. CrossRef
- Tailored psychoeducation for multiple myeloma patients: a step toward enhancing quality of life and health outcomes
- 1,909 View
- 92 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Perceived Self-Management Support and Health-Related Quality of Life among Cancer Survivors
- Bo Gyeong Lee, Tae Sook Lee, Soo Hyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):298-306. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.298
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to examine the levels of perceived self-management support, self-efficacy for self-management, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in cancer survivors, and to identify the mediating effect of self-efficacy in the relationship between perceived self-management support and HRQoL.
Methods This study used a descriptive correlational design. Two hundred and four cancer survivors who had completed treatment participated in the study. Measurements included the Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care Scale, the Korean version of the Cancer Survivors’ Self-Efficacy Scale, and the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation coefficient analysis, and multiple regression analysis using Baron and Kenny's method for mediation.
Results The mean score for perceived self-management support was 3.35 out of 5 points, self-efficacy was 7.26 out of 10 points, and HRQoL was 65.90 out of 100 points. Perceived self-management support was significantly positively correlated with self-efficacy (r=.29,
p <.001) and HRQoL (r=.27,p <.001). Self-efficacy was also significantly correlated with HRQoL (r=.59,p <.001). Furthermore, self-efficacy (β=.55,p <.001) had a complete mediating effect on the relationship between perceived self-management support and HRQoL (Z=3.88,p <.001).Conclusion The impact of perceived self-management support on HRQoL in cancer survivors was mediated by self-efficacy for self-management. This suggests that strategies for enhancing self-efficacy in cancer survivors should be considered when developing self-management interventions for improving their HRQoL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
Soo Hyun Kim, Yu Hyeon Choe, Jingyeong Choi, Ji Young Park, Eun Yi
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(1): E47. CrossRef - Effects of Symptom Burden, Self-Efficacy, and Stigma on Cancer Coping in Patients with primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
Ah-Reum Han, Euna Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(3): 158. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Enhee Jo, Ju-Young Park, Young Jun Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 315. CrossRef - An Integrated Review of Health Care in Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
Hye Jin Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 82. CrossRef - Trajectories of quality of life in breast cancer survivors during the first year after treatment: a longitudinal study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of perceived chronic illness management support, health literacy, and social support on the care burden of families caring for older people with multiple chronic conditions at home: A cross-sectional study
Eun Sil Lee, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 76. CrossRef - Effects of Uncertainty, Appraisal of Uncertainty, and Self-Efficacy on the Quality of Life of Elderly Patients with Lung Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy: Based on Mishel’s Theory of Uncertainty
Min-Kyung Hwang, Hee-Kyung Kim, Ki-Hyeong Lee
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1051. CrossRef - Between Personality Traits and Postpartum Depression: The Mediated Role of Maternal Self-Efficacy
Lingli Han, Ji Zhang, Jingxuan Yang, Xiaoyu Yang, Hua Bai
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment.2022; Volume 18: 597. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Quality of Life in Patients after Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Jeong Won Yeom, Yeon Ok Suh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2564. CrossRef - The influence of Digital Informatization Level, Self-efficacy, and Social Support on Digital Health Literacy in the Elderly with Cancer
Hye Su Kim, Ji Hyun Sung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(4): 255. CrossRef - The Correlation Between Quality of Life and Positive Psychological Resources in Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis
Xinxin Zhao, Siqi Tong, Ye Yang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated, cross-sectoral psycho-oncology (isPO): a new form of care for newly diagnosed cancer patients in Germany
Michael Kusch, Hildegard Labouvie, Vera Schiewer, Natalie Talalaev, Jan C. Cwik, Sonja Bussmann, Lusine Vaganian, Alexander L. Gerlach, Antje Dresen, Natalia Cecon, Sandra Salm, Theresia Krieger, Holger Pfaff, Clarissa Lemmen, Lisa Derendorf, Stephanie St
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-efficacy, post-traumatic growth, and quality of life of pediatric cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Yeunhee Kwak, Yoonjung Kim, Eun Seok Choi, Ho Joon Im
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102019. CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of patient assessment of chronic illness care among Korean cancer survivors
Soo Hyun Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee, Yu Hyeon Choe, Francesca Chiesi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0256119. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef
- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
- 1,878 View
- 41 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):143-163. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate effects of psychoeducational intervention for cancer survivors.
