Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Psychometric testing of the Korean version of the Undergraduate Nursing Student Academic Satisfaction Scale: a methodological study
- Da-In Park, Joohee Shim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):51-66. Published online February 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to translate, cross-culturally adapt, and evaluate the psychometric properties of the Korean version of the Undergraduate Nursing Student Academic Satisfaction Scale (K-UNSASS).
Methods
The K-UNSASS was developed using Brislin’s team-based translation–back-translation approach, with semantic and conceptual equivalence examined. Face validity was assessed, and a pilot test was conducted in November 2022. Content validity was evaluated by an expert panel. Formal data collection was conducted from December 2022 to January 2023. Structural validity was examined using exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients.
Results
A total of 482 full-time nursing students, most of whom were in the fourth year of their nursing program, were included in the psychometric testing. Construct validity supported a four-factor structure accounting for 65.9% of the total variance. After removal of three items with unsatisfactory factor loadings, a 45-item K-UNSASS was established. Confirmatory factor analysis of the 45-item K-UNSASS demonstrated an acceptable model fit, and both Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients were .97.
Conclusion
The K-UNSASS demonstrates acceptable reliability and validity for assessing academic satisfaction among Korean nursing students. As a culturally relevant instrument, it supports educational improvement through targeted strategies and program evaluation.
- 153 View
- 3 Download

- Research trends in generative artificial intelligence in nursing: a scoping review
- Myung Jin Choi, Myoung Hee Seo, Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):468-487. Published online August 5, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has yet to be comprehensively analyzed in the nursing literature. This study aimed to identify research trends in generative AI within the nursing field through a scoping review and propose strategies for its effective utilization in nursing.
Methods
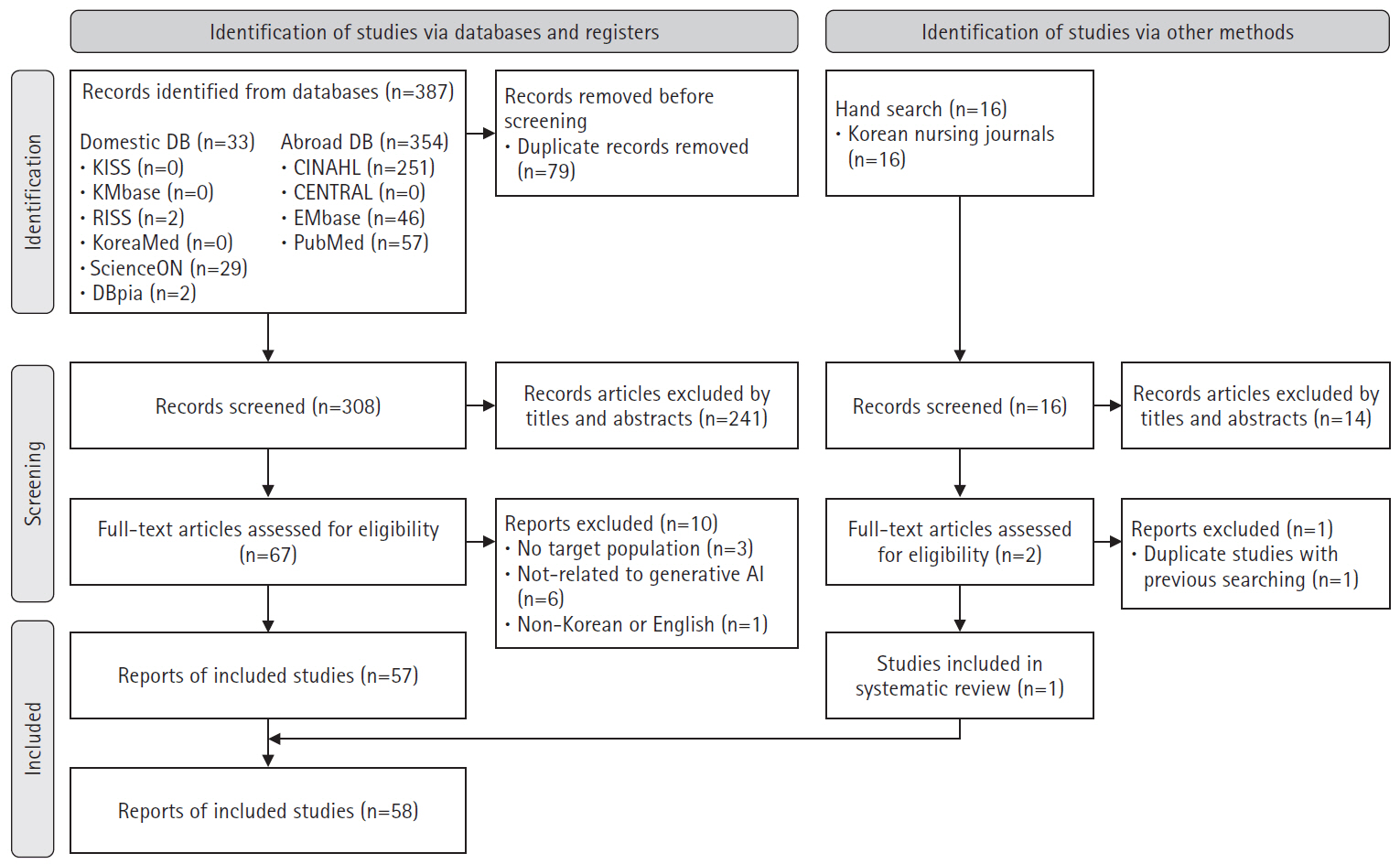
A scoping review was conducted following Arksey and O’Malley’s six-stage framework. The inclusion criteria included: (1) studies conducted in nursing; (2) research related to generative AI; and (3) original research articles, theses, communications, editorials, letters, or commentaries published in academic journals. Database used PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL, CINAHL, KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, DBpia, and 27 nursing-specific journals.
Results
In total, 403 studies were initially identified, and 58 were included in the final analysis. In the care domain, strengths included rapid information retrieval and improved nurse-patient communication, while limitations included the irreplaceable human element and low reliability. The administration domain had no relevant studies. In the research domain, generative AI exhibited strengths such as enhanced efficiency in the paper writing process and improved dissemination speed, but its weaknesses included lack of ethical and legal accountability and a risk of inaccurate or biased information. In the education domain, generative AI was effective in saving time in educational design and implementation, as well as supporting content creation, but challenges included algorithmic bias and risks of plagiarism.
Conclusion
This study identified potential benefits and limitations of generative AI across nursing domains. For effective application, it is essential to develop comprehensive guidelines and policies, provide user education and support, and create opportunities for nurses, educators, and students to learn about strengths and risks of generative AI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Sukyung Son, Eunyoung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(Special Is): 9. CrossRef
- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
- 6,919 View
- 505 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study
- Sunmi Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):137-151. Published online February 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study investigated the effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea.
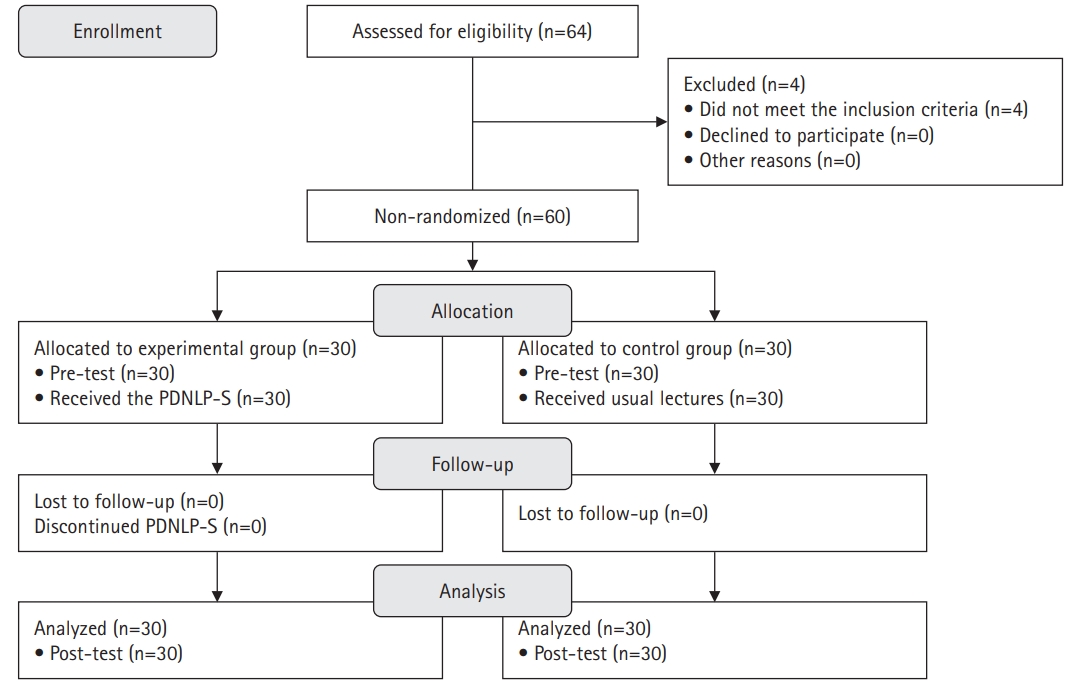
Methods
A quasi-experimental study was conducted. The Practice-Driven Nursing Leadership Program for Students (PDNLP-S) was developed based on the ADDIE model (analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation). This quasi-experimental study design included 60 nursing students. The experimental group (n=30) participated in the PDNLP-S for 120-minute sessions over 5 weeks, while the control group (n=30) received usual lectures. The PDNLP-S included lectures, discussions, and individual and group activities to cultivate core nursing leadership competencies such as individual growth, collaboration, nursing excellence, creative problem-solving, and influence. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the Mann-Whitney U-test, and the independent t-test with IBM SPSS Windows ver. 26.0.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in self-leadership (t=3.28, p=.001), interpersonal relationships (t=3.07, p=.002), clinical performance (U=268.50, p=.004), and problem-solving abilities (t=2.20, p=.017) compared to the control group. No significant difference was observed in nursing professionalism (t=0.50, p=.311).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the PDNLP-S improved nursing students’ self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, and problem-solving abilities. The PDNLP-S can play a significant role in cultivating future nurse leaders by enhancing these nursing leadership competencies among nursing students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
Kexin Chen, Ling Yang, Jiajia Tu
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2025; Volume 18: 7539. CrossRef
- Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
- 7,373 View
- 300 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development and effects of a media-based reproductive health promotion program for male high school students at male high school: a quasi-experimental study
- Joon-Young Lee, Yeoungsuk Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):34-49. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24050
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This quasi-experimental study was conducted to develop a media-based reproductive health promotion program (MRHPP) among male high school students and to evaluate its effectiveness.
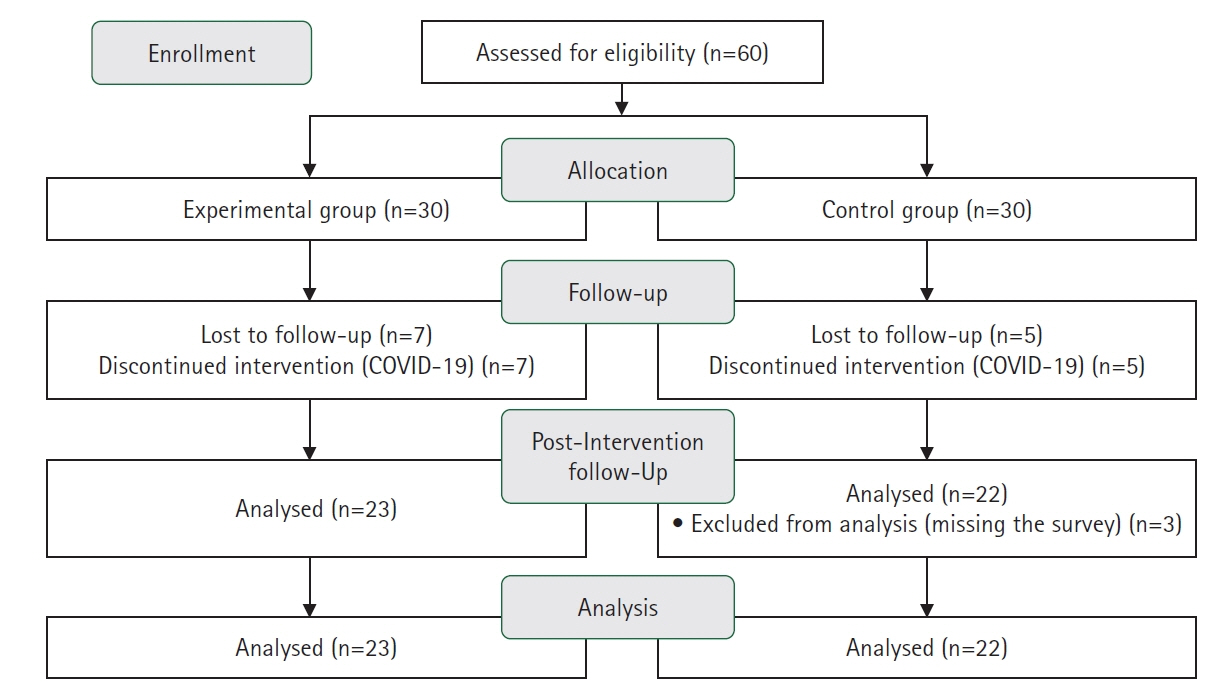
Methods
The ADDIE model (analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation model) was used to develop the MRHPP based on Ajzen’s theory of planned behavior. The research was conducted using a non-equivalent control group with a pretest-posttest design (experimental group=23; control group=22). The program consisted of six sessions and was conducted twice a week. The participants were assessed through a pre-test, post-test immediately after training (post-test 1), and follow-up after 4 weeks (post-test 2) by using questionnaires. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the independent t-test, chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, and repeated-measures analysis of variance.
Results
The analysis of the group-by-time interaction showed statistically significant differences in attitudes toward reproductive health behavior (RHB) (F=4.09, p=.049), subjective norms of RHB (F=5.31, p=.026), and intention to engage in RHB (F=3.78, p=.016). The effect sizes for attitudes, subjective norms, and intention to engage in RHB ranged from 0.75 (medium) to 1.02 (large) (p<.001) at post-test 1, and those for attitudes and subjective norms of RHB ranged from 0.36 (small) to 0.69 (medium) (p<.001) at post-test 2.
Conclusion
The MRHPP was demonstrated to be an effective intervention for promoting reproductive health behavior among male high school students.
- 2,570 View
- 236 Download

- The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience in Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity and Learning Burnout
- Liu Zhang, Qin Zhang, ShuWen Li, YuHong Li, GuoCui Wu, Ying Chen, YunNa Zhou
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):509-518. Published online November 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24044
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study investigated whether professional identity predicts learning burnout among Chinese nursing students, and whether resilience moderates this relationship.
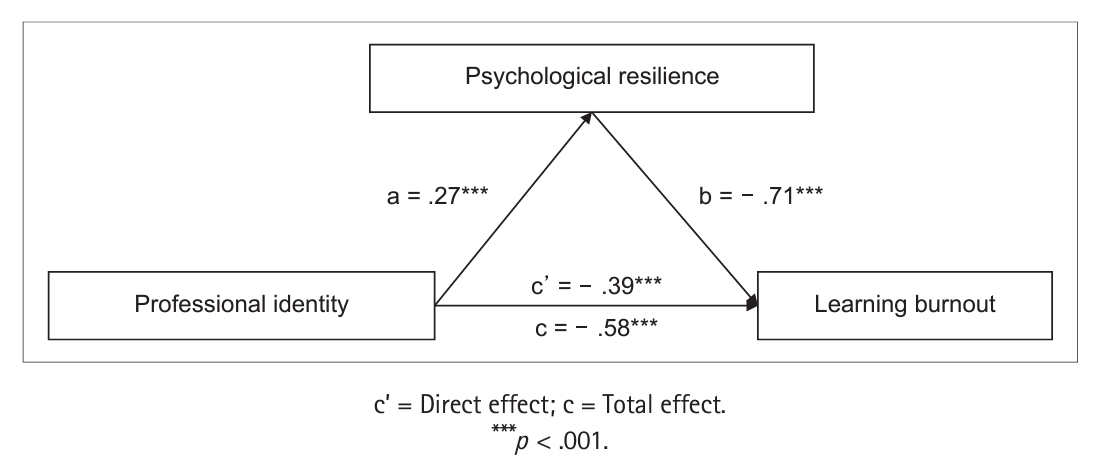
Methods This cross-sectional study recruited 635 students from a nursing college at a medical university in Hefei, China. Data were collected using the professional identity questionnaire, learning burnout scale for college students, and 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale. Pearson’s correlation analysis was used to investigate the relationships between variables. The mediation effect was evaluated using linear regression and the bootstrap method in SPSS.
Results Nursing students exhibited intermediate learning burnout levels (score: 54.95 ± 10.42). Professional identity was positively correlated with psychological resilience (r = .42,
p < . 001), whereas learning burnout was negatively correlated with professional identity (r = - .54,p < . 001) and psychological resilience (r = - .57,p < . 001). Psychological resilience mediated the relationship between professional identity and learning burntout to the tune of 32.8%.Conclusion Psychological resilience mediates the relationship between professional identity and learning burnout. Thus, nursing educators can mitigate student burnout by developing their students' professional identities and psychological resilience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of creative anxiety on professional identity among master’s nursing students: a chain mediation effect of psychological resilience and achievement motivation
Yao Ding, Xiaolan Guo, Ruifeng Wang, Lu Xu, Shajie Hou, Fengjiao Chang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sense of Coherence and Perceived Academic Stress Among Nursing Students: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
David Ballester-Ferrando, Esther Cáceres-Malagelada, Carolina Rascón-Hernán, Teresa Botigué, Ana Lavedán, Olga Masot, Dolors Burjalés, Luis González-Osorio, Ximena Osorio-Spuler, Eva Serrat-Graboleda, Concepció Fuentes-Pumarola
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(8): 288. CrossRef
- The impact of creative anxiety on professional identity among master’s nursing students: a chain mediation effect of psychological resilience and achievement motivation
- 4,312 View
- 183 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Development and Effectiveness of Progressive Simulation Education Program on Medication Safety for Nursing Students
- Se-Young Jung, Eun-Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):563-576. Published online October 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to develop and verify a progressive simulation education program aimed at enhancing nursing students’ medication safety competency.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was adopted. The participants were 40 third-year nursing students with no prior simulation education experience, comprising 20 each in the experimental and control groups. The experimental treatment utilized a hybrid simulation approach incorporating both full-body mannequins and standardized patients and was, conducted over three sessions with durations of 65, 80, and 95 minutes for the first, second, and third sessions, respectively, for a total of 240 minutes. The program was constructed based on Jeffries’ simulation model.
Results The levels of medication safety competencies, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving abilities of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group.
Conclusion Our results confirm that the program effectively improves nursing students’ medication safety competence, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Therefore, this program can serve as a basis for developing educational strategies related to medication safety for nursing education institutions. Furthermore, the program is anticipated to have a positive impact on novice nurses’ education and practice in clinical settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
Jiyoung Kim, Yeji Kim, Hyunji Park, Jiyeong Won, Jiwon Yun, Yuran Lee
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2026; 111: 101899. CrossRef
- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
- 4,788 View
- 414 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development of the Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students
- Seoyoung Yoon, Hye-Ah Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):340-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students (HCPES-NS) and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
The HCPES-NS was constructed following the DeVellis guidelines. The initial items were written based on a literature review and individual in-depth interviews. Content validity was verified through an expert panel review. To confirm the validity and reliability of the scale, a survey was conducted with 449 nursing students enrolled in 12 nursing colleges. Data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, concurrent validity, and reliability tests.
Results
Factor analysis showed that the HCPES-NS consists of 15 items on five subdomains: clinical site atmosphere, interpersonal relationship, alternative online practicum contents, provision of learning information, and clinical performance facilitation. A higher score indicated a more positive perception of the clinical practicum environment. The concurrent validity of the HCPES-NS was confirmed by its positive correlation with the Clinical Learning Environment Scale (r = .77). The Cronbach’s α reliability of the HCPES-NS was .84.
Conclusion
The HCPES-NS is both valid and reliable. This scale reflects the clinical practicum environment and includes an online practicum factor. It may be used effectively by faculty members and educators to evaluate nursing students’ perceptions of clinical practicum environments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Ui Rim Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 355. CrossRef
- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
- 2,962 View
- 96 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Nursing Students’ Experiences of Observing the Use of Physical Restraints: A Qualitative Study
- Sun Mi Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):610-621. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23032
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand the experiences of final-year undergraduate nursing students in observing the use of physical restraints on patients in the course of clinical practice.
Methods
Three focus group interviews were conducted with 12 Korean nursing students who could provide sufficient information about their observation of physical restraints. The collected data was analyzed through conventional content analysis.
Results
The data were classified into four theme clusters, and nine themes. The four theme clusters included ‘recognized as an unavoidable means,’ ‘experienced problems with the use of physical restraints,’ ‘realized the importance of the nurse's role and efforts,’ and ‘aspire to learn about correct use of physical restraints.’ While nursing students recognized the necessities and problems of using physical restraints in clinical practice, and the importance of nurses’ role and effort, the results found that education related to the use of physical restraints should be more systematic within the nursing curriculum.
