Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Papers
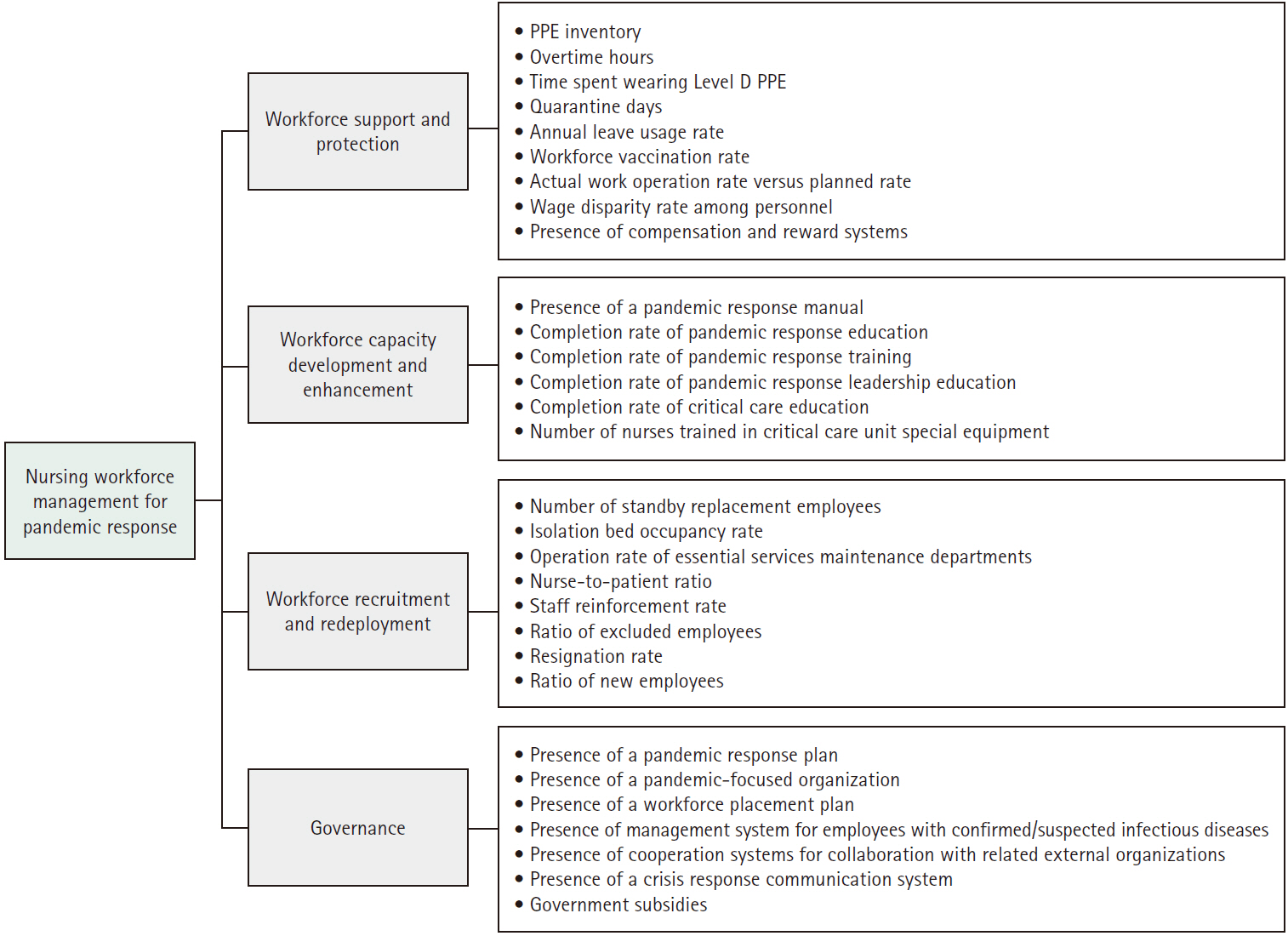
- Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
- Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):236-248. Published online May 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals and to analyze the relative importance of these factors.
Methods
A validity test was conducted with experts to select four categories and 30 key factors related to nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Surveys were collected from 25 nursing managers in general hospitals and 21 nursing managers in long-term care hospitals, and the relative importance of the key factors was analyzed using the analytic hierarchy process method.
