Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A qualitative exploration of acute stroke patients’ experiences with aphasia in Korea
- Jiyeon Kang, Hyunyoung Heo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):621-633. Published online November 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the lived experiences of patients with acute stroke-related aphasia within the Korean healthcare context.
Methods
A qualitative research design using inductive content analysis was employed, following the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research guidelines. Fourteen adults with acute stroke-related aphasia participated in one-on-one, in-depth interviews conducted between January and May 2025. Participants were recruited through purposive sampling until theoretical saturation was reached. Data were analyzed using an inductive qualitative content analysis approach.
Results
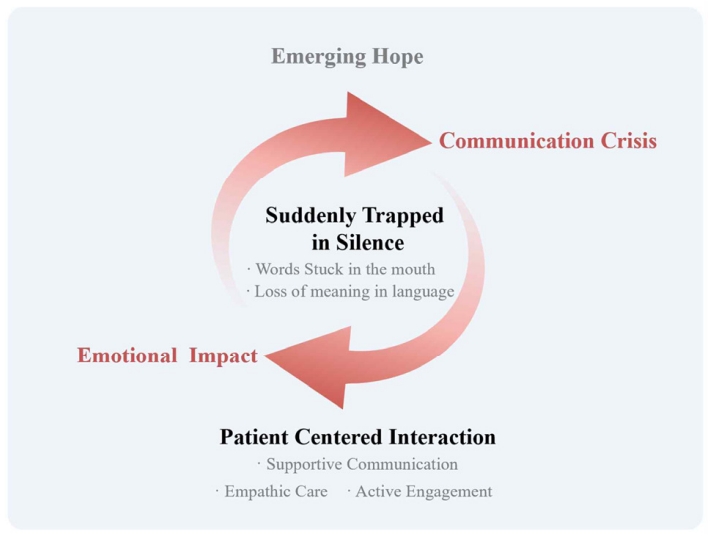
Five main categories emerged: “suddenly trapped in silence” described the abrupt loss of language, including the inability to articulate intended words and understand others; “emotional impact” captured psychological shock and feelings of loss; “communication crisis” encompassed expressive difficulties, exclusion from decision-making, and social withdrawal; “patient-centered interaction” highlighted supportive communication, empathic care, and active engagement by others; and “emerging hope” reflected signs of recovery, self-directed efforts, and anticipation of improvement. These categories converged into the overarching theme, “communication beyond language,” illustrating how patients sought meaningful interaction despite linguistic limitations.
Conclusion
Acute aphasia extends beyond a language disorder to encompass profound emotional and social experiences. Although communication barriers exist, meaningful interaction remains possible through empathetic, person-centered approaches. Healthcare professionals should recognize that patients with aphasia retain cognitive competence despite expressive limitations. These findings underscore the need to integrate emotional sensitivity into clinical care and to develop training programs that enhance person-centered communication skills in stroke rehabilitation settings.
- 1,248 View
- 129 Download

- Impact of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on parental anxiety and depression in severe hypospadias patients in China: a randomized controlled trial
- Ruijuan Wu, Lucai Jia, Biyu Ding, Ying Li, Yaqing Cao, Zhaojun Shi, Yanfang Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):327-341. Published online August 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the effects of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on alleviating perioperative and post-surgical anxiety and depression in parents of children with severe hypospadias.