Conclusion
This study highlights the necessity of educating nursing students to ensure they acquire accurate knowledge and awareness regarding the use of physical restraints, and suggests the inclusion of systematic guidelines through simulation or extracurricular activities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Nurses’ and Nursing Students’ Attitudes Toward Coercive and Technological Measures in Mental Health: A Conceptual Framework and Study Protocol
Giuliano Anastasi, Roberto Latina, Yari Longobucco, Alessandro Stievano, Stefano Bambi
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(4): 4129. CrossRef
- Exploring Nurses’ and Nursing Students’ Attitudes Toward Coercive and Technological Measures in Mental Health: A Conceptual Framework and Study Protocol
- 3,967 View
- 111 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Education for Caring Patients with COVID-19
- Min Hye Lee, Eun-Young Noh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):397-411. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The role of medical staff gained immense significance in the context of the prolonged coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. However, few studies had explored the impact of simulation-based education on the ability of nursing students to care for the patients of COVID-19. This study provided nursing students with simulation-based education in caring for the patients of COVID-19 and confirmed its effectiveness.
Methods
This study used a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants were recruited from the nursing departments of two universities in Korea through convenience sampling. A total of 79 participants were included: 37 in the intervention group and 42 in the control group. The intervention group received four sessions of simulation training based on the National League for Nursing Jeffries simulation theory.
Results
The intervention group showed an improvement compared to the control group in terms of knowledge related to coronavirus, confidence in performing infection control skills, and perception of preparedness for caring for the patients of COVID-19, with a high-level of satisfaction and self-confidence in learning. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of anxiety.
Conclusion
This simulation is expected to be a significant strategy for alleviating the global burden in terms of staff safety and patient outcomes by improving the competencies of prospective medical staff in responding to pandemics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Utilization and impact of simulation-based education in prelicensure nurse education; an integrative review
Robyn Cant, Colleen Ryan
Journal of Professional Nursing.2026; 63: 6. CrossRef - Building Skills in Infection Prevention Through Simulation: Insights from Nursing Students in Brazil and Peru
Luciene Muniz Braga, Pedro Paulo do Prado-Junior, Andréia Guerra Siman, Talita Prado Simão Miranda, Mara Rúbia Maciel Cardoso do Prado, Luana Vieira Toledo, Rodrigo Siqueira-Batista, Andréia Patrícia Gomes, Yanet Castro Vargas, Luis Alberto Chihuantito-Ab
Nursing Reports.2026; 16(1): 14. CrossRef - Determinants of Standard Precautions Performance Among Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Se Gyeong Jeon, Eun Jung Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(21): 2803. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of a Novel Education Approach to Prevention and Control of Healthcare-Associated Infections: Insights from PrevInf Pilot Study
Paulo Santos-Costa, Filipe Paiva-Santos, João Graveto
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(2): 1494. CrossRef
- Utilization and impact of simulation-based education in prelicensure nurse education; an integrative review
- 5,942 View
- 103 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Related to Clinical Competence among Graduating Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Su Kyoung Chung, Jinsook Kim, Pratibha Bhandari
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):145-154. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated clinical competency, COVID-19-related anxiety, coping strategies, self-efficacy, and perceived stress among graduating nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional survey. Participants were recruited from universities located in four major cities in South Korea. General demographic information, clinical competency, self-efficacy, perceived stress, COVID-19-related anxiety, and coping strategies were assessed using reliable questionnaires. Descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression tests were used to analyze the data.
Results
The mean clinical competency, self-efficacy, perceived stress, adaptive coping, and maladaptive coping were 138.16 ± 18.34, 83.85 ±14.02, 21.37 ± 5.79, 53.15 ± 4.64, and 30.98 ± 6.73, respectively. COVID-19-related anxiety was reported by 4.3% of participants. Clinical competency was significantly positively correlated with self-efficacy (r = .44, p < .001) and adaptive coping (r = .20, p = .035) and was significantly negatively correlated with maladaptive coping (r = .20, p = .035). The predictors of clinical competency were self-efficacy (β = .434, p < .001) and adaptive coping (β = .173, p < .039), which explained 23% of the variance in clinical competency.
Conclusion
Self-efficacy and adaptive coping strategies are significant predictors of clinical competence during the pandemic. Planning and implementing various curricular and non-curricular activities to increase senior students' self-efficacy and adaptive coping strategies will help prepare competent nursing graduates for the pandemic when they enter the nursing workforce. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Educational Stress and Competence of Intern Nurses' Following Two Years of Online Education: A Cross-Sectional Study
Fatma Dursun Ergezen, Ayşe Yacan Kök, Emine Kol
Ordu Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Çalışmaları Dergisi.2026; 9(1): 83. CrossRef - The Effect of Internship Length on Self‐Efficacy and Clinical Competence: Accelerating Entry Into the Nursing Workforce in Saudi Arabia
Sitah S. Alshutwi, Majed Alamri
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring Educational Stress and Competence of Intern Nurses' Following Two Years of Online Education: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 2,909 View
- 63 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Preventive Behaviors for COVID-19 in Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
- Jeong Sil Choi, Kyung Mi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):554-563. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22047
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to determine how undergraduate nursing students’ knowledge and health beliefs affected their COVID-19-related infection-prevention behaviors.
Methods
This study used a descriptive survey. A total of 188 undergraduate nursing students from two universities in South Korea participated in this study. The data were collected from June 2020 to August 2020. Factors influencing infection-prevention behaviors were identified using multiple regression analysis.
Results
The participants’ mean knowledge level regarding COVID-19 was 84.05 ± 11.78 out of 100. The average health belief score was 2.80 ± 0.32 points out of 5. COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors were correlated with experiences of searching for COVID-19 information (r = .22, p < .01), perceived severity (r = .24, p < .01), perceived benefits (r = .29, p < .01), cues to action (r = .30, p < .01), knowledge (r = .27, p < .01), and perceived barriers (r = - .19, p < .05). Factors that significantly affected COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors were the participants’ years of study, experiences regarding COVID-19 prevention education, perceived severity, perceived barriers, and cues to action.
Conclusion
COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors are promoted by increasing awareness about the disease and promoting COVID-19 education in nursing curriculums. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The multiple mediating effects of health beliefs on the relationship between infection control knowledge and infection-preventive behaviors among health science college students
Yoonmi Lee, Hyejin Kim, Jieun Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(2): 196. CrossRef - Effect of an educational intervention on nursing students’ knowledge about COVID-19 and compliance with standard and transmission-based precautions: a quasi-experimental study
Ana Beatriz de Almeida Lima, Cristine Maria Pereira Gusmão, Lais do Espirito Santo Lima, Daniel de Macedo Rocha, Mayra Gonçalves Menegueti, Ana Cristina de Oliveira e Silva, Renata Karina Reis
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing factors related to perceived control and preventive behaviors from COVID‐19 between Japanese and American nursing students: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The multiple mediating effects of health beliefs on the relationship between infection control knowledge and infection-preventive behaviors among health science college students
- 2,119 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Influence of Learning Presence of Non-Face-to-Face Class Experience in Nursing Students on Academic Achievement: Mediating Effect of Learning Flow and Moderated Mediation of Digital Literacy
- Eui Jeong Ryu, Keum Seong Jang, Eun A Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):278-290. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the mediating effect of learning flow and the moderated mediation effect of digital literacy on the effect of the learning presence of non-face-to-face class experience in nursing students on academic achievement.
Methods
Participants were 272 nursing students from six universities in two different cities. A self-report questionnaire was used to measure learning presence, learning flow, digital literacy, and academic achievement. Analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 and SPSS PROCESS Macro (4.0).
Results
The mediating effect of learning flow on the effect of learning presence on academic achievement was 0.42, and the moderated mediation index of digital literacy was 0.17. Learning flow showed a mediating effect on the relationship between learning presence and academic achievement. Digital literacy had a moderated mediation effect on the relationship between learning presence and academic achievement that was mediated by learning flow.
Conclusion
The intensity of the mediating effect of nursing students’ learning presence on academic achievement through learning flow increases as the level of digital literacy increases. These results suggest that educational programs considering the level of learning presence, learning flow, and digital literacy are required to promote the academic achievement of nursing college students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between freshmen’s perceived social support and learning flow: the chain mediating role of perceived stress and depression
Ye Lin, Xixi Wang, Zhengmei Zhou, Yan Li, Li Liu, Yuanyuan Zhang, Zijiao Zhou, Xiaona Li
BMC Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
Shin Hyang Kim, Jong Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 358. CrossRef - The influence of nursing students’ digital literacy on academic achievement in a blended learning environment: Parallel multiple mediation effects of learning presence
Ja Hyeon Ha, Eun Ju Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 452. CrossRef - Study on the Attitudes toward Artificial Intelligence and Digital Literacy of Dental Hygiene Students
Seon-Ju Sim, Ji-Hye Kim, Min-Hee Hong, Su-Min Hong, Myung-Jin Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(3): 171. CrossRef - The influence of e-learning digital literacy on cognitive flexibility and learning flow in nursing students
Jeongim Lee, Su Ol Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(2): 87. CrossRef - The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Nurses’ Well-Being: Does Digital Competence Matter?
Yali Li, Qi Jing, Taiwen Feng, Xiaoling Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 385. CrossRef - Relationship between learning flow and academic performance among students: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis
Zhang Jinmin, Fang Qi
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The relationship between freshmen’s perceived social support and learning flow: the chain mediating role of perceived stress and depression
- 2,650 View
- 186 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Head-Mounted Display-Based Home-Visits Virtual Reality Simulation Program for Nursing Students
- Min Kweon Ahn, Chong Mi Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):465-477. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21051
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of head monted display based home-visits virtual reality simulation (HVRS) program developed for undergraduate nursing students.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group with a non-synchronized design was utilized and 84 participants (experimental group, 44; control group, 40) were recruited from August 31, 2020 to November 8, 2020 in Gwangju metropolitan city. The HVRS program consisted of scenarios of three nursing cases, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and stroke. Data were analyzed SPSS version 25.0 for Windows.
Results
At the completion of HVRS, significant differences were found between groups in knowledge of home-visits (t = 4.73, p < .001), self-confidence (t = 6.63, p < .001), self-efficacy (t = 3.13, p = .002), and clinical competency (t = 4.13, p < .001). No significant difference was shown between groups in nursing knowledge about strokes, a subcategory of knowledge pertaining to home visits.
Conclusion
The HVRS program developed for undergraduate nursing students is effective in improving knowledge of home-visits, self-confidence, self-efficacy, and clinical competency for nursing students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Icarus new rising? A narrative review on virtual reality-based motor interventions in older adults
André Ramalho, Pedro Duarte-Mendes, Rui Paulo, João Serrano, João Petrica
Human Movement.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between virtual reality and traditional lecture methods in educating respiratory therapy on pediatric airway diseases
Wen-Jing Hsu, Yi-Hsuan Tang, Wei-Chih Chen, Yu-Sheng Lee, Pei-Chen Tsao, Wei-Yu Chen, Ying-Ying Yang, Hsin-Kuo Ko, Sheng-Wei Pan, Yu-Fen Ting, Shih-Hsing Yang, Mei-Jy Jeng
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2025; 88(3): 205. CrossRef - Effects of Community Nursing Simulation Education on Nursing Core Competencies, Clinical Judgment, and Clinical Performance of Nursing College Students
Hoo-Jeung Cho, Kyong-Sun Chong
European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education.2025; 15(6): 92. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the IPE-Sim based dementia management (IPE-SDM) program on community-dwelling elders for nursing and medical students
Sooyoung Jun
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2025; 106: 101790. CrossRef - Immersive virtual reality in nursing education: A scoping review of components, outcome variables, and interaction modes
Sunghwa Na, Jihyung Son, Hyun Joo Lee
Nurse Education Today.2025; 155: 106877. CrossRef - Effects of virtual reality-based disaster simulation education on nursing students
Kyeng-Jin Kim, Moon-Ji Choi, MinJi Kim, Yong-Hong Kuo
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0329563. CrossRef - A VR-Based Trauma Nursing Education Program for Clinical Nurses: Integrating Jeffries’ Model and the 5E Learning Cycle
Heeyeon Kim, Gyuli Baek, Eunju Lee
Healthcare.2025; 13(19): 2542. CrossRef - Effects of Diabetes Home-Visiting Healthcare Simulation Education on Nursing Students Using Virtual Reality
Young-Sun Ha, Yong-Kyung Park, Hye-Sun Byun, Kyeng-Jin Kim, Moon-Ji Choi
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(9): 2501. CrossRef - Exploring the effects of extended reality head-mounted display nervous system assessment training for nursing students: A pilot feasibility study
Jiyoung Kim, Hyunjung Shin
Nurse Education Today.2024; 133: 106089. CrossRef - Are virtual reality intravenous injection training programs effective for nurses and nursing students? A systematic review
Jin Young Kim, Juri Kim, Mikyoung Lee
Nurse Education Today.2024; 139: 106208. CrossRef - Enhancing nursing competency through virtual reality simulation among nursing students: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Immersive Technology–Based Education for Undergraduate Nursing Students: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) Approach
Subin Park, Hui Ju Shin, Hyoeun Kwak, Hyun Joo Lee
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024; 26: e57566. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Metaverse-Based Intradermal Injection Content for Nursing Students
Min-Kweon Ahn
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2024; 25(9): 2543. CrossRef - Pressure Ulcer Management Virtual Reality Simulation (PU-VRSim) for Novice Nurses: Mixed Methods Study
Soo Youn Jung, Kyoung Ja Moon
JMIR Serious Games.2024; 12: e53165. CrossRef - Effect of virtual reality head-mounted display on academic motivation and skills of millennial nursing students in teaching infection prevention and control
Andri Nugraha, Iin Patimah, Engkus Kusnadi, Wikky Fawwaz Al Maki
Journal of Research Development in Nursing and Midwifery.2024; 21(3): 3. CrossRef - Effect of Augmented Reality Smart Glasses-based Nursing Skills Training for Nursing Students’ Medication Administration Safety Competency: A Quasi-experimental Study
Jiyoung Kim, Narae Heo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(4): 449. CrossRef - Instructor's Experience of Extended Reality Applied to Nursing Education
Jiyoung Kim, Hyeoncheol Jeong
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2023; 84: 101450. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of positive attitudes toward and perceived importance of wearable display technology as an effective learning tool among nursing students
Jiyoung Kim, Narae Heo, Hyuncheol Kang
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 73: 103812. CrossRef - A Study on the Feasibility of Introducing XR in Nursing Education Core Fundamental Nursing Skills
Yunja Hwang, Jaeyeon Jeong, Yoo Mi Jeong
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(4): 775. CrossRef - Virtual Reality Simulation for Advanced Infection Control Education in Neonatal Intensive Care Units: Focusing on the Prevention of Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infections and Ventilator-Associated Infections
Jimin Ryu, Mi Yu
Healthcare.2023; 11(16): 2296. CrossRef - A Delphi study on the Needs for the Development of a Customized Program based on Augmented Reality for Preterm infants and their Families in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Jae Eun Sin, Ah Rim Kim
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2022; 23(3): 455. CrossRef - The development and effects of metaverse-based core nursing skill contents of vital signs measurements and subcutaneous injections for nursing students
Min Kweon Ahn
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 378. CrossRef - Nurses’ behavioral intention in using virtual clinical simulation training: By structural equation modeling
Hyein Choi, Sunghee H. Tak
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 65: 103492. CrossRef
- Icarus new rising? A narrative review on virtual reality-based motor interventions in older adults
- 2,450 View
- 123 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref

- Disease Prevention Knowledge, Anxiety, and Professional Identity during COVID-19 Pandemic in Nursing Students in Zhengzhou, China
- Yuyan Sun, Dongyang Wang, Ziting Han, Jie Gao, Shanshan Zhu, Huimin Zhang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):533-540. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate nursing students’ understanding of the prevention of COVID-19, as well as their anxiety towards the disease and their perception of their professional identity in the wake of the pandemic, in Zhengzhou, China.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was designed to investigate 474 nursing students by cluster sampling using a stratified questionnaire from February 15 to March 31, 2020. Multiple linear regression was used to identify the factors affecting professional identity. Binary and multiple logistic regression were used to identify the factors affecting anxiety.
Results
Responders with a high level of understanding of COVID-19 and frequent use of behavioral strategies for its prevention comprised 93.2% and 30.0% of the cohort, respectively. Professional identity was significantly associated with gender and anxiety (p < .050). The prevalence of anxiety among nursing students was 12.4%. Male (odds ratio [OR] = 2.39; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.26~4.52), sophomores (OR = 5.30; 95% CI = 1.61~7.45), and infrequent use of prevention measures (OR = 3.49; 95% CI = 1.16~5.19) had a significant effect on anxiety.
