Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development and evaluation of the Trauma-nursing Education and Skill Support program to enhance trauma nursing competencies: a quasi-experimental study
- Tae Yeong Yang, Myung Jin Jang, Ki Ung Kim, Min So, Mi Na Choi, Eun Jung Lee, Jin Su Jo, Ji Yun Lee, Kwang Kyun Lim, Kyoung Mi Kim, Hae Jun Baek, Sun Ho Wang, Jin Oh Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):67-80. Published online February 24, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of the Trauma-nursing Education and Skill Support (TESS) program based on the ADDIE model (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation model). The program was designed to enhance trauma nurses’ clinical competencies, including trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability, through the integration of theoretical education and simulation-based practice.
Methods
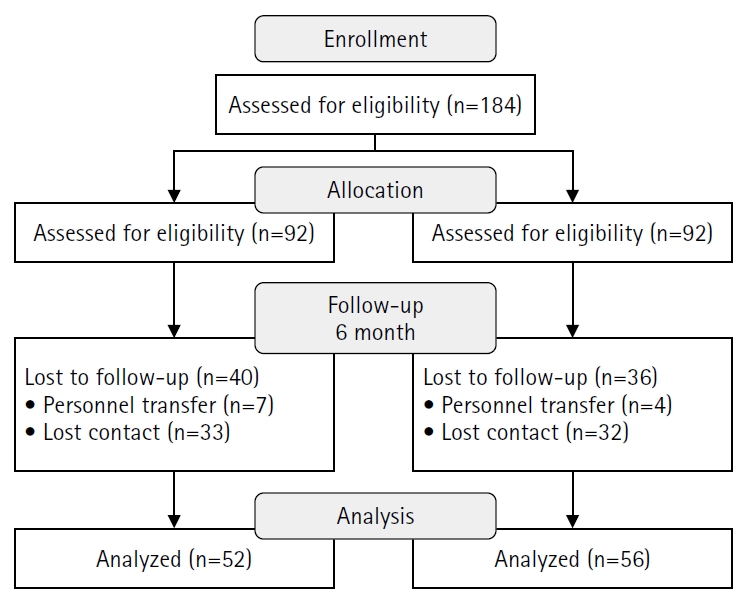
A quasi-experimental study using a non-equivalent control group pretest–posttest design was conducted. Participants included 108 trauma nurses from regional trauma centers, military trauma centers, and emergency care facilities, who were assigned to an experimental group (n=52) or a control group (n=56). The TESS program consisted of a 2-day, 14-hour blended-learning course that included eight lecture sessions and four simulation-based practice stations. Data were collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at 6 months using validated instruments measuring trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance was used for data analysis.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability compared with baseline (all p<.001). These improvements were sustained at 6 months, although trauma-related knowledge scores showed a slight decline compared with immediate posttest levels. Between-group analyses confirmed significant group-by-time interaction effects for all outcomes: trauma-related knowledge (η2=0.12, p<.001), self-efficacy (η2=0.09, p=.002), and problem-solving ability (η2=0.08, p=.003).
Conclusion
The TESS program effectively enhanced trauma nurses’ trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability, with effects sustained for up to 6 months. Incorporating blended learning and simulation-based training into standardized trauma nursing education may strengthen clinical competencies and ultimately contribute to improved patient outcomes.
- 70 View
- 6 Download

- Development and psychometric testing of the Perceived Postoperative Care Competency Scale for Nursing Students: a methodological study
- Perihan Şimşek, Gül Çakir Özmen, Melek Ertürk Yavuz, Sema Koçan, Dilek Çilingir
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):81-97. Published online February 24, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
To improve the quality of postoperative care and promote recovery after surgery, it is important that nursing education is competency-based and that competency assessment is an integral part of the educational process. The purpose of this study was to develop a tool to evaluate nursing students’ perceived competence in postoperative care.
Methods
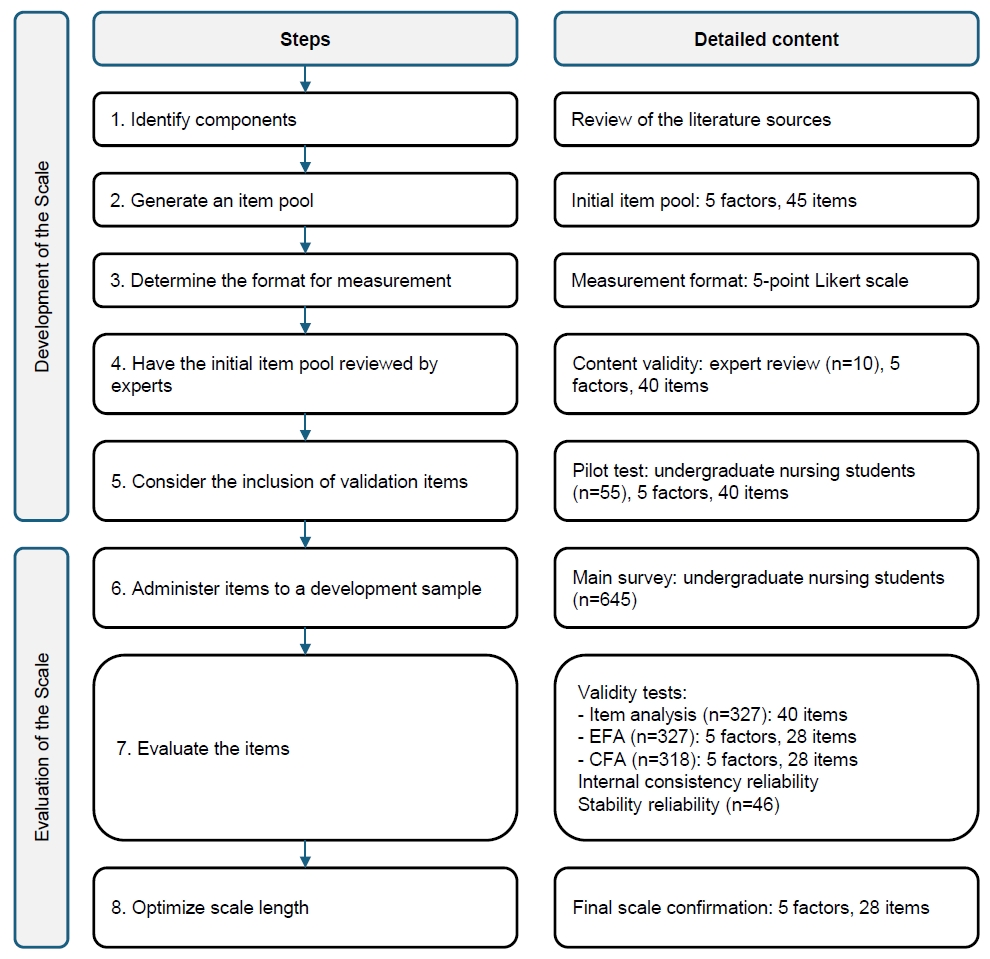
This cross-sectional methodological study followed DeVellis’s scale development steps and was conducted between December 2022 and March 2023. In this study, 892 students were invited and 703 responded. After exclusions, data from 645 students were analyzed to examine the psychometric structure of the scale using exploratory factor analysis (n=327) and confirmatory factor analysis (n=318). Reliability was assessed by calculating Cronbach’s α coefficients and by test–retest measurement (n=46).
Results
The proposed scale was confirmed to consist of five factors and 28 items (χ2/degrees of freedom=2.25, root mean square error of approximation=.06, normed fit index=.90, and goodness-of-fit index=.85). Cronbach’s α was .97 for the total scale. The data demonstrated high test–retest stability (intraclass correlation coefficient=.88). The scale developed and psychometrically tested in this study revealed a five-factor structure: legal responsibilities and ethical principles (seven items), postoperative nursing care (seven items), interpersonal relations and communication (four items), leadership (six items), and education and professional development (four items).
Conclusion
The scale, which demonstrated very good psychometric properties, would be helpful in assessing perceived postoperative nursing competence among nursing students. This may help students graduate with the necessary knowledge and skills required for postoperative care. However, further research involving larger samples and more diverse cultural contexts is needed to enhance the generalizability of the scale.
- 51 View
- 1 Download

- Psychometric testing of the Korean version of the Undergraduate Nursing Student Academic Satisfaction Scale: a methodological study
- Da-In Park, Joohee Shim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):51-66. Published online February 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to translate, cross-culturally adapt, and evaluate the psychometric properties of the Korean version of the Undergraduate Nursing Student Academic Satisfaction Scale (K-UNSASS).
Methods
The K-UNSASS was developed using Brislin’s team-based translation–back-translation approach, with semantic and conceptual equivalence examined. Face validity was assessed, and a pilot test was conducted in November 2022. Content validity was evaluated by an expert panel. Formal data collection was conducted from December 2022 to January 2023. Structural validity was examined using exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients.
Results
A total of 482 full-time nursing students, most of whom were in the fourth year of their nursing program, were included in the psychometric testing. Construct validity supported a four-factor structure accounting for 65.9% of the total variance. After removal of three items with unsatisfactory factor loadings, a 45-item K-UNSASS was established. Confirmatory factor analysis of the 45-item K-UNSASS demonstrated an acceptable model fit, and both Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients were .97.
Conclusion
The K-UNSASS demonstrates acceptable reliability and validity for assessing academic satisfaction among Korean nursing students. As a culturally relevant instrument, it supports educational improvement through targeted strategies and program evaluation.
- 159 View
- 4 Download

- Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
- Jeung-Im Kim, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park, Ju-Eun Song, Eunjung Ryu, JuHee Lee, YeoJin Im
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):39-50. Published online February 5, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to address the shift toward competency-based education and the planned 2028 “Integrated Nursing” National Licensing Examination (NLE), this study aimed to establish structural alignment among NLE domains, the seven integrated nursing competencies (INCs), and curriculum goals, with a particular focus on implementing symptom-based clinical reasoning (SBCR).
Methods
This Delphi-based methodological study included seven content experts for content validity index (CVI) assessment and 24 nursing education experts who participated in a consensus workshop. The item-level CVI and the scale-level CVI/average were calculated to confirm the linkage between INCs and NLE domains. In addition, qualitative analysis of workshop materials and meeting records was conducted to derive 10 integrated learning topics and to develop an SBCR educational model for the key symptom of headache, grounded in Miller’s Clinical Competence Pyramid (levels 2–4).
Results
The analysis confirmed the validity of integrating the INCs within the overall curriculum structure. The resulting framework delineates staged learning objectives and core clinical questions designed to systematically enhance clinical reasoning, promote safe nursing practice, and support professional reflection within a unified curriculum.
Conclusion
This study provides a practical foundation for nursing curriculum redesign by facilitating a transition from fragmented, subject-based instruction to a holistic, patient-centered SBCR model. This approach aligns with the requirements of the integrated NLE and is expected to contribute to meaningful improvements in actual clinical competency.
- 161 View
- 11 Download

- Lessons from the US Advanced Practice Registered Nurse system
- Eun-Ok Im, Dongmi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):492-505. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This review compares the development of South Korea’s Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) system the well-established APRN system in the United States and provides recommendations for future improvements to the APRN system in South Korea.
Methods
To compare the APRN systems between the two countries, an integrative literature review was conducted using multiple databases and professional nursing organization documents and reports from both the United States and South Korea.
Results
Issues were identified in five major domains: (1) research evidence, (2) education and training, (3) the scope of practice, (4) financial mechanisms, and (5) public awareness and acceptance.
Conclusion
Recommendations are made in four areas: (1) building evidence to support APRN programs; (2) strengthening APRN education; (3) establishing legal support and reimbursement mechanisms; and (4) improving public awareness and acceptance of APRNs.
- 1,059 View
- 154 Download

- Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
- Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):568-583. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25106
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to propose strategies for strengthening the nursing workforce by expanding their roles as advanced practice providers (APPs).
Methods
A mixed-methods approach was employed, consisting of five focus group interviews (FGIs) with 30 healthcare professionals (including 10 physicians) and a two-round Delphi survey with 49 experts. The FGIs explored practical insights from clinical settings, while the Delphi process validated and prioritized strategic recommendations through expert consensus.