Methods
Parents of children with severe hypospadias were recruited and randomly allocated into a control group (n=87), which received standard nursing care, and an intervention group (n=93), which was given an integrated disease-specific nursing intervention in addition to standard care. Parental anxiety and depression were measured using the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) at admission, discharge, and 6-month follow-up post-surgery.
Results
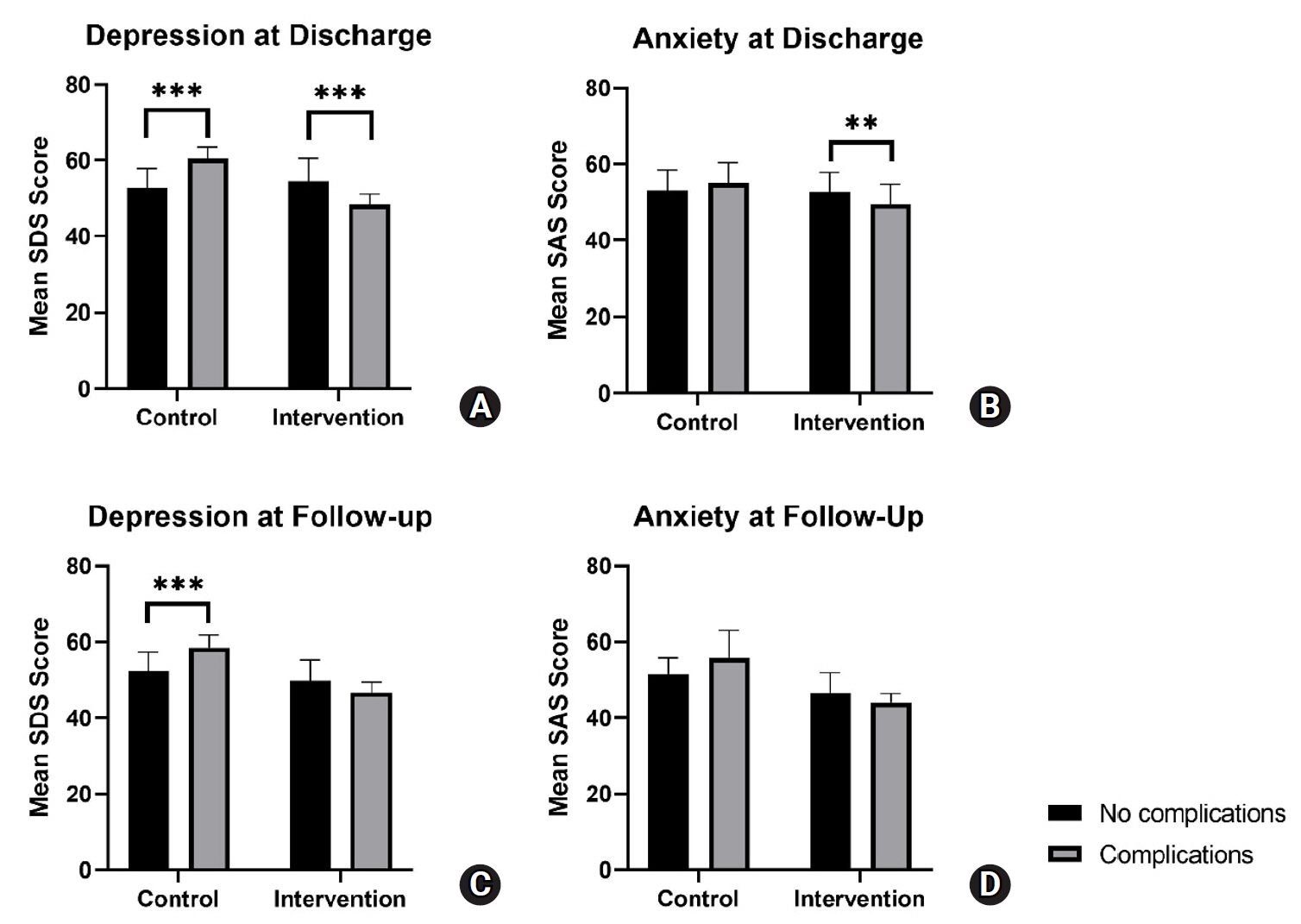
A linear mixed-effects model showed that SAS and SDS scores in the intervention group decreased to a significantly greater extent over time, from admission to follow-up, compared to the control group. Post-hoc analysis showed a trend for increased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up for the control group. Meanwhile, the intervention group exhibited a trend for decreased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up.
Conclusion
The integrated disease-specific nursing model significantly alleviated parental anxiety and depression over time compared to standard care, highlighting its effectiveness in supporting families of children with severe hypospadias. Notably, the intervention appeared to mitigate the negative emotional impact of postoperative and follow-up complications, suggesting its potential as a targeted approach to improve both emotional well-being and overall care outcomes.
- 2,470 View
- 165 Download

- Factors Affecting the Intention to Use Smartmonitor-Based Mobile Health in Middle-Aged in Patients Applying the Technology Acceptance Model II
- Ol Eum Joo, Yi Kyung Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):620-632. Published online November 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24091
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to identify factors that influence the intention to use smart monitor-based mobile health (SBM) technology among middle-aged inpatients, based on the technology acceptance model II (TAM II).
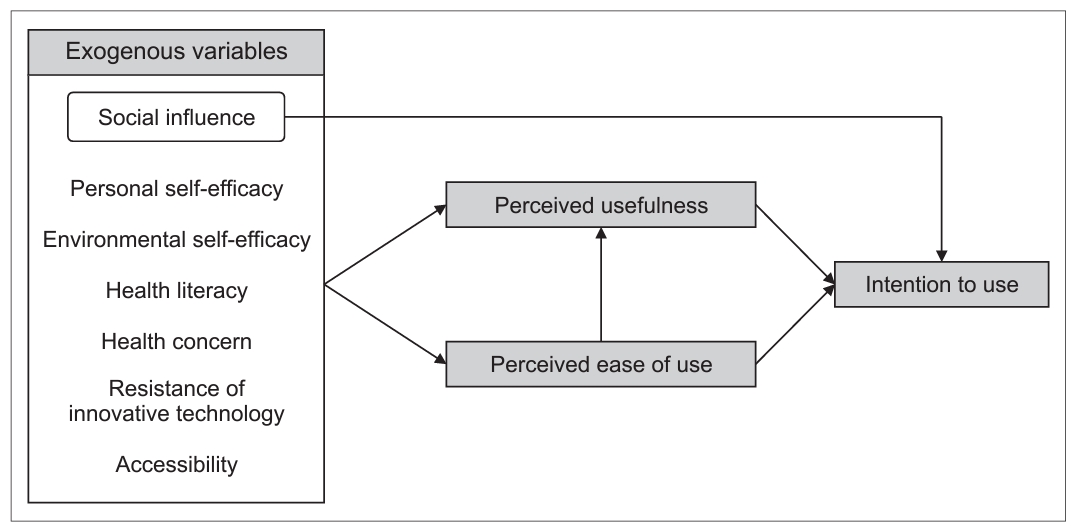
Methods A total of 222 participants were surveyed. Data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics 23.0 and IBM SPSS Amos 23. Seven exogenous variables–social influence (SI), personal self-efficacy, (PSE), environmental self-efficacy (ESE), health literacy, health concerns, resistance to innovative technology (RIT), accessibility (AC)– and three endogenous variables–perceived ease of use (PEOU), perceived usability (PU), and intention to use (ITU)–were investigated.