Methods Ten databases were searched. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of the studies, data extraction and assessment. The risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane Collaboration's tool. To estimate the effect size, meta-analysis of the studies was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and RevMan programs.
Results Of 18,781 publications identified, 35 met inclusion criteria, and 25 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychoeducational intervention. Effect sizes (standardized mean difference [SMD]) were heterogeneous and random effects models were used in the analyses. Psychoeducational intervention was effective for quality of life (n=2,410, ES=0.23; 95% CI: 0.09~0.37), coping and self-efficacy (n=179, ES=0.68; 95% CI: 0.26~1.11), anxiety (n=1,786, ES=-0.26; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.15), depression (n=1,910, ES=-0.28; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.18), and psychological distress (n=2,242, ES=-0.31; 95% CI: -0.46~-0.17). Subgroup analysis showed that counseling was the most effective intervention for quality of life, and behavioral therapy was an effective intervention for all positive and negative outcomes. Publication bias was not detected except for psychological distress.
Conclusion Psychoeducational intervention appears to be effective in improving quality of life and coping and self-efficacy, and it is effective in reducing psychological symptoms in cancer survivors. Behavioral therapy, especially, is commonly effective in improving psychosocial outcomes. However, low-quality evidence, variability in the designs of existing studies, and publication bias suggest that additional high-quality trials should be conducted in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
Safa Elkefi, Corina T. Lelutiu-Weinberger, Jean-Marie Bruzzese, Alicia K. Matthews
Discover Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Group‐Based Support Interventions for Adolescents and Young Adults With Lymphoma: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Dalnim Cho, Sairah Ahmed, Stella Snyder, Juliet Kroll, Minxing Chen, Michael Roth, Kathrin Milbury
Psycho-Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mind Health of Persons with Cancer: Psycho-Oncology and Nursing
Park Eun Young
Journal of Clinical Psychooncology.2025; 11(1): 24. CrossRef - Psychosocial interventions for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease and their caregivers: a scoping review
Juyeon Oh, Jiwon An, Kyongok Park, Youngok Park
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of telemedicine psychoeducational interventions for adults with non‐oncological chronic disease: A systematic review
Carmen Sánchez‐Gutiérrez, Eugenia Gil‐García, Adriana Rivera‐Sequeiros, José M. López‐Millán
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(5): 1267. CrossRef - Cancer-Related Psychological Distress in Lymphoma Survivor: An Italian Cross-Sectional Study
Giulia Agostinelli, Barbara Muzzatti, Samantha Serpentini, Michele Spina, Maria Antonietta Annunziata
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 245. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Physical Function and Depression in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jinhyang YANG, Changwan KANG, Hye-Won PARK, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 396. CrossRef - Development of A Nurse-Led Educational Intervention Program in Managing the Nutrition Impact Symptom Cluster in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma following the Medical Research Council Framework
Wenli Xiao, Carmen W Chan, Jinnan Xiao, Cho L Wong, Ka M Chow
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 653. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Education and Support: A Model for Use in the Ambulatory Care Setting
Terri Jabaley, Patricia Rizzo, Nina Grenon, Clare Sullivan, Janet Bagley, Maritza Nassif, Renee Siegel, Meghan Underhill-Blazey
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 24(4): E43. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Chronic Pain Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hee-Sook Kang, Sung-Dong Hwang, Sang-Eun Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(3): 271. CrossRef
- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
- 2,055 View
- 35 Download
- 12 Crossref

- A Study on the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors based on Social Network Analysis
- Sun Young Kwon, Ka Ryeong Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(1):50-58. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the knowledge structure of cancer survivors.