Results
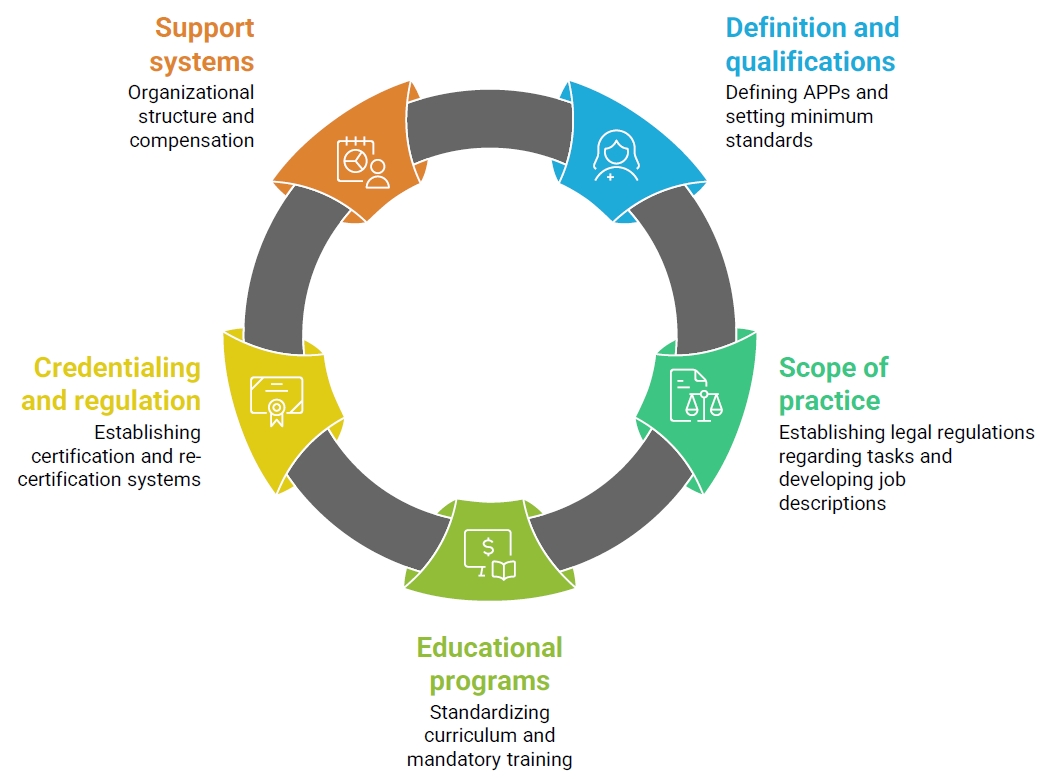
Four major themes emerged from the FGI analysis: (1) utilization of diverse APPs to ensure quality care, (2) expanding the scope of practice of APPs, (3) requirements to ensure the quality of APPs, and (4) strategies for sustainable management of the APP workforce. Building on these findings, the Delphi survey identified five strategic domains: “definition and qualifications,” “scope of practice,” “educational programs,” “credentialing and regulation,” and “support systems.” Key areas of consensus included the need for mandatory clinical experience and specialty training, legal clarification of role boundaries, standardized curricula with certification mechanisms, and institution-led support systems such as task-specific job descriptions and recredentialing processes.
Conclusion
To effectively strengthen APP roles, it is essential to build on the existing advanced practice nurse (APN) framework, which already includes structured curricula and national certification. Furthermore, integrative strategies should be developed to incorporate experienced clinical nurses without APN licenses into the APN system.
- 1,609 View
- 164 Download

- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
- Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):557-567. Published online November 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study compared trends in research designs and keywords by analyzing the abstracts of four major nursing journals over the past decade, focusing on the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing (JKAN) in comparison with the International Journal of Nursing Studies (IJNS), Journal of Advanced Nursing (JAN), and Japan Journal of Nursing Science (JJNS).
Methods
A bibliometric analysis was conducted, encompassing 5,522 abstracts published between 2015 and 2024. Research designs were first classified as “quantitative,” “qualitative,” or “other,” and then further sub-classified based on international evidence-based frameworks. Text preprocessing was also conducted, and term frequency–inverse document frequency was applied to evaluate keyword importance. The 2015–2019 and 2020–2024 periods were compared to examine changes in both research designs and keyword importance.
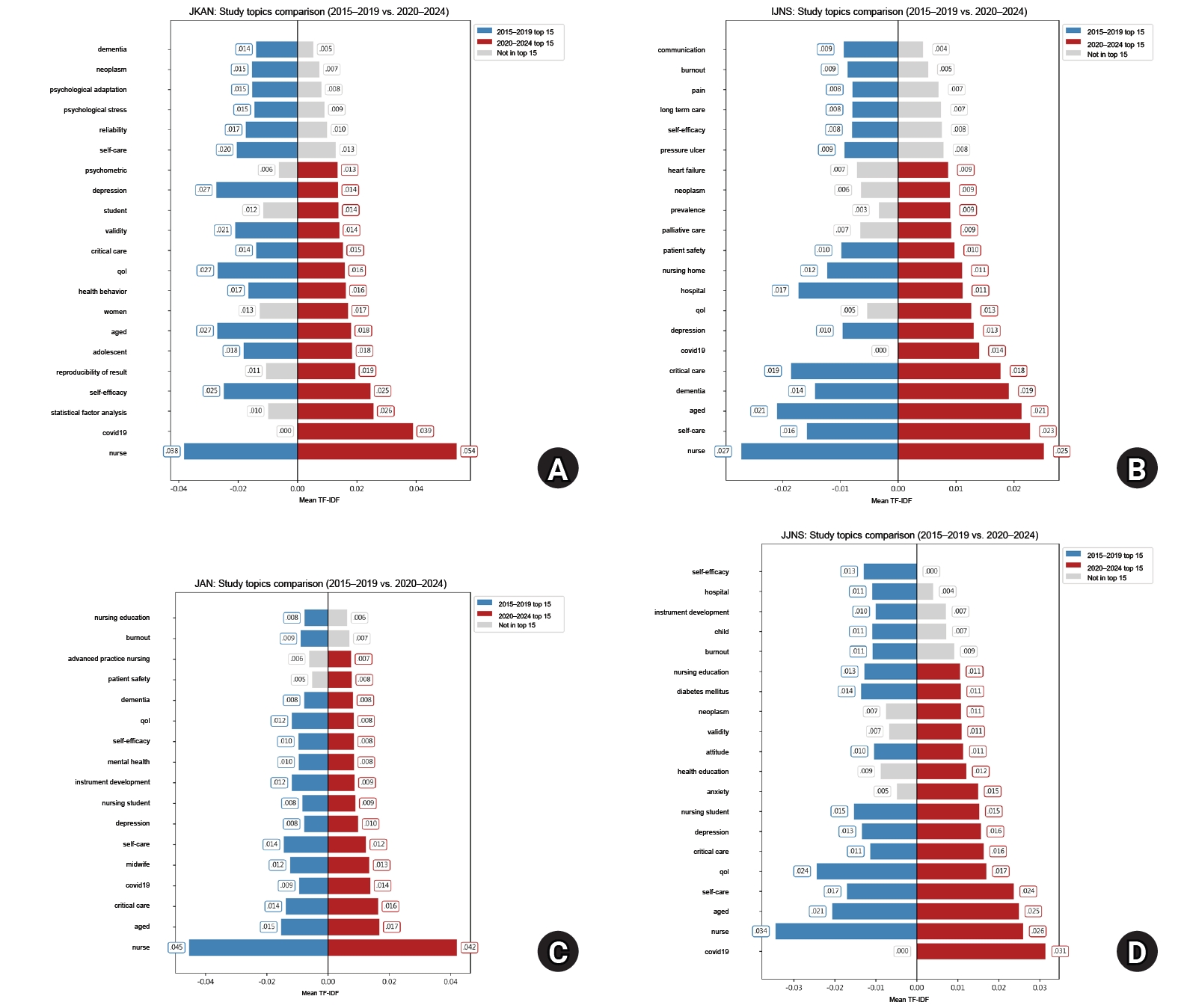
Results
Compared to IJNS, JAN, and JJNS, JKAN published more instrument development and analytic studies but fewer randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews. Over time, the number of instrument development and mixed-methods studies in JKAN increased, while high-evidence designs remained scarce. Keyword analysis showed JKAN’s emphasis on psychosocial themes such as self-efficacy, quality of life, and depression, whereas the other journals more often highlighted policy- and institution-related topics. Across journals, COVID-19 and patient safety emerged as important themes after 2020.
Conclusion
JKAN demonstrates strengths in methodological diversity within quantitative research and in digital health–related analytics. However, high-evidence study designs and policy-oriented keywords are underrepresented in JKAN. Strategic expansion toward randomized controlled trials, systematic review, global and digital health, and policy-relevant research is recommended to strengthen JKAN’s international competitiveness.
- 943 View
- 115 Download

- Effects of presenteeism on turnover intention in clinical nurses through the serial mediating roles of missed nursing care and job satisfaction: a cross-sectional predictive correlational study
- Hyeonseon Cheon, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):584-597. Published online November 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the two-mediator serial mediation effect of missed nursing care and job satisfaction on the relationship between presenteeism and turnover intention in clinical nurses.
Methods
A cross-sectional predictive correlational study was conducted, and the participants were 208 clinical nurses working in advanced general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected from October 6 to November 7, 2023 using self-reported questionnaires, including general characteristics, presenteeism, missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 29.0 and PROCESS macro ver. 4.2.
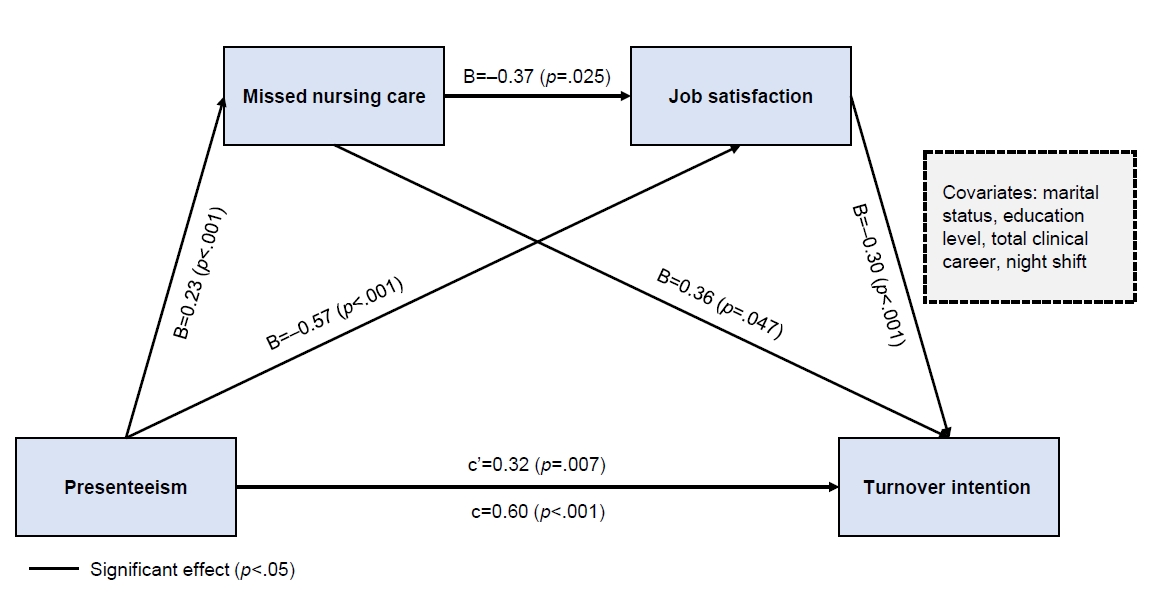
Results
Missed nursing care and job satisfaction exhibited a double mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. In addition, missed nursing care showed a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Job satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Presenteeism had a direct effect on missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Missed nursing care exerted a direct effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Job satisfaction had a direct effect on turnover intention.
Conclusion
To reduce nurses’ turnover intention, it is essential to develop and implement programs focused on preventing presenteeism. Additionally, organizational initiatives should prioritize active support for nurses’ health management, alleviating the shortage of nursing staff, augmenting job satisfaction, and improving the overall working environment.
- 1,537 View
- 217 Download

- Impact of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on parental anxiety and depression in severe hypospadias patients in China: a randomized controlled trial
- Ruijuan Wu, Lucai Jia, Biyu Ding, Ying Li, Yaqing Cao, Zhaojun Shi, Yanfang Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):327-341. Published online August 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the effects of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on alleviating perioperative and post-surgical anxiety and depression in parents of children with severe hypospadias.
Methods
Parents of children with severe hypospadias were recruited and randomly allocated into a control group (n=87), which received standard nursing care, and an intervention group (n=93), which was given an integrated disease-specific nursing intervention in addition to standard care. Parental anxiety and depression were measured using the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) at admission, discharge, and 6-month follow-up post-surgery.
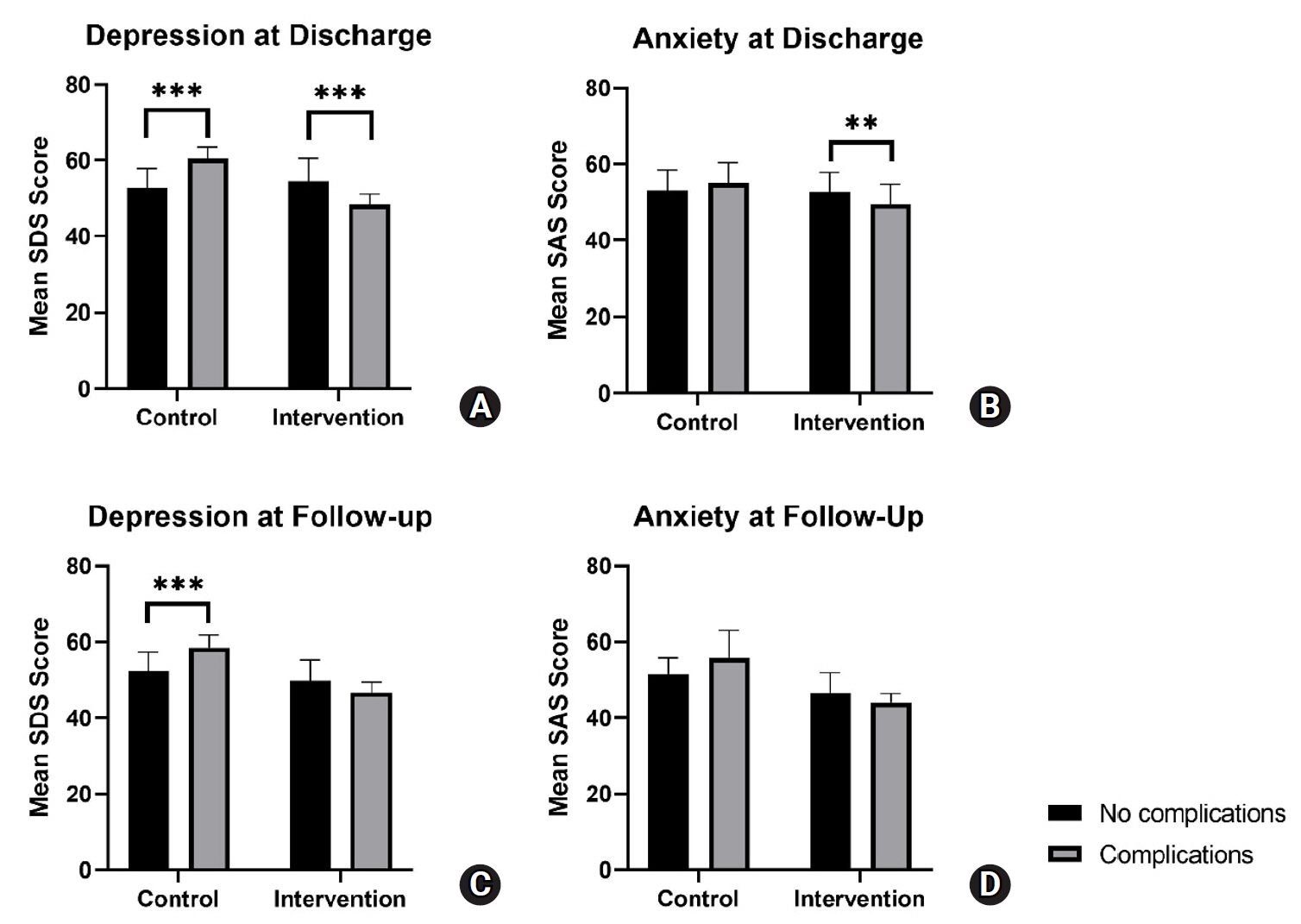
Results
A linear mixed-effects model showed that SAS and SDS scores in the intervention group decreased to a significantly greater extent over time, from admission to follow-up, compared to the control group. Post-hoc analysis showed a trend for increased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up for the control group. Meanwhile, the intervention group exhibited a trend for decreased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up.