Results The hypothesized path model demonstrated a good fit for the data. SI (β = .13,
p = .042), PU (β = .46,p < .001), and PEOU (β = .16,p = .008) had significant direct effects on the ITU, which explained 39.5% of the variance. Additionally, SI (β = .27,p < .001), ESE (β = .16,p = .010), RIT (β = - .12,p = .026), AC (β = .28,p < .001), and PEOU (β = .20,p = .001) indirectly affected ITU through PU, which explained 50.7% of the variance. Furthermore, PSE (β = .38,p < .001) indirectly influenced ITU via PEOU, which explained 38.4% of the variance.Conclusion This study demonstrates that the TAM II can be used to effectively predict ITU in SBMs among middle-aged inpatients. To expand the intention to use SBMs, it is necessary to develop SBMs that include content and programs that promote PU, SI, and PEOU.
- 1,748 View
- 85 Download

- Development of Nursing Clinical Judgment Scale
- Shi Nae Kwon, Hyojung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):652-665. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23042
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a nursing clinical judgment scale (NCJS) and verify its validity and reliability in assessing the clinical judgment of nurses.
Methods
A preliminary instrument of the NCJS comprising 38 items was first developed from attributes and indicators derived from a literature review and an in-depth/focus interview with 12 clinical nurses. The preliminary tool was finalized after 7 experts conducted a content validity test based on a data from a preliminary survey of 30 hospital nurses in Korea. Data were collected from 443 ward, intensive care unit, emergency room nurses who voluntarily participated in the survey through offline and online for the verification of the construct validity and reliability of the scale.
Results
The final scale comprised 23 items scored on a 5-point Likert scale. Six factors – integrated data analysis, evaluation and reflection on interventions, evidence on interventions, collaboration among health professionals, patient-centered nursing, and collaboration among nurse colleagues – accounted for 64.9% of the total variance. Confirmatory factor analysis supported the fit of the measurement model, comprising six factors (root mean square error of approximation = .07, standardized root mean square residual = .04, comparative fit index = .90). Cronbach’s α for all the items was .92.
Conclusion
The NCJS is a valid and reliable tool that fully reflects the characteristics of clinical practice, and it can be used effectively to evaluate the clinical judgment of Korean nurses. Future research should reflect the variables influencing clinical judgment and develop an action plan to improve it. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
Mi Hwa Seo, Eun A. Kim, Hae Ran Kim, Mohammad Jamil Rababa
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0316654. CrossRef - Effects of Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Judgement, and Nurse–Physician Collaboration on Triage Competency Among Triage Nurses
Ji-Won Song, Hyung-Ran Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(4): 405. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality nursing simulation for pediatric pneumonia care: a Korean pilot study using a single-group pre-post test design
Eun Joo Kim, Seong Kwang Kim, Sung Sook Song
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(4): 198. CrossRef - The Influence of Clinical Nurses' Clinical Judgment, Nursing Work Environment and Ethical Nursing Competence on Patient Safety Nursing Activities
Eunseo Hong, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(3): 368. CrossRef
- How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
- 4,832 View
- 293 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory–Staff for Nurses
- Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):363-379. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory– Staff (PCPI-S) for nurses.
Methods
The English PCPI-S was translated into Korean with forward and backward translation. Data were collected from 338 nurses at one general hospital in Korea. Construct validity was evaluated with confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. Known-group validity was also evaluated. Cronbach’s α was used to assess the reliability.
Results
The PCPI-S Korean version consisted of 51 items in three areas: prerequisites, the care environment, and person-centered process. The comparative fit index (CFI) and values of person-centered care process were improved after engagement and having sympathetic presence items were combined as one component. The construct validity of PCPI-S Korean version was verified using four-factor structures (.05 < RMSEA < .10, AGFI > .70, CFI > .70, and AIC). The convergent validity and discriminant validity of the entire PCPI-S question were verified using a two-factor structures (AVE > .50, construct reliability > .70). There was an acceptable known-group validity with a significant correlation between the PCPI-S level and the degree of person-centered care awareness and education. Internal consistency was reliable with Cronbach’s α .95.
