Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development of a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission after kidney transplantation: a retrospective study
- Hye Jin Chong, Ji-hyun Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):528-542. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and validate a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission (EHR) post-kidney transplantation.
Methods
The study was conducted at the organ transplantation center of a university hospital, utilizing data from 470 kidney transplant recipients. We built and trained four machine learning models and tested them to identify the strongest EHR predictors. Predictive performance was evaluated using confusion matrices and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC AUC).
Results
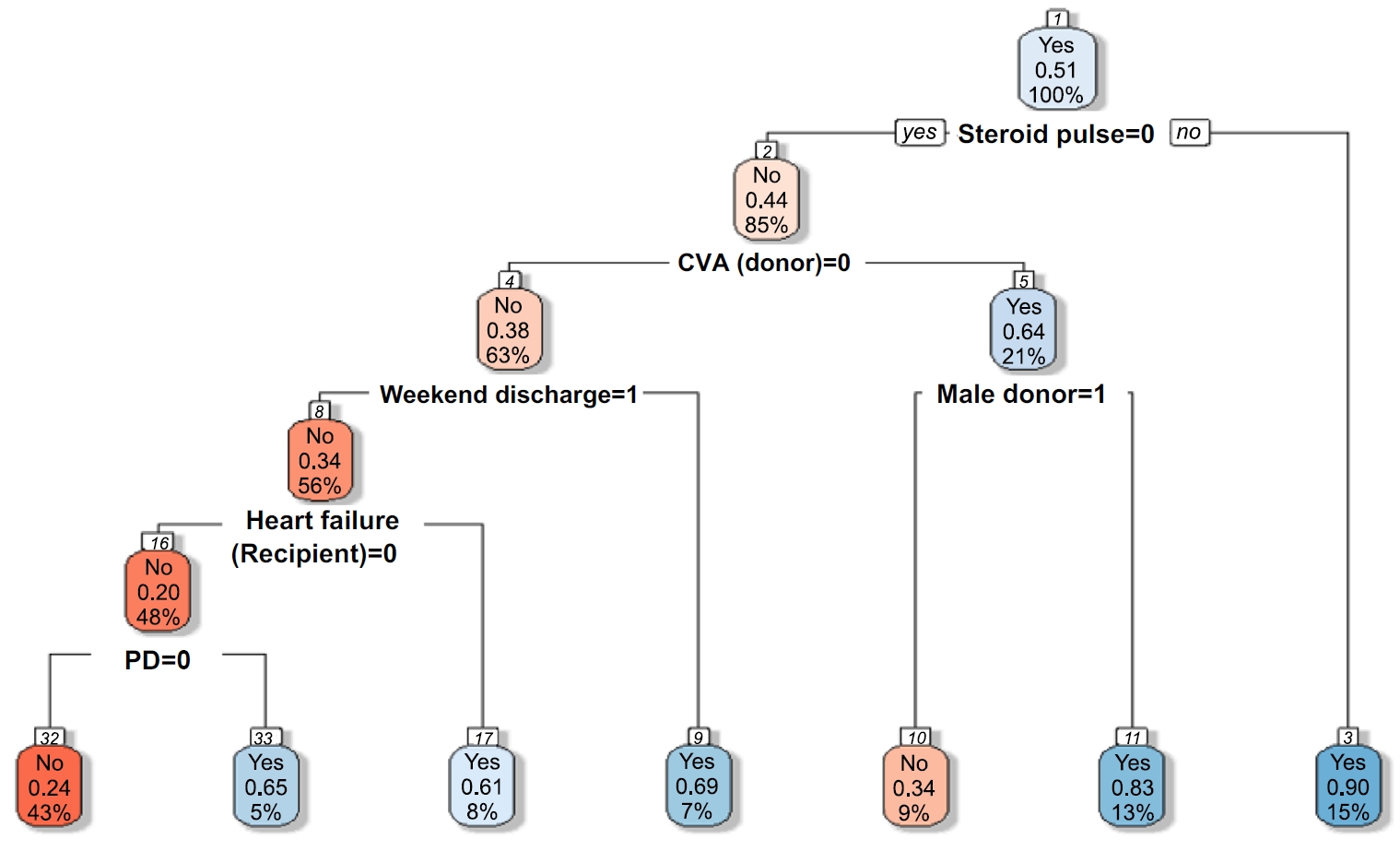
Among the 470 kidney transplant recipients with a mean age of 46.1 ± 12.02 years, 322 (68.5%) were males, and 74 (15.7%) were readmitted within 30 days after kidney transplantation. In total, 241 (51.2%) recipients were found to have experienced EHR after applying the random over-sampling examples method. The random forest model achieved the best performance, with an ROC AUC of .87 (validation set) and .82 (test set). The 15 most important features were steroid pulse therapy (recipient), cerebrovascular accident (recipient), heart failure (recipient), male sex (donor), cardiovascular disease (recipient), weekend discharge (recipient), peritoneal dialysis (recipient) cerebrovascular accident as the cause of brain death (donor), current smoker (recipient), cardiac arrest (donor), previous kidney transplantation (recipient), age (donor), hypertension (donor), male sex (recipient), and dialysis duration (recipient).
Conclusion
Our framework demonstrated strong predictive interpretability. It can support appropriate and effective clinical decision-making by assisting transplant professionals in stratifying recipients based on their risk of EHR. prioritizing post-discharge care and follow-up for high-risk individuals, and allocating targeted interventions such as closer monitoring or education.
- 1,195 View
- 164 Download

- Effects of social support on organizational commitment among experienced nurses experiencing department rotation: the mediating effect of organizational socialization
- Young Jun Jang, Jeong A Jeong, Yu Seung Ban, Seon Hwa Park, Eun Jee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):364-376. Published online August 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25042
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study explored the mediating role of organizational socialization in the relationship between social support and organizational commitment among nurses in hospitals who had experienced department rotation.
Methods
A descriptive survey design was used with 202 nurses from a tertiary hospital who had experienced department rotation within the past 12 months. Data were collected via an online questionnaire from August 1 to August 30, 2024. Analyses included frequency analysis, descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, and multiple regression. The mediating effect was tested using IBM SPSS WIN ver. 23.0 and the PROCESS macro (model 4) with 10,000 bootstrap resamples.
Results
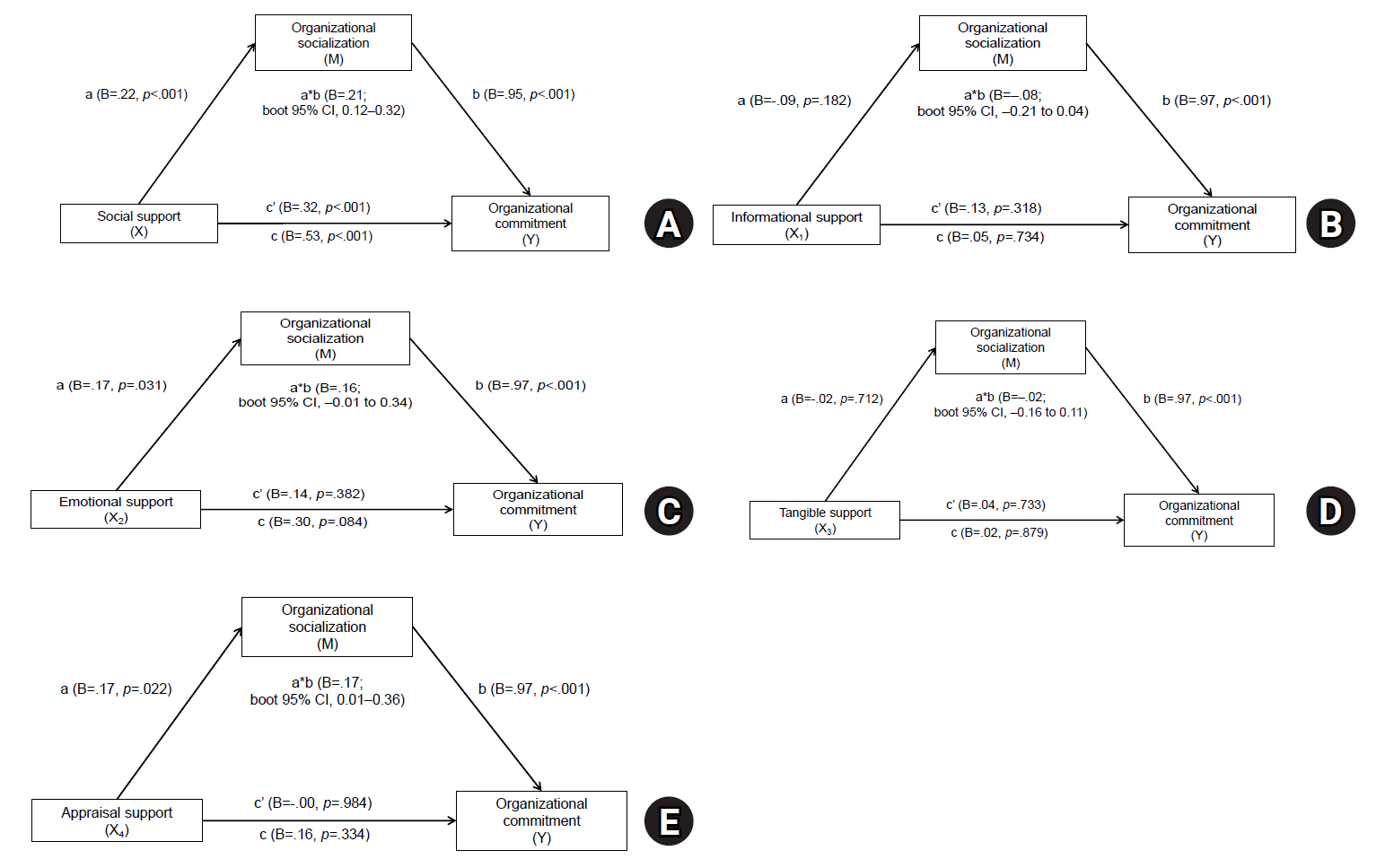
Organizational socialization partially mediated the relationship between social support and organizational commitment (B=.21; bootstrapped 95% confidence interval, 0.12–0.32).
Conclusion
The findings suggest that both social support and organizational socialization play essential roles in improving nurses’ organizational commitment following department rotation. Thus, practical programs, such as mentoring systems, should be implemented that both enhance social support and actively promote organizational socialization. These efforts have the potential to help nurses adjust more effectively to new units and ultimately improve retention and performance within healthcare organizations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
Eejee Jung, Gunjeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 560. CrossRef - Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
- 2,084 View
- 236 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
- Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):19-33. Published online February 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24070
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study examined the direct effects of fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression on anxiety in pregnant women with high-risk pregnancy-related conditions and their husbands. Furthermore, it aimed to explore the serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression in the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety.
Methods
A survey-based study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy conditions at 24–32 weeks and their husbands, recruited from a pregnant women’s online community between January 20, 2021 and July 20, 2022. Data were collected from 294 individuals (147 couples) using self-report questionnaires. Correlations between variables were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.), and the mediation effects were assessed using the PROCESS macro, model 6.
Results
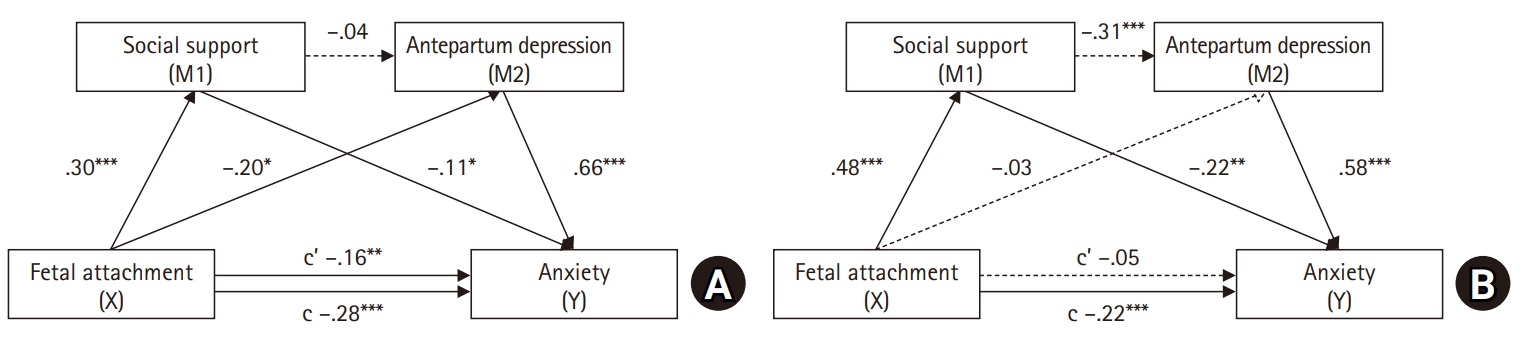
In the maternal model, maternal-fetal attachment directly affected anxiety (p=.005), with antepartum depression partially mediating this relationship (95% confidence interval [CI], –0.26 to –0.01). In the paternal model, paternal-fetal attachment had no direct effect on anxiety (p=.458). However, social support and antepartum depression fully mediated the relationship between paternal-fetal attachment and anxiety (95% CI, –0.14 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that social support in the relationship between fetal attachment and depression in high-risk pregnant women and their partners can have direct or indirect effects on the negative emotions of high-risk pregnant couples. It is necessary to assess the level of anxiety in couples experiencing high-risk pregnancies and provide comprehensive nursing interventions that address fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression in order to reduce anxiety.
- 2,654 View
- 247 Download

- Structural Equation Modeling of Health Promotion Behavior on Migrant Workers: A Multi-Group Analysis Based on the Period of Residence
- Hanna Jeong, Youngsuk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):73-92. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed and tested a hypothetical model of health promotion behavior on migrant workers based on the Health Promotion Model and the Health Literacy Skills Framework.
Methods
Data were collected from 298 migrant workers in 9 regions across the country from December 2020 to March 2021. The exogenous variables were e-health literacy, occupational stress, acculturation, and social support. The endogenous variables were perceived benefits of action, self-efficacy, and health promotion behavior. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 25.0, AMOS 20.0, and R-4.0.3 program.
Results
The model fit was appropriate. Social support had the most significant direct impact on the health promotion behavior of migrant workers. Perceived benefits of action and self-efficacy played a mediating role in the relationship among e-health literacy, social support, and health promotion behavior. Based on multi-group analysis, the migrant worker group with less than 5 years of residency had a more statistically significant effect on the relationship between perceived benefits of action and health promotion behavior than those with over 5 years.
Conclusion
Providing social support as a critical administrative strategy to enhance the health promotion behavior of migrant workers is necessary. Furthermore, when developing an intervention program utilizing the internal mechanism between social support and health promotion behavior, a self-efficacy-enhancing strategy is considered to be more effective. Additionally, educating migrant workers with short-term residence of less than 5 years about the benefits of health behaviors is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
Yu Zhu Zhang, Seon Young Hwang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated With Physical Activity in Home‐Based Rehabilitation Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Prospective Longitudinal Study
Heng‐Ying Fang, Ying‐Hua Pan, Yi‐Heng Zhang, Yu‐Hua Deng, Xiao‐Wen Li, Lei Huang, Hui‐Ting Gu, Yue Ding, Xin‐Xin Hu, Mu Liu, Rui‐Chong Wang, MeiFen Zhang
Musculoskeletal Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
- 2,728 View
- 104 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of an Intervention Using Voice Recording of a Family Member on Patients Undergoing Mechanical Ventilator Weaning Process
- Ah Young Choi, Min Young Kim, Eun Kyeung Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):32-43. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23082
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to determine the impact of an intervention using voice recording of family members on pain, anxiety, and agitation in patients undergoing weaning from mechanical ventilation.