Conclusion
Anxiety during the COVID-19 epidemic gives an adverse effect on the professional identity of nursing in students. Nursing education institutions need to provide psychological counseling services for nursing students, in addition to improving their teaching of COVID-19 prevention strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global prevalence of different levels of anxiety and stress symptoms in healthcare students: A meta-analysis and meta-regression
Ying Xuan Loh, Ying Lau, Wen Wei Ang, Shean Ern Shannen Lee, Siew Tiang Lau
Annals of General Psychiatry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomical dissection influences emotions of podiatry students
Alicia Mohedano‐Moriano, Carmen Romo‐Barrientos, Alicia Flores‐Cuadrado, Isabel Ubeda‐Bañon, Jaime Gonzalez‐Gonzalez, Maria Teresa Gil Ruiz, Daniel Saiz‐Sanchez, Veronica Astillero‐Lopez, Felix Marcos‐Tejedor, Alino Martinez‐Marcos, Antonio Viñuela, Juan
Journal of Foot and Ankle Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Hand Hygiene Practices and Educational Interventions Among Indonesian Nursing Students: An Analysis Using ATP Wipe Tests and Hand Hygiene Checkers
Mayumi Sato, Syahrul, Tantut Susanto, Fithria, Naoki Hokama, Ruka Saito, Andi Muhammad Fiqri Muslih Djaya, Hiroshi Sugimoto
Journal of Rural Community Nursing Practice.2025; 3(1): 60. CrossRef - The transformation of ambivalent professional identity of nursing students following clinical placement in China: A qualitative study from the perspectives of the “post-00s” generation
Jingyi Chen, Xiao Zhang, Yidan Yang, Rong Hu
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 86: 104387. CrossRef - Resilience, perceived control, and intention to receive additional vaccines for COVID‐19 among healthcare university students: Mediating role of knowledge of vaccine and infection‐preventive behaviors
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Erika Ota, Tomomi Oki, Kazuko Naruse
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influences of nursing students’ prevention and control practice behaviours on emerging and re-emerging respiratory viral illnesses: An integrative review and narrative synthesis
Gift A. Mutsonziwa, Paul Glew, Rona Pillay
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 88: 104564. CrossRef - Ser enfermeiro na perspectiva de estudantes de enfermagem do nordeste brasileiro no contexto pandemico
Thais Araujo da Silva, Ruth Silva dos Santos, Nayhara Rayanna Gomes da Silva, Ryanne Carolynne Marques Gomes Mendes
Journal of Nursing and Health.2025; 15(2): e1528145. CrossRef - Kayseri İlinde Öğrenim Gören Paramedik Öğrencilerinin Mesleki Kaygı Düzeyinin Belirlenmesi
Emre Bulbul, Etem Hızaler, Mehmet Doğan
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2025; 6(1): 8. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of Factors Influencing Nursing Intentions toward COVID-19 Patients
Nari Lee, Hae Ran Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 285. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of the training on “Home care of COVID-19 positive/suspicious patients” given to nursing students: A quasi-experimental study
Hande Sabandüzen, Öznur Kavaklı
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of alexithymia, anxiety, social pressure, and academic burnout on depression in Chinese university students: an analysis based on SEM
Mingyang Sun, Ming Piao, Zhaona Jia
BMC Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between anxiety and academic identity and the motivation to study nursing and midwifery in the covid-19 pandemic: A structural model
Ashraf Khoramirad, Sarallah Shojaei, Heydar Ghaderi, Zahra Abedini
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Holistic Approach to Nursing Students’ Changing Life and Anxiety in the Pandemic: A Descriptive Cross Sectional Study Utilizing Positive Psychotherapy
Ayşe Kuzu Durmaz, Ferhan Açıkgöz, Çiğdem Şen Tepe
Journal of Higher Education and Science.2024; 14(2): 349. CrossRef - The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience in Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity and Learning Burnout
Liu Zhang, Qin Zhang, ShuWen Li, YuHong Li, GuoCui Wu, Ying Chen, YunNa Zhou
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(4): 509. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Nurses’ Perceptions of Spirituality and Spiritual Care and Their Attitudes Towards the Nursing Profession
İbrahim Nas, Gülay İpekçoban
Gümüşhane Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 13(2): 542. CrossRef - Anxiety in Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Aroa García-Rivas, María Begoña Martos-Cabrera, María José Membrive Jiménez, Raimundo Aguayo-Estremera, Nora Suleiman Martos, Luis Albendín-García, José L. Gómez-Urquiza
Healthcare.2024; 12(16): 1575. CrossRef - Work environment as perceived by nursing interns and its relation to their professional identity
Habiba A.A. Gadallah, Sahar H.A. El Banan, Faten S.A. Ahmed
Egyptian Nursing Journal.2024; 21(2): 129. CrossRef - Assesment of Occupational Anxiety of Emergency Aid and Disaster Management Students
Cüneyt Çalışkan, Kerem Kınık
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2024; 5(1): 51. CrossRef - COVID-19 Perceptions, Avoidance and Vaccine Attitudes of Nursing Students: Case of Türkiye
Gülşen ULAŞ KARAAHMETOĞLU, Zeynep ARABACI
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektronik Dergisi.2024; : 111. CrossRef - COVID-19 Pandemi Süreci Uzaktan Eğitim Döneminde Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinde Anksiyete ve Klinik Performans Öz-Yeterlilik Algısı İlişkisi
Yeliz AKKUŞ, Nihal BOSTANCI DAŞTAN
Sağlık Bilimlerinde Değer.2024; 14(1): 106. CrossRef - Comparing factors related to perceived control and preventive behaviors from COVID‐19 between Japanese and American nursing students: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksekokulu Öğrencilerinin Mesleğe Yönelik Kaygı Düzeylerinin Belirlenmesi
Dilan AKTEPE COŞAR, Nuray BİNGÖL, Hatice DEMİRAĞ
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2023; 4(2): 66. CrossRef - Satisfied with teaching? Psychometric properties of the Teaching Satisfaction Scale
Tyrone B. Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni, Kyle M. Jackson, Brendon D. Faroa
African Journal of Psychological Assessment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors for Anxiety Symptoms among Student Nurses in Gauteng Province of South Africa
Maleke Manana, Sam Thembelihle Ntuli, Kebogile Mokwena, Kgomotso Maaga
Behavioral Sciences.2023; 13(8): 630. CrossRef - Factors related to mental health effect among nursing students in Japan and the United States during the coronavirus pandemic: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(1): 186. CrossRef - Effects of a Nursing Simulation Learning Module on Clinical Reasoning Competence, Clinical Competence, Performance Confidence, and Anxiety in COVID-19 Patient-Care for Nursing Students
Ye-Eun Kim, Hee-Young Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(1): 87. CrossRef - Research Progress of Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity during COVID-19
毓 徐
Nursing Science.2023; 12(01): 7. CrossRef - Prevalence and levels of burnout in nursing students: A systematic review with meta-analysis
José L. Gómez-Urquiza, Almudena Velando-Soriano, María José Membrive-Jiménez, Lucia Ramírez-Baena, Raimundo Aguayo-Estremera, Elena Ortega-Campos, Guillermo A. Cañadas-De la Fuente
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 72: 103753. CrossRef - Psychological impacts of transition to distance learning due to COVID‐19 on nursing students
Ahmad Rayan
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(3): 767. CrossRef - COMPARISON OF TWO DIFFERENT TECHNIQUES FOR TEACHING LEARNING SKILLS: EVALUATION IN THE PERIOD OF PANDEMIC
Sevim ÇELİK, Elif KARAHAN, Sibel ALTINTAŞ, Özge UÇAR
International Journal of Health Services Research and Policy.2023; 8(2): 114. CrossRef - How has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced nursing students' academic experience and career choices? A qualitative descriptive analysis
Masamitsu Kobayashi, Yuji Koga, Jun Kako, Takahiro Kakeda, Hana Kiyohara, Yasutaka Kimura, Michiko Ishida, Michihiro Tsubaki, Yoko Nishida, Kimie Harada, Yuki Wakiguchi, Yoji Endo, Yoshiyasu Ito, Shinsuke Sasaki, Kohei Kajiwara, Seiji Hamanishi, Makoto Ya
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2023; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Perceived social support and professional identity in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic era: the mediating effects of self-efficacy and the moderating role of anxiety
Zhi-Hui Zhao, Jin-Yi Guo, Jie Zhou, Jia Qiao, Shu-Wen Yue, Yan-Qiong Ouyang, Sharon R. Redding, Rong Wang, Zhong-Xiang Cai
BMC Medical Education.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety, depression, and stress prevalence among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chunyi Wang, Wen Wen, Haifu Zhang, Jie Ni, Jingjie Jiang, Yongran Cheng, Mengyun Zhou, Lan Ye, Zhanhui Feng, Zhongjun Ge, Hong Luo, Mingwei Wang, Xingwei Zhang, Wenmin Liu
Journal of American College Health.2023; 71(7): 2123. CrossRef - Factors associated with mental health among undergraduate nursing students early in the COVID-19 pandemic: an integrative review
Keiko Sugimoto, Rieko K. Fukuzawa, Ganchimeg Togoobaatar, Chang G. Park, Susan C. Vonderheid
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - PANDEMİ SÜRECİNDE KLİNİK UYGULAMA YAPAMAYAN İLK VE ACİL YARDIM ÖĞRENCİLERİNİN MESLEKİ YAŞAM İLE İLGİLİ KAYGI DÜZEYLERİNİN VE İLİŞKİLİ FAKTÖRLERİN BELİRLENMESİ
Elif KILIÇ GÜNER, Özge AKBABA, Elanur YILMAZ KARABULUTLU, Havva ÖZTÜRK
Hastane Öncesi Dergisi.2023; 7(3): 331. CrossRef - Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinin Mesleğe Yönelik Tutumu ile COVID-19 Enfeksiyonu Korkusu Arasındaki İlişki
Süreyya Bulut, Nihal Taşkıran
Hacettepe Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 10(3): 207. CrossRef - Investigation of the Stress Level and Coping Behaviors of Nursing Students, and Their Thoughts on Professional Life in COVİD-19 Pandemic
Belkız KIZILTAN, Nurgül KAPLAN, Seda UZUNALİ
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2023; 4(1): 26. CrossRef - The development and effects of a COVID-19 nursing education program for nursing students
Hyewon Choi, Hyunju Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 368. CrossRef - Hemşirelik Son Sınıf Öğrencilerinin Mezuniyet Sonrası Covid-19 Kliniklerinde Çalışmaya İlişkin Görüşleri: Nitel Bir Çalışma
Ilknur TURA, Sevilay ERDEN
Hemşirelik Bilimi Dergisi.2022; 5(3): 149. CrossRef - The multidimensionality of anxiety among nursing students during COVID‐19 pandemic: A cross‐sectional study
Rizal Angelo N. Grande, Daniel Joseph E. Berdida, Rolan Rodolfo Jr C. Paulino, Eric A. Anies, Reinhard Roland T. Ebol, Roger R. Molina
Nursing Forum.2022; 57(2): 267. CrossRef - Identity Matters: Validation of the Professional Identification Scale in a Sample of Teachers in South Africa During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tyrone B. Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni, Serena Ann Isaacs
Trends in Psychology.2022; 32(4): 1426. CrossRef - The study of psychological traits among Chinese college students during the COVID-19 campus lockdown
Haibo Xu, Zhen Wang, Lixin Peng, Yanyan Mi, Ping Zeng, Xin Liu
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived professional identity and related factors in Iranian nursing students: a cross-sectional study
Tahereh Gilvari, Hassan Babamohamadi, Fatemeh Paknazar
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing students’ experiences of mental wellness during the COVID-19 pandemic: A phenomenological study
Dana Laczko, Alex Hodson, Melissa Dykhuizen, Kelsey Knipple, Kassandra Norman, Paula Hand-Cortes
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2022; 17(4): 392. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Infection Control Performance of School Health Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea
Mi-Ra Yim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2022; Volume 15: 805. CrossRef - The Beneficial Effects of Professional Identity: The Mediating Role of Teaching Identification in the Relationship between Role Stress and Psychological Distress during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tyrone Brian Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11339. CrossRef - Being a Nursing Student In a Pandemic: Fear of COVID-19 and Clinical Practice
Pınar TUNÇ TUNA, Halil İbrahim TUNA, Birsel MOLU, Alev YILDIRIM KESKİN
Genel Tıp Dergisi.2022; 32(5): 506. CrossRef - Mental Health Among Medical Students During COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Qingwen Jia, Yi Qu, Huiyuan Sun, Huisheng Huo, Hongxia Yin, Dianping You
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination among student nurses from Saudi Arabia
Romeo Mostoles Jr, Richard Maestrado, Joyce Buta, Salman Alsaqri, Evalynn Rondilla, Hamdan Mohammad Albaqawi
Jurnal Ners.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of anxiety symptoms among Chinese university students amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaohang Wang, Quzhi Liu
Heliyon.2022; 8(8): e10117. CrossRef - Has the COVID-19 pandemic affected nursing students’ career self-efficacy and professional calling? The mediating impact of professional identity
Li Yang, Mengfan Xu, Jinke Kuang, Kexin Zhou, Xuemei Zhu, Lingna Kong, Li QI, Heng Liu
BMC Medical Education.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research on Health Education Strategies for Improving Student Knowledge on Infectious Disease Prevention
Shailly Gupta , Manashree Mane , Debashree Priyadarshini , Ajab Singh Choudhary
Health Leadership and Quality of Life.2022; 1: 126. CrossRef - Relationship between nursing students’ attitudes toward nursing profession and online learning satisfaction during COVID-19 lockdown
Maša Černelič-Bizjak, Petra Dolenc, Ali B. Mahmoud
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0277198. CrossRef - Anxiety and fear of COVID‐19 among nursing students during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A descriptive correlation study
Nilgun Kuru Alici, Ebru Ozturk Copur
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(1): 141. CrossRef - Professional Identity of 0.24 Million Medical Students in China Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Three Waves of National Cross-Sectional Studies
Chen Yu, Qiao Liu, Weimin Wang, Ana Xie, Jue Liu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Attitudes of Nursing Students towards Vaccination and Other Preventive Measures for Limitation of COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-Sectional Study in Three European Countries
Nevenka Kregar Velikonja, Beata Dobrowolska, Sanja Stanisavljević, Karmen Erjavec, Vislava Globevnik Velikonja, Ivan Verdenik
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 781. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Preventive Practice of International Students in South Korea against COVID-19 during the Pandemic
Gun Ja Jang, Ginam Jang, Sangjin Ko
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2259. CrossRef - Perceived Control, Preventative Health Behaviors, and the Mental Health of Nursing Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Kosuke Niitsu, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Individual and Joint Effects of Cumulative Confirmed Cases and Attention Level of COVID-19 on Medical Students' Professional Identity: A National Cross-Sectional Study in China
Qiao Liu, Chen Yu, Ana Xie, Weimin Wang, Jue Liu
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of mental health problems and sleep disturbances in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mulyadi Mulyadi, Santo Imanuel Tonapa, Suwandi Luneto, Wei-Ting Lin, Bih-O Lee
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 57: 103228. CrossRef - Transition in learning during COVID‐19: Student nurse anxiety, stress, and resource support
Anita Fitzgerald, Sharon Konrad
Nursing Forum.2021; 56(2): 298. CrossRef - Nursing Students in Crisis Mode
Bella Savitsky, Yifat Findling, Anat Ereli, Tova Hendel
Nurse Educator.2021; 46(3): E33. CrossRef - Impact of Anxiety on Readiness for COVID-19 Vaccination among Polish Nursing Undergraduate Students: Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Joanna Gotlib, Mariusz Jaworski, Dominik Wawrzuta, Tomasz Sobierajski, Mariusz Panczyk
Vaccines.2021; 9(12): 1385. CrossRef
- Global prevalence of different levels of anxiety and stress symptoms in healthcare students: A meta-analysis and meta-regression
- 2,533 View
- 19 Download
- 48 Web of Science
- 63 Crossref

- The Predictive Strength of Students’ Self-Efficacy, Problem Solving Skills to Perform Catheter Care
- Dogu Kokcu Ozlem, Cevik Celalettin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):411-418. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to determine the predictive strength of students’ self-efficacy, problem-solving skills, and other characteristicsin performing intravenous practices and monitor phlebitis and infiltration.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was carried outwith 736 third and fourth-year students studying at the Health Sciences Faculties of Balikesir and Sakarya universities. The data were collectedusing the Self-Efficacy Scale, Problem-Solving Inventory and Catheter Care and Infiltration Monitoring Questionnaire.
Results
Theparticipants’ mean Catheter Care and Infiltration Monitoring Questionnaire score significantly and positively correlated with their meanSelf-Efficacy Scale score on a moderate level (r=.25; p <.001) but significantly and negatively correlated with their mean Problem-SolvingInventory score on a moderate level (r=-.21; p <.001). In other words, because a low Problem-Solving Inventory score indicates that theperson’s problem-solving skill is high, the Care and Infiltration Monitoring Questionnaire score increased as the problem-solving skill increased.While the Self-Efficacy Scale predicted the year of study and catheter care and infiltration monitoring variables positively, theProblem-Solving Inventory predicted the satisfaction with the profession variable negatively.
Conclusion
Self-efficacy, problem-solving, likingthe profession, and year of study predict success in catheter care and infiltration monitoring. For this reason, guidance may be providedin the development of a comprehensive education system toward increasing students’ problem-solving skills, self-efficacy, and professionalknowledge and skills. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of nurse’s knowledge and self-efficacy on nursing performance in pediatric intravenous fluid management in South Korea: a descriptive study
Se-Won Kim, Mi-Young Choi
Child Health Nursing Research.2024; 30(4): 288. CrossRef - Decision-based learning for teaching arterial blood gas analysis
Sheri Tesseyman, Tracy Poulsen, Samantha Rainsdon-Meek, Heather Leary, Ursula Sorensen, Kenneth Plummer
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Problem-Based Learning on the Problem-Solving Ability and Self-Efficacy of Students Majoring in Dental Hygiene
Jin-Sun Choi, Soo-Myoung Bae, Sun-Jung Shin, Bo-Mi Shin, Hyo-Jin Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(12): 7491. CrossRef - Relationships between Nursing Students’ Skill Mastery, Test Anxiety, Self-Efficacy, and Facial Expressions: A Preliminary Observational Study
Myoung Soo Kim, Byung Kwan Choi, Ju-Yeon Uhm, Jung Mi Ryu, Min Kyeong Kang, Jiwon Park
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 311. CrossRef - The Relationship between Self-Directed Learning and Problem-Solving Ability: The Mediating Role of Academic Self-Efficacy and Self-Regulated Learning among Nursing Students
Younghui Hwang, Jihyun Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1738. CrossRef - Evidence of learning on the insertion and care of peripheral venous catheters in nursing students: A mixed study
Judith García-Expósito, Mercedes Reguant, Olga Canet-Vélez, Francisca Ruiz Mata, Teresa Botigué, Judith Roca
Nurse Education Today.2021; 107: 105157. CrossRef
- Effects of nurse’s knowledge and self-efficacy on nursing performance in pediatric intravenous fluid management in South Korea: a descriptive study
- 1,747 View
- 19 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Nurses and Nursing Students’ Recognition of Good Instruction
- Mina Park, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):101-115. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: The purpose of this study was to identify and assess from nursing students and nurses in the clinical field what constitute good instruction, through the review of nursing students’ opinions and clinical field demands.
Methods: The study design was used Creswell’s exploratory sequential design by collecting and analyzing qualitative data obtained from interviews and then analysis of quantitative data. The participations were 79 seniors in nursing schools and 85 nurses with less than three years of clinical experience. The data were collected through individual interviews and analyzed based on Elo and Kyngäs’s content analysis method. The quantitative data were collected using the questionnaire developed based on qualitative results and analyzed by SPSS 23.0 program and Importance Performance Analysis (IPA).
Results: The results showed that IPA extracted seven items with high importance but low satisfaction: “nursing fads and trends,” “teacher-learner communication and reflection,” “materials used in clinical settings such as monitoring results and test results,” “special presentations by experienced practitioners,” “instruction assures learners’ comprehension,” “accurate and detailed evaluation standards” and “feedback on homework and exam.”
Conclusion The factors comprising good instruction were verified, and the necessity for additional efforts to improve high importance and low performance factors was noted. Therefore, this study can serve as a guide for nursing education facilities and educators in developing of a thorough education system with excellent instruction designed to achieve an ideal nursing education.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Learning Flow of Nursing College Students in Online Classes
Soonyang JANG, Inju SEO
THE JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2025; 37(3): 578. CrossRef - Perceptions of Effective Nursing Handover Education
Ji Sun Lee
Nurse Educator.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expectations and concerns about transitioning to face-to-face learning among Korean nursing students: A mixed methods study
Hyeongsuk Lee, Hye Jin Yoo, Chao Gu
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0296914. CrossRef - Educational needs of severe trauma treatment simulation based on mixed reality: Applying focus group interviews to military hospital nurses
Seon Mi Jang, Sinwoo Hwang, Yoomi Jung, Eunyoung Jung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 423. CrossRef - The Effect of the Education Applying Havruta's Method on Communication Competency, Critical Thinking Competency, and Self-leadership of Nursing Students
Jae-Hyun Ha, Hyun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(3): 337. CrossRef - The mediating effect of self-regulated learning ability on the relationship between experience of good class and problem solving ability of nursing students
Ju Young Park, Chung Hee Woo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(2): 185. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Learning Flow of Nursing College Students in Online Classes
- 1,864 View
- 35 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Factors Affecting Clinical Practicum Stress of Nursing Students: Using the Lazarus and Folkman's Stress-Coping Model
- Sung Hae Kim, JuHee Lee, MiRa Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):437-448. Published online August 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.437
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to test a path model for the factors related to undergraduate nursing students' clinical practicum stress, based on Lazarus and Folkman's stress-coping model.
Methods This study utilized a path analysis design. A total of 235 undergraduate nursing students participated in this study. The variables in the hypothetical path model consisted of clinical practicum, emotional intelligence, self-efficacy, Nun-chi, and nursing professionalism. We tested the fit of the hypothetical path model using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 22.0.
Results The final model fit demonstrated a satisfactory statistical acceptance level: goodness-of-fit-index=.98, adjusted goodness-of-fit-index=.91, comparative fit index=.98, normed fit index=.95, Tucker-Lewis index=.92, and root mean square error of approximation=.06. Self-efficacy (β=−.22,
p =.003) and Nun-chi behavior (β=−.17,p =.024) were reported as significant factors affecting clinical practicum stress, explaining 10.2% of the variance. Nursing professionalism (β=.20,p =.006) and self-efficacy (β=.45,p <.001) had direct effects on emotional intelligence, explaining 45.9% of the variance. Self-efficacy had indirect effects on Nun-chi understanding (β=.20,p <.001) and Nun-chi behavior (β=.09,p =.005) through emotional intelligence. Nursing professionalism had indirect effects on Nun-chi understanding (β=.09,p =.005) and Nun-chi behavior (β=.09,p =.005) through emotional intelligence. The variables for self-efficacy and nursing professionalism explained 29.1% of the Nun-chi understanding and 18.2% of the Nun-chi behavior, respectively.Conclusion In undergraduate nursing education, it is important to identify and manage factors that affect clinical practicum stress. The findings of this study emphasize the importance of Nun-chi, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and nursing professionalism in the development of an educational strategy for undergraduate nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationships between demographic variables and stress coping strategies in sample of Iranian teenage girls
Nasibe Farmani Qasabe, Gholamreza Garmaroudi, Ehsan Kazemnezhad Leyli, Hassan Farrahi
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of professional identity, psychological resilience, and coping styles in mitigating compassion fatigue among geriatric services and management interns
Li-Hong Fan, Guo-Hao Wang, Jin-Mei Lei, Chao Shi, Li-Juan Yi
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 64: 103372. CrossRef - The Impact of Dietary Habits and Nutrition Knowledge on Harmful Alcohol Use and Nicotine Dependence Among Medical Students: A Single-Center, Cross-Sectional Study
Aureliusz Andrzej Kosendiak, Bartosz Bogusz Adamczak, Zofia Kuźnik, Szymon Makles, Weronika Hariasz
Nutrients.2025; 17(11): 1788. CrossRef - Cerrahi Klinik Uygulamasına Çıkan Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinde Klinik Stres Düzeyi ve Etkileyen Faktörler
Tuğba Çam Yanık, Canan Kanat, Merve Nur Tanrıverdi, Hatice Ural
Mersin Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Lokman Hekim Tıp Tarihi ve Folklorik Tıp Dergisi.2025; 15(2): 721. CrossRef - Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Ui Rim Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 355. CrossRef - Effect of structured community-based older people education program on empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behavior among nursing students
Jing Ma, PingLei Chui, Mei Chan Chong, Jingru Yuan, Yongyan Zhu, Luyao Liu, Zhenqing Sun
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of stress on burnout among infection control nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating effects of social support and self-efficacy
Su-jin Lee, Ju-Young Park, Seo-Hyeon Kim
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of verbal violence, clinical practice stress, and coping with stress on nursing students’ major satisfaction during clinical practice
Heejung Heo, Yeoungsuk Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 190. CrossRef - Examining Students’ Experience with the Nursing Management Practicum Based on the Service Design
Yoomi Jung, Myungja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 214. CrossRef - Effects of a group poetry therapy program on stress, anxiety, ego-resilience, and psychological well-being of nursing students
Jung Hyun Park, Ji Young Kim, Hyeon Ok Kim
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2022; 41: 144. CrossRef - The mediating effect of media usage on the relationship between anxiety/fear and physician–patient trust during the COVID-19 pandemic
Yidi Chen, Jianhui Wu, Jinjin Ma, Huanya Zhu, Wenju Li, Yiqun Gan
Psychology & Health.2022; 37(7): 847. CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional Study: What Contributes to Nursing Students’ Clinical Reasoning Competence?
Soomin Hong, JuHee Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Yoonju Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(13): 6833. CrossRef
- Relationships between demographic variables and stress coping strategies in sample of Iranian teenage girls
- 3,395 View
- 154 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of Nursing Students’ Anxiety and Self-Confidence with Clinical Decision Making Scale
- Mi Yu, Young Eun, KA White, KyungJa Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):411-422. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.411
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to adapt, modify, and validate the Nursing Anxiety and Self-Confidence with Clinical Decision-Making Scale (NASC-CDM©) for Korean nursing students.
Methods Participants were 183 nursing students with clinical practice experience in two nursing colleges. The construct validity and reliability of the final Korean version of the NASC-CDM© were examined using exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses and testing of internal consistency reliability. For adaptation and modification, the instrument was translated from English to Korean. Expert review and a cross-sectional survey were used to test the instrument's validity.
