Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development and evaluation of the Trauma-nursing Education and Skill Support program to enhance trauma nursing competencies: a quasi-experimental study
- Tae Yeong Yang, Myung Jin Jang, Ki Ung Kim, Min So, Mi Na Choi, Eun Jung Lee, Jin Su Jo, Ji Yun Lee, Kwang Kyun Lim, Kyoung Mi Kim, Hae Jun Baek, Sun Ho Wang, Jin Oh Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):67-80. Published online February 24, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
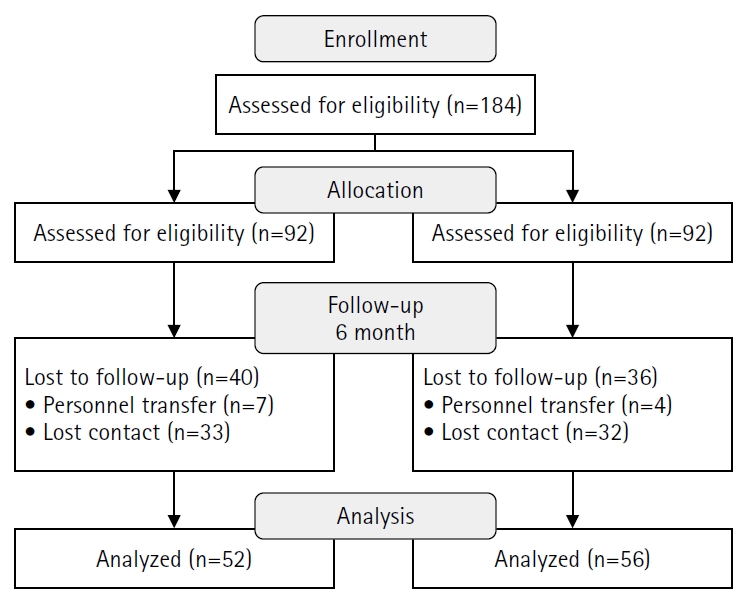
This study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of the Trauma-nursing Education and Skill Support (TESS) program based on the ADDIE model (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation model). The program was designed to enhance trauma nurses’ clinical competencies, including trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability, through the integration of theoretical education and simulation-based practice.
Methods
A quasi-experimental study using a non-equivalent control group pretest–posttest design was conducted. Participants included 108 trauma nurses from regional trauma centers, military trauma centers, and emergency care facilities, who were assigned to an experimental group (n=52) or a control group (n=56). The TESS program consisted of a 2-day, 14-hour blended-learning course that included eight lecture sessions and four simulation-based practice stations. Data were collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at 6 months using validated instruments measuring trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance was used for data analysis.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability compared with baseline (all p<.001). These improvements were sustained at 6 months, although trauma-related knowledge scores showed a slight decline compared with immediate posttest levels. Between-group analyses confirmed significant group-by-time interaction effects for all outcomes: trauma-related knowledge (η2=0.12, p<.001), self-efficacy (η2=0.09, p=.002), and problem-solving ability (η2=0.08, p=.003).
Conclusion
The TESS program effectively enhanced trauma nurses’ trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability, with effects sustained for up to 6 months. Incorporating blended learning and simulation-based training into standardized trauma nursing education may strengthen clinical competencies and ultimately contribute to improved patient outcomes.
- 427 View
- 57 Download

- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Soo Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):269-284. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
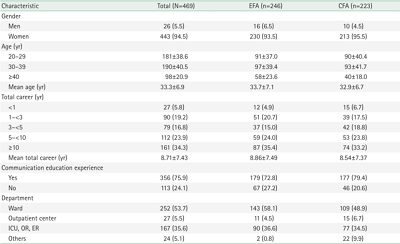
ePub - Purpose
This methodological study was conducted to develop a scale to measure communication self-efficacy in nurses and examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
We selected 54 initial items from literature reviews and interviews with 10 clinical nurses. Thirty-two preliminary items were derived from consultations with 10 experts. To verify the scale’s factor structure, we conducted exploratory factor analysis (EFA), and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) among 469 nurses. Data were analyzed using item analysis, EFA, CFA, discriminant validity, convergent validity, and internal consistency using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 29.0 (IBM Corp.) and IBM SPSS AMOS ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp.).
Results
The scale consisted of 18 items with three factors (ability to apply therapeutic communication skills, crisis management capabilities, and communication competence), which explained 46.1% of the total variance. Convergent validity and discriminant validity were confirmed for the factors. CFA supported the fit of the measurement model comprising three factors (standardized root mean square residual=.04, root mean square error of approximation=.03, goodness of fit index=.92, Tucker-Lewis index=.97, comparative fit index=.98, normed fit index=.89, critical N=216). Internal consistency was confirmed by a Cronbach’s α coefficient of .91.
Conclusion
The communication self-efficacy scale for nurses is expected to measure communication self-efficacy among nurses. It will be useful for improving nurses’ professional communication abilities.
- 3,656 View
- 281 Download

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy Scale for Nurses
- Youngrye Park, Sunah Park, Hee Ran Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):633-644. Published online November 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24094
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the occupational coping self-efficacy for nurses (K-OCSE-N) scale.
Methods The English version of the OCSE-N scale was translated into Korean using a translation and back-translation process. Data were gathered from 213 nurses employed in a general hospital in South Korea. The content validity was assessed using the content validity index. The construct validity was verified through exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Criterion validity was assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients with the job stress coping and general self-efficacy scales. Reliability was examined using item-total score correlation and Cronbach’s α coefficient for internal consistency.
Results The exploratory factor analysis identified two factors that explained 61.8% of the cumulative variance: occupational burden and relational difficulty. In confirmatory factor analysis, the model exhibited adequate fit (
χ 2/df = 2.07, GFI = .95, SRMR = .04, RMSEA = .07, CFI = .97, and TLI = .95), with both convergent and discriminant validity deemed acceptable. The criterion validity presented a positive correlation of the K-OCSE-N with both job stress coping (r = .72,p < .001) and general self-efficacy (r = .72,p < .001). The internal consistency of the scale using Cronbach’s α for the total items was .89.Conclusion The K-OCSE-N scale is a valid and reliable tool for measuring nurses’ occupational coping self-efficacy. This study suggests that various intervention studies can use the scale to assess and strengthen nurses’ occupational coping self-efficacy in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
Hyun Suk Gwag, Jin Ah Kim
Healthcare.2026; 14(2): 270. CrossRef
- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
- 7,349 View
- 414 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of a Self-Efficacy Theory-Based Exercise Program for Patients Undergoing with Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Kyung-Hye Park, Hee-Young Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):547-562. Published online October 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material ePub
ePub Purpose This study was performed to develop a self-efficacy theory-based exercise program for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and to test the program’s efficacy in ameliorating knee pain and restoring function as measured by lower extremity muscle strength, 3 meter walking time, Korean Western Ontario McMaster Index (WOMAC), exercise self-efficacy, and length of hospital stay for TKA patients.
Methods This quasi-experimental study incorporating a non-equivalent control group and pretest-posttest non-synchronized design non-synchronous design was applied to assess self-efficacy reinforcement strategies based on self-efficacy theory. The exercise program consisted of the following steps: TKA, education to prevent postoperative complications, and muscle strength exercises. Respective exercise and control groups included 29 and 27 participants. The experimental group received eight sessions of the program from three weeks before TKA to four weeks after TKA. Collected data were analyzed using the chi-square test, Mann–Whitney U test, and ranked ANCOVA and t-tests using IBM SPSS Statistics 23.
Results Experimental group showed significant improvement in lower extremity muscle strength (F = 8.63,
p = .005), 3 meter walking time (z = - 5.02,p < .001), WOMAC index (z = - 2.22,p = .027), self-efficacy for exercise (z = - 3.29,p = .001), and length of hospital stay (t = - 2.11,p = .040) compared to the control group. No significant differences in knee pain and range of motion were observed.Conclusion These findings indicate that a self-efficacy theory-based exercise program can be an effective exercise strategy that patients undergoing TKA can easily follow at home without assistance. It is thus recommended as an exercise intervention for TKA patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-efficacy and implementation intentions in home rehabilitation of stroke patients: the parallel mediating role of recurrence risk perception and outcome expectations
Xiaowen Jiang, Qiuxue Sun, Rong Tang, Shuxian Liu, Xi Chen, Yumei Lv
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Decision-Making and Rehabilitation Among Older Women Who Underwent Total Knee Replacement: A Qualitative Study in Taiwan
Ching Han Huang, Yun Yee Chen, Shu Wen Chen, Chen Ti Wang, Mei Hsiang Lin
Patient Preference and Adherence.2025; Volume 19: 3931. CrossRef
- Self-efficacy and implementation intentions in home rehabilitation of stroke patients: the parallel mediating role of recurrence risk perception and outcome expectations
- 3,332 View
- 284 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of a Pre-Conception Care Program in Women with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Mixed-Methods Study Including a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Young Jin Lee, Hae Won Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Suk-Kyun Yang, Ji-Yeon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):386-402. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to conduct a pre-conception care program for women of childbearing age with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Korea and verify its effects on self-efficacy for IBD management, IBD-related pregnancy knowledge, and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety. It also aimed to explore the changes in participants through the program.
Methods
A convergent mixed-methods study design was adopted. In the quantitative phase, 35 women (17 and 18 in the intervention and control group, respectively) participated. The intervention group attended a program that included small-group sessions and individual tele-coaching. To confirm the effects, data were collected before and one and four weeks after the intervention. In the qualitative stage, focus group interviews and tele-coaching were conducted with the intervention group.
Results
After the program ended, significant differences were observed over time between the intervention and control groups for self-efficacy for IBD management (Wald χ2 = 4.41, p = .036), IBD-related pregnancy knowledge (Wald χ2 = 13.80, p < .001) and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety (Wald χ2 = 8.61, p = .003). Qualitative data analysis revealed the following themes: (1) improving confidence in IBD management and awareness for planned pregnancy; (2) improving IBD awareness related to pregnancy and childbirth; and (3) relieving anxiety about and actively facing pregnancy.
Conclusion
This study is meaningful in that, to the best of our knowledge, it is the first to develop a pre-conception care program for women diagnosed with IBD and confirm its effectiveness. Furthermore, this program is expected to be suitable for patient counseling and education in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
Lewei Tu, Qiaoyu Wu, Mengxiao Jiang, Meihao Wei, Ying Wang, Ying Xiao
BMC Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Literacy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Health Outcomes, Predictors and Barriers
Caterina Mercuri, Rita Nocerino, Vincenzo Bosco, Teresa Rea, Vincenza Giordano, Michele Virgolesi, Patrizia Doldo, Silvio Simeone
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(23): 8577. CrossRef
- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
- 2,493 View
- 97 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Moderating Effect of General Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Pregnancy Stress, Daily Hassles Stress, and Preterm Birth Risk in Women Experiencing Preterm Labor: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Hyun-Jeong Cho, Jeung-Im Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):329-339. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the moderating role of general self-efficacy (GSE) on how stress caused by pregnancy and daily hassle affect the risk of preterm birth (PTB) in women experiencing preterm labor.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 196 pregnant women experiencing preterm labor before 37 weeks of gestation. We used IBM SPSS Statistics 27 and employed Hayes process macro version 4 (model 1) and hierarchical regression to analyze the moderating effect of GSE on the relationship between pregnancy stress, daily hassle stress, and PTB risk.
Results
Stress caused by pregnancy and daily hassle was positively correlated to PTB risk (r = .54, p < .001; r = .25, p < .001, respectively). While GSE did not significantly correlate with pregnancy stress, it negatively correlated with daily hassle stress (r = - .19, p = .009). GSE significantly moderated the relationship between combined stressors and PTB risk. As GSE levels increased, escalation in PTB risk in response to increasing stress levels was a more pronounced, highlighting a complex interaction between higher GSE levels and response to escalating stress levels. This model accounted for 39.5% of the variance in the PTB risk.
Conclusion
Higher GSE may amplify the impact of stress on PTB risk, rather than mitigate it, which suggests a more nuanced role of GSE in the stress response of pregnant women at risk of preterm labor. GSE should be considered in care strategies, and managing its impact on stress perception and responses in pregnant women is crucial. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Digital Interventions for Stress Management in Pregnant Women: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeung-Im Kim, Joo Yun Lee, So-Hee Park
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2026; 14: e66267. CrossRef - Pregnancy stress in women at high risk of preeclampsia with their anxiety, depression, self-management capacity: a cross-sectional study
Xing Cong, Jinmei Wang, Liu Yang, Lingling Cui, Yurong Hua, Ping Gong
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety, Coping, and Self-Efficacy as a Psychological Adjustment in Mothers Who Have Experienced a Preterm Birth
Agata Białas, Karolina Kamecka, Paweł Rasmus, Dariusz Timler, Remigiusz Kozłowski, Anna Lipert
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4174. CrossRef - Associations Among Pregnancy Stress, Childbirth Confidence, and COVID-19 Infection Experience in Pregnant Women in the Early Third Trimester (28–32 Weeks)
Yun-Sun Yang, Jeung-Im Kim
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(3): 147. CrossRef
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Digital Interventions for Stress Management in Pregnant Women: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 2,024 View
- 81 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of Comprehensive Mobile-Based, Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Gestational Diabetes
- Eunju Kwak, Seungmi Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):224-236. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of a mobile-based breastfeeding promotion program (M-BFGDM) that helps mothers with gestational diabetes.
Methods
Forty-seven mothers participated in the study, of whom 22 were in the experimental group and 25 in the control group. To verify the effects, a lag design before and after the non-equivalence control group was used. The data collection for the experimental group was done before and after the intervention.
Results
In the results, breastfeeding knowledge showed a significant difference in the interaction between measurement period and group (χ2 = 8.14, p = .017), whereas breastfeeding intention did not show a significant difference in the interaction (χ2 = 4.73, p = .094). There was no difference in self-efficacy interaction (F = 0.13, p = .856). The breastfeeding method showed no difference in interaction (F = 0.04, p = .952), whereas cross-analysis showed a significant difference in breastfeeding practice rate between the experimental group and the control group at 1 month postpartum (χ2 = 7.59, p = .006).
Conclusion
A mobile-based breastfeeding promotion program was developed and applied for gestational diabetic mothers, resulting in an increase in breastfeeding knowledge and an improvement in breastfeeding practice rate one month after childbirth. In addition, M-BFGDM managed to create a breastfeeding practice environment with fewer time and place restrictions. A program study that complements motivation is needed to improve breastfeeding in pregnant diabetic mothers in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- 3,066 View
- 183 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling of Health Promotion Behavior on Migrant Workers: A Multi-Group Analysis Based on the Period of Residence
- Hanna Jeong, Youngsuk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):73-92. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed and tested a hypothetical model of health promotion behavior on migrant workers based on the Health Promotion Model and the Health Literacy Skills Framework.
Methods
Data were collected from 298 migrant workers in 9 regions across the country from December 2020 to March 2021. The exogenous variables were e-health literacy, occupational stress, acculturation, and social support. The endogenous variables were perceived benefits of action, self-efficacy, and health promotion behavior. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 25.0, AMOS 20.0, and R-4.0.3 program.
Results
The model fit was appropriate. Social support had the most significant direct impact on the health promotion behavior of migrant workers. Perceived benefits of action and self-efficacy played a mediating role in the relationship among e-health literacy, social support, and health promotion behavior. Based on multi-group analysis, the migrant worker group with less than 5 years of residency had a more statistically significant effect on the relationship between perceived benefits of action and health promotion behavior than those with over 5 years.
Conclusion
Providing social support as a critical administrative strategy to enhance the health promotion behavior of migrant workers is necessary. Furthermore, when developing an intervention program utilizing the internal mechanism between social support and health promotion behavior, a self-efficacy-enhancing strategy is considered to be more effective. Additionally, educating migrant workers with short-term residence of less than 5 years about the benefits of health behaviors is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
Yu Zhu Zhang, Seon Young Hwang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated With Physical Activity in Home‐Based Rehabilitation Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Prospective Longitudinal Study
Heng‐Ying Fang, Ying‐Hua Pan, Yi‐Heng Zhang, Yu‐Hua Deng, Xiao‐Wen Li, Lei Huang, Hui‐Ting Gu, Yue Ding, Xin‐Xin Hu, Mu Liu, Rui‐Chong Wang, MeiFen Zhang
Musculoskeletal Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
- 2,841 View
- 104 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
- Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Mi-So Shim, Seoyoung Baek, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Youngjin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):295-308. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the validity and reliability of Shively and colleagues’ self-efficacy for HIV disease management skills (HIVSE) among Korean participants.
Methods
The original HIV-SE questionnaire, comprising 34 items, was translated into Korean using a translation and back-translation process. To enhance clarity and eliminate redundancy, the author and expert committee engaged in multiple discussions and integrated two items with similar meanings into a single item. Further, four HIV nurse experts tested content validity. Survey data were collected from 227 individuals diagnosed with HIV from five Korean hospitals. Construct validity was verified through confirmatory factor analysis. Criterion validity was evaluated using Pearson’s correlation coefficients with the new general self-efficacy scale. Internal consistency reliability and test-retest were examined for reliability.