Methods For data, 1099 articles were collected, with 365 keywords as a Noun phrase extracted from the articles and standardized for analyzing. Co-occurrence matrix were generated via a cosine similarity measure, and then the network analysis and visualization using PFNet and NodeXL were applied to visualize intellectual interchanges among keywords.
Results According to the result of the content analysis and the cluster analysis of author keywords from cancer survivors articles, keywords such as 'quality of life', 'breast neoplasms', 'cancer survivors', 'neoplasms', 'exercise' had a high degree centrality. The 9 most important research topics concerning cancer survivors were 'cancer-related symptoms and nursing', 'cancer treatment-related issues', 'late effects', 'psychosocial issues', 'healthy living managements', 'social supports', 'palliative cares', 'research methodology', and 'research participants'.
Conclusion Through this study, the knowledge structure of cancer survivors was identified. The 9 topics identified in this study can provide useful research direction for the development of nursing in cancer survivor research areas. The Network analysis used in this study will be useful for identifying the knowledge structure and identifying general views and current cancer survivor research trends.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Self-Assessment, TAilored Information, and Lifestyle Management for Cancer Patients’ Returning to Work (START): A Multi-center, Randomized Controlled Trial
Danbee Kang, Ka Ryeong Bae, Yeojin Ahn, Nayeon Kim, Seok Jin Nam, Jeong Eon Lee, Se Kyung Lee, Young Mog Shim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Seung Yeop Oh, Mison Chun, Jaesung Heo, Juhee Cho
Cancer Research and Treatment.2023; 55(2): 419. CrossRef - Web-Based Research Trends on Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Over the Last 5 Years: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling Study
Hyun-Yong Kim, Kyung-Ah Kang, Suk-Jung Han, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(2): e32309. CrossRef - Network analysis based on big data in social media of Korean adolescents’ diet behaviors
JongHwi Song, SooYeun Yoo, JunRyul Yang, SangKyun Yun, YunHee Shin, Girish C. Melkani
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0273570. CrossRef - An Overview of Cognitive Reserve in Aging Based on Keyword Network Analysis
Jihyun Kim, Mi So Kim
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of research on metabolic syndrome in cancer survivors using topic modeling and social network analysis
Ji-Su Kim, Hyejin Kim, Eunkyung Lee, Yeji Seo
Science Progress.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Identification of the Knowledge Structure on the Resilience of Caregivers of People with Dementia using a Text Network Analysis
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 66. CrossRef - Research Topics and Trends in Interprofessional Education in Nursing
Kisook Kim, Ki-Seong Lee
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(10): 554. CrossRef - Social Determinants of Health of Multicultural Adolescents in South Korea: An Integrated Literature Review (2018~2020)
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Hyeyeon Lee, Mikyung Lee, Sookyung Kim, Kennedy Diema Konlan
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(4): 430. CrossRef - A Network Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in End-of-Life Care and Nursing
Kisook Kim, Seung Gyeong Jang, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(1): 313. CrossRef - Research Trends on Factors Influencing the Quality of Life of Cancer Survivors: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling Approach
Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Sun Hyoung Bae, Hee-Jun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(4): 231. CrossRef - Knowledge Structure of Nursing Studies on Heart Failure Patients in South Korea through Text Network Analysis
Seang Ryu, Hyunyoung Park, Yun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 409. CrossRef - Semantic Network Analysis of Iussues Related to Mental Illness in Korea Media: Focusing on the Five Major Media from 2016 to 2018
Sun Joo Park, Na Ri Shin, Seung Hye Kim, Su Bin Park, Chul Eung Kim
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2020; 59(1): 72. CrossRef - Identification of the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors’ Return to Work and Quality of Life: A Text Network Analysis
Kisook Kim, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9368. CrossRef - Using Text Network Analysis for Analyzing Academic Papers in Nursing
Chan Sook Park
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2019; 16(1): 12. CrossRef - Identification of Knowledge Structure of Pain Management Nursing Research Applying Text Network Analysis
Chan Sook Park, Eun-Jun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 538. CrossRef - Exploring the Knowledge Structure of Nursing Care for Older Patients With Delirium
Jung Eun Choi, Mi So Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(5): 216. CrossRef - A Comparison of Hospice Care Research Topics between Korea and Other Countries Using Text Network Analysis