Results
Differences were found between the two groups in the relative importance of nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Specifically, the highest-ranking category was “workforce recruitment and redeployment” for general hospitals, but “workforce support and protection” for long-term care hospitals. The most important factor regarding nursing workforce management was the “nurse-to-patient ratio” for both general and long-term care hospitals.
Conclusion
General and long-term care hospitals need to establish nursing workforce management strategies to effectively respond to pandemics with appropriate consideration of the relative importance and prioritization of key factors based on hospital characteristics.
- 1,958 View
- 74 Download

- Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
- SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):584-596. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23048
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the perspectives of frontline nurses working during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Methods
An online qualitative study was conducted using a pragmatic approach. The data were collected in August 2021. Registered Korean nurses who provided direct nursing care to patients with confirmed COVID-19 were eligible for this study. An online survey was used to gather free-text data, which were then analyzed using machine-based network analysis and summative content analysis.
Results
The analysis examined the responses of 126 participants and led to the identification of six prominent themes. These themes were further classified into three distinct levels: personal, task, and organizational. The identified themes are as follows: “collapse of personal life,” “being overwhelmed by the numerous roles required,” “personal protective equipment was sufficiently provided, but that is not enough,” “changes in interprofessional collaboration,” “inappropriate workforce management,” and “diverted allocation of healthcare services and resources.” Conclusion: Our findings highlight areas for improvement in resources, systems, and policies to enhance preparedness for future pandemics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Skill mix changes in healthcare professions during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review
Natalia Petka-Nosal, Iwona A Bielska, Katarzyna Badora-Musiał, Katarzyna Nowak-Zając, Alicja Domagała, Małgorzata Gałązka-Sobotka, Iwona Kowalska-Bobko
BMJ Open.2025; 15(10): e100024. CrossRef
- Skill mix changes in healthcare professions during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review
- 2,829 View
- 37 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Experience of Nurses in Charge of COVID-19 Screening at General Hospitals in Korea
- Boo Young Ha, Yun-Sook Bae, Han Sol Ryu, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):66-79. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21166
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand and describe the experiences of nurses in charge of COVID-19 screening at general hospitals in South Korea.
Methods
Data were collected through individual in-depth interviews with 14 nurses who had been working for more than a month at a screening clinic operated by two general hospitals from May 11 to July 20, 2021. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis.
Results
As a result of analysis, four theme clusters were extracted from nurses’ experiences, as follow: the role of the hospital gatekeeper entrusted with managing the COVID-19 pandemic, struggling to maintain the protective barrier, boundlessness like a Mobius strip, and driving force to endure as a nurse in charge of COVID-19 screening.
Conclusion
The results of this study provide a deeper understanding of the lives of screening clinic nurses who are struggling with the COVID-19 situation. The results are expected to be useful in providing basic data for improving the infection control system and response strategies that can be applied to nursing practice in other pandemic situations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Moderating Effect of Calling in the Relationship between Post-Traumatic Stress and Turnover Intention of Nurses Who Cared for COVID-19 Patients
Min Ju Woo, Bu Kyung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 75. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experience of Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in Residential Treatment Centers: A Qualitative Study
Jung Hwan Heo, Heeje Yun, Yeong Hun Park
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 226. CrossRef - Improving Emerging Infectious Disease Control Based on the Experiences of South Korean Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Systematic Review
Ha-Young Park, In-Sun Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - The impact of nurse’s sense of calling, organizational commitment, job stress, and nursing work environment on patient safety management activities in comprehensive nursing care service units during the covid-19 pandemic
YeJi Lee, Won Ju Hwang
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses’ intention to care of COVID-19 patients in hospitals dedicated to infectious disease in South Korea: application of the theory of planned behavior and verification of the moderating effect of ethical nursing competence
Mira Mo, Seongmi Moon, Eun Kyeung Song
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 584. CrossRef - Influence of Job Stress and Resilience on Burnout of Clinical Nurses Working in Small and Medium-Sized Hospital: Focusing on Comparing National Safety Hospital and COVID-19 Dedicated Hospital
Su-Young Jang, Young Ko
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(2): 65. CrossRef
- The Moderating Effect of Calling in the Relationship between Post-Traumatic Stress and Turnover Intention of Nurses Who Cared for COVID-19 Patients
- 1,615 View
- 18 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Collaborative Disaster Governance Recognized by Nurses during a Pandemic
- Dahae Rim, Hyunsook Shin, Hyejin Jeon, Jieun Kim, Hyojin Chun, Hee Oh, Soonyoung Shon, Kaka Shim, Kyung Mi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):703-719. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21163
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
We aimed to identify collaborative disaster governance through the demand and supply analysis of resources recognized by nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
We used a descriptive study design with an online survey technique for data collection. The survey questions were developed based on focus group interviews with nurses responding to COVID-19 and expert validity testing. A 42-question online survey focusing on disaster governance was sent to nurses working in COVID-19 designated hospitals, public health offices, and schools. A total of 630 nurses participated in the survey. Demand and supply analysis was used to identify the specific components of disaster governance during a pandemic situation and analyze priority areas in disaster governance, as reported by nurses.