Results
The Korean version of HIV-SE (K-HIV-SE) comprises 33 items across six domains: “managing depression/mood,” “managing medications,” “managing symptoms,” “communicating with a healthcare provider,” “getting support/help,” and “managing fatigue.” The fitness of the modified model was acceptable (minimum value of the discrepancy function/degree of freedom = 2.49, root mean square error of approximation = .08, goodnessof-fit index = .76, adjusted goodness-of-fit index = .71, Tucker-Lewis index = .84, and comparative fit index = .86). The internal consistency reliability (Cronbach’s α = .91) and test-retest reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient = .73) were good. The criterion validity of the K-HIV-SE was .59 (p < .001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that the K-HIV-SE is useful for efficiently assessing self-efficacy for HIV disease management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Sooyoung Kwon, Ji Min Kim, Jun Yong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2025; 13: e60905. CrossRef - Factors associated with health-related quality of life among people living with HIV in South Korea: Tobit regression analysis
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, SangA Lee, Mi-So Shim, Youngjin Lee, Seoyoung Baek, Claus Kadelka
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(5): e0303568. CrossRef - Three cycles of mobile app design to improve HIV self-management: A development and evaluation study
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Mi-So Shim, SangA Lee, Ji Min Kim, Jong Yae Yoon, Jin Kim, JunYong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
- 2,984 View
- 66 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Related to Clinical Competence among Graduating Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Su Kyoung Chung, Jinsook Kim, Pratibha Bhandari
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):145-154. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated clinical competency, COVID-19-related anxiety, coping strategies, self-efficacy, and perceived stress among graduating nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional survey. Participants were recruited from universities located in four major cities in South Korea. General demographic information, clinical competency, self-efficacy, perceived stress, COVID-19-related anxiety, and coping strategies were assessed using reliable questionnaires. Descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression tests were used to analyze the data.
Results
The mean clinical competency, self-efficacy, perceived stress, adaptive coping, and maladaptive coping were 138.16 ± 18.34, 83.85 ±14.02, 21.37 ± 5.79, 53.15 ± 4.64, and 30.98 ± 6.73, respectively. COVID-19-related anxiety was reported by 4.3% of participants. Clinical competency was significantly positively correlated with self-efficacy (r = .44, p < .001) and adaptive coping (r = .20, p = .035) and was significantly negatively correlated with maladaptive coping (r = .20, p = .035). The predictors of clinical competency were self-efficacy (β = .434, p < .001) and adaptive coping (β = .173, p < .039), which explained 23% of the variance in clinical competency.
Conclusion
Self-efficacy and adaptive coping strategies are significant predictors of clinical competence during the pandemic. Planning and implementing various curricular and non-curricular activities to increase senior students' self-efficacy and adaptive coping strategies will help prepare competent nursing graduates for the pandemic when they enter the nursing workforce. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Educational Stress and Competence of Intern Nurses' Following Two Years of Online Education: A Cross-Sectional Study
Fatma Dursun Ergezen, Ayşe Yacan Kök, Emine Kol
Ordu Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Çalışmaları Dergisi.2026; 9(1): 83. CrossRef - The Effect of Internship Length on Self‐Efficacy and Clinical Competence: Accelerating Entry Into the Nursing Workforce in Saudi Arabia
Sitah S. Alshutwi, Majed Alamri
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring Educational Stress and Competence of Intern Nurses' Following Two Years of Online Education: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 2,968 View
- 65 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of Clinical Nurses’ Job Crafting on Organizational Effectiveness Based on Job DemandsResource Model
- Eun Young Lee, Eungyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):129-143. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the mediating effects of clinical nurses’ job crafting on organizational effectiveness based on the job demands-resources model proposed by Bakker and Demerouti (2017).
Methods
The participants consisted of 393 nurses working in nursing units of a tertiary general hospital located in Cheongju region. The data, collected using questionnaire from August 9 to August 20, 2021, were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 27.0.
Results
The goodness-of-fit (GoF) test results on the modified model (χ 2 = 2.7, GFI = .94, SRMR = .03, RMSEA = .06, NFI = .92, CFI = .94, TLI = .92, AGFI = .90), indicated that the GoF index satisfied the recommended level. Regarding the effects of each variable on organizational effectiveness, job crafting showed statistically significant direct (β = .48, p < .001), indirect (β = .23, p < .001), and total effects (β = .71, p < .001). Burnout showed statistically significant direct effect (β = - .17, p < .001). Work engagement showed statistically significant direct (β = .41, p < .001) and total effects (β = .41, p < .001). The factors explaining organizational effectiveness were job crafting, burnout, and work engagement, which had an explanatory power of 76.7%.
Conclusion
Nurses’ job crafting is an important mediating factor for enhancing the organizational effectiveness of nursing organizations. Hospitals should develop job-crafting success cases and related education and training programs as a strategy for enhancing the job crafting of nurses and, consequently organizational effectiveness. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hospital Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life Model: A Cross‐Sectional Study Based on the Expanded Job Demands‐Resources Model
Younghee Kim, Mi Yu, Jacopo Fiorini
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of grit and job crafting on organizational commitment and job satisfaction among hospital nurses in Korea
Mi-Suk Hyun
Medicine.2025; 104(45): e45890. CrossRef - Effects of Attitude Toward Interdepartmental Transfer, Career Growth Opportunity, and Role Breadth Self-Efficacy on Job Crafting among Nurses with Transfer Experience
Yu Jin Lee, Chung Hee Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 497. CrossRef - Job Crafting as the Missing Link: Understanding Its Role in Nurses’ Work Engagement
Kyungjin Lee, Ja Kyung Seo, Seung Eun Lee, Yunhong Liu
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Commitment to Organizational Change in Clinical Nurses: A Structural Model Applying Lewin's Change Theory
Mihwa Hong, Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 38. CrossRef
- Hospital Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life Model: A Cross‐Sectional Study Based on the Expanded Job Demands‐Resources Model
- 4,049 View
- 171 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of Self-Care Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Inventory (SC-COPD) and Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale (SCES-COPD)
- Ja Yun Choi, So Young Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):522-534. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22062
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Self-Care in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Inventory (SC-COPDI) and the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale (SCES-COPD). The SC-COPDI consists of the Self-Care Maintenance Scale (SCMES), Self-Care Monitoring Scale (SCMOS), and Self-Care Management Scale (SCMAS).
Methods
The original tool was translated using a back-translation process. Participants were 241 patients with COPD at the Chonnam National University Hospital in Korea. The construct validity was verified through confirmatory factor analysis, and reliability was verified using Cronbach’s α.
Results
The SCMES consisted of 10 items of three factors―one of four factors was deleted from the original tool. In the SC-MOS, there were six items of two factors after two items were deleted from the original tool. The SCMAS consisted of the original 10 items of three factors. The SCES-COPD consisted of six items of two factors, with one item removed from the original tool. The model fit indices of all tools were good, and the construct validity was confirmed. Cronbach’s α of SCMES was .72, SCMOS was .90, SCMAS was .81, and SCES-COPD was .85.
Conclusion
The Korean version of SC-COPDI and SCES-COPD are valid and reliable instruments for measuring selfcare in people with COPD. These instruments can be used in self-care studies of COPD patients in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Ruminative Thinking on Breathlessness Catastrophizing With Elderly COPD Patients: The Mediating Role of Self‐Efficacy
Yuye Zhang, Qiufang Li, Xiaokai Wang, Tianci Xiao, Chenmeng Wei, Na Song, Lamei Liu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(11): 4854. CrossRef - The influence of depression, social support, and uncertainty on self-management compliance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases: A descriptive survey study
Han-na Jang, Jeong-soo Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 318. CrossRef - Enhancing deep learning models for predicting smoking Status using clinical data in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Sehyun Cho, Hyeonseok Jin, Kyungbaek Kim, Sola Cho, Ja Yun Choi
DIGITAL HEALTH.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influences of Illness Uncertainty, Health Literacy, and Self-Care on Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Min Jin Chu, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 530. CrossRef - E-health literacy and attitudes toward internet health information in relation to self-care adherence among Korean patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional study
Na Yeong Park, Insook Lee
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric testing of the cross-culturally adapted Thai version of the Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale version 3.0 in individuals with chronic illnesses
Chennet Phonphet, Jom Suwanno, Chonchanok Bunsuk, Wanna Kumanjan, Ladda Thiamwong
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(4): 473. CrossRef
- Impact of Ruminative Thinking on Breathlessness Catastrophizing With Elderly COPD Patients: The Mediating Role of Self‐Efficacy
- 2,724 View
- 72 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-Item Scale
- Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee, So-Young Kim, Nayoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):617-629. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to examine the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the self-efficacy for managing chronic disease 6-item scale (SECD-6-K).
Methods
The English version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-item Scale first underwent forward and backward translation procedures. The SECD-6-K was then used to collect data from 350 adults diagnosed with chronic diseases. Content, construct, convergent, discriminant, and criterion validity were all evaluated. Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s α. SPSS 25.0 and the data were analyzed using AMOS 26.0 software.
Results
The SECD-6-K consists of six items in two domains: disease management and health behavior. The results for construct, convergent, and discriminant validity were good. Exploratory factor analysis produced eigen values between 2.27 and 3.28, with factors total explained cumulative variance of 91.1%. Confirmatory factor analysis supported goodness of fit and reliability for the modified SECD-6-K model. The criterion validity also showed significant correlation with both the Patient Health Questionnaire and 12-item Short-Form Health Survey version 2. Finally, reliability was found to be excellent.
Conclusion
This study identified the high reliability and validity of SECD-6-K. The SECD-6-K is an appropriate tool for determining Korean patients’ self-efficacy in managing their chronic conditions. Therefore, this scale may be used in clinical settings as well as in educational and research settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Generic instruments for assessing self-management abilities and behaviors in patients with chronic diseases: a COnsensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review
Ke Liu, Guangyan Meng, Caixia Li, Shuyi Wang, Xianwen Fan, Qirong Chen
Quality of Life Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life for Community-Dwelling Vulnerable Older Adults with Chronic Diseases in Korea
Hyun-Ju Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 315. CrossRef - Development of a self-care scale for women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a methodological approach
Miok Kim
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Short Form of Core Competencies Scale of Nursing Care for Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sung Hae Kim, Seyong Lee, Sang Hee Kim, Jung Ok Choi, Gie Ok Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(4): 184. CrossRef - Factors influencing self-management behaviors in older people with multiple chronic conditions based on the individual and family self-management theory: A cross-sectional study
Youngji Seo, Sunyoung Jung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(3): 332. CrossRef - Psychometric property of the Japanese version of self-efficacy for managing chronic disease scale in individuals with chronic diseases
Megumi Hazumi, Mayumi Kataoka, Ayako Nakashita, Kentaro Usuda, Michi Miyake, Chiaki Kamikawa, Daisuke Nishi, Naoaki Kuroda
Heliyon.2024; 10(22): e40218. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the self-efficacy scale for chronic disease management (SEMCD-S) in older Colombian adults
Lorena Cudris-Torres, Stefano Vinaccia Alpi, Álvaro Barrios-Núñez, Natali Gaviria Arrieta, Martha Luz Gómez Campuzano, Giselle Olivella-López, Juan Hernández-Lalinde, Valmore Bermúdez, Olaiza Lobato Pérez, Jorge Armando Niño-Vega, Jorge Navarro-Obeid, Rom
BMC Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ambulatory Chemotherapy (Portable Infusion Pump Use) Video Education on Knowledge, Self-efficacy and Anxiety of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Young Park, Young A Park, You Hee Son, Myung Jin Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 193. CrossRef
- Generic instruments for assessing self-management abilities and behaviors in patients with chronic diseases: a COnsensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review
- 4,670 View
- 219 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Drinking Reduction Program Focused on Self-Determination Enhancement for College Students with Problematic Drinking
- Jin-Kyoung Ma, Moon-Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):265-279. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20247
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the impact of a drinking reduction program on drinking motivation, drinking refusal self-efficacy, and problematic drinking behaviors in college students with problematic drinking habits.
Methods
This study incorporated a non-equivalent control group prepost-test design. Study participants included 58 college students who scored 12 or more in the AUDIT-K test (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Korean version) (experimental group: 30; control group: 28). The intervention consisted of eight sessions and was conducted once a week. It was designed to promote autonomy, competence, and relatedness-the three elements of basic psychological needs in self-determination theory. The participants were assessed before the intervention, immediately after, and four weeks post intervention. Data were collected from October 12 to December 31, 2017. The analysis employed the chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, independent t-test, and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN 22.0.
Results
The mean age of participants was 21.8 years. There were 30 men (51.7%) and 28 women (48.3%). The differences in drinking motivation, drinking refusal self-efficacy, and problematic drinking behaviors were statistically significant for the group by time interaction (F = 42.56, p < .001; F = 54.96, p < .001; F = 39.90, p < .001, respectively). Conclusion: The findings indicate that the intervention effectively decreases drinking motivation, increases drinking refusal self-efficacy, and decreases problematic drinking behaviors. It can be an efficient strategy for college students with problematic drinking habits to enhance their self-determination ability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Self-Determination Theory–Based Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Program for Community-Dwelling Middle-Aged Women
Yein Lee, Yunhee Kim
Journal of Community Health Nursing.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Effects of an intervention based on self-determination theory on self-health management capabilities of middle-aged women in rural areas through the concept of leisure cafeteria
Yang Jun Park, Heui Sug Jo, Hyang Hee Hwang, Yukyung Park
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(1): 59. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Self-Determination Improvement Program for Preventing Non-Suicidal Self-Injury in Adolescents: A Pilot Study
Jae Woon Lee, In Sook Kim, Ji Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(4): 506. CrossRef
- A Self-Determination Theory–Based Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Program for Community-Dwelling Middle-Aged Women
- 1,823 View
- 49 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of Direct Breastfeeding Program for Premature Infants in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Ji Hyun Kang, Hyunmi Son, Shin Yun Byun, Gyumin Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):119-132. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the effects of a direct breastfeeding program for premature infants in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
Methods
This quasi-experimental study was conducted during August 2016 to April 2017. Sixty mothers of premature infants were assigned to the experimental (n = 31) or control groups (n = 29). The program was comprised of breastfeeding education and direct breastfeeding support. The experimental and control groups were provided with education and counseling on breastfeeding at the time of admission and discharge. In the experimental group, the mothers initiated oral feeding with direct breastfeeding and engaged in breastfeeding at least seven times during the NICU stay. The collected data were analyzed by the χ2 -test and repeated measures ANOVA using an SPSS program.
Results
The experimental group showed a higher direct breastfeeding practice rate (χ2 = 19.29, p < .001), breastfeeding continuation rate (χ2 = 3.76, p < .001), and self-efficacy (F = 25.37, p < .001) than the control group except for maternal attachment.
Conclusion
The direct breastfeeding program in the NICU has significant effects on the practice and continuation rate of breastfeeding and breastfeeding self-efficacy. Therefore, this program can be applied in the NICU settings where direct breastfeeding is limited. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploration of Family-Centered Care in NICUs: A Grounded Theory Methodology
Young Ah Park, YeoJin Im
Qualitative Health Research.2025; 35(10-11): 1231. CrossRef - Fresh Parent’s Own Milk for Preterm Infants: Barriers and Future Opportunities
Carrie-Ellen Briere, Jessica Gomez
Nutrients.2024; 16(3): 362. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of Comprehensive Mobile-Based, Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Gestational Diabetes
Eunju Kwak, Seungmi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 224. CrossRef
- Exploration of Family-Centered Care in NICUs: A Grounded Theory Methodology
- 3,261 View
- 178 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance in Adult Moyamoya Patients
- Bo Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing health behavior compliance in adult patients with moyamoya.
Methods
A descriptive correlation study was conducted to investigate the factors influencing health behavior compliance. Participants were 142 adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease who were hospitalized or visited an outpatient clinic in the Gyeonggi province. Data were collected from December 16, 2019 to April 14, 2020 using self-report questionnaires and analyzed using the IBM SPSS 26.0 Win software.
Results
The hierarchical multiple regression analysis demonstrated that self-efficacy (β = .60, p < .001), social support (β = .13, p = .032), and age (β = .21, p = .005) affected the health behavior of adults with moyamoya disease. These 3 variables explained 62.0% of the variance of health behavior compliance, and the most influential factor was self-efficacy.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, it concludes that nursing interventions should be focused on self-efficacy and social support to improve health behavior compliance with adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease. For that, various strategies to enhance self-efficacy and social support should be developed and actively applied in the clinical setting for adult moyamoya patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
Hae-Na Woo, Yong-Cheol Lim, Joo Hee Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
- 1,513 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Emotional Coaching Program for Clinical Nurses on Resilience, Emotional Labor, and Self-efficacy
- Kyung Ryu, Jong Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):419-430. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to assess the effect of the emotional coaching program for hospital nurses.
Methods
The study used anon-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design, and participants included 60 nurses (30 in the experimental group and 30 in thecontrol group) who worked at a general hospital. The experimental group attended four sessions, one per week, with each session lastingtwo and a half hours. Collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Fisher’s exact test, x2 test, t-test, paired t-test, and repeatedmeasures ANOVA using SPSS WIN 23.0 program.
Results
Significant differences were shown between the experimental and the controlgroups regarding emotional labor (F=68.40, p<.001), resilience (F=48.77, p<.001), and self-efficacy (F=15.31, p<.001).