Conclusion
The integrated disease-specific nursing model significantly alleviated parental anxiety and depression over time compared to standard care, highlighting its effectiveness in supporting families of children with severe hypospadias. Notably, the intervention appeared to mitigate the negative emotional impact of postoperative and follow-up complications, suggesting its potential as a targeted approach to improve both emotional well-being and overall care outcomes.
- 2,468 View
- 165 Download

- Research trends in generative artificial intelligence in nursing: a scoping review
- Myung Jin Choi, Myoung Hee Seo, Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):468-487. Published online August 5, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has yet to be comprehensively analyzed in the nursing literature. This study aimed to identify research trends in generative AI within the nursing field through a scoping review and propose strategies for its effective utilization in nursing.
Methods
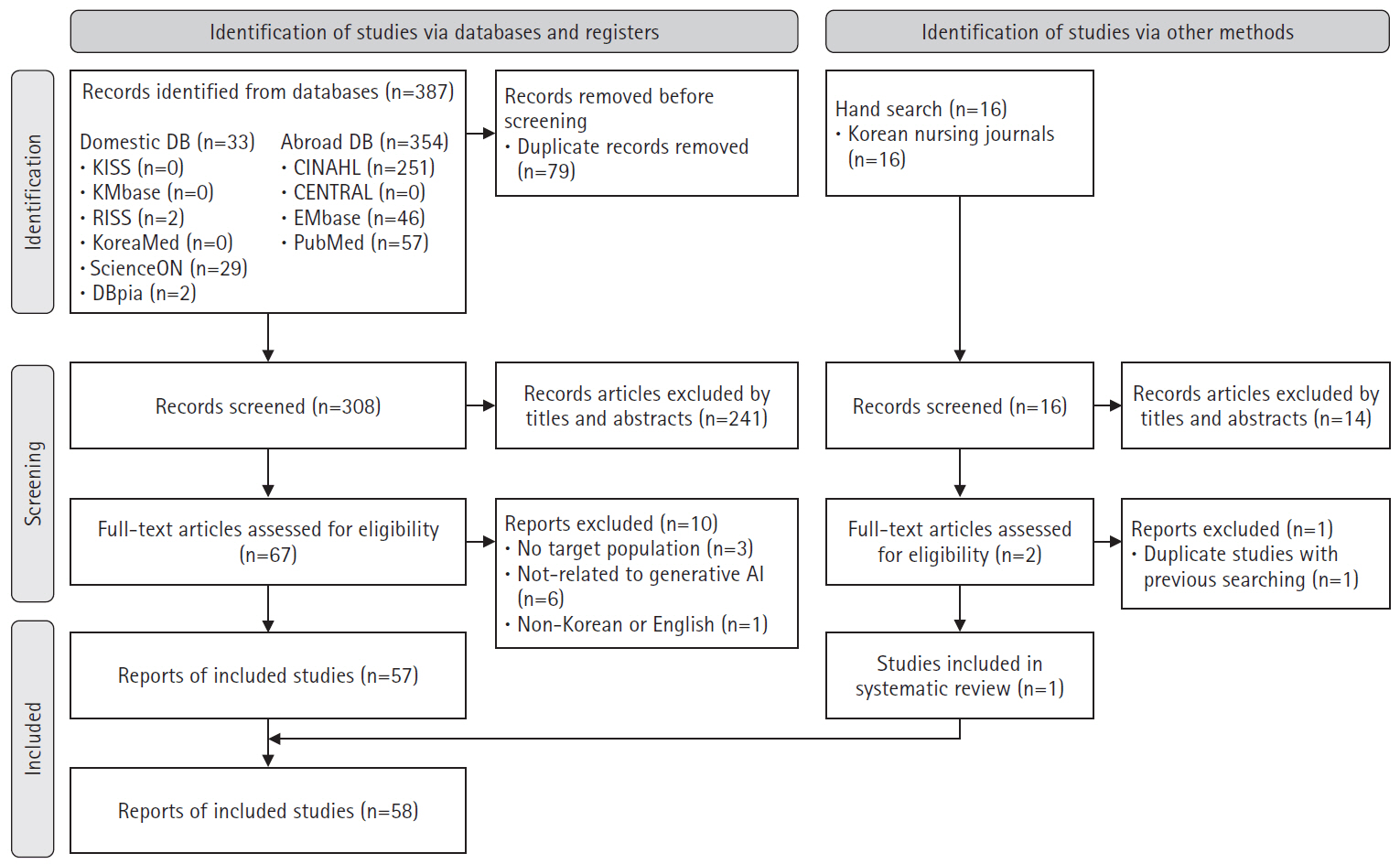
A scoping review was conducted following Arksey and O’Malley’s six-stage framework. The inclusion criteria included: (1) studies conducted in nursing; (2) research related to generative AI; and (3) original research articles, theses, communications, editorials, letters, or commentaries published in academic journals. Database used PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL, CINAHL, KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, DBpia, and 27 nursing-specific journals.
Results
In total, 403 studies were initially identified, and 58 were included in the final analysis. In the care domain, strengths included rapid information retrieval and improved nurse-patient communication, while limitations included the irreplaceable human element and low reliability. The administration domain had no relevant studies. In the research domain, generative AI exhibited strengths such as enhanced efficiency in the paper writing process and improved dissemination speed, but its weaknesses included lack of ethical and legal accountability and a risk of inaccurate or biased information. In the education domain, generative AI was effective in saving time in educational design and implementation, as well as supporting content creation, but challenges included algorithmic bias and risks of plagiarism.
Conclusion
This study identified potential benefits and limitations of generative AI across nursing domains. For effective application, it is essential to develop comprehensive guidelines and policies, provide user education and support, and create opportunities for nurses, educators, and students to learn about strengths and risks of generative AI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Sukyung Son, Eunyoung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(Special Is): 9. CrossRef
- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
- 6,924 View
- 505 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Media discourse on physician assistant nurses in South Korea: a text network and topic modeling approach
- Young Gyu Kwon, Daun Jeong, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Chan Woong Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):388-399. Published online July 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study quantitatively examined the portrayal of physician assistant (PA) nurses in Korean media by integrating text network analysis with latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) topic modeling.
Methods
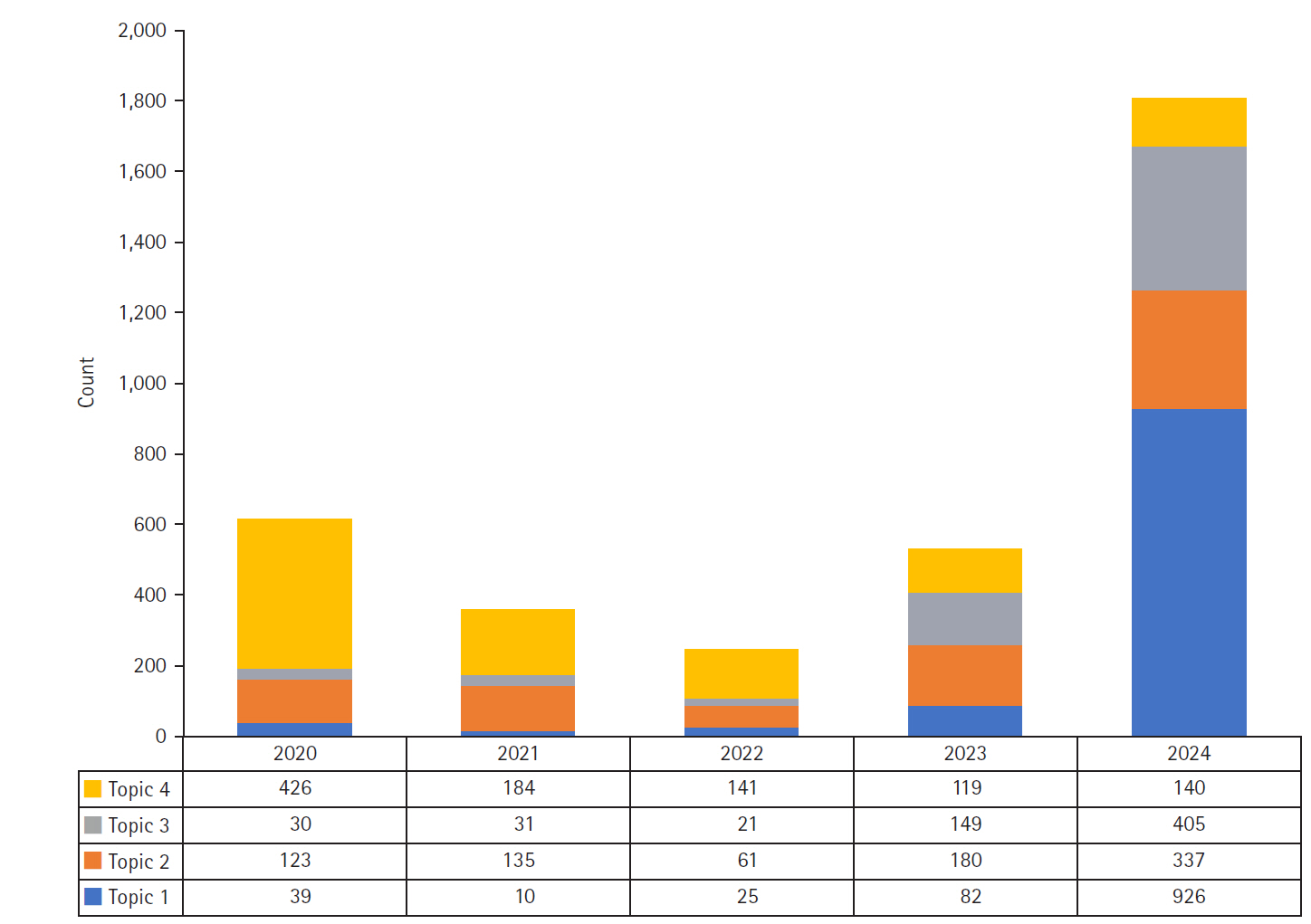
A total of 3,564 news articles published by nine major Korean media outlets between 2020 and 2024 were analyzed. Content analysis was conducted using term frequency-inverse document frequency calculations, network centrality analysis, and LDA topic modeling to extract key terms, map discourse structures, and identify latent topics.
Results
The analysis identified four primary topics in Korean media discourse: “healthcare workforce expansion policies” (30.4%), “hospital clinical practice and operational management” (23.5%), “institutionalization of the PA nursing role” (17.8%), and “COVID-19 response and public health crisis management” (28.3%). High-centrality keywords included “hospital,” “medical,” “patient,” “physician,” “government,” and “nurse,” indicating that the discourse primarily focused on clinical settings. Topic modeling revealed a major shift from pandemic-centered coverage in 2020 to a focus on healthcare workforce policy and PA nurse institutionalization in 2024, coinciding with the passage of the Nursing Act.
Conclusion
This study provides empirical evidence suggesting that the portrayal of PA nurses in Korean media discourse evolved from a peripheral regulatory issue to a central healthcare delivery solution, particularly in the contexts of workforce management, clinical practice, and crisis response. Our findings suggest that PA nurse institutionalization received broader attention when positioned as part of systemic healthcare improvements addressing concrete clinical needs. These results offer valuable insights for policymakers and administrators in framing and implementing workforce policy reforms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of role conflict and job stress on turnover intention among Korean physician assistant nurses: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Won Lee, Eun-Hi Choi, Ji-Sun Back
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of role conflict and job stress on turnover intention among Korean physician assistant nurses: A cross-sectional study
- 3,466 View
- 118 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A review of domestic and international contexts for establishing a communication platform for early-career nurse scientists
- Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Hye Young Kim, Mi Yu, Sun Joo Jang, Yeonsoo Jang, Sangeun Jun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):317-325. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
As nursing continues to advance through digital health, clinical specialization, and interdisciplinary research, early-career nurse scientists are central to advancing innovation. However, Korea lacks a structured platform to support their research, collaboration, and career development. This review aimed to identify the needs of early-career nurse scientists and examine international best practices to guide the creation of an effective communication platform.
