Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Psychometric testing of the Korean version of the Undergraduate Nursing Student Academic Satisfaction Scale: a methodological study
- Da-In Park, Joohee Shim
- Received September 4, 2025 Accepted December 18, 2025 Published online February 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25125 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to translate, cross-culturally adapt, and evaluate the psychometric properties of the Korean version of the Undergraduate Nursing Student Academic Satisfaction Scale (K-UNSASS).
Methods
The K-UNSASS was developed using Brislin’s team-based translation–back-translation approach, with semantic and conceptual equivalence examined. Face validity was assessed, and a pilot test was conducted in November 2022. Content validity was evaluated by an expert panel. Formal data collection was conducted from December 2022 to January 2023. Structural validity was examined using exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients.
Results
A total of 482 full-time nursing students, most of whom were in the fourth year of their nursing program, were included in the psychometric testing. Construct validity supported a four-factor structure accounting for 65.9% of the total variance. After removal of three items with unsatisfactory factor loadings, a 45-item K-UNSASS was established. Confirmatory factor analysis of the 45-item K-UNSASS demonstrated an acceptable model fit, and both Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients were .97.
Conclusion
The K-UNSASS demonstrates acceptable reliability and validity for assessing academic satisfaction among Korean nursing students. As a culturally relevant instrument, it supports educational improvement through targeted strategies and program evaluation.
- 150 View
- 3 Download

- Development of a scale to measure fear of falling in older adults: a psychometric validation study
- Dayeon Lee, Sunghee H Tak
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):413-424. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25036
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
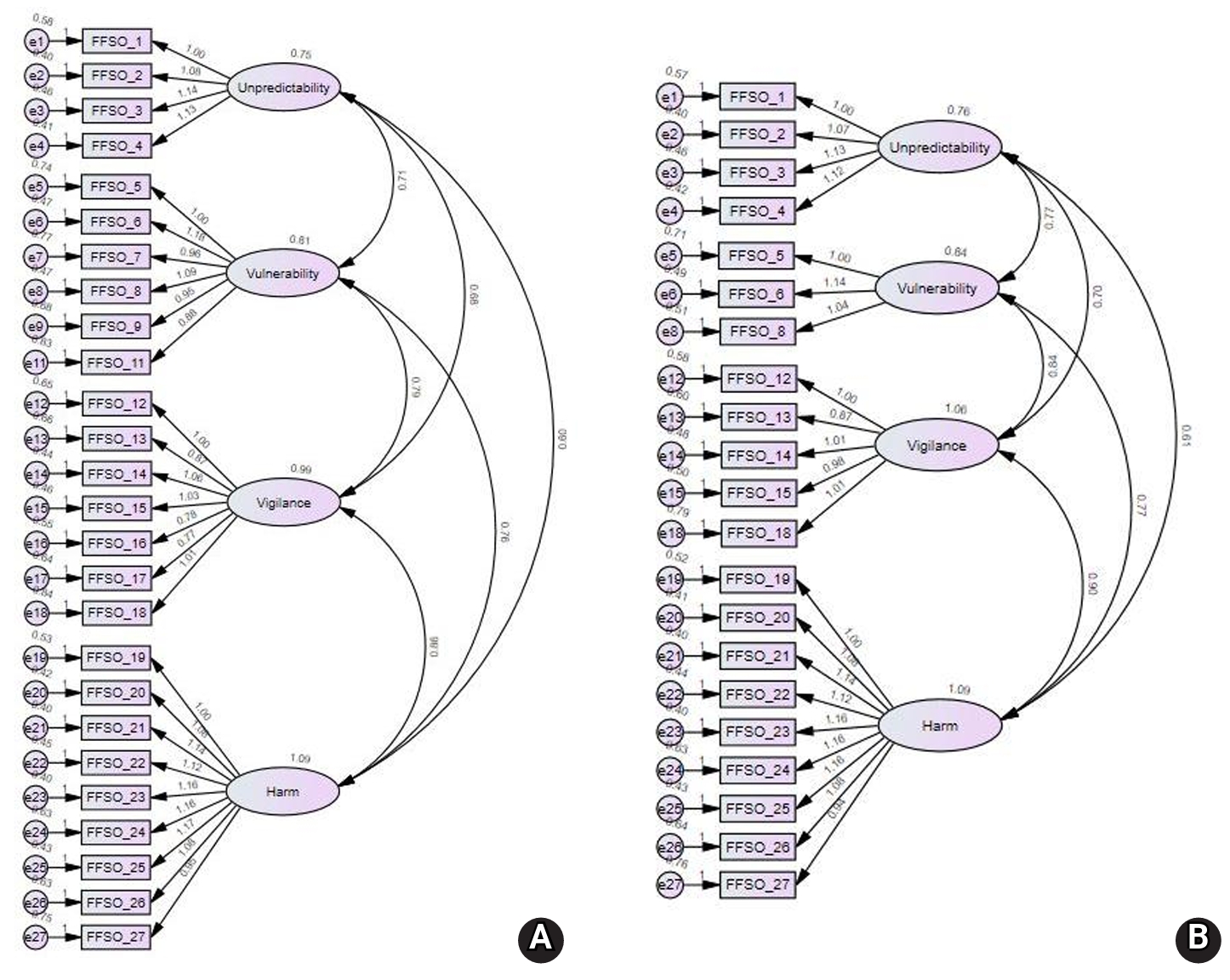
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure fear of falling in older adults and to validate its reliability and validity.
Methods
In total, 31 initial items were developed by referring to expressions from previous studies and items from existing instruments. After verifying content validity through expert evaluation, the remaining 27 items were used to construct a survey. Data from 252 participants recruited at three senior welfare centers in the metropolitan area were analyzed to examine item analysis, construct validity, convergent validity, discriminant validity, and reliability. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted to test construct validity. The correlation with the Korean version of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (KFES-I) was used to assess convergent validity. Cronbach’s alpha was calculated to determine reliability.
Results
The final instrument consisted of 21 items. CFA confirmed acceptable model fit. Convergent validity was also acceptable and discriminant validity was partially supported. Correlations with the KFES-I ranged from .54 to .63. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for the total score and all factors ranged from .84 to .97.
Conclusion
The Fear of Falling Scale for Older Adults developed in this study is a validated tool capable of measuring various dimensions of fear of falling. It provides a foundation for accurately assessing fear of falling in older adults and addressing its specific aspects.
- 1,355 View
- 166 Download

- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Soo Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):269-284. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
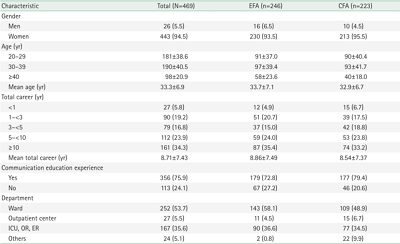
This methodological study was conducted to develop a scale to measure communication self-efficacy in nurses and examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
We selected 54 initial items from literature reviews and interviews with 10 clinical nurses. Thirty-two preliminary items were derived from consultations with 10 experts. To verify the scale’s factor structure, we conducted exploratory factor analysis (EFA), and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) among 469 nurses. Data were analyzed using item analysis, EFA, CFA, discriminant validity, convergent validity, and internal consistency using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 29.0 (IBM Corp.) and IBM SPSS AMOS ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp.).
Results
The scale consisted of 18 items with three factors (ability to apply therapeutic communication skills, crisis management capabilities, and communication competence), which explained 46.1% of the total variance. Convergent validity and discriminant validity were confirmed for the factors. CFA supported the fit of the measurement model comprising three factors (standardized root mean square residual=.04, root mean square error of approximation=.03, goodness of fit index=.92, Tucker-Lewis index=.97, comparative fit index=.98, normed fit index=.89, critical N=216). Internal consistency was confirmed by a Cronbach’s α coefficient of .91.
Conclusion
The communication self-efficacy scale for nurses is expected to measure communication self-efficacy among nurses. It will be useful for improving nurses’ professional communication abilities.
- 3,571 View
- 272 Download

- Formative versus reflective measurement models in nursing research: a secondary data analysis of a cross-sectional study in Korea
- Eun Seo Park, Young Il Cho, Hyo Jin Kim, YeoJin Im, Dong Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):107-118. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
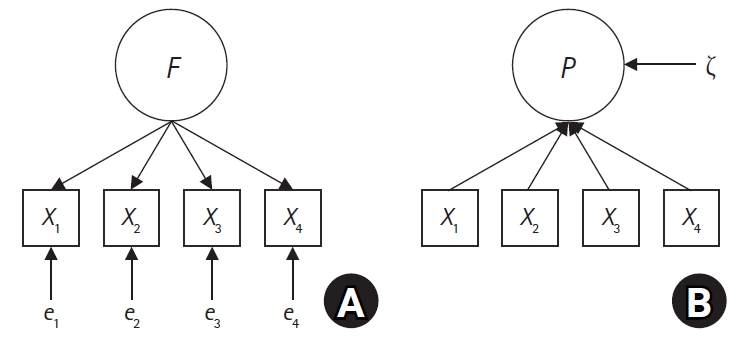
This study aimed to empirically verify the impact of measurement model selection on research outcomes and their interpretation through an analysis of children’s emotional and social problems measured by the Pediatric Symptom Checklist (PSC) using both reflective and formative measurement models. These models were represented by covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM) and partial least squares SEM (PLS-SEM), respectively.
Methods
This secondary data analysis evaluated children’s emotional and social problems as both reflective and formative constructs. Reflective models were analyzed using CB-SEM, while formative models were assessed using PLS-SEM. Comparisons between these two approaches were based on model fit and parameter estimates.
Results
In the CB-SEM analysis, which assumed a reflective measurement model, a model was not identified due to inadequate fit indices and a Heywood case, indicating improper model specification. In contrast, the PLS-SEM analysis, assuming a formative measurement model, demonstrated adequate reliability and validity with significant path coefficients, supporting the appropriateness of the formative model for the PSC.
Conclusion
The findings indicate that the PSC is more appropriately analyzed as a formative measurement model using PLS-SEM, rather than as a reflective model using CB-SEM. This study highlights the necessity of selecting an appropriate measurement model based on the theoretical and empirical characteristics of constructs in nursing research. Future research should ensure that the nature of measurement variables is accurately reflected in the choice of statistical models to improve the validity of research outcomes.
- 2,266 View
- 141 Download

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy Scale for Nurses
- Youngrye Park, Sunah Park, Hee Ran Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):633-644. Published online November 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24094
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the occupational coping self-efficacy for nurses (K-OCSE-N) scale.
Methods The English version of the OCSE-N scale was translated into Korean using a translation and back-translation process. Data were gathered from 213 nurses employed in a general hospital in South Korea. The content validity was assessed using the content validity index. The construct validity was verified through exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Criterion validity was assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients with the job stress coping and general self-efficacy scales. Reliability was examined using item-total score correlation and Cronbach’s α coefficient for internal consistency.