Conclusion
Theemotional coaching program for nurses is useful for enhancing nurses’ emotional labor management, resilience, and self-efficacy. In addition,this program may serve as a basis for providing emotional coaching to nurses in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship Between Perceived Self-Efficacy and Resilience Among Pediatric Nurses in Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia
Bushra Bawazier, Hebah Almulla, Mansour Mansour, Sama Hammad, Rana Alameri, Latifa Aldossary, Tahani AlShammari
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2025; Volume 18: 739. CrossRef - Analysis of the correlation between work stress and emotional labor in college counselors: the moderating effect of psychological resilience
Tianlin Chen, Shijian Sun, Lan Luo, Yongfei Chen
BMC Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Nursing Organizational Culture on the Relationship between Resilience and Clinical Competence of New Graduate Nurses
Hanna Lee, Eun-Jun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 483. CrossRef - Impact of Emotional Labor and Positive Psychological Capital on the Turnover Intention of Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19: A Descriptive Survey Study
Mira Kwon, Yeoungsuk Song, Majd T. Mrayyan
Journal of Nursing Management.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Mentorship in nursing: A review of approaches to defining the concept in international and Russian publications
K. V. Kuzmin, L. E. Petrova, V. S. Kharchenko
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2024; 31(4): 89. CrossRef - Effects of grit, calling, and resilience on the retention intention of general hospital nurses
Gi Ran Lee, Imsun Lee, Mihee Chung, Jiyeon Ha
International Nursing Review.2024; 71(4): 766. CrossRef - Effect of Transition Shock on Intention to Stay in Newly Graduated Nurses : The Mediating Effect of Positive Psychological Capital
Hyuna Kam, Chanhee Kim, Yeonok Yoon, Heeyoung Shin, Junghwa Lee, Myoungohk Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 25. CrossRef - Psychological Intervention to Promote Resilience in Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Suk-Jung Han, Young-Ran Yeun
Healthcare.2023; 12(1): 73. CrossRef - The relationship between secondary traumatic stress and burnout in critical care nurses: The mediating effect of resilience
Yun Jeong Jeong, Sujin Shin
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2023; 74: 103327. CrossRef - Effects of the Resilience of Nurses in Long-Term Care Hospitals during on Job Stress COVID-19 Pandemic: Mediating Effects of Nursing Professionalism
Bom-Mi Park, Jiyeon Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10327. CrossRef
- The Relationship Between Perceived Self-Efficacy and Resilience Among Pediatric Nurses in Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia
- 2,590 View
- 112 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Smartphone App-Based Walking Exercise Program for Taxi Drivers: Based on Bandura’s Self Efficacy Theory
- Yun Ha Choi, Min-Jeong Chae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):242-254. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.242
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of smart-phone app-based walking exercise programs for taxi drivers on self-efficacy and outcome expectations for exercise, health-related quality of life, walking as an exercise, and physiological indexes.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group with a pre-post-test design was used. The subjects were recruited in G metropolitan city. Subjects were assigned to the experimental (n=31) or control groups (n=30). The smart phone app-based walking exercise program consisted of educations via the app, twelve short message services, and one individual telephone counseling session, which was spread over 12 weeks.
Results
Self-efficacy, outcome expectations, and health-related quality of life had significantly higher pre-post test differences in scores in the experimental group. Additionally, blood pressure, body mass index, and waist circumference had significantly decreased prepost- test difference levels in the experimental group. Walking as an exercise (which consisted of days walked, number of steps walked, and amount of time walked) had significantly increased in the experimental group after 7~12 weeks in the period following the intervention program rather than 1~6 weeks after the program.
Conclusion
The smart phone app-based walking exercise program based on the self-efficacy theory demonstrates a significant effect on improving self-efficacy, outcome expectations physical activities, and health-related quality of life for taxi drivers. Therefore, it is recommended to actively use the program as a tool to promote self-efficacy, physical activities, and health behaviors in taxi drivers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring physical therapists’ approach to addressing home exercise program-related low self-efficacy: knowledge, strategies, and barriers
Mariana Wingood, Patricia M. Bamonti, Justin B. Moore, Kelsey J. Picha
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(8): 2065. CrossRef - Intervención educativa en la actividad física de médicos residentes durante la pandemia COVID-19. Estudio cuasiexperimental
Paola María Moreno-Pesquera, Clara Lilia Varela-Tapia, Hermelinda Hernández-Amaro, Daniel Martínez-Barro
Revista Mexicana de Medicina Física y Rehabilitación.2025; 37(1-2): 21. CrossRef - A Mobile App for Comprehensive Symptom Management in People With Parkinson’s Disease
JuHee Lee, Yujin Suh, Eunyoung Kim, Subin Yoo, Yielin Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(4): 289. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Mobile Application to Prevent Recurrent Stroke by Enhancing Self-management on Health Outcomes for Stroke Survivors
Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Hyun Goo Kang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(1): 53. CrossRef - mHealth Interventions to Promote Physical Activity of Adults in Korea: Health Equity-Focused Systematic Review
Hana Kim, Jisan Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(Suppl 1): S1. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of a mHealth Program Using Wearable Devices and Health Coaching among Bus Drivers for Promoting Physical Activity
Yeongmi Ha, Sang-Ho Lee, Suyeon Lee, Yeojoo Chae
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(3): 332. CrossRef - Effect of the SNS-Based Physical Activity-Related Psychological Intervention on Physical Activity and Psychological Constructs among Inactive University Students
Youngho Kim, Jonghwa Lee
International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology.2022; 22(2): 100299. CrossRef - PERFORMANCE OF PHYSICAL EXERCISE IN SEDENTARY PEOPLE’S AUTONOMY
Zaiyong Shou
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2022; 28(6): 785. CrossRef - An eHealth intervention (ManGuard) to reduce cardiovascular disease risk in male taxi drivers: protocol for a feasibility randomised controlled trial
James McMahon, David R. Thompson, Kevin Brazil, Chantal F. Ski
Pilot and Feasibility Studies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Mobile Wellness Program for Nurses with Rotating Shifts during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Pilot Cluster-Randomized Trial
Yeongmi Ha, Sang-Ho Lee, Dong-Ha Lee, Young-Hun Kang, Woonjoo Choi, Jinung An
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 1014. CrossRef - Co-Design of an eHealth Intervention to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Male Taxi Drivers: ManGuard
James McMahon, David R. Thompson, Kevin Brazil, Chantal F. Ski
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 15278. CrossRef
- Exploring physical therapists’ approach to addressing home exercise program-related low self-efficacy: knowledge, strategies, and barriers
- 2,330 View
- 50 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Applying Extended Theory of Planned Behavior for Lung Cancer Patients Undergone Pulmonary Resection: Effects on Self-Efficacy for Exercise, Physical Activities, Physical Function, and Quality of Life
- Yeonjung Lim, Haejung Lee, Do Hyung Kim, Yeong Dae Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):66-80. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.66
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: This study aims to examine the effects of nursing interventions based on the Extended Theory of Planned Behavior (ETPB) regarding self-efficacy for exercise (SEE), physical activity (PA), physical function (PF), and quality of life (QOL) in patients with lung cancer who have undergone pulmonary resection.
Methods: This quasi-experimental study was conducted between July 2015 and June 2018 in two university-affiliated hospitals. The intervention included pre-operative patient education, goal setting (action and coping planning), and feedback (behavior intention and perceived behavioral control). The intervention group (IG) (n=51) received nursing interventions from the day before surgery to 12 months after lung resection, while the comparison group (CG) (n=36) received usual care. SEE, PA, PF (dyspnea, functional status, and 6-minute walking distance [6MWD]), and QOL were measured before surgery and at one, three, six, and 12 months after surgery. Data were analyzed using the χ2 test, Fisher’s exact test, Mann-Whitney U test, t-test, and generalized estimation equations (GEE).
Results: There were significant differences between the two groups regarding SEE (χ2=13.53,
p =.009), PA (χ2=9.51,p =.049), functional status (χ2=10.55,p =.032), and 6MWD (χ2=15.62,p =.004). Although there were no time or group effects, the QOL mental component (Z=-2.78,p =.005) of the IG was higher than that of the CG one month after surgery. Interventions did not affect dyspnea or the QOL physical component.Conclusion The intervention of this study was effective in improving SEE, PA, functional status, and 6MWD of lung cancer patients after lung resection. Further extended investigations that utilize ETPB are warranted to confirm these results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- [Retracted] Dynamic Changes and Influencing Factors for the Quality of Life in Nursing Care after Lung Cancer Resection
Shuzhen Hu, Aihong Fang, Mohammad Farukh Hashmi
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on influence factors of public participation willingness in substation project based on integrated TPB-NAM model
Xin Ma, Junpeng Li, Fuli Guo, Caocao Cui, Tengfei Chen, Fan Xv, Wenbin Wang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- [Retracted] Dynamic Changes and Influencing Factors for the Quality of Life in Nursing Care after Lung Cancer Resection
- 2,617 View
- 107 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Smartphone App-Based Exercise Program for Hemodialysis Patients
- Eun Jeong Ki, Hyang Sook So
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):52-65. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: To examine the effects of a smartphone application-based exercise program on self-efficacy expectations (SEE) and outcome expectations regarding exercise (OEE), physical fitness, activity level, physiological indices, and health-related quality of life in a sample of hemodialysis patients.
Methods: A quasi-experimental control group pre-test post-test design was used. Subjects were recruited from two university hospitals in G city. The subjects were assigned randomly by coin toss: 33 participants to the experimental group and 30 to the control group. A literature review and the self-efficacy theory were used to develop the smartphone program. Experts designed and verified the program to be userfriendly and in consideration of user interaction. Data were collected through a self-report pre-test post-test questionnaire and online medical records.
Results: In the experimental group, the levels of physical fitness and physical activity were significantly improved post-test, but the scores on health-related quality of life and the physical indices did not improve. In the experimental group, the SEE and OEE post-test scores were also significantly higher than the pre-test scores, but the control group’s scores did not change.
Conclusion The smartphone application-based exercise program based on self-efficacy theory significantly improved the level of physical fitness and activity, SEE, and OEE for hemodialysis patients. The use of this application-based exercise program for hemodialysis patients might be an effective nursing intervention tool for improving SEE, OEE, level of physical fitness, and physical activity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of digital health interventions in older adults with frailty: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Meng-Yao Liang, Jin-Rui Cui, Xin Fan, Jun-Jie Zhang, Xiao-Ling Liu, Dong-Gui Liu
International Journal of Nursing Studies Advances.2026; 10: 100470. CrossRef - The impacts of a mHealth platform-enabled lifestyle-integrated multicomponent exercise program on reversing pre-frailty in community-dwelling older adults: A randomized controlled trial
Na Li, Nan Wang, Yuqing Xu, Siyang Lin, Yin Yuan, Feng Huang, Pengli Zhu
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2025; 167: 105072. CrossRef - A Prospective Study of Relation between Academic & Exercise Stress, Quality of Life and Mibyeong in the College Students Majoring Physical Education
Yeonju Woo, Soojin Lee
Journal of Physiology & Pathology in Korean Medicine.2025; 39(1): 36. CrossRef - The Mediating Effects of Symptom Experiences on the Relationship between Body Image and Quality of Life among Hemodialysis Patients in a Single Center
Yaki Yang
Healthcare.2024; 12(17): 1779. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a mHealth platform-based lifestyle integrated multicomponent exercise (PF-Life) program to reverse pre-frailty in community-dwelling older adults: a randomized controlled trial study protocol
Na Li, Feng Huang, Nan Wang, Siyang Lin, Yin Yuan, Pengli Zhu
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Physical Activity and Exercise Interventions for People Living with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review of Health Outcomes and Feasibility
Meg E. Letton, Thái Bình Trần, Shanae Flower, Michael A. Wewege, Amanda Ying Wang, Carolina X Sandler, Shaundeep Sen, Ria Arnold
Journal of Medical Systems.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lifestyle interventions delivered by eHealth in chronic kidney disease: A scoping review
Ffion Curtis, James O. Burton, Ayesha Butt, Harsimran K. Dhaliwal, Matthew M.P. Graham-Brown, Courtney J. Lightfoot, Rishika Rawat, Alice C. Smith, Thomas J. Wilkinson, Daniel S. March, Henry H.L. Wu
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0297107. CrossRef - The effect of an educational app on hemodialysis patients’ self-efficacy and self-care: A quasi-experimental longitudinal study
Amin Hosseini, Alun C Jackson, Najmeh Chegini, Mohsen Fooladzadeh Dehghan, Danyal Mazloum, Shima Haghani, Fatemeh Bahramnezhad
Chronic Illness.2023; 19(2): 383. CrossRef - Effects of an arteriovenous fistula stenosis prevention program in patients receiving hemodialysis
Haegyeong Lee, Gyuli Baek, Eunju Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(4): 279. CrossRef - The effectiveness of structured educational programs for hemodialysis patients in Korea: an integrated literature review
Young Ran Chae, Jeong-Joo Choi, Min Sub Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(3): 143. CrossRef - Effect of the SNS-Based Physical Activity-Related Psychological Intervention on Physical Activity and Psychological Constructs among Inactive University Students
Youngho Kim, Jonghwa Lee
International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology.2022; 22(2): 100299. CrossRef - Self-Management Micro-Video Health Education Program for Hemodialysis Patients
Qingli Ren, Suhua Shi, Chen Yan, Yang Liu, Wei Han, Min Lin, Honggu He, Qu Shen
Clinical Nursing Research.2022; 31(6): 1148. CrossRef - Mobile health platform based on user-centered design to promote exercise for patients with peripheral artery disease
Mihui Kim, Yesol Kim, Mona Choi
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effect of digital health interventions in older adults with frailty: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1,914 View
- 55 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of a Web-Based Korean Triage and Acuity Scale Learning Program on Triage Self-Efficacy and Triage Performance Ability for Nurses in Emergency Department
- Hyo-Jin Kim, Hee-Young Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):171-180. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The Korean Triage and Acuity Scale (KTAS) is a tool used to classify the severity and urgency of emergency department (ED) patients, focusing on their symptoms. In consideration of the importance of the KTAS, a web-based learning program has emerged as a new mode of education; it enables ED triage nurses to access it anytime and anywhere, and according to their own learning abilities. This study aimed to develop a web-based KTAS learning program and evaluate its effects on self-efficacy and triage performance ability in ED nurses.
Methods A quasi-experimental design with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest was used. The conceptual framework was Bandura's self-efficacy theory. There were 30 participants in the experimental group and 29 in the control group. The experimental group attended an orientation and 4 sessions of a web-based KTAS learning program. The learning program lasted 280 minutes over five weeks, consisting of 40 minutes of orientation and four 60-minute sessions.
Results The scores of self-efficacy, triage performance ability in KTAS level, and chief complaints significantly increased in the experimental group compared to the control group. In addition, the numbers of under-triage in KTAS significantly decreased in the experimental group in comparison to the control group.
Conclusion The results suggest that the learning program was effective in improving ED nurses' level of self-efficacy and triage performance ability (KTAS level and KTAS chief complaint). Accordingly, the web-based KTAS learning program can be applied as an education intervention to improve ED nurses' triage skill.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimizing triage education for emergency room nurses: A scoping review
Hui Ju Shin, Subin Park, Hyun Joo Lee
Nurse Education Today.2025; 144: 106452. CrossRef - Strategies to improve the quality of nurse triage in emergency departments: A systematic review
Simon Ouellet, Maria Cécilia Gallani, Guillaume Fontaine, Éric Mercier, Alexandra Lapierre, Fabian Severino, Céline Gélinas, Mélanie Bérubé
International Emergency Nursing.2025; 81: 101639. CrossRef - Construction of learning objectives and content for emergency triage nurses in tertiary general hospitals: A Delphi study
Linyuan Zhang, Bo Gao, Fang He, Chao Wu, Juan Du, Li Zhang, Juan Liang, Hongjuan Lang
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 80: 104145. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the Patient’s Severity Classification Competency Promotion Virtual Reality Program of Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period
Eunju Lee, Gyuli Baek, Yeonhui Hwang
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1122. CrossRef - Effects on Triage Competency Based on Nursing Task Performance and Self-Efficacy of Nurses in Regional Emergency Medical Institutions
Su Jin Kim, Su Ol Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 304. CrossRef - The Effect of Competency-Based Triage Education Application on Emergency Nurses’ Triage Competency and Performance
Sun-Hee Moon, In-Young Cho
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 596. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Patient Satisfaction in an Emergency Department Based on the Use of the Korea Triage and Acuity Scale
Keun Hee Park, Min Yoon, Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 338. CrossRef - Factors associated with the undertriage of patients with abdominal pain in an emergency room
Boo Young Oh, Kisook Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2021; 54: 100933. CrossRef - Facilitators and Barriers of the Triage Process based on Emergency Nurses’ Experience with the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale: A Qualitative Content Analysis
Sun-Hee Moon, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Deok Ju
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(4): 255. CrossRef - Effect of problem-based learning on severity classification agreement by triage nurses
Kyeongmin Jang, Eunmi Jo, Kyoung Jun Song
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Remote Diagnosis System of Uremia Complicated with Sleep Disorder and Effectiveness of Nursing Intervention
Yiqian Wang, Jing Zhu, Jun Cao, Dan Zheng, Lihua Wang, Yuvaraja Teekaraman
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Comparing the Effect of Web-based Networking Education and Lectures on Learning of Hospital Triage in Nursing Students in Armed Forces Universities of the Islamic Republic of Iran in the Covid-19 Pandemic
Ashkan Morovati, Zahra Farsi, Nahid Rajai, Seyede Azam Sajadi
Military Caring Sciences.2021; 8(2): 127. CrossRef
- Optimizing triage education for emergency room nurses: A scoping review
- 2,465 View
- 47 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Effects of a Daily Life-Based Physical Activity Enhancement Program for Middle-Aged Women at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
- Kyung Ae Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):113-125. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a daily life-based physical activity enhancement program performed by middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease.
