Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development and psychometric testing of the Perceived Postoperative Care Competency Scale for Nursing Students: a methodological study
- Perihan Şimşek, Gül Çakir Özmen, Melek Ertürk Yavuz, Sema Koçan, Dilek Çilingir
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):81-97. Published online February 24, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
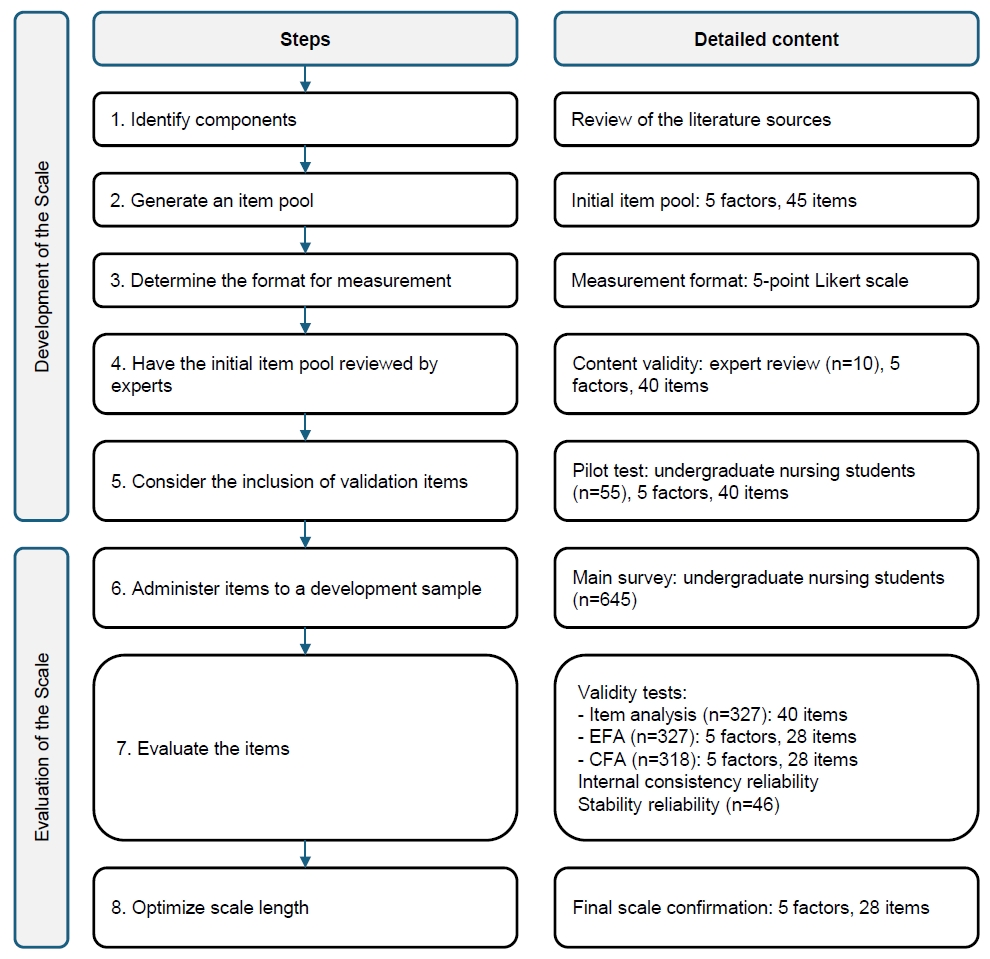
To improve the quality of postoperative care and promote recovery after surgery, it is important that nursing education is competency-based and that competency assessment is an integral part of the educational process. The purpose of this study was to develop a tool to evaluate nursing students’ perceived competence in postoperative care.