Methods
This study involved a secondary analysis of the final report from the project “Establishment of a communication platform for young nursing scientists,” carried out by the Korean Society of Nursing Science. The report comprises data from focus group interviews with domestic graduate students and early-career researchers, a literature review of international communication and support systems, and a global policy analysis related to young nursing scientists. Based on this report, the present review synthesizes key findings and draws implications for the development of a communication platform in Korea.
Results
International examples, such as grant writing programs, mentoring initiatives, and digital collaboration hubs, showed positive outcomes in strengthening research capacity and promoting the professional growth of nurse scientists. Based on these findings, key considerations for platform development include: (1) establishing clear leadership and a participatory governance model; (2) providing demand-driven content such as research guides, mentoring, and mental health resources; (3) implementing mechanisms to ensure sustainability, content quality, and user data protection; and (4) designing an integrated platform that fosters synergy across research, policy development, education, and global networking.
Conclusion
A digital platform for early-career nurse scientists should function not merely as an information portal, but also as dynamic infrastructure for collaboration, mentorship, and growth. It is recommended that the Korean Society of Nursing Science spearhead this initiative, with governmental support, to enhance the research capacity and expand the global engagement of Korean nursing scientists.
- 2,373 View
- 80 Download

- Core domains for pre-registered nurses based on program outcomes and licensing competencies
- Soyoung Yu, Hye Young Kim, Jeung-Im Kim, JuHee Lee, Ju-Eun Song, Hyang Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):249-268. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify core domains for pre-registered nurses by comparing licensing competencies with program outcomes (POs) in undergraduate nursing education. This was accomplished in preparation for the transition of the Korean Nurse Licensing Examination (KNLE) from a tradition seven-subject format to a newly integrated, competency-based single-subject format that reflects current trends in nursing assessment.
Methods
A literature review and survey were conducted. From 828 studies retrieved via PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar using keywords such as “newly graduated registered nurses” and “competency OR competence,” 18 were selected according to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Documents from national and international nursing organizations were included to extract relevant licensing competencies. We also reviewed POs from all undergraduate nursing schools in South Korea to align educational outcomes with the identified core domains.
Results
The core domains identified were clinical performance and decision-making, professional attitudes and ethics, communication and interpersonal skills, leadership and teamwork, quality improvement and safety, health promotion and prevention, and information technology and digital health. These domains showed strong alignment with POs under the fourth-cycle accreditation standards.
Conclusion
It concludes the seven core domains will be appropriate for evaluating pre-registered nurses in the integrated KNLE. Based on the seven identified core domains, expert consensus should be sought in the next phase to support the development of integrated, competency-based test items grounded in these domains.
- 4,070 View
- 156 Download

- Effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study
- Sunmi Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):137-151. Published online February 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
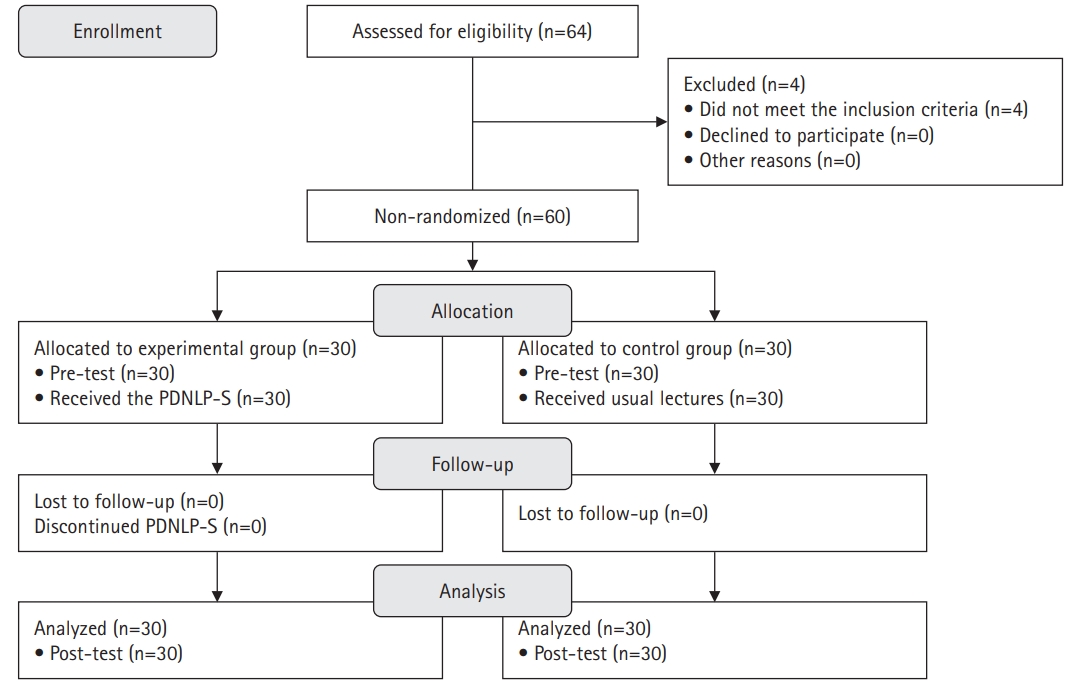
This study investigated the effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea.
Methods
A quasi-experimental study was conducted. The Practice-Driven Nursing Leadership Program for Students (PDNLP-S) was developed based on the ADDIE model (analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation). This quasi-experimental study design included 60 nursing students. The experimental group (n=30) participated in the PDNLP-S for 120-minute sessions over 5 weeks, while the control group (n=30) received usual lectures. The PDNLP-S included lectures, discussions, and individual and group activities to cultivate core nursing leadership competencies such as individual growth, collaboration, nursing excellence, creative problem-solving, and influence. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the Mann-Whitney U-test, and the independent t-test with IBM SPSS Windows ver. 26.0.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in self-leadership (t=3.28, p=.001), interpersonal relationships (t=3.07, p=.002), clinical performance (U=268.50, p=.004), and problem-solving abilities (t=2.20, p=.017) compared to the control group. No significant difference was observed in nursing professionalism (t=0.50, p=.311).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the PDNLP-S improved nursing students’ self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, and problem-solving abilities. The PDNLP-S can play a significant role in cultivating future nurse leaders by enhancing these nursing leadership competencies among nursing students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
Kexin Chen, Ling Yang, Jiajia Tu
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2025; Volume 18: 7539. CrossRef
- Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
- 7,375 View
- 300 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Nurses Professional Values Scale-3 for nursing students: a methodological study
- Eun Hee Yang, Mi Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):93-106. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to adapt the Nurses Professional Values Scale-3 (NPVS-3) for Korean nursing students and assess its reliability and validity.
Methods
The NPVS-3 was translated into Korean using forward and back translation with expert review. Data from 206 nursing students at four universities were analyzed to assess content, construct, discriminant, and criterion validity, as well as internal consistency.
Results
The Korean version (NPVS-3K) consisted of 21 items in three subscales: caring (eight items), activism (eight items), and professionalism (five items), explaining 60.9% of the total variance. For convergent validity, standardized coefficients for the items ranged from .56 to .81, construct reliability ranged from .89 to .95, and the average variance extracted ranged from .61 to .72. The model was validated by confirmatory factor analysis (χ2=526.00 [p<.001], χ2/degrees of freedom=2.83, standardized root mean residual=.03, goodness of fit index=.81, comparative fit index=.87, Turker Lewis index=.85). Discriminant validity was confirmed using a multi-trait and multi-item matrix. Criterion validity showed positive correlations between the three NPVS-3K factors and professional identity (factor 1: r=.40, p<.001; factor 2: r=.55, p<.001; factor 3: r=.43, p<.001). Internal consistency, as measured by Cronbach’s α, was .94 overall, with subscale values of .90 for caring, .92 for activism, and .78 for professionalism.
Conclusion
The NPVS-3K demonstrated satisfactory validity and reliability, establishing it as a valuable tool for assessing the professional values of Korean nursing students. Additionally, it can aid in developing educational strategies to strengthen these values, although further research is required to confirm its broader applicability.
- 4,318 View
- 349 Download

- The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience in Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity and Learning Burnout
- Liu Zhang, Qin Zhang, ShuWen Li, YuHong Li, GuoCui Wu, Ying Chen, YunNa Zhou
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):509-518. Published online November 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24044
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
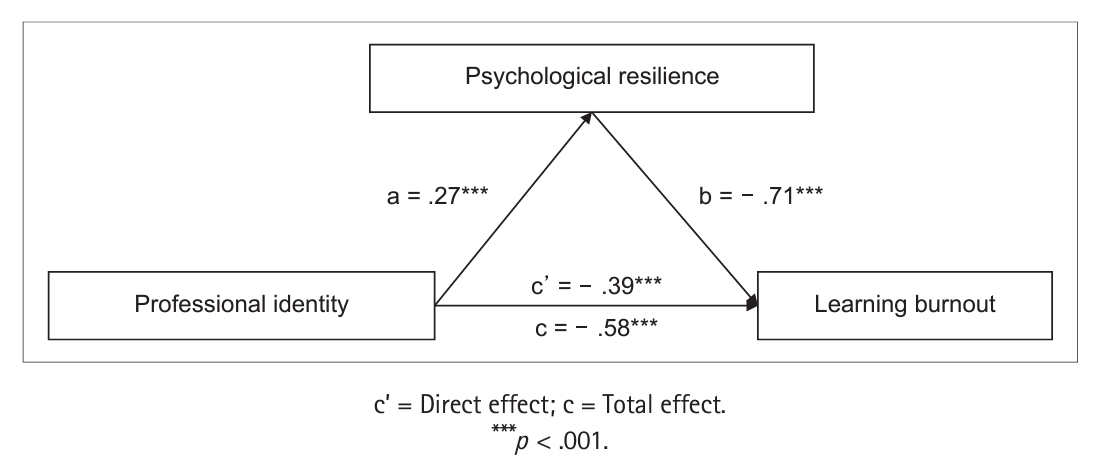
ePub Purpose This study investigated whether professional identity predicts learning burnout among Chinese nursing students, and whether resilience moderates this relationship.
Methods This cross-sectional study recruited 635 students from a nursing college at a medical university in Hefei, China. Data were collected using the professional identity questionnaire, learning burnout scale for college students, and 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale. Pearson’s correlation analysis was used to investigate the relationships between variables. The mediation effect was evaluated using linear regression and the bootstrap method in SPSS.
Results Nursing students exhibited intermediate learning burnout levels (score: 54.95 ± 10.42). Professional identity was positively correlated with psychological resilience (r = .42,
p < . 001), whereas learning burnout was negatively correlated with professional identity (r = - .54,p < . 001) and psychological resilience (r = - .57,p < . 001). Psychological resilience mediated the relationship between professional identity and learning burntout to the tune of 32.8%.Conclusion Psychological resilience mediates the relationship between professional identity and learning burnout. Thus, nursing educators can mitigate student burnout by developing their students' professional identities and psychological resilience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of creative anxiety on professional identity among master’s nursing students: a chain mediation effect of psychological resilience and achievement motivation
Yao Ding, Xiaolan Guo, Ruifeng Wang, Lu Xu, Shajie Hou, Fengjiao Chang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sense of Coherence and Perceived Academic Stress Among Nursing Students: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
David Ballester-Ferrando, Esther Cáceres-Malagelada, Carolina Rascón-Hernán, Teresa Botigué, Ana Lavedán, Olga Masot, Dolors Burjalés, Luis González-Osorio, Ximena Osorio-Spuler, Eva Serrat-Graboleda, Concepció Fuentes-Pumarola
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(8): 288. CrossRef
- The impact of creative anxiety on professional identity among master’s nursing students: a chain mediation effect of psychological resilience and achievement motivation
- 4,315 View
- 185 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Experiences of Patients and Their Families Receiving Medical Services Provided by Advanced Practice Nurses at Tertiary General Hospitals
- Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Su Jung Choi, Ji Eun Han, Eun Kyung Kwon, Jeong Hee Park, Jeong Hye Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):594-606. Published online November 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to understand and describe the experiences of patients and their families who have received medical services from advanced practice nurses in tertiary general hospitals in Korea.
Methods Data were collected through four focus group interviews with 20 patients and their families who had received medical services from advanced practice nurses for more than six months at four tertiary hospitals from November 29 to December 28, 2023. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using qualitative content analysis.
Results The four themes extracted from the experiences of patients and their families were as follows: unfamiliar medical personnel encountered during the treatment process, healthcare professionals who exhibited excellence, companions to light my way through the tunnel of illness, and an advanced practice nurse system that must be activated urgently.