Results The Korean version of the NASC-CDM© (KNASC-CDM) was composed of 23 items divided into four dimensions: (i) Listening fully and using resources to gather information; (ii) Using information to see the big picture; (iii) Knowing and acting; and (iv) Seeking information from clinical instructors. The instrument explained 60.1% of the total variance for self-confidence and 63.1% of the variance for anxiety; Cronbach's α was .93 for self-confidence and .95 for anxiety.
Conclusion The KNASC-CDM can be used to identify anxiety and self-confidence in nursing students’ clinical decision-making in Korea. However, further research should be done to test this instrument, as it is classified differently from the original NASC-CDM© version.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of a “Speak-Up” Program for Patient Safety: A Virtual Reality-Based Intervention for Nursing Students
Jeong Hee Jeong, Mi Jin Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(22): 2860. CrossRef - The relationship between clinical decision-making levels and self-efficacy levels of operating room nurses
Sedat Kaya, Gizem Kubat Bakir
Perioperative Care and Operating Room Management.2024; 37: 100416. CrossRef - Clinical decision making: validation of the nursing anxiety and self-confidence with clinical decision making scale (NASC-CDM ©) into Spanish and comparative cross-sectional study in nursing students
Daniel Medel, Tania Cemeli, Krista White, Williams Contreras-Higuera, Maria Jimenez Herrera, Alba Torné-Ruiz, Aïda Bonet, Judith Roca
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Implementation of a Mobile-Integrated Simulation for COVID-19 Nursing Practice: A Randomized Controlled Pretest–Posttest Experimental Design
Sun-Hwa Lee, Jeong-Sil Choi
Healthcare.2024; 12(4): 419. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a collaborative reflection-based debriefing strategy for simulation-based education using virtual simulations in practical nursing: A randomized controlled trial
Ji-Ah Yun, In-Soon Kang
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 81: 104170. CrossRef - Constructing a Mixed Simulation With 360° Virtual Reality and a High-Fidelity Simulator
Sun Kyung Kim, Youngho Lee, Younghye Go
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(8): 569. CrossRef - Path model on decision‐making ability of clinical nurses
Minsook Park, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(7-8): 1343. CrossRef - Achieving nursing students' clinical practice hours during the COVID‐19 pandemic: Effects of alternative and nonstandard practicum methods
Min Kyung Song, Ji‐Soo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Related to the Problem-solving Ability of Nursing Students Who Experienced Simulation Training
Ji-Won Han
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2023; 11(2): 17. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis of Nurses’ Clinical Decision Making: Implications for Korea
Sunyoung Oh, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3596. CrossRef - The Korean version of the Virtual Patient Learning System Evaluation Tool: Assessment of reliability and validity
Hae Jeong An, Jung Suk Choi, Min Roh, Hyun Mi Cho, Eun Ju Choi
Nurse Education Today.2021; 106: 105093. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of a “Speak-Up” Program for Patient Safety: A Virtual Reality-Based Intervention for Nursing Students
- 2,994 View
- 89 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- A Structural Model on the Nursing Competencies of Nursing Simulation Learners
- Soo Jin Park, Eun Sun Ji
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):588-600. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.588
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test a model of nursing competencies of nursing simulation learners. The conceptual model was based on the theory of Jeffries's simulaton theory.
Methods Data collection was conducted in October 2017 for 310 students from two nursing universities in Kyungbuk area for 20 days. Data analysis methods were covariance structure analysis using SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 22.0 statistical programs.
Results The hypothetical model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were comparative fit index=.97, normed fit index=.94, Tucker-Lewis Index=.97, root mean square error of approximation=.44, and standardized root mean square residual=.04. Teacher factors were directly related to simulation design characteristics, and it was confirmed that the curriculum, classroom operation and teaching method of the instructors were important factors. Learner factors were found to have a direct effect on nursing competence, self-confidence, and clinical performance that belong to nursing capacity. In particular, the results of this study indicate that the simulation design characteristics have a partial mediating effect on learner factors and clinical performance, and a complete mediating effect on learner factors and clinical judgment ability.
Conclusion In order to improve the learner's clinical performance and clinical judgment ability, it is necessary to conduct practical training through nursing simulation besides preparing the learner and the educator.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Care Simulation Learning Module on Nursing Knowledge, Clinical Competence, Team Psychological Safety, and Learning Satisfaction in Nursing Students
MinHee Jo, SungJung Hong
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 95. CrossRef - The mediating role of flow in the relationship between simulation design and simulation educational satisfaction in korean nursing students: a cross-sectional study
Eun-Kyung Lee, Eun-Joo Ji
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Students’ Self-confidence in Simulation Learning Based on National League for Nursing/Jeffries Simulation Framework
Jung-Suk Kim
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2024; 12(1): 73. CrossRef - The Development and Evaluation of the Online Respiratory Infectious Disease Nursing Simulation Course for Nursing Students
Jisu Lee, Hye Won Yoon
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2023; 11(2): 91. CrossRef - Does a preterm labor-assessment algorithm improve preterm labor-related knowledge, clinical practice confidence, and educational satisfaction?: a quasi-experimental study
Hee-Young Choi, Jeung-Im Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(3): 219. CrossRef - Relationship between Simulation Design Characteristics and Clinical Reasoning Competence: Multiple Additive Moderating Effects of Teaching Effectiveness and Students' Anxiety on Nursing Students
Kyung-In Cheon, Hea Kung Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(4): 322. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Leukemia Nursing Simulation Based on Clinical Reasoning
Aeri Jang, Miok Song, Suhyun Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4190. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Learning Outcomes according to the Integration Sequences of S-PBL in Nursing Students: Randomized Crossover Design
So Young Yun, Ja Yun Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 92. CrossRef
- The Effect of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Care Simulation Learning Module on Nursing Knowledge, Clinical Competence, Team Psychological Safety, and Learning Satisfaction in Nursing Students
- 1,908 View
- 76 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effects of Communication Empowerment Program Based on Situated Learning Theory for Nursing Students
- Soo Jin Kim, Boyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):708-719. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.708
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to examine the effects of a communication empowerment program based on situated learning theory for nursing students.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The study participants were 61 nursing students (31 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group) from G city. Data were collected from November 3, 2015 to December 10, 2015. The experimental group received eight sessions of the program, which were scheduled twice a week, with each session lasting two hours. The data were analyzed using chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, and an independent t-test using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results There were significant increases in self-efficacy for communication (t=2.62,
p =.011), emotional intelligence (t=2.66,p =.010), and interpersonal communication competence (t=2.87,p =.006) in the experimental group compared to the control group.Conclusion Based on the findings, our study suggests a need to include content from communication curricula or clinical communication training programs for improving undergraduate nursing students’ communication skills in practice settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Virtual reality education for preventing safety incidents in pediatric hospital settings: Quasi-experimental design pre-post-testing
Raim Hyeon, Won-Oak Oh
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 80: 56. CrossRef - Gamification as a Tool for Understanding Mental Disorders in Nursing Students: Qualitative Study
Pablo Del Pozo-Herce, Alberto Tovar-Reinoso, Eva García Carpintero-Blas, Ana Casaux Huertas, Regina Ruiz de Viñaspre-Hernández, Antonio Martínez-Sabater, Elena Chover-Sierra, Marta Rodríguez-García, Raul Juarez-Vela
JMIR Nursing.2025; 8: e71921. CrossRef - Therapeutic Communication Using Mirroring Interventions in Nursing Education: A Mixed Methods Study
Seung Hee Lee, Hye Jin Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(5): 435. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of Patient-Centered Care Tool: For Outpatients
Yeo Ju Kim, Gunjeong Lee, Sunyeob Choi
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1525. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a neonatal intensive care unit medication safety simulation for nursing students in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study
Mi Seon Son, Minyoung Yim, Eun Sun Ji
Child Health Nursing Research.2022; 28(4): 259. CrossRef - Patient handover education programme based on situated learning theory for nursing students in clinical practice
Jung Hee Kim, Jong Mi Lim, Eun Man Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Situation-Based Flipped Learning and Gamification as Combined Methodologies in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Haeran Kim, Boyoung Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 644. CrossRef - Cyberbullying in the University Setting. Relationship With Emotional Problems and Adaptation to the University
María Carmen Martínez-Monteagudo, Beatriz Delgado, José Manuel García-Fernández, Cecilia Ruíz-Esteban
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Virtual reality education for preventing safety incidents in pediatric hospital settings: Quasi-experimental design pre-post-testing
- 2,039 View
- 31 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Development and Psychometric Testing of the Clinical Nursing Competency Scale for Clinical Preceptor Use (CNCS-CP)
- Eunmi Kwak, Heeyoung Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):419-431. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.419
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and establish the psychometric properties of a clinical nursing competency evaluation tool to be utilized by clinical preceptors.
Methods The initial items were identified through in-depth literature review and field interviews based on a hybrid model. Content validation of the items was evaluated through three rounds of content validity testing. Participants were 34 clinical preceptors and 443 nursing students participating in clinical practice. Data were analyzed using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, convergence and discriminant validity, internal consistency and inter-rater reliability.
Results The final scale consisted of 23 items and four factors, fundamental nursing skills performance, critical thinking skills based on the nursing process, basic nursing knowledge, and professional attitude; these factor explained 69.7% of the total variance. The analysis with multi-trait/multi-item matrix correlation coefficients yielded 100.0% and 95.7 % convergence and discriminant validity, respectively. Cronbach's alpha for the total items was .95. The four subscale model tested by confirmatory factor analysis was satisfactory. Inter-rater reliability ranged from .912 to .967.
Conclusion This scale was found to be a reliable and valid instrument that clinical preceptors can apply for evaluating the clinical nursing competency of nursing students in clinical settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on the Perception of Non-Cognitive Skills Education according to the Type of Clinical Training Institution in Optometry
Se-Hoon Jung
Journal of Korean Ophthalmic Optics Society.2025; 30(2): 109. CrossRef - Core dimensions and measurement characteristics of multidimensional nursing competency assessment instruments: A systematic review
Lianfeng Wang, Junlin Chen, Othman Talib
Journal of Professional Nursing.2025; 61: 96. CrossRef - Evaluation and Analysis of English Teaching Ability Based on Nonlinear Random Matrix Model
Jianliang Zhou, Huixin Zhou, Zaoli Yang
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Development of Core Competency Scale for clinical nursing student educators
Hyun Sook Park, Eun Hee Choi, Gyung Duck Kim, Young Hee Kim, Mi Yang Jeon, Hyenam Hwang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 345. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Self-Efficacy Scale for Nursing Educators’ Role in Sri Lanka
Shyamamala S. Weerasekara, Jina Oh, Haeryun Cho, Mihae Im
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 7773. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Practice Satisfaction on Major Satisfaction Based on the Survey of Satisfaction of Clinical Laboratory Science Students on Clinical Practice
Kyung A Shin, Hyo Shin Kim, Sun Kyung Lee
The Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2019; 51(2): 252. CrossRef
- A Study on the Perception of Non-Cognitive Skills Education according to the Type of Clinical Training Institution in Optometry
- 1,689 View
- 61 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Threats to Identity: A Grounded Theory Approach on Student Nurses’ Experience of Incivility during Clinical Placement
- Jiyeon Kang, Yeon Jin Jeong, Kyoung Ran Kong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):85-95. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.85
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This qualitative study aimed to explore the experience of incivility among nursing students.
Methods Sixteen nursing students who had experienced incivility during their clinical placement were invited for one-on-one interviews until the point of theoretical saturation. The grounded theory approach of Corbin and Strauss was adopted to analyze transcribed interview contents.
Results Incivility occurred in the context of a hierarchical organizational culture, due to nursing students’ position as outsiders, non-systematic clinical education, and poor nursing work environment. The experience of incivility was identified as “being mistreated as a marginal person,” and nursing students responded to this phenomenon in the following three steps: reality shock, passive action, and submissive acceptance. This process caused students to lose self-esteem and undergo role conflict. Furthermore, nursing students’ experience of incivility could eventually lead to workplace bullying in nurses.
Conclusion The results of this study suggest that nursing students’ experience of incivility can be a process that threatens their identity. It is necessary to develop educational programs and provide appropriate counseling services so that nursing students can actively cope with the incivility. In addition, institutional plans are needed to ensure safe and supportive clinical learning environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Turkish Validity and Reliability of the Nursing Students' Rights Awareness Scale in Clinical Practice
Elif Sözeri Öztürk, Tuğba Karataş
Journal of Nursology.2025; 28(1): 20. CrossRef - Exploring relationships among workplace incivility, organizational commitment, work engagement and job burnout in Vietnamese primary schools
Quan H.N. Tran
Industrial and Commercial Training.2025; 57(4): 345. CrossRef - Systemic antecedents of academic incivility in nursing: An integrative review
Justin Fontenot, Michael Hebert, Robbie Stefanski, Dawn Morris
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2024; 19(2): 192. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perception of Injustice in Clinical Practice
Hye Young Cho, Kyoung Ah Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 433. CrossRef - A structural model of nursing students’ performing communication skills
Cho Rong Gil, Kyung Mi Sung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 148. CrossRef - The effect of verbal violence, clinical practice stress, and coping with stress on nursing students’ major satisfaction during clinical practice
Heejung Heo, Yeoungsuk Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 190. CrossRef - Nursing students' rights in clinical practice in South Korea: a hybrid concept-analysis study
Sunghee Park, Mi-Young Choi
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(4): 260. CrossRef - Effects of a Nonviolent Communication-Based Empathy Education Program for Nursing Students: A Quasi-Experimental Pilot Study
Jieun Sung, Youngran Kweon
Nursing Reports.2022; 12(4): 824. CrossRef - Impact of incivility and psychological capital on nursing students’ transition shock
Chung Hee Woo, Chanhee Kim
Collegian.2022; 29(5): 621. CrossRef - The influence of nursing students’ perfectionism tendency and perception of instructor caring on incivility experienced by nursing students
Eun Nam Lee, Na Geong Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 436. CrossRef - The influence of experienced violence and the clinical learning environment on vocational identity in nursing students
Mira Lee, Hee Ok Park, Insook Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 321. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Nursing Students’ Rights Awareness Scale in Clinical Practice: A Scale Development Study
Sung-Hee Park, Mi-Young Choi
Healthcare.2021; 9(10): 1323. CrossRef - Effects of clinical practice stress and moral sensitivity on clinical competency in nursing students
Yeoungsuk Song, Joon-Young Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(2): 157. CrossRef - Radiotherapy students’ perceptions of support provided by clinical supervisors
L. Armstrong-James, R. N. M. Khine, R. J. Thorne, M. J. E. Tuckey, C. Bennett
Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice.2020; 19(1): 15. CrossRef - Experiences of Perception of Nursing Students' Rights in Clinical Practice
Sunghee Park, Hyeyoung Cho
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(4): 471. CrossRef - Interventions for coping with bullying need further investigation and should be built into nursing curricula
Jiyeon Kang
Evidence Based Nursing.2018; 21(3): 70. CrossRef - Educating our future generation-The role of nurse managers in encouraging civility
Annamaria Bagnasco, Giuseppe Aleo, Fiona Timmins, Gianluca Catania, Milko Zanini, Loredana Sasso
Journal of Nursing Management.2018; 26(8): 899. CrossRef - “Loving Nursing” and “Taking Responsibility”: Strategies for Transitioning to Practice in Lebanon
Michael Clinton, Sawsan Ezzeddine, Myrna Doumit, Ursula Rizk, Murielle Madi
Sage Open.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Turkish Validity and Reliability of the Nursing Students' Rights Awareness Scale in Clinical Practice
- 2,153 View
- 60 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version Scale of the Clinical Learning Environment, Supervision and Nurse Teacher Evaluation Scale (CLES+T)
- Sun-Hee Kim, So Yeon Yoo, Yae Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):70-84. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.70
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher evaluation scale (CLES+T) that measures the clinical learning environment and the conditions associated with supervision and nurse teachers.
Methods The English CLES+T was translated into Korean with forward and back translation. Survey data were collected from 434 nursing students who had more than four days of clinical practice in Korean hospitals. Internal consistency reliability and construct validity using confirmatory and exploratory factor analysis were conducted. SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 22.0 programs were used for data analysis.
Results The exploratory factor analysis revealed seven factors for the thirty three-item scale. Confirmatory factor analysis supported good convergent and discriminant validities. The Cronbach's alpha for the overall scale was .94 and for the seven subscales ranged from .78 to .94.
Conclusion The findings suggest that the 33-items Korean CLES+T is an appropriate instrument to measure Korean nursing students'clinical learning environment with good validity and reliability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research progress of measuring tools for nursing students’ clinical learning environment
Yun Xu, Qing Wang, Qi Wei
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Learning Environment, Supervision, and Nurse Teacher Evaluation (CLES + T) Scale: Saudi Arabic Version—A Cross‐Sectional Validation Study of Nursing Interns and Students
Naif Hamdi Alanazi, Martin Cerveny
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing career identity in relation to the clinical practice learning environment, satisfaction, and stress among nursing students in the Republic of Korea: a comparative survey
Se Young Im, Min Ha Park, Hyeon Seok Kang, Sung Min Cho, Hye Won Lim, Myung Kyung Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of the Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students
Seoyoung Yoon, Hye-Ah Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 340. CrossRef - Personal Factors and Clinical Learning Environment as Predictors of Nursing Students' Readiness for Practice: A Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
Taewha Lee, Su Jeong Lee, Yea Seul Yoon, Hyunju Ji, Sookhee Yoon, SangA Lee, Yoonjung Ji
Asian Nursing Research.2023; 17(1): 44. CrossRef - Clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher (CLES+T) scale: Translation and validation of the Arabic version
Khadija Guejdad, Ali Ikrou, Camilla Strandell-Laine, Redouane Abouqal, Jihane Belayachi
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 63: 103374. CrossRef - The clinical learning environment, supervision and future intention to work as a nurse in nursing students: a cross-sectional and descriptive study
Juxia Zhang, Linda Shields, Bin Ma, Yuhuan Yin, Jiancheng Wang, Rong Zhang, Xueke Hui
BMC Medical Education.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of the Nursing Profession Self-Efficacy Scale: A Methodological Study
Jina Oh, Haeryun Cho, Yae Young Kim, So Yeon Yoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 1080. CrossRef - Are Traditional and Simulated Clinical Environments Meeting Nursing Students’ Learning Needs?
Kim Leighton, Suzan Kardong-Edgren, Gregory E. Gilbert
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2021; 59: 85. CrossRef - Clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher scale (CLES+T): Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version
Rong Zhao, Lu Xiao, Roger Watson, Yanhua Chen
Nurse Education Today.2021; 106: 105058. CrossRef - Testing the measurement invariance of the Korean clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher (CLES+t) scale
Sun-Hee Kim, Yae Young Kim, So Yeon Yoo
Nurse Education Today.2021; 107: 105140. CrossRef - Exploratory Factor Analysis of the Indonesian Version of the Clinical Learning Environment, Supervision, and Nurse Teacher Scale (CLES + T)
Christine L. Sommers, Ian Ruddy Mambu, Lisa McKenna, Sonia Reisenhofer, Julie McCaughan
Journal of Nursing Measurement.2021; 29(1): E39. CrossRef - The Clinical Learning Environment, Supervision and the Nurse Teacher Evaluation Scale: Turkish Version
Emine Iyigun, Sevinc Tastan, Hatice Ayhan, Berrin Pazar, Yasemin Eda Tekin, Halise Coskun, Mikko Saarikoski
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural Model of Professional Socialization of Nursing Students With Clinical Practice Experience
Soo-yeon Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Journal of Nursing Education.2020; 59(3): 133. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of a Korean Version of Nursing Student Perceptions of Dishonesty Scale
Hee-Yeong Woo, Jeongwon Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(2): 176. CrossRef - Nursing Students' Practice Experience on Community Visiting Nursing
Jae-Hyun Ha, Jeong-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(1): 43. CrossRef - The clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher scale (CLES+T): psychometric properties measured in the context of postgraduate nursing education
Dorota Ozga, Aleksandra Gutysz-Wojnicka, Bogumił Lewandowski, Beata Dobrowolska
BMC Nursing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating clinical placements in Saudi Arabia with the CLES+T scale
Norah A. Al-Anazi, Dalyal Alosaimi, Isabelita Pandaan, Denis Anthony, Sue Dyson
Nurse Education in Practice.2019; 39: 11. CrossRef
- Research progress of measuring tools for nursing students’ clinical learning environment
- 2,686 View
- 82 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Premenstrual Coping in University Students: Based on Biopsychosocial Model
- Myung-Ock Chae, Hae Ok Jeon, Ahrin Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):257-266. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.257
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aims of this study were to construct a hypothetical structural model which explains premenstrual coping in university students and to test the fitness with collected data.
Methods Participants were 206 unmarried women university students from 3 universities in A and B cities. Data were collected from March 29 until April 30, 2016 using self-report structured questionnaires and were analyzed using IBM SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 18.0.