Results The exploratory factor analysis identified two factors that explained 61.8% of the cumulative variance: occupational burden and relational difficulty. In confirmatory factor analysis, the model exhibited adequate fit (
χ 2/df = 2.07, GFI = .95, SRMR = .04, RMSEA = .07, CFI = .97, and TLI = .95), with both convergent and discriminant validity deemed acceptable. The criterion validity presented a positive correlation of the K-OCSE-N with both job stress coping (r = .72,p < .001) and general self-efficacy (r = .72,p < .001). The internal consistency of the scale using Cronbach’s α for the total items was .89.Conclusion The K-OCSE-N scale is a valid and reliable tool for measuring nurses’ occupational coping self-efficacy. This study suggests that various intervention studies can use the scale to assess and strengthen nurses’ occupational coping self-efficacy in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
Hyun Suk Gwag, Jin Ah Kim
Healthcare.2026; 14(2): 270. CrossRef
- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
- 7,172 View
- 407 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development of the Hospital Nurses’ Silence Behavior Scale
- Soojin Chung, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):279-295. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure hospital nurses’ silence behavior and examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
A total of 52 preliminary items on hospital nurses’ silence behavior were selected using a content validity test by seven experts on 53 candidate items derived from a literature review and in-depth interviews with 14 nurses. A total of 405 hospital nurses participated in a psychometric testing. Data analysis comprised item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and convergent and discriminant validity tests. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used for assessing concurrent validity, and Cronbach’s alpha was used for the reliability test.
Results
The final scale consisted of nine factors with 31 items, exhibiting acceptable model fit indices, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. The score of the entire scale was positively correlated with the ‘Organizational Silence Scale (OSS)-the issues on which nurses remain silent’ (r = .60, p < .001) and ‘OSS-the reasons why nurses remain silent’ (r = .68, p < .001). Cronbach’s α of the scale was .92, and α of each subscale ranged from .71 to .90.
Conclusion
The Hospital Nurses’ Silence Behavior Scale is a useful tool for assessing multifaceted silence behavior among nurses. It can provide basic data for developing better communication strategies among nurses and other hospital staff. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effect of Emotional Labour on the Role Pressure and Silence Behaviour of Nurses
Lianci He, Jianhua Liu, Rong Sun, Yuan Deng, Ling Tang, Shaochuan Chen
Evaluation & the Health Professions.2026; 49(1): 3. CrossRef - Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 81. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurses’ Organizational Silence on Organizational Citizenship Behavior: Mediating Effect of Organizational Commitment Moderated by Organizational Justice
Shin Ae Hwang, Haeyoung Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 416. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation and translation of the Persian version of the Organizational Silence Behavior Scale (OSBS-P) for clinical nurses
Alireza Mirzaei, Mobina Jamshidinia, Mehrzad Aghabarari, Pouya Dolat Abadi, Reza Nemati-Vakilabad, Ehsan Namaziandost
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(12): e0314155. CrossRef
- Mediating Effect of Emotional Labour on the Role Pressure and Silence Behaviour of Nurses
- 4,734 View
- 280 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Psychometric Properties of the Fall Risk Perception Questionnaire-Short Version for Inpatients in Acute Care Hospitals
- Jeeeun Choi, Sujin Lee, Eunjin Park, Sangha Ku, Sunhwa Kim, Wonhye Yu, Eunmi Jeong, Sukhee Park, Yusun Park, Hye Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):151-161. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Patients’ perception of fall risk is a promising new indicator for fall prevention. Therefore, a fall risk perception questionnaire that can be used rapidly and repeatedly in acute care settings is required. This study aimed to develop a short version of the fall risk perception questionnaire (Short-FRPQ) for inpatients.
Methods
For the psychometric measurements, 246 inpatients were recruited from an acute care hospital. The construct (using confirmatory factor analysis and discriminant validity of each item), convergent, and known-group validities were tested to determine the validity of the Short-FRPQ. McDonald’s omega coefficient was used to examine the internal consistency of reliability.
Results
In the confirmatory factor analysis, the fit indices of the Short-FRPQ, comprising 14 items and three factors, appeared to be satisfactory. The Short-FRPQ had a significantly positive correlation with the original scale, the Korean Falls Efficacy Scale-International, and the Morse Fall Scale. The risk of falls group, assessed using the Morse Fall Scale, had a higher score on the Short-FRPQ. McDonald’s omega coefficient was .90.
Conclusion
The Short-FRPQ presents good reliability and validity. As patient participation is essential in fall interventions, evaluating the fall risk perception of inpatients quickly and repeatedly using scales of acceptable validity and reliability is necessary.
- 3,345 View
- 137 Download

- Development of a Reward Scale for Hospital Nurses
- Sun Hee Kim, Eun-Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(5):525-537. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23057
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and test a reward scale for hospital nurses.
Methods
The initial items were identified through a literature review and focus group interviews with ten hospital nurses. The content validity of the items was evaluated by ten experts. Fifty-one items were derived from the pilot survey. Four hundred eighty-eight nurses participated in the study: 248 for exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and 240 confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Data were analyzed using item analysis, EFA, CFA, convergent validity, known-group validity, and internal consistency using IBM SPSS Statistics 29.0 and IBM SPSS AMOS 29.0.
Results
The final scale consisted of 31 items and eight factors (decent wage, opportunity to grow and develop, support for special situations, various benefits, flexibility of work, job-related achievement, reflecting career and performance, and recognition), which explained 67.3% of the total variance. The eight-subscale model was validated by CFA. Convergent validity was evaluated by analyzing correlation with intention to leave (r = - .63, p < .001) and job satisfaction (r = .54, p < .001). The known-group validity was evaluated by comparing the reward scales according to age, clinical career, income level and hospital type. The scale was found to be reliable with a Cronbach’s α of .89.
Conclusion
Both the validity and reliability of the reward scale for hospital nurses are verified, which can enhance the understanding of the range of rewards and may assist nurse managers in establishing an effective reward system. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimized nursing management in the Central Sterile Supply Department and Gastroenterology Department: a retrospective controlled study
Dali Wang
American Journal of Translational Research.2024; 16(12): 7480. CrossRef
- Optimized nursing management in the Central Sterile Supply Department and Gastroenterology Department: a retrospective controlled study
- 4,245 View
- 151 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Internal Structure of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8-Items in a Nationally Representative Population
- Eun-Hyun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):359-369. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the internal structure (structural validity, internal consistency, and measurement invariance) of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with Eight Items (HINT-8), developed to measure Korean people’s health-related quality of life.
Methods
A secondary analysis was conducted using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, involving 6,167 adults aged over 18 years. The structural validity of the HINT-8 was assessed using exploratory graph analysis and confirmatory factor analysis. Internal consistency and measurement invariance were analyzed using McDonald’s omega (ω) and multigroup confirmatory factor analysis, respectively.
Results
The HINT-8 had a single dimension and good internal consistency (ω = .804). The one-dimension HINT-8 ex-hibited matric invariance but not scalar invariance across sociodemographic groups (sex, age, education, and marital status). Further, it exhibited scalar or partial scalar invariance across medical condition groups (hypertension, diabetes, depressive symptoms, and cancer).
Conclusion
The study finds that the HINT-8 demonstrated satisfactory structural validity and internal consistency, indicating its suitability for practice and research. However, the HINT-8 scores cannot be compared across different groups regarding sex, age, education, and marital status, as the interpretation varies within each sociodemographic category. Conversely, interpretation of the HINT-8 is consistent for individuals with and without hypertension, diabetes, depressive symptom, and cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between obstructive sleep Apnea–Related factors and HINT-8 utility scores in adults: a secondary analysis of the 2023 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES)
Mima Park, Seon-Ha Kim
Quality of Life Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients With Geographic Atrophy, a Late Stage of Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Findings From the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yeji Kim, Yun Tae Kim, Mingui Kong, Jae Hui Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictors of Dietary Supplement Use Among Women With Musculoskeletal Disease: A Population-Based Complex Sample Designed Study
Myoungjin Kwon, Sun Ae Kim, Youngshin Song
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Network Analysis of Quality of Life Among Older Adults With Arthritis
Dahee Wi, Chang G. Park, Jiae Lee, Eunjin Kim, Yoonjung Kim
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Network analysis of quality of life among young and middle-aged Korean cancer survivors
Yoonjung Kim, Dahee Wi, Eunjin Kim, Jiae Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100684. CrossRef - Quality of Life Based on the Experience of Psychological Counseling in Adults with Depressive Symptoms
Jihyeon Seo, Jihye Lim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(1): 39. CrossRef - Validation of the health-related quality of life instrument with 8 items for assessing health-related quality of life in patients with oropharyngeal cancer: a comparison with the EQ-5D-5L
Gyeong-U Hong, Bon Seok Koo, Min-Ju Kim, Woo-Jeong Sim, Ah-Yeon Lee, Ji-Eun An, Su-Yeon Yu, Sei Young Lee, Soo Hyun Lee
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative effectiveness and safety of herbal medicine therapy for low back pain and radiculopathy caused by lumbar intervertebral disc herniation: a study protocol for a pragmatic randomized controlled trial
Jung-Hyun Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Won-Suk Sung, Eun-Jung Kim, Yeoncheol Park, Yonghyeon Baek, Sang-Soo Nam, Byung-Kwan Seo
Frontiers in Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the health behavior and nutrition status of young-old women according to the vitality in their quality of life: based on the 2019, 2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jiyoung Jeong, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 496. CrossRef
- Association between obstructive sleep Apnea–Related factors and HINT-8 utility scores in adults: a secondary analysis of the 2023 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES)
- 4,677 View
- 132 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Development and Psychometric Evaluation of the Ischemic Stroke Distress Scale (ISDS)
- Jaejin Kang, Yang-Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):12-27. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure distress in patients with ischemic stroke and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
Preliminary items were developed from literature review and in-depth interviews. The final preliminary scale was confirmed through a content validity test of eight experts and a preliminary survey of 10 stroke patients. The participants for psychometric testing were 305 stroke patients in the outpatient clinic. Validity and reliability analyses included item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, known-group validity, and internal consistency of the scale.
Results
The final scale consisted of 17 items and 3 factors. The three distinct factors were ‘self-deprecation, worry about future health, and withdrawal from society’ and this structure was validated using a confirmatory factor analysis. Convergent validity was supported by comparison with the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (r = .54, p < .001) and Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire (r = .67, p < .001). Known-groups validity was verified by dividing groups according to ‘duration since diagnosis’ (t = 2.65, p = .009), ‘presence of sequela’ (t = 10.16, p < .001), and ‘awareness of distress’ (t = 12.09, p < .001). The internal consistency of the scale using Cronbach’s α for the total items was .93.
Conclusion
The Ischemic Stroke Distress Scale is a valid and reliable tool that reflects stroke distress effectively. It is expected to be used as a basic tool to develop various intervention strategies to reduce distress in ischemic stroke patients.
- 1,643 View
- 75 Download

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Assessment of Health Literacy in Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening
- Hye Sook Shin, Eunlim Chi, Hae-Ra Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):769-781. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Health literacy is a significant determinant of health and health behaviors such as cancer screening. Despite its significance, there are limited instruments available to assess health literacy targeting Koreans. The purpose of this study was to test the psychometric properties of Korean translation of a validated health literacy instrument in cancer screening—Korean version of assessment of health literacy in breast and cervical cancer screening (K-AHL-C).
Methods
A total of 555 women aged 20~65 participated in the online survey study. Of 52 items addressing five domains included in the original version, we focused on 36 items addressing three key domains closely associated with cancer screening: familiarity, health navigation, and comprehension.
Results
During content validation, two items from the health navigation domain were removed, yielding 34 items. Using Rasch analysis and confirmatory factor analysis, we found the evidence of construct validity of K-AHL-C. The Korean version was also significantly correlated with measures of Functional Health Literacy scale, cancer prevention behaviors, and subjective health status, suggesting convergent validities respectively. Finally, K-AHL-C had acceptable reliability coefficients (α) ranging from 0.71 to 0.92 for each domain and the total scale.