Methods
This cross-sectional methodological study followed DeVellis’s scale development steps and was conducted between December 2022 and March 2023. In this study, 892 students were invited and 703 responded. After exclusions, data from 645 students were analyzed to examine the psychometric structure of the scale using exploratory factor analysis (n=327) and confirmatory factor analysis (n=318). Reliability was assessed by calculating Cronbach’s α coefficients and by test–retest measurement (n=46).
Results
The proposed scale was confirmed to consist of five factors and 28 items (χ2/degrees of freedom=2.25, root mean square error of approximation=.06, normed fit index=.90, and goodness-of-fit index=.85). Cronbach’s α was .97 for the total scale. The data demonstrated high test–retest stability (intraclass correlation coefficient=.88). The scale developed and psychometrically tested in this study revealed a five-factor structure: legal responsibilities and ethical principles (seven items), postoperative nursing care (seven items), interpersonal relations and communication (four items), leadership (six items), and education and professional development (four items).
Conclusion
The scale, which demonstrated very good psychometric properties, would be helpful in assessing perceived postoperative nursing competence among nursing students. This may help students graduate with the necessary knowledge and skills required for postoperative care. However, further research involving larger samples and more diverse cultural contexts is needed to enhance the generalizability of the scale.
- 51 View
- 1 Download

- Assessment of Risk Factors for Postoperative Delirium in Older Adults Who Underwent Spinal Surgery and Identifying Associated Biomarkers Using Exosomal Protein
- Wonhee Baek, JuHee Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Jeongmin Kim, Dong Ah Shin, Hyunki Park, Bon-Nyeo Koo, Hyangkyu Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):371-384. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22146
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
With an increase in the aging population, the number of patients with degenerative spinal diseases undergoing surgery has risen, as has the incidence of postoperative delirium. This study aimed to investigate the risk factors affecting postoperative delirium in older adults who had undergone spine surgery and to identify the associated biomarkers.
Methods
This study is a prospective study. Data of 100 patients aged ≥ 70 years who underwent spinal surgery were analyzed. Demographic data, medical history, clinical characteristics, cognitive function, depression symptoms, functional status, frailty, and nutritional status were investigated to identify the risk factors for delirium. The Confusion Assessment Method, Delirium Rating Scale-R-98, and Nursing Delirium Scale were also used for diagnosing deliri-um. To discover the biomarkers, urine extracellular vesicles (EVs) were analyzed for tau, ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1), neurofilament light, and glial fibrillary acidic protein using digital immunoassay technology.
Results
Nine patients were excluded, and data obtained from the remaining 91 were analyzed. Among them, 18 (19.8%) developed delirium. Differences were observed between partici-pants with and without delirium in the contexts of a history of mental disorder and use of benzodiazepines (p = .005 and p = .026, respectively). Tau and UCH-L1—concentrations of urine EVs—were comparatively higher in participants with severe delirium than that in partici-pants without delirium (p = .002 and p = .001, respectively).
Conclusion
These findings can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the risk factors before surgery, classifying high-risk patients, and predicting and detecting delirium in older patients. Moreover, urine EV analysis revealed that postoperative delirium following spinal surgery is most likely associated with brain damage. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emerging biomarkers of postoperative delirium at the intersection of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration
Kun Leng, Mervyn Maze, Odmara L. Barreto Chang
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Emerging biomarkers of postoperative delirium at the intersection of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration
- 1,969 View
- 68 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of Early Oral Feeding versus Delayed Oral Feeding on Bowel Function, Gastrointestinal Complications and Surgical Recovery after Cesarean Section under Regional Anesthesia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- HyoJin Kim, YeongKyung Jeon, SoYoung Yoon, GeumMoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):732-745. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to assess combined effects of early oral feeding after Cesarean section (C/S) under regional anesthesia on bowel function, gastrointestinal complications and surgical recovery.