Conclusion The study’s findings indicate that patients and their families view the care provided by advanced practice nurses as excellent, reliable, and holistic. Research suggests that advanced practice nurses are valuable healthcare professionals in team-based care. The findings suggest that hospitals should utilize an advanced practice nurse system to improve patient outcomes and ensure the quality of care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
Su Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 69. CrossRef - Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 568. CrossRef - Nurses' Patient Care Experiences in a Changing Healthcare Environment Following One Year of Healthcare Policy Conflict - A Focus Group Interview
Eun Hee Kang, Yunhyung Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 280. CrossRef
- Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
- 4,478 View
- 266 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Effectiveness of Progressive Simulation Education Program on Medication Safety for Nursing Students
- Se-Young Jung, Eun-Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):563-576. Published online October 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to develop and verify a progressive simulation education program aimed at enhancing nursing students’ medication safety competency.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was adopted. The participants were 40 third-year nursing students with no prior simulation education experience, comprising 20 each in the experimental and control groups. The experimental treatment utilized a hybrid simulation approach incorporating both full-body mannequins and standardized patients and was, conducted over three sessions with durations of 65, 80, and 95 minutes for the first, second, and third sessions, respectively, for a total of 240 minutes. The program was constructed based on Jeffries’ simulation model.
Results The levels of medication safety competencies, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving abilities of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group.
Conclusion Our results confirm that the program effectively improves nursing students’ medication safety competence, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Therefore, this program can serve as a basis for developing educational strategies related to medication safety for nursing education institutions. Furthermore, the program is anticipated to have a positive impact on novice nurses’ education and practice in clinical settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
Jiyoung Kim, Yeji Kim, Hyunji Park, Jiyeong Won, Jiwon Yun, Yuran Lee
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2026; 111: 101899. CrossRef
- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
- 4,791 View
- 414 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Legal and Practical Solutions for the Expanding the Roles of Medical Support Staff Nurses
- Su Jung Choi, Min Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):300-310. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24075
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Medical support staff nurses have traditionally performed various supportive tasks for physicians, often extending beyond standard nursing roles. Despite these long-standing practices, there is a notable lack of official recognition and legal protection for these expanded responsibilities, leading to increasing legal concerns. Therefore, there is a need for proposing a rational solution to address these issues.
Methods
The number of medical support staff nurses is rising, particularly as they fill gaps left by the 2024 resident physician strike. The study focuses on identifying potential challenges arising from this shift and developing strategic improvements to address these challenges effectively.
Results
This study proposed legally expanding the scope of nursing duties and creating a robust system for training and certifying nurses to handle these responsibilities effectively, by integrating these roles within the advanced practice nurse (APN) framework.
Conclusion
Integrating these roles within the framework of APN can offer a sustainable and legally sound solution to the ongoing healthcare crisis, ensuring patient safety and safeguarding healthcare workers’ legal rights. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of role conflict and job stress on turnover intention among Korean physician assistant nurses: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Won Lee, Eun-Hi Choi, Ji-Sun Back
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
Su Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 69. CrossRef - Role Transformation and Adaptation of Physician Assistants during the 2024 Medical Workforce Shortage: A Phenomenological Study
Tae Yeong Yang, Nahyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 259. CrossRef - Effects of Role Conflict, Work Environment, and Meaning of Work on Job Embeddedness among Physician Assistants
Kwang Hoon Seo, Tae Yeong Yang, Nam Gyu Park, Jung Eun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 249. CrossRef - Media discourse on physician assistant nurses in South Korea: a text network and topic modeling approach
Young Gyu Kwon, Daun Jeong, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Chan Woong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 388. CrossRef - Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 400. CrossRef - Predictors of end-of-life care among emergency nurses: A cross-sectional study in Korea
Ji Seon Lee, Sook Jung Kang
Australasian Emergency Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Clinical Practice Nurses' Self-Leadership, Role Conflict, and Practice Environment on Patient Safety Competency
Jeong Hwa Heo, Ji Hyun Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 458. CrossRef - Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 568. CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Novice Nursing Practitioner Role Transition Scale
Eun Sook Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Su Jung Choi, Onam Ok, Genehee Lee, Ahyeong Song
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(5): 462. CrossRef - Nurses' Patient Care Experiences in a Changing Healthcare Environment Following One Year of Healthcare Policy Conflict - A Focus Group Interview
Eun Hee Kang, Yunhyung Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 280. CrossRef
- Impact of role conflict and job stress on turnover intention among Korean physician assistant nurses: A cross-sectional study
- 5,266 View
- 301 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- An Exploratory Study on Non-Contact Nursing Experiences of Clinical Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):446-458. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to understand the non-contact nursing experiences of clinical nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
A qualitative research design applying thematic analysis was used. The participants were purposive sampled from three institutes: a tertiary hospital, a general hospital, and a residential treatment center in Seoul. Data were collected between December 2021 and January 2022 through individual in-depth interviews with 12 clinical nurses. The data were analyzed using Braun and Clarke’s method to identify the meaning of the participants’ experiences.
Results
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the fields where the participants performed non-contact nursing included intensive care units and isolation wards of hospitals, a residential treatment center, and home cares. Their tasks in non-contact nursing commonly involved remote monitoring using digital devices or equipment, consultation and education. From their experiences performing tasks in these fields, the four theme clusters and nine themes were derived. The four theme clusters are as follows: (1) Confusion of nursing role; (2) Conflict due to insufficient support system; (3) Concern about the quality of nursing; (4) Reflection on the establishment of nursing professionalism.
Conclusion
This study highlights the necessity for institutionalizing professional nursing areas, nursing education, and practical support by clarifying the purpose and goals of non-contact nursing and developing nursing knowledge through frameworks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef - Telecare legislation priorities: A Delphi study grounded in ethical challenges
Seongyu Han, Eun Kyoung Yun
Nursing Ethics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,824 View
- 87 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- How Do We Approach Quality Care for Patients from Middle Eastern Countries? A Phenomenological Study of Korean Nurses’ Experiences
- Dael Jang, Seonhwa Choi, Gahui Hwang, Sanghee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):372-385. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24036
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Although more people from Middle Eastern countries are visiting South Korea for medical treatment, Korean nurses lack experience in treating them. Understanding and describing Korean nurses’ experiences can help them provide quality care to these patients by enhancing their competency in culturally appropriate care. This study described the experiences of nurses who provide care to Middle Eastern patients in clinical settings in South Korea.
Methods
We conducted a phenomenological study to describe nurses’ experience of caring for patients from Middle Eastern countries. Ten nurses with prior experience in caring for these patients were recruited from a university-affiliated tertiary hospital. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews were conducted between May 1 and June 4, 2020. The transcribed data were analyzed using Giorgi’s phenomenological method to identify the primary and minor categories representing nurses’ experiences.
Results
Four major categories (new experiences in caring for culturally diverse patients, challenges in caring for patients in a culturally appropriate manner, nursing journey of mutual agreement with culturally diverse patients, and being and becoming more culturally competent) and 11 subcategories were identified.
Conclusion
Nurses experience various challenges when caring for Middle Eastern patients with diverse language and cultural needs. However, nurses strive to provide high-quality care using various approaches and experience positive emotions through this process. To provide quality care to these patients, hospital environments and educational programs must be developed that center on field nurses and students and support them in delivering quality care while utilizing their cultural capabilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The roles of nurses employed as medical tourism facilitators in Taiwan: A qualitative study
Eimi Nakada, Keiko Sugimoto, Rieko K. Fukuzawa, Thomas Mayers, Yi-Chuan Chen, Judith S. C. Shiao
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2026; : 1. CrossRef
- The roles of nurses employed as medical tourism facilitators in Taiwan: A qualitative study
- 2,632 View
- 71 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development of the Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students
- Seoyoung Yoon, Hye-Ah Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):340-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students (HCPES-NS) and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
The HCPES-NS was constructed following the DeVellis guidelines. The initial items were written based on a literature review and individual in-depth interviews. Content validity was verified through an expert panel review. To confirm the validity and reliability of the scale, a survey was conducted with 449 nursing students enrolled in 12 nursing colleges. Data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, concurrent validity, and reliability tests.
Results
Factor analysis showed that the HCPES-NS consists of 15 items on five subdomains: clinical site atmosphere, interpersonal relationship, alternative online practicum contents, provision of learning information, and clinical performance facilitation. A higher score indicated a more positive perception of the clinical practicum environment. The concurrent validity of the HCPES-NS was confirmed by its positive correlation with the Clinical Learning Environment Scale (r = .77). The Cronbach’s α reliability of the HCPES-NS was .84.
Conclusion
The HCPES-NS is both valid and reliable. This scale reflects the clinical practicum environment and includes an online practicum factor. It may be used effectively by faculty members and educators to evaluate nursing students’ perceptions of clinical practicum environments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Ui Rim Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 355. CrossRef
- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
- 2,964 View
- 96 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Analysis of the Adequacy of Nurse Staffing Level through the Estimation of Nursing Activity Hours and Implementation of Focus Group Interviews in a Tertiary Hospital: Using a Mixed-Method Design
- Hyun-Joo Kim, Sun-Hee Lee, Jai-Jung Lee, Sun-Suk Seong, Hee Yang, Hyang-Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):237-249. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the adequacy of current nurse staffing levels by identifying nursing activities and workload.
Methods
The study used a mixed-method design. A nursing activity survey was conducted using the work sampling method over 2 working days with 119 general ward nurses. A focus group interview was conducted with 12 nurses. Quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and content analysis, respectively.
Results
The most amount of time was spent on medication (in direct nursing) and electronic medical record documentation (in indirect nursing). The appropriate nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:7.7 for the day shift, 1:9.0 for the evening shift, and 1:11.9 for the night shift. However, the current nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:9.4, 1:11.0, and 1:13.8 for the day, evening, and night shifts, respectively. Therefore, the current nurse staffing level is insufficient for the workload. In the focus group interview, the main reasons cited for being unable to complete tasks within working hours were communication and coordination, and the nursing electronic medical record. The essential nursing activities of basic nursing and emotional support were overlooked owing to a heavy workload. Therefore, an adequate nurse staffing level should be higher than the measured quantitative workload.
Conclusion
These results suggest the general wards of tertiary hospitals should evaluate the adequacy of their current nurse staffing and allocate sufficient nurses to improve patient safety and nursing care quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
- 3,042 View
- 262 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Descriptive Review of Patents in Healthcare and Nursing: Based on Network Analysis
- Misun Jeon, Nayung Youn, Sanghee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):1-17. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23064
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The significance of the healthcare industry has grown exponentially in recent years due to the impact of the fourth industrial revolution and the ongoing pandemic. Accordingly, this study aimed to examine domestic healthcare-related patents comprehensively. Big data analysis was used to present the trend and status of patents filed in nursing.
Methods
The descriptive review was conducted based on Grant and Booth’s descriptive review framework. Patents related to nursing was searched in the Korea Intellectual Property Rights Information Service between January 2016 to December 2020. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, phi-coefficient for correlations, and network analysis using the R program (version 4.2.2).
Results
Among 37,824 patents initially searched, 1,574 were selected based on the inclusion criteria. Nursing-related patents did not specify subjects, and many patents (41.4%) were related to treatment in the healthcare delivery phase. Furthermore, most patents (56.1%) were designed to increase effectiveness. The words frequently used in the titles of nursing-related patents were, in order, “artificial intelligence,” “health management,” and “medical information,” and the main terms with high connection centrality were “artificial intelligence” and “therapeutic system.” Conclusion: The industrialization of nursing is the best solution for developing the healthcare industry and national health promotion. Collaborations in education, research, and policy will help the nursing industry become a healthcare industry of the future. This will prime the enhancement of the national economy and public health.
- 2,330 View
- 83 Download

- Association between Resilience, Professional Quality of Life, and Caring Behavior in Oncology Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Misun Jeon, Sue Kim, Sanghee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):597-609. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The degree of caring behavior of oncology nurses is a crucial factor in the care provided to patients with cancer. In this study, we aimed to investigate factors related to oncology nurses’ caring behavior, including their resilience and professional quality of life.