Eun-Jun Park, Youngji Kim, Chan Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 600. CrossRef - The Network Analysis of Nursing Diagnoses for Children Admitted in Pediatric Units Determined by Nursing Students
Mikyung Moon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(3): 223. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Articles Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration for 3 Years (2013~2015): The Application of Text Network Analysis
Tae Wha Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, GyeongAe Seomun, Miyoung Kim, Jee-In Hwang, Soyoung Yu, Seok Hee Jeong, Min Jung, Mikyung Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 101. CrossRef - Social Network Analysis on Mapping the Knowledge Structure of Dementia Research
Jung-Hee Han, Young-Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(2): 69. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Self-Assessment, TAilored Information, and Lifestyle Management for Cancer Patients’ Returning to Work (START): A Multi-center, Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,148 View
- 4 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Posttraumatic Growth, Dyadic Adjustment, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors and Their Husbands
- Seunghee Song, Eunjung Ryu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(5):515-524. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.515
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify whether the couple perceived breast cancer as a traumatic event, to evaluate the association among posttraumatic growth, dyadic adjustment, and quality of life and to explore the predictors affecting quality of life of the couple.
Methods A cross-sectional comparative survey design was utilized. Participants were 57 couples recruited from a national cancer center in Korea. Data were analyzed using paired t-test, McNemar test and independent t-test. On the basis of variables found to be significantly associated with quality of life, multiple regression was used to examine the simultaneous influence of multiple predictors.
Results Breast cancers survivors and spouses perceived breast cancer as a traumatic event (43.9% and 24.6%, respectively). The global quality of life was explained by perception as trauma (β=-19.79) and posttraumatic growth (β=0.46) in survivors, and perception as trauma (β=-18.81) and dyadic adjustment (β=0.53) in spouses.
Conclusion Results suggest that future research should use qualitative methods to evaluate why contemplating reasons for cancer contributed to posttraumatic growth, examine other potential predictors of quality of life such as dyadic adjustment and intimacy, and identify links between posttraumatic growth and other psychological outcomes such as distress and well-being, using prospective analyses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Equation Model for Psychosocial Adjustment of Breast Cancer Survivors Based on Family Resilience Model
Jiyoung Seo, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(2): 178. CrossRef - Relationship among Post-traumatic Stress Disorder, Resilience, and Retention Intention in Nurses who had Perceived Traumatic Events
Jin Young Lee, Ja Yun Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(4): 403. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Post-Traumatic Growth in Patients with Breast Cancer Based on a Model of Post-Traumatic Growth
Hee Yeon Park, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(2): 65. CrossRef - Factors influencing posttraumatic growth in ovarian cancer survivors
Jeong Min Oh, Yoonjung Kim, Yeunhee Kwak
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(4): 2037. CrossRef - The effect of web-based training on life quality and spousal adjustment for women with breast cancer and their spouses
Saadet Çömez, Özgül Karayurt
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 47: 101758. CrossRef - Influence of lifestyle, depression, and marital intimacy on quality of life in breast cancer survivors
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Myoungha Lee, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 28. CrossRef - The Influence of Spiritual Well-Being, Self-Esteem, and Perceived Social Support on Post-Traumatic Growth among Breast Cancer Survivors
Eun Young Seo, Suhye Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(4): 232. CrossRef - Effects of stress appraisal on the quality of life of adult patients with multiple myeloma and their primary family caregivers in Korea
In Seo La, Eun Kyoung Yun
Psycho-Oncology.2017; 26(10): 1640. CrossRef - Effects of stress, dyadic communication and adaptation on prostatectomy patients' quality of life
Hae Sook Kim, Han Jong Ahn
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2017; 11(1): 13. CrossRef - Posttraumatic growth in breast cancer survivors and their husbands based on the actor‐partner interdependence model
MyoSuk Lee, Kyunghee Kim, Changwon Lim, Ji‐Su Kim
Psycho-Oncology.2017; 26(10): 1586. CrossRef - Influencing Factors for Post-traumatic Growth in Patients with Breast Cancer
Sung-Hee Choi, Young-Whee Lee
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2016; 16(11): 499. CrossRef - Breast Cancer Survivors’ Mental Health Related to Attachment Injury and Marital Satisfaction