Results Physiological factor was identified as a significant predictor of premenstrual syndrome (t=6.45,
p <.001). This model explained 22.1% of the variance in premenstrual syndrome. Psychological factors (t=-2.49,p =.013) and premenstrual syndrome (t=8.17, p<.001) were identified as significant predictors of premenstrual coping. Also this model explained 30.9% of the variance in premenstrual coping in university students. A physiological factors directly influenced premenstrual syndrome (β=.41,p =.012). Premenstrual syndrome (β=.55,p =.005) and physiological factor (β=.23,p =.015) had significant total effects on premenstrual coping. Physiological factor did not have a direct influence on premenstrual coping, but indirectly affected it (β=.22,p =.007). Psychological factors did not have an indirect or total effect on premenstrual coping, but directly affected it (β=-.17,p =.036).Conclusion These findings suggest that strategies to control physiological factors such as menstrual pain should be helpful to improve premenstrual syndrome symptoms. When developing a program to improve premenstrual coping ability and quality of menstrual related health, it is important to consider psychological factors including perceived stress and menstrual attitude and premenstrual syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of coping behaviors and premenstrual syndrome among university students
Özlem Akın, Nülüfer Erbil
Current Psychology.2024; 43(2): 1685. CrossRef - Investigating influencing factors on premenstrual syndrome (PMS) among female college students
Su Jeong Yi, Miok Kim, Ina Park
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Sleep Pattern, Stress, Menstrual Attitude, and Behavior That Reduces Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals on Premenstrual Syndrome in Adolescents
Hye Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Haeyoung Min
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 423. CrossRef
- Investigation of coping behaviors and premenstrual syndrome among university students
- 1,418 View
- 30 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Smoking Cessation Intention in Male Technical High School Students
- Eun Su Do, Eunsuk Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):211-221. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.211
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop and test a structural model on smoking cessation intention in technical high school men. The conceptual model was based on the theory of reasoned action and health promotion model.
Methods From May 29 to April 13, 2015, 413 technical high school students who smoked completed a structured questionnaire. Data were analyzed to calculate the direct and indirect effects of factors affecting smoking cessation intention. The SPSS WIN 20.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs were used.
Results The hypothetical model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were χ2/df=2.36, GFI=.95, AGFI=.92, NFI=0.97, and RMSEA=.05. Self-esteem had direct and indirect effects on smoking cessation intention. Attitude, subjective norm, and self-efficacy had direct effects on smoking cessation intention. Smoking knowledge and environmental factor had indirect effects on smoking cessation intention. This model explained 87.0% of the variance in smoking cessation intention.
Conclusion These results indicate that technical high school students' intention to stop smoking can be improved through an increase in self-esteem, negative environmental factors, attitude toward smoking cessation, subjective norm about smoking cessation, and self-efficacy for smoking cessation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Modelo de Nola Pender para promoção da saúde do adolescente
Daniela Bulcão Santi, Iara Sescon Nogueira, Vanessa Denardi Antoniassi Baldissera
REME-Revista Mineira de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Integrated Change Model-based Smoking Cessation Program for High School Students
Hae Seon Lee, Su Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(2): 195. CrossRef - The Structural Equation Model of Intention to Discontinue Drinking Highly Caffeinated Beverage of Undergraduate Students
Kyu Eun Lee, Yunsoo Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2020; 26(1): 35. CrossRef
- Modelo de Nola Pender para promoção da saúde do adolescente
- 1,089 View
- 14 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A Study into Pattern of Smoking Behavior of University Students
- Moon Sil Kim, Ae Kyoung Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):843-856. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.843
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to explore the subjective opinions related to of smoking behavior of university students with a history of smoking. The research period was from Feb, 1. 1996 to Sep. 10. 1997. The research method used was Q-methodology. The process of the research was as follows : 1. Collection of concourse : The statement of self-reference was derived from fact to face interviews with 50 university students. Statement were categorized by researcher according to semantics. 2. Extraction of Q-sample 38 of the self-reference statements from the 32 categories of the Q-population were selected. 3. Selection of P-sample : 30 of university students were selected by consideration of diversity in sociodemographic background. 4. Based on a 1 to 9 point scale, the selected university students were made to participate in Q-sorting. 5. Analysis of Q-type was obtained by use of the QUANAL program. The results of this study revealed as follows : There are three types of smoking behavior of Korean university students. 1. The first type focused on the right of the individual to smoke and the lack of recognition of smoking behavior as a health hazard. 2. The second type cared about smoking behavior as a hazard to health. 3. The third type was habitual smoker. They are bored and smoke habitually. It is suggested that the results of this study may contribute to the development of strategies for the purpose of decreasing the incidence of smoking of university students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health Promotion Behavior of Chinese International Students in Korea Including Acculturation Factors: A Structural Equation Model
Sun Jung Kim, Il Young Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 25. CrossRef
- Health Promotion Behavior of Chinese International Students in Korea Including Acculturation Factors: A Structural Equation Model
- 541 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study of Factors Influencing Drug Use in High School Students
- So Young Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):777-786. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.777
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to examine the conditions of drug use and the find the main factors that lead students to start and select drugs in their circumstances. The "other drugs" in this study means analgesics, hypnotics, stimulants, tranqualizers, and drinks including caffeine. The sample was 1,900 students and 1,412 responses were analyzed. Variables in the study included prescription provision by parents, drug use by friends, attitudes to drugs, drinking and smoking activities, and poly drug use. Analysis of the data was done using descriptive statistics, chi square, and to find the determinants on other drug use, multiple logistic regression was performed. Data were analysed by SAS/PC programs. Of the subjects 86.6% of the students have had experienced with alcohol and 49.8% of them continue to use it, and 37.9% of the students have had experienced with smoking and 22.1% of them continue to smoke. The rates of using other drugs were as followed; analgesic 33.3%, hypnotics 4.3%, sedatives 4.4%, stimulants 8.7%, and 242 students have had experienced with more than two different kinds of drugs of the same time including alcohol and smoking. With the exception of alcohol and smoking, 126 students were continuing to use more than two different kinds of drugs. And 2.3 kinds of drugs were the average that the being used at the same time by poly drug users, alcohol and smoking excepting. In conclusion, the determinants of other drug use can be summarized as ploy drug use, drug use by friends, obedience to drug prescription of parents, and time of first using drugs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Age group characteristics of children who visited the emergency department with acute poisoning by ingestion
Weon Seon Ryu, Jea Yeon Choi, Jin Seong Cho, Yong Su Lim, Sung Youl Hyun, Hyuk Jun Yang
Pediatric Emergency Medicine Journal.2018; 5(1): 5. CrossRef
- Age group characteristics of children who visited the emergency department with acute poisoning by ingestion
- 668 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Prevention Stages for Sexually Transmitted Diseases of College Students
- Soon Bok Chang
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):423-432. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.423
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This is a descriptive study to understand the preventive stage for STDs to provide a basis for sex education for college students. The colleges were selected by quota sampling in five representative cities in Korea, but the1,691 college students were selected by convenient sampling in the cities nationwide, and the data were collected by self-reporting using questionnaire consisting of 33 items. The results were as follows : 1. Their mean ages were 21.8 for female and 23.3 for male students, 2. 78.0% of the males and 46.5% of the females permitted premarital sex, 57.1% of male and 10.3% of female college students had experienced sexual intercourse, 7.1% of males and 2.4% of females had experienced pregnancy, 10.3% of males and 3.4% of females had been infected with STDs, 72.1% of male and 13.8% of female didn't use condoms at the time of infection. 3. Most of the factors related to STDs infection, such as drinking, smoking, frequency of sexual intercourse, pregnancy, knowledge of STDs, the score of STDs prevention were statistically higher in the male student group than in the female group. 4. The student's mean score of knowledge about STDs was similar between the male group(7.80)and the female group(7.84) with a possible score range from 0-18. 5. Only fifteen percent of male and 9.6% of female students expressed that they will do something to prevent STD. 6. The group having the experience of sexual intercourse(t=3.924, P=.048) and the group of having experience of contracting STDs(t=16.638, P=.000) had shown statistically higher STDs prevention score than the group not having that kind of experience, but the group not having experience with pregnancy didn't show any difference from the group not having experience with pregnancy. Considering that 57.1% of males and 10.3% of females had sexual intercourse experience, 78% of male and 46.5% of female permitted premarital sex, 10.3% of male and 3.4% of female had been infected with STDs. It could be concluded that the college students were ignorant about the prevention of STDs and had unrealistic stage of the STDs prevention. Therefore, enforcement of education for the prevention of STDs including the dynamics of the sexual intercourse and STDs infection is needed.
- 483 View
- 2 Download

- Determinants of Health Promoting Lifestyle of College Students
- Mi Ra Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):156-168. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was undertaken in order to examine the relationship of self-efficacy, control, perceived health status, self-esteem, social support, and demographic characteristics to health promoting lifestyle of college students, and to determine factors affecting health promoting lifestyle of college students. The subjects were 92 students of one university in Taejon. The instruments used for this study were a survey of general characteristics, health promoting lifestyle(44 items), self-efficacy (28 items), self-esteem(10 items), control(8 items), perceived health status( 1 item), and social support(12 items) Analysis of data was done by use of mean, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient and stepwise regression with SAS program. The results of this study are as follows. 1) The average item score for the health promoting lifestyles was low at 2.30. n the sub-categories, the highest degree of performance was interpersonal support(2.90), and the lowest degree was exercise(1.67). 2) Male students showed a significant higher score in exercise subscale than female students. Students who had more income had higher scores in self actualization subscale. Students who's family had experienced severe disease had higher scores in health responsibility and interpersonal support subscale. Students who had experienced exercise had higher scores interpersonal support, and stress management subscale. 3) Significant correlation between perceived health status and self-efficacy, perceived health status and self-esteem, control and self-efficacy, control and self-esteem, control and social support, self-esteem and self-efficacy was found. 4) Self-efficacy and control revealed significant correlations with total health promoting lifestyle and all subscales of health promoting lifestyle except self actualization. A significant correlation between perceived health status and self actualization subscale was found. Self-esteem revealed significant correlations only with self actualization and interpersonal support subscale. 5) Significant correlations were found between most of the subscales of total health promoting lifestyle. 6) Self-efficacy was the highest factor predicting health promoting lifestyles of college students (30.55%). Self-efficacy and control accounted for 36.55% in health promoting lifestyle of college students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health Promotion Behavior of Chinese International Students in Korea Including Acculturation Factors: A Structural Equation Model
Sun Jung Kim, Il Young Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 25. CrossRef - Effects of a Health Education Program based on Social Cognitive Theory on the Health Promotion of University Students with Metabolic Syndrome
Hee-Gerl Kim, Jinhwa Lee, Jiyun Kim, Hyunju Park, Hyun Sook Oh, Won Jae Lee, Eun Aae Kim, Hye Kyung Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(4): 451. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Promotion Lifestyles and Self-esteem of Korean and Chinese Nursing Students.
Hee Cho, Suk Jeong Lee, Ren Shan Cui
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(1): 22. CrossRef - The Relations among ADL, Self-efficacy, Physical Activity and Cognitive Function in Korean Elders
Myoung Ja Wang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 101. CrossRef - HEALTH-PROMOTING BEHAVIORS OF Older Adults Compared to Young and Middle-Aged Adults in Korea
Mee Ock Gu, Young Eun
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2002; 28(5): 46. CrossRef
- Health Promotion Behavior of Chinese International Students in Korea Including Acculturation Factors: A Structural Equation Model
- 737 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Social Support, Stressful Life Events, and Health Behaviors of Korean Undergraduate Students
- Young Joo Park, Sook Ja Lee, Ka Sil Oh, Kyoung Ok Oh, Jeong Ah Kim, Hee Soon Kim, Sang Soon Choi, Sung Eun Yi, Choo Ja Chung, Hoa Yun Jun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):792-802. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.792
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This cross-sectional study was designed to explore the relationship among social support, experienced stressful life events and health behaviors of Korean undergraduate students, and validate the mediator effect of social support. METHOD: One thousand four hundred fifty-three undergraduate students were randomly selected from five universities located in the middle area of Korea. RESULT: The health behaviors of Korean undergraduates tend to have unhealthy patterns. In the case of the students living without family, experiencing more stressful life events and perceiving lower social support, health behaviors are poor. The relationship between perceived social supports, the frequency of the experienced stressful life events and the score of health behavior patterns is statistically significant. After controlling the effect of social support, the correlation coefficient between the frequency of experienced stressful life events and the score of health behavior patterns was slightly lower. The score of health behaviors between the group with an extremely high score of social support and the group with an extremely low score were statistically significantly different. CONCLUSION: Future studies need to be pursued to develop various strategies such as a health education programs and counseling programs for health maintenance and health promotion of undergraduates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Affecting the Eating Behavior Disorders of Korean College Students
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim, Gisoo Shin
The Open Nursing Journal.2021; 15(1): 55. CrossRef - Relationship between Health Literacy and Self-care Behavior in Patients with Stomach Cancer after Gastrectomy: Mediating Effects of Subjective Health Status and Specific Self-efficacy
Min Jung Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 259. CrossRef - Cultural fit of emotions and health implications: A psychosocial resources model
Jiah Yoo, Yuri Miyamoto
Social and Personality Psychology Compass.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - What Causes Health Promotion Behaviors in College Students?
Mi Young Kim, Yu Jeong Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2018; 12(1): 106. CrossRef - The Sugars Intake through Processed Foods and Its Related Factors in College Students
Eun Kyung Shin, Young Taek Doo
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2016; 41(2): 85. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behavior, Stress and Stress Coping Type between Undergraduate Nursing Students and Female Students in Other Majors
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2015; 21(1): 28. CrossRef - A Relevance on Health Perception, Health Knowledge and Health Promotion Behavior of the University students
Sun-Jung KIm, Eun-Young Jung
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(8): 5394. CrossRef - An Influencing Health Promoting Behavior of Perceived Health Status and Self-Efficacy according to major of college students
Hee-Joo Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(2): 989. CrossRef - Influence of Negative Emotion on the Suicidal Ideation in University Student: Mediated Moderating Effect of Explosive Behavior through Gender
Goo-Churl Jeong
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(12): 775. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promotion Behaviors of College Students
Hwanhui Sim, Misook Kim, Kyeongsook Jeong, Jeeun Heo, Eunjung Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(3): 97. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Depression of Korean Female University Students
Kyung-Sook Lee, Chin-Kang Koh, Joo Hyun Kim, Haeng-Mi Son, Mi Ryeong Song, Su Jeong Yu, Kyung Sook Cho
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(2): 112. CrossRef - Depression Cognition and Health Promoting Behaviors of Smoking and Non-smoking College Students
Mi-Ok Kim, Mi Yu, Se-Jin Ju, Kyeong-Suk Kim, Jung-Hyun Choi, Hee-Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(3): 35. CrossRef
- Factors Affecting the Eating Behavior Disorders of Korean College Students
- 964 View
- 2 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Self-Directedness in Learning of Nursing Students
- Won Oak Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):684-693. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.684
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was conducted to detect the correlations and the main factors influencing self-directedness in learning of nursing students. METHOD: The samples were composed of 224 nurse students who were from three nursing department in Seoul, Chungnam and Kyunbook. The reliability of 4 instruments was tested with Cronbach's alpha from .63 to .86. The data was analyzed using a SAS program for descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation coefficients and stepwise multiple regression. RESULT: The results were as follows: 1. The mean self-directedness score was 91.23 which was slightly high. The self-directedness in learning was influenced significantly by grade, perception of self-level, self-study in majoring and self-study except for majoring(F= 3.33-7.14, p<.05). 2. There were significant correlations between all the predictive variables and the self-directedness(r=.27-48, p<.01). 3. Stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that 35% of the self-directedness in learning of nursing students were significantly explained by self-esteem(23%), locus of control(6%), self-study except for majoring(2 kind, 2%), self study in majoring(good, 2%), and self-study except for majoring( above 3 kind, 2%). CONCLUSION: Based upon these findings, sociopsychological variables like self-esteem and locus of control are very important factor influencing self-directedness in learning of nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effectiveness of using situational awareness and case-based seminars in a comprehensive nursing skill practice course for undergraduate nursing students: a quasi-experimental study
Yuanhao Sun, Xiangdong Li, Haiyang Liu, Yuqing Li, Jiaofeng Gui, Xiaoyun Zhang, Xiaoping Li, Lu Sun, Lin Zhang, Congzhi Wang, Jing Li, Mingming Liu, Dongmei Zhang, Jingyi Gao, Xuefeng Kang, Yunxiao Lei, Ting Yuan
BMC Medical Education.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between optimism, emotional intelligence, and academic resilience of nursing students: the mediating effect of self-directed learning competency
Eun Hee Hwang, Kon Hee Kim
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The self-directed learning readiness of access to HE students at City College Plymouth, United Kingdom
Cyril Mbeau‐ache, Brian Banks, Chris Ford
Journal of Adult and Continuing Education.2022; 28(2): 449. CrossRef - Self-Directed Learning versus Problem-Based Learning in Korean Nurse Education: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Jaehee Jeon, Sihyun Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(12): 1763. CrossRef - A Study on the Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of Self-directed Learning Instrument
Eun Mi Kwak, Joo Young Lee, Jin Ju Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(1): 12. CrossRef - The Effects of Clinical Convergence Self-directedness Practice Learning Program on Self-directedness and Competency in Fundamental Nursing Skills in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Jihyun Park
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(4): 51. CrossRef - A Study on the Level of Awareness and the Current Performance Level of Self-directed Learning in Nursing Students
Jeong Ah Kim, Moonhae Bae, Ja-kyung Ko
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(12): 621. CrossRef - Influence of Self-directed Learning Ability and Creativity on College Adjustment in Nursing Students
Hyeon-Sook Park, Kyung-Soon Jeong
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 549. CrossRef - Academic Achievement, Self-directed Learning, and Critical Thinking Disposition According to Learning Styles of Nursing Students
Sun-Hee Yang, Eun-Ho Ha, Og-Cheol Lee, In-Ok Sim, Young-Mi Park, Hyun-A Nam, Jeong-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(3): 334. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Self-directed Learning of Students at Clinical Practice Course for Advanced Practice Nurse
Miyoung Kim, Seong-Yeon Park
Asian Nursing Research.2011; 5(1): 48. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Problem Solving Abilities of Freshmen Nursing Students
Yun Min Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(2): 190. CrossRef - Effects of Teaching Method using Standardized Patients on Nursing Competence in Subcutaneous Injection, Self-Directed Learning Readiness, and Problem Solving Ability
Mi-Ran Eom, Hyun-Sook Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Kayeon Seong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 151. CrossRef
- The effectiveness of using situational awareness and case-based seminars in a comprehensive nursing skill practice course for undergraduate nursing students: a quasi-experimental study
- 979 View
- 7 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Korean Nursing Students' Experience of Ethical Problems and Use of Ethical Decision-Making Models
- Sung Suk Han, Hyeoun Ae Park, Sung Hee Ahn, Miriam E Cameron, Hyo Sook Oh, Kyeong Uoon Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(5):846-857. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.5.846
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was conducted to study on 1) What is nursing students' experience of ethical problems involving nursing practice? 2) What is nursing students' experience of using ethical decision-making models?
METHOD
In order to answer these two questions, we selected 97 senior baccalaureate nursing students from two Korean universities using a conceptual framework and method of content analysis.
RESULT
From 97 ethical problems emerged five content categories, the largest being ethical problems involving health professionals (69%); the basic nature of the nursing students' experience of ethical problems consisted of conflict, resolution, and rationale; 94% of the students stated that using an ethical decision-making model was helpful.