Methods
A systematic literature search was conducted using KISS, RISS, PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, CENTRAL and Google Scholar to identify randomized clinical trials comparing early oral feeding (EOF) with delayed oral feeding (DOF) after C/S. Outcome variables were bowel function and gastrointestinal complications and surgical recovery. Effect size was calculated using weighted mean differences (WMDs) and relative risks (RRs), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
Seven studies involving 1,911 patients from 568 studies, 7 studies were included in meta-analysis. EOF was significantly associated with shorter time to recover bowel movement compared with DOF (WMD, - 2.50; CI, - 3.50~- 1.50). EOF was not associated with nausea (RR, 1.15; CI, 0.87~1.53) and vomiting (RR, 0.96; CI, 0.65~1.42), but lower incidence of abdominal distension (RR, 0.70; CI, 0.50~0.98). EOF was significantly associated with shorter time to discontinuation of intravenous fluids (WMD, - 8.88; 95% CI, - 16.65~- 1.11) and removal of urinary catheter (WMD, - 15.23; CI, - 25.62~- 4.85).
Conclusion
This meta-analysis provides evidence that EOF after C/S under regional anesthesia not only accelerates return of bowel function and surgical recovery but also reduces gastrointestinal complications. These results suggest that EOF should be offered to women who have undergone C/S to improve the recovery experience and reduce overall medical costs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coffee Intake to Enhance Gastrointestinal Recovery Following Cesarean Delivery
Nour A El-Goly, Ahmed M Maged, Sally A El-Attar, Doaa Turki, Aimy Essam
Maternal-Fetal Medicine.2026; 8(1): 80. CrossRef - Effect of Early vs Delayed Oral Feeding Following Cesarean Delivery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Anuradha Murugesan, Dharani Saravanan, Karthiga Prabhu, Shanmugapriya Chandrasekaran, Prithiv Raj
Journal of South Asian Federation of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2025; 16(S3): S158. CrossRef - Evidence-based medical procedures to optimise caesarean outcomes: an overview of systematic reviews
Virginia Diaz, Celina Gialdini, Mónica Chamillard, Julia Pasquale, Guillermo Carroli, Maria Regina Torloni, Ana Pilar Betran
eClinicalMedicine.2025; 83: 103212. CrossRef - Effect of oral feeding following elective caesarean section on paralytic ileus among participants in a tertiary institution in Southern Nigeria
Kpoobari Bema, Esther I. Nonye-Enyidah Esther, Leesi Sapira-Ordu, Elizabeth Bozibe Bema, Iwo-Amah Rose Sitoama, Ikiroma Sokeipirim Erasmus
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology.2025; 14(10): 3246. CrossRef - Effect of nurse-led informational video on cesarean section-induced anxiety, satisfaction, and recovery among the patients admitted at tertiary care hospital, Uttarakhand: A quasi-experimental study
Prerna Mishra, Anupama Bahadur, Maneesh Sharma, Prasuna Jelly
Journal of Integrative Nursing.2025; 7(3): 155. CrossRef - Comparison of Operation Time, Vital Signs, Bleeding Tendency, and Recovery Time Based on Anesthesia Methods in Patients Undergoing Hip Fracture Surgery
Je Bog Yoo, Woo Young In, Chang Ok Pyo, Jeung Hee Kwon, Min Ji Lee, Kwang Hee Kim, Kyoung Ok Kim, Mi Yu
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The awareness of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) cesarean delivery guidelines among anesthesiology and reanimation assistants in Turkey; a questionnaire study
Zeliha Dedebagı, Eyyüp Sabri Özden, Mustafa Soner Özcan, Filiz Alkaya Solmaz, Pakize Kırdemir
BMC Anesthesiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors affecting gastrointestinal function recovery after cesarean section among Chinese mothers: A cross-sectional study
Yi Liu, Jie Xiang, Jianhua Ren, Li Gu, Yu Wang, Xiuping Liu, Jiao Wen
Medicine.2023; 102(38): e35200. CrossRef
- Coffee Intake to Enhance Gastrointestinal Recovery Following Cesarean Delivery
- 2,049 View
- 71 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Factors Related to Persistent Postoperative Pain after Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jaewon Bae, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):159-177. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.159
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed at identifying factors related to persistent postoperative pain after cardiac surgery and estimating their effect sizes.