Methods
A randomized control pre-post experimental design was implemented to 53 participants, with 27 and 26 participants in the experimental and control groups, respectively. A 70-second voice recording of a family member, repeated three times at 10-minute intervals was used as an intervention for the experimental group. Meanwhile, participants in the control group used headset for 30 minutes. Structured instruments were utilized to measure pain, anxiety, agitation, and the weaning process. Wilcoxon Signed Ranks test and the Mann-Whitney U test, or χ2 test, were used for data analysis.
Results
The experimental group exhibited significant decrease in pain (Z = - 3.53, p < .001), anxiety (t = 5.45, p < .001), and agitation (Z = - 2.99, p = .003) scores compared with those of the control group. However, there was no significant difference between groups in the weaning process’ simplification (χ2 = 0.63, p = .727).
Conclusion
Intervention using family members’ voice recording effectively reduces pain, anxiety, and agitation in patients undergoing weaning from mechanical ventilation. This can be actively utilized to provide a more comfortable process for patients.
- 2,488 View
- 155 Download

- A Structural Equation Model on Social Re-Adjustment of Stroke Patients: Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
- Jungmi Kim, Hwasoon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):480-495. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22140
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and test a structural equation model on social re-adjustment of individuals with stroke based on a literature review and Roy’s adaptation model.
Methods
This study involved 321 participants who had a stroke and visited the outpatient department after discharge. The hypothetical model was developed based on Roy’s adaptation model and a comprehensive review of previous literature on the topic. The model comprised four exogenous variables (neurological damage, gender [man], age, and social support) and five endogenous variables (activities of daily living, acceptance of disability, depression, rehabilitation motivation, and social re-adjustment). The data were analyzed using SPSS Windows software version 22.0 and AMOS 23.0.
Results
Out of 28 research hypotheses, 18 were supported, and they indicated approximately 64% probability of social re-adjustment. Social re-adjustment is directly and significantly affected by age, social support, activities of daily living, and depression. Social re-adjustment is indirectly affected by neurological impairment, gender (men), age, social support, and rehabilitation motivation.
Conclusion
Continuous assistance and care should be provided for individuals with disabilities caused by sudden neurological damage to facilitate gradual improvement in their social re-adjustment. To enhance social re-adjustment, especially among older adults, newly developed interventions should focus on improving their activities of daily living, preventing depression, and enhancing support from family and healthcare personnel. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Roy Adaptation Model-Based nursing care improves quality of life for elderly burn patients
Yudan Wang
American Journal of Translational Research.2025; 17(6): 4679. CrossRef - The Effects of Aromatherapy on Stroke Symptoms in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
A Reum Lim, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(2): 85. CrossRef
- Roy Adaptation Model-Based nursing care improves quality of life for elderly burn patients
- 3,141 View
- 301 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- A Predictive Model of Resilience in Mothers of Children with Developmental Disabilities
- Youyoung Cho, Hyeonok Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):407-420. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This structural model study was constructed and verified a hypothetical model to examine the effects of parenting stress, social resources, family resources, and positive coping on resilience among mothers of children with developmental disabilities.
Methods
Data were collected using self‐report structured questionnaires, from October 19 to October 30, 2018, with 214 mothers caring for chil-dren with developmental disabilities under the age of 20 years.
Results
In the fitness test results of the hypothesis model, with the fit index χ 2 (p) = 69.27 (< .001), and the normed fit indices (χ 2 = 1.87, GFI = .94, CFI = .97, NFI = .93, and TLI = .95, RMSEA = .06, SRMR = .06), this study satisfies the good fitness in standards. There are seven statistically significant paths among the 10 paths set in the hypotheti-cal model. The explanatory power of parenting stress and social resources, which affects the family resources was 41.4%, the explanato-ry power of parenting stress, social resources, and family resources affecting the positive coping was 58.9%, and the explanatory power of parenting stress, social resources, family resources, and positive coping affecting resilience was 55.5%.
Conclusion
Positive coping, family resources, and social resources of mothers of children with developmental disabilities directly affect their resilience, and parenting stress indirectly affects it. Therefore, to improve the resilience of mothers of children with developmental disabilities, it is necessary to develop a systematic nursing intervention that considers parenting stress, social resources, family resources, and positive coping. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ÖZEL GEREKSİNİMLİ ÇOCUK ANNELERİ: MUĞLA-MENTEŞE ÖRNEĞİ
Ebru Açık Turguter
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Edebiyat Fakültesi Dergisi.2025; 12(1): 320. CrossRef - Factors influencing the family management of children with atopic dermatitis: an integrative review
Sunyeob Choi, Hyewon Shin
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(4): 187. CrossRef
- ÖZEL GEREKSİNİMLİ ÇOCUK ANNELERİ: MUĞLA-MENTEŞE ÖRNEĞİ
- 2,765 View
- 77 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Nurses’ Performance of Care in COVID-19 Wards
- Yoon Sun Kim, Mi-Ae Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):678-688. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing nurses’ performance of care in COVID-19 wards.
Methods
The participants were 132 nurses who worked in COVID-19 wards at three hospitals, and were recruited from April 1 to May 31, 2021. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-test, ANOVA, and multiple regression analysis with SPSS/WIN 24.0 program.
Results
Nursing performance was significantly and positively correlated with ethical sensitivity (r = .75, p < .001), nursing professionalism (r = .67, p < .001), and social support (r = .67, p < .001). Nursing professionalism was positively correlated with ethical sensitivity (r = .64, p < .001) and social support (r = .55, p < .001). Multiple regression analysis for nursing performance revealed that the most significant factor was ethical sensitivity (β = .47, p < .001). Ethical sensitivity, nursing professionalism, and social support explained 66.0% of total variance in nursing performance.
Conclusion
Ethical sensitiviy, nursing professionalism, and social support significantly influence nurses’ performace of care in COVID-19 wards. It suggests that intervention programs should be directed at improving nurses’ ethical sensitivity, bolstering social support, and enhancing nursing professionalism. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Knowledge on Standard Precautions, Nursing Professionalism, and Organizational Culture for Infection Control on Hospital Nurses’ Performance with Guidelines for Standard Precautions
Jiwon Kim, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 225. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Infection Control Practices of Nurses at University Hospitals
Mi Hyang Lee, Sun Hwa Jun
Healthcare.2022; 10(8): 1517. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Anxiety of Nursing Students in Clinical Practice during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Gun Ja Jang, Shin Jeong Park, Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(4): 363. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Post-traumatic Growth of Nurses at Nationally Designated Infectious Disease Hospital
Ji Eun Oh, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 499. CrossRef
- The Influence of Knowledge on Standard Precautions, Nursing Professionalism, and Organizational Culture for Infection Control on Hospital Nurses’ Performance with Guidelines for Standard Precautions
- 1,956 View
- 40 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- The Influence of Family Function on Occupational Attitude of Chinese Nursing Students in the Probation Period: The Moderation Effect of Social Support
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):746-757. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to explore the factors influencing the occupational attitudes of nursing students in the probation period.
Methods
Nursing students in the probation period from five hospitals completed an anonymous survey. The instruments included the nursing occupational attitude scale, family adaptability, partnership, growth, affection, and resolve index, and perceived social support scale. The study examined the moderation model between family function, perceived social support, and occupational attitudes using PROCESS 3.2.
Results
For nursing students, when social support was low, family function had a significant positive impact on occupational attitudes and intentions, and the effect was much higher than that of perceived social support.
Conclusion
Family function has a significant positive explanatory effect on attitude and intention (β = .13, p < .001 and β = .12, p < .001); the interaction term between family function and perceived social support are significant (β = .01, p < .001 and β = .01, p < .001). Perceived social support has a significant moderating effect on the relationship between family function and occupational attitudes of nursing students in the probation period. Family function has a significant difference in the occupational attitudes and intentions of nursing students with low perceived social support. Nursing students perceive social support in the probation period has a significant moderation effect in the relationship between their family function and occupational attitudes. Interns with low family function should be given more social support to improve their occupational attitudes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-disclosure, perceived social support, and reproductive concerns among young male cancer patients in China: A mediating model analysis
Lihua Wu, Xingyu Chen, Tingting Dong, Wei Yan, Linying Wang, Wanling Li
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 11(7): 100503. CrossRef - Moderating role of family functioning and resource support in the relationship between career calling and academic burnout among Chinese medical students during the controlled COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study
Jia-Jun He, Zi-Jiao Wang, Xiao-Ning Liu, Yan-Ping Wang, Chen-Xi Zhao, Feng Lu, Shu-E Zhang, De-Pin Cao
Annals of Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of family function on social anxiety among Chinese nursing students: The mediating role of alexithymia
Yuying Chu, Yuqiang Zhang, Dan Yang, Suyan Wang, Chunguang Liang, Xue Wang, Hongliang Dai
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1356. CrossRef - The association between academic stress, social support, and self-regulatory fatigue among nursing students: a cross-sectional study based on a structural equation modelling approach
Zhang Yuhuan, Zheng Pengyue, Chen Dong, Niu Qichao, Pang Dong, Song Anqi, Jiang Hongbo, Di Zhixin
BMC Medical Education.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Self-disclosure, perceived social support, and reproductive concerns among young male cancer patients in China: A mediating model analysis
- 1,456 View
- 20 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance in Adult Moyamoya Patients
- Bo Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing health behavior compliance in adult patients with moyamoya.
Methods
A descriptive correlation study was conducted to investigate the factors influencing health behavior compliance. Participants were 142 adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease who were hospitalized or visited an outpatient clinic in the Gyeonggi province. Data were collected from December 16, 2019 to April 14, 2020 using self-report questionnaires and analyzed using the IBM SPSS 26.0 Win software.
Results
The hierarchical multiple regression analysis demonstrated that self-efficacy (β = .60, p < .001), social support (β = .13, p = .032), and age (β = .21, p = .005) affected the health behavior of adults with moyamoya disease. These 3 variables explained 62.0% of the variance of health behavior compliance, and the most influential factor was self-efficacy.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, it concludes that nursing interventions should be focused on self-efficacy and social support to improve health behavior compliance with adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease. For that, various strategies to enhance self-efficacy and social support should be developed and actively applied in the clinical setting for adult moyamoya patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
Hae-Na Woo, Yong-Cheol Lim, Joo Hee Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
- 1,464 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Actor and Partner Effects of Couple’s Daily Stress and Dyadic Coping on Marital Satisfaction
- Su Kyung Won, Kyoung Ok Seol
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):813-821. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the actor and partner effects of daily stress and dyadic coping on marital satisfaction using the Actor-Partner Interdependence Mediational Model (APIeM).
Methods
Participants were 314 couples who met the study’s eligibility criteria. Data were collected from March to April 2016 through apartment and cooperative company communities in Seoul. Two APIeMs of positive and negative dyadic coping were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and Mplus 7.4. All measures were self-administered.
Results
Daily stress and positive and negative dyadic coping in both spouses had direct actor effects on their marital satisfaction. Daily stress in both spouses had an indirect actor effect on marital satisfaction through their positive and negative dyadic coping. The husband’s daily stress had an indirect partner effect on the wife’s marital satisfaction through his positive dyadic coping, while the wife’s positive dyadic coping had a direct partner effect on the husband’s marital satisfaction. The husband’s daily stress had an indirect partner effect on the wife’s marital satisfaction through his negative dyadic coping, while the wife’s negative dyadic coping had a direct partner effect on the husband’s marital satisfaction.
Conclusion
Dyadic coping is an effective way to deal with couple’s daily hassles as it increase their satisfaction in marriage. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of risk factors for co-morbid anxiety and depression in pregnant women
Wei Zhang, Ling Li, Xiabidan Tuxunjiang, Bahedana Sailike, Xiaoting Wang, Weicui Meng, Sufeila Shalayiding, Ting Jiang
Psychiatry Research.2025; 344: 116323. CrossRef - Pregnant Women’s Dyadic Coping and Associated Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study Utilizing Latent Profile Analysis
Shiqiong Yan, Wenzhuo Fan, Yonghong Ma, Sijia Xie, Rong Li, Yao Lan, Linli Xie, Jie Jing
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 1009. CrossRef - Spouse Burnout and Marriage Satisfaction in Married Individuals: The Mediating Role of Psychologıcal Well-being
Bülent Şen, Nergüz Bulut Serin, Kadriye Karagülmez
Batı Anadolu Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 15(2): 1266. CrossRef - Dyadic coping and associated factors in women with high-risk pregnancy and their spouses: Do they interact?
Mengjie Liu, Yu Fang, Mengshi Liu, Min Wu, Jingshuo Zhang, Tianchen Niu, Xiaoman Zhang
Midwifery.2024; 134: 104006. CrossRef - 중년부부의 문제해결 유형과 결혼만족도의 관계
수산나 주, 미선 강, 인혜 정, 서진 조
Journal of Family Relations.2023; 28(1): 33. CrossRef - Relationship between Chinese middle-aged and old couples' Confucian coping thinking and marital quality
Zhiguang Fan, Hanwei Wu, Min Tao, Lei Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of avoidant attachment on marital satisfaction of Chinese married people: Multiple mediating effect of spousal support and coping tendency
Lian Xiong, Caihua Zhou, Liangshi Yan, Pan Zhao, Mengting Deng, Yan Hu
Acta Psychologica.2022; 228: 103640. CrossRef - Interrelation of Attachment and Coping Behavior In Adults
E.V. Kuftyak
Counseling Psychology and Psychotherapy.2021; 29(1): 28. CrossRef
- Analysis of risk factors for co-morbid anxiety and depression in pregnant women
- 1,590 View
- 45 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Predictive Model for Quality of Life of the Older Men Living Alone
- Su Jin Kim, Gyeong-Suk Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):799-812. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to construct and test a predictive model that explains and predicts the quality of life in older men living alone.
Methods
A self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from 334 older adult men living along aged 65 years or over living in Jeollanam-do provinces. The endogenous variables were depression, self-rated health, instrumental activity of daily life, health promotion behaviors, the number of social participation activities and quality of life. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs.
Results
The final model with 14 of the 8 analysed paths showed a good fit to the empiri cal data: χ2= 173.26(p < .001, df = 53),normed χ2= 3.27, GFI = .92, NFI = .90, CFI = .93, TLI = .89, RMSEA = .08 and SRMR = .06. Activities had direct effect on quality of life of older men living alone and social support had both direct and indirect effects. Meanwhile, function and socioeconomic status showed only indirect effects.The variables included in the eight significant paths explained 83.7% of variance in the prediction model.