Conclusion
The Korean version of PCPI-S is valid and reliable. It can be used as a standardized Korean version of person-centered care measurement tool. Abbreviation: RMSEA = root mean square error of approximation; AGFI = adjusted goodness of fit index; AIC = Akaike information criterion; AVE = average variance extracted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The moderating effects of nurses’ characteristics on the perceptions and practices of family-centered care for chronically ill children and their families in Saudi Arabia
Nada Alqarawi, Eman Alhalal, Ibrahim Alasqah
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric validation and cultural adaptation of the family-centered care Questionnaire-Revised for use among nurses in Saudi Arabia
Nada Alqarawi, Ibrahim Alasqah
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptación transcultural y validación del Person-centred Practice Inventory-Staff para la cultura brasileña
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Person-centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Brazilian culture
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptação transcultural e validação do Person-centred Practice Inventory-Staff para a cultura brasileira
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Self-Compassion, Burden of BPSD, Communication Behavior, and Nursing Work Environment on Person-Centered Care for Patients with Dementia Among Long-Term Care Hospital Nurses
Yong Min Kim, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2025; 14(1): 15. CrossRef - Impact of Moral Distress, Person-Centred Care, and Nursing Professional Pride on Turnover Intention Among Intensive Care Unit Nurses in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
WonSuk Choi, Younjae Oh
Healthcare.2025; 14(1): 22. CrossRef - Influence of Nursing Professionalism, Nursing Work Environment, and Compassion Competence on Person-Centered Care of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care
Yeon-Jin Lee, Eun-Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 572. CrossRef - Person-Centred Care: A Support Strategy for Managing Non-Communicable Diseases
Mateja Lorber, Nataša Mlinar Reljić, Barbara Kegl, Zvonka Fekonja, Gregor Štiglic, Adam Davey, Sergej Kmetec
Healthcare.2024; 12(5): 526. CrossRef - Nurses' practices of children and family-centered care for chronically ill children: A cross-sectional study
Nada Alqarawi, Eman Alhalal
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 77: 172. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care Among Psychiatric Nurses in Hospitals
Ji Su Lee, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2024; 12(22): 2269. CrossRef - Translation, Cultural Adaptation, and Validation of the Spanish Version of the Person-Centred Practice Inventory-Staff (PCPI-S)
Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel, Edgar Benitez, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, María José Galán-Espinilla, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Ana Choperena, Brendan McCormack, Vaibhav Tyagi, Virginia La Rosa-Salas
Healthcare.2024; 12(23): 2485. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of Patient-Centered Care Tool: For Outpatients
Yeo Ju Kim, Gunjeong Lee, Sunyeob Choi
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1525. CrossRef - The influence of Critical Reflection Competency, Nursing Work Environment and Job Crafting on Person-Centered Care in Tertiary Hospital Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
Jinseon Hwang, Sujin Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(3): 245. CrossRef - Translation and transcultural adaptation of the Person-Centred Practice Inventory Staff (PCPI-S) for health professionals in Spain
Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Virginia La Rosa-Salas, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, Yvonne Gavela-Ramos, Ana Choperena, Leire Arbea Moreno, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, María José Galán-Espinilla, Brendan McCormack, Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel
Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Hospice Nurses
Sinyoung Kwon, Kyoung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(2): 66. CrossRef - Moral sensitivity and person‐centred care among mental health nurses in South Korea: A cross‐sectional study
Sun Joo Jang, Eun Hye Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2227. CrossRef - Translation and transcultural adaptation of the theoretical Person-Centred Practice Framework to the Spanish context
Ana Choperena, Yvonne Gavela-Ramos, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, María José Galán-Espinilla, Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Virginia La Rosa-Salas, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, Brendan McCormack, Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel
Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The moderating effects of nurses’ characteristics on the perceptions and practices of family-centered care for chronically ill children and their families in Saudi Arabia
- 3,152 View
- 124 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- A Predictive Model on Patient-Centered Care of Hospital Nurses in Korea
- Hyun Jeong, Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):191-202. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Patient-centered care is a widely utilized concept in nursing and health care. However, the key components of patient-centered nursing have not yet been reported. Moreover, previous studies on patient-centered care have mostly focused on components of nursing rather than organizational factors. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of influential factors of patient-centered care is required.
Methods The purpose of this study was to develop a theoretical model based on person-centered care theory, and the relevant literature and to test the developed model with covariance structure analysis in order to determine the causal paths among the variables.
Results The model fit indices for the hypothetical model were suitable for the recommended level (goodness of fit index=.87, standardized root mean residual=.01, root mean square error of approximation=.06, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.92, parsimonious normed fit index=.75). In this study, five of the six paths established in the initial hypothetical model were supported. The variables of teamwork, self-leadership, and empathy accounted for 56.4% of hospital nurses' patient-centered care. Among these, empathy was the strongest predictor of patient-centered care.