Conclusion
These psychometric properties support the K-AHL-C is a valid and reliable instrument for measuring Koreans’ health literacy in cancer screening. Also it is expected to use the instrument to detect breast and cervical cancer early and improve the screening rate, and ultimately to contribute to the promotion of women's health and women's health nursing practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Web-Based Delivery of an Effective Church-Based Intervention Program to Promote Cancer Screening (Community-based Health litEracy-focused intervention for breast and cervical Cancer Control) Among Korean Immigrant Women in the United States: Randomized Co
Hae-Ra Han, Yoon-Jae Lee, Deborah Min, Joyline Chepkorir, DaSol Amy Hwang, Steve Chae
JMIR Human Factors.2025; 12: e66092. CrossRef - Associations and gender differences between OHI-seeking behaviors and eHealth literacy among Chinese university students
Jie Chen, Hua Tian
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Information Seeking Pathways and Factors Influencing Health Literacy Among Cancer Patients: Based on Data from the 2nd Korean Health Panel 2021
Yun-La Hur, Eun-Jeong Hong
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 155. CrossRef - A Psychometric Validation of the Korean Version of Disaster Response Self-Efficacy Scale for Nursing Students
Sung Hae Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 2804. CrossRef - Health literacy measures in South Korea: A scoping review
Heeran Chun, Su Hyun Kim, Eunja Park
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(4): 39. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Climate, Health, and Nursing Tool
Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim, Min Kyung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 173. CrossRef
- Web-Based Delivery of an Effective Church-Based Intervention Program to Promote Cancer Screening (Community-based Health litEracy-focused intervention for breast and cervical Cancer Control) Among Korean Immigrant Women in the United States: Randomized Co
- 2,627 View
- 49 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Self-Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention Scale in the Community Dwelling Elderly with Risk of Dysphasia
- Eun Young Yang, Shin-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):474-486. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop and validate a Korean version of the Self-Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention(SCAPP-K) scale in older adults at risk of dysphasia.
Methods
The Hertz and Baas model of scale development and validation was used. Inthe development stage, items were generated via literature review and interviews with medical experts, older adults, and caregivers. Tenexperts assessed the items for content validity. Subsequently, 12 older adults participated in a pilot test to determine the comprehensibilityand appropriateness of the SCAPP-K scale. The validation stage involved a cross-sectional survey with 203 older adults for exploratoryfactor analysis (EFA) and 200 older adults for confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and to determine convergent and discriminant validity. Totest the validity and reliability of the scale, EFA using principal component analysis with varimax rotation and CFA were conducted, andconvergent and discriminant validity as well as internal consistency reliability were determined.
Results
As a result of EFA, three self-carefactors (knowledge, resources, behaviors) with 21 items were validated. The CFA and convergent and discriminant validity indicated theapplicability of the three-factor self-care scale. The reliability of the SCAPP-K scale was acceptable, with Cronbach’s a=.87~.91.
Conclusion
The SCAPP-K scale has acceptable validity and reliability and can contribute to clinical practice, research, and education to improveself-care for the prevention of aspiration pneumonia in older adults at risk of dysphasia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cause-specific mortality in Korea during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
Jinwook Bahk, Kyunghee Jung-Choi
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022110. CrossRef - Translation of the Chinese version of the Self‐Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention Scale and its validation among Chinese community dwelling elderly with risk of dysphasia
Zhen Yang, Fengmin Chen, Yibo Zhang, Sien Pan, Yingying Lu, Huijun Zhang
Nursing Open.2022; 9(3): 1902. CrossRef - Development and validation of a self-care scale for older adults undergoing hip fracture surgery: the HFS-SC
Eun-Jeong Jeon, Kyeong-Yae Sohng, Hye-Ah Yeom
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the characterization, biocompatibility and efficacy of sponge brush products for oral care
Song-Yi Yang, Ji-Won Choi, Sang-Hwan Oh
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2021; 48(1): 27. CrossRef
- Cause-specific mortality in Korea during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
- 2,217 View
- 77 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Development of the Transition Shock Scale for Newly Graduated Nurses
- Eun-Young Kim, Jung Hee Yeo, Kyeong Im Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):589-599. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.589
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a scale to assess the transition shock experienced by newly graduated nurses, and test the validity and reliability of the scale.
Methods The initial items were identified through a review of literature and in-depth interviews with nine newly graduated nurses. Content validation of the items was evaluated by five nurse professors and three nurses. Participants were 269 newly graduated nurses who worked at six acute care hospitals in Busan, Ulsan, and Yangsan, South Korea. Data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, criterion related validity, and internal consistency.
Results The final scale consisted of 18 items and six factors (conflict between theory and practice, overwhelming workload, loss of social support, shrinking relationship with co-workers, confusion in professional nursing values, and incongruity in work and personal life), which explained 71.3% of the total variance. The six subscale model was validated by confirmatory factor analysis. Cronbach's alpha for the total items was. 89. Convergent validity was evaluated by analyzing total correlation with burnout (r=.71,
p <.001) and turnover intention (t=5.84,p <.001).Conclusion This scale can be used in the development of nursing interventions to reduce the transition shock experienced by newly graduated nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Professional Nursing Values in Nursing Students During Transitional Period to Nurses From the Perspective of Generation Z: A Longitudinal Study
Taewha Lee, Yoonjung Ji
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025; 81(8): 4723. CrossRef - Assessing validity and reliability of the Transition Shock Scale for Undergraduate Nursing Students (TSS, Chinese version) in associate degree nursing students
Huiting Weng, Ziwei Ding, Li Yang, Bo Zhang, Yuanyuan Luo, Qin Wang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Transition Shock on the Relationships among Grit, Social Support, and Retention Intention for New Graduate Nurses
Hye Yeong Ji, Haeyoung Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 99. CrossRef - Development and psychometric testing of the reality shock scale for nursing students
Cennet Çiriş Yildiz, Berna Kahveci Ceylan, Yasemin Ergün, Mustafa Mete
Nurse Education Today.2025; 153: 106795. CrossRef - Exploring personal, community, and societal conditions associated with South Korean new graduate nurses’ organizational socialization: a cross-sectional survey study
Jihye Song, Jeongsuk Lee, Youmin Cho, Ahyoung Jeon, Moonhee Gang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Turnover prevalence and the relationship between transition shock and turnover intention among new nurses: A meta-analysis
Khin Sandi Myint Lay, Khemaradee Masingboon
International Journal of Nursing Studies Advances.2025; 9: 100390. CrossRef - From student to nurse: exploring transition shock through stress, locus of control, and coping strategies in newly graduated nurses
Rasha Kadri Ibrahim, Mirna Safi, Amani Darwish, Yasir S. Alsalamah, Lisa Babkair, Nasiru Mohammed Abdullahi, Basma Maher, Manar Nasser Alotaibi, Monerh Abdullah Alfalaij, Shorok Hamed Alahmedi, Sally Mohammed Farghaly Abdelaliem, Abdelaziz Hendy
BMC Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Nursing Students’ Practice Transition Shock, Resilience, and Professional Self-concept on Career Identity
Sein Ryu
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(2): 153. CrossRef - Navigating transition shock: The role of system thinking in enhancing nursing process competency among early career nurses
Mohamed Hussein Ramadan Atta, Ahmed Abdelwahab Ibrahim El‐Sayed, Samira Ahmed Alsenany, Heba Abdel‐Hamid Hammad, Nadia Waheed Elzohairy, Maha Gamal Ramadan Asal
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2024; 21(6): 611. CrossRef - Effect of Transition Shock on Intention to Stay in Newly Graduated Nurses : The Mediating Effect of Positive Psychological Capital
Hyuna Kam, Chanhee Kim, Yeonok Yoon, Heeyoung Shin, Junghwa Lee, Myoungohk Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 25. CrossRef - The mediating effect of transition shock on the relationship between readiness for practice and turnover intention of new graduate nurses in South Korea: A longitudinal study
Taewha Lee, Eunkyung Kim, Yoonjung Ji
Nurse Education Today.2024; 143: 106394. CrossRef - Effects of Resilience, Nursing Managers’ Empowering Leadership on Turnover Intention among New Nurses: Mediating role of Transition Shock
Hyun Jin Jung, Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 212. CrossRef - Influence of Nursing Practice Readiness and Social Support from Clinical Nurse Educators on Reality Shock among Newly Graduated Nurses
Kyoung Hee Youn, Eun Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 494. CrossRef - Nursing practice readiness improvement program tailored for newly graduated registered nurses: A quasi-experimental study
Eun A Kim, Ji Sun Lee, Young Sook Bong, Eun Hee Jang, Yang Hwa Lim, Jung Ah Kim, Nan Song
Nurse Education Today.2024; 133: 106077. CrossRef - Predicting New Graduate Nurses’ Retention during Transition Using Decision Tree Methods: A Longitudinal Study
Taewha Lee, Yea Seul Yoon, Yoonjung Ji
Journal of Nursing Management.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Transition shock, future time perspective, professional self-concept, and professional identity among nursing interns: A cross-sectional study
Ziwei Ding, Huiting Weng, Li Yang, Bo Zhang, Yuanyuan Luo, Qin Wang
Heliyon.2024; 10(5): e26207. CrossRef - Relationship between Transition Shock, Professional Stressors, and Intent to Leave the Nursing Profession during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Dario Nakić, Ivana Gusar, Ivana Franov, Marijana Matek Sarić, Marija Ljubičić
Medicina.2023; 59(3): 468. CrossRef - Transition Shock of Newly Employed Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
Ivana Gusar, Emila Peroš, Sonja Šare, Marija Ljubičić
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2023; 11(G): 82. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Clinical Practicum Transition Shock Scale (CPT-Shock) for Korean Nursing Students
Soo-Yeon Kim, Yeong-Ju Ko
Healthcare.2023; 11(20): 2789. CrossRef - Factors influencing the transition shock of dental hygienists - focusing on the new dental hygienist -
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of incivility and psychological capital on nursing students’ transition shock
Chung Hee Woo, Chanhee Kim
Collegian.2022; 29(5): 621. CrossRef - Job change among early career nurses and related factors: A postgraduation 4‐year follow‐up study
Eun‐Young Kim, Sun‐Hee Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 3083. CrossRef - Development of the Nursing Practice Readiness Scale for new graduate nurses: A methodological study
Jeonghyun Kim, Sujin Shin
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 59: 103298. CrossRef - Transition Shock Experience of Nursing Students in Clinical Practice: A Phenomenological Approach
Yeong-Ju Ko, Soo-Yeon Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 613. CrossRef - Factors influencing the transition shock of newly-graduated nurses
Kil Je Moon, Moo Yong Cho,
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(2): 156. CrossRef - Transition shock and job satisfaction changes among newly graduated nurses in their first year of work: A prospective longitudinal study
Eun‐Young Kim, Jung Hee Yeo
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(3): 451. CrossRef - Developing and validating the transition status scale for newly graduated nurses in China
Weiguang Ma, Yuqing He, Weike Zhao, Ruiyang Xu, Tao Liang
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(6): 1819. CrossRef - Transition of newly graduated nurses in China: An evaluation study
Tingting Cai
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 50: 102951. CrossRef - Development and psychometric testing of the Reality Shock Scale for newly graduated nurses
Cennet Çiriş Yildiz, Yasemin Ergün
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(12): 4950. CrossRef - Association of work environment and resilience with transition shock in newly licensed nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Soon Ok Kim, Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(7-8): 1037. CrossRef - Structural Model of Professional Socialization of Nursing Students With Clinical Practice Experience
Soo-yeon Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Journal of Nursing Education.2020; 59(3): 133. CrossRef - Relationships between reality shock, professional self-concept, and nursing students' perceived trust from nursing educators: A cross-sectional study
Ji-Soo Kim
Nurse Education Today.2020; 88: 104369. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Transition Shock Scale for Undergraduate Nursing Students
Soo Yeon Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 17. CrossRef - Effects of pre-graduation characteristics and working environments on transition shock of newly graduated nurses: A longitudinal study
Eun-Young Kim, Jung Hee Yeo
Nurse Education Today.2019; 78: 32. CrossRef
- Professional Nursing Values in Nursing Students During Transitional Period to Nurses From the Perspective of Generation Z: A Longitudinal Study
- 4,310 View
- 267 Download
- 34 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Peer Group Caring Interaction Scale-Korean Version
- Jeong-Hee Kim, Moon Yeon Kong, Yun Hee Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):431-442. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.431
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This paper was conducted to validate the Korean version of the Peer Group Caring Interaction Scale (PGCIS-K) that measures caring behaviors as experienced by nursing students.