Methods
A cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted with 107 oncology nurses at an urban tertiary hospital from May 18 to 24, 2015. We used a self-report questionnaire to measure resilience, professional quality of life, and degree of caring behavior. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression analysis using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results
Oncology nurses presented with low levels of resilience and caring behavior, and high levels of compassion satisfaction, burnout, and secondary traumatic stress. There was a statistically significant relationship between the degree of caring behavior, resilience (r = .43, p < .001), compassion satisfaction (r = .51, p < .001), and burnout (r = - .42, p < .001), as well as between secondary traumatic stress and burnout (r = .34, p < .001). Factors associated with oncology nurses’ degree of caring behavior were compassion satisfaction (t = 6.00, p < .001) and educational level (t = 3.45, p = .001).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that oncology nurses’ degree of caring behavior is related to their professional quality of life and education. These findings suggest that enhancing oncology nurses’ healthy coping strategies at both the individual and organizational levels can further develop holistic nursing care. Additionally, it is necessary to examine the factors affecting nurses’ compassion satisfaction and to try to promote this aspect. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of the Quranic Teachings on the Resilience and Caring Behaviors of Nursing Students Amid Crises Such as the COVID-19 Pandemic
Maryam Shaygan, Fatemeh Vizeshfar, Azadeh Amiri, Marzieh Kargar Jahromi
International Perspectives in Psychology.2026; 15(1): 5. CrossRef - The Mediating Role of Resilience Between Empathy and Professional Competence Among Emergency Nurses in the West Bank, Palestine: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling
Anas Shehadeh, Ahmad Shuhaiber, Malakeh Z. Malak, Ahmad Ayed, Hisham Zahran
International Nursing Review.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Terminal Care Performance in Korean Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jiwon Oh, Jooyoung Cheon
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Burnout among health professionals working in oncology: current evidence and challenges for future research
Javier Martinez-Calderon, Cristina García-Muñoz
Current Opinion in Oncology.2025; 37(4): 302. CrossRef - Personal and work-related factors associated with nurse resilience: An updated systematic review using meta-analysis and narrative synthesis
Fiona Yu, Deborah Raphael, Lisa Mackay, Melody Smith, Ritin Fernandez
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2025; 166: 105054. CrossRef - Impact of an oncology training program on nursing personnel knowledge: A pilot study
Sara Gabriela Yeverino-Castro, Francisco Zamora-Rosales, Rodrigo Álvarez-Calderon , Oswaldo Enrique Sánchez-Dávila , Erika Evangelina Coronado-Cerda , Sonia Esquivel Ochotorena
Revista de Estudios e Investigación en Psicología y Educación.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Compassion fatigue, psychological resilience, moral sensitivity, and humanistic caring ability in clinical nurses: a structural equation model
Shuqi Zhai, Qinqin Liu, Congcong Dai, Yifan Lu, Huanhuan Zhang, Jie Liu, Chaoran Chen
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Resilience on Professional Quality of Life Among Oncology Nurses
Asma Al Yahyaei, Wafa Al Jabri, Nabiha Al Hasni, Zainab Al Kindi, Sulaiman Al Sabei, Omar Al Omari, Joshua Muliira, Foroozan Atashzadeh-Shoorideh
Nursing Forum.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Professional Quality of Life in Nursing: The Role of Psychological Resources—A Cross-Sectional Study
Lovorka Brajković, Dora Korać, Vanja Kopilaš
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(12): 434. CrossRef - Connectedness to Nature and Professional Quality of Life Among Nurses in South Korea in the Context of COVID-19
Hyeon Sik Chu, Young Ran Tak, Hanyi Lee
HERD: Health Environments Research & Design Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on Moral Distress, Compassion Fatigue, Compassion Satisfaction, and Their Predictors among Nurses Caring for Patients with Cancer
Soomin Hong, Yesol Kim, Mi Sook Jung, Yoonjung Lee, Hyunju Hong, Mijin Jeon, Mee-Young Cho, Jiyeon Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(4): 217. CrossRef - Mindful self-care among oncology nurses in China: a latent profile analysis
Yan Shi, Peng Wang, Lamei Liu, Mengmeng Li
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating role of compassion fatigue between perceived organization support and caring behavior among outpatient nurses in China: a cross-sectional study
Xingxing Liu, Fang He, Tian Tian, Jun Zhang, Yuanjiao Ji, Yuexia Zhong
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Critical Role of Nursing in Identifying and Managing Care Fatigue Among Hospitalized Patients
Haya Semah D Alreshidi, Alanazi, Maryam Munadi, May Farhan Salem Alanazi, Hamidah Matrouk Alruwaili, Alruwaili, Rehab Mulhi A, Awatif Rakyan Murayr Alruwaili, Huda Alshawi J Alruwaili, Adhwaa Alohaylim Aldaghmani, Almatrafi, Rawan Wadi S, Hana M
International Journal of Computational and Experimental Science and Engineering.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TYPE D PERSONALITY AND COMPASSION SATISFACTION, BURNOUT AND COMPASSION FATIGUE
IN SURGICAL NURSES
Müslüm Gün, Yasemin Eda Tekin
Health Problems of Civilization.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Impact of the Quranic Teachings on the Resilience and Caring Behaviors of Nursing Students Amid Crises Such as the COVID-19 Pandemic
- 4,786 View
- 205 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
- HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):635-651. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the main keyword, network structure, and main topics of the national petition related to “nursing” in South Korea.
Methods
Data were gathered from petitions related to the national petition in Korea Blue House related to the topic “nursing” or “nurse” from August 17, 2017, to May 9, 2022. A total of 5,154 petitions were searched, and 995 were selected for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were analyzed using the Netminer 4.5.0 program.
Results
Regarding network characteristics, a density of 0.03, an average degree of 144.483, and an average distance of 1.943 were found. Compared to results of degree centrality and betweenness centrality, keywords such as “work environment,” “nursing university,” “license,” and “education” appeared typically in the eigenvector centrality analysis. Topic modeling derived four topics: (1) “Improving the working environment and dealing with nursing professionals,” (2) “requesting investigation and punishment related to medical accidents,” (3) “requiring clear role regulation and legislation of medical and nonmedical professions,” and (4) “demanding improvement of healthcare-related systems and services.” Conclusion: This is the first study to analyze Korea's national petitions in the field of nursing. This study's results confirmed both the internal needs and external demands for nurses in South Korea. Policies and laws that reflect these results should be developed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hyunjung Ko, Nara Han, Seulki Jeong, Jeong A Jeong, Hye Ryoung Yun, Eun Sil Kim, Young Jun Jang, Eun Ju Choi, Chun Hoe Lim, Min Hee Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Dong Hyu Cho, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 529. CrossRef - A Study on Internet News for Patient Safety Campaigns: Focusing on Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2024; 12(19): 1914. CrossRef
- Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
- 2,790 View
- 44 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
- SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):584-596. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23048
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the perspectives of frontline nurses working during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Methods
An online qualitative study was conducted using a pragmatic approach. The data were collected in August 2021. Registered Korean nurses who provided direct nursing care to patients with confirmed COVID-19 were eligible for this study. An online survey was used to gather free-text data, which were then analyzed using machine-based network analysis and summative content analysis.
Results
The analysis examined the responses of 126 participants and led to the identification of six prominent themes. These themes were further classified into three distinct levels: personal, task, and organizational. The identified themes are as follows: “collapse of personal life,” “being overwhelmed by the numerous roles required,” “personal protective equipment was sufficiently provided, but that is not enough,” “changes in interprofessional collaboration,” “inappropriate workforce management,” and “diverted allocation of healthcare services and resources.” Conclusion: Our findings highlight areas for improvement in resources, systems, and policies to enhance preparedness for future pandemics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Skill mix changes in healthcare professions during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review
Natalia Petka-Nosal, Iwona A Bielska, Katarzyna Badora-Musiał, Katarzyna Nowak-Zając, Alicja Domagała, Małgorzata Gałązka-Sobotka, Iwona Kowalska-Bobko
BMJ Open.2025; 15(10): e100024. CrossRef
- Skill mix changes in healthcare professions during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review
- 2,829 View
- 37 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Nursing Students’ Experiences of Observing the Use of Physical Restraints: A Qualitative Study
- Sun Mi Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):610-621. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23032
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand the experiences of final-year undergraduate nursing students in observing the use of physical restraints on patients in the course of clinical practice.
Methods
Three focus group interviews were conducted with 12 Korean nursing students who could provide sufficient information about their observation of physical restraints. The collected data was analyzed through conventional content analysis.
Results
The data were classified into four theme clusters, and nine themes. The four theme clusters included ‘recognized as an unavoidable means,’ ‘experienced problems with the use of physical restraints,’ ‘realized the importance of the nurse's role and efforts,’ and ‘aspire to learn about correct use of physical restraints.’ While nursing students recognized the necessities and problems of using physical restraints in clinical practice, and the importance of nurses’ role and effort, the results found that education related to the use of physical restraints should be more systematic within the nursing curriculum.
Conclusion
This study highlights the necessity of educating nursing students to ensure they acquire accurate knowledge and awareness regarding the use of physical restraints, and suggests the inclusion of systematic guidelines through simulation or extracurricular activities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Nurses’ and Nursing Students’ Attitudes Toward Coercive and Technological Measures in Mental Health: A Conceptual Framework and Study Protocol
Giuliano Anastasi, Roberto Latina, Yari Longobucco, Alessandro Stievano, Stefano Bambi
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(4): 4129. CrossRef
- Exploring Nurses’ and Nursing Students’ Attitudes Toward Coercive and Technological Measures in Mental Health: A Conceptual Framework and Study Protocol
- 3,969 View
- 111 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Nurses’ Well-Being: Does Digital Competence Matter?
- Yali Li, Qi Jing, Taiwen Feng, Xiaoling Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):385-396. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23037
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Drawing on person–environment fit theory and social cognitive theory, this study aimed to examine how self-efficacy affects nurses’ workplace well-being via person-job fit and the moderating role of digital competence.
Methods
A two-wave survey was conducted to collect data. Data were collected from six hundred and ninety-five nurses at three Chinese hospitals between May 2022 and September 2022. We employed hierarchical regression analysis and bootstrapping to analyze the data.
Results
Self-efficacy positively influenced person-job fit (β = .55, p < .001), which positively affected nurses’ workplace well-being (β = .32, p < .001). Person-job fit mediated the effect of self-efficacy on nurses’ workplace well-being. Additionally, digital competence strengthened the positive impact of self-efficacy on person-job fit (β = .12, p < .001).
Conclusion
Recruiting nurses with both self-efficacy and digital competence benefits hospitals. It is critical for nurses to improve their digital competence for achieving person-job fit and attaining workplace well-being in the post-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) era. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing digital competencies of Slovenian nurses in clinical practice: A pilot study
Melita Peršolja, Svetlin Grmšek
Annals of Nursing.2026; (00): 16. CrossRef - Work-family balance mediates self-efficacy and subjective well-being among nurses in Chinese intensive care units: A cross-sectional study
Lating Zhang, Xianzhen Jin, Na Cheng, Ruhua Wang, Xinhui Liang, Haiyan Fan, Xue Jiang
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 82: 151932. CrossRef - Translation and psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the Digital Competence Questionnaire for clinical nurses
Zhengang Wei, Hongli Liu, Jicheng Zhang, Yan Chen, Lixia Chang, Huiyu Cheng, Xue Bai, Xiaohua Wang, Su Li
DIGITAL HEALTH.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of high involvement work systems on nurses team creative performance in the public service industry of Pakistan
Abdul Waheed, Salma Waheed, Shahid Mahmood, El-Sayed M. El-Kenawy, Amal H. Alharbi, Marwa M. Eid
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Nurses' Perceptions of Digital Nursing Technology: A Qualitative Analysis Using the Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB)
Young‐Eun Jang, Hwa‐Mi Yang
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Digital Competence on Nurses’ Career Sustainability: A Cross‐Sectional Study
Zeyu Zhang, Shuang Zhao, Yujiao Shao, Xiaocui Duan, Ping Sun, Lingling Chen, Fei Wang, Changjiang Yuan, Xiumu Yang, Lesley Barr
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing digital competencies of Slovenian nurses in clinical practice: A pilot study
- 4,556 View
- 134 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Analysis of Media Trends and Social Perceptions on Nursing Law Legislation
- Seung-Hee Lee, Min-Ho Joo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):439-452. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to derive considerations for the enactment of nursing law by analyzing the trends and social perceptions of nursing law mentioned in major daily newspapers, cafes, and blogs.
Methods
Main texts and comments that included nursing law as a keyword were collected from major daily news and online postings from January 2021 to August 2022. The data collected through web crawling were analyzed using a TousFlux program used for big data analysis.
Results
During the period of study, the awareness level around nursing law enactment increased. In particular, public concern over nursing law enactment intensified due to the two political parties' policy pledges related to nursing law in January 2022 and the failure to introduce the nursing law to the national assembly judiciary committee in May 2022. Except in December 2021, public perception of nursing law enactment was generally favorable, with public opinion tilting more in favor of than against enactment.
Conclusion
Public opinion should be considered when drafting and implementing the nursing law to make it easier for the people to understand what the law constitutes. In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to and continuously promote the relationship between medical care and nursing in the nursing law system of developed nations. Lastly, nursing law enactment can enhance nurses' retention intention and provide a sense of efficacy to medical services. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- General Nurses’ Experience of Passing and Repealing the Nurses Act in Parliament
Yeon Hee Kim, Bo Kyung Kim, Su Jin Lee, Ha Young Lim, Hyang Ju Jung, Ju Song Cha
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(1): 65. CrossRef
- General Nurses’ Experience of Passing and Repealing the Nurses Act in Parliament
- 3,605 View
- 108 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Education for Caring Patients with COVID-19
- Min Hye Lee, Eun-Young Noh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):397-411. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The role of medical staff gained immense significance in the context of the prolonged coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. However, few studies had explored the impact of simulation-based education on the ability of nursing students to care for the patients of COVID-19. This study provided nursing students with simulation-based education in caring for the patients of COVID-19 and confirmed its effectiveness.
Methods
This study used a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants were recruited from the nursing departments of two universities in Korea through convenience sampling. A total of 79 participants were included: 37 in the intervention group and 42 in the control group. The intervention group received four sessions of simulation training based on the National League for Nursing Jeffries simulation theory.
Results
The intervention group showed an improvement compared to the control group in terms of knowledge related to coronavirus, confidence in performing infection control skills, and perception of preparedness for caring for the patients of COVID-19, with a high-level of satisfaction and self-confidence in learning. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of anxiety.
Conclusion
This simulation is expected to be a significant strategy for alleviating the global burden in terms of staff safety and patient outcomes by improving the competencies of prospective medical staff in responding to pandemics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Utilization and impact of simulation-based education in prelicensure nurse education; an integrative review
Robyn Cant, Colleen Ryan
Journal of Professional Nursing.2026; 63: 6. CrossRef - Building Skills in Infection Prevention Through Simulation: Insights from Nursing Students in Brazil and Peru
Luciene Muniz Braga, Pedro Paulo do Prado-Junior, Andréia Guerra Siman, Talita Prado Simão Miranda, Mara Rúbia Maciel Cardoso do Prado, Luana Vieira Toledo, Rodrigo Siqueira-Batista, Andréia Patrícia Gomes, Yanet Castro Vargas, Luis Alberto Chihuantito-Ab
Nursing Reports.2026; 16(1): 14. CrossRef - Determinants of Standard Precautions Performance Among Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Se Gyeong Jeon, Eun Jung Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(21): 2803. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of a Novel Education Approach to Prevention and Control of Healthcare-Associated Infections: Insights from PrevInf Pilot Study
Paulo Santos-Costa, Filipe Paiva-Santos, João Graveto
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(2): 1494. CrossRef
- Utilization and impact of simulation-based education in prelicensure nurse education; an integrative review
- 5,943 View
- 103 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of a Modified Six-Sigma-Methodology-Based Training Program on Core Competencies in Rehabilitation Nurse Specialists
- Jiayi Gu, Lan Luo, Chengjuan Li, Sumin Ma, Fanghua Gong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):412-425. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Nurses play an important role in ensuring patient rehabilitation and are involved in all aspects of multidimensional rehabilitation. Therefore, strengthening rehabilitation nursing education is vital to ascertain high-quality rehabilitation and optimum outcomes. This study examined the effectiveness of a new teaching reform—a modified Six-Sigma-based training program—against a conventional educational program on rehabilitation specialist nurses’ core competencies, post-training performance, and satisfaction.