서미아, Dong-Young Noh, 민준원
Health and Social Welfare Review.2015; 35(3): 278. CrossRef
- Structural Equation Model for Psychosocial Adjustment of Breast Cancer Survivors Based on Family Resilience Model
- 1,068 View
- 10 Download
- 12 Crossref

- A Path Analysis on Factors Influencing Second Primary Cancer Screening Practices in Stomach, Colon, and Breast Cancer Survivors
- Young Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(2):139-148. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.2.139
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to identify the factors influencing second primary cancer (SPC) screening practice by examining the relationships of physical symptoms, knowledge and attitudes regarding SPC screening, perceived risk, primary cancer type, and demographic factors of cancer survivors.
Methods Participants were 308 survivors of stomach, colon, or breast cancer recruited from 2 university hospitals in Korea. Data were collected using a questionnaire and analyzed using IBM SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 18.0.
Results The proportion of participants taking all cancer screenings according to national guidelines was 40%. They had moderate knowledge and a relatively positive attitude regarding SPC screening and high cancer risk perception. The participants had taken fewer SPC screenings after than before cancer diagnosis. The factors influencing cancer risk perception were age, physical symptoms, knowledge regarding SPC and primary cancer type (stomach). The factors influencing SPC screening practice were age, gender, economic status, knowledge regarding SPC screening, and primary cancer types (colon).
Conclusion It is important for clinical professionals to recognize that survivors of cancer are susceptible to another cancer. Education on SPC screening for these survivors should focus on communicating with and encouraging them to have regular cancer screenings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Integrated Supportive Care Nursing Competence Scale for Cancer Survivors
Eun-Jung Bae, Yun-Hee Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(7): 755. CrossRef - Health Behaviors of Cancer Survivors According to the Employment Status and Occupation: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ka Ryeong Bae, Wi-Young So, Su Jung Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2974. CrossRef - Survivors’ health competence mediates the association between wearable activity tracker use and self-rated health: HINTS analysis
Steven De La Torre, Donna Spruijt-Metz, Albert J. Farias
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2022; 16(6): 1268. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Health Check-up and Cancer Screening Participation among Family Caregivers of Patients with Dementia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Bomgyeol Kim, Yejin Lee, Jin-Won Noh, Tae Hyun Kim
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Supportive Care Needs of Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyekyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 60. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life among Cancer Survivors: Based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) for 2019
Hee Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(2): 109. CrossRef - Colorectal cancer screening practices among cancer survivors five years after diagnosis
Adeline Monet, Rajae Touzani, Anne-Déborah Bouhnik, Marc-Karim Bendiane, Julien Mancini
Journal of Public Health.2021; 29(4): 805. CrossRef - An Integrated TK-TD Model for Evaluation of Radix Aconitikusnezoffii (RAK)
Xin Miao, Ren Bu, Yang Liu, Bing Li, Xiaofei Zhang, Haiyan Xing, Gang Li
Pharmacology.2020; 105(11-12): 669. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Characteristics of Cancer Patients and Cancer Survivors
So Young Baek, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 11. CrossRef - Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening Behavior in Female Cancer Survivors: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2012
Eun-Ae Lee, Jinyoung Shin, Eun-Joo Hwang, Jung-Woong Lee
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2017; 38(3): 116. CrossRef - The necessity of analysis of cancer survivor concept in Korea
Jiyoung Kim
Journal of Comprehensive Nursing Research and Care.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Factors Related to the Non-Practice of Cancer Screening in Cancer Survivors: Based on the 2007-2012 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Song-Ei Yang, Nam-Kyung Han, Sun-Mi Lee, Tae-Hyun Kim, Woojin Chung
Health Policy and Management.2015; 25(3): 162. CrossRef
- Development of Integrated Supportive Care Nursing Competence Scale for Cancer Survivors
- 1,105 View
- 4 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Late Effects, Social Adjustment, and Quality of Life in Adolescent Survivors of Childhood Leukemia
- Sung Sil Hong, Ho Ran Park, Kwang Sung Kim, Sun Hee Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):55-63. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to examine the late effects, social adjustment, and quality of life in adolescents who had been completely treated for childhood leukemia and their parents.