Methods Translation of the PGCIS-K was validated through forward-backward translation methods. Survey data were collected from 218 nursing students in a nursing school. Construct validity and criterion-related validity were evaluated. Internal consistency and the Guttman split-half coefficient were calculated to assess reliability.
Results The PGIS-K showed reliability except for 4 items (Cronbach's α=.91, Guttman split-half coefficient=.85), which were low (<.30) or negatively correlated with the total scale. A 12-item reduced form of the PGCIS-K was developed by item-analysis and construct validity evidence. Factor loading for the 12 items on 2 factors ranged from .47~.82, which explained 58.4% of the total variance. Two factors were named 'modeling and assistance (Cronbach's α=.87)' and 'communication and sharing (Cronbach's α=.82)'. Convergent validity, discriminant validity, and criterion validity were supported according to the correlation coefficients of the 2 factors with other measure.
Conclusion The findings suggest preliminary evidence that the 12-item PGCIS-K can be used to measure nursing students' peer group caring interactions in Korea. Additional studies are recommended to continue the psychometric evaluation of this scale. Also, it can be extended to measure graduate nursing students or staff nurses' peer group caring interaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Peer caring and clinical adaptation as mediators between emotional intelligence and nursing professionalism in students
SeolHwa Moon, Sun Young You, Juyeon Oh
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2025; 20(4): e1149. CrossRef - Hospital organisational health as a mediator between positive nursing organisational culture, caring behaviour, and quality of nursing care
Bo Ram Ku, Mi Yu
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A structural model of nursing students’ performing communication skills
Cho Rong Gil, Kyung Mi Sung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 148. CrossRef - Adapting and Validating the COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy and Vaccine Conspiracy Beliefs Scales in Korea
Hyesung Ock, Mihyeon Seong, Insook Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(11): 2274. CrossRef - Influence of Nurse Manager and Peer Group Caring Behaviors as Perceived by Nurses on Organizational Socialization and Nursing Performance
Na Yeon Shin, Soyoung Yu, Seong Suk Kang, Seung Shin Lee, Min Jeung Park, DaeYeon Lee, Sun Mi Nam
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(2): 110. CrossRef - A Review of the Korean Nursing Research Literature with Focus on Quantitative Measurement of Caring
Jeong-Hee Kim, Young Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(2): 155. CrossRef - Influence of Nurse Manager and Peer Group Caring Behaviors as Perceived by Nurses on Intention to Retention
Moon Yeon Kong, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(2): 191. CrossRef
- Peer caring and clinical adaptation as mediators between emotional intelligence and nursing professionalism in students
- 1,305 View
- 21 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Psychometric Properties and Item Evaluation of Korean Version of Night Eating Questionnaire (KNEQ)
- Beomjong Kim, Inja Kim, Heejung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(1):109-117. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to develop a Korean version of Night Eating Questionnaire (KNEQ) and test its psychometric properties and evaluate items according to item response theory.
Methods The 14-item NEQ as a measure of severity of the night eating syndrome was translated into Korean, and then this KNEQ was evaluated. A total of 1171 participants aged 20 to 50 completed the KNEQ on the Internet. To test reliability and validity, Cronbach's alpha, correlation, simple regression, and factor analysis were used. Each item was analyzed according to Rasch-Andrich rating scale model and item difficulty, discrimination, infit/outfit, and point measure correlation were evaluated.
Results Construct validity was evident. Cronbach's alpha was .78. The items of evening hyperphagia and nocturnal ingestion showed high ability in discriminating people with night eating syndrome, while items of morning anorexia and mood/sleep provided relatively little information. The results of item analysis showed that item2 and item7 needed to be revised to improve the reliability of KNEQ.
Conclusion KNEQ is an appropriate instrument to measure severity of night eating syndrome with good validity and reliability. However, further studies are needed to find cut-off scores to screen persons with night eating syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - Prevalence and correlates of night eating syndrome among Chinese nurses: focus on depression and sleep quality
Shijie Fang, Ruixuan Zhao, Jimin Feng, Hongxu Wang, Dongwen Li
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Night Eating Questionnaire through the lens of the Rasch model
Vojkan Aleksic, Marija Milic, Jelena Dotlic, Biljana Jeremic, Branislav Djerkovic, Ivan Radic, Ana Karanovic, Ljiljana Kulic, Milivoje Galjak, Tatjana Gazibara
Heliyon.2024; 10(11): e31929. CrossRef - The association between night eating syndrome and health-related quality of life in Korean adults: a nationwide study
Woorim Kim, Yeong Jun Ju, Soon Young Lee
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between episodes of night eating and levels of depression in the general population
Woorim Kim, Yeong Jun Ju, Soon Young Lee
International Journal of Eating Disorders.2022; 55(2): 254. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Assessment of Health Literacy in Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening
Hye Sook Shin, Eunlim Chi, Hae-Ra Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 769. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Quality of Sleep in Young Adults
Ae Kyung Chang, Kyung Hye Lee, Chong Mi Chang, Jin Yi Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(4): 497. CrossRef - Psychometric properties and gender invariance of the simplified Chinese version of Night Eating Questionnaire in a large sample of mainland Chinese college students
Jinbo He, Feng Ji, Xiaoya Zhang, Xitao Fan
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity.2019; 24(1): 57. CrossRef - Night Eating Habits of High School Students by Sex in Gyeonggi Region
Hee Jin Kim, Yeong Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(1): 56. CrossRef - Lived Experiences toward Harmful Work Environment among Clinical Nurses: Phenomenological Approach
Yeong Ju Ko, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(3): 173. CrossRef - Effects of Psychiatric Nurses' Secondary Traumatic Stress and Compassion Satisfaction on Burnout: The Moderating Effect of Social Support
Hyun Jung Lee, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 399. CrossRef
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,421 View
- 9 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Properties of the Measures to Assess Oxaliplatin-induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Literature Review
- Sang Hui Chu, Yoon Ju Lee, Young Joo Lee, Charles S. Cleeland
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):783-801. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.783
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study is to provide a comprehensive overview of the various measures available for assessment of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OXLIPN) and to evaluate the measurement properties of each assessment tool.
Methods A systematic review was conducted to identify existing measures for OXLIPN found in the databases of PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, RISS and KoreaMed. The quality of the 24 identified tools was evaluated based on their properties of measurement including content validity, internal consistency, criterion validity, construct validity, reproducibility, responsiveness, floor-ceiling effects and interpretability.
Results Ten (41.7%) of the 24 tools were identified as specific measures for assessing OXLIPN and the most popular type of measures were clinical grading systems by clinicians (58.3%) and only 29.2% of measures were identified as patient reported outcomes. The most frequently used tool was National Cancer Institute-Common Toxicity Criteria (NCI-CTC), but the validity of NCI-CTC has not been reported appropriately. Overall, the Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory (NPSI) received the best psychometric scores, and the Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy Assessment Tool (CIPNAT) and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy/Gynaecologic Oncology Group-neurotoxicity-12 (FACT/GOG-Ntx-12) followed NPSI.
Conclusion To select appropriate measure, evidences should be accumulated through the clinical use of tools. Therefore, practitioner and researchers are urged to report relevant statistics required for the validation of the currently used measures for assessment of OXLIPN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Assessment Tool
Mi Sook Jung, Mijung Kim, Kyeongin Cha, Xirong Cui, Ji Wan Lee
Research and Theory for Nursing Practice.2022; 36(4): 422. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Measurement Properties of Spirituality related Assessment Tools Published in Korean Journals
Il-Sun Ko, Jin Sook Kim, Soyoung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(1): 133. CrossRef - The Efficacy of Acupuncture in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tsai-Ju Chien, Chia-Yu Liu, Ching-Ju Fang, Chun-Yu Kuo
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Assessment Tool (CIPNAT)
Sevinç Kutlutürkan, Elif Sözeri Öztürk, Fatma Arıkan, Burcu Bayrak Kahraman, Keziban Özcan, Mürvet Artuk Uçar
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2017; 31: 84. CrossRef
- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Assessment Tool
- 1,569 View
- 8 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of ARQ-K (Korean Version of the Assault Response Questionnaire) for Emergency Department Nurses in Korea
- Moon Jung Jang, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):544-553. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.544
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To investigate the validity and reliability of the Korean Version of the Assault Response Questionnaire (ARQ-K) measuring the intensity of reaction to victimization of emergency nurses in Korea.
Methods An internal consistency reliability and construct validity using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis were conducted using SPSS WIN (20.0) and AMOS (20.0). Survey data were collected from 321 nurses who worked in 3 levels - wide regional emergency centers, regional emergency centers, appointed emergency centers - of emergency care facilities in Busan, Korea.