Methods
The literature search and selection was conducted in four different databases (CINAHL, Cochrane Library, PubMed, and PQDT) using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Statement. A total of 14 studies met the inclusion criteria and were systematically reviewed. For the meta-analysis, R was used to analyze 30 effect sizes of for both individual and operative factors as well as publication biases from a total of nine studies.
Results
The meta-analysis revealed that persistent postoperative pain after cardiac surgery was related to one individual factor (gender) and two operative factors (acute postoperative pain and use of the internal mammary artery). Operative factors (OR=5.26) had a larger effect size than individual factors (OR=1.53).
Conclusion
Female gender, acute pain after surgery, and use of the internal mammary artery are related factors to persistent postoperative pain. The development of interventions focusing on modifiable related factors, such as acute postoperative pain, may help to minimize or prevent PPP after cardiac surgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pain-Friendly Strategies: Nursing Intervention in Postoperative Myocardial Revascularization
Debora Milena Alvarez Yañez, Gloria Carvajal Carrascal
Revista de Investigación e Innovación en Ciencias de la Salud.2025; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Prognostic factors for chronic post‐surgical pain after lung and pleural surgery: a systematic review with meta‐analysis, meta‐regression and trial sequential analysis
P. R. D. Clephas, S. E. Hoeks, P. M. Singh, C. S. Guay, M. Trivella, M. Klimek, M. Heesen
Anaesthesia.2023; 78(8): 1005. CrossRef - Regional anesthesia in coronary artery bypass grafting: a narrative review
Viktor A. Koriachkin, Maksim A. Dzhopua, Beka S. Ezugbaia, Vaagn A. Avetisian, Dmitriy V. Zabolotskiy, Vladimir A. Evgrafov
Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Management.2023; 17(3): 161. CrossRef
- Pain-Friendly Strategies: Nursing Intervention in Postoperative Myocardial Revascularization
- 1,594 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of Breathing Exercise Using Panflutes on the Postoperative Compliance, Pulmonary Infections and Life Satisfaction in Elderly Patients Undergoing Spinal Surgery
- Hyun Mi Jo, Hyunsook Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):279-288. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.279
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of breathing exercises performed using panflutes in elderly patients undergoing spinal surgery.
Methods The study design was a nonequivalent control group non-synchronized pre-post test. The study included 24 patients in both the experimental group and the control group. The experimental group completed a daily breathing exercise regimen using panflutes for 30minutes after meals, whereas the control group was provided standard preoperative education, including breathing exercises using incentive spirometers. After the exercise regimen, breathing exercise compliance, pulmonary infections, and life satisfaction were measured in both groups, and the data were analyzed using the SPSS/WIN program.
Results The compliance rate of breathing exercises was significantly higher in the experimental group. The experimental group presented no pulmonary infections in the later period, whereas the control group presented higher pulmonary infection rates in the same period. In addition, the life satisfaction score in the experimental group significantly increased.