CONCLUSION
Although additional research is needed, these findings have important implications for nursing ethics education and practice.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences of Ethical Issues and Needs for Ethics Education in Clinical Nurses
Ja Hyun Shin, Seok Hee Jeong, Myung Ha Lee, Youngran Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(3): 327. CrossRef - The Effects of Debate Classes based on an Ethical Decision-Making Model on Ethical Knowledge, Class Satisfaction, and Ethical Values
Chang-Hee Kim, Sun-Young Jeong
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(10): 405. CrossRef - A Study of Moral Judgment and Ethical Decision Making and Ethical Dilemmas Experienced in Practice by Nursing Students
Yoon Goo Noh, Myun Sook Jung
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(6): 2915. CrossRef - Hospital Nurses' Experience of Do-Not-Resuscitate in Korea
Myungsun Yi, Sang Eun Oh, Eun Ok Choi, In Gak Kwon, Sungbok Kwon, Kyung-mi Cho, Youngah Kang, Jeonghui Ok
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 298. CrossRef - Korean Nursing Students’ Ethical Problems and Ethical Decision Making
Hyeoun-Ae Park, Miriam E Cameron, Sung-Suk Han, Sung-Hee Ahn, Hyo-Sook Oh, Kyeong-Uoon Kim
Nursing Ethics.2003; 10(6): 638. CrossRef - Legal and ethical issues: our best ethical and spiritual values
Miriam E Cameron
Journal of Professional Nursing.2003; 19(3): 117. CrossRef
- Experiences of Ethical Issues and Needs for Ethics Education in Clinical Nurses
- 918 View
- 7 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Factors that Influence Nursing Image Perceived by College Students
- Kyung Ae Park, Mi Ryung Song
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(4):584-597. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.4.584
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF No Abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Introduction of nursing and Bioethics subject on Nurse Image and Nursing Professionalism of Freshmen Nursing Students
Kwuy-Im Jung, Kyung-Soo Lee, Ha-Yun Jung
Journal of Korean Clinical Health Science.2016; 4(4): 689. CrossRef - Effects of Work Intensity and Physical Discomfort on Job Satisfaction in Clinical Nurses
Hyojin Kim, Soonjoo Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(4): 362. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Nurse Images Perceived by Nursing Students
Sun-Jung Park, Byung-Jun Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(6): 3696. CrossRef - High School Boys' Images of Men as Nurses
Hwee Wee, Youngrye Park, Mi Seung Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2013; 20(2): 118. CrossRef - Changes in the Image of Nursing in First Year Nursing Students after History & Philosophy of Nursing Courses
Sang Dol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(3): 301. CrossRef
- Effects of a Introduction of nursing and Bioethics subject on Nurse Image and Nursing Professionalism of Freshmen Nursing Students
- 728 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Nursing Student's Methods of Learning
- Myung Ok Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1521-1530. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1521
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This descriptive study identifies nursing students' methods of studying related to the learning stages, based on a sample of 251 nursing students in a Korean university. The main findings of the study are as follows. The major learning styles of nursing students were accomodation (68.6%), divergen (53.6%), and convergence (38.8%) for the first, second, third, and fourth year group. For all students, the majority (71.3%) showed accomodation or the divergence. The learning styles for grade level were significantly different, (x2=110.021, df=9, p=0.001). The stage of concrete experience was the majority for all of the first year group (51.8%), the second year group (57.1%), and the third year group (61.3%). But, active experimentation (41.9%) was the majority for the fourth year group. Also there were significant differences between the stages of learning by age (x22= 64.391, df=9, p=0.001). The most significant result of the study was the establishment of different modes of learning stages by year, thus supporting the experiential learning theory. The greatest change of style from the first year group to the second year group was reflective observation (7.3%-->12.9%). That from the second year group to the third year group was the abstractive conceptualization (14.3%-->21.3%); and that from the third year group to the fourth year group was active experimentation (12.0%-->41.9%). This reflects the same cycle as indicated by the experimental learning theory of Kolb. According to the study, nursing students' learning stages tended to be more unbalanced as year increases. Therefore this calls for a careful review of the current nursing curriculum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Different outcomes of active and reflective students in problem-based learning
Yera Hur, Sun Kim
Medical Teacher.2007; 29(1): e18. CrossRef
- Different outcomes of active and reflective students in problem-based learning
- 644 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of Exercise Program on Fatigue, Perceived Health State, Exercise-related Affect, Perceived benefits, and Self-Efficacy: From the samples of female college students
- Eun Sook Choi, Mi Ra Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1254-1262. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1254
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of 6-wk low intensity exercise program on fatigue, perceived health state, exercise-related affect, perceived benefits, and exercise self-efficacy for female college student's. The subjects of the study consisted of thirty-four female college students. The research subjects were assigned to experimental and control group. The experimental group participated in 13-17 and 30-60 minute sesseions of exercise program over 6 weeks. Data analysis was done by t-test with SAS program. The results of this study are as follows. 1) The first hypothesis, "The fatigue of experimental group will be lower than control group", was supported. 2) The second hypothesis, "The perceived health state of experimental group will be higher than control group", was not supported. 3) The third hypothesis, "The exercise-related affect of experimental group will be higher than control group", was not supported. 4) The fourth hypothesis, "The benefits of exercise of experimental group will be higher than control group", was not supported. 5) The fifth hypothesis, "The self-efficacy for exercise of experimental group will be higher than control group", was supported.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Health Education Program based on Social Cognitive Theory on the Health Promotion of University Students with Metabolic Syndrome
Hee-Gerl Kim, Jinhwa Lee, Jiyun Kim, Hyunju Park, Hyun Sook Oh, Won Jae Lee, Eun Aae Kim, Hye Kyung Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(4): 451. CrossRef
- Effects of a Health Education Program based on Social Cognitive Theory on the Health Promotion of University Students with Metabolic Syndrome
- 585 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Relationship of Perceived Stress, Ways of Coping, and Stress Response of Nursing Students
- Na Sun Ha, Kuem Sun Han, Jung Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):358-368. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.358
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This was designed to identify the relationship of perceived stress, ways of coping, and stress response in student nurses. The subjects of this study were 320 student nurses from two universities and three junior colleges located in Seoul. The data were collected from November 28 to December 10, 1997 by a questionnaire survey method. The instruments for this study were the perceived stress scale developed by Levenstein(1993), ways of coping scale developed by Lazarus and Folkman(1984), and the stress response scale developed by Choi(1991). The data were analyzed by SAS program, using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation coefficient, and ANOVA. The results are summarized as follows : 1. The mean score for the level of perceived stress was 2.55. 2. The mean score for the level of problem oriented coping was 1.61 and the mean score for the level of emotional oriented coping was 1.37. 3. The mean score for the level of stress response was 3.74. Stress was classified into nine factors and the order of scoring for the most frequent was; assignments(3.98), as a nurse(3.97), interpersonal relationship(3.88). 4. The relationship between perceived stress and stress response revealed a positive significant correlation(r=0.23, p=0.0001). 5. The relationship between emotional oriented coping and stress response revealed a positive significant correlation(r=0.22, p=0.0001). 6. The relationship between perceived stress and emotional oriented coping revealed a positive significant correlations(r=0.13, p=0.020). In conclusion, this study revealed that the level of perceived stress and ways of coping were important factors influencing the stress response of student nurses. Therefore, in consideration of perceived stress, ways of coping should be included in the development of a stress management program for student nurses. Further research with an expanded area and subjects is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Smartphone Addiction and Intolerance of Uncertainty on Mental Health in Nursing Students: Mediating Effects of Resilience
Jeong Mi Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(3): 296. CrossRef - The Relationship of Communication Competence, Professional Self-Concept and Stress in Clinical Practice of Nursing Students
Min-Ah Kang, Soo-Kyoung Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(4): 452. CrossRef - Impact of Nursing Students' Emotional Labor on Burnout during Nursing Practice in a Hospital: Moderating Effect of Emotional Intelligence
So-Young Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 77. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Leadership and Stress Coping on College Life Adjustment in Nursing Students
Hyo-Jin Won
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(1): 123. CrossRef - The Relationship between Anxiety, Anger and Fatigue among Stress factor of Nursing Students in Clinical Practice
San-Young Han, Young-Mee Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(2): 554. CrossRef - An Analysis Study on stress factor of Emergency medical Students during preparing Examination for Korea Registered licence
Ji-Yeon Jung, Jong-Geun Yun, Jin-Hwan Oh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(1): 194. CrossRef - Experience on Delivery Room Practice of Male Nursing Students
Ok Bun Jung, Hyun Joo Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(1): 64. CrossRef
- Effects of Smartphone Addiction and Intolerance of Uncertainty on Mental Health in Nursing Students: Mediating Effects of Resilience
- 880 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Nursing Students' Perceptions on Diet and as Environmental Factors Related to Cancer Risk Factors
- Hae Kyung Lee, Seong Joo Cheon, Mi Hye Hwang, Soon Rim Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):193-200. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify how students majoring in nursing perceive cause of cancers and the effects of diet for preventing cancers. Data for the study were collected by 651 nursing students, who were registered in the second and third year in three technical colleges and third and fourth year in two universities. The research instruments included items on general characteristics of subjects, items about the degree of perception of the frequency of cancer onset and items on the perception of mortality, risk factors, preventive diets, knowledge, and high risk factor for cancer in specific body areas. The findings of this study are as follows : 1. Almost all subjects(92.8%) reported that the frequency of cancer onset increases and that it is 93.9% for people over 40. Degree of perception about cancer mortality was low at 33.0%. 2. As far as the perception of risk factors for cancer onset was concerned, smoking, stress, heredity, family history, and alcohol were rated high, over 80.0%. Risk factor in clouding, virus, hormones, pesticides were rated as low. 3. As to the perception of risk factor for body area as associated with diet salted and scorched food were rated at 44.5% for stomach cancer, alcohol, 50.4% for liver cancer, smoking, 72.8% for lung cancer, pregnancy times, 25.3%, and marriage age, 23.0% for uterine cancer, and no delivery experience, 40% for breast cancer. 4. The knowledge score for cancer was between 12 and 36, with a mean score of 26.75(SD=4.13). There was a statistically significant difference between experience in caring for cancer patients during clinical practice and knowledge score(t=3.09, p=.002).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Cancer Risk Perception and Cancer Related Health Behavior in College Students
Gye Young Shin, Mee Kyoung Joo
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 137. CrossRef
- Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
- 712 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Comparison of Stress Levels of Elementary Students by Geographical Regions
- Chung Yul Lee, Gyu Young Lee, Yang Heui Ahn, Hyeon Kyeong Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):986-993. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.986
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare stress levels of elementary students according to three regional levels: a large city, a medium-sized city, and a rural area.
Methods This was a descriptive comparative survey using a convenience sample of 1,161 5th-and 6th-grade students. The stress level was measured by a stress scale that consisted of 65 items regarding personal characteristics, family, school, and peer factors. The data were analyzed by χ2-test, t-test, ANOVA and multiple regression using the SPSS 10.0 statistical program.
Results Overall, the mean stress scores reported by the participants were near the middle of a 5-point scale and the level of familyrelated stress was highest, followed by peer, school, and individual-related stress. Sixth-graders and female students showed higher stress levels than 5th-graders and male students, respectively. The participants reporting unsatisfaction with their lives and those living in large cities tended to have significantly higher stress levels.
Conclusion Grade, gender, life satisfaction, and regional levels were all significant factors associated with high stress levels among elementary students. Development of stress management programs for this specific population, especially targeting students who are female and living in large cities, is needed.
- 518 View
- 1 Download

- Development of a Critical Thinking Disposition Scale for Nursing Students
- In Soo Kwon, Ga Eon Lee, Gyung Duck Kim, Young Hee Kim, Kyung Min Park, Hyun Sook Park, Sue Kyung Sohn, Woo Sook Lee, Keum Seong Jang, Bok Yae Chung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(6):950-958. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.6.950
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a critical thinking disposition scale for nursing students.
Method The developmental process was construction of a conceptual framework, development of preliminary items, verification of content validity, development of secondary items, verification of construct validity and extraction of final items. The conceptual framework and first preliminary 60 items were obtained through a review of relevant literature and the development of critical disposition scales by 10 researchers who had been studying critical thinking for one year. These items were reviewed by five specialists for content validity and finally 55 items were chosen. The data was collected from October 1 to 15, 2004 and was analyzed using factor analysis and Cronbach's alpha with the SPSS program. The subjects were composed of 560 Bachelor of Science nursing students from 8 nursing schools.
Result There were 35 final items which were sorted into 8 factors. The factors were identified as ‘ intellectual integrity(6 items)’, ‘ creativity(4 items)’, ‘ challenge(6 items)’, ‘ open-mindedness(3 items)’, ‘ prudence(4 items)’, ‘ objectivity(4 items)’, ‘ truth seeking(3 items)’ and ‘ inquisitiveness(5 items)’. The cumulative percent of variance was 55.107%. The reliability of the scale, Cronbach's alpha was .892 and the factors' ranged from .562-.836.
Conclusion The result of this study could be used for measuring critical thinking dispositions of nursing students. However, for further validity and reliability, repeated research is necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influences of New Graduate Nurses’ Fatigue, Critical Thinking, and Nursing Work Environment on Patient Safety Nursing Behaviors
Myojeong Kim, Yujeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2026; 32(1): 49. CrossRef - From film to simulation: Mixed-methods study of learner-driven artificial intelligence-generated ethical dilemma scenarios and role-play to enhance ethical competence in nursing students
Bo Yeon Hwang, Mi Yu
Nurse Education in Practice.2026; 92: 104773. CrossRef - Influence of Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Reasoning Competence, and Nursing Practice Environment on Medication Safety Competence of Hospital Nurses
Jeong An Oh, Eun A Kim, Hae Ran Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(5): 542. CrossRef - Teaching and interconnecting research and evidence-based practice in midwifery and nursing education: A mixed methods systematic review
Elina Leiviska, Sally Pezaro, Rosie Kneafsey, Luca Morini, Alun DeWinter
Nurse Education Today.2025; 150: 106701. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Evidence-Based Practice Implementation Among Nurses in Psychiatric–Mental Health Hospitals
Moonhee Gang, Yujin Ahn, Donghyeon Gwak
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Effects of Flipped Learning Utilizing Digital Literacy on Critical Thinking and Self-directed Learning in Nursing Students in Korea: A Quasi-experimental Study
Minjae Lee, Insoon Kang, Seung-Bin Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(3): 342. CrossRef - The influence of final-year undergraduate nursing students’ participation in simulation on their critical thinking: A mixed methods systematic review
Kate Harry, Beth Pierce, Elizabeth Forster
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 89: 104617. CrossRef - Effectiveness of an Evidence-Based Practice Education Program for Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Dain Jeong, Chang Park, Keiko Sugimoto, Miyang Jeon, Dooyoung Kim, Young Eun
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2024; 21(5): 637. CrossRef - Development of an infection control competency scale for clinical nurses: an instrument design study
Yong Hwan Hyeon, Kyoung Ja Moon
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing triage accuracy in emergency nurses: The impact of a game-based triage educational app
Sun-Hee Moon, Su Ol Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2024; 72: 101398. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Adult Nursing Education Programs Using Virtual Reality Simulations
Eunju Lee, Gyuli Baek
Healthcare.2024; 12(13): 1313. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Leadership in Pharmacy Students: A Nationwide Survey
Hye Kyung Jin, Eunyoung Kim
Journal of Healthcare Leadership.2024; Volume 16: 213. CrossRef - Association between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture, Willingness to Report Near Misses, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Nursing Care Activities for Patient Safety
Da Eun Lee, Bo Gyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 283. CrossRef - Validity assessment for competency development in clinical dental hygiene education based on dental hygiene process of care
Jin-Sun Choi, Sun-Jung Shin, Bo-Mi Shin, Hyo-Jin Lee, Hye-Young Yoon, Soo-Myoung Bae
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2024; 24(1): 45. CrossRef - The effectiveness of high-fidelity simulation on undergraduate nursing students' clinical reasoning-related skills: A systematic review
Fadiyah D. Alshehri, Sophie Jones, Denise Harrison
Nurse Education Today.2023; 121: 105679. CrossRef - Do IB students have higher critical thinking? A comparison of IB with national education programs
Kit S. Double, Yasmine El Masri, Joshua A. McGrane, Therese N. Hopfenbeck
Thinking Skills and Creativity.2023; 50: 101416. CrossRef - Effects of Increased Intracranial Pressure Patient Care Nursing Education Program Using Web-based Simulation
Wonjeong Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2023; 11(2): 1. CrossRef - Clinical Competence of Nurses and the Associated Factors in Public Hospitals of Gamo Zone, Southern Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Shitaye Shibiru, Zeleke Aschalew, Mekidim Kassa, Agegnehu Bante, Abera Mersha, Judie Arulappan
Nursing Research and Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Path model on decision‐making ability of clinical nurses
Minsook Park, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(7-8): 1343. CrossRef - Factors affecting nursing students' patient safety competencies
Deulle Min, Eunju Kwak, Seungmi Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(3): 259. CrossRef - The Effect of Competency-Based Triage Education Application on Emergency Nurses’ Triage Competency and Performance
Sun-Hee Moon, In-Young Cho
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 596. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Pre-clinical Research Nurse Programs of Nursing Students
Eun Hee Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(4): 322. CrossRef - The influence of critical thinking disposition, deep approaches to learning and learner-to-learner interaction on nursing process confidence in nursing students, with a focus on team-based learning
Hanna Choi, Eunseon Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 251. CrossRef - Influence of Perceived Helicopter Parenting, Critical Thinking Disposition, Cognitive Ability, and Learning Motivation on Learning Behavior among Nursing Students
Hyunjoo Oh, Haeryun Cho, So Youn Yim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 1362. CrossRef - Critical Thinking Disposition, Job Competency, and Educational Needs of Home Visiting Nurses in the Long-term Care Insurance
Keunyoung Shin, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 54. CrossRef - Effects of a transformative learning theory based debriefing in simulation: A randomized trial
Yun-Jeong Oh, Hee-Young Kang, Yeoungsuk Song, Ruth Lindquist
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 50: 102962. CrossRef - The effect of case-based learning based on flipped learning for nursing students
Min Hee Lee, Myung Sook Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 107. CrossRef - Relationship of a Team-based Learning Using Cardiac Arrest Simulation and Learning Competency in Nursing Students: Comparison of High Self-efficacy Group with Low Self-efficacy Group
Gun Ja Jang, Eun Young Lee, Hye Sook Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2020; 45(2): 208. CrossRef - Nursing student and faculty competency improvement through a nurse-bridging program in Cambodia
Chiyoung Cha, Hyeyoung Hwang, Bomi An, Sookyung Jeong, Sook Ja Yang
Nurse Education Today.2020; 93: 104523. CrossRef - Effects of an evidence-based practice education program using multifaceted interventions: a quasi-experimental study with undergraduate nursing students
Jeong Sook Kim, Mee Ock Gu, HeeKyung Chang
BMC Medical Education.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Team-based Learning using Concept Mapping on Critical Thinking Disposition and Metacognition of Nursing Students
Yeo Won Jeong, Hae Young Min
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 277. CrossRef - Effect of a Situational Module Learning Course on Critical Thinking Disposition and Metacognition in Nursing Students: A Quasi-experimental Study
Kwang Ok Park, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(2): 251. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Self-Reflection and Insight Scale for Korean Nursing Students
Mi Ok Song, Heeyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Effect of Team-based Learning using Reflection Journal on Pregnancy Nursing Course for Nursing Students
Jin Young Kim, Mi-Kyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 404. CrossRef - Quasi‐experimental study on the effectiveness of a flipped classroom for teaching adult health nursing
Esther O. Park, Ji Hyun Park
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2018; 15(2): 125. CrossRef - Effects of Critical Thinking Disposition and Empathy on Cultural Competency in Dental Hygiene Students
Ji-Min Hwang, Ji-Hyoung Han
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2018; 18(1): 24. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-efficacy, Critical Thinking Disposition, Self-leadership, and Communication Competency on the Core Competencies of the Preceptor in Advanced General Hospitals
Yun Mi Kang, Young Eun
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2018; 24(3): 279. CrossRef - Critical Thinking, Stress of Clinical Practice and Competence of Clinical Practice of the Nursing Students
Gyoo-Yeong CHO
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2018; 30(4): 1223. CrossRef - Individual and School Factors Affecting Critical Thinking Ability among Nursing Students
Sujin Shin, Inhee Park, Eunhee Hwang, Dukyoo Jung, Kon Hee Kim
Korean Medical Education Review.2018; 20(1): 44. CrossRef - The Factor Influencing Problem Solving Ability of Nursing Students in Nursing Simulation Learning
Gyoo-Yeong CHO
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2017; 29(4): 1083. CrossRef - Development of Clinical Performance Examination(CPX) using Flipped Learning
Jeong Sook PARK, Soon Yang JANG
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2017; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Factors Influencing of Evidence based Practice Competency and Evidence based Practice Readiness in General Hospital Nurses
Seang Ryu, Yun-Sook Kim, Yun Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(5): 448. CrossRef - Influence of Ego-Resilience, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Self Leadership on Career Decision-Making Self-Efficacy in Nursing Students
Kon-Hee Kim, Eun-Hee Hwang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 436. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Clinical Competence of Dental Hygienists
Hee-Su Lee, Kyeung-Ae Jang
Journal of dental hygiene science.2016; 16(5): 331. CrossRef - Factors influencing Evidence-Based Practice Attitudes among Undergraduate Nursing Students
Mi-Hyang Choi, Young-Hae Kim, Hyun-Mi Son
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(3): 274. CrossRef - Relationship among Emotional Intelligence, Critical thinking and Major satisfaction in Nursing students
Young-Soon Kim, Eun-Ju Oh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(7): 103. CrossRef - The Influence of Academic Self-efficacy, and Critical Thinking Disposition on Problem Solving Ability of Nursing Students
Yeonha Kim, Yeongah Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 589. CrossRef - The relationship among critical thinking disposition, nursing process competency and evidence-based practice competency in nurses working in hospitals
Kyoung Yun Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(2): 451. CrossRef - Relationship between Problem Solving Ability, Critical Thinking Disposition, Creativity, Self Efficacy and Nursing Process Competence of Nursing Students
Sun-Hee Yang, In-Ok Sim
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2016; 16(5): 612. CrossRef - Effect of practice education using the simulator, critical thinking, problem solving ability and nursing process confidence of nursing students
Jung-Mi Kim, Young-Sil Choi
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(4): 263. CrossRef - A Design for and Evaluation of a Critical Thinking Class for New Community Health Practitioners
Ji Yeon Park, MinGyu Seo, Hyoung Suk Kim, Kyung Hee Yoo, Kyung Ja June
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 141. CrossRef - The Effects of Team-Based Learning on Outcome based Nursing Education
Hyo-Sook Oh
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(9): 409. CrossRef - Affecting Factors on Clinical Competence of Nursing Students
Mi-Yeon Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(3): 1884. CrossRef - Affecting Factors on Stress of Clinical Practice in Nursing Students
Ae Kyong Lee, Hye Sook You, In Hyae Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(2): 154. CrossRef - The Effects of Preclinical Clinical Performance Examination on Nursing Students' Confidence in Nursing Skills and Critical Thinking Competence
Jeong Sook Park, Mi Jung Choi, Soon Yang Jang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 75. CrossRef - Self-leadership, critical thinking disposition, satisfaction of clinical practice and clinical practice competency of nursing students
Hyeon-Sook Park, Ji-Young Han
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(3): 695. CrossRef - Implementation and outcome evaluation of high-fidelity simulation scenarios to integrate cognitive and psychomotor skills for Korean nursing students
Heejung Ahn, Hyun-Young Kim
Nurse Education Today.2015; 35(5): 706. CrossRef - A Study on Interpersonal Relation Disposition, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Communication Competence in Undergraduate Students in Nursing
Narae Heo
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2015; 24(1): 22. CrossRef - Validation of Yoon's Critical Thinking Disposition Instrument
Hyunsook Shin, Chang Gi Park, Hyojin Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(4): 342. CrossRef - A literature Review (1996-2014) on Critical Thinking in Korean Nursing Education for the Era of Convergence
Na-Sun Ha, So-Young Pak, Mi-Ja Lee
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(9): 341. CrossRef - Critical Thinking Disposition, Problem Solving Process, and Simulation-Based Assessment of Clinical Competence of Nursing Students in Pediatric Nursing.