Methods This study used a randomized control group pretest-posttest design. Middle-aged women aged 45 to 64 were recruited from two outpatient cardiology departments, and randomly assigned to an experimental group (n=28) and a control group (n=30). For the experimental group, after providing one-on-one counseling and education, we provided customized text messages to motivate them in daily life. To monitor the practice of physical activity, they also used an exercise diary and mobile pedometer for 12 weeks. Subjects' physical activities (MET-min/week) were measured using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). Their physiological data were obtained by blood tests using a portable analyzer, and the data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0/WIN program.
Results There were significant differences in exercise self-efficacy, health behavior, IPAQ score, body fat, body muscle, and fasting blood sugar between the two groups. However, there were no significant differences in total cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and waist-to-hip ratio.
Conclusion Strengthening physical activity in daily life without being limited by cost burden and time and space constraints. Therefore, it is essential to motivate middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease to practice activities that are easily performed in their daily lives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
Miseon Seo, Eun-Young Jun, Hyunjin Oh
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Effects of Breathing Exercises Using Virtual Reality and Schroth Breathing Exercises on the Lung Function of Adults in Their 20s
Byung-Kon Kim, Wook-Jin Lee
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(2): 67. CrossRef - Effectiveness of physical activity monitors in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis
Rasmus Tolstrup Larsen, Vibeke Wagner, Christoffer Bruun Korfitsen, Camilla Keller, Carsten Bogh Juhl, Henning Langberg, Jan Christensen
BMJ.2022; : e068047. CrossRef - Trajectories of subjective health status among married postmenopausal women based on the ecological system theory: a longitudinal analysis using a latent growth model
Eun Jin Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 123. CrossRef - Effect and mechanism of tai chi on blood pressure of patients with essential hypertension: a randomized controlled study
Bo LIN, Qiu JIN, Chunhua LIU, Wenhui ZHAO, Runyuan JI
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of behaviour change interventions on changes in physical activity and anthropometrics in ambulatory hospital settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Stephen Barrett, Stephen Begg, Paul O’Halloran, Owen Howlett, Jack Lawrence, Michael Kingsley
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to the Identification of Middle-Aged Women Who are Disadvantaged by Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease
Moon Jung Kang, Jee Seon Yi, Chang Seung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(2): 185. CrossRef
- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
- 2,375 View
- 47 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Health Promotion Program Using Action Planning Strategy for Young Adults
- Su Hyun Kim, Min Ji Kim, Sang Hee Kim, So Yeon Kim, Chae Yeon Park, Jee Yun Bang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):461-471. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.461
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a health promotion program utilizing action planning strategy for young adults.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pre-post-test design was used. One hundred three university students participated in the study. Participants in the experimental group (n=51) were provided the health promotion program utilizing action planning strategy for five weeks. The program consisted of weekly sessions that included action planning and group feedback. The control group (n=52) was provided with health information every week for 5 weeks. Program outcomes, including self-efficacy, physical activity health behaviors, total exercise time per week, daily cigarette consumption, frequency of alcohol drinking per month, nutritional health behaviors, and subjective health status, were assessed at baseline and at follow-up after 5 weeks.
Results The participants in the experimental group demonstrated significant increases in self-efficacy, physical activity health behaviors, weekly exercise time, and nutritional health behaviors and significant decreases in daily cigarette consumption than those in the control group.
Conclusion The health promotion program utilizing action planning strategy is a brief and effective intervention to promote health behaviors among young adults. Further investigation is warranted to assess the program's effectiveness among other age groups and populations at high risk for chronic illness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Meta-Analysis of Implementation Intentions Interventions in Promoting Physical Activity among University Students
Sanying Peng, Ahmad Tajuddin Othman, Ahmad Zamri Khairani, Zhuang Zhou, Xiaogang Zhou, Fang Yuan, Jinghong Liang
Sustainability.2023; 15(16): 12457. CrossRef - Validation of Types of Body Pain Areas and Related Factors in the Korean Aged Using Latent Class Analysis
Sang Ye Shin, Eun Suk Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2023; 34: 22. CrossRef - E-Questionnaire on health knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP-Health) for Brazilian students in distance learning
Jane Biscaia Hartmann, Amanda Tribulato Rego, Julia Vieira Khoury, Marcelo Picinin Bernuci, Mirian Ueda Yamaguchi
Global Health Action.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Meta-Analysis of Implementation Intentions Interventions in Promoting Physical Activity among University Students
- 2,130 View
- 57 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Perceived Self-Management Support and Health-Related Quality of Life among Cancer Survivors
- Bo Gyeong Lee, Tae Sook Lee, Soo Hyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):298-306. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.298
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to examine the levels of perceived self-management support, self-efficacy for self-management, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in cancer survivors, and to identify the mediating effect of self-efficacy in the relationship between perceived self-management support and HRQoL.
Methods This study used a descriptive correlational design. Two hundred and four cancer survivors who had completed treatment participated in the study. Measurements included the Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care Scale, the Korean version of the Cancer Survivors’ Self-Efficacy Scale, and the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation coefficient analysis, and multiple regression analysis using Baron and Kenny's method for mediation.
Results The mean score for perceived self-management support was 3.35 out of 5 points, self-efficacy was 7.26 out of 10 points, and HRQoL was 65.90 out of 100 points. Perceived self-management support was significantly positively correlated with self-efficacy (r=.29,
p <.001) and HRQoL (r=.27,p <.001). Self-efficacy was also significantly correlated with HRQoL (r=.59,p <.001). Furthermore, self-efficacy (β=.55,p <.001) had a complete mediating effect on the relationship between perceived self-management support and HRQoL (Z=3.88,p <.001).Conclusion The impact of perceived self-management support on HRQoL in cancer survivors was mediated by self-efficacy for self-management. This suggests that strategies for enhancing self-efficacy in cancer survivors should be considered when developing self-management interventions for improving their HRQoL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
Soo Hyun Kim, Yu Hyeon Choe, Jingyeong Choi, Ji Young Park, Eun Yi
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(1): E47. CrossRef - Effects of Symptom Burden, Self-Efficacy, and Stigma on Cancer Coping in Patients with primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
Ah-Reum Han, Euna Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(3): 158. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Enhee Jo, Ju-Young Park, Young Jun Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 315. CrossRef - An Integrated Review of Health Care in Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
Hye Jin Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 82. CrossRef - Trajectories of quality of life in breast cancer survivors during the first year after treatment: a longitudinal study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of perceived chronic illness management support, health literacy, and social support on the care burden of families caring for older people with multiple chronic conditions at home: A cross-sectional study
Eun Sil Lee, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 76. CrossRef - Effects of Uncertainty, Appraisal of Uncertainty, and Self-Efficacy on the Quality of Life of Elderly Patients with Lung Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy: Based on Mishel’s Theory of Uncertainty
Min-Kyung Hwang, Hee-Kyung Kim, Ki-Hyeong Lee
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1051. CrossRef - Between Personality Traits and Postpartum Depression: The Mediated Role of Maternal Self-Efficacy
Lingli Han, Ji Zhang, Jingxuan Yang, Xiaoyu Yang, Hua Bai
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment.2022; Volume 18: 597. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Quality of Life in Patients after Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Jeong Won Yeom, Yeon Ok Suh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2564. CrossRef - The influence of Digital Informatization Level, Self-efficacy, and Social Support on Digital Health Literacy in the Elderly with Cancer
Hye Su Kim, Ji Hyun Sung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(4): 255. CrossRef - The Correlation Between Quality of Life and Positive Psychological Resources in Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis
Xinxin Zhao, Siqi Tong, Ye Yang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated, cross-sectoral psycho-oncology (isPO): a new form of care for newly diagnosed cancer patients in Germany
Michael Kusch, Hildegard Labouvie, Vera Schiewer, Natalie Talalaev, Jan C. Cwik, Sonja Bussmann, Lusine Vaganian, Alexander L. Gerlach, Antje Dresen, Natalia Cecon, Sandra Salm, Theresia Krieger, Holger Pfaff, Clarissa Lemmen, Lisa Derendorf, Stephanie St
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-efficacy, post-traumatic growth, and quality of life of pediatric cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Yeunhee Kwak, Yoonjung Kim, Eun Seok Choi, Ho Joon Im
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102019. CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of patient assessment of chronic illness care among Korean cancer survivors
Soo Hyun Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee, Yu Hyeon Choe, Francesca Chiesi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0256119. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef
- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
- 2,117 View
- 42 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Combined Exercise Program for Older Adults with Sarcopenia Based on Transtheoretical Model
- Seoyoun Park, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):656-668. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.656
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and examine the effects of combined exercise program for older adults with sarcopenia based on transtheoretical model (TTM).
Methods A non-equivalent control group with a pretest-posttest design was used. The subjects consisted of 43 older adults with sarcopenia in precontemplation stage, contemplation stage and preparation stage of TTM (experimental group: 22, control group: 21). The developed program consisted of 36 sessions for 12 weeks including combined exercise (60 minutes) and TTM based strategies for enhancing exercise behavior (10 minutes) per session. Data were collected before, immediately after the program between July 31 to October 27, 2017. The data were analyzed using independent t-test, Mann-Whitney U test with SPSS/WIN 18.0.
Results Compared with their counterparts in the control groups, older adults with sarcopenia in the experimental group showed a significantly greater improvement in process of exercise behavior change, pros and cons of decisional balance for exercise behavior, exercise self-efficacy, parameters of muscle, and the level of physical performance.
Conclusion The study findings indicate that this combined exercise program for older adults with sarcopenia based on TTM model was effective and can be recommended as a nursing intervention for older adults with sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 175. CrossRef - Research Progress of Body Composition Changes in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
鹏霞 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(08): 7181. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Diagnostic Tools and Interventions for Sarcopenia
Moon Joo Cheong, Yeonseok Kang, Sungchul Kim, Hyung Won Kang
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 199. CrossRef - Research of Home-Based Exercise Program Development and Effect Analysis: Prevention of Sarcopenia in Hemiplegic Disorder
Myung Nam Ha, Gyoo Yeong Cho
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(2): 97. CrossRef - Effects of a 12-Week Transtheoretical Model–Based Exercise Training Program in Chinese Postoperative Bariatric Patients: a Randomized Controlled Trial
Ziqi Ren, Hanfei Zhu, Tianzi Zhang, Hongxia Hua, Kang Zhao, Ningli Yang, Hui Liang, Qin Xu
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(10): 4436. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Physical Activity Promotion Programs for Elderly Patients Hospitalized in Long-term Care Hospital
Se In Ryu, Aekyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(4): 400. CrossRef - Study on the Relationship between Hand Grip Strength, Depression, Somatic Symptoms and Health-related Quality of Life of the Elderly in Rural Area
Sun-Sook Moon, Chang Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 23(1): 80. CrossRef
- Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
- 3,122 View
- 90 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The Effects of an Acceptance-Commitment Therapy Based Stress Management Program on Hospitalization Stress, Self-Efficacy and Psychological Well-Being of Inpatients with Schizophrenia
- Jae Woon Lee, Jae Hyun Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):443-453. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.443
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct an acceptance-commitment therapy (ACT)-based stress management program for inpatients with schizophrenia and to examine its effects on hospitalization stress, self-efficacy, and psychological well-being.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. Participants were 44 inpatients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia. The experimental group (n=22) received the ACT-based stress management program twice a week for a total of four weeks. The control group (n=22) received the usual care from their primary health care providers. The study was carried out from August 7 to September 1, 2017, and data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN 22.0 with a Chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, and an independent t-test.
Results The experimental group showed a significant decrease in hospitalization stress (t=5.09,
p <.001) and an increase in self-efficacy (t=2.44,p =.019). However, there was no significant difference in psychological well-being between the two groups (t=0.13,p =.894).Conclusion The results of this study suggest that the ACT-based stress management program can be used as an effective mental health nursing intervention for hospitalization stress and self-efficacy for inpatients with schizophrenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors that influence hospitalization stress in patients with chronic schizophrenia: A cross‐sectional study in psychiatric hospitals
Sumin Chai, Goun Kim
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 32(1): 102. CrossRef - Positive mental health interventions for people with schizophrenia: A scoping review
Catarina Nogueira, Emanuel Dias Pereira, Joana Catarina Ferreira Coelho, Antonio Rafael Moreno-Poyato, Carlos Alberto Cruz Sequeira
Schizophrenia Research.2025; 276: 40. CrossRef - Effects of entrapment, anger, psychological flexibility, and self-compassion on the ward climate and reactive aggression in forensic psychiatric hospital patients
Sul Hwan Kim, ChongNak Son
International Journal of Law and Psychiatry.2024; 94: 101986. CrossRef - The effect of Treatment based on Acceptance and Commitment on Pathological Worry and Death Anxiety in Nurses with the Experience of Complicated Grief Caused by COVID-19
V Aghaei, R Kazemi, S Taklovi, V Nazari
Journal of Health and Care.2024; 26(1): 52. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy on Pain
Coping Strategies and Pain Self-efficacy in Chronic Neuropathic Pain
Patients
farzaneh Dehestani, Bahram mirzaian, ramazan hassanzadeh, payam saadat
Scientific Journal of Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences.2023; 27(6): 97. CrossRef - Effects of Structured Group Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Psychological Acceptance and Recovery Among Inpatients With Psychotic Disorder: A Pilot Study
Narae Jeong, Hyesu Jeon, Dowon You, Yu Sang Lee
Korean Journal of Schizophrenia Research.2022; 25(2): 32. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) on Sexual Self-Efficacy and Sexual Quality of Life in Reproductive-Age Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Behnaz Enjezab, Marzieh Rejaezadeh, Mahshid Bokaie, Hajar Salimi
Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy.2021; 47(8): 764. CrossRef - Training coping skills and coping with stress self-efficacy for successful daily functioning and improved clinical status in patients with psychosis: A randomized controlled pilot study
Débora Godoy Izquierdo, María Luisa Vázquez Pérez, Raquel Lara Moreno, Juan F Godoy García
Science Progress.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Smartphone Overdependence Prevention Program for University Students Based on Self-Determination Theory
Myung Soon Kwon, Jeong Soon Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(1): 116. CrossRef - Effects of Acceptance Commitment Therapy Based Recovery Enhancement Program on Psychological Flexibility, Recovery Attitude, and Quality of Life for Inpatients with Mental Illness
In Sook Kim, Jae Woon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(1): 79. CrossRef - Development and Effects of an Acceptance Commitment-based Cognitive Behavioral Program for Patients with Schizophrenia
Jae Woon Lee, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2018; 27(4): 342. CrossRef
- Factors that influence hospitalization stress in patients with chronic schizophrenia: A cross‐sectional study in psychiatric hospitals
- 1,741 View
- 35 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Actor and Partner Effects of Health Status, Marital Satisfaction and Self Efficacy on Retirement Preparation of Middle Aged Couples: Actor-Partner Interdependence Model Analysis
- Eun Hee Jung, Sung Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):154-166. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.154
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to identify the actor and partner effects of health status, marital satisfaction, and self efficacy on retirement preparation in middle aged couples using the Actor-Partner Interdependence Model.
Methods Participants were 121 middle aged couples living in Seoul, Gyeonggi-do and Daegu City, Korea. All measures were self-administered. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0.
Results 1) Wife's self efficacy and marital satisfaction showed direct actor and partner effects on retirement preparation in middle aged couples. Wife's health status showed an indirect actor effect through wife's self efficacy and marital satisfaction on wife's retirement preparation, and showed an indirect partner effect through husband's self efficacy on husband's retirement preparation. 2) Husband's self efficacy and marital satisfaction showed only direct actor effect on retirement preparation. Health status among the husbands showed an indirect actor effect on husband's retirement preparation through their self efficacy and marital satisfaction, and an indirect partner effect through wife's marital satisfaction on wife's retirement preparation. 3) The actor effect size of health status on self efficacy and marital satisfaction was larger among husband's than wife's. Additionally, the partner effect size of health status on self efficacy and marital satisfaction was different between the two groups; however, the actor and partner effect size of self efficacy and marital satisfaction on retirement preparation was the same for husband and wife.