Results The Cronbach's alpha values regarding internal consistency were .77~.93 for the subscales of ARQ-K. Factor loadings of the 26 items on the four subscales ranged from .59 to .84. The four-subscale model was validated by confirmatory factor analysis (χ2/df=3.85,
p < .001, RMR=.06, GFI=.80, NFI=.81, TLI=.83, CFI=.85, RMSEA=.09).Conclusion This study shows that the Korean Version of the Assault Response Questionnaire is a valid and reliable instrument to assess nurses' reaction to victimization of emergency nurses in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Violence Experience, Violence Response and Coping with Violence on Professional Quality of Life among Emergency Department Nurses
Eunju Choi, Youngjin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(2): 91. CrossRef - High-Risk Symptom Cluster Groups for Work-Life Quality and Turnover Intention among Nurses
Chiyoung Cha, Miran Lee
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2023; 45(3): 192. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Nurses' Responses to Violence on Burnout: The Moderating Role of Positive Psychological Capital
Haejun Choi, Sujin Shin, Seungji Kim, Sungran Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(4): 406. CrossRef - Experience of Violence and Factors Influencing Response to Violence Among Emergency Nurses in South Korea: Perspectives on Stress-Coping Theory
Seung-Yi Choi, Hyunlye Kim, Kwang-Hi Park
Journal of Emergency Nursing.2022; 48(1): 74. CrossRef - Verbal violence and turnover intention among new nurses in Korea: A time‐lagged survey
Ae Kyung Chang, Ah Young Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1823. CrossRef - Factors Affecting on Turnover Intentions of Emergency Department Nurses who have Experienced Verbal Abuse
Gyoo-Yeong CHO, Mi-Kyung SEO
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 314. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of Korean version of the Grit Scale for Korean nursing students
Hyo-Suk Song, So-Hee Lim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(3): 322. CrossRef - Effects of Hospital-Based Violence-Prevention and Coping Programs on Nurses' Violence Experience, Violence Responses, Self-Efficacy, and Organizational Commitment
Yu Jeong Yang, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 550. CrossRef - Investigating the moderating effects of multi group on safety performance: The case of civil aviation
Vedant Singh, Somesh Kumar Sharma, Indu Chadha, Tej Singh
Case Studies on Transport Policy.2019; 7(2): 477. CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Social Support on the Relationship between Violence Experiences and Violence Responses of Psychiatric Nurses
Jinhee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(2): 144. CrossRef - Experience of Violence from the Clients and Coping Methods Among Intensive Care Unit Nurses Working in a Hospital in South Korea
Hye Jin Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh, Soon Haeng Lee, Jin Hee Hwang, Ji Hye Kwon
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(2): 77. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Resilience on the Association between Violence Experience and Violence Response among Nurses
Cheol Jeong, Eun Nam Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 41. CrossRef - Hardiness Mediates Stress and Impact Level in ED Nurses Who Experienced a Violent Event
Jin Hee Park, Eun Nam Lee, Kyung Ran Kong, Moon Jung Jang
Journal of Emergency Nursing.2017; 43(6): 539. CrossRef - Convergent approach of phenomenological methodology about Emergency Nurses' experience of hospital violence
Young-Hee Jeong
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2015; 6(5): 63. CrossRef
- The Influence of Violence Experience, Violence Response and Coping with Violence on Professional Quality of Life among Emergency Department Nurses
- 1,150 View
- 8 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Psychometric Properties of Korean Minimal Insomnia Screening Scale
- Inja Kim, Sungjae Kim, Beomjong Kim, Heejung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(6):853-860. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.6.853
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to develop a Minimal Insomnia Screening Scale for Korean adults (KMISS) and to evaluate psychometric properties and discriminant ability of the developed scale.
Methods Data from a cross-sectional survey of 959 Korean adults were analyzed to develop the summated insomnia scale, which was evaluated in terms of reliability, validity, and discriminant ability by receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis.
Results Item-total correlations ranged between .71-.79 and Cronbach's α was .87. Adequate validity was also evident. ROC-curve analysis showed area under ROC was .87 (95% CI: .84-.90) and identified the optimal cut-off score as ≤ 20 (sensitivity, .83; specificity, .75; positive/negative predictive values, .40/.95). Using this cut-off score, the prevalence of insomnia in the study sample was 26.3% and most frequent among women and the oldest group.
Conclusion Data supports the psychometric properties of KMISS as a possible insomnia screening instrument. KMISS also shows promise as a convenient ultra-short screening measure of insomnia for adults and epidemiological studies in community health care settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing Sleep Quality Using Mobile EMAs: Opportunities, Practical Consideration, and Challenges
Jiyoun Lim, Chi Yoon Jeong, Jeong Muk Lim, Seungeun Chung, Gague Kim, Kyoung Ju Noh, Hyuntae Jeong
IEEE Access.2022; 10: 2063. CrossRef - Factors that Influence Sleep among Residents in Long-Term Care Facilities
Da Eun Kim, Ju Young Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(6): 1889. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Korean Versions of Three Sleep Evaluation Questionnaires
Heejung Choi, Sungjae Kim, Beomjong Kim, Inja Kim
Clinical Nursing Research.2015; 24(5): 526. CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Sleep Disturbance in Community Dwelling Adults in Korea
Heejung Choi, Beomjong Kim, Inja Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(2): 183. CrossRef
- Assessing Sleep Quality Using Mobile EMAs: Opportunities, Practical Consideration, and Challenges
- 1,167 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Validation of a Korean Translated Version of the Critical Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) for ICU Patients
- Eun-Mi Kwak, Heeyoung Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(1):76-84. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.1.76
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this methodological study was to examine the reliability and validity of a translated Korean version of the Critical Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) developed for assessment of pain in critically ill nonverbal patients.
Methods A cross-sectional study design was used. Data were collected from a convenience sample of 202 critically ill patients admitted to a university hospital. Upon establishment of content and translation equivalence between the English and Korean version of CPOT, psychometric properties were evaluated.
Results The interrater reliability was found to be acceptable with the weighted kappa coefficients of .81-.88. Significant high correlations between the CPOT and the Checklist of Nonverbal Pain Indicators were found indicating good concurrent validity (r=.72-.83,
p <.001). Data showed the area under the ROC curve of 0.86 with a cut-off point of 1, which resulted in 76.9% sensitivity and 88.6% specificity. The mean score of CPOT during suctioning was significantly different from that of before (t=-14.16,p <.001) or 20 minutes after suctioning (t=16.31,p <.001).Conclusion Results of this study suggest that the CPOT can be used as a reliable and valid measure to assess pain in critically ill nonverbal patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validation of Nonverbal Pain Assessment Tools in Brain-Injured Patients
Ji-Young Lee, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(3): 64. CrossRef - Effect of an Intervention Using Voice Recording of a Family Member on Patients Undergoing Mechanical Ventilator Weaning Process
Ah Young Choi, Min Young Kim, Eun Kyeung Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 32. CrossRef - Validation of the PAINAD-K Scale for Nonverbal Pain Assessment in the Post Anesthesia Care Unit
Hyemin Kang, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 90. CrossRef - Pain assessment of the adult sedated and ventilated patients in the intensive care setting: A scoping review
Samira Hamadeh Kerbage, Loretta Garvey, Gavin W. Lambert, Georgina Willetts
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2021; 122: 104044. CrossRef - A Systematic Review on Pain Assessment Tools for Intensive Care Unit Patients
Eun-Jeong Kim, Jiwon Hong, Jiyeon Kang, Na geong Kim, NaRi Kim, Su-Youn Maeng, Hye-Ryeon Park, Min Kyung Ban, Gun Young Yang, Kyung Suk Lee, Eun Hye Jang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(1): 44. CrossRef - Translation into Spanish and Cultural Adaptation of the Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool
Carmen Mabel Arroyo-Novoa, Milagros I. Figueroa-Ramos, Kathleen A. Puntillo, Céline Gélinas
American Journal of Critical Care.2020; 29(3): 226. CrossRef - The Diagnostic Accuracy of Critical Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) in ICU Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yue Zhai, Shining Cai, Yuxia Zhang
Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.2020; 60(4): 847. CrossRef - Validation of the Dutch version of the critical‐care pain observation tool
Willemke Stilma, Saskia Rijkenberg, Hilde M Feijen, Jolanda M Maaskant, Henrik Endeman
Nursing in Critical Care.2019; 24(3): 132. CrossRef - The German version of the Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool for critically ill adults
I. Kiesewetter, U. Bartels, A. Bauer, G. Schneider, S. Pilge
Der Anaesthesist.2019; 68(12): 836. CrossRef - A Psychometric Analysis Update of Behavioral Pain Assessment Tools for Noncommunicative, Critically Ill Adults
Céline Gélinas, Aaron M. Joffe, Paul M. Szumita, Jean-Francois Payen, Mélanie Bérubé, Shiva Shahiri T., Madalina Boitor, Gerald Chanques, Kathleen A. Puntillo
AACN Advanced Critical Care.2019; 30(4): 365. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU
John W. Devlin, Yoanna Skrobik, Céline Gélinas, Dale M. Needham, Arjen J. C. Slooter, Pratik P. Pandharipande, Paula L. Watson, Gerald L. Weinhouse, Mark E. Nunnally, Bram Rochwerg, Michele C. Balas, Mark van den Boogaard, Karen J. Bosma, Nathaniel E. Bru
Critical Care Medicine.2018; 46(9): e825. CrossRef - The Critical care Pain Observation Tool is reliable in non-agitated but not in agitated intubated patients
Hoda Chookalayia, Mehdi Heidarzadeh, Mohammad Hassanpour-Darghah, Masoomeh Aghamohammadi-Kalkhoran, Mansoreh Karimollahi
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2018; 44: 123. CrossRef - Processus d’implantation d’une échelle d’évaluation de la douleur pour les patients cérébrolésés : description d’un projet de changement de pratique clinique basé sur le Modèle Intégré de la Consultation
Véronique de Goumoëns, François Décaillet, Amélia Didier, Chantal Montreuil, Karin Diserens, Anne-Sylvie Ramelet
Recherche en soins infirmiers.2017; N° 128(1): 79. CrossRef - Validation of the Danish version of the Critical Care Pain Observation Tool
J. B. Frandsen, K. S. O'Reilly Poulsen, E. Laerkner, T. Stroem
Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica.2016; 60(9): 1314. CrossRef - Comparison of Domestic and International Research (1992-2011): Intensive Care Nursing Studies
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Hee Jang, Ji Youn Choi, So Jung Lee, Hyo Kuyng Seo, Kyung Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(4): 384. CrossRef - The Effects of Music Intervention on Pain among Critically Ill Patients with Ventilatory Support
Mi Na Ahn, Hye Young Ahn
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(4): 247. CrossRef
- Validation of Nonverbal Pain Assessment Tools in Brain-Injured Patients
- 1,477 View
- 12 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Construct Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Practice Environment Scale of Nursing Work Index for Korean Nurses
- Eunhee Cho, Mona Choi, Eun-Young Kim, Il Young Yoo, Nam-Ju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(3):325-332. Published online June 13, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.325
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To develop and test the validity and reliability of the Korean version of PES-NWI measuring nursing work environments in hospitals.
Methods The Korean version of the PES-NWI was developed through forward-backward translation techniques, and revision based on feedback from focus groups. An internal consistency reliability and construct validity using confirmatory factor analysis were conducted using SPSS WIN (16.0) and AMOS (18.0). Survey data were collected from 733 nurses who worked in three acute care hospitals in Seoul, South Korea.
Results The Korean version of PES-NWI showed reliable internal consistency with a Cronbach's alpha for the total scale of .93. Factor loadings of the 29 items on the five subscales ranged from .28 to .85. The five subscales model was validated by confirmatory factor analysis (RMR<.05, CFI>.9).