Results
Demand and supply analysis showed that supplies procurement, cooperation, education, and environment factors clustered in the high demand and supply quadrant while labor condition, advocacy, emotional support, and workload adjustment factors clustered in the high demand but low supply quadrant, indicating a strong need in those areas of disaster governance among nurses. The nurses practicing at the public health offices and schools showed major components of disaster governance plotted in the second quadrant, indicating weak collaborative disaster governance.
Conclusion
These findings show that there is an unbalanced distribution among nurses, resulting in major challenges in collaborative disaster governance during COVID-19. In the future and current pandemic, collaborative disaster governance, through improved distribution, will be useful for helping nurses to access more required resources and achieve effective pandemic response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Effectiveness of a Basic Epidemiological Investigation Simulation Program of Emerging Respiratory Infectious Diseases for Nursing Students: Application of Standardized Patients
Jiyun Park, Gye Jeong Yeom
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2023; 34: 267. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef
- Development and Effectiveness of a Basic Epidemiological Investigation Simulation Program of Emerging Respiratory Infectious Diseases for Nursing Students: Application of Standardized Patients
- 1,377 View
- 31 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Untact Visit Service Development Based on an Application Reflecting the Circumstances during COVID-19: Focusing on Utilization in the Pediatric Intensive Care Units
- Dahae Woo, Hanui Yu, Hyo Jin Kim, Minyoung Choi, Dong Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):573-584. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an untact visit service based on an application that can be utilized in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) during COVID-19.
Methods
This study adopted the double diamond process of service design comprising the discovery, defining, and development stages.
Results
We developed an untact visit service based on an application that considered the child’s status, schedule, photo, and video messages, and so on. Moreover, we derived a service flow regarding the required roles and the type of flow shown between each stakeholder.
Conclusion
Considering the ongoing pandemic, the untact visit service is designed to increase rapport and participation of parents, share the child’s information in real-time, and provide one-stop service without increasing healthcare providers’ work. It will be a useful visit service that can be applied and evaluated in various hospital settings and the PICU. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting pediatric nurses’ development of partnerships with parents of hospitalized children: An evaluation based on the stress-coping adaptation model
In Young Cho, So Hyoung Hong, Ji Yeong Yun
Journal of Child Health Care.2025; 29(1): 53. CrossRef - Correlation between oral health knowledge, demand for remote education tools, and self-efficacy among parents of children and adolescents
Min-Ji Park, Herry Novrinda, Jae-Young Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2025; 25(1): 69. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Family-centered Care Application for Intensive Care Unit Families Based on the Facilitated Sensemaking Model : Focusing on Family Satisfaction, Family Stress, and Self-Efficacy
Yun Ha Oak, Eun Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(2): 1. CrossRef - Experiences of Family Members With Visitation Prohibition for Critically Ill Patients
Sunjung Kim, Sunghee H. Tak
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 46(11): 854. CrossRef - Factors influencing neonatal intensive care unit nurses' parent partnership development
Eun Kyoung Kim, In Young Cho, Ji Yeong Yun, Bobae Park
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2023; 68: e27. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - Relationship between parental stress and post‐traumatic stress disorder: The moderating effect of visitation restrictions in paediatric intensive care units during COVID‐19
Young Il Cho, Hyo Jin Kim, Dong Hee Kim
Nursing in Critical Care.2023; 28(5): 808. CrossRef - Need for Information and Communication Technology during COVID-19: An Exploratory Study Using Nurses’ Activity Diaries
Hyeongsuk Lee, Dongmin Lee, Seungmin Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2023; 29(3): 256. CrossRef - Effects of a Noncontact Visit Program in the NICU for the Prevention of COVID-19
Hye Young Ahn, Hee Jee Jo, Hyun Jeong Ko
Healthcare.2023; 11(15): 2152. CrossRef - The Development of Automated Personalized Self-Care (APSC) Program for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 535. CrossRef
- Factors affecting pediatric nurses’ development of partnerships with parents of hospitalized children: An evaluation based on the stress-coping adaptation model
- 1,629 View
- 28 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- A Phenomenological Study of the Lived Experience of Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in Korea
- Hee Oh, Na Kyoung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):561-572. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to understand nurses’ lived experiences of caring for patients with COVID-19.