Conclusion The breathing exercise program using panflutes for elderly patients undergoing spinal surgery enhanced their breathing exercise compliance and their daily life satisfaction in addition to reducing their pulmonary infection rates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pranayama and Breathing Exercises - Types and Its Role in Disease Prevention & Rehabilitation
Naresh Kumar Satyanarayan Dhaniwala, Venkatesh Dasari, Mukunda Naresh Dhaniwala
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(44): 3325. CrossRef
- Pranayama and Breathing Exercises - Types and Its Role in Disease Prevention & Rehabilitation
- 969 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study on Postoperative Pain Perception by Effects of the Video Program as Preoperative Nursing Intervention
- Mee Kyung Joo
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1995;25(2):210-221. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1995.25.2.210
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify relationships between a preoperative video program as nursing intervention and the perception of postoperative pain. The subjects consisted of an experimental group of 17 children and a control group of 13 children, for a total of 30 patients who were admitted the ENT Department for tonsilectomies. Data were collected from August 1, 1993 to September 31. The video program was made by the pediatric operating theater nursing staff. Postoperative pain was measured using the Face Pain Rating Scales devised by Beyer in 1984. The data were analyzed by a SPSS using frequencies, means, percentages, t-test and ANOVA to analyze the variables and demographic characteristics. The results of this study are as follows: The hypothesis, "Score of the experimental group which was shown the preoperative video program as a nursing intervention will be lower than the control group which did not see the video in postoperative pain perception." was rejected by t= -.42, p>.05. No significant difference was found between the experimental group and the control group according demographic characteristics. From the above findings, this study suggests the following: 1. Further studies as randomized control-group pretest-posttest design are needed to control the extraneous variables. 2. A review will be suggested to be done by the preoperative video program as nursing intervention and an exploration to improve preoperative nursing care for pediatric patients with the inclusion such activities as preoperative visiting, operation theater tour etc.
- 514 View
- 0 Download

- Effects of Pain Control Education on Pain Control Barrier, Postoperative Pain and Pain Control Satisfaction in Gynecological Patients
- Bok Nam Lee, Ga Eon Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(6):968-975. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.6.968
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of preoperative pain control education on the pain control barrier, postoperative pain and pain control satisfaction in gynecological patients.
Method The study was a quasi-experimental research design. There were 58 subjects who were admitted for gynecological surgery to D University Hospital in B city. Pain control education was provided individually to the experimental group one day before their operation day for 20 minutes with the ‘ Pain Control Guide Book’ in the patient's admission room. The education book was made by researchers based on pain management references and patient interviews. For assessing the pain control barrier, a simplified version of Barriers Questionnaire was used, postoperative pain was assessed on a numeric scale(0-10) and satisfaction of pain control was assessed by one question.
Results The pain control barrier(F=15.828, p<.001) and the post pain score of the experimental group was lower than that of the control group. In addition, pain control satisfaction of the experimental group(t=3.612, p<.001) was higher than the control group's.
Conclusion With the above results, preoperative pain control education could be an effective nursing intervention for pain control of surgical patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Aroma Essential Oil Inhalation on Stress, Pain, and Sleep Quality in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
JiA Lee, Myung-Haeng Hur
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Assessment of the analgesic effectiveness of rectus sheath block in patients who had emergency midline laparotomy: Prospective observational cohort study
Debas Yaregal Melesse, Wubie Birlie Chekol, Hailu Yimer Tawuye, Zewuditu Abdissa Denu, Abatneh Feleke Agegnehu
International Journal of Surgery Open.2020; 24: 27. CrossRef - Effects of Active Mandibular Exercise for Mouth Opening Limitation Patients after Maxillomandibular Fixation Release: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
Hyo Jin Jang, Myung Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(1): 26. CrossRef - Comparing effects of intravenous patient‐controlled analgesia and intravenous injection in patients who have undergone total hysterectomy
Sung‐Jung Hong, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2014; 23(7-8): 967. CrossRef - Effects of Provision of Concrete Information about Patient-controlled Analgesia in Hysterectomy Patients
Bo Gyeong Lee, Young Whee Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(3): 204. CrossRef - Effect of Evidence-based Postoperative Pain Guidelines via Web for Patients undergoing Abdominal Surgery in South Korea
Sung-Jung Hong, Eunjoo Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(2): 135. CrossRef - Effects of a structured educational programme on patient‐controlled analgesia (PCA) for gynaecological patients in South Korea
Sung‐Jung Hong, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2012; 21(23-24): 3546. CrossRef - Pain Management in Cancer Patients Who Are Registered in Public Health Centers
So Young Choi, Kyung Oh Chang, Myoung Nam Park, Eunjung Ryu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(1): 77. CrossRef
- The Effects of Aroma Essential Oil Inhalation on Stress, Pain, and Sleep Quality in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 875 View
- 6 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Combination Effects of Capsicum Plaster at the Korean Hand Acupuncture Points K-D2 with Prophylactic Antiemetic on Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting after Gynecologic Laparoscopy
- Hyun Jung Jung, Sang Youn Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(2):215-224. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to evaluate the combination effects of capsicum plaster at the Korean hand acupuncture points K-D2 with prophylactic antiemetic on Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting (PONV).
