Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
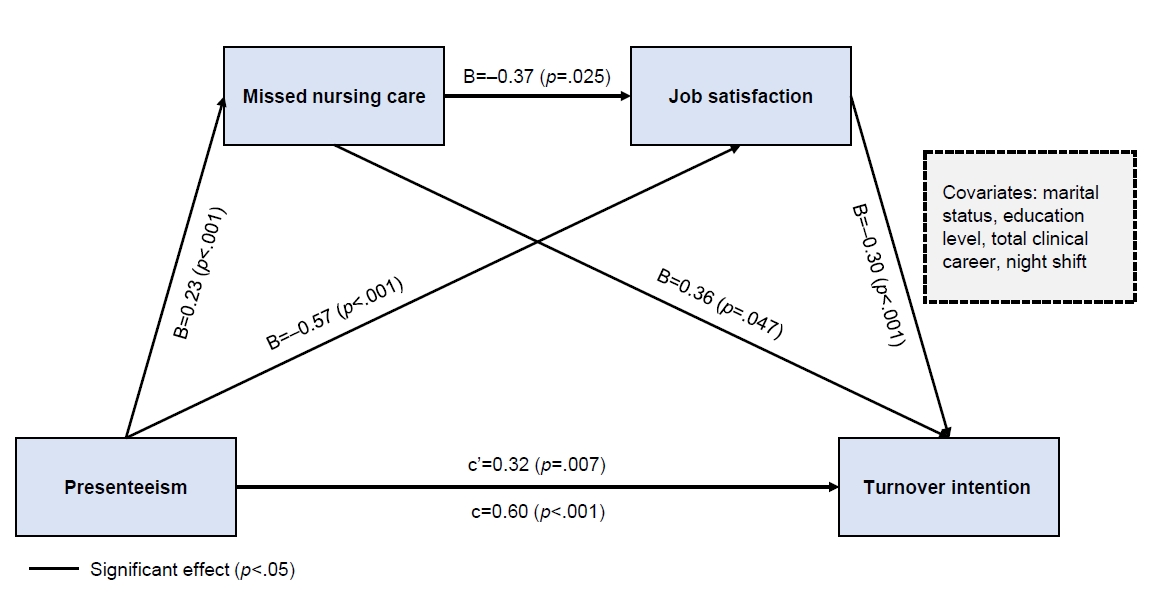
- Effects of presenteeism on turnover intention in clinical nurses through the serial mediating roles of missed nursing care and job satisfaction: a cross-sectional predictive correlational study
- Hyeonseon Cheon, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):584-597. Published online November 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the two-mediator serial mediation effect of missed nursing care and job satisfaction on the relationship between presenteeism and turnover intention in clinical nurses.
Methods
A cross-sectional predictive correlational study was conducted, and the participants were 208 clinical nurses working in advanced general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected from October 6 to November 7, 2023 using self-reported questionnaires, including general characteristics, presenteeism, missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 29.0 and PROCESS macro ver. 4.2.
Results
Missed nursing care and job satisfaction exhibited a double mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. In addition, missed nursing care showed a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Job satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Presenteeism had a direct effect on missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Missed nursing care exerted a direct effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Job satisfaction had a direct effect on turnover intention.
Conclusion
To reduce nurses’ turnover intention, it is essential to develop and implement programs focused on preventing presenteeism. Additionally, organizational initiatives should prioritize active support for nurses’ health management, alleviating the shortage of nursing staff, augmenting job satisfaction, and improving the overall working environment.
- 1,536 View
- 216 Download

- Effects of an Integrated Physical Activity Program for Physically Inactive Workers - Based on the PRECEDE-PROCEED Model -
- Hye-Jin Kim, Jina Choo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):692-707. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.692
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose We aimed to examine the effects of an integrated physical activity (PA) program developed for physically inactive workers on the theoretical basis of the PRECEDE-PROCEED model.
Methods Participants were 268 workers in three departments of L manufacturing unit in South Korea. The three departments were randomly allocated into integration (n=86) (INT), education (n=94) (ED), and control (n=88) (CT) groups. The INT group received self-regulation, support, and policy-environmental strategies of a 12-week integrated PA program, the ED group received self-regulation strategies only, and the CT group did not receive any strategies. After 12 weeks, process evaluation was conducted by using the measures of self-regulation (autonomous vs. controlled regulation), autonomy support, and resource availability; impact evaluation by using PA measures of sitting time, PA expenditure, and compliance; and outcome evaluation by using the measures of cardiometabolic/musculoskeletal health and presenteeism.