Methods
The phenomenological research method was used. The study participants were 16 Korean nurses who had experiences in caring for patients with COVID-19 in clinical settings. Data was collected using one-on-one in-depth interviews, from June 30 to September 30, 2020. During the interview, the quarantine rules were observed.
Results
The study derived four themes clusters and thirty-eight sub themes. Four theme clusters were identified, i.e., ‘a repetitive sense of crisis’, ‘enduring a drastic change,’ ‘sacrifice of personal life,’ and ‘pride in nursing’. The nurses’ experiences of caring for patients with COVID-19 were an uneasy, unfamiliar, and threatening experiences for an individual, but it is an opportunity for a nursing organization to renew. Accordingly, it was found that nurses faithfully fulfill their individual roles with a vocation and responsibility.
Conclusion
The study provides an in-depth understanding of the situational, psychological, and environmental aspects of challenges facing nurses in the pandemic situation. Based on the findings, institutional follow-up measures should be provided to establish support systems for better nursing care. In addition, studies are needed to track nurses' experiences in the prolonged COVID-19 situation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Death Attitude, Self-esteem, and Perceived Risk of Respiratory Infectious Diseases on Death Anxiety among Nurses in COVID-19 Wards
Yeon Hee Jeong, Hun Ha Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(1): 5. CrossRef - Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(2): 236. CrossRef - Development of Standard Operating Procedures for Infectious Disease Disaster Response in Healthcare Institutions
Kyungah Woo, Sungmo Jung, HyeMin Byun, Keunhee Yoo, Eunkyoung Yun
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2025; 31(1): 46. CrossRef - Experiences of Person‐Centred Care Among Nurses in COVID‐19 Wards: A Qualitative Study
Myoungsuk Kim, Yongmi Lee, Hyun‐Ju Kang
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses’ Experience of Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in Residential Treatment Centers: A Qualitative Study
Jung Hwan Heo, Heeje Yun, Yeong Hun Park
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 226. CrossRef - Terminal Care Performance of Nurses Caring for COVID‐19 Patients: A Cross‐Sectional Descriptive Study
Juyeon Oh, Dong‐Hee Kim, Yujin Kim
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experiences of Nurses Working as Helpers in a Dedicated COVID-19 Ward of a Certified Tertiary Hospital
Eun Hyang Park, Hee Kyung Chang
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(2): 93. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Non-Contact Nursing Experiences of Clinical Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 446. CrossRef - The lived experiences of operating room nurses from the surgery on COVID-19 patients: a phenomenological study
Behzad Imani, Mehrnush Mostafayi, Shirdel Zandi
Perioperative Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Delphi Study on the Changes in Work, Organizational Culture, and Health Issues of Nurses at Tertiary Hospitals in South Korea during the COVID‐19 Pandemic
MiRa Yun, WonJong Kim, Boas Yu, Eun-Hi Choi, Paolo C. Colet
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses’ Experiences with the Use of Electronic Nursing Record: A Qualitative Study
Yul Hee LEE, Min Sun KIM, Hee Jung KIM
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2024; 24(3): 110. CrossRef - Nurses’ healthy behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic and related factors
Eun-Kyoung Lee, Ji-Soo Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(1): 39. CrossRef - Nurses’ intention to care of COVID-19 patients in hospitals dedicated to infectious disease in South Korea: application of the theory of planned behavior and verification of the moderating effect of ethical nursing competence
Mira Mo, Seongmi Moon, Eun Kyeung Song
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety among nurses in caring for COVID-19 patients: a qualitative study
Sri Eka Wahyuni, Budi Anna Keliat, Herni Susanti, Besral Besral
Healthcare in Low-resource Settings.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving Emerging Infectious Disease Control Based on the Experiences of South Korean Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Systematic Review