Conclusion These results suggest that it is necessary to use strategies to improve self-leadership and empathy. In addition to enhancing the personal factors of nurses, nursing organizations should strive for effective multidisciplinary cooperation with active support for patient-centered care and openness to change.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Clinical Nursing Competency and Nursing Working Environment of Psychiatric Nurses on Person-Centered Care
Pan Heui Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(3): 229. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care Among Psychiatric Nurses in Hospitals
Ji Su Lee, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2024; 12(22): 2269. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Changes in Patient-Centered Care in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Seongkum Heo, Brandy Haley, Patricia Wright, Claudia P. Barone, Michael Anders, Tara Bertulfo, Patricia Troyan
Nursing Education Perspectives.2023; 44(2): 82. CrossRef - Factors associated with the person-centered care competence of nursing students
Ju Young Park, Chung Hee Woo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(1): 48. CrossRef - Listening to patients' voices: Applying the design‐thinking method for teaching person‐centered care to nursing students
Myonghwa Park, Thi‐Thanh‐Tinh Giap, Insook Jang, Miri Jeong, Jahyeon Kim
Nursing Forum.2022; 57(1): 9. CrossRef - Factors influencing mental health nurses in providing person-centered care
Suyoun Ahn, Yeojin Yi
Nursing Ethics.2022; 29(6): 1491. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale*
Seong Eun KIM, Jeong Suk KIM
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2022; 25(2): 137. CrossRef - A Meta-Synthesis Study of Person-Centered Care Experience from the Perspective of Nursing Home Residents
Eun-Young Kim, Sung-Ok Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(14): 8576. CrossRef - Effects of health literacy competencies on patient-centered care among nurses
Yaki Yang
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Person-Centered Care Experience of Nursing Home Workers: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 33. CrossRef - Nurse Spiritual Care Therapeutics Scale
Kyung-Ah Kang, Elizabeth Johnston Taylor, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2022; 24(6): E250. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Hospice Nurses
Sinyoung Kwon, Kyoung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(2): 66. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Person-Centered Fall Prevention Program for Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals: For Older Adults with Dementia and Caregivers in Long-Term Care Hospitals
Jeong Ok Lim, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 341. CrossRef - Role of self‐efficacy in nursing organizational climate: A way to develop nurses' humanistic practice ability
Mengru Bu, Haiqi Ma, Huimin Zhai, Yue Ma, Ningjun Xu
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2107. CrossRef - Effects of Compassionate Competence, Communication Skills, and Nursing Work Environment on Person-centered Care in General Hospital Nurses who Care for Cancer Patients
Mi Jin Han, Seonho Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Performance of Person-centered Care Among Nurses in Designated COVID-19 Hospitals
Hyun-Joung Yun, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(4): 413. CrossRef - Hospital Culture and Healthcare Workers' Provision of Patient-Centered Care: A Moderated Mediation Analysis
Xianhong Huang, Yuan Gao, Hanlin Chen, Hao Zhang, Xiaoting Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Performance of Person-Centered Care among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: An Ecological Perspective
Yein Lee, Yunhee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 522. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Care Workers at Long-term Care Facilities
Geun-Young Kim, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 13. CrossRef - A predictive model of the perceptions of patient-centered care among nurses in long-term care hospitals: A cross-sectional study
Myonghwa Park, Hyun Jeong, Thi-Thanh-Tinh Giap
Geriatric Nursing.2021; 42(3): 687. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Nurses
Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 363. CrossRef - Hospital Nurses’ Experience of Patient-Centered Nursing
Soojin Chung, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2021; 27(1): 26. CrossRef - Inducing a sense of worthiness in patients: the basis of patient-centered palliative care for cancer patients in Iran
Mir Hossein Aghaei, Zohreh Vanaki, Eesa Mohammadi
BMC Palliative Care.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of the Nursing Practice Environment and Self-leadership on Person-centered Care Provided by Oncology Nurses
Sun-Ui Shin, Hyun-E Yeom
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2021; 24(3): 174. CrossRef - The influence of health literacy competencies on patient-centered care among clinical nurses
Minyeon Kim, Jieun Cha
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 132. CrossRef - “Walking in the patient’s shoes”: An innovative training method using storytelling to promote knowledge transfer of patient-centered care in hospital: A quasi-experimental study
Myonghwa Park, Insook Jang, Thi-Thanh-Tinh Giap
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 56: 103199. CrossRef - Factors affecting to the Person-Centered Care among Critical Care Nurses
Seunghye Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(2): 36. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis on Patient-Centered Care in Hospitalized Older Adults with Multimorbidity
Youn-Jung Son, Heun-Keung Yoon
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 61. CrossRef - The Relationship between Person-Centered Nursing and Family Satisfaction in ICUs
Jiyeon Kang, Eun-Ja Shin
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Lateral Violence on Burnout and Empathy with Patients among Nurses: The Moderating Effect of Communication
Soohyun Nam, Boyoung Hwang
Stress.2019; 27(3): 224. CrossRef
- Influence of Clinical Nursing Competency and Nursing Working Environment of Psychiatric Nurses on Person-Centered Care
- 5,103 View
- 185 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref

- Development and Validation of a Measurement to Assess Person-centered Critical Care Nursing
- Jiyeon Kang, Young Shin Cho, Yeon Jin Jeong, Soo Gyeong Kim, Seonyoung Yun, Miyoung Shim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):323-334. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.323
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a scale to measure person-centered critical care nursing and verify its reliability and validity.
Methods A total of 38 preliminary items on person-centered critical care nursing were selected using content validity analysis of and expert opinion on 72 candidate items derived through literature review and qualitative interviews. We conducted a questionnaire survey with 477 nurses who worked in intensive care units. The collected data were analyzed using exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmative factor analysis (CFA) with SPSS and AMOS 24.0 program.