Results Among process measures, autonomous regulation did not differ by group, but significantly decreased in the CT group (
p =.006). Among impact measures, PA compliance significantly increased in the INT group compared to the CT group (p =.003). Among outcome measures, the changes in cardiometabolic/musculoskeletal health and presenteeism did not differ by group; however, systolic blood pressure (p =.012) and a presenteeism variable (p =.041) significantly decreased only in the INT group.Conclusion The integrated PA program may have a significant effect on increases in PA compliance and significant tendencies toward improvements in a part of cardiometabolic health and presenteeism for physically inactive workers. Therefore, occupational health nurses may modify and use it as a workplace PA program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms on Depressive Symptoms and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Korean Coast Guards: The Mediating Role of Social Support
Hyung-Eun Seo, Mijung Yeom, Hye-Jin Kim
Workplace Health & Safety.2025; 73(5): 236. CrossRef - The characteristics, components, and fidelity of interventions promoting physical activity in people living with musculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review
Alex Thompson, Robert Copeland, Rachel Young, Angela Reilly, Jeff Breckon, Sionnadh McLean
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(23): 6020. CrossRef - Strategies for preventing presenteeism in nursing
Luís Sousa, Ricardo Mestre, João Tomás, Sandy Severino, Nelson Guerra, Helena José
Management (Montevideo).2025; 3: 147. CrossRef - Use of the PRECEDE–PROCEED Model to Pilot an Occupational Physical Activity Intervention: Tailored Through a Community Partnership
Debra L. Fetherman, Joan Cebrick-Grossman
Workplace Health & Safety.2023; 71(8): 367. CrossRef - Corporate Well-Being Programme in COVID-19 Times. The Mahou San Miguel Case Study
José M. Núñez-Sánchez, Ramón Gómez-Chacón, Carmen Jambrino-Maldonado, Jerónimo García-Fernández
Sustainability.2021; 13(11): 6189. CrossRef - Effects of an Integrated Physical Activity Program for Physically Inactive Workers: Based on the PRECEDE-PROCEED Model
Hye-Jin Kim, Jina Choo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 692. CrossRef
- The Impact of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms on Depressive Symptoms and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Korean Coast Guards: The Mediating Role of Social Support
- 1,914 View
- 73 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Economic Impact according to Health Problems of Workers
- Young-Mi Lee, Moon-Hee Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(4):612-619. Published online August 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.4.612
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine health problems and to estimate economic impact based on health problems of workers.
Methods The subjects of this study consisted of 301 workers who received a group occupational health service. Data was collected from February 1 to March 30, 2006. The questionnaire contained questions based on general characteristics and the Stanford Presenteeism Scale. Data was analyzed with descriptive statistics, t-test using SPSS program.
Results The primary health conditions as reported by workers were ranked in order as stomach or bowel disorders, back or neck disorders, or liver function disorders. The reason of absenteeism per worker was ranked in order as asthma, or a breathing disorder. The reason of presenteeism was ranked in order as asthma, insomnia or a sleep disorder. The cost of the total economic impact on the workplace in this study was 8,851,838 won. The cost of absenteeism per worker was 8,390 won. The cost of presenteeism per worker was 941,732 won.
Conclusion Presenteeism had a strong correlation to health conditions of the workers. Therefore, improving the work conditions of the workers is very important. If employers improve the health condition of workers, they will benefit from improved productivity in their business.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Association Between Clinical Nurses’ Work Environment, Job Stress, and Health Locus of Control and Presenteeism in South Korea
Jin-Young Park, Yong-Sook Eo
Healthcare.2024; 12(22): 2293. CrossRef - Economic evaluation of acupuncture as an adjunctive treatment with usual care for mild-to-moderate knee osteoarthritis: A Markov model-based analysis
Eunhye Hyun, Byung-Cheul Shin, NamKwen Kim, Byungmook Lim
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(3): 100982. CrossRef - Relationship between occupational stress, sleep disturbance, and presenteeism of shiftwork nurses
Jihyun Baek, Jison Ki, Jaegeum Ryu, Choi‐Kwon Smi
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2022; 54(5): 631. CrossRef - Traditional medicine for the treatment of common cold in Korean adults: A nationwide population-based study
Hyungtae Kim, Jun-Yong Choi, Minna Hong, Hae Sun Suh
Integrative Medicine Research.2021; 10(1): 100458. CrossRef - Effects of an Integrated Physical Activity Program for Physically Inactive Workers: Based on the PRECEDE-PROCEED Model
Hye-Jin Kim, Jina Choo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 692. CrossRef - Perceived discrimination and low back pain among 28,532 workers in South Korea: Effect modification by labor union status
Nagyeong Lee, Hyoju Sung, Ji-Hwan Kim, Laura Punnett, Seung-Sup Kim
Social Science & Medicine.2017; 177: 198. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Workplace Interventions for Depression in Asia: A Meta-Analysis
Rebecca W. M. Lau, W. H. Mak
Sage Open.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between prevalence of adult atopic dermatitis and occupational characteristics
Yeunhee Kwak, Yoonjung Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Oral Health Education for Occupational Health Nurses
Hyo-Jin Lee, Dai-Il Paik
Journal of dental hygiene science.2016; 16(1): 77. CrossRef - A Study on the Presenteeism of Call Center Workers in the Customer Service Business
Myung-Hee Jung, Hye-Sun Jung
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(2): 142. CrossRef - Impact of working environment on the subjective health symptoms in the dental hygienists
Ka-Young Jeong, Hye-Eun Cho
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2015; 15(3): 539. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promoting Behaviour according to the Type A/B Personality of White Collar Workers
Jin Yi Choi, Young Mi Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(4): 305. CrossRef - Effect of Workplace Health Manager's Role Performance on Presenteeism in the Workers
Myung-Hee Jung, Hye-Sun Jung, Bok-Im Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(2): 171. CrossRef - Socioeconomic and Employment Status of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Korea
Jeong-Mi Kwon, Jinnie Rhee, Hyemin Ku, Eui-Kyung Lee
Epidemiology and Health.2012; 34: e2012003. CrossRef - Loss of Productivity due to Depression among Korean Employees
Young‐Mi Lee
Journal of Occupational Health.2010; 52(6): 389. CrossRef
- The Association Between Clinical Nurses’ Work Environment, Job Stress, and Health Locus of Control and Presenteeism in South Korea
- 978 View
- 3 Download
- 15 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