Methods An experimental research design (a randomized, a double-blinded, and a placebo-control procedure) was used. The participants were female patients undergoing gynecologic laparoscopy; the control group (n=34) received intravenous prophylactic ramosetron 0.3mg, while the experimental group (n=34) had Korean Hand Therapy additionally. In the experimental group, capsicum plaster was applied at K-D2 of both 2nd and 4th fingers by means of Korean Hand Therapy for a period of 30 minutes before the induction of anesthesia and removed 8 hours after the laparoscopy.
Results The occurrence of nausea, nausea intensity and need for rescue with antiemetic in the experimental group was significantly less than in the control group 2 hours after surgery.
Conclusion Results of the study show capsicum plaster at K-D2 is an effective method for reducing PONV in spite of the low occurrence of PONV because of the prophylactic antiemetic medication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interleukin-31 Serum And Pruritus Dimension After Acupuncture Treatment In Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Dedi Ardinata, Rozaimah Zain-Hamid, Irma. D. Roesyanto-Mahadi, Hasan Mihardja
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(B): 196. CrossRef - Effects of Korean hand acupressure on opioid-related nausea and vomiting, and pain after caesarean delivery using spinal anaesthesia
Na Young Ahn, Hye-Ja Park
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2017; 28: 101. CrossRef - Effects of Preoperative Dehydration on Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting in Gynecological Surgery Patients
Yunjeong Hwang, SoMi Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(1): 23. CrossRef - Herbs as Adjuncts to Surgery
Eric Yarnell, Kathy Abascal
Alternative and Complementary Therapies.2014; 20(5): 270. CrossRef - Postoperative nausea and vomiting: pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies
Soo Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Anesthesiology.2013; 65(6): 491. CrossRef
- Interleukin-31 Serum And Pruritus Dimension After Acupuncture Treatment In Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- 1,397 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effect of Ondansetron combined with Dexamethasone on Postoperative Nausea & Vomiting and Pain of Patients with Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
- Miok Nam, Haesang Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(1):44-52. Published online February 17, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.1.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of ondansetron combined with dexamethasone on Post-Operative Nausea and Vomiting (PONV) and pain with ondansetron alone in patients with laparoscopy assisted vaginal hysterectomy under general anesthesia.
Methods: Data were collected from April 1 through September 30, 2005 using a double blind method. Ondansetron 4 mg and dexamethasone 10 mg were administered to the experimental group (25 patients), and ondansetron 4 mg only to the control group (25 patients). The medications were administered through an intravenous line at the beginning peritoneum suture. PONV by Index of Nausea Vomiting and Retching (INVR), nausea by Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), and pain (VAS) were assessed at postoperative 1 hr, 3 hr, 6 hr, 24 hr, and 48 hr. Data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA, and Bonferroni methods.
Results: The experimental group that received ondansetron combined with dexamethasone had less PONV (p=.048), and nausea (p=.012) than control group that received ondansetron alone. However, there was no difference in pain (p=.557) between the patients in the two groups.