Conclusion
Instrumental activities of daily living and social support effect directly on quality of life in the older men living alone. Findings suggest that health care providers including community nurses need to provide social support as well as empowerment programs of instrumental activities of daily living and health promotion for improving quality of life of the older men living alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in the health status and health-related quality of life of community-dwelling older adults living alone: one-year follow-up from a cohort study
Hana Ko, Belong Cho, Kyung-Choon Lim, Soong-Nang Jang, Sun Ju Chang, Yu Mi Yi, Hye Ryung Cho, So Im Ryu, Eun-Young Noh, Yeon-Hwan Park
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influencing factors on self-care of older adults living alone in a community during COVID-19: A cross-sectional study
Heeyoung Woo, Minkyung Gu
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - A novel nomogram to stratify quality of life among advanced cancer patients with spinal metastatic disease after examining demographics, dietary habits, therapeutic interventions, and mental health status
Yue Li, Ze Long, Xiuju Wang, Mingxing Lei, Chunzi Liu, Xiaolin Shi, Yaosheng Liu
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associated Factors with Health-related Quality of Life among Older Adults with Diabetes in Korea
Eun-Kyung Lee, Sun-Young Jung
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(2): 61. CrossRef
- Changes in the health status and health-related quality of life of community-dwelling older adults living alone: one-year follow-up from a cohort study
- 2,082 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Reversals in Decisions about Life-Sustaining Treatment and Associated Factors among Older Patients with Terminal Stage of Cardiopulmonary Disease
- Jung-Ja Choi, Su Hyun Kim, Shin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):329-339. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the frequency, patterns, and factors of reversals in decisions about life-sustaining treatment (LST) among older patients with terminal-stage chronic cardiopulmonary disease.
Methods This was a retrospective correlational descriptive study based on medical chart review. De-identified patient electronic medical record data were collected from 124 deceased older patients with terminal-stage cardiopulmonary disease who had made reversals of LST decisions in an academic tertiary hospital in 2015. Data were extracted about the reversed LST decisions, LST treatments applied before death, and patients’ demographic and clinical factors. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify the factors associated with the reversal to higher intensity of LST treatment.
Results The use of inotropic agents was the most frequently reversed LST treatment, followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation, intubation, ventilator therapy, and hemodialysis. Inconsistency between the last LST decisions and actual treatments occurred most often in hemodialysis. One-third of the reversals in LST decisions were made toward higher intensity of LST treatment. Patients who had lung diseases (vs. heart diseases); were single, divorced, or bereaved (vs. married); and had an acquaintance as a primary decision maker (vs. the patients themselves) were significantly more likely to reverse the LST decisions to higher intensity of LST treatment.
Conclusion This study demonstrated the complex and turmoil situation of the LST decision-making process among older patients with terminal-stage cardiopulmonary disease and suggests the importance of support for patients and families in their LST decision-making process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristics of Life-Sustaining Treatment Decisions: National Data Analysis in South Korea
Jiyeon Choi, Heejung Jeon, Ilhak Lee
Asian Bioethics Review.2024; 16(1): 33. CrossRef - Decision and Practice of End-of-Life Care in Lung Disease Patients with Physicians Orders for Life Sustaining Treatment
Yu Mi Oh, Yoon Na Kang, Soo Jung Han, Jeong Hye Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2023; 26(1): 7. CrossRef - Same, same, but different? A longitudinal, mixed-methods study of stability in values and preferences for future end-of-life care among community-dwelling, older adults
Malin Eneslätt, Gert Helgesson, Carol Tishelman
BMC Palliative Care.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferences for life-sustaining treatment in Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
HyunChul Youn, Suk-young Lee, Han-yong Jung, Shin-Gyeom Kim, Seung‑Hyun Kim, Hyun-Ghang Jeong
BMJ Open.2021; 11(1): e039470. CrossRef - Life-Sustaining Treatment in End-Stage Liver Disease Patients: Patients’ Decisions and Results
Hyun Jung Jung, Jeong Yun Park
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2020; 23(2): 85. CrossRef
- Characteristics of Life-Sustaining Treatment Decisions: National Data Analysis in South Korea
- 1,164 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Psychosocial Well-Being of Clinical Nurses Performing Emotional Labor: A Path Analytic Model Approach
- Yoonjeong Lee, Hyunli Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):307-316. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.307
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to investigate the influence of emotional expressivity, emotional intelligence, affectivity, job autonomy, social support, and emotional labor on clinical nurses’ individual well-being and to provide guidelines for interventions and strategies for its improvement.
Methods The sample consisted of 207 nurses recruited from a general hospital in Korea. The participants completed a structured self-report questionnaire comprising measures of emotional expressivity, emotional intelligence, positive affectivity, negative affectivity, job autonomy, supervisor support, coworker support, deep acting, surface acting, emotional exhaustion, and job satisfaction. Data were analyzed using SPSS statistics 22.0 and AMOS 22.0.
Results The final model was a good fit for the data based on the model fit indices. In the path analysis, surface acting, negative affectivity, supervisor support, and coworker support had statistically significant effects on emotional exhaustion, explaining 29.0% of the variance. Deep acting, emotional exhaustion, positive affectivity, and emotional intelligence had statistically significant effects on job satisfaction, explaining 43.0% of the variance.
Conclusion Effective strategies to improve clinical nurses’ individual well-being should focus on surface acting, deep acting, affectivity, social support, and emotional intelligence. The results of this study can be utilized as base data to manage emotional labor and improve clinical nurses’ individual well-being.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validity and Reliability of the Korean version of the Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale for Nurses
Hye-Ja Park, Soyoung Yu
Sage Open.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Validity and Reliability of the Korean version of the Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale for Nurses
- 1,051 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Psychoeducational Approach to Distress Management of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer
- Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Yong Sik Jung, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):669-678. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.669
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of integrated psychoeducational program for distress management of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer.
Methods A quasi-experimental trial was conducted. The participants consisted of 47 female patients with breast cancer assigned to an intervention group (n=25) and control group (n=22). The intervention group participated in integrated psychoeducational program, consisting of individual face-to-face education and telephone-delivered health-coaching sessions. Data were collected at three time points: pre-intervention (T1), post-intervention (T2), and 6-month follow-up (T3). Study instruments were Distress thermometer, Supportive Care Needs Survey Short Form 34 and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast.
Results Compared with the control group, breast cancer patients in the intervention group reported lower distress and supportive care needs than the control group. The intervention group reported higher quality of life (QOL) overall and higher emotional well-being than the control group.
Conclusion These findings indicate that the integrated psychoeducational program is an effective intervention for reducing distress and supportive care needs and increasing QOL of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer. Oncology nurses need to provide psychoeducational intervention to support patients with breast cancer in managing their distress and helping them adjust to their life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Tailored Psychoeducational Intervention for Patients With Advanced Cancer in Indonesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nurul Huda, Made Satya Nugraha Gautama, Wan Nishfa Dewi, Agung Waluyo, Hsiu Ju Chang, Malissa Kay Shaw
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2025; 57(5): 848. CrossRef - Evidence on the benefits of mind-body Qigong exercise in women with breast cancer
Michel Marcos Dalmedico, Jackson Adriano Canavarro Ribeiro, Juliana Londero Silva Avila, Prisley Pereira de Oliveira, Paula Karina Hembecker, Sergio Ossamu Ioshii
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Distress and Influencing Factors in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Yu Jin Jeong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 311. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions for Patients with Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis
Kyu-Sic Hwang, Kuy-Haeng Lee, Chan-Mo Yang, Hye-Jin Lee, Sang-Yeol Lee
Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience.2023; 21(1): 118. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Adjustment to life with metastatic cancer through psychodrama group therapy: A qualitative study in Turkey
Songül Kamışlı, Bahar Gökler
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(2): 488. CrossRef - Integration of longitudinal psychoeducation programmes during the phases of diagnosis, management and survivorship of breast cancer patients: A narrative review
Athena Michaelides, Constantina Constantinou
Journal of Cancer Policy.2020; 23: 100214. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer
Kavitha Konnakkaparambil Ramakrishnan, Sreekumar Damodaran
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2020; 7(28): 1368. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef - Uncertainty and unmet care needs before and after surgery in patients with gastric cancer: A survey study
Ji Yea Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Sanghee Kim, Woo Jin Hyung
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(2): 427. CrossRef - Effects of Different Exercise Interventions on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Tetiana Odynets, Yuriy Briskin, Valentina Todorova
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,836 View
- 41 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Symptom Distress and Coping in Young Korean Breast Cancer Survivors: The Mediating Effects of Social Support and Resilience
- Ji Hyun Lee, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):241-253. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the mediating effect of social support and resilience on the relationship between symptom distress and coping in young Korean breast cancer survivors.
Methods A purposive sample of 209 young breast-cancer survivors (mean age 39.9) was recruited for a cross-sectional survey, and the data were collected between June and October 2015. The instruments used in this study were the Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale-Short Form, the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support, 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale, and Cancer Coping Questionnaire. The collected data were then analyzed using the SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 programs.
Results Symptom distress was found to have a significant indirect effect on coping (beta=-.32,
p =.002), but not a significant direct effect (beta=.06,p =.577). Additionally, based on the values obtained for the squared multiple correlation, symptom distress, social support, and resilience were found to explain 46.4% of the total variance of coping.Conclusion Based on the results of this study, it can be suggested that in order to enhance young breast cancer survivors’ ability to cope with the distress they commonly feel, intervention methods that strengthen resilience and provide social support should be developed and made available to them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sexual well-being in cancer care services: the role of body image and coping strategies
Judith Partouche-Sebban, Saeedeh Rezaee Vessal, Youssef Souak, Aymen Ammari, Alain Toledano
Journal of Services Marketing.2026; : 1. CrossRef - How Online Patient-Provider Communication Alleviates Psychological Distress Among Patients with Chronic Diseases: The Role of Perceived Patient-Centered Communication and Adaptive Coping Strategies
Bingqing Ling, Yu Zheng
Health Communication.2025; 40(8): 1559. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Not Returning to Work Among Breast Cancer Survivors
Leni Merdawati, Hui-Chen Lin, Chieh-Hsin Pan, Hui-Chuan Huang
Workplace Health & Safety.2025; 73(5): 216. CrossRef - Factors affecting resilience among young breast cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Hye Young Min, Yoonjung Kim, Hae Jeong An
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 75: 102837. CrossRef - Latent classes of health‐promoting lifestyle in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in China: A cross‐sectional survey
Meixuan Song, Qiuyao He, Juan Yang, Jinyu Zhang
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Postmastectomy Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Sajad Ahmad Salati, Lamees Alsulaim, Mariyyah H Alharbi, Norah H Alharbi, Thana M Alsenaid, Shoug A Alaodah, Abdulsalam S Alsuhaibani, Khalid A Albaqami
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the CALM intervention on resilience in Chinese patients with early breast cancer: a randomized trial
Shaochun Liu, Runze Huang, Anlong Li, Sheng Yu, Senbang Yao, Jian Xu, Lingxue Tang, Wen Li, Chen Gan, Huaidong Cheng
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(20): 18005. CrossRef - Perceived social support and depressive symptoms in Chinese patients with ovarian cancer and the mediating role of resilience:a cross-sectional study
Xiaoyan Pang, Fangmei Li, Lei Dou, Yichang Tian, Yi Zhang
Current Psychology.2023; 42(24): 20485. CrossRef - Resilience-related Breast Cancer: A Concept Analysis
Fitria Endah Janitra, Nur Aini, Anggi Lukman Wicaksana
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing.2023; 13(1): 31. CrossRef - Factors influencing the coping strategies of liver cancer patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolization
Su‐Chih Chen, Shu‐Fang Wu, Tsae‐Jyy Wang, John Rosenberg, Yu‐Ying Lu, Shu‐Yuan Liang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived social support and coping style as mediators between resilience and health-related quality of life in women newly diagnosed with breast cancer: a cross-sectional study
Kaina Zhou, Fan Ning, Xiao Wang, Wen Wang, Dongfang Han, Xiaomei Li
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - A Mobile Healing Program Using Virtual Reality for Sexual Violence Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Mi‐ran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2021; 18(1): 50. CrossRef - Factors related to the resilience and mental health of adult cancer patients: a systematic review
Saori Tamura, Kumi Suzuki, Yuri Ito, Akiko Fukawa
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(7): 3471. CrossRef - Resilience in women with breast cancer: A systematic review
Ibane Aizpurua-Perez, Joana Perez-Tejada
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 49: 101854. CrossRef - Individual resilience in adult cancer care: A concept analysis
Dan Luo, Manuela Eicher, Kate White
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 102: 103467. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Effects of cyclic adjustment training delivered via a mobile device on psychological resilience, depression, and anxiety in Chinese post-surgical breast cancer patients
Kaina Zhou, Jin Li, Xiaomei Li
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2019; 178(1): 95. CrossRef
- Sexual well-being in cancer care services: the role of body image and coping strategies
- 1,975 View
- 22 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Successful Aging in Elders with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Selection-Optimization-Compensation Strategy
- Young Mi Jang, Rhayun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(4):488-498. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.4.488
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The focus of the study was on the selection-optimization-compensation (SOC) strategy to predict successful aging mediated by dyspnea symptoms in older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The model was constructed based on the hypotheses that coping strategy and social support of the elders predict successful aging through the SOC strategies.
Methods Participants were 218 outpatients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease recruited for the study. Data collection was done from March 25 to September 11, 2015, and analyzed using SPSSWIN 22.0 and AMOS 21.0.
Results The hypothetical model appeared to be fit to the data. Seven of eight hypotheses selected for hypothetical model were statistically significant. The SOC strategy has only significant indirect effects through dyspnea symptoms on successful aging. Coping strategy, social support, SOC strategies and dyspnea symptoms explained 62% of variance in successful aging.
Conclusion The SOC strategies with social support and dyspnea symptoms significantly explained successful aging among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nursing strategies should be focused on social support and coping strategies to optimize SOC strategies so that older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are able to manage dyspnea symptoms and eventually achieve successful aging.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A structural equation modeling analysis of successful aging in older adults with osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Jeong Hwa Kum
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(2): 131. CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure selection, optimization, compensation (SOC) strategy in late middle-aged women: a methodological study
Do-Young Lee, Gie Ok Noh
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 216. CrossRef - Factors contributing to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients' functional performance: Structural equation modelling based on theory of unpleasant symptoms
Hye Suk Jun, Younhee Kang
Nursing Open.2023; 10(5): 3132. CrossRef - Experiences on Self Management of Aged Men with Mild Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Jeong-Soo KIM
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(3): 758. CrossRef - The Relationships among Social Support, Bowel Function Symptoms and Uncertainty in Rectal Cancer Patients
Kyungmi Lee, Semi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - Life experience of older women with chronic conditions: Flow and Balance as a coping resource
Sanghee Lee, Jinmoo Heo
Educational Gerontology.2019; 45(4): 259. CrossRef
- A structural equation modeling analysis of successful aging in older adults with osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional descriptive study
- 1,108 View
- 13 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Burnout among Mothers of Children with Cerebral Palsy
- Ji-Young Seo, Hae-Jin Lee, Mi-Ae You
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):233-241. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.233
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of parental stress, social support, and coping behavior on burnout among mothers caring for children with cerebral palsy.
Methods Participants in this cross-sectional, descriptive study were 185 mothers who completed a self-report structured questionnaire. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-test, one-way ANOVA, correlation and multiple linear regression analyses with IBM SPSS Win 22 program.
Results Parental stress and coping behavior were strong predictors of burnout among mothers of children with cerebral palsy. These variables explained 50.0% of the variance in burnout. Social support was not a predictor of burnout. A higher level of burnout was associated with higher levels of parental stress and lower levels of social support and coping behavior.