Results EFA was performed with principal axis factor analysis and Varimax rotation. The 15 items in 4 factors that accounted for 50.8% of the total variance were identified by deleting the items that were not meet the condition that the commonality should be .30 or more and the factor loading over .40. We named the factors as compassion, individuality, respect, and comfort, respectively. The correlation coefficient between this scale and the Caring Perception Scale was
r =.57 (p <.001), which determined concurrent validity. The item-total correlation values ranged from .39 to .63, and the internal consistency for the scale was Cronbach's α=.84.Conclusion The reliability and validity of the 15 item person-centered critical care nursing scale were verified. It is expected that the use of this scale would expand person-centered care in critical care nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the Intensive care unit Dignified Care Questionnaire (IDCQ)
Sejin Kang, So Hyun Park, Youn-Jung Son
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross‐Cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Yonsei‐Social Play Evaluation Tool (Y‐SPET) for Preschool Children in the United States: A Delphi Study
Sarah Kim, Rachelle Lydell, Sanghee Yoo, Sarah Tucker, Claudia Hilton, Ickpyo Hong
Child: Care, Health and Development.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
Mi Hwa Seo, Eun A. Kim, Hae Ran Kim, Mohammad Jamil Rababa
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0316654. CrossRef - Development and validation of the nurses’ touch comfort evaluation scale in China
Yaohong Liu, Sainan Qiu, Hao Li, Chong Chen, Renhe Yu, Su’e Yuan
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with good death for end-of-life patients in the intensive care unit based on nurses’ perspectives: A systematic review
Ifa Hafifah, Wasinee Wisesrith, Noraluk Ua-Kit
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2025; 87: 103930. CrossRef - Impact of Interprofessional Communication and Person-centered Care on Perceived Quality of Death in Intensive Care Units by Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
Hye-Jin Kim, So-Hi Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 153. CrossRef - Trends in person-centered care research: A quantitative content analysis using text network analysis
Dajung Ryu, Hyun Su Lee, Mi Sun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(2): 141. CrossRef - Workload, Teamwork, Compassion Competence, and Person-centered Critical Care Nursing among Critical Care Nurses
Hyun A Lee, Myung Sun Hyun, Jin-Hee Park, Eun Ji Seo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(2): 14. CrossRef - A Predictive Model for Person-Centered Care in Intensive Care Units in South Korea: A Structural Equation Model
Sunmi Kwon, Kisook Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 467. CrossRef - Analysis of Factors Affecting the Inpatient Satisfaction in Integrated Nursing Care Service Wards using a Healthcare Service Survey Database
Young Shin Cho, Jiwon Hong
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 76. CrossRef - The Influence of Ethical Nursing Competence and Positive Nursing Organizational Culture on Person-Centered Care in Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jae Eun Lee, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 304. CrossRef - Emotional Touch Nursing Competencies Model of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Instrument Validation Study
Sun-Young Jung, Ji-Hyeon Lee
Asian/Pacific Island Nursing Journal.2024; 8: e67928. CrossRef - Development and validation of a patient-centered communication scale for nurses
Youngshin Joo, Yeonsoo Jang, Chang Gi Park, You Lee Yang
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a cyberbullying victimization scale for adolescents in South Korea
JongSerl Chun, Jinyung Kim, Serim Lee
Children and Youth Services Review.2023; 144: 106744. CrossRef - The effect of nursing work environment on slow nursing among long-term care hospital nurses: A descriptive study
Hyeon-mi Woo
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(2): 206. CrossRef - Birey Merkezli Perioperatif Hemşirelik Ölçeği: Türkçe’ye Uyarlama, Geçerlik ve Güvenirlik Çalışması
Nadide YILMAZ ESENBOĞA, Seher YURT
Ege Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 39(1): 21. CrossRef - Comparison of Nursing Needs and Nursing Performance Perceived by Patients and Nurses in Integrated Nursing Care Service Wards in Small and Medium-Sized Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Hee-Sun Choi, Young Shin Cho
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(3): 234. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care among Nurses in COVID-19 Special Care Units at Tertiary General Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Kisook Kim, Sunmi Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 127. CrossRef - Moral sensitivity and person‐centred care among mental health nurses in South Korea: A cross‐sectional study
Sun Joo Jang, Eun Hye Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2227. CrossRef - Person-Centered Care Experience of Nursing Home Workers: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 33. CrossRef - Intersections of the arts and art therapies in the humanization of care in hospitals: Experiences from the music therapy service of the University Hospital Fundación Santa Fe de Bogotá, Colombia
Mark Ettenberger, Nayibe Paola Calderón Cifuentes
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between person-centred care and the intensive care unit experience of critically ill patients: A multicentre cross-sectional survey
Jiyeon Kang, Minju Lee, Young Shin Cho, Jin-Heon Jeong, Sol A Choi, Jiwon Hong
Australian Critical Care.2022; 35(6): 623. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Communication Competence in the Relationship between Compassion and Patient-Centered Care in Clinical Nurses in South Korea
Miri Jeong, Kawoun Seo
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 2069. CrossRef - Person-centred care among intensive care unit nurses: A cross-sectional study
Hyuna Youn, Miyoung Lee, Sun Joo Jang
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2022; 73: 103293. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Performance of Person-centered Care Among Nurses in Designated COVID-19 Hospitals
Hyun-Joung Yun, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(4): 413. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Practice for Physical Restraints among Nurses in the Intensive Care Unit
Da Eun Kim, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 62. CrossRef - Effectiveness of blood glucose control protocol for open heart surgery patients