Conclusion The findings of this study demonstrate that the Korean version of PES-NWI has satisfactory construct validity and reliability to measure nursing work environments of hospitals in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analyzing the Drivers of Job Satisfaction and Nurse Retention Among Kazakh Nurses in Public Clinical Centers: Key Factors and Insights
Joseph Almazan, Alyona Demidenko, Gaukhar Kassimova, Moldir Majanova, Botakoz Zhienbayeva, Aruzhan Asanova, Jonas P. Cruz, Shashank Kaushik
Nursing Forum.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influences of New Graduate Nurses’ Fatigue, Critical Thinking, and Nursing Work Environment on Patient Safety Nursing Behaviors
Myojeong Kim, Yujeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2026; 32(1): 49. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Professional Socialization Among Korean Male Nurses: A Cross‐Sectional Study
Jae Jun Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Soo Young Han, You Lee Yang, Young Man Kim, Eui Geum Oh, Malakeh Malak
Journal of Nursing Management.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Theoretical Model of Clinical Nurses’ Intentions to Stay During Disasters: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach
Hyerine Shin, Kyunghee Kim, Suk Jeong Lee, Park So Hyun, Changwon Lim, Hyun Jun Kim, Ji-Su Kim, Majed Alamri
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a Nursing Practice Environment, Nursing Performance on Retention Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Nursing Professional Pride
Shin Hee Kim, Mi Sook Oh, Yun Bok Kwak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 64. CrossRef - The mediating effects of nurses’ professional values on the relationship between work environment and organizational commitment among long-term care hospital nurses
Won Hee Jun
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural Equation Model for Intent of Return to Nursing Practice among Inactive Korean Nurses
Ji-Yeon Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 87. CrossRef - Factors influencing nursing care competences in neonatal intensive care units: Generalized equation estimation analysis
Eun Sook Kim, Hyoyeong Kim, Heemoon Lim, Jungwoo Hwang, Hyejung Lee
Journal of Neonatal Nursing.2025; 31(3): 101668. CrossRef - Influence of Perception of Patient Safety Culture, Job Stress, and Nursing Work Environment on Patient Safety Nursing Activities by Emergency Room Nurses
Eon Mi Lee, Jeong Hyun Cho, Seung Gyeong Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 264. CrossRef - Effects of Grit and Nursing Work Environment on Work Engagement in Clinical Nurses
Young Ju Kim, Hye Young Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 312. CrossRef - Influences of Generation Z Characteristics on Job Embeddedness and Turnover Intention
Su Hyun Kim, Chae Yeon Park, Seung Mok Shin, Seung Hun Shin, Grace Choe, Da Yeong Hwang, Young Hee Chae, Geun-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 291. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Team Effectiveness of the Nursing Unit on the Nursing Work Environment and Patient-Centered Nursing: A Cross-Sectional Study
Se Young Kim, Young Ko
Healthcare.2025; 13(17): 2080. CrossRef - Predictors of end-of-life care among emergency nurses: A cross-sectional study in Korea
Ji Seon Lee, Sook Jung Kang
Australasian Emergency Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frequency and Associated Factors of Interruptions During the Medication Administration Process Among Nurses in South Korea: A Cross‐Sectional Study
Seung Gyeong Jang, Eun Young Choi, Seung Ju Baek, Hye‐Mi Moon, Sang Hee Hong, Jin Kyung Cho, Won Lee
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Burnout Among Hospice and Palliative Care Ward Nurses
Young-Mi Kim, Chieun Song, Jeoungmin Park
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Predictive Model for Person-Centered Care in Intensive Care Units in South Korea: A Structural Equation Model
Sunmi Kwon, Kisook Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 467. CrossRef - The Influences of Positive Psychological Capital and Nursing Work Environment on Job Embeddedness among Advanced Beginner Nurses
Eunhye Gil, Mi-Ae You, Ji Yea Lee, Sunjoo Boo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 549. CrossRef - Structural Equation Model of Turnover Intention Among Integrated Nursing Care Service Wards Nurses in Small- and Medium-Sized Hospitals
So Hyeon Yun, Won Hee Jun
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Self-Compassion, Burden of BPSD, Communication Behavior, and Nursing Work Environment on Person-Centered Care for Patients with Dementia Among Long-Term Care Hospital Nurses
Yong Min Kim, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2025; 14(1): 15. CrossRef - The Korean Version of Health Work Environment Assessment Tool for Clinical Nurses: A Validation and Reliability Study
Im Sun Seo, Mihyun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 483. CrossRef - Job Crafting as the Missing Link: Understanding Its Role in Nurses’ Work Engagement
Kyungjin Lee, Ja Kyung Seo, Seung Eun Lee, Yunhong Liu
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Nursing Professionalism, Nursing Work Environment, and Compassion Competence on Person-Centered Care of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care
Yeon-Jin Lee, Eun-Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 572. CrossRef - Effect of Work-Family Conflict on Turnover Intention among Married Female Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Nursing Work Environment
Min Gyeong Jeong, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 451. CrossRef - A Study on Impact of Nursing Work Environment, Interpersonal Skills, and Grit on Field Adaptation of Nurses Who Have Experienced Department Transfers
Su Jeong Lee, Yun Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(2): 71. CrossRef - The Influence of Positive Psychological Capital, Perceived Value of Work, and Nurse Practice Environment on Retention Intention in Small-Medium Sized Hospital Nurses
Su Hye Kwon, Miseon Bang, Young Kyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 189. CrossRef - Factors associated with clinical nurses’ preconception health behavior in Korea: a cross-sectional survey
Yoon-Jung Park, Sun-Hee Kim
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(1): 79. CrossRef - Comparison of Factors Affecting Delirium Nursing Stress between Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Wards and General Wards
Sumin Gwon, Gaeun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 517. CrossRef - Validation of the Psychometric Properties of the Practice Environment Scale of Nursing Work Index (PES-NWI) Questionnaire in the Context of Kenya’s Nursing Organizational Work Culture
Evans Kasmai Kiptulon, Mohammed Elmadani, Godfrey Mbaabu Limungi, Anna Szőllősi, Dahabo Adi Galgalo, Peter Murage, Pauline Okari, Orsolya Maté, Adrienn Ujváriné Siket
International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences.2024; 20: 100750. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Performance of Intensive Care Unit Nurses: Role of Clinical Reasoning Competence, Positive Psychological Capital, and Nursing Work Environment
MiRim Heo, Haena Jang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(2): 83. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Field Adaptation of Early-Stage Nurses in South Korea
Eunhee Hwang, Miyeong Kim, Yunkyeong Lee
Healthcare.2024; 12(14): 1447. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Practice Environment on Intent to Leave in Hospital Nurses: Focused on the Mediating Effect of Reciprocity
So Young Lee, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 201. CrossRef - The impact of nurse’s sense of calling, organizational commitment, job stress, and nursing work environment on patient safety management activities in comprehensive nursing care service units during the covid-19 pandemic
YeJi Lee, Won Ju Hwang
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Job crafting, positive psychological capital, and social support as predictors of job embeddedness on among clinical nurses- a structural model design
Mi-Soon Yun, Miyoung Lee, Eun-Hi Choi
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric Evaluation of the Decision Fatigue Scale among Korean Registered Nurses
Yujin Hur, Ronald L. Hickman
Healthcare.2024; 12(15): 1524. CrossRef - Influence of Work Environment, Missed Nursing Care, and Non-Nursing Tasks of Hospital Nurses on Job Stress
Ji Yeong Park, Kyoung Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 246. CrossRef - Influential factors affecting nursing performance amid COVID-19: A cross-sectional study on nurse preparedness for infectious diseases
Kyung-sook Cha, Dohyun Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies Advances.2024; 7: 100239. CrossRef - Experience of violence, social support, nursing practice environment, and burnout on mental health among mental health nurses in South Korea: A structural equation modeling analysis
Jung Suk Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Mihyoung Lee
Applied Nursing Research.2024; 78: 151819. CrossRef - Development and validation of a quality of healthy work environment instrument for shift nurses
Sun-Hwa Shin, Eun-Hye Lee
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing-sensitive Indicators in East Asian Hospitals: A Scoping Review
Jae Jun Lee, Won Jin Seo, Dong Ah Park, Hwa Yeong Oh, Seung Eun Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2024; 30(2): 88. CrossRef - Factors Impacting on Nurse Unit Managers’ Knowledge and Ability Importance of Managerial Competencies
Jihae Lee, Miyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 428. CrossRef - Influence of the Nursing Work Environment on Job Satisfaction in Male Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Social Support
DongHyun KIM, Hyunjin OH
Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 32(6): e356. CrossRef - The Effect of Professional Autonomy and Nursing Work Environment on Nurses’ Patient Safety Activities: A Perspective on Magnet Hospitals
Songyi Yuk, Soyoung Yu, Shawn Yong-Shian Goh
Journal of Nursing Management.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - The effect of nursing work environment on slow nursing among long-term care hospital nurses: A descriptive study
Hyeon-mi Woo
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(2): 206. CrossRef - Factors associated with post-traumatic stress disorder in nurses after directly caring for COVID-19 patients: a cross-sectional study
Hyo-Jeong Yoon, Soon Yeung Bae, Jihyun Baek
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Translations of the Practice Environment Scale of the Nursing Work Index: A systematic review
Eileen T. Lake, Kathleen E. Fitzpatrick Rosenbaum, Christina Sauveur, Catherine Buren, Priscilla Cho
Nursing & Health Sciences.2023; 25(3): 365. CrossRef - Effects of Emergency Nurses’ Experiences of Violence, Resilience, and Nursing Work Environment on Turnover Intention: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Ji Eun Park, Mi Ryeong Song
Journal of Emergency Nursing.2023; 49(3): 461. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Grit on the Relationship between Work Environment and Intention to Stay at Work among Regional Trauma Center Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ji Sun Yang, Myung Jin Jang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 107. CrossRef - Effect of the Nursing Work Environment on Turnover Intention: Serial Mediation Effects of Career Motivation and Job Satisfaction
Young Deok Park, Sun Ju You
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(5): 529. CrossRef - The Effect of Work Value, Psychological Ownership and Nursing Working Environment on Intention of Retention in Hospital Nurses
Ji Hey Kim, Yoon Ju Cho, So Eun Jang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(3): 62. CrossRef - Path model on decision‐making ability of clinical nurses
Minsook Park, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(7-8): 1343. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Preparedness to Care for Patients with Highly Infectious Diseases among Nursing Staff in Long-term Care Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Ye Seul Lee, Min Hye Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(1): 35. CrossRef - The influence of Critical Reflection Competency, Nursing Work Environment and Job Crafting on Person-Centered Care in Tertiary Hospital Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
Jinseon Hwang, Sujin Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(3): 245. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Work Environment, Need Satisfaction, and Depression on Turnover Intention in Korea
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek, Eun-Hye Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(12): 1698. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care among Nurses in COVID-19 Special Care Units at Tertiary General Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Kisook Kim, Sunmi Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 127. CrossRef - Effects of External Employment Opportunities, Nursing Professionalism, and Nursing Work Environments on Korean Hospital Nurses’ Intent to Stay or Leave
Mi-Aie Lee, So-Hee Lim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(5): 4026. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Work Environment on Intention to Stay of Hospital Nurses: A Two-Mediator Serial Mediation Effect of Career Motivation and Job-Esteem
Yu Na Lee, Eungyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 622. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction on the Relationship between Nursing Practice Environment and Turnover Intention of Nurses in a National Forensic Psychiatic Hospital
Moonhee Gang, Donghyeon Gwak
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(3): 307. CrossRef - The impacts of nurses' attitudes towards dementia, critical reflection competency, and nursing work environment on person-centered nursing in acute care hospitals: A descriptive study
Minkyung Kim, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(4): 346. CrossRef - Impact of Nursing Organizational Culture and Nursing Practice Environment on Generational Conflict in Organization among Hospital Nurses