Conclusion Mothers of children with cerebral palsy are vulnerable to burnout. These results show that effective strategies for reducing parental stress and improving positive coping behavior are needed to reduce burnout in these mothers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between Dyadic Coping and Parental Burnout: The Chain Mediation Effect of Marital Satisfaction and Co-Parenting
都尼戈·库尔班 库
Advances in Psychology.2024; 14(04): 661. CrossRef - Characteristics of the parent-child relationship in families of children with cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis (literature review)
E. A. Boiko, V. L Malygin, E. I. Glushchenko
Neurology, Neuropsychiatry, Psychosomatics.2024; 16(6): 83. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Burnout in Primary Family Caregivers of Hospital-based Home Care Patients
Ju Ok Yang, Hye Kyung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(1): 54. CrossRef
- Relationship between Dyadic Coping and Parental Burnout: The Chain Mediation Effect of Marital Satisfaction and Co-Parenting
- 1,163 View
- 16 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effect of Supportive Nursing on the Stress Reaction of Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
- Jum Hee Park
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):912-922. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.912
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of supportive nursing one stress reaction of breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. The nonequivalent control group pre-test/post-test design was used for this experimental study. The subjects were 32 patients who were receiving chemotherapy after mastectomies at K hospital in Taegu from June, 1994 to June 1995. Among 32 subjects, 16 were placed in the experimental group and 16 in the control group. The experimental and control groups were tested for general characteristics, trait anxiety, health locus of control, family support, state anxiety, hopelessness, physical stress, and anxiety behavior. Collected data was analyzed by means of a chisquare test and a t-test for the comparative analysis of the general characteristics and homogeneity of subjects. ANOVA, and MANOVA were used for testing the hypothesis. Reliability of the tools were analyzed using the Pearson Correlation coefficient. The results of this study were as follows : 1. The hypothesis ; The stress reaction of the experimental group which took supportive nursing was lower than the stress reaction of the control group ; this was supported statistically. The main variable influenced in stress reaction was hopelessness. Supportive nursing for breast cancer patients, who are receiving chemotherapy, was especially effective in the reduction of hopelessness compared to state anxiety, physical stress, and anxiety behavior. 2. An analysis of the difference on stress reaction, according to the frequency of supportive nursing between the control and experimental group showed the level of hopelessness of the experimental group was lower than the control group after four supportive meeting sessions. But there was no statistical difference in state anxiety, physical stress, and anxiety behavior. In conclusion, this study supported utilization of supportive care as well as demonstrating the effectiveness of the System-Developmental Stress Model developed by Chrisman and Riehl-Sisca.
- 355 View
- 1 Download

- Effects of a Social Support Group on Burden and Well-being of Mothers of Developmentally Delayed Children
- Ka Sil Oh
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):389-400. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.389
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study examined the effects of group social support on the reduction of burden and increase in well-being of mothers of developmentally delayed children. The research used a one group pre-post experimental design. The independent variable in the experiment was group social support. Two series of 4-weekly meetings for group social support were conducted by the researcher with the intention of developing a self-help group. The dependent variables were burden and well-being. Well-being was operationalized as physical symptoms and quality of life. Thirty mothers of developmentally delayed infants from the rehabilitation center of a medical center participated in the study. Data were collected by interview and a self-administered questionnaire. The mean age of the subjects was 29.9 years. Changes of the dependent variables between pre and post tests were compared using the t-test. Even though there was a slight improvement in the scores for the dependent variables, they were not statistically significant. The items, "I resent my baby", "I feel angry about my interactions with my baby", "I feel guilty in my relationship with my baby" showed a significant decrease in burden score and were statistically significant. Symptoms of loneliness, constipation, anxiety, restlessness were less and feeling of happiness was greater after participation in the group social support, than on the pretest. The mothers showed emotional instability and frustrations during the group sessions but their reactions in general were positive. Emotional support, stress management and information provided were identified as the most valuable content of the sessions. However, participation was not active due to the mother's denial, delayed acceptance and/or avoidance of their infants' problems. It can be seen that group social support for the mothers with developmentally delayed children should be provided after infancy when the mothers have time to accept their children's conditions and are ready to receive support. The use of comprehensive instruments which measure burden in both families and mothers needs to be developed for future research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Sociodrama-based Communication Enhancement Program on Mothers of Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Pilot Study
Sun Joo Jang, Jong-Sook Han, Myoung Hee Bang, Jung-Won Ahn
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(2): 114. CrossRef
- Effects of a Sociodrama-based Communication Enhancement Program on Mothers of Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Pilot Study
- 766 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study, on the Quality, of Life, Family, Support and Hope of Hospitalized and Home Care Cancer Patients
- Kae Wha Jo, Myung Ja Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):353-363. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.353
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the occurrence of cancer, most cancer patients experience various emotional changes such as anxiety, depression, and emotional shock. Especially in our country, cancer has been recognized as an incurable disease resulting in death. The number of cancer patients increases daily. But as the survival rate of cancer patients is also increasing, there is a need to find the better methods of nursing care for cancer patients. The purposes of this paper are as follows : 1) To understand family support and hope and quality of life for the cancer patient both during hospitalization and at home. 2) To determine the relationship between family support, hope and quality of life. To examine the problems, we used a questionnaire and obtained data form the records of 45 home care and 94 hospitalized(in 3 university hospitals) Patients in Taegu area from the period of June 15 to August 15, 1996. SPSS /PC was used for the data analysis and the statistical methods used were the T-test and ANOVA. The results of this paper are as follow : 1 ) In the aspect of family support, there is no difference between hospitalized and home care cancer patients(t=1.63, P>0.01 ). 2) In the aspect of hope, hospitalized cancer patients have a higher score than home care cancer patients (t=3.08, P>0.01 ) 3) In the aspect of quality of life, hospitalized cancer patients have a higher score than home care patients(t=2.96, P<.01). 4) There is a correlation between quality of life and hope with a correlation coefficient r=0.5199 and P=0.000. In addition. the correlation coefficient between quality of life and family support is 4179 with P =0.000. 5) The family support of the cancer patient is influenced by sex(F=9.1863, P<0.01), education(F=4.3641, P<0.01) and the level of life (F=5.5002, P<0.01 ). 6) The hope of cancer patients is influenced by the number of hospitalizations (F=3.6413, P<.05), education(F=B.01 13, P<.01 ) and the level of life (F=5.0649, P <.01 ). 7) The quality of life of cancer patients is influenced by the number of hospitalization( F=5.1167, P<0.05), education( F=3.1590, P<0.01 ) and the level of life (F=5.6942, P<1.01 ).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influences of Family Support on the Meaning of Life in Cancer Patients
Min Jung Kim, Min Sung Kim
Journal of Families and Better Life.2023; 41(2): 19. CrossRef - Needs of Hospice Care and Quality of Life for Cancer Patients
In Sun Suh, Mi Hwa Shin, Se Hwa Hong
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2010; 13(2): 89. CrossRef
- The Influences of Family Support on the Meaning of Life in Cancer Patients
- 618 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Pre-post changes of sexual satisfaction and spouse support of women who have had a hysterectomy
- Soon Bok Chang, Seung Eun Jeong
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1995;25(1):173-183. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1995.25.1.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The research questions of this study were: Will the level of sexual satisfaction of women who have had a hysterectomy 4 months before be decreased compare to the level of sexsual satisfaction before the hysterectomy?, Will the level of perceived spouse support of women who have had a hysterectomy 4 months before be decreased compare to the level before the hysterectomy?, and What is the relationship between sexual satisfaction and spouse support? This is a perspective descriptive correlational study. The number of subjects was 44. The subjects were limited to Korean women who had an abdominal or vaginal hysterectomy for non-malignant diseases, were married (living with their husbands), mentally healthy, and premenopause at the time of operation. The instrument was consisted of 4 items of demographic characteristics, 13 items of spouse support, and 10 items of sexual satisfaction. The instrument of sexual satisfaction was a component of the Derogatis Sexual Function Inventory. Data analysis was done by paired t-test to see the differences between the pre- post scores of sexual satisfaction and spouse support. The Pearson Correlation Coefficiency was calculated to see the relationship between the scores of sexual satisfaction and spouse spport of pre-post hysterectomy. Results were summerized as follow: The mean age of the subjects was 43.5 years; 72. 1% of the subjects were above middle school graduates: their mean income level was 1,453,000 Korean won and 86.4% of the subjects have had bilateral oophrectomy. 1. The scores of sexual satisfaction of women at 4 months after hysterectomy was decreased significantly compare to the score before hysterectomy (paired t=. 274, p=.009). 2. The scores of spouse support of the women at 4 months after hysterectomy was not decreased significantly compare to the score before hys-terectomy(paired t=.19, p=.847). 3. The scores of sexual satisfaction and spouse support before hysterectomy was significantly related(r=.5186, p=.000). 4. The scores of sexual satisfaction and spouse support at 4 months after hysterectomy was significantly related (r=.4110, p=.005) It can be concluded that the sexual satistaction level could be decreased 4 months after the hysterectomy, but the spouse support level may not be decreased at 4 months after hysterectomy. Further studies have to be done to identify the factors related to the decrease of sexual satisfaction and spouse support after hysterectomy.
- 450 View
- 0 Download

- Social Support, Stressful Life Events, and Health Behaviors of Korean Undergraduate Students
- Young Joo Park, Sook Ja Lee, Ka Sil Oh, Kyoung Ok Oh, Jeong Ah Kim, Hee Soon Kim, Sang Soon Choi, Sung Eun Yi, Choo Ja Chung, Hoa Yun Jun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):792-802. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.792
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This cross-sectional study was designed to explore the relationship among social support, experienced stressful life events and health behaviors of Korean undergraduate students, and validate the mediator effect of social support. METHOD: One thousand four hundred fifty-three undergraduate students were randomly selected from five universities located in the middle area of Korea. RESULT: The health behaviors of Korean undergraduates tend to have unhealthy patterns. In the case of the students living without family, experiencing more stressful life events and perceiving lower social support, health behaviors are poor. The relationship between perceived social supports, the frequency of the experienced stressful life events and the score of health behavior patterns is statistically significant. After controlling the effect of social support, the correlation coefficient between the frequency of experienced stressful life events and the score of health behavior patterns was slightly lower. The score of health behaviors between the group with an extremely high score of social support and the group with an extremely low score were statistically significantly different. CONCLUSION: Future studies need to be pursued to develop various strategies such as a health education programs and counseling programs for health maintenance and health promotion of undergraduates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Affecting the Eating Behavior Disorders of Korean College Students
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim, Gisoo Shin
The Open Nursing Journal.2021; 15(1): 55. CrossRef - Relationship between Health Literacy and Self-care Behavior in Patients with Stomach Cancer after Gastrectomy: Mediating Effects of Subjective Health Status and Specific Self-efficacy
Min Jung Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 259. CrossRef - Cultural fit of emotions and health implications: A psychosocial resources model
Jiah Yoo, Yuri Miyamoto
Social and Personality Psychology Compass.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - What Causes Health Promotion Behaviors in College Students?
Mi Young Kim, Yu Jeong Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2018; 12(1): 106. CrossRef - The Sugars Intake through Processed Foods and Its Related Factors in College Students
Eun Kyung Shin, Young Taek Doo
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2016; 41(2): 85. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behavior, Stress and Stress Coping Type between Undergraduate Nursing Students and Female Students in Other Majors
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2015; 21(1): 28. CrossRef - A Relevance on Health Perception, Health Knowledge and Health Promotion Behavior of the University students
Sun-Jung KIm, Eun-Young Jung
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(8): 5394. CrossRef - An Influencing Health Promoting Behavior of Perceived Health Status and Self-Efficacy according to major of college students
Hee-Joo Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(2): 989. CrossRef - Influence of Negative Emotion on the Suicidal Ideation in University Student: Mediated Moderating Effect of Explosive Behavior through Gender
Goo-Churl Jeong
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(12): 775. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promotion Behaviors of College Students
Hwanhui Sim, Misook Kim, Kyeongsook Jeong, Jeeun Heo, Eunjung Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(3): 97. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Depression of Korean Female University Students
Kyung-Sook Lee, Chin-Kang Koh, Joo Hyun Kim, Haeng-Mi Son, Mi Ryeong Song, Su Jeong Yu, Kyung Sook Cho
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(2): 112. CrossRef - Depression Cognition and Health Promoting Behaviors of Smoking and Non-smoking College Students
Mi-Ok Kim, Mi Yu, Se-Jin Ju, Kyeong-Suk Kim, Jung-Hyun Choi, Hee-Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(3): 35. CrossRef
- Factors Affecting the Eating Behavior Disorders of Korean College Students
- 966 View
- 2 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Information and Social Support Regarding Breastfeeding: A Survey of Mothers in Seoul, South Korea
- Heasook Kim, Andrea Crivelli Kovach
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(7):1151-1159. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.7.1151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BACKGROUND: Pediatric societies throughout the world recommend breastfeeding as the optimal form of infant nutrition. This recommendation is based on extensive epidemiologic research that documents the health, developmental, psychological, social, economic, and environmental benefits to infants, mothers, families, and society. The purpose of this study was to examine breastfeeding information and emotional support received by mothers prenatally, hospital breastfeeding practices, and the relationship between information and support received and breastfeeding initiation and planned feeding method post discharge from the hospital.
METHODS
A 36-item questionnaire was distributed during the Spring 2000 to mothers who delivered babies at maternity centers in Seoul, South Korea. A sample of 52 mothers was surveyed at the time of hospital discharge. The questionnaire was developed based on the literature and reviewed by experts including internationally board certified lactation consultants, a nutritionist, and perinatal nurses. The survey instrument consists of five components: sociodemographic information, breastfeeding information received by mothers prenatally, emotional support regarding the mothers' infant feeding choice, breastfeeding initiation and supplementation, and hospital breastfeeding practices.
RESULTS
Fifty-two breastfeeding mothers at three hospitals completed the survey. The majority of the mothers were 26 to 35 years of age, college graduates, married, had uncomplicated vaginal or planned cesarean deliveries, and primiparas. Forty-nine mothers responded that they decided to breastfeed during their pregnancy. Mothers reported that the information they received during pregnancy was provided primarily by their mothers, or friends and other relatives. The majority of mothers reported that others influenced their infant-feeding decision. Forty mothers reported receiving emotional support for their infant feeding choice during their pregnancy with mothers or mothers-in-law and friends providing the greatest support.
DISCUSSION
Women obtain information prenatally about breastfeeding from many sources-family, friends, written materials, prenatal classes, and health care professionals. There are benefits and drawbacks to information received from multiple sources. Additionally, research has shown that a woman's infant-feeding decision is affected by the type of professional and social support the mother receives. Postpartum professional support for new breastfeeding mothers encompasses multiple dimensions ranging from a follow-up telephone call from the hospital nursing staff to referral to a community resource. Prenatal breastfeeding education on a community-wide basis can provide essential information for future mothers, families, and community support networks. Additional research needs to be done exploring the impact of prenatal, postpartum, and post-discharge support for women on breastfeeding initiation and duration rates.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Immediate Skin‐to‐Skin Contact on Exclusive Breastfeeding: An Instrumental Variable Approach
Sangyun Lee, Yongnam Kim
Acta Paediatrica.2025; 114(9): 2367. CrossRef - Postnatal women’s breastfeeding beliefs, practices, and support during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional comparative study across five countries
K. P. Coca, E. Y. Lee, L. Y. Chien, A. C. P. Souza, P. Kittikul, S. A. Hong, Y. S. Chang
International Breastfeeding Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Postpartum Breast-feeding Support by Nurse on the Breast-feeding Prevalence
Gun Ja Jang, Sun Hee Kim, Kyung Soon Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 172. CrossRef
- The Effect of Immediate Skin‐to‐Skin Contact on Exclusive Breastfeeding: An Instrumental Variable Approach
- 757 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Prediction Model of Exercise Behavior in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Eun Ok Lee, In Ja Kim, Jong Im Kim, Hyun Sook Kang, Sang Cheol Bae
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(4):681-691. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.4.681
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The exercise status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, associations between exercise behavior and personal factors, and associations between exercise behavior and exercise-specific cognitions and their effects were assessed. METHOD: Four hundred thirty nine outpatients with rheumatoid arthritis were studied. The exercise status was measured by a single item. The intensity was multiplied by the frequency and duration of each exercise. The product of these intensity values for all exercises was defined as exercise behavior. Based on the Pender's revised health promotion model, exercise benefit, barrier, self-efficacy, enjoyment and social support were chosen as exercise specific cognitions and affect variables. Path analysis was used to identify the predictors of exercise behavior. Results: Compared to the duration before being diagnosed, the number of subjects who exercised regularly increased after being diagnosed. However over half of the subjects refrain from any sort of exercise and the type of exercise is very limited. Among the variables, exercise barrier, self-efficacy, and social support were found to be significant predictors of exercise behavior, and only previous exercise experience was found to be significant predictors of all behavior specific cognitions and affect variables. CONCLUSION: These findings suggest that studies should explore exercise behaviors and strategies to emphasize the cognitive-motivational messages to promote exercise behaviors.