Conclusion The results of this study indicate that nursing intervention strategies for improving self efficacy and marital satisfaction are strongly needed to enhance retirement preparation of middle aged couples in Korean community.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dyadic Research of Patients and Their Family Caregivers in the Context of Chronic Illness: Current Status and Challenges
Youn-Jung Son
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 415. CrossRef - The Effects of Climacteric Symptom Cognition, Self-efficacy on Aging Anxiety in Middle-Aged Couples: Actor and Partner Interdependence Mediation Model
Yeon-Suk Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 247. CrossRef - Actor and Partner Effects of Couple's Daily Stress and Dyadic Coping on Marital Satisfaction
Su Kyung Won, Kyoung Ok Seol
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 813. CrossRef
- Dyadic Research of Patients and Their Family Caregivers in the Context of Chronic Illness: Current Status and Challenges
- 1,280 View
- 16 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Effects of a Children's Sex Education Program for the Parents of Lower Elementary Grade Students
- Eun Mi Lee, Hyunlye Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):222-232. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop a children's sex education program for the parents of lower elementary grade students and to evaluate its effects on sexual knowledge, gender role attitude, parent efficacy for child's sex education, and marital consistency.
Methods A quasi-experimental with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The participants were 29 couples (58 parents, experimental group=28, control group=30) from G city. The 5-week (5-session) program was developed based on ‘A theory of protection: parents as sex educators’ and used the case-based small group learning method. Data were collected during July and August 2015. The characteristics of the program developed in the present study were a theoretical-based, client-centered, multi-method.
Results After the intervention, the experimental group showed a significant improvement in sexual knowledge, gender role attitudes, parent efficacy for child's sex education, and marital consistency, compared to the control group. The effect sizes of the program were .64 (knowledge), .65 (gender role attitudes), and .68 (parent efficacy).
Conclusion The results of this study provided implications for the parents as effective sex educator and the role expansion of school health nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parental Attitude Towards Sex Education: A Study of Demographic and Socio-Cultural Determinants in Rural Nigeria
Abdullateef Raji, Lanre Abdul-Rasheed Sulaiman, Moshood Issa, Abubakar Yunusa Muhammed, Ridwan Olabisi Yusuff, Salihu Zakariyyah Abdulbaqi, Sunday Joseph Akor
Sexuality Research and Social Policy.2026; 23(1): 217. CrossRef - A study on the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the parenting outcome expectancy scale for parents of elementary school students
Yoonjung Kim, Jungmin Lee, Ratchneewan Ross
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of parents in hygienic and sexual education of children and adolescents
NO Demchenkov, ED Krasilnikova, NI Sheina, VV Korolik
Российский вестник гигиены.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Children’s Sexual Health Education Program on Knowledge and Attitude of Primary School Health Care Providers
Zahra Barimani Aboksari, Jila Ganji, Nouraddin Mousavinasab, Soghra Khani
Journal of Child Sexual Abuse.2021; 30(5): 563. CrossRef - Comparison of the Effects of Sex Education with Two Methods of Educational Pack and Group Discussion on Awareness in Mothers of Pre-school Children
F Alaee karahroudy, Z Aryaeefar, S Maleki
Journal of Health and Care.2021; 22(4): 339. CrossRef - The significance of understanding psychosexual development and sexuality education for Vietnamese adolescents
Nguyen Thi Lan, Nguyen Huy Huong
International Journal of Research Studies in Education.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Parental Attitude Towards Sex Education: A Study of Demographic and Socio-Cultural Determinants in Rural Nigeria
- 2,519 View
- 27 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of a Strength Based I-Change Smoking Cessation Program for Smoking Middle School Boys
- Jung Hee Kim, Yeon Hee Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):164-177. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop a strength based I-change smoking cessation program for middle school boys and identified its effects.
Methods The study design was a nonequivalent control group pre-post test design. The participants were 97 middle school students from D city, who were in school from April 6 to September 25, 2015. The experimental group participated in the strength based I-change smoking cessation program, while the comparative group participated in a general smoking cessation program. The control group did not participate in any program. Data analyses involved χ2-test, Fishers' exact test, Bonferroni test, and Repeated measures ANOVA, with the IBM SPSS for Windows (version 20.0) program.
Results Compared to the comparison and control groups, the experimental group showed significant improvement in knowledge, attitude, self-efficacy, behavior change. Also cotinine in urine and modeling of social influence in the experimental group significantly decreased after the strength based I-change smoking cessation program.
Conclusion These findings indicate that the strength based I-change smoking cessation program is an effective intervention for middle school boys who smoke. The findings suggest that such programs can be used at public health centers or through school health education to decrease smoking in adolescents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Adler's Theory‐Based nudge volunteer program on middle school students
Eunae Kim, Jongeun Lee
Psychology in the Schools.2025; 62(1): 136. CrossRef - The development and evaluation of an I-message smoking prevention program for high school students: A randomized controlled trial
Song Hwa Chae, Bu Kyung Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(2): 161. CrossRef - Association of Smoking Media Literacy with Vietnamese and South Korean Adolescents’ Susceptibility to Smoking
Sun Young Shim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Sookyung Kim, Nguyen Thi Thanh Huong, Young-Me Lee, Phương Lê Thị, Bui Thi Thanh Loan
The Journal of School Nursing.2024; 40(4): 391. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a media literacy‐based smoking prevention program in female adolescents
Sookyung Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Sanghee Kim, Kyung Hee Lee, Seunghyun Yoo, Jin Eui Hong
Public Health Nursing.2024; 41(3): 525. CrossRef - Adolescents and youths’ opinions about the factors associated with cannabis use: a qualitative study based on the I-Change model
María González-Cano-Caballero, María-Carmen Torrejón-Guirado, María Dolores Cano-Caballero, Isotta Mac Fadden, María-Del-Carmen Barrera-Villalba, Marta Lima-Serrano
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of the Smoking Cessation Program of Life Skill Training Using Flipped Learning for Middle School Male Students
Eun Hee Seo, Eun Suk Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(3): 268. CrossRef - The effects of smoking cessation program using breath-mindfulness meditation
Hyeon-Ah Cho
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2021; 38(3): 23. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Integrated Change Model-based Smoking Cessation Program for High School Students
Hae Seon Lee, Su Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(2): 195. CrossRef
- Effects of Adler's Theory‐Based nudge volunteer program on middle school students
- 1,365 View
- 20 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Study on the Relationship of Perceived Self-efficacy and Sick-role behavioral Compliance in Diabetic children
- Yeon Hee Choi
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(1):127-137. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.1.127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to identify the relationship of perceived self-efficacy and sick-role behavioral compliance in diabetic children. The forty-two diabetic children participating in this study were selected from outpatients. The period of data collection was August 8 to December 9, 1994. Collected data were analyzed by means of chi-square test, t-test, Pearson correlation using SPSS/PC+. The result are summarized as follows: 1. The mean score of perceived self-efficacy was 3. 21 that of sick-role behavioral compliance 3.17. 2. Perceived self-efficacy and sick-role behavioral compliance had a positive correlation which was statistically significant (r=0.77, P<0.001). 3. There were statistically significant difference in perceived self-efficacy according to age(p<0. 01) and acknowledgment of prescribed calories in the diabetic diet (p<0.001). 4. There were statistically significant difference in sick-role behavioral compliance according to age(p<0.01) and acknowledgment of prescribed calories in the diabetic diet (p<0.001). These results suggest that perceived self-efficacy is an important variable in the compliance of diabetic children. Nursing intervention needs to be directed at promoting perceived self-efficacy to maintain sick ?role behavioral compliance for diabetic children. Therefore programs of nursing intervention should be revised in order to promote perceived self ?efficacy in diabetic children.
- 433 View
- 1 Download

- A Predictive Model Comparison by Sex for Alcohol Consumption Behavior among Korea University Students
- Myung Sook Choi, Mee Young Im, Young Mi Yoon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(1):77-88. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was designed to develope and test the structural model that explains alcohol consumption behaviors among university students in Republic of Korea. The hypothetical model was constructed on the basis of the literature review and Pender's Health promotion model. Data was collected from questionnaires from 512 university students in Republic of Korea, from August to September, 2000. The reliability of instruments was adequate (Cronbach's alpha= .69-.90). Data analysis was done with SAS 6.12 for descriptive statistics and LISREL 8.13 program for covariance structural analysis. The results are as follows;1. The overall fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate. Thus it was modified by male and female models.2. The revised model has become parsimonious and had a better fit to the empirical data (male: x2=87.21 p=.00, GFI=.97, AGFI= .94, NFI=.99, NNFI=1.0, CN=619.17, female: x2=49.29 p=.31, GFI=.45, AGFI= .95, NFI=.99, NNFI=1.0, CN=370.02).3. Self-efficacy was most significant factor and personality of novelty seeking, reward compensation, alcohol expectancy and drinking attitude have significant effects on male alcohol consumption behavior. 4. Personality of novelty seeking was most significant factor and personality of harm avoidance, friend influence, self-efficacies, alcohol expectancy and drinking attitude have significant effects on female alcohol consumption behavior.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Equation Model for the Analysis of Alcohol-related Problem of Alcohol Use Disorders
Hee Jung Son, Won Kee Lee, Young Shin Park, Hae Sook Hong
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(2): 192. CrossRef - Affecting factors of the Drinking Behavior of Liver Cirrhosis Patients The Aspects of Convergence of Drinking Behavior and Disease-related of factors
Young-Sook Seo, Eun-Su Do
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(7): 249. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of a Drinking Refusal Self-Efficacy Questionnaire-Revised (DRSEQ-R) in Korean College Students
Young-Ran Tak, Ji-Yeon An, Hae-Young Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 344. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of a Drinking Refusal Self-Efficacy Questionnaire-Revised (DRSEQ-R) in Korean College Students
Young-Ran Tak, Ji-Yeon An, Hae-Young Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 344. CrossRef - Challenges in Coming of Age in Korea
Mihyoung Lee, Miok Lee, Steven L. Baumann
Nursing Science Quarterly.2005; 18(1): 71. CrossRef
- Structural Equation Model for the Analysis of Alcohol-related Problem of Alcohol Use Disorders
- 752 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- The Effect of the Self Efficacy Promotion and Exercise Training Program of Kidney Transplant Recipients
- Jae Hyun Ahn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(5):1181-1194. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.5.1181
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was attempted to evaluate how the self efficacy promotion and exercise training program effect on the postoperative general conditions of transplant recipients after kidney transplantations. The subjects were selected randomly among the patients who underwent renal trans- plantations at three major transplantation hospitals in Seoul, Korea. This study was carried out between November 1999 and March 2000. The observed subjects in this study consisted of 56 patients. The exercise training group(n=16) received the self efficacy promotion and exercise training program for 12 weeks which contained general knowledge for compliance instruction, exercise training and self efficacy promotion education. The self efficacy group(n=18) received general knowledge for compliance instruction and self efficacy promotion education but no exercise training was given. The control group(n=22) were not offered any education. The knowledge for compliance, self efficacy, physical conditions(weight, muscle strength, muscle endurance, flexibility), lab studies (hemoglobin, creatinine, cholesterol), activities of daily living and quality of life were evaluated 3 times, before the experiment, at 8 weeks and at 12 weeks. The data were analyzed with mean, standard deviation, Chi-square test, ANOVA and Scheff test. The results were as follows: 1. The knowledge and self efficacy score of the exercise training group and self efficacy group were significantly increased than those of the control group(p=.0001). 2. The weight of the exercise training group was significantly decreased compared to those of the self efficacy group and the control group(p=.0001). Muscle strength (grip strength, back lift strength), and flexibility of all 3 groups were significantly changed(p=.0001). However, muscle endurance in all 3 groups showed no significant differences. 3. The hemoglobin level of the exercise training group and the self efficacy group were significantly increased compared to that of the control group(p=.0001) and the cholesterol levels of the exercise training group and the self efficacy group were significantly decreased compared to that of the control group(p=,0001). However, the creatinine levels in all 3 groups showed no significant differences. 4. The activities of daily living scores of the exercise training group was significantly increased than that of the control group (p=.0003), and the quality of life scores of the exercise training group and the self efficacy group were significantly better than that of the control group(p=.0001). It would be expected that this self efficacy promotion and exercise training program could be applied widely as an effective nursing intervention for kidney transplant recipients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Self-efficacy and Transplant-related Knowledge on Compliance with a Therapeutic Regimen for Recipients of Liver Transplant
So Jung Moon, Hyun-Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(3): 166. CrossRef - A Study on Self-efficacy, Coping, and Compliance in Patients with Kidney Transplantation
Jeong Lan Lee, Hyojung Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(1): 11. CrossRef - Development of a Comprehensive Self-Management Program Promoting Self Efficacy for Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Ju-Young Park, Il-Sun Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 74. CrossRef - Exercise training for adults with chronic kidney disease
Susanne Heiwe, Stefan H Jacobson
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2011;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of Self-efficacy and Transplant-related Knowledge on Compliance with a Therapeutic Regimen for Recipients of Liver Transplant
- 868 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of a Memory Training Program Using Efficacy Sources on Memory Improvement in Elderly People
- Jeong Hwa Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(5):1170-1180. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.5.1170
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was a quasi-experimental study to confirm the effects of a memory training program using efficacy sources. The purpose was to develop an effective memory training program for elderly people and to identify the effects of the memory training program. This study was carried out between February 24 and July 18, 1999 and the subjects of the study were 102 elderly people who were participants at a welfare institute in Seoul. The experimental group (51) and the control group (51) were assigned by means of participation order. The control group was matched to the experimental group and was selected considering age, sex, and religion. The experimental group participated in the memory training program. The memory training program was based on the literature of Fogler & Stern (1994), Wang & Lee (1990), Lee (1991) and Lee (1993). The memory training program was given twice a week for two weeks with each program lasting two hours. Task centered memory self-efficacy was measured using the Memory Self-Efficacy Scale developed by Berry & Dennehey (1989) and Meta Memory was measured by the MIA developed by Dixon et al. (1988) Memory performance was measured by the Data were analyzed by SPSS PC and the results are described below. 1. The experimental group which participated in the Memory Training Program showed higher task centered memory self-efficacy scores as compared to the control group (t=4.354, P=.0001). 2. The experimental group which participated in the Memory Training Program showed higher metamemory scores as compared to the control group (t=4.733, P=.0001). 3. The experimental group which participated in the Memory Training Program showed higher memory performance scores as compared to the control group (t=7.500, P=.0001). The memory performance involved an immediate word recall task, a delayed word recall task, a word recognition task, and the face recognition task. 4. In the experimental group, there was significant correlation between the task centered memory self-efficacy scores and the metamemory scores (r=.382, P=.006), but the correlation between the task centered memory self-efficacy scores and the memory performance scores and between the metamemory scores and the memory performance scores were not significant. The results showed that task centered memory self-efficacy, meta memory and memory performance improved following the Memory Training Program including the memory process, changes in memory with aging, and appropriate use of memory strategies. Memory Training Program is an effective nursing intervention for improving memory in elderly people and, also, in people with complaints of memory loss. word list developed by Cho Sung Won (1995) and the face recognition task (Face Recognition Task developed for this study).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving cognitive and functional outcomes in rural older adults living with dementia through paper-and-pencil training
Jung Mi Sook, Chung Eunyoung
Geriatric Nursing.2026; 67: 103718. CrossRef - Application of a cognitive program with a comprehensive strategy feedback for Korean older adults
Mi Kyeong Kim, Ji-Hyuk Park, Dae-Sung Han, Hae Yean Park
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 55: 213. CrossRef - Simultaneous cognitive-physical dual task training based on fairy tales in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: A pilot study
Younkyoung Kim, Myeongjeong Chae, Hyunju Yang
Geriatric Nursing.2021; 42(5): 1156. CrossRef - A Comparison of Memory Beliefs, Cognitive Activity, and Depression Among Healthy Older Adults, Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Patient with Alzheimer’s Disease
JongSik Park, Jooyeon Jamie Im, In-Uk Song, Yeonwook Kang
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2019; 23(1): 16. CrossRef - Effects of a Memory and Visual-Motor Integration Program for Older Adults Based on Self-Efficacy Theory
Eun-Hwi Kim, Soon-Rim Suh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 431. CrossRef - The Effects of a Cognitive Enhancement Group Training Program for Community-dwelling Elders
Young Ran Han, Mi Sook Song, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 724. CrossRef
- Improving cognitive and functional outcomes in rural older adults living with dementia through paper-and-pencil training
- 814 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Crossref

- The Relationship of Self Efficacy and Social Support to the Psychosocial Adjustment in People with Epilepsy
- Seong Mi Moon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):694-708. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.694
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The main purpose of this study was to identify the relationship of self efficacy and social support to the psychosocial adjustment in people with epilepsy. Data were collected from October 1 to October 15, 1999 from 101 people with epilepsy who were being treated regularly at one of the university hospitals located in Seoul. The research instruments were a questionnaire to gather demographic and disease-specific data, the Epilepsy Psycho- Social Effects Scale developed by Chaplin et al(1990), the Epilepsy Self Efficacy Scale developed by DiIorio et al(1992a) and translated by Park(1999), the Norbeck Social Support Questionnaire developed by Norbeck et al(1981) and translated by Oh(1985). Data were analyzed using the SPSS program. The results are as follow : 1. Of the 14 psychosocial adjustment areas, 75 of 101 subjects experienced problems in ten or more areas and 28 in all 14 areas. The severity of the psychosocial adjustment problem was moderate or more in six areas. 2. The score for self efficacy was an average of 1103.86 out of a possible 1800, for social support 117.57 for total functional out of a possible 720, and 48.21 for total network out of a possible 264. There were an average of five people on the network. The main network people were parents, brothers and sisters, spouse, friends. 3. Of the 14 psychosocial adjustment areas, six areas correlated with self efficacy and 'problems with taking medication' area had a negative correlation with social support. In conclusion, people with epilepsy have various problems in psychosocial adjustment. Nursing interventions using self efficacy should be developed to improve psychosocial adjustment in people with epilepsy. Also, instruments and interventions for regimen-specific supports which are suitable for epilepsy should be developed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Equation Modeling on Health-Related Quality of Life in Adults with Epilepsy