Methods
A quasi-randomized controlled trial was conducted to assess the effectiveness of the modified training program. We recruited 56 learners from the 2020 training course at the Hunan Rehabilitation Specialist Nurse Training Base as the control group. Sixty learners from the base’s 2021 training course were recruited as the intervention group. Data were collected in a consistent manner from both groups after the training program was implemented.
Results
Those who underwent the modified training program showed better improvement in all core competencies than those who underwent the conventional training program (p < .05); the scores for theoretical knowledge, clinical nursing lectures, reviews, and nursing case management improved significantly following the teaching reform (p < 0.05). Further, overall satisfaction as well as base management and theoretical teaching satisfaction improved significantly (p < .05).
Conclusion
The modified training program strengthens rehabilitation nurses’ base management abilities; enhances their core competencies; expands their interest in and breadth, depth, and practicability of theoretical courses; and updates the teaching methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of bedside comprehensive ability training on teaching and training in operating room
Yi Zhong, Wenjun Bu, Qifan Li, Lili Zheng
Frontiers in Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of rehabilitation nursing training for clinical nurses based on the Kirkpatrick model
Manzhou Yang, Xiuying Zhang, Ruiyang Han, Xiao Ding, Runguo Gao, Qi Jing, Weiqin Cai, Anning Ma, Qianqian Gao, Hongmei Li
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Availability of Six Sigma trials for quality improvement in healthcare: an emerging challenge
Ivan David Lozada-Martinez, Ornella Fiorillo-Moreno, Jessica Manosalva-Sandoval, Yelson Alejandro Picón-Jaimes
International Journal For Quality In Health Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Professional competencies in geriatric nursing for geriatric nurses: a latent profile analysis
Mengxue Wang, Dongdong Li, Jingjing Li, Xiumei Zhang
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A longitudinal assessment of factors affecting training transfer among new clinical nurse specialists
Ardani Latifah Hanum, Qiulan Hu, Wei Wei, Fang Ma
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(3): 308. CrossRef
- Effect of bedside comprehensive ability training on teaching and training in operating room
- 2,514 View
- 48 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Development and Validation of a Dignity in Care Scale of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses
- Yun Sil Ahn, Pok Ja Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):340-358. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23039
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an instrument to showcase Dignity in Care of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses and to examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
A total of 58 preliminary items on dignity in care of terminally ill patients for nurses were selected using content validity analysis and expert opinions on 97 candidate items derived through a literature review and qualitative focus group interviews. Questionnaires were administered to 502 nurses caring for terminally ill cancer patients at hospice and palliative care institutions. The data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, convergent and discriminant validity, and Pearson correlation for criterion validity, reliability was tested using Cronbach’s alpha.
Results
The final instrument consisted of 25 items, with four factors identified through confirmatory factor analysis. Four factors-ethical values and moral attitudes, interaction-based communication, main-taining comfort, professional insight and competence–accounted for 61.8% of the total variance. Cronbach’s ⍺ for total items was .96, and test-retest reliability of intraclass correlation coefficient was .90.
Conclusion
Since its validity and reliability have been verified through various methods, the Dignity in Care Scale of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses can be used for develop nursing interventions and improve dignity in care of terminally ill patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the Intensive care unit Dignified Care Questionnaire (IDCQ)
Sejin Kang, So Hyun Park, Youn-Jung Son
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Testing of the Nurses’ Professional Dignity Scale
Michela Piredda, Maddalena De Maria, Rosario Caruso, Anna Marchetti, Giorgia Petrucci, Anna Cerra, Joyce J. Fitzpatrick, Alessandro Stievano
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(4): 127. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Compassionate Care among Nurses: A Hybrid Model
Ae Kyung Chang, Jin Ah Kim, Yu Kyung Jin, Woo Jung Hong, Yeon Kyung Cho, Ah Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 275. CrossRef - Dignity in Care of Older Patients with Cancer in Korea: A Hybrid Model Concept Analysis
Yun Sil Ahn, Pok-Ja Oh, Gye Jeong Yeom
Healthcare.2025; 13(22): 2935. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Dignity in Care Scale of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses
Yun Sil Ahn, Pok Ja Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 340. CrossRef
- Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the Intensive care unit Dignified Care Questionnaire (IDCQ)
- 3,101 View
- 114 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Evidence-Based Nursing Protocol for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation to Critically Ill Patients
- Soomi Kim, Chul-Gyu Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):275-294. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an evidence-based extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) nursing protocol for critically ill patients receiving ECMO treatment by using an adaptation process, and to verify the effects of the protocol.
Methods
The protocol was developed according to the adaptation guidelines. A non-randomized controlled trial was conducted to test the protocol’s effects. Data were collected between April 2019 and March 2021. The differences in physiological indicators and complication rates between the two groups were investigated using a chart review to evaluate patient outcomes. The nurses’ outcome variables were evaluated using a questionnaire.
Results
First, after reviewing 11 guidelines by appraisal of the guidelines for research and evaluation collaboration II, 5 guidelines with a standardization grade of over 50 points were selected. An ECMO nursing protocol was developed based on these guidelines. Second, there were no statistically significant differences in physiological indicators between the two groups of patients. However, the experimental group showed a statistically significant decrease in the infection rate (p = .026) and pressure injury rates (p = .041). The levels of satisfaction with ECMO nursing care, and empowerment and performance of the nurses who used the ECMO nursing protocol were higher than those of nurses who did not (p < .001).
Conclusion
This protocol may help prevent infections and pressure injuries in patients, and improve nurses’ satisfaction and empowerment. The nursing protocol developed for critically ill patients receiving ECMO treatment can be utilized in evidence-based nursing practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Advances in Evidence-Based Nursing for Clinical Practice Standards and Technological Optimization in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
晓婷 汤
Asian Case Reports in Emergency Medicine.2025; 13(03): 300. CrossRef - Factors associated with nursing workload in patients undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: a retrospective cohort study
André Lucas da Silva Guideli, Luana Letícia Ribeiro de Luna, Larissa Fernandes Araújo da Silva, Marcele Liliane Pesavento, Lilia de Souza Nogueira, Filipe Utuari de Andrade Coelho
einstein (São Paulo).2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of ECMO training program for ICU nurses knowledge gain and self-efficacy outcomes assessment: quasi-experimental evaluation
Hafize Savaş, Sevil Güler, Sinan Sabit Kocabeyoğlu
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A comprehensive evidence-based intervention programme significantly reduces intensive care unit-acquired weakness and improves functional recovery: a retrospective analysis
Hongrui Zhu, Yueming Zhang, Yan Zhou, Hongxia Yan
Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine.2025; 57: jrm43563. CrossRef
- Research Advances in Evidence-Based Nursing for Clinical Practice Standards and Technological Optimization in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
- 9,141 View
- 398 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Pathway Analysis on the Effects of Nursing Informatics Competency, Nursing Care Left Undone, and Nurse Reported Quality of Care on Nursing Productivity among Clinical Nurses
- Mi Yu, Se Young Kim, Ji Min Ryu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):236-248. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Nursing informatics competency is used to manage and improve the delivery of safe, high-quality, and efficient healthcare services in accordance with best practices and professional and regulatory standards. This study examined the relationship between nursing informatics competency (NIC), nursing care left undone, and nurse reported quality of care (NQoC) and nursing productivity. A path model for their effects on nursing productivity among clinical nurses was also established.
Methods
Data were collected using structured questionnaires answered by 192 nurses working in a tertiary hospital located in J city, Korea, and analyzed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 21.0 program.
Results
The fit indices of the alternative path model satisfied recommended levels χ2 = .11 (p= .741), normed χ2 (χ2/df) = .11, SRMR = .01, RMSEA = .00, GFI = 1.00, NFI = 1.00, AIC = 18.11. Among the variables, NIC (β = .44, p < .001), NQoC (β = .35, p < .001) had a direct effect on nursing productivity. Due to the mediating effect of NQoC on the relationship between NIC and nursing productivity, the effect size was .14 (95% CI .08~.24). Meanwhile, nursing care left undone through NQoC in the relationship between NIC and nursing productivity, has a significant mediation effect (estimate .01, 95% CI .00~.03). The explanatory power of variables was 44.0%.
Conclusion
Education and training for enhancing NIC should be provided to improve nursing productivity, quality of care and to reduce missed nursing care. Furthermore, monitoring the quality of nursing care and using it as a productivity index is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
Shin Hyang Kim, Jong Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 358. CrossRef - The impact of nursing informatics competency, social influence, and medical information culture on nurses’ intention to use new medical technology in general hospitals
Jeong Ho Ji, Kyungja Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 484. CrossRef - Effects of digital literacy and nursing informatics competency as job resources on nurses’ burnout and work engagement: a cross-sectional study
Jeehae Chung, Hyesil Jung, Sang Mi Park, Kyeongmin Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Care Left Undone by Cancer Ward Nurses
Chung Hee Woo, Yeon Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 594. CrossRef
- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
- 2,919 View
- 124 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Affecting Radiation Protective Behaviors in Perioperative Nurses Applying the Theory of Planned Behavior: Path Analysis
- Se Young Jang, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Young Man Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):222-235. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22099
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to identify the factors explaining protective behaviors against radiation exposure in perioperative nurses based on the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study. A total of 229 perioperative nurses participated between October 3 and October 20, 2021. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 software. The three exogenous variables (attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control) and two endogenous variables (radiation protective intention and radiation protective behaviors) were surveyed.
Results
The hypothetical model fit the data (χ2/df = 1.18, SRMR = .02, TLI = .98, CFI = .99, RMSEA = .03). Radiation protective intention (β = .24, p = .001) and attitude toward radiation protective behaviors (β = .32, p = .002) had direct effects on radiation protective behaviors. Subjective norm (β = .43, p = .002) and perceived behavior control (β = .24, p = .003) had direct effects on radiation protective intention, which explained 38.0% of the variance. Subjective norm (β = .10, p = .001) and perceived behavior control (β = .06, p = .002) had indirect effects via radiation protective intention on radiation protective behaviors. Attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control were the significant factors explaining 49.0% of the variance in radiation protective behaviors.
Conclusion
This study shows that the theory of planned behavior can be used to effectively predict radiation protective behaviors in perioperative nurses. Radiation safety guidelines or education programs to enhance perioperative nurses’ protective behaviors should focus on radiation protective intention, attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health Protective Behavior in Occupational Health Practice: A Concept Analysis
Fenggang Liu, Juanjuan Wang, Weeraporn Suthakorn, Li Liao
Health Science Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to preventive measures towards PM2.5 exposure: A systematic review
Jeevan Bhatta, Orapin Laosee, Cheerawit Rattanapan
Global Transitions.2024; 6: 212. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Radiation Protection Behavior of Nurses in Intensive Care Units
Seo Jeong Kim, Yun Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 1. CrossRef - A Review of the Relationship between Health Behaviors and Career Adaptability among University Students
Dongming Jia, Xia Yuan
Journal of Medicine and Health Science.2024; 2(4): 43. CrossRef
- Health Protective Behavior in Occupational Health Practice: A Concept Analysis
- 2,610 View
- 98 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Related to Clinical Competence among Graduating Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Su Kyoung Chung, Jinsook Kim, Pratibha Bhandari
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):145-154. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated clinical competency, COVID-19-related anxiety, coping strategies, self-efficacy, and perceived stress among graduating nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional survey. Participants were recruited from universities located in four major cities in South Korea. General demographic information, clinical competency, self-efficacy, perceived stress, COVID-19-related anxiety, and coping strategies were assessed using reliable questionnaires. Descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression tests were used to analyze the data.
Results
The mean clinical competency, self-efficacy, perceived stress, adaptive coping, and maladaptive coping were 138.16 ± 18.34, 83.85 ±14.02, 21.37 ± 5.79, 53.15 ± 4.64, and 30.98 ± 6.73, respectively. COVID-19-related anxiety was reported by 4.3% of participants. Clinical competency was significantly positively correlated with self-efficacy (r = .44, p < .001) and adaptive coping (r = .20, p = .035) and was significantly negatively correlated with maladaptive coping (r = .20, p = .035). The predictors of clinical competency were self-efficacy (β = .434, p < .001) and adaptive coping (β = .173, p < .039), which explained 23% of the variance in clinical competency.