Ha-Young Park, In-Sun Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Influences of Organizational Culture, Nursing Workplace Spirituality, and Nurses’ Perceived Health Status on Quality of Nursing Work Life according to Nursing Clinical Ladder
Hyun Sook Lee, Ju Hyun Jin, Ju Ri Lee, Hye Jin Kim, Yeon Jae Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(1): 31. CrossRef - The COVID-19 Pandemic Experience of A Cohort of Quarantined University Hospital Nurse Managers
Soon-Youl Lee, Suk Jung Han, Hee Jung Hong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(2): 205. CrossRef - Parenting Experience of Shift Nurses With Elementary School-Aged Children During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Phenomenological Study
Jeung-Im Kim, Mi-Youn Jang, A-Ri Song, Jung-Eun Yu, Myung-Sook Baik
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2023; 27(3): 154. CrossRef - Development of a Reward Scale for Hospital Nurses
Sun Hee Kim, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(5): 525. CrossRef - Treatment of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and cross‐infection in dental clinics in Korea
Na‐Young Lee, Han‐Na Kim
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2023; 21(2): 438. CrossRef - Influence of Job Stress and Resilience on Burnout of Clinical Nurses Working in Small and Medium-Sized Hospital: Focusing on Comparing National Safety Hospital and COVID-19 Dedicated Hospital
Su-Young Jang, Young Ko
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(2): 65. CrossRef - Beyond the case numbers: Social determinants and contextual factors in patient narratives of recovery from COVID-19
Danielle Hitch, Elle Deféin, Melanie Lloyd, Bodil Rasmussen, Kimberley Haines, Eleanor Garnys
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health.2023; 47(1): 100002. CrossRef - Experiences of Caring for Cohort-Isolated Patients among Nurses in Locked Psychiatric Units
Hyeran An, Kyungmi Kim, Jongeun Lee, Sunhwa Won
Healthcare.2023; 11(19): 2650. CrossRef - Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 584. CrossRef - Experiences of Psychiatric Nurses Working in a Closed Psychiatric Unit during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 374. CrossRef - Burnout among Nurses in COVID-19 Designated Units Compared with Those in General Units Caring for Both COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Patients
Kyung Ah Woo, Eun Kyoung Yun, JiSun Choi, Hye Min Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 374. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Organizational Commitment of Nurses at an Infectious Disease Hospital of COVID-19
Su Hee Moon, Min Hye Kim, Doo Young Kim, Yoon Ji Ryu, Soo Joung Lee, Jin Nyoung Jang, Mi Yeoul Jung, Yoon Ju Cho, Hyo Jeong Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(2): 39. CrossRef - The COVID-19 Correspondence Work Experience of Community Health Practitioners
Jae-Hyun Ha, Hyun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(2): 139. CrossRef - Exploring the Experiences of Nurse Managers during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hyunjin Jang, Eun-Mi An, Ki-Eun Kim, Yoounjoong Jung, Youjung Choi, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 460. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nursing Intention for Patients with Emerging Infectious Diseases among Nurses in Hospitals Dedicated to COVID-19: A Focus on the Mediating Effects of Job Crafting
Yu Na Lim, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 105. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experiences of Care for Patients in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection Wards during the Early Stages of the Pandemic
Nanhui Kim, Youngran Yang, Junhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(1): 109. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Educational Needs and Nursing Intention Regarding COVID-19 Patient Care among Undergraduate Nursing Students
Eun-Joo Ji, Eun-Kyung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15671. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Post-traumatic Growth of Nurses at Nationally Designated Infectious Disease Hospital
Ji Eun Oh, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 499. CrossRef
- Effects of Death Attitude, Self-esteem, and Perceived Risk of Respiratory Infectious Diseases on Death Anxiety among Nurses in COVID-19 Wards
- 3,606 View
- 91 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