- 424 View
- 0 Download

- Major Effect Models of Social Support and Its Statistical Methods in Korean Nursing Research
- Eun Hyun Lee, Jin Sun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1503-1520. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1503
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of the present study is 1) to explain major effect models (main, moderating, and mediating) of social support and statistical methods for testing the effect models and 2) to analyze and evaluate the consistency in the use of the effect models and its statistical methods in Korean nursing studies. A total of 57 studies were selected from Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing, Journal of Korean Academic Society of Adult Nursing, Journal of Korean Women's Health Nursing Academic Society, Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing, Journal of Korean Community Nursing, Journal of Korean Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing Academic Society, and Journal of Korean Pediatric Nursing Academic Society published in the year of 1990-1999. In results, most studies on social support performed in Korea Nursing Society were about a main effect model. There are few studies on moderating or mediating model of social support. Thus, it was difficult to find research findings how, why, under what conditions social support impacted on health outcomes. Most studies on the moderating or mediating effect model of social support used statistical methods for testing main effect model rather than for testing moderating or mediating effect model. That is, there are inconsistency between effect models of social support and its statistical methods in Korean nursing researches. Therefore, it is recommended to perform studies on moderating or mediating effect model and use appropriate statistical methods.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Social support for nursing students: A concept analysis study
Mi-Young Choi, Sunghee Park, Gie Ok Noh
Nurse Education Today.2024; 132: 106038. CrossRef - Measurement Properties of Self-report Questionnaires Published in Korean Nursing Journals
Eun-Hyun Lee, Chun-Ja Kim, Eun Jung Kim, Hyun-Ju Chae, Soo-Yeon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 50. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Caring Behavior of Mothers of Disabled Children
Ae-Ran Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 673. CrossRef
- Social support for nursing students: A concept analysis study
- 709 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effect of Social Support Intervention on Mood and Maternal Confidence of Premature's Mothers
- In Hae Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(5):1111-1120. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.5.1111
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to examine the effect of social support intervention on mood and maternal confidence of premature's mothers. The social support intervention is known to induce improved mood state and provide information on caretaking so as to increase the maternal confidence in the mother of a premature. To systematically investigate its effect, this study employed a nonequivalent randomized post-repeated quasi-experimental design. The intervention was given individually to mothers of prematures five times spanning five weeks. The sample consisted of the 50 mothers (experimental 27, control 23) of a premature. The data were collected using the structured questionaires twice as post tests. Various instruments were used in this study. The POMS developed by Lee(1990) was used to measure the mothers' mood state, Mother and Baby Scales by Wolke et al (1987). The results are as follows: 1. For the hypothesis test to see the effect of the social support intervention, the mean of the experimental group and the control group was compared by means of t-test and the following results are obtained. Hypothesis I. "The mood state of mothers with social support intervention is more positive than that of the mothers without such intervention." was not statistically supported and thus discarded (t=.799, p=.429). However the mean scores were 49.68 and 51.38 for the experimantal and control group, respectively, indicating more positive mood for the experimental group. Hypothesis II. "The maternal confidence of mothers with social support intervention is higher than that of the mothers without the intervention." was statistically supported (t=3.667, p=.001). 2. The mean score of the mood state was highest before discharge (52.29), meaning most negative, declined to 49.68 shortly after the discharge, again increased a bit to 50.07 at four weeks after the discharge, and stabilized to 49.22 around six weeks after the discharge. On the other hand the mean score of the maternal confidence was continuously increased with time. In view of the above results, it is concluded that the social support intervention with a preprogrammed protocol has the definite positive effect on increasing the maternal confidence and positive effect on improving mother's mood state.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of stress, depression, and spousal and familial support on maternal identity in pregnant women
Hye-Jung Seo, Ju-Eun Song, Youngjin Lee, Jeong-Ah Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 84. CrossRef - Construction a Website for Premature Infant - Based on the Survey of Previous Homepages -
In Hae Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2009; 15(2): 210. CrossRef - Emotional adjustment and concerns of Korean mothers of premature infants
Inhae Lee, Kathleen F. Norr, Kasil Oh
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2005; 42(1): 21. CrossRef
- Effects of stress, depression, and spousal and familial support on maternal identity in pregnant women
- 682 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Relationship of Self Efficacy and Social Support to the Psychosocial Adjustment in People with Epilepsy
- Seong Mi Moon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):694-708. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.694
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The main purpose of this study was to identify the relationship of self efficacy and social support to the psychosocial adjustment in people with epilepsy. Data were collected from October 1 to October 15, 1999 from 101 people with epilepsy who were being treated regularly at one of the university hospitals located in Seoul. The research instruments were a questionnaire to gather demographic and disease-specific data, the Epilepsy Psycho- Social Effects Scale developed by Chaplin et al(1990), the Epilepsy Self Efficacy Scale developed by DiIorio et al(1992a) and translated by Park(1999), the Norbeck Social Support Questionnaire developed by Norbeck et al(1981) and translated by Oh(1985). Data were analyzed using the SPSS program. The results are as follow : 1. Of the 14 psychosocial adjustment areas, 75 of 101 subjects experienced problems in ten or more areas and 28 in all 14 areas. The severity of the psychosocial adjustment problem was moderate or more in six areas. 2. The score for self efficacy was an average of 1103.86 out of a possible 1800, for social support 117.57 for total functional out of a possible 720, and 48.21 for total network out of a possible 264. There were an average of five people on the network. The main network people were parents, brothers and sisters, spouse, friends. 3. Of the 14 psychosocial adjustment areas, six areas correlated with self efficacy and 'problems with taking medication' area had a negative correlation with social support. In conclusion, people with epilepsy have various problems in psychosocial adjustment. Nursing interventions using self efficacy should be developed to improve psychosocial adjustment in people with epilepsy. Also, instruments and interventions for regimen-specific supports which are suitable for epilepsy should be developed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Equation Modeling on Health-Related Quality of Life in Adults with Epilepsy
Jeong Ok Ko, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 624. CrossRef
- Structural Equation Modeling on Health-Related Quality of Life in Adults with Epilepsy
- 650 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study Burden, Social Support and Quality of Life in Mothers of a Child with Nephrotic Syndrome
- Mi Hae Sung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):670-681. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.670
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identity the level of burden, social support and quality of life of the subjects. The subjects of this study were 68 mothers of nephrotic syndrome patients whose children were hospitalized in one pediatric ward of the University Hospital in Seoul. The data was collected using questionnaires, and the period of the data collection was from Nov. 15 to Dec. 31, 1999. The instruments used for this study were the Burden Measurement Instrument developed by Montgomery et. al(1985), social support measurement instrument designed Brandt an Weinert(1978) and Quality of life scale designed by Ro,Yoo JA(1988). The data analysis was done by SPSS, t-test, ANOVA and the Pearson correlation coefficient. The results of were as follows. 1. The level of burden showed a mean score of 54.47, the level of social support, a mean score of 86.00 and the level quality of life, a mean score of 140.20. 2. The level of burden differed according to mother's religion, patient's purpose for admission and perceived patient's condition by mothers. 3. The level of social support and the level of quality of life differed according to perceived patient's condition by mothers. 4. There was a negative correlation between burden and social support(r=-.348, p<.001). Also, burden was negatively related with quality of life(r=-3.97, p<.001). Social support was positively related with quality of life(r=.064, p<.001).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the Quality of Life in Mothers of Children with Precocious Puberty
Suyoung Lee, Gaeun Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(3): 312. CrossRef - Research Trends on Parent-Child Relationships from the Perspective of Nursing
Mi Ran Kim, Young Hee Park, Eun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 249. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the Quality of Life in Mothers of Children with Precocious Puberty
- 690 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Relations between Perceived Burden and Social Support of Stroke Patient's Family Caregiver
- Yeo Shin Hong, Moon Ja Suh, Keum Soon Kim, In Ja Kim, Nam Ok Cho, Hee Jung Choi, Sung Hee Jung, Eun Man Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):595-605. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.595
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to describe the perceived burden of the stroke patient's caregiver and related factors to analyze relationships between perceived burden and social supports. A convenient sample of 225 caregivers who take care for a stroke patient at home participated in this study. Caregiver's perceived burden was measured by the objective and subjective burden scale developed by Montgomery (1985). Related factors of burden were studied in terms of the patient's instrumental activties of daily living, cognitive function, caregiver's demographic variables and caregiver's illness intrusiveness. The results were as follows: (1) The mean of objective burden score was 4.5, and subjective burden score was 3.1. These scores show that caregivers perceive moderate level of burden. (2) Caregivers' objective burden was significantly related to caregivers's illness intrusiveness (r=.62), patient's IADL (r=-.33), and patient's cognitive function (r=-.15). The subjective burden was related to the caregiver's illness intrusiveness (r=.29), the patient's IADL (r=.24), and the caregiver's age(r=.23). (3) The percentage of stroke caregivers who perceived physical support was 49.1%. The percentage of those who perceived emotional support was 61.0%, and those who perceived financial support totaled 37.6%. (4) Caregivers who received any type of social supports perceived lower subjective burden, and caregivers who received physical or psychological support perceived lower objective burden. These results emphasized the necessity of a rehabilitation programs for stroke patients and support program for family caregivers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influencing Factors on Stress in Caregivers of Stroke Patients Being Admitted in Rehabilitation Centers
Nam-Hee Kim, Young-Sook Tae, Yooun-Sook Choi, Joo-Hee Bae
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 188. CrossRef - The effectiveness of home‐based individual tele‐care intervention for stroke caregivers in South Korea
S.S. Kim, E.J. Kim, J.Y. Cheon, S.K. Chung, S. Moon, K.H. Moon
International Nursing Review.2012; 59(3): 369. CrossRef - The Burden of Aged Parents Caring for Adult Children with Disabilities
Min-Hyun Suk, Eunhye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 439. CrossRef - Korean version of the Revised Caregiving Appraisal Scale: a translation and validation study
JuHee Lee, Erika Friedmann, Sandra J. Picot, Sue Ann Thomas, Cho Ja Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2007; 59(4): 407. CrossRef
- Influencing Factors on Stress in Caregivers of Stroke Patients Being Admitted in Rehabilitation Centers
- 725 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Associated with Weight Control Behaviors Among High School females with Normal Body Weight
- Ok Soo Kim, Hee Sang Yoon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):391-401. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.391
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This descriptive study was designed to identify the factors associated with weight control behaviors among 273 high school girls with normal body weight. The objectives of the study were i) to evaluate subjective obesity and satisfaction with the body shape, ii) to describe the weight control behaviors and the motivation, iii) to reveal the relationships between the weight control behaviors and BMI (Body Mass Index), iv) to investigate the relationships between the weight control behaviors and subjective obesity and satisfaction with the body shape, and v) to investigate the relationships between the weight control behaviors and family support. The results showed that 62.6% of the adolescent girls with normal weight perceived that they were fatty and 9.9% thought they were obese. Seventy-five percent of them were not satisfied with their body shape. Eighty percent of the participants reported the main motivation of weight control was to have an attractive appearance. In this study, self-reported weight control methods included dieting (64.8%, skipping or reducing meals), exercise (36.6%), and special dieting (20.1%) such as eating an increased amount of juice or vegetables. It was shown that the subjects who were not satisfied with their body shape and perceived themselves as fatty or obese were active in exercise, diet, and other special diets. Subjects who were on diets and special diets had a higher level of BMI than who were not on diet and special diet. Subjects who exercise had a lower level of BMI than who did not exercised. Family support was significantly related to exercise behavior. The research suggested that there is a increasing responsibility for school nurse to instruct on the body shape and weight control behaviors through health education and consultation. Also, the results suggested that it is important to develop proper diet and exercise methods for adolescents girls to maintain their weight and health.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The associations between body dissatisfaction, body figure, self‐esteem, and depressed mood in adolescents in the United States and Korea: A moderated mediation analysis
Eunsoo Choi, Injae Choi
Journal of Adolescence.2016; 53(1): 249. CrossRef - Convergence Relationship between Self-Esteem and Obesity Stress among Women in Korea
Eun-Hee Park, Hae-Ryoung Park
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(9): 479. CrossRef - A Study on Body Mass Index, Body Attitude and Clothing Attitude of Women in Their Twenties
Juyoung Lee
Fashion business.2014; 18(5): 1. CrossRef - Impact of Parental Socioeconomic Status on Childhood and Adolescent Overweight and Underweight in Korea
Jin-Won Noh, Young-eun Kim, Jumin Park, In-Hwan Oh, Young Dae Kwon
Journal of Epidemiology.2014; 24(3): 221. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-Forgiveness, the Forgiveness of Others, Shame and Guilt on Female Adolescents' Eating Attitude
Hye Sun Lee, Jung Min Kim
Journal of Korean Home Management Association.2014; 32(1): 117. CrossRef - Factors Related to Obesity of Mid-year Korean American Women and Their Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
Sukyong Seo
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(1): 8. CrossRef - Weight control behavior in women college students and factors influencing behavior
Hyun-Young Yang, Young-Soon Byeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(2): 190. CrossRef - A Study of Correlation among Bone Mineral Density, Body Composition and Body Circumference on 20's Women
Sang-Min Lee, Joong-San Wang, Sung-Kyu Park, Hong-Rae Kim, Jin-Hee Ko, Yu-Jung Oh, Hae-Ran Yoon, Ji-Sung Kim
Journal of International Academy of Physical Therapy Research.2012; 3(1): 383. CrossRef - Bone Mineral Density, Body Mass Index, Stress, and Health Promotion Lifestyle of Female College Students
Chunmi Kim, Eun Man Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(3): 333. CrossRef - Analysis of Weight Control in Korean Adolescents Using the Transtheoretical Model