Methods Participants consisted of 41 pairs of adolescent survivors (13-18 years) and their parents. Parents checked for their child's physical late effects. The Korean Version of Post-Traumatic Symptoms for psychological late effects, social functioning questionnaire for social adjustment and the PedsQL 4.0 Generic Core Scales for quality of life were completed by adolescents and parents. Data were analyzed using SPSS.
Results Twenty out of 41 adolescents had one or more physical late effects. Adolescents showed more serious psychological late effect than parents. Five children and seven parents had above cut-off scores and they were considered the high risk group for posttraumatic symptoms. Parent-reported scores were significantly higher than child-reported scores in terms of social adjustment and emotional functioning of quality of life. Low school functioning in adolescents was associated with physical late effects.
Conclusion The results indicate that long-term and systematic management for childhood leukemia survivors affect positive social adjustment and can further improve quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Integrated Review of Health Care in Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
Hye Jin Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 82. CrossRef - Technology-based psychosocial support for adolescent survivors of leukemia
Tuba ARPACI, Naime ALTAY
Journal of Integrative Nursing.2022; 4(3): 157. CrossRef - Self-efficacy, post-traumatic growth, and quality of life of pediatric cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Yeunhee Kwak, Yoonjung Kim, Eun Seok Choi, Ho Joon Im
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102019. CrossRef - Difficulty in returning to school among adolescent leukemia survivors: A qualitative descriptive study
Hyeran An, Sunhee Lee
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2019; 38: 70. CrossRef - Sleep Pattern and Factors Causing Sleep Disturbance in Adolescents with Cancer before and after Hospital Admission
Jin Jung, Eun-Hye Lee, You-Jin Yang, Bo-Yoon Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(3): 143. CrossRef - Qualitative Evaluation of Effectiveness of ‘Family Hope Partner Project’ for Pediatric Cancer Patients and their Families
김선희
Korean Journal of Family Social Work.2017; null(55): 59. CrossRef - The Experiences of Korean Young Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer
Jaehee Yi, Min Ah Kim, Sangmin An
Qualitative Health Research.2016; 26(8): 1044. CrossRef - The Effect of Perceived Social Stigma on Self-Esteem of Childhood Cancer Survivors
김민아, 남석인, 장은혜, Lee Daji
Health and Social Welfare Review.2016; 36(1): 497. CrossRef - Health-related Needs and Quality of Life in Childhood Cancer Survivors
Su-Jin Lim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(4): 246. CrossRef
- An Integrated Review of Health Care in Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
- 1,058 View
- 4 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Symptom Experience and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
- Jin Hee Park, Eun-Young Jun, Mi-Young Kang, Yong-Sik Joung, Gu-Sang Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(5):613-621. Published online October 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.5.613
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to evaluate symptom experience and quality of life (QOL) and to identify the predictors of QOL among breast cancer survivors.
Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted on 200 disease-free breast cancer survivors at two hospitals between December 2007 and July 2008. Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy Scale-B, Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale-short Form and The Linear Analogue Self Assessment Scale were used to assess symptom experience and QOL in these patients. Data were analyzed using the Pearson correlation, t-test, ANOVA, and stepwise multiple regression with SPSS/WIN 12.0.
Results The mean score of QOL for breast cancer survivors was 95.81 (±18.02). The highest scores among physical and psychological symptoms were sexual interest and anxiety. Year since treatment completion was significantly associated with QOL in sociodemographic variables. Physical and psychological symptoms have a significant negative association with QOL. The results of the regression analyses showed that physical and psychological symptoms were statistically significant in predicting patients' QOL.
Conclusion Symptom experience and QOL are essential variables that should be acknowledged when delivering health care to breast cancer survivors. More attention to the reduction and management of psychological distress could improve QOL among breast cancer survivors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction Model for Postoperative Quality of Life Among Breast Cancer Survivors Along the Survivorship Trajectory From Pretreatment to 5 Years: Machine Learning–Based Analysis
Danbee Kang, Hyunsoo Kim, Juhee Cho, Zero Kim, Myungjin Chung, Jeong Eon Lee, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jonghan Yu, Byung Joo Chae, Jai Min Ryu, Se Kyung Lee
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e45212. CrossRef - Impact of post-treatment symptoms on supportive care needs among breast cancer survivors in South Korea
Unhee Kim, Ju-Young Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(10): 100295. CrossRef - The Influence of Anxiety, Uncertainty, and Cancer Coping on the Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Dong-Rim Hyun, Young Suk Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 37. CrossRef - Association between sleep quality, anxiety and depression among Korean breast cancer survivors
Ok‐Hee Cho, Kyung‐Hye Hwang
Nursing Open.2021; 8(3): 1030. CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - Unmet Needs for Job Maintenance of Breast Cancer Survivors
Su Jeong Han, Hye Won Kim, Mi Ran Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(3): 298. CrossRef - Analysis of Health management Awareness and Practice Experience of Breast Cancer Survivors using Focus Group Interviews
Hye Won Kim, Su Jeong Han, Mi Ran Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 23(1): 48. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Lymph Massage Method among Breast Cancer Survivors
Hyenam Hwang
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 23(2): 112. CrossRef - The mediating effect of social support on uncertainty in illness and quality of life of female cancer survivors: a cross-sectional study
Insook Lee, Changseung Park
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise Program Based on Preferences of Breast Cancer Survivors
Ji Yong Byeon, Min Jae Kang, Ji Hye Park, Ji Hee Min, Justin Y. Jeon
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(2): 611. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Constipation in Patients With Breast Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy: A Randomized Control Trial
Jeongran Shin, Hyojung Park
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2018; 40(1): 67. CrossRef - Factors influencing the quality of life of patients with advanced cancer
Sun-A Park, Seung Hyun Chung, Youngjin Lee
Applied Nursing Research.2017; 33: 108. CrossRef - Effects of a Group Coaching Program on Depression, Anxiety and Hope in Women with Breast Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
So Ryoung Seong, Moon-kyung Cho, Jeeyoon Kim, Yeo Ok Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(3): 188. CrossRef - The Influences of Quality of Sleep and Mood State on Fatigue in Primary Brain Tumor Patients
Jae Hyun Hwang, Hyoung Sook Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(2): 87. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - Effects of a self-managed home-based walking intervention on psychosocial health outcomes for breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: a randomised controlled trial
Kajal Gokal, Deborah Wallis, Samreen Ahmed, Ion Boiangiu, Kiran Kancherla, Fehmidah Munir
Supportive Care in Cancer.2016; 24(3): 1139. CrossRef - Return-to-Work Experiences among Nurses after Receiving Cancer Treatment