Jeong Ok Ko, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 624. CrossRef
- Structural Equation Modeling on Health-Related Quality of Life in Adults with Epilepsy
- 691 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Prediction Model for Stage of Change of Exercise In the Korean Elderly: Based on the Transtheoretical Model
- Soon Yong Kim, So In Kim, Young Ja Chun, Pyoung Sook Lee, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Sung Ok Chang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):366-379. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.366
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify causal relationships among variables of transtheoretical model for exercise in the elderly. A predictivel model explaining the stage of change was constructed based on a transtheoretical model. Empirical data for testing the hypothetical model was collected from 198 old adults over 60 years old in a community setting in Seoul, Korea in April and May,1999. Data were analyzed by descriptive statistics and correlational analysis using pc-SAS program. The Linear Structural Modeling (LISREL) 8.0 program was used to find the best fit model which predicts causal relationship of variables. The fit of the hypothetical model to the data was X2=132.85. (df=22, p=.000). GFI=.88, NNFI=.35, NFI=.77, AGFI=.59 which was not favorable but the fit of modified model to the data was X2=46.90. (df=27, p=.01).GFI= .95, NNFI=.91, NFI=.92, AGFI=.87) which was more than moderate. The predictable variables of stage of change for exercise of the Korean elderly were helping relationship, self cognitive determination, conversion of negative condition in process of change and efficacy for exercise . These variables explained 68% of stage of change for exercise of the Korean elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Stages of Exercise Behavior Change of Residents in a Community
Kyung-Shin Paek
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(3): 316. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Self-Efficacy in the Transtheoretical Model Among Adolescent Male Smokers in Korea
Ok Kyung Ham, Jae Bok Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2009; 3(1): 15. CrossRef - Korean adolescents' exercise behavior and its relationship with psychological variables based on stages of change model
Y KIM
Journal of Adolescent Health.2004; 34(6): 523. CrossRef - Korean adolescents' exercise behavior and its relationship with psychological variables based on stages of change model
Young-ho Kim
Journal of Adolescent Health.2004; 34(6): 523. CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Stages of Exercise Behavior Change of Residents in a Community
- 717 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Effects of a Epilepsy Education Program on Self Efficacy and Self Management in Patients with Epilepsy
- Yeong Sook Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):405-417. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.405
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to test the effects of a epilepsy education program as a nursing intervention for patients with epilepsy. A quasi treatment research (non equivalent control group pretest-posttest design) was used in this study. The subjects were 40 epilepsy patients visiting an outpatient department of a general hospital in Daegu city(treatment group : 20 patients, control group : 20 patients). The study was carried out from June, 19998 to September, 1998. Data was collected before the education program(pretest), immediately after(posttest 1) and 4 weeks later(posttest 2) and were analyzed with repeated measures ANOVA, t-test, Chi-square test and Pearson correlation coefficient. The results are as follows : There was a significant difference in epilepsy self efficacy between two groups(F=26.27, p=.000). There was a significant difference according to pretest, posttest 1 and posttest 2(F=111.20, p=.000), and interaction effect between treatment and time(F=109.42, p=.000). There was a significant difference in epilepsy self management between two groups(F=78.02, p=.000). There was a significant difference according to pretest, posttest 1 and posttest 2 test(F=94.02, p=.000), and interaction effect between treatment and time(F=88.14, p=.000). There was a significant correlation(r=.76, p=.000) between epilepsy self efficacy and epilepsy self management. These results suggest that a epilepsy education program is effective in promoting self efficacy and self management of the patient with epilepsy. Thus this program can be recommended as an effective nursing intervention for the epilepsy patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gender differences in factors associated with resilience for health-related quality of life in persons with epilepsy
Sang-Ahm Lee, Soo Jeong Kim, Noh Eul Han, Sun-Mi Lee, Young-Joo No
Epilepsy & Behavior.2021; 115: 107710. CrossRef - Self-efficacy in seizure management differentially correlated with quality of life in persons with epilepsy depending on seizure recurrence and felt stigma
Sang-Ahm Lee, Soo Jeong Kim
Seizure.2020; 81: 91. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of the Empowering A Self-Efficacy (EASE) Program for Children with Epilepsy
Hana Yoo, Hee-Soon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 54. CrossRef - Association of knowledge about epilepsy with mood and self-efficacy in Korean people with epilepsy
Sang-Ahm Lee, Byung-In Lee
Epilepsy & Behavior.2015; 52: 149. CrossRef
- Gender differences in factors associated with resilience for health-related quality of life in persons with epilepsy
- 675 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Determinants of Smoking-Cessation Behaviors in Female University Students
- Hae Won Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(1):48-60. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.1.48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to determine the factors influencing smoking-cessation behavior in female university students. a total of 534 students participated in this cross sectional study by answering a questionnaire. The data collection was done between September 1 and October 31, 1997. The measurement tools used in this study were the self help change process scale(Cronbach's alpha=.9930 : developed by Oh&Kim, 1996) for smoking-cessation behaviors, the self efficacy scale(Cronbach's alpha=.8250 : developed by Sherer et al, 1982), the sex role acceptance scale(KR-20=.7757 : developed by Kim, 1991) and the social support scale(Cronbach's alpha=.9172 : developed by Park, 1985). The summarized results are follows : 1. The mean scores for smoking-cessation behaviors in smokers(N=150) was 91.72 that was considered a middle score compared to the total possible score of measurement tool(150.0). The mean score for smoking-cessation behaviors by smoking-cessation step showed significant different between the groups(F=11.71, p= .000). 2. The group with no experience in smoking(N=332) showed a high general self efficacy score(t=5.24, p= .000), and more openness to sex role acceptance(t=-2.15, p= .032) compared to the group with smoking experience(N=202). 3. General self efficacy, sex role acceptance, and social support were not different significantly between the groups according to the steps in smoking-cessation. 4. Significant factors influencing smoking-cessation behavior(total, sub concepts) were religion, sex role acceptance, social support, smoking duration, smoking attitude, time of smoking onset, amount of smoking, drinking, and perception of health status. 5. Smoking-cessation behaviors which explained 11% of the variance were smoking attitude, and smoking duration. In conclusion, this study identified factors influencing smoking-cessation behavior. Thereby it will help in the development of smoking-cessation ration other determinants of smoking cessation behaviors, evaluation of intervention efficiency, and comparative study by gender characteristics are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrative Smoking Cessation Stage Model for Chinese Students Studying in Korea
Hyunsoo Oh, Hyesun Jeong, Whasook Seo
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(4): 182. CrossRef
- Integrative Smoking Cessation Stage Model for Chinese Students Studying in Korea
- 712 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effect of an Internet Community on Knowledge, Self-efficacy and Self Care Behavior in Workers with Hypertension
- Jung Ok Yu, Young Bok Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(7):1258-1267. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.7.1258
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was aimed to evaluate the effect of an internet community on knowledge, self-efficacy, and self-care behavior in workers with hypertension.
Methods The research design used was a nonequivalent control group pre-test and post-test design. Sixty hypertensive workers participated in this study(Exp.=29, Cont.=31). The data was collected from the 3rd of November 2003 to the 27th of February 2004 using an interview with questionnaires. Information related to hypertension was provided on the internet community weekly and an e-mail newsletter was sent in order to increase participation in the internet community. We used a tool developed by Park Young-Im(1994) that measured knowledge related to hypertension and self-efficacy. A tool developed by Jung Mi-Young(2001) was used for self-care behavior. The collected data was analyzed with an chi2-test and t-test using the SPSS WIN 10.0 program.
Results The internet community helped workers with hypertension to increase their knowledge related to hypertension, as well as increasing their self-efficacy and self-care behavior.
Conclusion An internet community could be applied as hypertensive nursing intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictive Effect of Adolescents' Body Cathexis on General Self-efficacy and The Use of Instagram
Abdullah DALKIÇ, Zöhre KAYA
Participatory Educational Research.2021; 8(2): 476. CrossRef - Primary health institutions preference by hypertensive patients: effect of distance, trust and quality of management in the rural Heilongjiang province of China
Jingjing Liu, Hui Yin, Tong Zheng, Bykov Ilia, Xing Wang, Ruohui Chen, Yanhua Hao, Hong Sun, Mingli Jiao, Zheng Kang, Lijun Gao, Qunhong Wu
BMC Health Services Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of medication adherence and health literacy on health‐related quality of life in older people with hypertension
Nam Hee Park, Mi Sook Song, So Young Shin, Ji‐hye Jeong, Hyo Young Lee
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Application of a Web-based Expert System using Artificial Intelligence for Management of Mental Health by Korean Emigrants
Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(2): 203. CrossRef - Health Literacy in Rural Areas of China: Hypertension Knowledge Survey
Xia Li, Ning Ning, Yanhua Hao, Hong Sun, Lijun Gao, Mingli Jiao, Qunhong Wu, Hude Quan
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2013; 10(3): 1125. CrossRef - Self-management programs based on the social cognitive theory for Koreans with chronic disease: A systematic review
Yeonsoo Jang, Hyera Yoo
Contemporary Nurse.2012; 40(2): 147. CrossRef - Effective Intervention Strategies to Improve Health Outcomes for Cardiovascular Disease Patients with Low Health Literacy Skills: A Systematic Review
Tae Wha Lee, Seon Heui Lee, Hye Hyun Kim, Soo Jin Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2012; 6(4): 128. CrossRef - Impact of Health Literacy on Disease-related Knowledge and Adherence to Self-care in Patients with Hypertension
Youn-Jung Son, Eun-Kyeung Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 6. CrossRef
- Predictive Effect of Adolescents' Body Cathexis on General Self-efficacy and The Use of Instagram
- 789 View
- 1 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Body Weight, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Self-Efficacy of Diabetic Control among Obese Type II Diabetic Patients
- Hae Jung Lee, Kyung Yeon Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(5):787-797. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.5.787
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of problem solving nursing counseling and walking exerciseon weight loss, cardiovascular risk factors, and self-efficacy of diabetic control among obese diabetic patients. The Polar heart rate monitor was used for walking exercise to utilize the Biofeedback mechanism.
Method Fifty nine diabetic patients were conveniently placed into experimental (n=35) and control groups (n=24). The experimental group participated inweekly nursing counseling for 12 weeks and was encouraged to do walking exercise using a Polar monitor. The control group remained in the same treatment as before. The data wascollected from November 2003 to August 2004 and analyzed using t-tests and ANCOVAs.
Results After 12 weeks, the participants in the experimental group reported significantly decreased body weight (p=.004) and total scores on theParma scale (p=.001). While the participants in the control group reported significantly increased levels of blood triglyceride (p=.046) and HDL (p=.018).
Conclusion Based on the findings, we concluded that problem focused nursing counseling with intensified walking exercise could reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications and body weight among obese diabetic patients. Future research to explore the long-term effects of nursing counseling on diabetic complications is warranted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of e-health literacy on health-related quality of life in young adults with type 2 diabetes: Parallel mediation of diabetes self-efficacy and self-care behaviors
Yura Jang, Youngran Yang
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 82: 151917. CrossRef - Automated Personalized Self-care Program for Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot Trial
Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Yoonju Lee, Myoung Soo Kim, Sunyoung Jung, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 114. CrossRef - Using herbal medicine (Cheong-Yeol Sodang-decoction) for fasting blood glucose in patients with diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes mellitus: a retrospective chart review
Seonmi Shin, Yujin Choi, Heung Ko, Yeongmi Cho
Integrative Medicine Research.2020; 9(4): 100413. CrossRef - Study on antioxidative, antidiabetic and antiobesity activity of solvent fractions ofsmilax chinaL. leaf extract
Yun Hwan Kang, Young-Sil Lee, Kyoung Kon Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Tae Woo Kim, Myeon Choe
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(5): 401. CrossRef
- Effects of e-health literacy on health-related quality of life in young adults with type 2 diabetes: Parallel mediation of diabetes self-efficacy and self-care behaviors
- 873 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Prospective Study on the Relating Factors to the Stages of Change in Smoking Cessation and Barriers in Coronary Artery Disease Patients
- Hwa Soon Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(1):27-36. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.1.27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The main purpose of this study was to investigate that the stages of change in smoking cessation behavior among coronary artery disease patients for six months progressed following the stages of change suggested by the transtheoretical model.
Method Subjects for this descriptive survey were 59 coronary disease patients who were smoking or who had stopped smoking for less than six months.
Result In the baseline, the distribution of the subjects' stages of change was as follows: pre-contemplation stage 25.4%, contemplation stage 25.4%, preparation stage 22%, and action stage 27.1%. After six months, more subjects in the contemplation(33.3%) and preparation stages(30.8%) progressed to the action stage than those of the pre-contemplation stage(0%). Eighty-one percent of the subjects in the action stage at baseline progressed to the maintenance stage. The relationship between the numbers of smoking cessation attempts for six months and stages of change at baseline was significant(p=.001). However, the relationships between self-efficacy and nicotine dependence at baseline and progression in stages of change after six months were not significant.
Conclusion Progression in the stages of change for six months among subjects corresponded to the stages of change suggested by the transtheoretical model. Hence, future development and evaluation of intervention programs should be tailored individually considering each patient's stage of change.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Personal Training Is a Great Way for Psychotherapists to Empathize With Their Clients
Geon Ho Bahn
Psychoanalysis.2024; 35(3): 29. CrossRef - Body Fat Percentage and Natural Killer Cell Activity of Breast and Rectal Cancer Patients after Diagnosis but before Treatment
Dal Sook Kim, Myung Hee Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 321. CrossRef
- Personal Training Is a Great Way for Psychotherapists to Empathize With Their Clients
- 682 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of an Empowerment Program on the Burden of Mothers Having a Child with Cerebral Palsy
- Yong Sook Eo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(1):154-164. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.1.154
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an empowerment program as a nursing intervention for mothers who care for a child with cerebral palsy at home and to determine the effects of the program on those mothers' self efficacy, coping behavior and burden.
Method An non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used in this study. An Empowerment program was developed based on Dunst & Trivette's model. Using the program, the study was carried out from Dec. 13, 2003 to Jan. 17, 2004, mothers whose children, aged 1 to 6, were outpatients of the Dept. of Rehabilitation Medicine, at P University Hospital or registered at educational institutions for early disabled children. The experimental group of subjects were included in the new empowerment program which was held for two and half hours every week for 6 times.
Results After treatment with the Empowerment Program, the experimental group was found to be significantly increased in score for self efficacy(t=4.55, p<.01), coping behavior(t=5.54, p<.001), objective burden(t=-3.96, p<.01) and subjective burden(t=-5.05, p<.01), in comparison to the control group.
Conclusion The Empowerment Program is very effective in increasing self efficacy and coping behavior of mothers having a child with cerebral palsy and decreasing their burden. Finally, this study would recommend that an empowerment program should be extended to community facilities such as public health offices and welfare centers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of nursing-led empowerment program on care burden and social isolation among caregivers having children with cerebral palsy: A quasi-experimental study
Halla Ali Abd El hie Ali, Ayman Mohamed El-Ashry, Fatma Sayed Abdelaziz Mohamed, Dalia Ibrahem Mustafa Abdel-Azem, Mahmoud M. Noureldeen, Ahmed Abdellah Othman, Eslam Reda Machaly, Nahla Abdallah Abd El-Tawab
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2026; 87: 88. CrossRef - Online social support and collective empowerment: Serial mediation effect on self‐efficacy among mothers of children with type 1 diabetes
Ju‐Yeon Uhm, Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(10): 3225. CrossRef - Effects of Birth Control Empowerment Program for Married Immigrant Vietnamese Women in South Korea
Jihyun Kim, Nam Cho Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of a family empowerment program on family function and pulmonary function of children with asthma: A randomized control trial
Hsiu-Ying Yeh, Wei-Fen Ma, Jing-Long Huang, Kai-Chung Hsueh, Li-Chi Chiang
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2016; 60: 133. CrossRef - Self-care Agency and Quality of Life in Brain Tumor Patients after Surgery
Sunjoo Boo
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(4): 211. CrossRef - Effects of an Empowerment Program on Nicotine Dependency, Temptation, Self-esteem, Depression in Adolescents Who Smoke
Nam-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of a cardiovascular health promotion programme offered to low‐income women in Korea
Kyung Ok Ham, Bong Jeong Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2011; 20(9-10): 1245. CrossRef - Effects of an Empowerment Education Program in the Prevention of Internet Games Addiction in Middle School Students
Aeran Joo, Inhyae Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 255. CrossRef - Effects of Child-rearing Stress and Empowerment on Quality of Life in Caregivers of Children with Disabilities
Yong-Sook Eo, Moon-Jeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 409. CrossRef - Effects of a Breast-Feeding Empowerment Program on Exclusive Breast-Feeding
Yunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(2): 279. CrossRef - Effects of a breastfeeding empowerment programme on Korean breastfeeding mothers: A quasi-experimental study
Jung Sun Kang, So Young Choi, Eun Jung Ryu
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2008; 45(1): 14. CrossRef
- Effect of nursing-led empowerment program on care burden and social isolation among caregivers having children with cerebral palsy: A quasi-experimental study
- 901 View
- 10 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Self-efficacy Promoting Vestibular Rehabilitation Program for Patients with Vestibular Hypofunction
- Hyun Jung Lee, Smi Choi-Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(5):710-719. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.5.710
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose In this study an examination was done of the effect of self-efficacy promoting vestibular rehabilitation (S-VR) on dizziness, exercise selfefficacy, adherence to vestibular rehabilitation (VR), subjective and objective vestibular function, vestibular compensation and the recurrence of dizziness in patients with vestibular hypofunction.