Sun-Mi Chae, Insook Kwon, Chun-Ja Kim, Jaecheol Jang
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2010; 32(4): 511. CrossRef - Psychosocial Correlates of Body Image and Body Change Behaviors Among Malaysian Adolescent Boys and Girls
David Mellor, Lina A. Ricciardelli, Marita P. McCabe, James Yeow, Norul Hidayah bt Mamat, Noor Fizlee bt Mohd Hapidzal
Sex Roles.2010; 63(5-6): 386. CrossRef - Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating Among Early Adolescents From Korea and the US
Jaehee Jung, Gordon B. Forbes, Yoon-jung Lee
Sex Roles.2009; 61(1-2): 42. CrossRef - Analyses on the dieters' characteristics and the factors determining diet practice in college
Mee-Ra Kim, Hyo-Chung Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2008; 17(3): 521. CrossRef - A survey of body shape perception and weight control of adolescent girls in three areas of Korea
Yoon Lee, Hye-Kyoung Shin, Byung-Min Choi, Baik-Lin Eun, Sang-Hee Park, Kee-Hyoung Lee, Chol Shin
Korean Journal of Pediatrics.2008; 51(2): 134. CrossRef - Measures Based on Sociocultural Theory and Feminist Theory as Predictors of Multidimensional Measures of Body Dissatisfaction Among Korean and U.S. College Women
Gordon B. Forbes, Jaehee Jung
Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology.2008; 27(1): 70. CrossRef - Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating among College Women in China, South Korea, and the United States: Contrasting Predictions from Sociocultural and Feminist Theories
Jaehee Jung, Gordon B. Forbes
Psychology of Women Quarterly.2007; 31(4): 381. CrossRef - Multidimensional Assessment of Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating in Korean and US College Women: A Comparative Study
Jaehee Jung, Gordon B. Forbes
Sex Roles.2006; 55(1-2): 39. CrossRef - Body Mass Index, Body Shape Satisfaction, and Weight Control Behaviors among Korean Girls
Oksoo Kim, Kyeha Kim
Psychological Reports.2005; 96(3): 676. CrossRef - Comparisons of Body Mass Index, Perception of Body Weight, Body Shape Satisfaction, and Self-Esteem among Korean Adolescents
Oksoo Kim, Kyeha Kim
Perceptual and Motor Skills.2003; 97(3_suppl): 1339. CrossRef
- The associations between body dissatisfaction, body figure, self‐esteem, and depressed mood in adolescents in the United States and Korea: A moderated mediation analysis
- 663 View
- 0 Download
- 19 Crossref

- A Study on Quality of Life and Related Factors of Ostomates
- Kyung Sook Song, Young Sook Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):817-828. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.817
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This is a descriptive study on quality of life(QOL) and related factors of ostomates to provide a basic data for development of nursing interventions. The subjects were 110 ostomates who were members of the Daegu or Daejon branches of the Korean Ostomy Association. Data collection was performed between March 1st and April 6th, 1998. Measurements of QOL, self-care, family support, self-esteem, and hope were used as the study tools. Data were analyzed with the SAS program by using t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation and stepwise multiple regression. The results are as follows : 1) The score on the QOL scale ranged from 97 to 226 with a mean of 164.53(+/-28.29). 2) The score of QOL on the general and ostomate-related characteristic showed significant differences according to monthly income, monthly participation in ostomate meetings, combined treatments after operation, types of evacuation management, problems of ostomy, help in caring for the ostomy, length of time since ostomate surgery, and presence or absence of readmission after discharge. 3) There were significant positive correlations between quality in life and other factors ; self-esteem(r=0.7107, P<0.001), hope(r=0.6584, P<0.001) family support(r=0.6191, P<0.001), perception of health condition(r=0.6017, P<0.001), and self-care(r=0.2286, P<0.05). 4) The variables that affected the quality of life of the subjects were self-esteem, level of family support, perception of health condition, monthly participation in ostomate meetings, combined treatments after operation, monthly income, level of hope, and age in that order. The variance of quality of life was R2=77.20 percent by calculating the sum of those variables. In conclusion, it is necessary for nursing intervention to promote self-esteem, family support, and hope in the care of ostomates in order to improve QOL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of social support and self‐efficacy on the psychosocial adjustment of Korean ostomy patients
Keum Hee Nam, Heui Yeoung Kim, Jung Ho Kim, Ki‐Noh Kang, Soo Yang Na, Bok Hee Han
International Wound Journal.2019; 16(S1): 13. CrossRef
- Effects of social support and self‐efficacy on the psychosocial adjustment of Korean ostomy patients
- 693 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Identification of Attributes Constituiting Korean Social Support: Based on Middle Aged Women
- Ka Sil Oh, Kyong Ok Oh, Jeong Ah Kim, Sook Ja Lee, Hee Soon Kim, Chu Ja Jeong, Young Joo Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):780-789. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.780
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to identify the attributes constituting Korean social support and to validate the results of the previous study 'Search for the meaning of social support in Korean Society.' The informants were 41 Korean middle-aged women in three cities : Seoul, Dagjun and Daeku. The data were collected through indepth interviews using the interview guide from Jun. 1994 to Jun. 1995. The interview guide was developed in the simulated situations of 'Stroke attack' which expected to be in need of social support. The women were asked to answer what they felt and the appropriated terms representing the situations. Data analysis were conducted by content analysis. consequently, the Koran social support pyramid was modified as follows ; Support is the apex of the pyramid. The four sides of the pyramid are made up of 'Jung'(Bound by ties of affection, regard or shared common experience, Connectedness), Do-oom(both emotional and material help), Mi-dum(Faith or belief in) and Sa-Rang(Love). The base of the pyramid is 'yun'(the basic network of relationships in Korean culture) that connote the meaning of Eunhae(Benevolence), Euimu(duty, responsibility) and Dori(obligation).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Family Values and Expectation for Social Support on Marriage Intention Among Male and Female College Students
Juhee Park
Journal of Korean Home Management Association.2016; 34(4): 21. CrossRef - A Study on Social Support Networks for Each Life-cycle Stage of Adults
Chu-Ja Jeong, Sun-Ock Lee, Jung-Hee Kang, Jeong Ah Kim, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Kyong-Ok Oh, Sook-Ja Lee, Hoa-Yun Jun, Sung Kyung Hong
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2012; 18(3): 436. CrossRef - experience of social support among working mothers: a concept map
A Young Phang, Ki‐Hak Lee
Journal of Employment Counseling.2009; 46(4): 147. CrossRef - Psychometric Evaluation of the Korean Social Support Questionnaire
Kasil Oh, Kyong-Ok Oh, Sook-Ja Lee, Jeong-Ah Kim, Chu-Ja Jeong, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Hoa-Yun Jun, Jung-Hee Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 881. CrossRef
- The Effects of Family Values and Expectation for Social Support on Marriage Intention Among Male and Female College Students
- 786 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Effect of Supportive Nursing Education Program on Burden and Quality of Life in Mothers of Children with Nephrotic Syndrom
- Seung Nam Paik, Mi Hae Sung, Kyoul Ja Cho, Chang Ja Byun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(3):721-731. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.3.721
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of the supportive nursing intervention program on Burden and Quality of Life in Mothers of Children with Nephrotic Sybdrome. The data were collected from a group of 67 mothers of nephrotic syndrome patients(34 in the intervention group, 33 in the control group) from July 1, 1998 to Dec, 30, 1988, Measurements were burden and quality of life from both groups at pre and post intervention. The supportive nursing educational program consists of individual lectures and discussion at the individual level. Listed are the summarized result: 1. The intervention group had a lower level of burden (p<0.05) than the control group intervention. 2. The level of quality of life was not significant during the intervention. According to this study a developed supportive musing intervention program is effective for reduction of the burden. For future research, it is necessary that experiments concerning quality of life in mothers of children with nephrotic syndrome, be conducted.
- 464 View
- 0 Download

- Study on the Effects of the Supportive Nursing Intervention Program for Body Image and Self Esteem of the Child with Cancer
- Sang Eun Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(3):679-687. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.3.679
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The increased potential for the lifespan of a child with cancer is largely due to advance in drug treatment, radiation treatment, and surgical techniques. In this generation cancer has become associated with chronic illness. Therefore supportive nursing intervention for children with cancer is needed to promote normal growth and development. This study was designed to develop and test the supportive nursing intervention program for promoting body image and self-esteem of children with cancer. The supportive nursing intervention program involved emotional, physical, informational, and social support. The subjects were 41 children with cancer(20 in intervention group, 21 in control group) in K city. Measurements were taken concerning body image and self-esteem from both groups during pre and post test. The data were analyzed using Cronvach's alpha, x2-test, paired t-test and t-test. The results were as follows: The intervention group had a more positive body image as measured by the Body Cathexis Scale(t=2.436, p=.020) and a more self esteem as measured by the Cpopersmith self-inventory (t=2.768, p=.009) than the control group at post test. According to this study, the supportive nursing intervention program was effective for promoting the body image and self-esteem of children with cancer. Repeated research is needed to develop a refined supportive nursing intervention program for children with chronic illness.
- 483 View
- 1 Download

- Readjustment and Social Support of the Post Hospitalized Stroke Patients
- Moonja Suh, Samuel Noh, Gerald M Devins, Keumsoon Kim, Kookgi Kim, Jiyoung Song, Namok Cho, Ywoshin Hong, Inja Kim, Heejung Choi, Sunghee Jung, Eunman Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(3):639-655. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.3.639
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF An explanatory design was employed to identify the relationship of physical, emotional & social readjustment and social support of post hospitalized stroke patients and their caregiver. A convenient sample of 254 patients who given follow-up care at the outpatient department after discharge and 225 caregivers were recruited. Mental Status Questionnaire(MSQ), Social Support Inventory Stroke Survivors(SSISS), Illness intrusiveness(II), Instument Activity of Daily Living(IADL), Center of Epidnmilogic Studies-Depression(CES-D), social activity and caregiver burden were used for measurement in this study. Results showed patient's physical level measured by IADL and psychological level measured by depression were high. But social activity was low. Cognitive function, depression & social activity were not significantly different by the posthospitalized period, but IADL was. The source of professional support was mostly the physician at the outpatient department. The family support was found significantly related to patient's depression & social activity and caregiver's subjective related to patient's IADL & depression. ILLness intrusiveness as a mediating variable was a significantly predicting power on patient's IADL & depression. The path analysis was used to identify the variables to predict the physical, emotional, and social status of patients, the physical, emotional, and cognitive function, illness intursiveness and professional support significantly predicted the level of siveness and family support significantly predicted the level of depression ; and patient's age and family support significantly predicted the level of social activity of posthospitalized stroke patients. Based upon these results, the rehabilitation programs to reduce the illness intrusiveness and improve cognitive function were recommended for the readjustment of the stroke patients. This model of the readjustment of the posthospitalized stroke patients is recommended as the framework for care of the stroke patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Concept Analysis of Illness Intrusiveness in Chronic Disease: Application of the Hybrid Model Method
Youngjoo Do, Minjeong Seo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5900. CrossRef - Proposal for Health Insurance Policy When Telehealth Is Legalized: Focused on Telemedicine Platform, Remote Monitoring Device, Digital Therapeutics, and Homecare Medical Device
Kuyeong Han, Jiyoon Yoon, Eunkyung Jun
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2022; 2(1): 36. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth in Survivors of Breast Cancer
Jin-Hee Park, Yong-Sik Jung, Youngmi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 454. CrossRef - Using the Illness Intrusiveness Ratings Scale to understand health-related quality of life in chronic disease
Gerald M. Devins
Journal of Psychosomatic Research.2010; 68(6): 591. CrossRef - Factor Structure of the Korean Version of Illness Intrusiveness Rating Scale: Cross-cultural Implications
Daeho Kim, Kwang-iel Kim, Haewon Lee, Joonho Choi, Yong-Chon Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2005; 20(2): 302. CrossRef
- A Concept Analysis of Illness Intrusiveness in Chronic Disease: Application of the Hybrid Model Method
- 912 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Comparision of Group and Individual Social Support on Burden and Family Functioning in Families with Asthmatic Children
- Hoa Yun Jun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):418-428. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.418
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The main purpose of this study was to identify the effects of group social support and individual social support on the reduction of burden and improvement in family functioning of families with asthmatic children. The design of this study was a randomized pre-posttest quasi-experimental design to compare the two experimental groups. The theoretical framework for this study was derived from the study of burden in family caregivers by Suh and Oh(1993) based on the main effect model of social support theories. The data were collected from February 12, 1998 to May 29, 1998 at the pediatric out patient department of a university hospital located in Suwon city. The sample consisted of 39 family members who were identified as families with asthmatic children, Eighteen subjects were randomly assigned to the group social support group and 21 were assigned to the individual social support group. Group and individual social support members were seen for 60 to 90 minutes, four times over one to three weeks. The instruments used in this study were the Burden Scale developed by Suh and Oh(1993), the Visual Analogue Scale, and the Family Adaptability Cohesion Evaluation Scale(FACES-III) developed by Olson, Portner, and Lavee(1985). The collected data were analyzed using Mann-Whitney test, x2-test, Wilcoxon sign rank test, t-test, ANOVA(Scheff), pearson correlation coefficient, multiple regression, and social support process and content analysis. The results are as follow ; 1. There was no significant difference before the experimental treatment among the subjects in the group social support group and individual social support group for general characteristics, burden, or family functioning. 2. Hypothesis 1 ; "There will be a greater reduction on the burden score of the group social support group compared to the individual social support group" was not statistically significant(U=174.5, p=.683). The burden scores showed a significant decrease after participation in social support as compared to before participation for both groups. However there was a tendency for more reduction in the burden scores for the group social support than for individual social support. 3. Hypothesis 2 ; "There will be a greater improvement in the family functioning scores for the group social support group compared to the individual social support group" was not statistically significant(U=153.0, p=.309). There was a tendency toward improvement in the family functioning scores of the group social support as compared to that of the individual social support. 4. According to the length of the treatment period, families with asthmatic children displayed affirmative responses, and the families set up a self-help group of mothers with asthmatic children n order to share their experiences, to get information and to solve their problems. In conclusion, it was found that group social support was the more effective nursing intervention for reducing burden and for improving family functioning of families with asthmatic children.