Mi-Hye Kim, Jeong-Seon Kim, Han-Na Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(6): 215. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Empowerment Scale for Woman with Breast Cancer
Sun Hwa Shin, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 613. CrossRef - Changes of Symptom Distress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Adjuvant Therapy
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(2): 67. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of EQ-5D-3L for breast cancer patients in Korea
Seon-Ha Kim, Min-Woo Jo, Jong-Won Lee, Hyeon-Jeong Lee, Jong Kyung Kim
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors that Influence Korean Breast Cancer Patients to Undergo Cancer Rehabilitation Therapy
Hui-jeong Park, Kyunghee Kim, Ji-su Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(2): 106. CrossRef - Changes of Self-efficacy, Depression, and Posttraumatic Growth in Survivors with Breast Cancer Participating Breast Cancer Prevention Volunteering
Myungsun Yi, Jieun Cha, Youngmi Ryu
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(4): 256. CrossRef - Body Image and Physical suffering during Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients Following Breast Conserving Operations
Mi Ok Han, Jeong Yun Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(3): 155. CrossRef - Effect of brief psychoeducation using a tablet PC on distress and quality of life in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a pilot study
Joo-Young Lee, Hye Yoon Park, Dooyoung Jung, Mihye Moon, Bhumsuk Keam, Bong-Jin Hahm
Psycho-Oncology.2014; 23(8): 928. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in Patients with Breast Cancer on Hormone Therapy
Eunkyung Hwang, Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(1): 108. CrossRef - Effects of Resilience, Post-traumatic Stress Disorder on the Quality of Life in Patients with Breast Cancer
Boo Young Ha, Eun Jung Jung, So Young Choi
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(1): 83. CrossRef - Menopausal symptoms, sexual function, depression, and quality of life in Korean patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy
Hyojung Park, Hyeon Gyeong Yoon
Supportive Care in Cancer.2013; 21(9): 2499. CrossRef - Anxiety, Depression and Uncertainty in Cancer Patients Participating in Clinical Trial of Anticancer Drugs
Haejin Kim, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(1): 53. CrossRef - Factors Influencing on Quality of Life in Gynecological Cancer Patients
Jeong-Sook Park, Yun-Jung Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(1): 52. CrossRef - Impacts of Fatigue, Pain, Anxiety, and Depression on the Quality of Life in Patients with Breast Cancer
Hye Sun Byun, Gyung Duck Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(1): 27. CrossRef - A comparison of quality of life and satisfaction of women with early-stage breast cancer treated with breast conserving therapy vs. mastectomy in southern China
Z.-Y. He, Q. Tong, S.-G. Wu, F.-Y. Li, H.-X. Lin, X.-X. Guan
Supportive Care in Cancer.2012; 20(10): 2441. CrossRef - Quality of Life and Symptom Experience in Breast Cancer Survivors After Participating in a Psychoeducational Support Program
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong Sik Jung, Ku Sang Kim
Cancer Nursing.2012; 35(1): E34. CrossRef - Effects of Symptom Severity and Symptom Interference on Sleep Disturbance in Cancer Patients
Kyunghee Kim, Da Hye Park, Darlee Park, Eunjung Ryu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(4): 339. CrossRef - Factors affecting the quality of life of middle‐aged women suffering Hwa‐Byung
Young Mi Lim, In Chul Jung, Bok Nam Seo
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2012; 21(15-16): 2377. CrossRef - Postoperative Quality of Life in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ju-Sung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(3): 1260. CrossRef - Effects of Laughter Therapy on Depression, Quality of Life, Resilience and Immune Responses in Breast Cancer Survivors
Eun A Cho, Hyun Ei Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(3): 285. CrossRef - Analysis of Nursing Intervention Studies on Patients with Breast Cancer in Korea
Kyung Sook Choi, Mi Sook Kim, In Ja Lee, Sang Young Han, Jung Ae Park, Joohyun Lee
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(1): 74. CrossRef
- Prediction Model for Postoperative Quality of Life Among Breast Cancer Survivors Along the Survivorship Trajectory From Pretreatment to 5 Years: Machine Learning–Based Analysis
- 1,275 View
- 8 Download
- 37 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