Jieun Kwon, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(1): 45. CrossRef - Effect of Nurses’ Professionalism, Work Environment, and Communication with Health Professionals on Patient Safety Culture (AHRQ 2.0.): A Cross-Sectional Multicenter Study
Won Lee, Insil Jang, Majed Alamri
Journal of Nursing Management.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - The Nursing Work Environment, Supervisory Support, Nurse Characteristics, and Burnout as Predictors of Intent to Stay among Hospital Nurses in the Republic of Korea: A Path Analysis
Young-Bum Kim, Seung-Hee Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(11): 1653. CrossRef - Influence of Work Environment, Job Engagement, and Positive Psychological Capital on Job Embeddedness of Hospital Nurses
Hee Jung Kwag, Nam Young Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(2): 109. CrossRef - Clinical Competence of Nurses and the Associated Factors in Public Hospitals of Gamo Zone, Southern Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Shitaye Shibiru, Zeleke Aschalew, Mekidim Kassa, Agegnehu Bante, Abera Mersha, Judie Arulappan
Nursing Research and Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Influence of Nurses’ General and Job-related Characteristics, Nursing Practice Environment, and Grit on the Intent to Stay among Operating Room Nurses
Jeongha Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 203. CrossRef - Properties of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in North Korean Defectors: A Scoping Review
Ocksim Kim, Kyoung-A Kim, Sang Hui Chu
Psychiatry Investigation.2023; 20(7): 593. CrossRef - Comparative Study on Work-Life Balance, Nursing Work Environment, Nursing Organizational Culture, and Job Satisfaction before Turnover among Nurses Leaving Hospital: Current Clinical Nurses versus Non-clinical Nurses
Yejin Seo, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 385. CrossRef - Factors related to retention intention of new dental hygienists : focusing on working environment
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The structure of the Italian version of the Practice Environment Scale of the Nursing Work Index
Milko Zanini, Maria Emma Musio, Roger Watson, Giuseppe Aleo, Loredana Sasso, Gianluca Catania, Annamaria Bagnasco
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 3440. CrossRef - Structural Model of Retention Intention of Nurses in Small- and Medium-Sized Hospitals: Based on Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory
Joo Yeon Lee, Mi Hyang Lee
Healthcare.2022; 10(3): 502. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Resilience of New Nurses in Their Working Environment
Keunsook Park, Aeri Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5158. CrossRef - Workplace sexual harassment toward male nurses in South Korea: a cross-sectional online survey
Suyong Jeong, Hyoung Eun Chang
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Perceived Safety Culture, Nursing Work Environment, and Professional Self-concept on Patient Safety Care Activity of Nurses in Small-medium Sized Hospitals
Young Ok Cho, Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(1): 66. CrossRef - The effects of tertiary hospital nurses' ageism and nursing practice environment on geriatric nursing performance
Hyemin Kang, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(4): 355. CrossRef - The impact of resilience on turnover among newly graduated nurses: A 1‐year follow‐up study
Eunhee Lee, Jennie C. De Gagne
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(5): 1295. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Work Environment, Job Crafting and Organizational Commitment on Nurses’ Job Satisfaction
Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(1): 9. CrossRef - Influence of the Patient Safety Culture and Nursing Work Environment on Fall Prevention Activities of Hospital Nurses
Se-Young Jung, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(2): 78. CrossRef - Factors influencing the transition shock of newly-graduated nurses
Kil Je Moon, Moo Yong Cho,
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(2): 156. CrossRef - Posttraumatic stress disorder and related factors among nurses working during the COVID‐19 pandemic
Soon Yeung Bae, Hyo‐Jeong Yoon, Yunjung Kim, Jisun Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(5): 1096. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Person-Centered Nursing in Hospital Nurses
Yeon Hee Bae, Hye-Ah Yeom
Healthcare.2022; 10(3): 514. CrossRef - Effects of Compassionate Competence, Communication Skills, and Nursing Work Environment on Person-centered Care in General Hospital Nurses who Care for Cancer Patients
Mi Jin Han, Seonho Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Health Information Technology Usability Evaluation Scale: Psychometric Evaluation
Jisan Lee, Rebecca Schnall
JMIR Medical Informatics.2022; 10(1): e28621. CrossRef - Re-employment Hospital Types of Early Career Nurses and Changes in Work-Life Balance
Eun-Young Kim, Yun-Kyung Oh
STRESS.2022; 30(3): 163. CrossRef - Effects of job embeddedness and nursing working environment on turnover intention among trauma centre nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Hye Ju Lee, Soo‐Kyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2915. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Hospice Nurses
Sinyoung Kwon, Kyoung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(2): 66. CrossRef - Combination Relationship between Features of Person-Centered Care and Patient Safety Activities of Nurses Working in Small–Medium-Sized Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Study
Myoung Soo Kim, Young Ok Cho, Jiwon Park
Nursing Reports.2022; 12(4): 861. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Practice for Physical Restraints among Nurses in the Intensive Care Unit
Da Eun Kim, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 62. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Nursing Work Environment Scale of Clinical Nurses
Yeong Ju Ko, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 576. CrossRef - Evidence-based nursing practice and prevention of falls in hospitalized patients
Liliana Nancy Oporto
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2022; 2: 59. CrossRef - The Effect of the Nurses Practice Environment and Organizational Justice on Organizational Silence Perceived by Nurses
Sungjung Kwak, Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(4): 270. CrossRef - Association of Nursing Work Environment, Relationship with the Head Nurse, and Resilience with Post-Traumatic Growth in Emergency Department Nurses
Sun-Young Jung, Jin-Hwa Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(6): 2857. CrossRef - Effect of Self-efficacy, Resilience, and Nursing Work Environment on Intent to Stay among Newly Graduated Nurses in General Hospitals
Ju Na Jeon, Seung-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(4): 291. CrossRef - The Impact of Practice Environment and Resilience on Burnout among Clinical Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital Setting
Dzifa Dordunoo, Minjeong An, Min Sun Chu, Eun Ja Yeun, Yoon Young Hwang, Miran Kim, Yeonhu Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2500. CrossRef - The Factors Affecting Person-centered Care Nursing in Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Hye Suk Kang, Minjeong Seo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 14. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Secondary Traumatic Stress of Nurses Caring for COVID-19 Patients in South Korea
Mee Sun Lee, Sujin Shin, Eunmin Hong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(13): 6843. CrossRef - Relationships among Non-Nursing Tasks, Nursing Care Left Undone, Nurse Outcomes and Medical Errors in Integrated Nursing Care Wards in Small and Medium-Sized General Hospitals
Ju-Young Park, Jee-In Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Nurses
Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 363. CrossRef - Impact of Perceived Importance to Rehabilitation Nursing, Role Conflict, and Working Environment on Performance of Rehabilitation Nursing of Nurses in Rehabilitation Hospitals
Ji Hye Kim, Ji Yun Lee
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(1): 86. CrossRef - Validation of the Psychometric Properties of the Practice Environment Scale of Nursing Work Index in Primary Health Care in Portugal
Pedro Lucas, Elvio Jesus, Sofia Almeida, Beatriz Araújo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(12): 6422. CrossRef - Transition shock and job satisfaction changes among newly graduated nurses in their first year of work: A prospective longitudinal study
Eun‐Young Kim, Jung Hee Yeo
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(3): 451. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Retention Intention of Nurses at Long-Term Care Hospitals in Korea
So Young Shin, Joo Hee Kim
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2021; 47(10): 44. CrossRef - Unit work environment, psychological empowerment and support for patient activation among nurses
Hyeonmi Cho, Kihye Han, Eunjung Ryu
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(6): 1623. CrossRef - Licenced practical nurses' perceptions of their work environments and their intention to stay: A cross‐sectional study of four practice settings
Leah Adeline Phillips, Nyla de Los Santos, Jennifer Jackson
Nursing Open.2021; 8(6): 3299. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Re-Employment of Newly Graduated Nurses: Longitudinal Study
Yun Kyung Oh, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 162. CrossRef - The Effect of Nursing Competence on Patient-Centered Care among Nurses Caring for Patients with Chronic Disease: The Mediating Effect of Burnout and the Moderating Effect of Nursing Work Environment
Jin-Yeong Ahn, Young Eun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(2): 134. CrossRef - Association of work environment and resilience with transition shock in newly licensed nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Soon Ok Kim, Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(7-8): 1037. CrossRef - A multilevel investigation of cultural competence among South Korean clinical nurses
Duckhee Chae, Yunhee Park, Kyeonghwa Kang, Jongdae Kim
Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences.2020; 34(3): 613. CrossRef - Effects of Work Environment on the Job Satisfaction of Occupational Therapists: Mediating Effect of Empowerment
Bo-Young Son, Yo-Soon Bang, Jae-Hyeon Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2020; 28(3): 15. CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Nursing Practice Environment on the Relationship between Clinical Nurses’ Sleep Quality and Wellness
Kyung Jin Hong, Youngjin Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(19): 7068. CrossRef - Association of Happiness and Nursing Work Environments with Job Crafting among Hospital Nurses in South Korea
Sujin Chang, Kihye Han, Yongae Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(11): 4042. CrossRef - Factors related to nursing performance in South Korean intensive care units
Chiyoung Cha, Choa Sung
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction Model for Nursing Work Outcome of Nurses: Focused on Positive Psychological Capital
Soon Neum Lee, Jung A Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(1): 1. CrossRef - Development of Korea version of the Practice Environment Scale for Advanced Practice Registered Nurses
Mi Jung Ryu, Woo Young In, Eun Hee Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(2): 160. CrossRef - Association between nursing work environment and compassion satisfaction among clinical nurses
Jihyun Baek, Hyeonmi Cho, Kihye Han, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2020; 28(2): 368. CrossRef - A Comparison of Nursing Work Environment, Role Conflict, and Job Embeddedness of Nurses Working in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Wards and General Wards in a Tertiary Hospital
Hye-Eun So, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2020; 26(1): 11. CrossRef - Factors influencing clinical nurses’ advocacy for people with disability
Ji Young Jeon, Hyunkyung Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(3): 269. CrossRef - Effects of compassion competence on missed nursing care, professional quality of life and quality of life among Korean nurses
Chanhee Kim, Youngjin Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2020; 28(8): 2118. CrossRef - Validação da Practice Environment Scale entre técnicos e auxiliares de enfermagem
Renata Cristina Gasparino, Maria Carolina Pinto Martins, Daniela Fernanda dos Santos Alves, Thelen Daiana Mendonça Ferreira
Acta Paulista de Enfermagem.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Ecological Predictors of Recovery-Oriented Practices Among Psychiatric Nurses in South Korea
Suyon Baek
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2020; 58(11): 37. CrossRef - A study on the intent to leave and stay among hospital nurses in Korea: A cross‐sectional survey
Mi‐Aie Lee, Young‐Hee Ju, So‐Hee Lim
Journal of Nursing Management.2020; 28(2): 332. CrossRef - Development and Validation Study of an Instrument to Measure Work Environment of Nurses in Nursing Homes
Eunhee Cho, Deulle Min, Kyongeun Lee, Jeongah Kim, Soo Jung Chang, Hyang Kim, Sinhye Kim, Ari Min
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2019; 21(3): 144. CrossRef - Effects of Emotional Intelligence and Nursing Working Environment on Nursing Performance of Nurses Caring for Cancer Patients in Small and Medium Hospitals: The Mediating Effect of Communication Competence
Yoon-Ji Kang, Kwuy-Im Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(4): 233. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Clinical Decision Making Ability of Nurses
Min Kyoung Park, Soukyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 601. CrossRef - Shift‐work nurses’ work environments and health‐promoting behaviours in relation to sleep disturbance: A cross‐sectional secondary data analysis
Sungju Lim, Kihye Han, Hyeonmi Cho, Hyang Baek
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2019; 28(9-10): 1538. CrossRef - Influence of Communication Competency and Nursing Work Environment on Job Satisfaction in Hospital Nurses
Bongjeong Kim, Soon Young Lee, Gyeong Ju An, Guna Lee, Hyun Jung Yun
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(2): 189. CrossRef - Factors affecting Organizational Commitment of General Hospital Nurses in Small and Medium Sized Cities