- 381 View
- 0 Download

- A Prediction Model for health Promoting Behavior of The Korean Elderly
- Young Joo Park, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Sung Ok Chang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):281-292. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.281
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to construct a model that predicts the health promoting behavior of the Korean elderly. Data were collected by self-reported questionnaires from 254 Korean elderly in seoul, from June 1 to July 15, 1998. Data were analyzed by descriptive statistics and correlational analysis using pc-SAS program. The Linear Structural Modeling(LISREL) 8.0 program was used to find the best fit model which predicts causal relationships of variables. The overall fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate[X2=249.83(df=83, p=.00), RMR=.07, GFI=.90, NNFI=.92, NFI=.91]. The predictable variables of health promoting behavior of the Korean elderly were social activity, social support, self-integrity and helplessness except the perceived health status. These variables explained 17.1% of health promoting behavior of the Korean elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Association Between Depression and Death Anxiety Among Older Adults: Moderating Effect of Ego-Integrity
Jin-Hee Woo, Sung-Man Bae
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2025; 90(3): 1025. CrossRef - A study of the impact of dental hygienist concern on oral health care of the elderly
Jung Won Yun, Yu Hee Lee, Kyeung Ae Jang, Jung Hwa Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2019; 43(4): 217. CrossRef - Effect of social support and self-esteem on the oral health behaviors of Korean elderly people
Yuna Shin, Jinsil Hong, Youngsam Kim, Kee-Wan Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2017; 41(4): 282. CrossRef - The Effect of the Traditional Living Arrangement, Anpakkori, on Depressive Symptoms in Elderly People Residing on Jeju Island
Eun-Hui Oh, Moon-Doo Kim, Seong-Chul Hong
Psychiatry Investigation.2009; 6(3): 131. CrossRef - Barriers to Health Behaviors in Male and Female Elderly People in Korea
Young Eun, Mee Soon Song, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 332. CrossRef
- The Association Between Depression and Death Anxiety Among Older Adults: Moderating Effect of Ego-Integrity
- 755 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- The Burden and Social Support of Mothers of Nephrotic Syndrome Patients
- Mi Hae Sung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(1):84-96. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.1.84
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to identity the degree of burden and social support perceived by mothers of nephrotic syndrome patients. Also, relations between burden and social support were investigated to provide basis data for their family health and nursing intervention. The study subjects were mothers of nephrotic syndrome patients whose children were hospitalized in 2 Pediatric wards of University Hospital in Seoul and 1 in Pusan from Jun. 1, 1998 to Jun. 30, 1998. Burden measurement instrument for this study was designed by the researcher and its basis in one developed by Montgomery et al.(1985) and the reliability was .78. Also. P.R.Q. Part I II, by Brandt and Weinert(1981) was used as social support measurement instrument and the reliability .71. The data analysis was done by SPSS, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation. The result were as follows. 1. Burden felt by mothers shows an average value of 60.82 (Maximum 86, Standard deviation 1.244). 2. Of the mother characteristics, the score of burden was high in case of no religion and low income. Of the patient characteristics, the score burden ranked as high MCNS, doing oral therapy, injection therapy at the same time and negative perceived patients condition. 3. The mean score of support was 77.54(Maximum 96, Standard deviation 1.096). 4. The main supporters were husband(the highest), brother, sister, health speciality and the subject expressed the highest satisfaction toward supporters in chronic disease. 5. Of the patient characteristics, the higher age group and the elder group showed high support. Also, positive perceived patients condition, high support. 6. The relationship between burden and social support is not significant. In conclusion to the above study, the researcher suggests. 1. The Qualitative research to investigate influential factors on burden of family of nephrotic syndrome patients in needed.
- 367 View
- 0 Download

- Determinants of Smoking-Cessation Behaviors in Female University Students
- Hae Won Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(1):48-60. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.1.48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to determine the factors influencing smoking-cessation behavior in female university students. a total of 534 students participated in this cross sectional study by answering a questionnaire. The data collection was done between September 1 and October 31, 1997. The measurement tools used in this study were the self help change process scale(Cronbach's alpha=.9930 : developed by Oh&Kim, 1996) for smoking-cessation behaviors, the self efficacy scale(Cronbach's alpha=.8250 : developed by Sherer et al, 1982), the sex role acceptance scale(KR-20=.7757 : developed by Kim, 1991) and the social support scale(Cronbach's alpha=.9172 : developed by Park, 1985). The summarized results are follows : 1. The mean scores for smoking-cessation behaviors in smokers(N=150) was 91.72 that was considered a middle score compared to the total possible score of measurement tool(150.0). The mean score for smoking-cessation behaviors by smoking-cessation step showed significant different between the groups(F=11.71, p= .000). 2. The group with no experience in smoking(N=332) showed a high general self efficacy score(t=5.24, p= .000), and more openness to sex role acceptance(t=-2.15, p= .032) compared to the group with smoking experience(N=202). 3. General self efficacy, sex role acceptance, and social support were not different significantly between the groups according to the steps in smoking-cessation. 4. Significant factors influencing smoking-cessation behavior(total, sub concepts) were religion, sex role acceptance, social support, smoking duration, smoking attitude, time of smoking onset, amount of smoking, drinking, and perception of health status. 5. Smoking-cessation behaviors which explained 11% of the variance were smoking attitude, and smoking duration. In conclusion, this study identified factors influencing smoking-cessation behavior. Thereby it will help in the development of smoking-cessation ration other determinants of smoking cessation behaviors, evaluation of intervention efficiency, and comparative study by gender characteristics are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrative Smoking Cessation Stage Model for Chinese Students Studying in Korea
Hyunsoo Oh, Hyesun Jeong, Whasook Seo
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(4): 182. CrossRef
- Integrative Smoking Cessation Stage Model for Chinese Students Studying in Korea
- 678 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Structural model for Quality of Life in Women Having Hysterectomies
- Sook Nam Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(1):161-173. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.1.161
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to develope and test the structural model for quality of life in women having hysterectomies. A hypothetical model was constructed on the basis of previous studies and a review of literature. The conceptual framework was built around eight constructs. Exogenous variables included in this model were marital intimacy, importance of uterus, professional support, positive coping behavior and pre-operative symptoms. Endogenous variables were spouse's support sense of loss and quality of life. Empirical data for testing the hypothetical model was collected using a self-report questionnaire from 203 women having hysterectomies at the outpatient clinics of four general hospitals and a mail survey in Pusan City. The Data was collected from December, 1997 to January, 1998. Reliability of the eight instruments was tested with Cronbach's alpha which ranged from 0.639-0.915. For the data analysis, SPSS 7.5 WIN Program and LISREL 8.12 WIN Program were used for descriptive statistics and covariance structural analysis. The results of covariance structure analysis were as follows : 1. Hypothetical model showed a good fit with the empirical data. [x2=6.93(df=5, P=.23), GFI=.99, AGFI=.94, RMSR=.019, NNFI=.97, NFI=.98, CN=440, standardized residuals(-2.14-2.10)] 2. For the parsimony of model, a modified model was constructed by deleting 3 paths and adding 1 path according to the criteria of statistical significance and meaning. 3. the modified model also showed a good fit with the data. [x2=5.26(df=7, P=.63), GFI=.99, AGFI=.97, RMSR=.014, NNFI=1.02, NFI=.99, CN=710, standardized residuals(-1.46-1.70)] Results of the testing of the hypothesis were as follows : 1. Marital intimacy(gamma11=.78, t=14.37) and professional support(gamma13=.12, t=2.12) had a significant direct effect on the spouse's support. 2. Pre-operative symptoms(gamma25=.32, t=3.12) , importance of uterus(gamma22=.20, t=2.61) and spouse's support(beta21=-.19, t=-2.43) had a significant direct effect on the sense of loss. 3. Sense of loss(beta32=-.66, t=-9.83) had a direct effect on the quality of life. Marital intimacy had a direct(gamma31=.19, t=3.33), indirect(gamma31=.14, t=2.52) and total effect(gamma31=.25, t=4.41) on the quality of life. Professional support had a direct effect(gamma33=.11, t=2.07) and total effect(gamma33=.13, t=2.31) on the quality of life. The direct effect of pre-operative symptoms(gamma35=-.36, t=-4.02) and positive coping behavior(gamma34=.15, t=2.06) had the insignificant effect on the quality of life while, due to the indirect effect these variables had overall significant effect on the quality of life. The results of this study showed that the sense of loss had the most significant direct effect on the quality of life. Marital intimacy, pre-operative symptoms and spouse's support had a significant direct effect on this sense of loss. These four variables, the sense of loss, marital intimacy, pre-operative symptoms and spouse's support, were identified as relatively important variables. The results of this study suggested that there is needed to determine if nursing intervention would alleviate this sense of loss and promote a greater quality of life in women who have had hysterectomies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a sexual health enhancement program for women with breast cancer: A quasi-experimental study
Hye Sook Kim, Chaewon Yun
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 76: 102852. CrossRef - Factors influencing happiness and depression in high-risk pregnant women: a cross-sectional study using the ecological systems approach
Hyunkyung Choi
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 203. CrossRef - Pathway Analysis to Identify Factors Affecting Sexual Function in Postmenopausal Women with Hypertension Not Receiving Hormone Replacement Therapy
No Eul Kang, Eun Ko, Hyuk Joon Kim, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 469. CrossRef - Factors influencing quality of life in post-menopausal women
Hyunsook Shin, Eunjoo Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(4): 336. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Quality of Life in Patients With Uterine Cancer
So Yeun Jun, Il Sun Ko
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(2): 109. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Quality of Life in Patients with Radical Prostatectomy
Hyo Jung Park, Yoonju Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(2): 190. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Happiness among Pregnant Women in the Ecological Systems Theory
Gyuree Lee, Hyunkyung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(1): 11. CrossRef - Impact of Uncertainty on the Quality of Life of Young Breast Cancer Patients: Focusing on Mediating Effect of Marital Intimacy
Yeong Kyong Oh, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(1): 50. CrossRef - Impact of Sexual Attitude and Marital Intimacy on Sexual Satisfaction in Pregnant Couples: An Application of the Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Hee Eun Kim, Jung Hee Yeo
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(3): 201. CrossRef - Effects of Irrational Parenthood Cognition, Post Traumatic Stress Disorder and Spousal Support on Quality of Life of Infertile Women
So Ra Yang, Jung Hee Yeo
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(2): 145. CrossRef - Effect of Sexual Function Improvement Program for Breast Cancer Survivors on Sexual Distress, Sexual Satisfaction and Marital Intimacy
Duck Hee Moon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(1): 30. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Sexual Function in Postmenopausal Married Women
Hye Young Kim, Eun Ko
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(4): 287. CrossRef - Comparisons of Depression, Marital Intimacy, Sexual Function and Quality of Life in Sexual Active or Inactive Groups of Post-menopausal Married Women*
Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(3): 258. CrossRef - A Predictive Model for Factors Influencing Sexual Satisfaction of Women with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyoungnam Kim, Hyoung Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2013; 20(1): 6. CrossRef - A Study on the Predictive Factors of Sexual Function in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Jeong Sook Park, Soon Yang Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(2): 156. CrossRef - The Effect of a Sexual Life Reframing Program on Marital Intimacy, Body Image, and Sexual Function among Breast Cancer Survivors
Eun-Young Jun, Sue Kim, Soon-Bok Chang, Kasil Oh, Hee Sun Kang, Sung Soo Kang
Cancer Nursing.2011; 34(2): 142. CrossRef - Predictors of Sexual Desire, Arousal, Lubrication, Orgasm, Satisfaction, and Pain in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Nami Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 24. CrossRef - Model Construction of Sexual Satisfaction in Patients with a Colostomy
Seungmi Park, Keum-Soon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 539. CrossRef - Psychometric Evaluation of the Korean Social Support Questionnaire
Kasil Oh, Kyong-Ok Oh, Sook-Ja Lee, Jeong-Ah Kim, Chu-Ja Jeong, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Hoa-Yun Jun, Jung-Hee Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 881. CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model on Sexual Function in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Nami Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 639. CrossRef - Change of Cognitive Function and Associated Factors among the Rural Elderly: A 5-Year Follow-up Study
Sang-Kyu Kim, Pock-Soo Kang, Tae-Yoon Hwang, Joon Sakong, Kyeong-Soo Lee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2007; 40(2): 162. CrossRef
- Effects of a sexual health enhancement program for women with breast cancer: A quasi-experimental study
- 785 View
- 27 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Pain, Family Support and Quality of Lefe in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hyun Ja Lim, Young Im Moon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):329-343. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to identify the relationship between perceived pain, family support and quality of life in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. The purpose of this study was to contribute to the theoretical understanding of the relationship of these three variables and eventually to more effective adaptation of patients to their situation. The subjects for this study were the 68 patients who had been diagnosed with ankylsing spondylitis and registered as out-patients in the Rheumatism Center of one university hospital in Seoul. The data were collected during the period from October 10, 1997 to December 20, 1997. Pain was measured using the perceived pain scale(VAS: Visual Analog Scale)developed by Calin(1993), family support using the scale developed by Kang Hyun Suk(1985) and Quality of Life using the scale developed by Ro Yoo Ja(1988). The data were analyzed by descriptive statistics, Frequencies, Pearson correlation, using the SPSS program. The results of this can be summarized as followings. 1. The mean perceived pain score was 5.13 with a range of 2 to 10. 2. The mean perceived family support score was 41.08+/-5.34 with a range of 20 to 50. 3. The mean perceived quality of life score was 134.07+/-19.82 with a range of 83 to 176. 4. Significant statistical difference was found between family support and quality of life(r=.331, p<0.001). A significant negative statistical difference was found between the family support and quality of life and pain(r=-.250, p<0.05, r=-.460, p<0.001). 5. General characteristics related to pain were exercise(t=4.72, p<0.0006). 6. General characteristics related to family support were age(F=2.65, p<0.0246), educational level(F=2.84, p<0.0282) and exercise(t=3.24, p<0.0452). 7. General characteristics related to quality of life were educational level(F=3.03, p<0.0392) and exercise(t=3.12, p<0.0465). It was found that the higher the level perceived pain, the lower the degree of perceived family support and the quality of life. It was also fund that the higher the degree of perceived family support the higher the degree of perceived quality of life. Accordingly, the conclusions from this study are that reduction of pain is achieved through the family support. Therefore, it is proposed that family support is an appropriate nursing intervention to improve the quality of life of patients with anklosing spondylitis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Disease-related Knowledge, Depression, and Family Support on Health Behaviors in Older Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Ji Mi Mun, So Young Shin
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2019; 21(3): 155. CrossRef - Correlation between FamilyAPGARscores and health‐related quality of life of Filipino elderly patients with knee osteoarthritis
Anne T. C. Lim, James Manching, Ester G. Penserga
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2012; 15(4): 407. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in People with Chronic Illness in Korea
KuemSun Han, PyoungSook Lee, SookJa Lee, EunSook Park
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2003; 35(2): 139. CrossRef
- Influence of Disease-related Knowledge, Depression, and Family Support on Health Behaviors in Older Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
- 641 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effect of Social Support on Compliance with Sick Role Behavior in Hypertensive Clients and Duration of the Effect for up to 6 months
- Oh Jang Park, Mi Soon Hong, Kum Sung Jan, Ji Young Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):159-170. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.159
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done using a Quasi-experimental research design to determine the effects of social support on compliance with sick role behavior in hypertensive patients and to know if the effect of the social support on compliance lasted for at least 6 months. The subjects consisted of 81 hypertensive patients who were registered in the Cardio-Vascular OPD at Chonnam National University Hospital. They were divided by random sampling into 42 people for the experimental group and 39 for the control group. Data were gathered from June 3, 1996 to June 10, 1997 through individual interviews using a structured questionnaire. The results of the study were summarized as follows : 1. Compliance with sick role behaviors in hypertensive clients was significantly increased in the experimental group who received social support from the nurse as compared to the control group who did not receive social support(t=15.99, p<.001). 2. The effect of social support on compliance with sick role behaviors in hypertensive clients lasted for 6 months(t=7.99, p<.001). 3. Four of six people stopped smoking in experimental group after the intervention of social support, but none of the five in control group were able to stop smoking. Fisher's Exact test showed a significant difference between the experimental and control group(x2=4.385, p<.05). Mantel Haenszel test showed that the effect of social support on stopping smoking in the experimental group lasted for six months because there were no significant differences between one month after the social support and six months after, in the number of subjects who stopped smoking(x2=1.154, p>.05). Finally, social support was effective on compliance with sick role behaviors and stopping smoking in the hypertensive clients, and the effect of social support on compliance lasted for 6 months.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Depression on the Life Satisfaction of the Elderly with Hypertension
Hun-Hee Lee, Jung-Seo Lee, Gyeong-Nam Lee
Journal of the Korea Society of Computer and Information.2016; 21(8): 117. CrossRef - Effects of Community-based Case Management Program for Clients with Hypertension
Ae-Young So, Yun-Mi Kim, Eun-Young Kim, Chang-Yup Kim, Cheol-Hwan Kim, Hee-Gerl Kim, Eun-Young Shin, Weon-Seob Yoo, Ggod-Me Yi, Kyung-Ja June
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 822. CrossRef
- The Influence of Depression on the Life Satisfaction of the Elderly with Hypertension
- 676 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Effects of a Support Group Intervention on the Burden of Primary Family Caregivers of Stroke Patients
- Eun Kwang Yoo, Sanghee Jeon, Jeong Eun Yang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):693-702. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.693
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to develop and evaluate the effects of a support group intervention on the burden of primary family caregivers of stroke patients. METHOD: A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The subjects were 36 primary family caregivers of stroke patients [experimental(N=18) and control(N=18) groups] in a neurosurgery ward of a university hospital. The experimental group members participated in six sessions of a support group intervention for two weeks and the degree of their caregiving burden was evaluated. Data was analyzed by Chi-square tests, t-tests, and paired t-tests using SPSS 10.0. RESULT: The experimental group had a significantly lower total burden score (t=2.061, p= .047)and sub-scales of emotional(t=-3.319, p= .002), time-dependent(t=-2.045, p= .049) and developmental(t=-2.656, p= .012) burden scores than the control group, while no significant differences were found in physical, social or financial burden scores between the two groups. Within the experimental group, there was a significant decrease in physical(t=2.507, p= .023), emotional(t=4.754, p= .000), social(t=2.932, p= .009), time- dependent(t=5.015, p= .000) and developmental(t=7.541, p= .000) burden scores but not the financial burden score. CONCLUSION: The results suggest that a support group intervention can be utilized as an effective nursing program to reduce the burden of primary family caregivers of stroke patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison Between Comprehensive Nursing Care Ward and Private Care Ward on Functional Recovery in Stroke Patients
Yang Rok Hur, Woo Sup Song, Kyung Min Kim, Ki Hun Hwang
Brain & Neurorehabilitation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Development and Evaluation of Navigation Program for Caregivers of Stroke Patients Admitted to a Rehabilitation Centers: A Pilot Study
Nam Hee Kim, Young Sook Tae
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(3): 277. CrossRef - Effects of a Footbath Program on Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure, Body Temperature and Fatigue in Stroke Patients
Yu Lim Son, Myung Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2016; 18(1): 51. CrossRef - The Effect of Post-Stroke Depression on Rehabilitation Outcome and the Impact of Caregiver Type as a Factor of Post-Stroke Depression
Dong-Heun Ahn, Yung-Jin Lee, Ji-Hun Jeong, Yong-Rok Kim, Jong-Bum Park
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2015; 39(1): 74. CrossRef - Effects of a Telephone-based Support Group Program for Family Caregivers Providing Long-term Care for Elders
Eun-Young Kim, Jeong Ok Kwon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2014; 16(1): 38. CrossRef
- Comparison Between Comprehensive Nursing Care Ward and Private Care Ward on Functional Recovery in Stroke Patients
- 811 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Predictors of Participation in Support Groups among Women with Breast Cancer
- Jina Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):635-644. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.635
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study examined what characteristics and variables predict participation in support groups for women with breast cancer.