Conclusion: We conclude that the administration of ondansetron combined with dexamethasone is more effective than the administration of ondansetron alone to reduce PONV in patients with laparoscopic hysterectomy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analgesia for Gynecologic Oncologic Surgeries: A Narrative Review
Kaiwal Patel, Sukhman Shergill, Nalini Vadivelu, Kanishka Rajput
Current Pain and Headache Reports.2022; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis
Stephanie Weibel, Gerta Rücker, Leopold HJ Eberhart, Nathan L Pace, Hannah M Hartl, Olivia L Jordan, Debora Mayer, Manuel Riemer, Maximilian S Schaefer, Diana Raj, Insa Backhaus, Antonia Helf, Tobias Schlesinger, Peter Kienbaum, Peter Kranke
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Pain management after laparoscopic hysterectomy: systematic review of literature and PROSPECT recommendations
Philipp Lirk, Juliette Thiry, Marie-Pierre Bonnet, Girish P Joshi, Francis Bonnet
Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine.2019; 44(4): 425. CrossRef - Comparing Effects of Two Different Types of Nei-Guan Acupuncture Stimulation Devices in Reducing Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
Hanna Oh, Bo Hwan Kim
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2017; 32(3): 177. CrossRef - Combination of 5-HT3 Antagonist and Dexamethasone Is Superior to 5-HT3 Antagonist Alone for PONV Prophylaxis After Laparoscopic Surgeries
Anirban Som, Sulagna Bhattacharjee, Souvik Maitra, Mahesh K Arora, Dalim Kumar Baidya
Anesthesia & Analgesia.2016; 123(6): 1418. CrossRef - Effect of Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Promotion of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting of Patients with Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Sung-Hee Lee, Sung-Jung Hong, Hwa Sun Kim, Younghoon Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(5): 481. CrossRef - Cost Analysis of Post Operative Pain Management for Surgical Patients using PCA
Sung-Jung Hong, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2013; 20(2): 137. CrossRef - Impact of perioperative dexamethasone on postoperative analgesia and side-effects: systematic review and meta-analysis
N.H. Waldron, C.A. Jones, T.J. Gan, T.K. Allen, A.S. Habib
British Journal of Anaesthesia.2013; 110(2): 191. CrossRef
- Analgesia for Gynecologic Oncologic Surgeries: A Narrative Review
- 1,047 View
- 8 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The Effects of Ketamine Preemptive Analgesia on Postoperative Pain in Patients undergoing a Hystrectomy
- Hong Yeon Kim, Hae Sang Yoon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(1):114-126. Published online February 28, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.1.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to evaluate the pre-emptive analgesic effects of a small dose of intravenous ketamine on postoperative pain in patients undergoing a hysterectomy.
Method Sixty patients undergoing a hystrectomy under general anesthesia were randomly allocated to 2 groups. The experimental group(30 patients) received 0.3mg/kg of ketamine after induction of anesthesia, approximately 5 min prior to surgery, but the control group(30 patients)did not receive ketamine. Data was collected in a double-blind manner from April 1st, to October 30th, 2004. Postoperatively, the patients used a patient-controlled analgesia(PCA) pump. Blood pressure, pulse rate, pain, anxiety, count of times pressing the PCA button, administeration of additional analgesics and side effects of ketamine were measured at 1 hour, 3 hours, 6 hours and 24 hours after the operation.
Result There were no statistical differences in blood pressure, pulse rate, pain and anxiety between the experimental and control groups. There were statistical differences in blood pressure, pulse rate, pain and anxiety during the 24 hours postoperatively. In the experimental group, the number of times pressing the PCA button and administering additional analgesic drugs were significantly lower than those of the control group.
Conclusion A 0.3 mg/kg dose of ketamine given at approximately 5 min before surgery resulted in decreasing the number of times pressing the PCA and the administration of additional analgesics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Preemptive Analgesia of Morphine and Ketorolac on Postoperative Pain, Cortisol, O2 Saturation and Heart Rate
Yun Ju Seo, Haesang Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 720. CrossRef
- The Effects of Preemptive Analgesia of Morphine and Ketorolac on Postoperative Pain, Cortisol, O2 Saturation and Heart Rate
- 984 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