Hye Jin Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh, JaeLan Shim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(1): 275. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Patient-Centeredness among Korean Nursing Students: Empathy and Communication Self-Efficacy
Jaehee Jeon, Seunghye Choi
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 727. CrossRef - The Factors Affecting Person-centered Care Nursing in Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Hye Suk Kang, Minjeong Seo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 14. CrossRef - The Effect of a Multifaceted Family Participation Program in an Adult Cardiovascular Surgery ICU*
Hye Jin Yoo, JaeLan Shim
Critical Care Medicine.2021; 49(1): 38. CrossRef - Impact of Job Engagement on the Quality of Nursing Services: The Effect of Person-Centered Nursing in South Korean Nurses
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 826. CrossRef - The mediating effect of self-efficacy on the relationship between social anxiety and communication ability in nursing students
Mi-Jin You, Hye-Sook Han
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 298. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Nurses
Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 363. CrossRef - The Effects of the Nursing Practice Environment and Self-leadership on Person-centered Care Provided by Oncology Nurses
Sun-Ui Shin, Hyun-E Yeom
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2021; 24(3): 174. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Quality of Dying and Death in Korean Intensive Care Units: Perceptions of Nurses
Haeyoung Lee, Seung-Hye Choi
Healthcare.2021; 9(1): 40. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Performance of Person-Centered Care among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: An Ecological Perspective
Yein Lee, Yunhee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 522. CrossRef - Factors affecting to the Person-Centered Care among Critical Care Nurses
Seunghye Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(2): 36. CrossRef - Conceptualization of Person-Centered Care in Korean Nursing Literature: A Scoping Review
Ji Yea Lee, Sewon Lee, Eui Geum Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 354. CrossRef - Critical care nurses’ communication experiences with patients and families in an intensive care unit: A qualitative study
Hye Jin Yoo, Oak Bun Lim, Jae Lan Shim, Liza Heslop
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(7): e0235694. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Patient Version of Person-Centered Critical Care Nursing Questionnaire: A Methodological Study
Jiwon Hong, Jiyeon Kang
Sage Open.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a person‐centred care intervention in an intensive care unit: Using mixed methods to examine nurses’ perspectives
Hye Jin Yoo, JaeLan Shim
Journal of Nursing Management.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationship between the Work Environment and Person-centered Critical Care Nursing for Intensive Care Nurses
Jiyeon Kang, Yun Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 73. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Person-Centered Perioperative Nursing Scale
Soyeung Shin, Jiyeon Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(3): 221. CrossRef - The Relationship between Person-Centered Nursing and Family Satisfaction in ICUs
Jiyeon Kang, Eun-Ja Shin
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 1. CrossRef - Development of the Patient Caring Communication Scale
Myoung Lyun Heo, Sook Bin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 80. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis on Patient-Centered Care in Hospitalized Older Adults with Multimorbidity
Youn-Jung Son, Heun-Keung Yoon
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 61. CrossRef - The Meanings of Hands among Clinical Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital
Hye Jin Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh, Yeon Hee Shin, Jung Sun Choi, Kwang Hee Park, Jung Yoon Kim, Hyunsun Kim, Jiyoung Kang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 50. CrossRef
- Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the Intensive care unit Dignified Care Questionnaire (IDCQ)
- 3,159 View
- 128 Download
- 47 Crossref

- The Effect of Patient-centered CPR Education for Family Caregivers of Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases
- Hyun Sun Kim, Hyun-Jin Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):463-474. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.463
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose For cardiovascular patients, family caregivers play a vital role in daily nursing and cardiac emergencies. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of patient-centered CPR education (PCE) for family caregivers of patients with cardiovascular diseases.
Methods Fifty-four participants were randomly assigned to the PCE or control group. The PCE group received tailored counseling on overall cardiovascular disease information and CPR followed by interactive instructor-guided CPR training and re-education follow-up by telephone 2 weeks later. The control group received only video-based CPR self-education and booklets. Cardiovascular disease and CPR knowledge and self-efficacy were measured before (pre-test), immediately after (post-test 1), and 4 weeks after the PCE (post-test 2). CPR skills and performance were measured pre-test and at post-test1.
Results The PCE group demonstrated significant improvements in knowledge (F=91.09,
p <.001), self-efficacy (F=15.19,p <.001) and CPR skills and performance (F=8.10,p =.008), as well as significant differences over time (knowledge: F=364.25,p <.001; self-efficacy: F=1162.28,p <.001; CPR skills and performance: F=1798.81,p <.001). There were significant group-by-time interactions for knowledge (F=8.10,p =.001), self-efficacy (F=4.30,p =.019) and CPR skills and performance (F=4.81,p =.036) by repeated measures ANOVA.Conclusion This is the first study to demonstrate the effects of a patient-centered intervention with CPR education tailored for patients' and family caregivers' preferences, needs, and lifestyles. The results of this study encourage the use of tailored, patient-centered interventions in cardiovascular nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mastering the Art of Caregiving: Instructional Approaches to Teaching Healthcare‐Related Procedural Skills to Informal Caregivers—An Integrative Review
An Ling Siew, Esther Yin Hui Chew, Ee‐Yuee Chan, Elaine Kee Chen Siow
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2026; 82(1): 272. CrossRef - Effect of tailored cardiopulmonary resuscitation training for middle-aged and older adults with visual impairment: A cluster-randomized controlled trial