Method 282 women with breast cancer from 4 hospitals located in Busan were included in the study. Data was measured on each participant from September 2006 to February 2007. Data was collected using structured researcheradministered sheets and analyzed by descriptive statistics, t-test, chi-square test and logistic regression analysis.
Results The clients reported medium levels of illness perception, anxiety and depression, stress with coping, social support and self-efficacy. 48.9% of women with breast cancer participated in support groups. Significant influencing factors on the participation in support groups were 'operation time(+)', 'illness perception(+)', 'social support(-)', and 'self-efficacy(+)' Those variables explained 73.4%.
Conclusion It is necessary to develop a strategy or promoting program for promotion of illness perception and self-efficacy of women with breast cancer. Thus, it is essential to provide participation to a support group to a women with breast cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of stress appraisal on the quality of life of adult patients with multiple myeloma and their primary family caregivers in Korea
In Seo La, Eun Kyoung Yun
Psycho-Oncology.2017; 26(10): 1640. CrossRef - Effect of empowerment on the quality of life of the survivors of breast cancer: The moderating effect of self‐help group participation
Sunhwa Shin, Hyojung Park
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2017; 14(4): 311. CrossRef - The Experience of Self-help Group Activities among Women with Breast Cancer in Korea
Myungsun Yi, Young Mi Ryu, Eunkyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(4): 466. CrossRef - Factors influencing health-promoting behaviors in Korean breast cancer survivors
Myungsun Yi, Jeongeun Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2013; 17(2): 138. CrossRef
- Effects of stress appraisal on the quality of life of adult patients with multiple myeloma and their primary family caregivers in Korea
- 783 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Self-image and Social Support of Adolescents among the Korean-Chinese
- Wen Xiang Cui, Sheng Ji Jin, Kasil Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(7):1343-1352. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.7.1343
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to identify the degree of self-image and social support among Korean-Chinese adolescents and investigate the relationship between these variables.
Method A total of 621 Korean-Chinese adolescents in five middle schools in YanBian, China were recruited from March 1st to the 9th, 2005. Data was analysed using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation coefficient, t-test, and ANOVA with the SPSS 11.5 program.
Result In Korean-Chinese adolescents, the total self-image score was statistically different for age, parents' education status, parents' job and living with parents. In the 12 subscales, scoresof emotional tone, impulse control, sexuality, social functioning, vocational attitudes and self-reliance had significant differences between groups regarding gender. The total self-image was in the average range. However, areas of mental health and family function were lower than average and the scale of idealism washigher than average. The adolescents perceived parent's support was higher then friend's support. There was a positive correlation between self-image and social support.
Conclusion The findings suggest there is a need to examine self-image and social support of Korean- Chinese adolescents according to their parents' marital status and a need to develop a program to help these broken family's adolescents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Moderating Effect of Social Support on the Relationship Between Acculturation Stress and University Adjustment: Focused on Foreign Students Majoring Tourism at Universities in Korea
Sun Y. Yoon
Journal of Service Research and Studies.2015; 5(2): 177. CrossRef - Social Support and Acculturative Stress in Migrant Workers
Soon-Hee Lee, Young-Joo Lee, Sook-Young Kim, Shin-Jeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 899. CrossRef
- Moderating Effect of Social Support on the Relationship Between Acculturation Stress and University Adjustment: Focused on Foreign Students Majoring Tourism at Universities in Korea
- 772 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Family Resiliency Facto for the Adaptation of Family who have a Congenital Heart Disease
- Young Ran Tak, E Hwa Yun, Ji Yeon An, Sang Hwa Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(7):1298-1306. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.7.1298
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the relationships of family strain, perceived social support, family hardiness, and family adaptation and identify the family resiliency factors for the adaptation of families who have a child with congenital heart disease.
Method The sample consisted of 90 families who had a child diagnosed with congenital heart disease and completed surgical treatment. Data was collected from parents using a questionnaire.
Results Results from path analyses revealed that family strain had a direct effect on both perceived social support and family hardiness, and an indirect effect on family adaptation. Also, the findings revealed that perceived social support had a direct effect on both family hardiness and family adaptation, and family hardiness had a direct effect on family adaptation. Thus, these results indicated that perceived social support and family hardiness had a mediating effect on family strain.
Conclusion Findings provide the evidence for the theoretical and empirical significance of perceived social support and family hardiness as family resiliency factors for family adaptation. Clinical implications of these findings might be discussed in terms of family-centered nursing interventions for the families who have a child with congenital heart disease based on an understanding of family resiliency for adaptation.
- 667 View
- 7 Download

- Structural Equation Model for the Health Behaviors of University Students in Korea
- Sung Eun Yi, Ka Sil Oh, Young Joo Park, Jeong Ah Kim, Hee Soon Kim, Kyoung Ok Oh, Sook Ja Lee, Hoa Yun Jun, Choo Ja Chung, Sang Soon Choi, Hyun Chul Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(6):903-912. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.6.903
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose A structural equation model was analysed to explore the determinants of health behaviors of university students in Korea.
Metnod Nine hundred sixty nine university students were selected by random cluster sampling from five universities located in the central area of Korea.
Data Collection The data was collected by questionnaires about demographic characteristics, stressful life events, perceived social support, perceived health status and health behaviors.
RESULTS
1. Gender showed indirect effect on health behaviors. 2. Living together with(out) family had a direct effecton health behaviors: students living with family showed more positive health behaviors. 3. Stressful life events had an indirect effect on health behaviors via perceived health status;a higher score of stressful life events was the predictor for negative health behaviors. 4. A higher score of perceived health status predicted positive health behaviors.Recommendation Each university should be encouraged to develop a health behavior control program and health promotion program for their own university students. It would be more effective to develop health programs separately according to the demographic or social characteristics of the students. It is also necessary for the Ministry of Education to reform the School Health Act and school health policy to strengthen a health promotion program for university students. In conclusion, following studies should identify and promote the validity and reliability of perceived health status and health behaviors measurements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Obesity Stress, Weight Bias, and Heath Care on BMI in Soldiers of Non-combat Area
Kyeng Jin Kim, Yeon Kyung Na
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 199. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of the Personal Competence of Health Care (PCHC) Scale
Kyung-Sook Lee, Jung-Sook Choi, Ae-Young So, Eun-Hee Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(2): 197. CrossRef - The Relationship between Optimistic Bias about Health Crisis and Health Behavior
Su Ho Park, Sul Hee Lee, Eun Mi Ham
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 403. CrossRef
- The Effects of Obesity Stress, Weight Bias, and Heath Care on BMI in Soldiers of Non-combat Area
- 938 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Model Development of an Elderly Health Promotion Center: The Effect of a Social Support Program at a Community Health Center
- Oh Jang Park, Hyang Sook So
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(5):781-790. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.5.781
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a model of an elderly health promotion center after witnessing the effect of a social support program on dependent variables in older adults at a local community health center.
Method The subjects were 60 female adults over 65 years dwelling in a rural area, and they were divided into experimental and control groups each with 30 people. A social support program was implemented 6 hours a day, 3 times a week, for 4 months in the experimental group. Included was health assessment, health education, counseling, consultation, exercise, physical & occupational therapy, primary care, recreation, lunch & transfer service. Data was collected from May 1stto September 14th, 2002 by questionnaires, and analyzed by x2-test, t-test, Pearson's correlation coefficient and stepwise multiple regression using SAS.
Result The social support program in the elderly was very effective on all dependent variables of physical health (t= 4.68, p= .001), health knowledge (t= 3.60, p= .001), life satisfaction (t= 8.65, p= .001), and health promoting behaviors (t= 5.23, p= .001).
Conclusion The Social Support Program at a Community Health Center was effective on health promoting behaviors in the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Different Types of Perceived Social Support on Changes in Subjective Health among Older Adults: A Focus on Gender Differences
Miok Ha, Seungja Kang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 323. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Health Promotion Program for the Elderly
Mee Young Im, Young-Hee Mun
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(2): 384. CrossRef - Factors Related to Self-perception of Diet Quality among South Korean Adults
Su-Yeon Kye, E-Hwa Yun, Kee-Ho Park
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2012; 13(4): 1495. CrossRef
- Effects of Different Types of Perceived Social Support on Changes in Subjective Health among Older Adults: A Focus on Gender Differences
- 732 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Relationship of Stress, Social Support and Depression in the Elderly
- Pyoung Sook Lee, Yong Mi Lee, Ji Young Lim, Ra IL Hwang, Eun Young Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(3):477-484. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.3.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to identify the relationship between stress, social support and depression in the elderly.
Method The subjects were 283 elderly adults over 60 in Seoul. Data was collected by questionnaire surveys using convenience sampling. The instruments used in this study are the ELSI developed by Aldwin(1990), the Interpersonal Support Evaluation List developed by Cohen & Hoberman (1983), and the Geriatric Depression Scale by Yesavage & Brink(1982). Data was analyzed by the SAS program, using descriptive statistics, Pearson Correlation Coefficient, t-test, ANOVA and progressed Multiple Regression.
Result The relationship between stress and depression had a positive correlation (r= 0.33), but the relationship between stress and social support had no significant correlations. The relationship between social support and depression had a negative correlation (r= -0.38). The most powerful predictor of depression was the economic status and then a combination of stress, and social support account for 39% of the variance in depression in the elderly.
Conclusion These results suggested that stress and social support deficits can be potential risk factors in old age depression. Therefore, these findings give useful information for constructing an intervention program focused on depression in the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
ИНСОМНИЯ КАК ТРАНСДИАГНОСТИЧЕСКИЙ ФЕНОМЕН У ПОЖИЛЫХ С ДЕПРЕССИВНЫМИ И ТРЕВОЖНЫМИ РАССТРОЙСТВАМИ
Е.Б. Мизинова, Т.А. Караваева, А.В. Васильева, Д.С. Радионов
Успехи геронтологии.2024; 37(5): 546. CrossRef - Social Support, Activities of Daily Living, and Depression among Older Japanese and Koreans Immigrants in the U.S
Bumjung Kim, Hyeyoun Jun, Jisun Lee, Yun Min Kim
Social Work in Public Health.2020; 35(4): 163. CrossRef - Depressive Symptoms and Sociodemographic Risk Factors among Chronic Disease Inpatients at University Medical Centers
Gyong-Ae Choi, Hyun-Jung Choi, So-Young Park
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(1): 32. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression in Middle Aged Women: Focused on Quality of life on Menopause
Jung Nam Sohn
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(2): 148. CrossRef - Effects of Indirect Experience of Forest Healing Factors on Stress Reduction, Self-Esteem and Social Connectedness Improvements in the Elderly Participating in Horticultural Activities Program
Gue Hong Park, Chang Seob Shin, Yang Soon Hahn
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2018; 21(5): 411. CrossRef - Differences of Characteristics of Life and Psycho-social Factors in Elderly Women Participating in Leisure Activity
Kyung-Hee CHUN, Euna PARK
Journal of Fisheries and Marine Sciences Education.2016; 28(2): 428. CrossRef - The Relationships between Stress and ADL in Elderly Living Alone
Eun-Joo Seo, Nam-Hyun Cha
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(7): 251. CrossRef - Examination of the Adlerian constructs of activity and social interest with depression among recent Korean retirees: Meaning in life as a mediator
Eunha Kim, Hae-Jeong Park, Ingrid Hogge
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2015; 61(3): 378. CrossRef - The Effect of the Elderly's Stress on Depression -Focused on Mediating Effect of Resilience and Moderating Effect of Social Activity-
Young Ja Jeon
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2015; 24(2): 219. CrossRef - Factors Affecting a Health Promoting Lifestyle in Middle-Aged Women
Yong-Mi Lee, Geun-Myun Kim, You-Hee Jung
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(10): 570. CrossRef - Spiritual Well-Being, Social Support, Life Satisfaction and Depression in the Community Dwelling Elderly
So Nam Kim, Sang Bok Lee
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 186. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depressive Symptoms in Community Dwelling Older People
Jung Nam Sohn
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(2): 107. CrossRef - Gender Difference in Risk Factors for Depression in Community-dwelling Elders
Chul-Gyu Kim, Seungmi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 136. CrossRef - Prevalence and Correlates of Depression in Older Koreans: Comparison of Young-old and Old-old
Kyung-Choon Lim, Seonho Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(1): 1. CrossRef
-
ИНСОМНИЯ КАК ТРАНСДИАГНОСТИЧЕСКИЙ ФЕНОМЕН У ПОЖИЛЫХ С ДЕПРЕССИВНЫМИ И ТРЕВОЖНЫМИ РАССТРОЙСТВАМИ
- 896 View
- 2 Download
- 14 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