Sunghee Kim, Hyuna Nam, Miok Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(4): 294. CrossRef - Effects of Simulation based Training using a Post-operating Rehabilitation Case on Learning Outcomes
Hye Kyung Oh, Eun Young Jeon
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2014; 17(2): 90. CrossRef - Nursing students' critical thinking disposition according to academic level and satisfaction with nursing
Dong Hee Kim, Seongmi Moon, Eun Jung Kim, Young-Ju Kim, Sunhee Lee
Nurse Education Today.2014; 34(1): 78. CrossRef - Multiple intelligences and critical thinking disposition in nursing students*
Eunhee Hwang, Su Jin Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(4): 433. CrossRef - Critical Thinking Disposition and Problem-Solving Ability of Dental Hygiene Students
Ji-Hee Kim, Hee-Kyung Sung, Hye-Jin Kim
Journal of dental hygiene science.2014; 14(3): 356. CrossRef - Comparison of Blended Practicum Combined E-learning between Cooperative and Individual Learning on Learning Outcomes
Soon Hee Choi, Hyang Sook So, Ja Yun Choi, Sung Hee Yoo, So Young Yun, Myung Hee Kim, Mi Ok Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(2): 341. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Clinical Competence in Nursing Students
Eun Su Do, Young Sook Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(3): 283. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Evidence-Based Practice Readiness for Tertiary General Hospital Nurses
Jeong-Sook Kim, Mee-Ock Gu, Sun-Yon Jo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(6): 2945. CrossRef - Affecting Factors on Clinical Competence of Nursing Students
Hee-Jung Jang, Youn-Kyoung Kwag
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(9): 4380. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Clinical Critical Thinking Skills Scale
Su-Jin Shin, Eunbae Yang, Byunghea Kong, Dukyoo Jung
Korean Medical Education Review.2012; 14(2): 102. CrossRef - Creative Ability Factors Influencing Nursing Students' Problem Solving Process
So-Young Kang, Hyun-Ju Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(3): 1122. CrossRef - Impact of Critical Thinking Disposition, General Self-Efficacy, and Leadership on Clinical Competence in Nursing Students
Jee Won Park, Chun-Ja Kim, Yong Soon Kim, Moon Sook Yoo, Hyera Yoo, Sun-Mi Chae, Jeong-Ah Ahn
Korean Journal of Medical Education.2012; 24(3): 223. CrossRef - Influence of Nurses' Performance with Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Process
Haeran Choi, Dongsook Cho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 265. CrossRef - Constructing a Questionnaire on Male Workers' Sobriety Behavior: Based on Ajzen's Theory of Planned Behavior
Inhyae Park, Younkyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 156. CrossRef - Predictors of the Clinical Competence in New Graduate Nurses
Youn-Wha Shin, Haejung Lee, Yeonjung Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(1): 37. CrossRef - Development of a Korean Risk Behavior Scale for Middle School Adolescents
Hyun Sook Park, Geum Yi Jo
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 229. CrossRef - Critical Thinking Disposition and Clinical Competence in General Hospital Nurses
Jin-Ah Park, Bog-Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 840. CrossRef
- The Influences of New Graduate Nurses’ Fatigue, Critical Thinking, and Nursing Work Environment on Patient Safety Nursing Behaviors
- 3,113 View
- 138 Download
- 77 Crossref

- Effects of Gerontological Nursing Practicum on Attitudes toward Elders with Dementia and General Elders among Korean Nursing Students
- Jung Hee Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(4):645-651. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.4.645
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study investigated changes in attitudes toward elders in general and elders with dementia after students finished a gerontological nursing practicum.
Methods Questionnaires developed for Asian cultures were administered pre practicum, immediately post practicum, and at 8-months follow up to 31 senior students in a baccalaureate nursing program. The 1-week practicum occurred at two adult day care centers: a center for elders with dementia and a center for elders with stroke. Repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni correction procedures were used to analyze data.
Results Students' evaluation of elder vitality and flexibility increased significantly at post practicum, however this increase was not sustained at follow up. Score of generosity of elders, the only positively evaluated dimension for elders in general, improved partly at post practicum. Students evaluated flexibility and generosity of elders with dementia more negatively than general elders. All of the decreased attitudes at follow up were not significantly different from those at pre practicum.
Conclusions Students had more negative attitudes toward elders with dementia. Attitudes of students in direct contact with elders with dementia were improved through the practicum regarding generosity and flexibility. However the sustainability of the immediate effect was not observed at follow up.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Educational interventions to improve student nurses’ knowledge, attitudes, or willingness to work with older people: a systematic review of quantitative findings
Xingjuan Tao, Margaret MacAndrew, Sherry Dahlke, Jeffrey I. Butler, Jo Rayner, Deirdre Fetherstonhaugh, Christina Parker
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing Students' Knowledge and Attitudes Toward Alzheimer's Disease in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jazi S Alotaibi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An analysis of nursing and medical students’ attitudes towards and knowledge of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
Asem Abdalrahim, Mohammed ALBashtawy, Abdullah Alkhawaldeh, Rasmieh M. Al-amer, Ahmad Bani Salameh, Sa’d ALBashtawy, Abdallah Abu Khait, Zaid ALBashtawy
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and Attitudes toward Dementia among Undergraduate Health Professional Students in China: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Anhong Dong, Guilan Gong, Elizabeth Reifsnider, Sha Huang, Zeyu Zhang, Jing Mao
Teaching and Learning in Medicine.2022; 34(5): 455. CrossRef - Teaching and learning about dementia care among undergraduate nursing students: A scoping review
Susana Cariñanos-Ayala, Marta Arrue, Jagoba Zarandona
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 61: 103326. CrossRef - Nursing Staff’s Knowledge and Attitudes toward Dementia: A Pilot Study from an Indian Perspective
Benedicte Sørensen Strøm, Knut Engedal, Lasse Andreassen
Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders Extra.2019; 9(3): 352. CrossRef - Student participation in a dementia-outreach research project as community-based experiential learning
Sora Choi, Myonghwa Park
Educational Gerontology.2017; 43(4): 186. CrossRef - Living as a nursing college students in Korea
Jung-ae Kim
The International Journal of Advanced Culture Technology.2016; 4(3): 20. CrossRef - Knowledge and attitudes of undergraduate nursing students toward dementia: An Indian perspective
Vijayalakshmi Poreddi, Brian D Carpenter, Sailaxmi Gandhi, Rama Chandra, Suresh BadaMath
Investigación y Educación en Enfermería.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Geriatric Nursing Education for Nursing Students' Attitude, Perception toward Dementia and Dementia Policy
Su-jin Park, Kyung-sook Park, Young-Ji Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(7): 4467. CrossRef - Nursing students' knowledge and attitudes towards dementia — A questionnaire survey
Anthony Scerri, Charles Scerri
Nurse Education Today.2013; 33(9): 962. CrossRef - The Effect of Dementia Education Program on Nursing Students
Hee-Young Kang, Myeong-Jeong Chae, Hee-Suk Seo, Kyung-Mi Yang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(1): 69. CrossRef - Student experiences in learning person‐centred care of patients with Alzheimer’s disease as perceived by nursing students and supervising nurses
Mari W Skaalvik, Hans Ketil Normann, Nils Henriksen
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2010; 19(17-18): 2639. CrossRef
- Educational interventions to improve student nurses’ knowledge, attitudes, or willingness to work with older people: a systematic review of quantitative findings
- 829 View
- 8 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effect of an Agreement on Means to Achieve Smoking Cessation Goals among College Student Smokers
- In Hee Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(7):1362-1370. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.7.1362
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the degree of attaining a smoking cessation goal when an agreement on means to achieve smoking cessation among male college student smokers was established.
Method This study was planned as a nonequivalent control group non-synchronized design and the sample was divided into an agreement group and a comparison group by convenience sampling in a college of G city. The data was analysed with SPSS Win10.0 using a Likelihood χ2-test, Odds ratio, Paired t-test and ANCOVA.
Result The theory that the degree of smoking cessation will be higher in the agreement group than the Comparison group was rejected (δ = 2.567, p = .055). The theory that nicotine dependency will be lower in the agreement group than the comparison group was supported (F = 3.965, p = .049); however, the theory that the number of cigarettes smoked per day will be lower in the agreement group than the comparison group was rejected (F = 1.342, p = .252).
Conclusion It has been shown that an agreement on means to achieve smoking cessation goals is a key factor to success in quitting smoking.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Knowledge on Cardiovascular Prevention and Nicotine Dependency among Smoking Male College Students
Seon Young Hwang, Kyongok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(2): 75. CrossRef - Effects of Smoking Cessation Education for Male College Students
Mi-Kyung Kwon, Kyung-Sook Bang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 640. CrossRef - Influence of Depression, Anxiety and Stress-Coping Aspect upon Smoking Desire of Undergraduates, according to Their Lifestyles
Sung-Sik Ahn, Chun-Sook Kim, Sung-Hwan Choi
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2012; 6(1): 205. CrossRef - Effects of a Smoking Cessation Program on Processes of Change, Situational Temptation and Decisional Balance in Male University Student Smokers
Ju-Sung Kim, Sun-Ok Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(2): 113. CrossRef
- Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 836 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Study on Nursing College Students' Subjectivity in Their Attitude Toward Jobs
- Yoon Sook Kim, Boon Han Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(4):680-685. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.4.680
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose The purpose of the study was to categorize nursing students' subjectivity in their attitude toward their jobs, and thereby understand the differences among these attitude types.
Methods The study used a Q-method to measure nursing students' attitude toward jobs identity types. In-depth and objective interviews and literature review formed Q sample. The P sample consisted of 25 nursing students.
Results The results of the study show that nursing students can be categorized into three types, depending on their attitudes toward their jobs. The firs type, “interest-oriented” students, strongly disagree to the following: giving priority to job over marriage, standing unfair treatment in the workplace, the importance of promotion opportunity, irresponsibility, and uncertainty. The “reward-oriented” students, on the other hand, strongly disagree to the following: indifference to career prospects, employment-related relocation of residence, irresponsibility, standing difficulties, and compromises with others. The third type of nursing students is the possession-oriented students, who strongly disapprove of irresponsibility, refusal to compromise with reality, standing unfair job allocation or promotion and career uncertainty.
Conclusions The study on nursing college students' attitude toward their jobs is meaningful in the following aspects: First, the study clarifies nursing college students' attitudes toward their job by categorizing it. Second, the study confirms the changing attitudes of nursing students toward jobs with the change of times and calls for proper educational programs to foster healthy career attitudes. Third, proper decision-making as regards jobs and job allocation for nurses, or their career attitudes, is beneficial to individuals, the medical industry, and society.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Q-method approach to perceptions of professional reasoning in occupational therapy undergraduates
Luis-Javier Márquez-Álvarez, José-Ignacio Calvo-Arenillas, Estíbaliz Jiménez-Arberas, Miguel-Ángel Talavera-Valverde, Ana-Isabel Souto-Gómez, Pedro Moruno-Miralles
BMC Medical Education.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Q-method approach to perceptions of professional reasoning in occupational therapy undergraduates
- 862 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Perception about Problem-based Learning in Reflective Journals among Undergraduate Nursing Students
- Seon Young Hwang, Keum Seong Jang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(1):65-76. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.1.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objective The aim of this study is to explore the variation in perceptions about problem-based learning(PBL) according to the level of academic achievement and learning attitude in the nursing students of a junior college (3-year program).
Method Students (n=39) learned the respiratory and cardiac system with seven PBL packages and group-based learning for a semester in 2002. Students were asked to write reflective journals that focused on their learning perception after an experience with each learning package. A total of 208 journals were used for analysis.
Result Students positively perceived that PBL making them increase their sense of responsibility for learning and felt satisfaction with the learning process, and had a confidence in the use of clinical nursing interventions. On the other hand, they negatively perceived that PBL was a burden because it took more time than traditional learning tasks, and they experienced an anxiety about regular tests and felt conflicts and diffidences in the learning process. The negative perceptions were expressed more often from students with a low academic achievement and low learning attitude compared to others.
Conclusion Students perceived the PBL as effective in understanding the learning concepts in the clinical practice environment. PBL need to be supplemented by feedback-based lecture and facilitative strategies for academically low-achieved students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between intrinsic motivation and learning outcomes in problem-based learning
Hye-Ryoung Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(3): 238. CrossRef - An analysis of medical students’ reflective essays in problem-based learning
Jihyun Si
Korean Journal of Medical Education.2018; 30(1): 57. CrossRef - Effect of Team-based Learning using Reflection Journal on Pregnancy Nursing Course for Nursing Students
Jin Young Kim, Mi-Kyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 404. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Self-Reflection and Insight Scale for Korean Nursing Students
Mi Ok Song, Heeyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Analysis of Students’ Reflective Journals on Medical Communication Role Plays
Young Jon Kim, Seung Hyun Lee, Hyo Hyun Yoo
Korean Medical Education Review.2017; 19(3): 169. CrossRef - Effects of Writing Reflective Journal on Meta-cognition and Problem Solving Ability in Nursing Students taking a Fundamental Nursing Skills Course Applying Blended Learning
Mi Young Jho
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(4): 430. CrossRef - Class Experience of the Students on 『Pregnancy, Delivery and Puerperium』 Nursing Course through Flipped Learning: Mixed Method Research
Byeongju Lee, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(4): 221. CrossRef - Effects of a Multicultural Education Program on the Cultural Competence, Empathy and Self-efficacy of Nursing Students
Eun-Hee Peek, Chai-Soon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 690. CrossRef - Effect of reflective journaling in team learning on the learning motivation of learners
In-Suk Park, Mi-Jeong Kim
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2012; 12(5): 849. CrossRef - An evaluation on the implementation of problem-based learning in medical education
박민정
The Journal of Curriculum Studies.2010; 28(2): 225. CrossRef - A comparison of problem-based learning and lecture-based learning in an adult health nursing course
Seon Young Hwang, Mi Ja Kim
Nurse Education Today.2006; 26(4): 315. CrossRef
- The relationship between intrinsic motivation and learning outcomes in problem-based learning
- 775 View
- 2 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Attitudes toward the Elderly among Nursing Students in Korea
- Jung Hee Kim, Gwi Ryung Son, Donna L. Algase
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(8):1499-1508. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.8.1499
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The primary purpose of this study was to reexamine underlying dimensions of attitudes toward the elderly held by undergraduate nursing students. A secondary purpose was to investigate characteristics of nursing students associated with attitudes toward elders.
Methods A survey was performed using self-report questionnaire completed by nursing students from a total of 10 nursing schools or departments each selected randomly from one province of Korea. Students' responses (N=366) were analyzed using factor analysis, correlation coefficients, t-test, and ANOVA.
Results Three attitudinal dimensions explaining 35.29% of the variance were extracted: vitality, generosity and flexibility. From a neutral point of 4.0 in the range of 1 to 7, only generosity (4.47) was evaluated positively, whereas vitality (3.31) and flexibility (2.91) were evaluated negatively. The mean scores of the vitality and generosity dimensions were significantly different by students' level of communication with the elderly, experience living with the elderly, and interest in elders or in issues related to elders. Interest in elders/elder issues was the only characteristic affecting significant mean score difference in flexibility.
Conclusion Educational process should increase students' exposure to healthy elderly to modify negative attitudes toward the elderly among nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Awareness and Attitudes of Dental Students toward Older Adults in Indonesia
Anton Rahardjo, Fakhira Hanna Safira Firdaus, Peter Andreas, Yuniardini Septorini Wimardhani, Diah Ayu Maharani
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(10): 183. CrossRef - Mapping evidence of nurses’ attitudes toward older adults in Africa: a scoping review protocol
Esther L. Wanko Keutchafo, Jane Kerr, Mary A. Jarvis, Desmond Kuupiel
Systematic Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Survey of attitude towards and understanding of the elderly amongst Chinese undergraduate medical students
Zuoyan Liu, Lihui Pu, Heng Wang, Xiuying Hu
Asian Biomedicine.2014; 8(5): 615. CrossRef
- Awareness and Attitudes of Dental Students toward Older Adults in Indonesia
- 866 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effect of Aroma Inhalation Method on Stress Responses of Nursing Students
- Mi Kyung Park, Eun Sook Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):344-351. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.344
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study is to identify the effect of aroma inhalation on stress responses (physical symptoms, levels of anxiety, perceived stresses)of nursing students.
Method This study was a quasi-experimental research using anon-equivalent pre-post design and was conducted from June 1 to June 5, 2002. The subjects consisted of 77 junior nursing students who were divided into 39 experimental group members and 38 control group members. A pretest and Post-test were conducted to measure body symptoms, the level of anxiety, and the level of perceived stress. In the experimental group, aromas were given using an aroma lamp, lavender, peppermint, rosemary and Clary-Sage. In the control group, the treatment was not administered.
Result As a result of administering aroma inhalation to nursing students, their physical symptoms decreased, their anxiety scores were low, and their perceived stress scores were low, showing that aroma inhalation could be a very effective stress management method.
Conclusion Nursing educators should play an important role in contributing to college students' physical and psychological health by helping enhance their recognition of stress management and effectively relieving their stress using essential oils.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effectiveness of aromatherapy interventions on psychological, physiological and academic outcomes in nursing and health sciences students: a meta-analysis
Seda Pehlivan, Öznur Erbay Dalli
BMC Medical Education.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Aromatherapy on Reducing Exam Anxiety in Pharmacy Students: A Double-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial
Fatemeh Mohammadpour, Ehsan Mohammadi, Saeid Eslami, Zhila Taherzadeh
Jundishapur Journal of Natural Pharmaceutical Products.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of lemon essential oil in reducing test anxiety in nursing students
Zülfinaz Özer, Neslihan Teke, Gülcan Bahcecioglu Turan, Ayşe Nefise Bahçecik
EXPLORE.2022; 18(5): 526. CrossRef - Development and Screening of Anxiolytic and Antistress activity of Novel Health Promoting Tea Fortified with Herbs
Samaresh Pal Roy, Sunil Kumar Kadiri, Rajpurohit Kirthi ParveenKumar, K.S Muralikrishna, Suchismita Bhowmik
Journal of Biologically Active Products from Nature.2022; 12(2): 146. CrossRef - Traditional Herbal Remedies Used for Managing Anxiety and Insomnia in Italy: An Ethnopharmacological Overview
Riccardo Motti, Bruna de Falco
Horticulturae.2021; 7(12): 523. CrossRef - Investigation of the Role of Complementary Medicine on Anxiety of Patients Before and After Surgery
Abed Ebrahimi, Jamshid Eslami, Isan Darvishi, Khadijeh Momeni, Marzieh Akbarzadeh
Holistic Nursing Practice.2020; 34(6): 365. CrossRef - Intranasal use of lavender and fennel decreases salivary cortisol levels and improves quality of sleep: A double-blind randomized clinical trial
Hudson Polonini, Dominique Mesquita, Julia Lanine, Eli Dijkers, Spiros Gkinis, Nádia Rezende Barbosa Raposo, Marcos Antônio Fernandes Brandão, Anderson de Oliveira Ferreira
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2020; 34: 101015. CrossRef - Effects of mindfulness meditation on anxiety, depression, stress, and mindfulness in nursing students: a meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yu-Feng Li, Wen-Xin Sun, Xiu-Jie Sun, Juan Sun, Dong-Mei Yang, Bei-Li Jia, Bin Yuan
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(1): 59. CrossRef - Health-promoting Lifestyle of Nursing Students: Using Mixed Methods Research
Hyun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(4): 414. CrossRef - The Effect of Inhaling the Aroma of Rosemary Essential Oil on the Pre-Hospital Emergency Personnel Stress and Anxiety: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Hossein Rahimi, Maryam Nakhaei, Nasim Mehrpooya, Seyedeh Masoomeh Hatami, Seyyed Abolfazl Vagharseyyedin
Modern Care Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Biofeedback Training on Stress, Stress Response and Academic Resilience of Nursing Students
Li-Hua Quan, Sungjae Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2018; 15(2): 107. CrossRef - The Convergence Study of Life Stress and Health Clinic User Satisfaction in Female Students: focused on the one women's University
Jin Hee Lee
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(5): 89. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma-Necklace Application on Perceived Stress, Symptoms of Stress and Changes in Autonomic Nervous System among Nursing Students in Clinical Training
Mi Hee Kim, Jin Il Kim, Eun Ha
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(4): 334. CrossRef - Effects of the Aroma Inhalation Method with a Roll-on on Life Stress, Salivary Cortisol and Fatigue in Nursing Student
In-Sook Kim, Seung-Ju Kang, Ja-Ok Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(12): 7214. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Inhalation Method on Test Anxiety, Stress Response and Serum Cortisol in Nursing Students
Ye-Jung Ko, Myoung-Soon Jung, Kyung-Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2013; 20(4): 410. CrossRef - Effects of Phytoncide Aromatherapy on Stress, Symptoms of Stress and Heart Rate Variability among Nursing Students
Chul-Gyu Kim, Mi-Kyoung Cho, Jin-Il Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2012; 14(4): 249. CrossRef - The effectiveness of a stress coping program based on mindfulness meditation on the stress, anxiety, and depression experienced by nursing students in Korea
Yune Sik Kang, So Young Choi, Eunjung Ryu
Nurse Education Today.2009; 29(5): 538. CrossRef - The Effects of Aromatherapy on Stress and Stress Responses in Adolescents
Ji-Yeong Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 357. CrossRef
- The effectiveness of aromatherapy interventions on psychological, physiological and academic outcomes in nursing and health sciences students: a meta-analysis
- 1,156 View
- 36 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Effects of SP-6 Acupressure on Dysmenorrhea, Cortisol, Epinephrine and Norepinephrine in the College Students
- Soon Bok Chang, Eun Mi Jun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(7):1038-1046. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.7.1038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify effects of the SP-6 acupressure on dysmenorrhea, and level of cortisol, epinephrine and norepinephrine in the college students.