Methods This was a randomized controlled study. Data were collected 3 times at baseline, 4 and 8 weeks after beginning the intervention. Outcome measures were level of dizziness, exercise self-efficacy, and level of adherence to VR. Subjective and objective vestibular function, vestibular compensation and the recurrence of dizziness were also obtained. Data were analyzed using Windows SPSS 21.0 program.
Results After 4 weeks of S-VR, there was no difference between the groups for dizziness, subjective and objective vestibular functions. However, exercise self-efficacy and adherence to VR were higher in the experimental group than in the control group. After 8 weeks of S-VR, dizziness (
p =.018) exercise self-efficacy (p <.001), adherence to VR (p <.001), total-dizziness handicap inventory (DHI) (p =.012), vision analysis ratio (p =.046) in the experimental group differ significantly from that of the control group. The number of patients with recurring dizziness were higher in the control group than in the experimental group (p <.001).Conclusion The results indicate that continuous 8 weeks of S-VR is effective in reducing dizziness, and improving exercise self-efficacy, subjective vestibular function and adherence to VR. Objective vestibular function and vestibular compensation were also improved in the experimental group at the end of 8 weeks of S-VR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Locus of Control and Dizziness: Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy
Yemo Jeong, Won Hwa Jin, Eun-Jin Kwon, In-Sun Kwon, Han Young Yu, Seong-Hae Jeong
Research in Vestibular Science.2021; 20(4): 126. CrossRef - A Improved Case of Post Cerebral Infarction Dizziness and Gait Discomfort after Treated with Korean Medicine Treatment and Vestibular Rehabilitation Practice
Hongmin Chu, Hyeon-Seo Lim, Kwangho Kim, Young-Ung Lee, Kyungtae Park, Jongwon Jang, Ho-sun Ryu, Su-hak Kim, Cheol-hyun Kim, Sangkwan Lee, Kang-keyng Sung
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(4): 179. CrossRef - Awareness about the necessity of vestibular rehabilitation education in Korean physical therapists
Yun-Hee Sung
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2020; 16(2): 197. CrossRef - Improving Balance through Virtual Reality and Physical Therapy Integration
Ben Joseph S. Esguerra, Kristen Johnson
International Journal of Clinical Medicine.2017; 08(05): 322. CrossRef - The Effects of Comprehensive Education Program on Anxiety, Uncertainty and Athletic Performance of Patients undergo Spinal Nerve Block
Seon Hee Kim, Eun Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(2): 143. CrossRef
- Locus of Control and Dizziness: Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy
- 1,206 View
- 11 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of Dietary Program based on Self-efficacy Theory on Dietary Adherence, Physical Indices and Quality of Life for Hemodialysis Patients
- Kyung Soon Yun, Ja Yun Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(4):598-609. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.4.598
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine effects of a dietary program based on self-efficacy theory on dietary adherence, physical status and quality of life (QoL) in hemodialysis patients.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pre-post test design was used. The intervention group received the dietary program for 8 weeks from August 4 to September 26, 2014. The control group received only usual care.
Results ANCOVA showed that dietary adherence (F=64.75,
p <.001) was significantly different between the two groups. Serum albumin (F=12.13, p =.001), interdialytic weight gain (F=56.97,p <.001), calories (F=15.80,p <.001) as physical status indices were significantly different, but serum potassium (F=2.69,p =.106) and serum phosphorus (F=1.08,p =.303) showed no significant difference between the two groups. In terms of health-related QoL, the physical component scale (F=10.05,p =.002) and the mental component scale (F=16.66,p <.001) were significantly different between the two groups. In addition, in terms of diet related QoL, diet level (F=35.33,p <.001) and satisfaction level (F=15.57,p <.001) were significantly different between the two groups, but dietary impact level (F=1.23, p =.271) was not significantly different.Conclusion Findings show that the dietary program based on self-efficacy theory is an effective nursing intervention program to improve adherence to diet, and to maintain physical status and QoL for hemodialysis patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of self‐management, self‐efficacy, depression and social support on quality of life in patients undergoing haemodialysis by disease stage in South Korea
Aekyung Chang, Jisoo Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(3): 978. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of Dietary Self-care Promotion Program Using Online Community for Hemodialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Hana Kim, Mi-Kyoung Cho
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(2): 126. CrossRef - Pharmacist-led behavioral change intervention improves adherence and clinical outcomes among hemodialysis patients
Thuraya Safaa Ansaf, Fadya Yaqoob Al-Hamadani, Sarah Brown, Delyth H. James
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic Review and Network Meta‐Analysis of the Comparative Effectiveness of Adherence Enhancement Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease
Bin Ma, Yuanmin Jia, Haixia Wang, Ou Chen
Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic Review and Network Meta‐Analysis of the Comparative Effectiveness of Self‐Management Support Strategies for Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease
Bin Ma, Haixia Wang, Yuanmin Jia, Yingying Cai, Xiaohe Ren, Yue Hou, Mengyuan Zhang, Ou Chen
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Self‐management training in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing hemodialysis: A systematic review
Ezgi Bağriaçik, Burcu Totur Dikmen
Seminars in Dialysis.2024; 37(2): 91. CrossRef - Effects of a Customized Diet Education Program Using a Mobile Instant Messenger for People Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: A Feasibility Test
Hyun-Jung Lee, Hee-Young Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(4): 367. CrossRef - The effect of nurse-led interventions on non-adherence to dietary and fluid restrictions among adults receiving haemodialysis: a randomised controlled trial
Vijay VR, Harmeet Kaur Kang
Journal of Kidney Care.2023; 8(Sup6): S6. CrossRef - The effect of nurse-led interventions on non-adherence to dietary and fluid restrictions among adults receiving haemodialysis: a randomised controlled trial
Vijay VR, Harmeet Kaur Kang
Journal of Kidney Care.2023; 8(1): 12. CrossRef - Effect of Treatment Adherence Improvement Program in Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hana Kim, I. Seul Jeong, Mi-Kyoung Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11657. CrossRef - Evaluation of the relationship between health literacy and self-efficacy: A sample of hemodialysis patients
Aysun Kazak, Ayşe Özkaraman, Hasret Topalı, Secil Duran
The International Journal of Artificial Organs.2022; 45(8): 659. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Diet-Related Quality of Life Among Hemodialysis Patients According to Age-group
Ae Kyung Chang, Jin Yi Choi
Clinical Nursing Research.2022; 31(6): 1172. CrossRef - Randomised controlled trial of a smartphone application‐based dietary self‐management program on haemodialysis patients
Songyi Pack, Jia Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(5-6): 840. CrossRef - Effects of the Combination of Auricular Acupressure and a Fluid-Restriction Adherence Program on Salivary Flow Rate, Xerostomia, Fluid Control, Interdialytic Weight Gain, and Diet-Related Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
AeKyung Chang, YoonChung Chung, MoonJa Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10520. CrossRef - Effects of a Mobile-App-Based Self-Management Support Program For Elderly Hemodialysis Patients
Youngsoon Min, Myonghwa Park
Healthcare Informatics Research.2020; 26(2): 93. CrossRef - Effects of a Repeated Hemodialysis Diet Education Program for Older Adults
Sangsuk Kim, Youngsil Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(5): 515. CrossRef - La persona con enfermedad renal crónica: una revisión sistemática de las intervenciones de salud
Alma de Coral Elías-Viramontes, Leticia Casiquen-Casique, José Ernesto Rodríguez-Loreto
Enfermería Nefrológica.2020; 23(4): 333. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Self-Care Behaviors of Renal Dialysis Patients
Yoonjung Kim, Sanggeon Park
STRESS.2019; 27(4): 320. CrossRef - Clinical trial for the control of water intake of patients undergoing hemodialysis treatment
Graziella Allana Serra Alves de Oliveira Oller, Marília Pilotto de Oliveira, Cláudia Bernardi Cesarino, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira, José Abrão Cardeal da Costa, Luciana Kusumota
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Self-Efficacy, Grit, Symptom Clusters on Self-Care Agency in Brain Neoplasms Patients
Sook Hee Cho, Kyung Soon Yun, Shin Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(4): 188. CrossRef - The study on developing the self care tool for the elderly cancer patient undergoing hemotherapy : Focusing on the effect of Health Monitoring Diary
Yeon Ok Lim, Yojin Kim, Hyunsook Yoon, Dae Young Zang, Dae Ro Choi, Kyoungwon Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2018; 35(2): 73. CrossRef - Effects of Education about Action Plans according to Self-Monitoring on Self-Management Adherence, Knowledge, Symptom Control, and Quality of Life among Adult Asthma Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Ja Yun Choi, Young-Ran Kweon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 613. CrossRef
- Influence of self‐management, self‐efficacy, depression and social support on quality of life in patients undergoing haemodialysis by disease stage in South Korea
- 1,568 View
- 43 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Effects of Breastfeeding Empowerment Program on Breastfeeding Self-efficacy, Adaptation and Continuation in Primiparous Women
- Seon Mi Song, Mi Kyung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):409-419. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.409
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a breastfeeding empowerment program and to investigate the effects of the breastfeeding empowerment program on self-efficacy, adaptation and continuation of breastfeeding for primiparous women.
Methods The 5 session breastfeeding empowerment program was developed and a non-equivalent control group non-synchronized quasi-experiment design was used. Fifty-five participants were assigned to either the experimental group (n=27) or the control group (n=28). Effects were tested using repeated measures ANOVA and χ2-test.
Results Scores for self-efficacy, adaptation and continuation of breastfeeding of in the experimental group after program were significantly higher than 1week, 4weeks, 8weeks scores in control group.
Conclusion The effects of the breastfeeding empowerment program for elevating self-efficacy, adaptation and continuation of breastfeeding in primiparous women were validated. Therefore, this program can be recommended for vigorous use in clinical practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the effectiveness of video and breastfeeding simulator support to mothers who could not breastfeed their babies in the neonatal intensive care unit: a randomized controlled study
Hatice Tetik Metin, Feride Yiğit
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of Comprehensive Mobile-Based, Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Gestational Diabetes
Eunju Kwak, Seungmi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 224. CrossRef - The effectiveness of prenatal breastfeeding education on breastfeeding uptake postpartum: A systematic review
Jennifer Kehinde, Claire O'Donnell, Annmarie Grealish
Midwifery.2023; 118: 103579. CrossRef - Effectiveness of distance education program on mothers’ empowerment in exclusive breastfeeding
Zeynab Taheri, Fatemeh Bakouei, Mouloud Agajani Delavar, Mahbobeh Faramarzi, Afsaneh Bakhtiari, Fatemeh Nasiri Amiri
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2022; 11(1): 420. CrossRef - Social policies and breastfeeding duration in South Korea: A survival analysis of the national data
Jung Hee Yeo, Eun-Young Kim
Midwifery.2022; 107: 103282. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Breastfeeding Behavior of First-Time Mothers
Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2021; 25(3): 184. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of the Parenting Support Group Program for Mothers with Infants
Sun Hwa Park, Kyung Ja June
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 40. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Adaptation Scale-Short Form for mothers at 2 weeks postpartum: construct validity, reliability, and measurement invariance
Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(4): 326. CrossRef - Knowledge of and Attitude toward Breastfeeding among Medical Staff Working in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and Obstetric Unit
Eun Sook Kim, Young Hee Cho, Hyejung Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2020; 24(2): 102. CrossRef - Knowledge and health beliefs about gestational diabetes and healthy pregnancy's breastfeeding intention
Seungmi Park, Jung Lim Lee, Jang In Sun, Youngji Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2018; 27(21-22): 4058. CrossRef
- Comparison of the effectiveness of video and breastfeeding simulator support to mothers who could not breastfeed their babies in the neonatal intensive care unit: a randomized controlled study
- 1,385 View
- 19 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Development and Psychometric Evaluation of the Transcultural Self-efficacy Scale for Nurses
- Won-Oak Oh, Eun Sook Park, Min Hyun Suk, Yeo Jin Im
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(2):293-304. Published online April 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.293
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This methodological study was conducted to develop and psychometrically test the Transcultural Self-efficacy scale (TCSEscale) for nurses.
Methods Initial 41 items for the TCSE-scale were generated based on extensive literature reviews and in-depth interviews with 18 nurses who had experience in caring for foreign patients. Cultural Competence and Confidence model was used as a conceptual framework. Content validity was evaluated by an expert panel. Psychometric testing was performed with a convenience sample of 242 nurses recruited from four general hospitals in the Seoul metropolitan area and Gyeonggi-do province of South Korea. To evaluate the reliability of TCSE-scale, a test-retest reliability and an internal consistency reliability were analyzed. Construct validity, concurrent validity, criterion validity, convergent validity and discriminative validity were used to evaluate the validity.
Results The 25-item TCSE-scale was found to have three subscales-Cognitive, Practical, and Affective domain-explaining 91.5% of the total variance. TCSE-scale also demonstrated a concurrent validity with the Cultural Competence Scale. Criterion-related validity was supported by known-group comparison. Reliability analysis showed an acceptable-to-high Cronbach's alpha-.88 in total, and subscales ranged from .76 to .87. The ICC was .90, indicating that the TCSE-scale has internal consistency and stability of reliability.
Conclusion This preliminary evaluation of the psychometric scale properties demonstrated an acceptable validity and reliability. The TCSE-scale is able to contribute to building up empirical and evidence based on data collection regarding the transcultural self-efficacy of clinical nurses. We suggest further testing of the applicability of TCSE-scale in different settings and community contexts.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Do individual or organizational factors influence cultural competency of maternal newborn nurses?: a cross-sectional study
Semi Lee, Hyunkyung Choi
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(4): 318. CrossRef - The moderating effect of cultural competence educational needs on the relationship between transcultural self-efficacy and cultural competence in Korean public health nurses
Young-Ran Han, Yeo-Won Jeong
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of nurses' compassion competence and transcultural self-efficacy on their global health nursing competency
Jiwon Kang, Jeongeun Song, Wonjung Noh
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 60: 151453. CrossRef - The Development of Chinese Version of Transcultural Nursing Self-Efficiency Scale: Using Rasch Model Analysis
Yi Tian, Li Wang, Yan Xu, Zhuang He
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2021; 32(1): 30. CrossRef - A multilevel investigation of cultural competence among South Korean clinical nurses
Duckhee Chae, Yunhee Park, Kyeonghwa Kang, Jongdae Kim
Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences.2020; 34(3): 613. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta‐analysis of the effects of global health competency improvement programs on nurses and nursing students
Jiwon Kang, Jeongeun Song, Wonjung Noh
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2020; 76(7): 1552. CrossRef - Effects of a Program to Promote Multicultural Awareness and Multicultural Efficacy toward North Korean Defectors for Nursing Students
Jin Kyoung Park
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 58. CrossRef - Development of the Cultural Competence Scale for Registered Nurses (CCS-RN)
Kyung Won Kim, Sun-Hee Kim, Young Hee Kim, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Hae Sook Park, Sun Hee Lee, Geum Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(3): 281. CrossRef - Development and Cross-Validation of the Short Form of the Cultural Competence Scale for Nurses
Duckhee Chae, Yunhee Park
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(1): 69. CrossRef
- Do individual or organizational factors influence cultural competency of maternal newborn nurses?: a cross-sectional study
- 1,728 View
- 15 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Healthy Menopausal Transition
- Eunyoung Hong, Young Sil Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):64-75. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.64
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose This study was designed to construct and test structural equation modeling on healthy menopausal transition in middle-aged women in order to identify variables affecting healthy menopausal transition.
Methods Participants, 276 women, 45 to 60 years of age, with menopausal symptom score higher than 5 on the Korean version of Menopause Rating Scale, were recruited in three cities and one county of Gyeongnam Province. Research data were collected via questionnaires and analysed using SPSS version 18.0 and AMOS version 20.0.
Results After confirmatory factor analysis, one of the observed variables was excluded due to relatively low factor loading. The model fit indices for the hypothetical model were suitable for the recommended level: GFI=.93, CFI=.92, RMSEA=.05. Self-efficacy, self-differentiation, and menopausal symptoms explained 67.7% of variance in menopausal transition, and self-differentiation was the most influential factor for menopausal transition. Self efficacy and menopausal symptoms explained 9.6% of variance in menopausal management, although "menopausal symptoms" was not significant.