Eunjin Yang, Kyung Hee Lee, Youngshin Joo
Disability and Health Journal.2025; 18(4): 101909. CrossRef - Basic life support training targeted to family members or carers of those at high-risk of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a systematic review
Zakary Doherty, Janet E. Bray, Judith Finn, Susie Cartledge
Resuscitation Plus.2025; 25: 101031. CrossRef - Education, Implementation, and Teams: 2025 International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation Consensus on Science With Treatment Recommendations
Robert Greif, Adam Cheng, Cristian Abelairas-Gómez, Katherine S. Allan, Jan Breckwoldt, Andrea Cortegiani, Aaron J. Donoghue, Kathryn J. Eastwood, Barbara Farquharson, Ming-Ju Hsieh, Tracy Kidd, Ying-Chih Ko, Kasper G. Lauridsen, Yiqun Lin, Andrew S. Lock
Circulation.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Education, Implementation, and Teams: 2025 International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation Consensus on Science With Treatment Recommendations
Robert Greif, Adam Cheng, Cristian Abelairas-Gómez, Katherine S. Allan, Jan Breckwoldt, Andrea Cortegiani, Aaron J. Donoghue, Kathryn J. Eastwood, Barbara Farquharson, Ming-Ju Hsieh, Tracy Kidd, Ying-Chih Ko, Kasper G. Lauridsen, Yiqun Lin, Andrew S. Lock
Resuscitation.2025; 215: 110807. CrossRef - 2022 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations: Summary From the Basic Life Support; Advanced Life Support; Pediatric Life Support; Neonatal Life Support; Education, I
Myra H. Wyckoff, Robert Greif, Peter T. Morley, Kee-Chong Ng, Theresa M. Olasveengen, Eunice M. Singletary, Jasmeet Soar, Adam Cheng, Ian R. Drennan, Helen G. Liley, Barnaby R. Scholefield, Michael A. Smyth, Michelle Welsford, David A. Zideman, Jason Acwo
Pediatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Expert opinion on evidence after the 2020 Korean Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines: a secondary publication
Sung Phil Chung, Youdong Sohn, Jisook Lee, Youngsuk Cho, Kyoung-Chul Cha, Ju Sun Heo, Ai-Rhan Ellen Kim, Jae Guk Kim, Han-Suk Kim, Hyungoo Shin, Chiwon Ahn, Ho Geol Woo, Byung Kook Lee, Yong Soo Jang, Yu Hyeon Choi, Sung Oh Hwang
Clinical and Experimental Emergency Medicine.2023; 10(4): 382. CrossRef - Application of the Modified Basic Life Support Training Model in Improving Community Residents’ Rescue Willingness in Nantong City in China
Yu-Fei Qian, Yu-Qin Ren, Li Wang, Rong-Qian Sun, Dan-Feng Li, Samar Tharwat
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - 2021 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations: Summary From the Basic Life Support; Advanced Life Support; Neonatal Life Support; Education, Implementation, and Teams
Myra H. Wyckoff, Eunice M. Singletary, Jasmeet Soar, Theresa M. Olasveengen, Robert Greif, Helen G. Liley, David Zideman, Farhan Bhanji, Lars W. Andersen, Suzanne R. Avis, Khalid Aziz, Jason C. Bendall, David C. Berry, Vere Borra, Bernd W. Böttiger, Richa
Circulation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - 2022 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations: Summary From the Basic Life Support; Advanced Life Support; Pediatric Life Support; Neonatal Life Support; Education, I
Myra H. Wyckoff, Robert Greif, Peter T. Morley, Kee-Chong Ng, Theresa M. Olasveengen, Eunice M. Singletary, Jasmeet Soar, Adam Cheng, Ian R. Drennan, Helen G. Liley, Barnaby R. Scholefield, Michael A. Smyth, Michelle Welsford, David A. Zideman, Jason Acwo
Resuscitation.2022; 181: 208. CrossRef - 2022 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations: Summary From the Basic Life Support; Advanced Life Support; Pediatric Life Support; Neonatal Life Support; Education, I
Myra H. Wyckoff, Robert Greif, Peter T. Morley, Kee-Chong Ng, Theresa M. Olasveengen, Eunice M. Singletary, Jasmeet Soar, Adam Cheng, Ian R. Drennan, Helen G. Liley, Barnaby R. Scholefield, Michael A. Smyth, Michelle Welsford, David A. Zideman, Jason Acwo
Circulation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicians for CARE: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis of Interventions to Support Caregivers of Patients With Heart Disease
Kellen A. Knowles, Helen Xun, Sunyoung Jang, Sharon Pang, Charles Ng, Apurva Sharma, Erin M. Spaulding, Rohanit Singh, Alaa Diab, Ngozi Osuji, Joshua Materi, Danielle Amundsen, Shannon Wongvibulsin, Daniel Weng, Pauline Huynh, Julie Nanavati, Jennifer Wol
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of the Family and Friends CPR course in learning cardiopulmonary resuscitation in relatives of patients with high cardiovascular risk or who have suffered a cardiovascular event
Bruno Enzo Vargas-Sánchez, Miluska Madeleine Salazar-Arteaga, Aida Del Carmen Rotta-Rotta, Roy Germán Dueñas-Carbajal
Iberoamerican Journal of Medicine.2021; 3(4): 307. CrossRef - 2021 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations
Myra H. Wyckoff, Eunice M. Singletary, Jasmeet Soar, Theresa M. Olasveengen, Robert Greif, Helen G. Liley, David Zideman, Farhan Bhanji, Lars W. Andersen, Suzanne R. Avis, Khalid Aziz, Jason C. Bendall, David C. Berry, Vere Borra, Bernd W. Böttiger, Richa
Resuscitation.2021; 169: 229. CrossRef - The impact of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation on patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrests
Fang-Yu Liou, Kun-Chang Lin, Chian-Shiu Chien, Wan-Ting Hung, Yi-Ying Lin, Yi-Ping Yang, Wei-Yi Lai, Tzu-Wei Lin, Shu-Hung Kuo, Wei-Chun Huang
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2021; 84(12): 1078. CrossRef - Formación de población adulta lega en soporte vital básico. Una revisión sistemática
Violeta González-Salvado, Emilio Rodríguez-Ruiz, Cristian Abelairas-Gómez, Alberto Ruano-Raviña, Carlos Peña-Gil, José Ramón González-Juanatey, Antonio Rodríguez-Núñez
Revista Española de Cardiología.2020; 73(1): 53. CrossRef - Training adult laypeople in basic life support. A systematic review
Violeta González-Salvado, Emilio Rodríguez-Ruiz, Cristian Abelairas-Gómez, Alberto Ruano-Raviña, Carlos Peña-Gil, José Ramón González-Juanatey, Antonio Rodríguez-Núñez
Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition).2020; 73(1): 53. CrossRef - Targeting relatives: Impact of a cardiac rehabilitation programme including basic life support training on their skills and attitudes
Violeta González-Salvado, Cristian Abelairas-Gómez, Francisco Gude, Carlos Peña-Gil, Carmen Neiro-Rey, José Ramón González-Juanatey, Antonio Rodríguez-Núñez
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2019; 26(8): 795. CrossRef
- Mastering the Art of Caregiving: Instructional Approaches to Teaching Healthcare‐Related Procedural Skills to Informal Caregivers—An Integrative Review
- 1,872 View
- 38 Download
- 18 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