Method Data were collected from May 1 to August 31, 2002. A total of 58 students from two universities participated in the study. Both groups were pretested before the intervention for three variables, the intensity of dysmenorrhea, level of cortisol, epinephrine and norepinephrine. Then, SP-6 acupressure was provided for 20 minutes for students in the experimental group. The instruments used in this study included the Visual Analogue Scale developed by Johnson(1974), Menstrual Attitudes Questionnaire Scale developed by Brooks-Gunn & Ruble(1980), and Stress scale developed by Cheun and Kim(1990).
Result There were statistically significant differences in the intensity of dysmenorrhea at the time immediately after, 30minutes after, one hour after, and two hours after the intervention. The experimental group had a lower intensity than the control group. There was a statistically significant difference in level of norepinephrine at the time 30minutes after the intervention with the experimental group.
Conclusion The SP-6 acupressure reduced the subjective perception of dysmenorrhea and the levels of norepinephrine. It was found out that the lasting period of 20 minutes of the SP-6 acupressure was two hours for college students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perimenstrüel Distresin Hafifletilmesinde Refleksolojinin Etkinliğinin İncelenmesi
Nursen BOLSOY, Ahsen ŞİRİN
Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; 4(2): 124. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Menstrual Pain, Difficulties in Daily Life, Negative Feelings and Autonomic Nervous Responses in Female College Students
Nan Young Kim, Min A Kim, So Eun Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2015; 17(2): 159. CrossRef - Effect of Heated Red Bean Pillow Application for College Women with Dysmenorrhea
Jeung-Im Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2013; 19(2): 67. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Menstrual Pain, Dysmenorrhea, and Academic Stress in Women College Students
Seung-Ok Ro, Hea-Young Lee, Jaeon Lee, Miyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(3): 356. CrossRef - Effect of the Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Dysmenorrhea of Puberty Girls
So Young Kim, Hyang Yeon Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 20. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Foot Reflexology on Stress, Fatigue and Blood Circulation in Premenopausal Middle-Aged Women
Soo Hyun Jang, Kye Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 662. CrossRef - Effects of Artemisia A. Smoke(Ssukjahun) on Menstrual Distress, Dysmenorrhea, and Prostaglandin F2α
Kwang Ok Lee, Sue Kim, Soon Bok Chang, Ji Soo Yoo
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(2): 150. CrossRef
- Perimenstrüel Distresin Hafifletilmesinde Refleksolojinin Etkinliğinin İncelenmesi
- 852 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The Lived Experience of a Student Transferring into the Nursing Program
- Kyung Rim Shin, Eun Jeong Cha, Young Hye Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(6):722-730. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.6.722
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study attempted to describe the essential structure of the lived experience of a students transferring into the nursing program.
Method The data was collected from 14 graduates and undergraduates who enrolled in nursing school as transfer students. The analysis of the data was made by phenominological analytic method suggested by Colaizzi(1978).
Result In this study, 6 essential themes were extracted: ‘ Constant anxiety of being a stranger’, ‘ Feeling of constant burden’, ‘ Thankfulness of a clinical practice group’, ‘ Being supportive with each other between transferring students’, ‘ Pleasure of studying a desired major’, ‘ Feeling the responsibility of own choice of a new major’.
Conclusion With rapidly increasing number of transferring students, the significance of this study in the field of nursing is that by understanding the transferring experience of nursing students, it describes the need of systematic and emotional support for transferring students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bridging the Gap: A Phenomenological Study of Transfer Students’ Journey into Professional Nursing
Seungeun Oh, Kyunghwa Lee, Hyungkyun Mok, Kyuhee Jo
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(2): 72. CrossRef - Students’ college life adaptation experiences in the accelerated second-degree bachelor of science in nursing program in South Korea
Hyun-Ju Lee, Nayoon Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(2): 167. CrossRef - The Experiences of Students Transferring into the Nursing Program at Local Universities
Moon-Jeong KIM, So-Hee KIM, Eun-Kyung BYUN
Journal of Fisheries and Marine Sciences Education.2016; 28(2): 366. CrossRef - Critical Thinking, Self-Concept and Stress Adaptation of Transfer Nursing Students
Hyoung Sook Park, Jung Mi Yun, Young Mi Kim, In Young Choi, Jae Hyun Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(3): 320. CrossRef
- Bridging the Gap: A Phenomenological Study of Transfer Students’ Journey into Professional Nursing
- 880 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of Debriefing Based on the Clinical Judgment Model on Simulation Based Learning Outcomes of End-of-Life Care for Nursing Students: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyung In Jeong, Ja Yun Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):842-853. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.842
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to identify effects of debriefing based on the clinical judgment model for nursing students on their knowledge, skill performance, clinical judgment, self-confidence and learner satisfaction during simulation based end-of-life care (ELC) education.
Methods Simulation based ELC education was developed in six steps as follows: selection of learning subjects and objects, development of learning tools, a trial run of simulation-based education, students’ skill training, and evaluators’ training. Forty-eight senior nursing students (25 in the experimental group and 23 in the control group) participated in the simulation-based ELC education using a high-fidelity simulator. Debriefing based on the clinical judgment was compared with the usual debriefing.
Results ANCOVA showed that there were differences in knowledge (F=4.81,
p =.034), skill performance (F=68.33,p <.001), clinical judgment (F=18.33,p <.001) and self-confidence (F=4.85,p =.033), but no difference in satisfaction (t=-0.38,p =.704) between the experimental and control groups.Conclusion This study found that debriefing based on the clinical judgement model is effective for supporting nursing students for reflecting on clinical judgment and improving their diverse competencies in complex clinical settings such as ELC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Judgment Model‐Based Critical Reflection Program for Newly Graduated Nurses: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial
Ae Ran Kim, Jeong Hee Hong, Kyeongsug Kim, Yuna Kim, Jung Min Lee, Heejin Lee, Ji Hyun Yoon, Mi Soon Kim
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(2): 234. CrossRef - Effects of a mobile simulation program for nursing delegation: A randomised controlled trial
Haena Lim, Yeojin Yi
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 83: 104283. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a simulation programme with lectures about end-of-life care using a standardised patient: a quasi-experimental study
Sunyoung Son, Deulle Min, Suhee Kim
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of the Silver Hour End-Of-Life Program for New Nurses: Based on Quint’s Model of Nursing Care for the Dying
Se Yeong Park, Jin Hwa Choi, Seung Ah Hong, Hyang Ok Choi, Sunyoung Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 421. CrossRef - Effectiveness of End-of-Life Care Debriefing for Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Sook Hyun Park, Jung Eun Lee, Yu-Jin Jung, Ha Neul Yoo, Yeon Su Kim, Young Hee Yi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 87. CrossRef - Effect of Simulation Case Complexity on Engagement During Distance Debriefing - A Randomized Controlled Trial
Cynthia J. Mosher, Perman Gochyyev, Adam Cheng, Alex Morton, Jabeen Fayyaz, Susan E. Farrell, Janice C. Palaganas
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2024; 91: 101538. CrossRef - Using Simulation to Develop Clinical Judgment in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Deborah Byrne, Stephanie Blumenfeld, Maureen Szulewski, Rita Ann Laske
Home Healthcare Now.2023; 41(2): 84. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of case video-based debriefing on a simulation of high-risk neonatal care for nursing students in South Korea: a mixed-methods study
Hyun Young Koo, Bo Ryeong Lee, Hyeran An
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Literature Review of Simulation-Based Nursing Education in Korea
Sumee Oh, Jungmin Park
Nursing Reports.2023; 13(1): 506. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Debriefing in Simulation-Based Education for Nursing Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Yeoungsuk Song, Seurk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(4): 399. CrossRef - The impact of clinical simulation with debriefing and self-regulation on academic performance in four clinical competencies of medical students
Gabriela Torres-Delgado, Ricardo Veloz Cárdenas
International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM).2022; 16(2): 613. CrossRef - The effects of neonatal resuscitation gamification program using immersive virtual reality: A quasi-experimental study
Sun-Yi Yang, Yun-Hee Oh
Nurse Education Today.2022; 117: 105464. CrossRef - Effectiveness of neonatal emergency nursing education through simulation training: Flipped learning based on Tanner’s Clinical Judgement Model
Sun‐Yi Yang
Nursing Open.2021; 8(3): 1314. CrossRef - Effectiveness of self-re-learning using video recordings of advanced life support on nursing students’ knowledge, self-efficacy, and skills performance
Kyeongmin Jang, Sung Hwan Kim, Ja Young Oh, Ji Yeon Mun
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Debriefing for Meaningful Learning-based simulation training on high-risk neonatal care: A randomized controlled simulation study
Sun-Yi Yang, Yun-Hee Oh
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2021; 61: 42. CrossRef - Development of a Clinical Judgment Measurement Model-Based Simulation Module for Ileus: A Mixed-Methods Study
Aeri Jang, Suhyun Kim, Mi Ok Song
Journal of Nursing Education.2020; 59(7): 382. CrossRef
- Clinical Judgment Model‐Based Critical Reflection Program for Newly Graduated Nurses: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial
- 3,244 View
- 47 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Effects of Bullying Experience on Psychological Well-Being Mediated by Conflict Management Styles and Psychological Empowerment among Nursing Students in Clinical Placement: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach
- Liping Ren, Hyunli Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):700-711. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.700
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to test a proposed structural equation model in which bullying experience, conflict management styles and psychological empowerment predict psychological well-being among Chinese nursing students in clinical placement.
Methods Three hundred and sixty-six nursing students recruited from five hospitals in J city and Y city were assessed with self-report questionnaires on bullying experience, conflict management styles, psychological empowerment and psychological well-being including depression, self-esteem, and academic major satisfaction. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 20.0 and AMOS version 22.0.
Results The evaluation parameters included the comparative fit index at .90, the goodness of fit index at .93, the root mean square error of approximation at .07, and c2/df ratio at 2.66, indicating that the proposed structural equation model provided a good fit to the data. Experience of being bullied during clinical placement, conflict management styles and psychological empowerment explained 93.0% of the variance and had significant effects on psychological well-being, with conflict management styles and psychological empowerment mediating the association between bullying and psychological well-being.
Conclusion The findings indicated that mediation by conflict management styles and psychological empowerment alleviated the negative influence of bullying on psychological well-being. To limit bullying and its negative effects, development of effective guidelines to deal with bullying will be a critical tool for both Chinese nursing students and their instructors. Further research should incorporate conflict management styles and psychological empowerment into the specific intervention strategies for handling bullying behaviors among nursing students and staff nurses and promoting nursing students’ psychological well-being.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bullying among nursing university students: Prevalence, characteristics, and public health implications
Fatema Alajaimi, Mohammed Al-Badi, Hoor Alhabsi, Maria AL Azri, Shahd Al-Ghawi, Maryam Alwahaibi, Sanjay Jaju, Nasar Alwahaibi, Somayeh Hessam
PLOS Global Public Health.2026; 6(1): e0005814. CrossRef - Social Anxiety Among Bullying Victims: A Case Study on the Role of Assertive Behavior and Self Regulation
Susi Adiawaty
Sinergi International Journal of Psychology.2025; 3(2): 97. CrossRef - Serial Multiple Mediation of Depressive Symptoms, Thwarted Belongingness, and Perceived Burdensomeness in the Relationship Between Personality Traits and Suicidal Ideation Among Nursing Students: A Cross-sectional Questionnaire Survey
Liping Ren, Sukhee Ahn
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(3): 247. CrossRef - Association Between Organizational Bullying, Moral Distress, and Disengagement Among Emergency Department Nurses in Ilam Hospitals: A Cross Sectional Study
Laya Besharaty, Alun C. Jackson, Zahra Rahmaty, Mohammad Namazi Nia, Fatemeh Bahramnezhad, Younjae Oh
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relation Between Psychological Empowerment and Academic Performance Among AL Ahsa Nursing Students
Marwa Abd Elfatah Ahmed Zewiel, Yasmin Ragab Saber Ahmed, Jehan Alrashed, Raghad AlKhalifah, Fatimah Alkhamis, Ghayda Alomran, Shahad Alali, Muzen Alsubaie, Basma Mahmoud Abd Elhamid Dawood, Shashank Kaushik
Nursing Forum.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of bullying and lateral violence against nursing students by clinical teachers: A scoping review
Flavio Gheri, Leonardo Ceccanti, Fabio Donnarumma, Domenica Petta
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of bullying behaviours among nursing students in Sierra Leone: a qualitative exploratory study
Jedidah Olayinka Johnson, Suzanna Anwagwa, Francess Yaata Kamara
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of self-confidence, academic achievement, intention to leave school and conflict management styles of nursing students
Hande Yeşilbaş, Filiz Kantek, Tangül Aytur Özen
Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 15(3): 350. CrossRef - Latent Profile Analysis of AI Literacy and Trust in Mathematics Teachers and Their Relations with AI Dependency and 21st-Century Skills
Tommy Tanu Wijaya, Qingchun Yu, Yiming Cao, Yahan He, Frederick K. S. Leung
Behavioral Sciences.2024; 14(11): 1008. CrossRef - Bullying in Nursing Students: A Cross-Sectional Study
Lidia Fernández-Gutiérrez, Maria-Pilar Mosteiro-Díaz, Elisabete Borges, Sara Franco-Correia
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2024; 21(11): 1431. CrossRef - Global prevalence of bullying and associated factors among nursing students during clinical practice: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jing Zhou, Yuqiang Wang, Qinglin Zeng, Yanli Zeng, Qin Liu, Shiliang Tan, Haiju Gang
Nurse Education Today.2024; 133: 106090. CrossRef - Co-worker incivility and task performance: The mediating effect of psychological empowerment
Emmanuel Ejiroghene Aruoren, Mohammed Igemohia, Fidelia Igemohia
Corporate Governance and Organizational Behavior Review.2024; 8(2, special): 285. CrossRef - The mediating role of academic support perception in the relationship between emotional intelligence and bullying behaviours in clinical practice: A cross-sectional study
Yi Huang, Dan Chen, Chaofeng Li, Yingying Fan, Yuwei Wu
Nurse Education Today.2024; 135: 106129. CrossRef - Prevalence, associated factors, and nursing practice-related outcomes of workplace violence towards nursing students in clinical practice: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xianying Lu, Chaoming Hou, Dingxi Bai, Jing Yang, Jiali He, Xiaoyan Gong, Mingjin Cai, Wei Wang, Jing Gao
Nurse Education Today.2024; 133: 106074. CrossRef - The Prevalence and Gender Differences of Bullying and Cyberbullying Victimization Among University Students in Jordan
Ayat Awawdeh, Jehad A. Rababah, Mohammed Munther Al-Hammouri, Ahlam Al-Natour, Shaher H. Hamaideh
Violence and Gender.2023; 10(3): 159. CrossRef - Serial multiple mediation of psychological empowerment and job burnout in the relationship between workplace bullying and turnover intention among Chinese novice nurses
Liping Ren, Hyunli Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(6): 3687. CrossRef - Nursing students’ experiences of unprofessional behaviours and associations with guideline compliance: A multicenter survey
Ilana Livshiz-Riven, Nancy Hurvitz, Keren Grinberg, Ofra Halperin, Ahuva Spitz, Michal Itzhaki, Orli Grinstein Cohen, Ayala Blau, Tomer Ziv-Baran, Johanna Westbrook, Rachel Urwin, Ling Li, Sivia Barnoy, Sima Reicher
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 71: 103739. CrossRef - Student nurses' experiences of workplace violence: A mixed methods systematic review and meta-analysis
Nutmeg Hallett, Alison Gayton, Rachel Dickenson, Maria Franckel, Geoffrey L. Dickens
Nurse Education Today.2023; 128: 105845. CrossRef - Incivility experiences and mental health among college nursing students: The moderating role of rumination
Shaoping Qiu, Jie Fan, Naizhu Huang
Journal of Psychology in Africa.2022; 32(5): 514. CrossRef - Postgraduate and undergraduate student nurses' well-being: A scoping review
I. Gede Juanamasta, Yupin Aungsuroch, Joko Gunawan, Mary L. Fisher
Journal of Professional Nursing.2022; 40: 57. CrossRef - Construction and Evaluation of College Students’ Psychological Quality Evaluation Model Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process
Wei Shi, Yanqiong Li
Journal of Sensors.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Structural and psychological empowerment and its influencing factors among nursing students in Oman
Arcalyd Rose R. Cayaban, Glenn Ford D. Valdez, Michael L. Leocadio, Jonas P. Cruz, Cyruz P. Tuppal, Leodoro J. Labrague, Jestoni Maniago, Frincy Francis
Journal of Professional Nursing.2022; 39: 76. CrossRef - The impact of bullying on the mental health and academic achievement of nursing students
Enas M. Abdelaziz, Hana M. Abu‐Snieneh
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(2): 623. CrossRef - Nursing students' experiences of violence and aggression: A mixed-methods study
Nutmeg Hallett, Chris Wagstaff, Tony Barlow
Nurse Education Today.2021; 105: 105024. CrossRef - Bullying in nursing students: A integrative literature review
Lidia Fernández‐Gutiérrez, Maria‐Pilar Mosteiro‐Díaz
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(4): 821. CrossRef - Workplace bullying, personality traits and health among hospital nurses: The mediating effect of social support
Li Fang, Li‐Ping Hsiao, Shu‐Hui Fang, Bao‐Chen Chen
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(23-24): 3590. CrossRef - Speaking Up Against Hierarchy: A Simulation Geared Towards Nursing Students
Celina Da Silva, Eva Peisachovich, Charles K Anyinam, Sue Coffey, Leslie Graham, Farideh Tavangar
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Student nurses' bullying, social support and their health status during clinical practicum programmes
Li Fang, Ching‐Lin Fang, Shu‐Hui Fang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding roles in health care through interprofessional educational experiences
Susan Furr, Susan Hayes Lane, Dana Martin, Dana E Brackney
British Journal of Nursing.2020; 29(6): 364. CrossRef - Impact of Psychological Empowerment on Workplace Bullying and Intent to Leave
Debra Hampton, Mary Kay Rayens
JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration.2019; 49(4): 179. CrossRef - Nursing Professional Development Anti-Bullying Project
Sonia Maria Balevre, Park S. Balevre, David J. Chesire
Journal for Nurses in Professional Development.2018; 34(5): 277. CrossRef
- Bullying among nursing university students: Prevalence, characteristics, and public health implications
- 1,642 View
- 35 Download
- 31 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Peer Group Caring Interaction Scale-Korean Version
- Jeong-Hee Kim, Moon Yeon Kong, Yun Hee Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):431-442. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.431
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This paper was conducted to validate the Korean version of the Peer Group Caring Interaction Scale (PGCIS-K) that measures caring behaviors as experienced by nursing students.
Methods Translation of the PGCIS-K was validated through forward-backward translation methods. Survey data were collected from 218 nursing students in a nursing school. Construct validity and criterion-related validity were evaluated. Internal consistency and the Guttman split-half coefficient were calculated to assess reliability.
Results The PGIS-K showed reliability except for 4 items (Cronbach's α=.91, Guttman split-half coefficient=.85), which were low (<.30) or negatively correlated with the total scale. A 12-item reduced form of the PGCIS-K was developed by item-analysis and construct validity evidence. Factor loading for the 12 items on 2 factors ranged from .47~.82, which explained 58.4% of the total variance. Two factors were named 'modeling and assistance (Cronbach's α=.87)' and 'communication and sharing (Cronbach's α=.82)'. Convergent validity, discriminant validity, and criterion validity were supported according to the correlation coefficients of the 2 factors with other measure.
Conclusion The findings suggest preliminary evidence that the 12-item PGCIS-K can be used to measure nursing students' peer group caring interactions in Korea. Additional studies are recommended to continue the psychometric evaluation of this scale. Also, it can be extended to measure graduate nursing students or staff nurses' peer group caring interaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Peer caring and clinical adaptation as mediators between emotional intelligence and nursing professionalism in students
SeolHwa Moon, Sun Young You, Juyeon Oh
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2025; 20(4): e1149. CrossRef - Hospital organisational health as a mediator between positive nursing organisational culture, caring behaviour, and quality of nursing care
Bo Ram Ku, Mi Yu
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A structural model of nursing students’ performing communication skills
Cho Rong Gil, Kyung Mi Sung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 148. CrossRef - Adapting and Validating the COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy and Vaccine Conspiracy Beliefs Scales in Korea
Hyesung Ock, Mihyeon Seong, Insook Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(11): 2274. CrossRef - Influence of Nurse Manager and Peer Group Caring Behaviors as Perceived by Nurses on Organizational Socialization and Nursing Performance
Na Yeon Shin, Soyoung Yu, Seong Suk Kang, Seung Shin Lee, Min Jeung Park, DaeYeon Lee, Sun Mi Nam
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(2): 110. CrossRef - A Review of the Korean Nursing Research Literature with Focus on Quantitative Measurement of Caring
Jeong-Hee Kim, Young Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(2): 155. CrossRef - Influence of Nurse Manager and Peer Group Caring Behaviors as Perceived by Nurses on Intention to Retention
Moon Yeon Kong, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(2): 191. CrossRef
- Peer caring and clinical adaptation as mediators between emotional intelligence and nursing professionalism in students
- 1,305 View
- 21 Download
- 7 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