Conclusion These results suggest that nursing interventions to improve self-differentiation, self efficacy, menopausal management and decrease menopausal symptoms are critical for healthy menopausal transition in middle-aged women. Continued development of a variety of community-based nursing interventions to facilitate healthy menopausal transition is suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Factors influencing
seogeulpeum
among middle-aged Korean women
Hyeja Gu, Eunyoung Hong
Climacteric.2025; 28(1): 40. CrossRef - Middle-aged Korean women’s experiences of physical activity during the transition to menopause: a grounded theory approach
Hee Jung Cho, Sukhee Ahn
Women's Health Nursing.2025; 31(3): 215. CrossRef - Psychological well-being of midlife women: a structural equation modeling approach
Jiwon Lee, Jong-Eun Lee
Menopause.2022; 29(4): 440. CrossRef - A menopausal transition model based on transition theory
Jisoon Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 210. CrossRef - Experiences on Psycho-social Health Support of Middle-aged Women
Jeong-Soo KIM, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2019; 31(5): 1432. CrossRef
-
Factors influencing
seogeulpeum
among middle-aged Korean women
- 1,247 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of the Empowering A Self-Efficacy (EASE) Program for Children with Epilepsy
- Hana Yoo, Hee-Soon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):54-63. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.54
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify effects of the Empowering A Self-Efficacy (EASE) program on self-efficacy, self-management, and child attitude toward illness in children with epilepsy.
Methods This was a quasi-experimental study with a non-equivalent control group pre-post test design. Participants were 10 to 15 year old children with epilepsy (11 in the experimental group and 10 in the control group) who were registered at one hospital in S city. The experimental group received the EASE program for 3 weeks. In the first week, a group meeting lasting 570 minutes was conducted on a single day. Over the next two weeks, telephone counselling was conducted twice a week. Data were analyzed using SPSS 18.0.
Results There was a significant difference of pre-post evaluation of the epilepsy self-management scores in the experimental group. However, differences between the experimental group and the control group for seizure self-efficacy and child attitude toward illness were not significant.
Conclusion This is the first study in Korea to develop and evaluate an intervention program for children with epilepsy. Further studies are needed to confirm the effects of the EASE program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concept Analysis of Self-management in Children with Chronic Kidney Diseases through Walker and Avant’s Method
Sug Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(1): 105. CrossRef - Service delivery, behavioural, and self-management interventions for children with epilepsy
Nigel Fleeman, Josephine Mayer, Yun Huang, Sarah J Nevitt, Mariangela Panebianco, Ruaraidh A Hill, Alison J Doherty, Neil Wilson, Paul Boland, Andrew J Clegg, Helena Bilsborough, Elsie J Williams, Elizabeth J Shaw, Michelle Maden, Rachael Kelly, Anthony G
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing and evaluating an evidence-based practice research competency enhancement program for clinical nurses in Korea: a pilot study
Suhyun Kim, Hye Won Jeong
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of an individual and family self-management theory-based education program given for adolescents with epilepsy and parents: Randomized controlled trial
Hilal Kurt Sezer, Sibel Küçükoğlu, Abdullah Canbal
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 79: 171. CrossRef - Psychological treatments for people with epilepsy
Rosa Michaelis, Venus Tang, Sarah J Nevitt, Janelle L Wagner, Avani C Modi, William Curt LaFrance Jr, Laura H Goldstein, Milena Gandy, Rebecca Bresnahan, Kette Valente, Kirsten A Donald, Markus Reuber
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficiency of the web-based epilepsy education program (WEEP) for youth with epilepsy and parents: A randomized controlled trial
Şerife Tutar Güven, Ayşegül İşler Dalgiç, Özgür Duman
Epilepsy & Behavior.2020; 111: 107142. CrossRef - The Effect of Educational Program on Self-Management of Patients with Epilepsy: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study
Narges Bahiraei, Maryam Dehghani, Alice Khachian
Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care.2019; 27(5): 361. CrossRef - Self-Management Experiences of the Adolescents with Chronic Kidney Disease
Sug Young Lee, Heesun Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(3): 266. CrossRef
- Concept Analysis of Self-management in Children with Chronic Kidney Diseases through Walker and Avant’s Method
- 1,352 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Relationship between Expectations Regarding Aging and Physical Activity among Middle Aged Adults in Urban Areas: Based on the Pender's Health Promotion Model
- Sung-Hye Cho, MoonKi Choi, JuHee Lee, Hyewon Cho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):14-24. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to measure the level of expectations regarding aging (ERA) and identify relationship between ERA and physical activity of middle aged adults.
Methods Participants were middle aged adults who resided in the community in three cities in Korea. Data were collected using questionnaires that contained items on individual characteristic, International Physical Activity Questionnaires (IPAQ), and behavior-specific cognitive factors including ERA-12. Hierarchical multiple regression was conducted to examine whether ERA would predict physical activity by controlling other factors.
Results The mean age of the participants was 51.1±6.9 years. The mean score for ERA (possible range=0 to 100) was 40.04±14.31. More than half of the participants (62.6%) were not engaged in health promoting physical activity. Gender, employment status and exercise confidence were associated with level of physical activity (F=7.14,
p <.001, R2=.36). After controlling for individual factors and behavior-specific cognitive factors, ERA was independently related to physical activity (F=7.19,p <.001, R2=.38).Conclusion The results demonstrate that individuals' belief about aging has effects on physical activity in Korean middle aged adults. Thus, nursing interventions which focused on ERA could help enhance physical activity in middle aged adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship Among Stress, Sense of Coherence and Sleep Quality in Middle-aged Women
So Hyeon Kim, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(3): 137. CrossRef - Family care and health-promoting behaviors among community elders: The chain mediating effect of self-efficacy and aging expectations
Yian Chen, Lin Zhang, Jiashuang Xu, Miaojing Song, Pengjuan Ji, Qiqi Ji, Leilei Guo
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 66: 103606. CrossRef - The Effects of Health Status and Social Support on Happiness in MiddleAged Women
Bok Hui Baek, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(1): 16. CrossRef - Impact of WhatsApp-Based Self-Care Education on Self-Care Behaviors and Lifestyle in Overweight and Obese Pregnant Women with Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Fatemeh Salarkarimi, Majid Karandish, Mehrnoosh Zakerkish, Zahra Abbaspoor
Jundishapur Journal of Chronic Disease Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Level of Expectations Regarding Aging Among Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Lunwei Lin, Shunqi Liao, Zhangrong Yan, Chaofan Liu, Qi Wang, Fang Wang
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2024; 25(3): 410. CrossRef - The Effect of a Training Intervention Based on Pender’s Health Promotion Model on the Lifestyle of Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Hossein Hassannezhad, Hasan Robabi, Fatihe Kerman Saravi
Medical-Surgical Nursing Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Persian Version of the 12-Item Expectations Regarding Aging Survey
Hamid Sharif Nia, Long She, Sotheeswari Somasundram, Fatemeh Khoshnavay Fomani, Omolhoda Kaveh, Lida Hosseini
The International Journal of Aging and Human Development.2023; 96(2): 248. CrossRef - Health-Related Expectations Regarding Aging among Middle-Aged and Older Japanese: Psychometric Performance and Novel Findings from the ERA-12-J
Michael Annear, Yasuo Shimizu, Tetsuhiro Kidokoro
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(20): 13509. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Physical Activity of Foreign Workers: Based on a Health Promotion Model
Jeong Eui Cho, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(3): 344. CrossRef - Lower serum levels of alpha tocopherol and lycopene are associated with higher pain and physical disability in subjects with primary knee osteoarthritis: A case-control study
Bina Eftekharsadat, Dawood Aghamohammadi, Neda Dolatkhah, Maryam Hashemian, Halale Salami
International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research.2021; 91(3-4): 304. CrossRef - Effects of a Daily Life-Based Physical Activity Enhancement Program for Middle-Aged Women at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
Kyung Ae Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(2): 113. CrossRef - Applying the theory of planned behavior to determine factors associated with physical activity by women with hypertension in rural areas of Iran
Effat Hatefnia, Kobra Alizadeh, Mostafa Ghorbani
Asian Biomedicine.2019; 12(2): 83. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Successful Aging of Late Middle-Aged Adults
YonJi Kim, JuHee Lee, Young Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(2): 90. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Exercise Behavior of the Male Manual Worker and Office Worker based on Health Promotion Model
SeungKyoung Yang, Yeongmi Ha, Mi-Ra Jung
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(3): 235. CrossRef
- The Relationship Among Stress, Sense of Coherence and Sleep Quality in Middle-aged Women
- 1,322 View
- 19 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Influence of Self Efficacy, Social Support and Sense of Community on Health-related Quality of Life for Middle-aged and Elderly Residents Living in a Rural Community
- Hyeonkyeong Lee, Sung Hye Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Yune Kyong Kim, Hyang Im Choo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(6):608-616. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.608
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between self-efficacy, social support, sense of community and health-related quality of life (HRQoL), including the direct and indirect effects of the variables on HRQoL.
Methods A cross-sectional survey was conducted with a convenience sample of 249 middle-aged and elderly residents living in a rural community in A-County, K Province. The structured questionnaire included 4 scales from the Euro Quality of life-5 Dimensions (mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, anxiety/depression), and measures of General Self-Efficacy, Social Support, and Sense of Community. Data were analyzed using SPSS WIN 20.0 and AMOS 21.0 program.
Results The mean HRQoL score for the participants was 0.87±0.13. Self-efficacy (β=.13,
p =.039) and age (β= -.38,p <.001) were significantly associated with HRQoL, explaining 21% of the variance. In the path analysis, self-efficacy showed a significant direct effect on HRQoL (β=.14,p =.040) and significantly mediating relationships between both social support (β=.05,p =.030) and sense of community (β=.02,p =.025) and HRQoL.Conclusion Although self-efficacy was found to be the main predictor for HRQoL, the findings imply that social environmental factors such as social support and sense of community need to be considered when developing interventions to increase HRQoL in middle-aged and elderly residents in rural communities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of health literacy, walking practice, and sarcopenia on health-related quality of life in rural older adults: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Yun Mi Lee, Eun-Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(2): 226. CrossRef - Relationship between perceived social support and disability with the mediating role of perceived stress among older adults
Leila Dehghankar, Saman Valinezhad, Mohammad Amerzadeh, Farnoosh Zarabadi Poor, Zahra Hosseinkhani, Seyedeh Ameneh Motalebi
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Job Stress on Health-related Quality of Life among Family Farm Succession of Young Farmers: Dual Mediating Effect of Healthcare Satisfaction and Culture-Leisure Satisfaction
Jung Shin Choi, Yoon Ji Choi, Yong Kyu Park
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(4): 683. CrossRef - The Impact of Self-Management Behaviors, Self-Efficacy, and Grit on Health-related Quality of Life in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Ji-Yeong Seo, Hyeon-Ok Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 158. CrossRef - A Clinical Incivility Management Module for Nursing Students: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Younglee Kim, Sook Young Kim, Eunhee Hong, Cheryl Brandt
Healthcare.2023; 11(19): 2680. CrossRef - The Effect of Focusing Manner on Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Pain: The Sequential Mediating Effects of Social Support and Self-efficacy
Song Hee Yoon, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(2): 248. CrossRef - Positive effects of citizens’ sense of community on health and quality of life in a Korean city
Min-Jung Kang, Myoung-Soon Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(5): 41. CrossRef - Multilevel Analysis of Factors Affecting Health-Related Quality of Life of the Elderly
Hyunjung Moon, Sunkyung Cha
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(3): 391. CrossRef - Social Frailty and Health-Related Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Young Ko, Kyounga Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5659. CrossRef - The mediating role of interpersonal needs on attitude towards ageing and its relationship with community sense and depression among community‐dwelling older adults
Eun‐Sil Jang, Kisook Kim
Health & Social Care in the Community.2021; 29(2): 547. CrossRef - Association of living arrangements with happiness attributes among older adults
Eun Jeong Hwang, In Ok Sim
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Mobility-Related Activities of Daily Living and Health-Related Quality of Life among Healthy Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Structural Equation Modeling
Hungu Jung, Shigeharu Tanaka, Yuji Iwamoto, Masahiro Yamasaki, Ryo Tanaka
Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Retracted:Water Scarcity May Lead to Poor Mental Health: A Community-Focused Study in Rural El Salvador
Carlo Lai, Gaia Romana Pellicano, Hilda Méndez, Bartolo Atilio Castellanos, Elpiniki Pomoni, Manuela Tomai, Viviana Langher, Federica La Longa, Massimo Crescimbene
Ecopsychology.2020; 12(4): e320. CrossRef - Prediction of the Quality of Life of Menopausal Women Based on Health Literacy and Self-Efficacy
Sara Jafarigiv, Nooshin Peyman, Habibollah Esmaily, Mohammad Tajfard
Journal of Education and Community Health.2020; 7(1): 29. CrossRef - Association between social health status and health-related quality of life among community-dwelling elderly in Zhejiang
Jieming Lu, Zhebin Yu, Xiaocong Zhang, Mengyin Wu, Shujuan Lin, Yao Zhu, Zenghao Xu, Liuqing You, Fang Wei, Mengling Tang, Mingjuan Jin, Jianbing Wang, Kun Chen
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender Difference in General Self-Efficacy among Young-Old Elderly Aged 60–74 in Rural Shandong China: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Yali Wang, Lingzhong Xu, Wenzhe Qin, Jiao Zhang, Yu Xia, Xiang Jing, Lu Lu, An’an Jiao, Yaozu Li
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(24): 5070. CrossRef - The correlation between quality of life and social support in female nurses
Ning Sun, Dong‐Mei Lv, Jing Man, Xiao‐yu Wang, Qin Cheng, Hong‐li Fang, Zhen Fu, Shuang Liu, Qun‐hong Wu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2017; 26(7-8): 1005. CrossRef - Health Empowerment of Older Adults with High-risk of Cardio-cerebrovascular Diseases
HyoJin Son, Gwang Suk Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2017; 28(4): 410. CrossRef - Study on Variables Affecting Rural Elderly’s Self Efficacy: Focused on Mediating Effect of Social Capital
Young Eun Oh, Jeonghwa Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2017; 28(4): 561. CrossRef - Effects of Frailty on Health-related Quality of Life of Rural Community-dwelling Elderly: Mediating and Moderating Effects of Fall-Related Efficacy and Social Support
Kyung Won Choi, Gyeong-Suk Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 380. CrossRef - A Review on the Use of Effect Size in Nursing Research
Hyuncheol Kang, Kyupil Yeon, Sang-Tae Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(5): 641. CrossRef - Health related Lifestyles, Self-efficacy and Health related Quality of Life by the Types of Hypertension Management in Community Health Posts
Myung Soon Kwon, Soon-Ok Yang, Ji-Hye Jang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(3): 565. CrossRef
- The impact of health literacy, walking practice, and sarcopenia on health-related quality of life in rural older adults: A cross-sectional descriptive study
- 1,630 View
- 26 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Effectiveness of a Self-management Program using Goal Setting based on a G-AP for Patients after a Stroke
- Min Gyeong Park, Yeongmi Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(5):581-591. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.581
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop a self-management program using goal setting for patients after a stroke. The program was based on a theory-based Goal setting and Action Planning framework (G-AP), and the effectiveness of the program was examined.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The experimental group (n=30) received the self-management program using goal setting based on the G-AP over 7 weeks. The education was delivered individually with a specifically designed stroke workbook. The control group (n=30) received only patient information leaflets about stroke.
Results There were significant differences between the two groups. Stroke knowledge, self-efficacy, and health behavior compliance were significantly higher (all
p <.001), and hospital anxiety (p <.001) and depression (p <.001) were significantly lower in the experimental group compared to the control group.Conclusion This self-management program using goal setting based on a G-AP was found to be useful and beneficial for patients in stroke rehabilitation settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study Protocol for a Hospital-to-Home Transitional Care for Older Adults Hospitalized with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in South Korea: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Heui-Sug Jo, Woo-Jin Kim, Yukyung Park, Yu-Seong Hwang, Seon-Sook Han, Yeon-Jeong Heo, Dahye Moon, Su-Kyoung Kim, Chang-Youl Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(15): 6507. CrossRef - Predictive Model of Self-management in Patients With Stroke Based on the Information-Motivation-Behavioral Skills Model
Sung Reul Kim, Sunho Kim, Hye Young Kim, Kyung-Hee Cho
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2023; 38(2): 158. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance in Adult Moyamoya Patients
Bo Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 80. CrossRef - The Effect of a Movie-Based Nursing Intervention Program on Rehabilitation Motivation and Depression in Stroke Patients
Hye Kyung Kwon, Sook Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - Comparison of Motivation for Rehabilitation, Family Support and Adherence to Rehabilitation between Depressive and Non-depressive Stroke Patients
An Suk Park, Eun Ko, Hee Sun Kang
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(2): 138. CrossRef - Influence of Uncertainty, Physiologic Risk Factors, Self-efficacy on Self-management in Stroke Patients
Sook Hee Cho, Kyung Soon Yun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(2): 114. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Stroke Risk Self-Management Intervention for Adults with Prehypertension
Hee-Young Song, Kyoung A Nam
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(4): 328. CrossRef - Factors related to Fear of Recurrence in Stroke Patients*
Ji won Chung, Jung-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(2): 190. CrossRef
- Study Protocol for a Hospital-to-Home Transitional Care for Older Adults Hospitalized with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in South Korea: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,378 View
- 19 Download
- 8 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