Jin Hee Kim, Min Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(1): 14. CrossRef - Factors affecting Korean neonatal nurses’ pain care: Psychometric evaluation of three instruments
Haeyoung Min, Catherine Vincent, Chang G. Park, Alicia K. Matthews, Linda L. McCreary, Margot Latimer
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2019; 16(2): 125. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Developmental Care Practice Among Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Jisun Park, Ji-Soo Kim
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2019; 47: e10. CrossRef - Effects of pre-graduation characteristics and working environments on transition shock of newly graduated nurses: A longitudinal study
Eun-Young Kim, Jung Hee Yeo
Nurse Education Today.2019; 78: 32. CrossRef - Effect of a Nursing Practice Environment on Nursing Job Performance and Organizational Commitment: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Job Embeddedness
Shin Hee Kim, Sook Kyoung Park, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(3): 208. CrossRef - Factors associated with Person-centered Care for Elderly in Long-term Care Hospital Nurses
So Bun Kim, Youngrye Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(6): 618. CrossRef - Relationship among Nursing Professionalism, Nursing Work Environment, and Patient Safety Nursing Activities in General Hospital Nurses
Mi-Aie Lee, Sunjoo Kang, Hye Sun Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(4): 317. CrossRef - Practice environment as perceived by nurses in acute care hospitals in Sharjah and North Emirates
Rowaida Al-Maaitah, Raeda F. AbuAlRub, Sumaya Al Blooshi
Nursing Forum.2018; 53(2): 213. CrossRef - Associations Among Nursing Work Environment and Health‐Promoting Behaviors of Nurses and Nursing Performance Quality: A Multilevel Modeling Approach
Hyeonmi Cho, Kihye Han
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2018; 50(4): 403. CrossRef - Reliability and validity of the practice environment scale of the nursing work index for Japanese hospital nurses
Yasuko Ogata, Miki Sasaki, Yoshie Yumoto, Yuki Yonekura, Midori Nagano, Katsuya Kanda
Nursing Open.2018; 5(3): 362. CrossRef - Validation Study of the Korean Version of the Jefferson Scale of Empathy-Health Professions Students for Measuring Empathy in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Jisoon Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2018; 24(3): 259. CrossRef - Nursing Tasks and Practice Environment for Nursing Work Perceived by Nurses Working on Comprehensive Wards versus General Wards
Sung Hee Ahn, Sun Hee Jung, Jung Hwa You, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(1): 10. CrossRef - Exploring the Influence of Nursing Work Environment and Patient Safety Culture on Missed Nursing Care in Korea
Kyoung-Ja Kim, Moon Sook Yoo, Eun Ji Seo
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(2): 121. CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Choices of Local Hospitals among New Graduate Nurses
Eun-Young Kim, Hun Ha Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(3): 202. CrossRef - Influence of Nurses' Work Environment, Organizational Commitment, and Nursing Professionalism on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Long Term Care Hospitals
Hyun Suk Joo, Won Hee Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(4): 265. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Managerial Competence of Frontline Nurse Managers
Ran Lee, Miyoung Kim, Sujin Choi, Hee Yeon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 435. CrossRef - Influence of Moral Sensitivity and Nursing Practice Environment in Person-centered Care in Long-term Care Hospital Nurses
Eun-Mi Park, Jin-Hwa Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(2): 109. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Empowering Leadership Questionnaire
Eun Kyung Kim, Se Young Kim, Myun Sook Jung, Jong Kyung Kim, Sun Ju You
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2017; 17(4): 275. CrossRef - Validation of the Practice Environment Scale to the Brazilian culture
Renata C. Gasparino, Edinêis de B. Guirardello
Journal of Nursing Management.2017; 25(5): 375. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Practice Environment and Self-esteem on Critical Thinking Disposition among Clinical Nurses
Eunju Choi, Jihyeon Hwang, Insil Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(2): 161. CrossRef - Effect of Work Environment on Nursing Performance of Nurses in Hemodialysis Units: Focusing on the Effects of Job Satisfaction and Empowerment
Jung Ae Seo, Byoung Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(2): 178. CrossRef - The Affect Factors of Geriatric Hospital Nurse’s Falls Prevention Activities
Ji-Young Jung, Gye Hyun Jung
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2016; 41(2): 203. CrossRef - Impact of Unit-level Nurse Practice Environment on Nurse Turnover Intention
Youngjin Lee, GyeongAe Seomun
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(6): 355. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Turnover Intention in Pediatric Nurses
Min Suk Im, Young Eun Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2016; 22(1): 37. CrossRef - Relationships among Nursing Work Environment, Job Embeddedness, and Turnover Intention in Nurses
Hae Jin Ko, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(3): 279. CrossRef - The Relationship among Practice Environment, Organizational Justice, and Job Satisfaction of Male Nurses
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Chul-Gyu Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 177. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Suicide Resilience Inventory-Korean Version for Korean University Students
Jun Hee Noh, Soo Jung Chang, Seong Eun Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 508. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention: Focusing on Organizational Characteristics, Job Satisfaction, and Job Embeddedness
Mi Ja Yoo, Jong Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(3): 292. CrossRef - The effects of workplace bullying on turnover intention in hospital nurses
Hyun-Jung Kim, Dahye Park
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(1): 241. CrossRef - The Relationships of Nurse Staffing Level and Work Environment With Patient Adverse Events
Eunhee Cho, Dal Lae Chin, Sinhye Kim, OiSaeng Hong
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2016; 48(1): 74. CrossRef - The Effects of Nursing Work Environment and Job Stress on Health Problems of Hospital Nurses
Young Eun Bang, Bohyun Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 227. CrossRef - Effects of Work Environment, Organizational Culture and Demands at Work on Emotional Labor in Nurses
Ji Yun Lee, Hye Ri Nam
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(2): 119. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurse Turnover Intention of Senior Convalescence Hospitals in the Metropolitan Area
Youn Sun Hwang, Eunyoung Cho
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 156. CrossRef - Influence of Professionalism, Role Conflict and Work Environment in Clinical Nurses with Expanded Role on Job Enbeddedness
Kyeong Hwa Kang, Yeon Jae Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(5): 424. CrossRef - Nurses' Perception of Organizational Commitment, Nursing Work Environment, and Social Support in a General Hospital
Sook Bin Im, Mi Young Lee, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Practice Environment, Compassion Fatigue and Compassion Satisfaction on Burnout in Clinical Nurses
Mi Young Han, Min Sook Lee, Ju Young Bae, Young Suk Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(2): 193. CrossRef - Effects of nurse staffing, work environments, and education on patient mortality: An observational study
Eunhee Cho, Douglas M. Sloane, Eun-Young Kim, Sera Kim, Miyoung Choi, Il Young Yoo, Hye Sun Lee, Linda H. Aiken
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(2): 535. CrossRef - Nurse perceptions of organizational culture and its association with the culture of error reporting: a case of public sector hospitals in Pakistan
Sara Rizvi Jafree, Rubeena Zakar, Muhammad Zakria Zakar, Florian Fischer
BMC Health Services Research.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - KoreanWorkEnvironmentScales forClinicalNurses
Jong‐Kyung Kim, Se‐Young Kim, Mi Yu, Myung Ja Kim, Kyoung‐A Lee
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2015; 12(1): 54. CrossRef - Relationship between the Practice Environment of Nursing and Critical Thinking Disposition of Nurses in Local General Hospitals
Ji Yun Lee, So Young Pak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(2): 145. CrossRef - Validation Study of the Practice Environment Scale of Nursing Work Index for Psychiatric Hospital Nurses in Korea
Hee Jung Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2014; 21(3): 224. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Burnout in Clinical Nurses based on CS-CF Model
Hyun-Jung Kim, Young-Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(3): 259. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurse Turnover Intention in Small and Medium Sized Hospitals in the Metropolitan Area
Youn Sun Hwang, Kyeong Hwa Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(5): 576. CrossRef - Canonical correlation between organizational characteristics and barrier to medication error reporting of nurses
Min-Jeong Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(2): 979. CrossRef - Factors associated with New Graduate Nurses' Reality Shock
Kyung Mi Sin, Jeong Ok Kwon, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(3): 292. CrossRef - The Influential Factors on Compassion Fatigue in Hospital Nurses
Hyeon Jeong Lee, Hye Sook Min
Journal of muscle and joint health.2014; 21(3): 236. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Nursing Productivity of Nurses in Korea
Se Young Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Heon Man Lim, Mi Young Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, Kyoung A Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 20. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Family Management Measure (Korean FaMM) for Families with Children having Chronic Illness
Dong Hee Kim, Yeo Jin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 123. CrossRef - Relationship of Nurse Practice Environment and Work-Family Conflict to Job Satisfaction in Hospital Nurses in Korea
Yu Kyung Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(2): 207. CrossRef - Application of Revised Nursing Work Index to Hospital Nurses of South Korea
Chul-Woung Kim, Sang-Yi Lee, Jeong-Hee Kang, Bo-Hyun Park, Sang-Chul Park, Hyeung-Keun Park, Keon-Hyung Lee, Yun-Jeong Yi, Baek-Geun Jeong
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(3): 128. CrossRef - Impact of Unit-level Nurse Practice Environment on Nurse Turnover Intention in the Small and Medium Sized Hospitals
Jeong Ok Kwon, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(4): 414. CrossRef
- Analyzing the Drivers of Job Satisfaction and Nurse Retention Among Kazakh Nurses in Public Clinical Centers: Key Factors and Insights
- 4,252 View
- 252 Download
- 175 Crossref

- Development and Psychometric Evaluation of a Scale to Measure Health Behaviors of Adolescents
- Yun Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(6):820-830. Published online December 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.6.820
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose was to develop a preliminary scale to measure Korean adolescents' health behaviors through a qualitative approach, to evaluate the scale psychometrically, and to develop a final scale.
Methods Participants were 61 adolescents for qualitative interviews and 1,687 adolescents for the psychometric evaluation. Procedure included content analysis of interviews to identify health behavior categories for Korean adolescents, pre-test to confirm that preliminary scale items were understandable, content validity by an expert panel, development of the web-based computer-assisted survey (CAS), and psychometric analysis to determine reliability and validity of the final scale.
Results A final scale was developed for both paper-and-pencil and CAS. It consisted of 14 health behaviors (72 items), including stress and mental health (10), sleep habits (5), dietary habits (12), weight control (4), physical activity (4), hygiene habits (5), tobacco use (5), substance use (2), alcohol consumption (4), safety (4), sexual behavior (9), computer use (3), health screening (4), and posture (1).
Conclusion The scale's strong points are: 1) Two thirds of the final scale items are Likert scale items, enabling calculation of a health behavior score. 2) The scale is appropriate to Korean culture. 3) The scale focuses on concrete health behaviors, not abstract concepts.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Moyamoya Health Behavior Scale for Adolescent Patients: Measurement Tool Development and Psychometric Evaluation
Won-oak Oh, Insun Yeom, Sung-Hyun Lim, Dong-Seok Kim, Kyu-won Shim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4064. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Related Demographic Factors among Korean Adolescents
YunHee Shin, Sook Jung Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(2): 150. CrossRef - Health Behaviors among Korean Adolescents: A Content Analysis
Yun Hee Shin, Jihea Choi
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2014; 14(3): 83. CrossRef - Lecturers’ Performance and Technology at Private Higher Education in South Sulawesi Indonesia
Sanusi Hamid
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences.2013; 83: 580. CrossRef - Effects of a Mentoring Program on Stress and Self-esteem for Middle School Girls of Low Income Families
Yun Hee Shin, Jee Hae Lee, So Young Lee, Kyeung Min Lim, Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(3): 220. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of the Personal Competence of Health Care (PCHC) Scale
Kyung-Sook Lee, Jung-Sook Choi, Ae-Young So, Eun-Hee Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(2): 197. CrossRef
- The Moyamoya Health Behavior Scale for Adolescent Patients: Measurement Tool Development and Psychometric Evaluation
- 1,142 View
- 6 Download
- 6 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