Conclusion
Self-efficacy and adaptive coping strategies are significant predictors of clinical competence during the pandemic. Planning and implementing various curricular and non-curricular activities to increase senior students' self-efficacy and adaptive coping strategies will help prepare competent nursing graduates for the pandemic when they enter the nursing workforce. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Educational Stress and Competence of Intern Nurses' Following Two Years of Online Education: A Cross-Sectional Study
Fatma Dursun Ergezen, Ayşe Yacan Kök, Emine Kol
Ordu Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Çalışmaları Dergisi.2026; 9(1): 83. CrossRef - The Effect of Internship Length on Self‐Efficacy and Clinical Competence: Accelerating Entry Into the Nursing Workforce in Saudi Arabia
Sitah S. Alshutwi, Majed Alamri
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring Educational Stress and Competence of Intern Nurses' Following Two Years of Online Education: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 2,909 View
- 63 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of a Nursing Simulation Learning Module on Clinical Reasoning Competence, Clinical Competence, Performance Confidence, and Anxiety in COVID-19 Patient-Care for Nursing Students
- Ye-Eun Kim, Hee-Young Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):87-100. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22130
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a nursing simulation learning module for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patient-care and examine its effects on clinical reasoning competence, clinical competence, performance confidence, and anxiety in COVID-19 patient care for nursing students.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pre- and post-test design was employed. The study participants included 47 nursing students (23 in the experimental group and 24 in the control group) from G City. A simulation learning module for COVID-19 patient-care was developed based on the Jeffries simulation model. The module consisted of a briefing, simulation practice, and debriefing. The effects of the simulation module were measured using clinical reasoning competence, clinical competence, performance confidence, and anxiety in COVID-19 patient-care. Data were analyzed using χ 2 -test, Fisher’s exact test, t-test, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, and Mann– Whitney U test.
Results
The levels of clinical reasoning competence, clinical competence, and performance confidence of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group, and the level of anxiety was significantly low after simulation learning.
Conclusion
The nursing simulation learning module for COVID-19 patient-care is more effective than the traditional method in terms of improving students’ clinical reasoning competence, clinical competence, and performance confidence, and reducing their anxiety. The module is expected to be useful for educational and clinical environments as an effective teaching and learning strategy to empower nursing competency and contribute to nursing education and clinical changes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of an acute myocardial infarction simulation on nursing students’ clinical judgment: Integrating faculty- and self-assessments
Hwa Sun Kim
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2026; 112: 101895. CrossRef - Clinical Judgment Model‐Based Critical Reflection Program for Newly Graduated Nurses: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial
Ae Ran Kim, Jeong Hee Hong, Kyeongsug Kim, Yuna Kim, Jung Min Lee, Heejin Lee, Ji Hyun Yoon, Mi Soon Kim
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(2): 234. CrossRef - Exploring nursing students' experiences with virtual patient-based health assessment simulation program: A qualitative study
Shinhye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
Nurse Education Today.2025; 153: 106826. CrossRef - Effects of Multi-Patient Simulation Education on Nursing Students’ Communication Competence and Clinical Reasoning
Minji Kown, Jihyun Park
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 29. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Simulation Training Program for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Nurses on Severe Respiratory
Emergency among Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants
Youngae Song, Jaehee Lee, Jiyoon Kang, Heekyung Kang, Junghee Lee, Inkyung Bong
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 15. CrossRef - Effects of Diabetes Home-Visiting Healthcare Simulation Education on Nursing Students Using Virtual Reality
Young-Sun Ha, Yong-Kyung Park, Hye-Sun Byun, Kyeng-Jin Kim, Moon-Ji Choi
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(9): 2501. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Virtual Reality-Based Educational Application to Enhance Clinical Practice Competence in Nursing Students
Yun-Ha Choi
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(11): 3165. CrossRef - The impact of unfolding case studies combined with think-aloud strategies on the clinical reasoning and self-directed learning abilities of postgraduate students: A mixed methods study
Yuehai Yu, Yuanjing Qiao, Yaoyao Zhu, Hao Pei, Yuting Wang, Qingyang Zhu, Shuo Liu
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 80: 104132. CrossRef - Effect of Infection Control Simulation Based on a Negative Pressure Isolation Room Using Mixed Reality
Kyeng-Jin Kim, Joonyoung Lee, Moon-Ji Choi
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(8): 608. CrossRef - Expectations and concerns about transitioning to face-to-face learning among Korean nursing students: A mixed methods study
Hyeongsuk Lee, Hye Jin Yoo, Chao Gu
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0296914. CrossRef
- Effects of an acute myocardial infarction simulation on nursing students’ clinical judgment: Integrating faculty- and self-assessments
- 4,229 View
- 114 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Keyword Network Analysis and Topic Modeling of News Articles Related to Artificial Intelligence and Nursing
- Ju-Young Ha, Hyo-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):55-68. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the main keywords, network properties, and main topics of news articles related to artificial intelligence technology in the field of nursing.
Methods
After collecting artificial intelligence-and nursing-related news articles published between January 1, 1991, and July 24, 2022, keywords were extracted via preprocessing. A total of 3,267 articles were searched, and 2,996 were used for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were performed using NetMiner 4.4.
Results
As a result of analyzing the frequency of appearance, the keywords used most frequently were education, medical robot, telecom, dementia, and the older adults living alone. Keyword network analysis revealed the following results: a density of 0.002, an average degree of 8.79, and an average distance of 2.43; the central keywords identified were ’education,’ ‘medical robot,’ and ‘fourth industry.’ Five topics were derived from news articles related to artificial intelligence and nursing: ‘Artificial intelligence nursing research and development in the health and medical field,’ ‘Education using artificial intelligence for children and youth care,’ ‘Nursing robot for older adults care,’ ‘Community care policy and artificial intelligence,’ and ‘Smart care technology in an aging society.’ Conclusion: The use of artificial intelligence may be helpful among the local community, older adult, children, and adolescents. In particular, health management using artificial intelligence is indispensable now that we are facing a super-aging society. In the future, studies on nursing intervention and development of nursing programs using artificial intelligence should be conducted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mapping the Landscape of AI-Driven Human Resource Management: A Social Network Analysis of Research Collaboration
Mehrdad Maghsoudi, Motahareh Kamrani Shahri, Mehrdad Agha Mohammad Ali Kermani, Rahim Khanizad
IEEE Access.2025; 13: 3090. CrossRef - Characteristics of Online Articles Related to Youth Drug Use: An Analysis Using Keyword Network Analysis
Ji-Min Kim
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(11): 3087. CrossRef - The Impact of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Learning on Nursing Students' Ethical Decision-making and Clinical Reasoning in Pediatric Care
Hyewon Shin, Jennie C. De Gagne, Sang Suk Kim, Minjoo Hong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(10): 704. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef
- Mapping the Landscape of AI-Driven Human Resource Management: A Social Network Analysis of Research Collaboration
- 6,784 View
- 174 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- The Effects of the Combined Biofeedback and Brief Emotion Regulation Nursing Intervention Based on the Gross Model for Sexually Abused Adolescents
- Jieun Kim, Wanju Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):608-623. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22088
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of a combined biofeedback and brief emotion regulation (C-BABER) program for sexually abused adolescents.
Methods
This study employed a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants included 26 sexually abused adolescents from eight Sunflower Centers of South Korea–with 13 in the experimental group and 13 in the control group. The experimental group received four sessions of the individual C-BABER program, each lasting 60 minutes.
Results
Compared with the control group, sexually abused adolescents in the experimental group exhibited significant score differences in traumatic symptoms, including depression (Z = - 2.24, p = .025), dissociation (Z = - 2.21, p = .027), anxiety (Z = - 2.02, p = .044), and posttraumatic stress (Z = - 2.01 p = .045); and impulsivity, including positive urgency (Z = - 3.35, p = .001) and negative urgency (Z = - 2.28, v = .023). Additionally, the experimental group exhibited significant score differences in meta-mood, including emotional attention (Z = - 2.45, p = .014), emotional clarity (Z = - 2.30, p = .021), and emotional repair (Z = - 2.28, p = .022); and emotional regulation modes, including emotional suppression (Z = - 2.65,p = .008) and cognitive reappraisal (Z = - 1.98, p = .047). Regarding bio-attention, significant changes were identified in the experimental group for the bio-attention rate and attention maintenance time in the posttest compared to the pretest (p = .001).
Conclusion
The C-BABER program for sexually abused adolescents is effective in decreasing traumatic symptoms and impulsivity, and in improving meta-mood, emotional regulation mode, and bio-attention. Therefore, we recommend providing sexually abused adolescents the C-BABER program to help them regulate their emotions and effectively adapt to their lives. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Biofeedback Training on Attention, Affect Balance, Academic Delay Behavior, and Problem-Solving Ability of Korean College Students
Jungmin Lee, Youngkyoung Kim, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(2): 150. CrossRef
- The Effect of Biofeedback Training on Attention, Affect Balance, Academic Delay Behavior, and Problem-Solving Ability of Korean College Students
- 2,480 View
- 68 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Preventive Behaviors for COVID-19 in Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
- Jeong Sil Choi, Kyung Mi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):554-563. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22047
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to determine how undergraduate nursing students’ knowledge and health beliefs affected their COVID-19-related infection-prevention behaviors.
Methods
This study used a descriptive survey. A total of 188 undergraduate nursing students from two universities in South Korea participated in this study. The data were collected from June 2020 to August 2020. Factors influencing infection-prevention behaviors were identified using multiple regression analysis.
Results
The participants’ mean knowledge level regarding COVID-19 was 84.05 ± 11.78 out of 100. The average health belief score was 2.80 ± 0.32 points out of 5. COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors were correlated with experiences of searching for COVID-19 information (r = .22, p < .01), perceived severity (r = .24, p < .01), perceived benefits (r = .29, p < .01), cues to action (r = .30, p < .01), knowledge (r = .27, p < .01), and perceived barriers (r = - .19, p < .05). Factors that significantly affected COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors were the participants’ years of study, experiences regarding COVID-19 prevention education, perceived severity, perceived barriers, and cues to action.
Conclusion
COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors are promoted by increasing awareness about the disease and promoting COVID-19 education in nursing curriculums. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The multiple mediating effects of health beliefs on the relationship between infection control knowledge and infection-preventive behaviors among health science college students
Yoonmi Lee, Hyejin Kim, Jieun Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(2): 196. CrossRef - Effect of an educational intervention on nursing students’ knowledge about COVID-19 and compliance with standard and transmission-based precautions: a quasi-experimental study
Ana Beatriz de Almeida Lima, Cristine Maria Pereira Gusmão, Lais do Espirito Santo Lima, Daniel de Macedo Rocha, Mayra Gonçalves Menegueti, Ana Cristina de Oliveira e Silva, Renata Karina Reis
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing factors related to perceived control and preventive behaviors from COVID‐19 between Japanese and American nursing students: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The multiple mediating effects of health beliefs on the relationship between infection control knowledge and infection-preventive behaviors among health science college students
- 2,121 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Readiness for Practice Survey for Nursing Students
- Tae Wha Lee, Yoonjung Ji, Yea Seul Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):564-581. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22032
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Readiness for Practice Survey (K-RPS).
Method
The English Readiness for Practice Survey was translated into Korean using the Translation, Review, Adjudication, Pretesting, and Documentation (TRAPD) method. Secondary data analysis was performed using the dataset from the New Nurse e-Cohort study (Panel 2020) in South Korea. This study used a nationally representative sample of 812 senior nursing students. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were also conducted. Convergent validity within the items and discriminant validity between factors were assessed to evaluate con-struct validity. Construct validity for hypothesis testing was evaluated using convergent and discriminant validity. Ordinary α was used to assess reliability.
Results
The K-RPS comprises 20 items examining four factors: clinical problem solving, learning experience, professional responsibilities, and professional preparation. Although the convergent validity of the items was successfully verified, discriminant validity between the factors was not. The K-RPS construct validity was verified using a bi-factor model (CMIN/DF 2.20, RMSEA .06, TLI .97, CFI .97, and PGFI .59). The K-RPS was significantly correlated with self-esteem (r = .43, p < .001) and anxiety about clinical practicum (r = - .50, p < .001). Internal consistency was reliable based on an ordinary α of .88.
Conclusion
The K-RPS is both valid and reliable and can be used as a standardized Korean version of the Readiness for Practice measurement tool. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Readiness for Practice among Senior Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-sectional Study
Jihye Kim, Kyungmi Lee, Hye Suk Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 54. CrossRef - Readiness for Practice Among Nursing College Graduates: A Cross-Sectional Correlation Study
Kim Jihye, Lee Kyungmi
SAGE Open Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Grit on Nursing Education Satisfaction and Readiness for Practice Among Nursing Graduates During COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Study
Lee Kyungmi, Kim Jihye
Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research.2025; 29(4): 862. CrossRef - The influence of nursing informatics competency, clinical practice self efficacy, and grit on clinical practice readiness of nursing students
Hae Ok Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 440. CrossRef - The mediating effect of transition shock on the relationship between readiness for practice and turnover intention of new graduate nurses in South Korea: A longitudinal study
Taewha Lee, Eunkyung Kim, Yoonjung Ji
Nurse Education Today.2024; 143: 106394. CrossRef
- Readiness for Practice among Senior Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-sectional Study
- 4,624 View
- 189 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- An Analysis of Tasks of Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in a Nationally-Designated Inpatient Treatment Unit
- Minho Jung, Moon-Sook Kim, Joo-Yeon Lee, Kyung Yi Lee, Yeon-Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):391-406. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22056
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to provide foundational knowledge on nursing tasks performed on patients with COVID-19 in a nationally-designated inpatient treatment unit.
Methods
This study employs both quantitative and qualitative approaches. The quantitative method investigated the content and frequency of nursing tasks for 460 patients (age ≥ 18y, 57.4% men) from January 20, 2020, to September 30, 2021, by analyzing hospital information system records. Qualitative data were collected via focus group interviews. The study involved interviews with three focus groups comprising 18 nurses overall to assess their experiences and perspectives on nursing care during the pandemic from February 3, 2022, to February 15, 2022. The data were examined with thematic analysis.
Results
Overall, 49 different areas of nursing tasks (n = 130,687) were identified based on the Korean Patient Classification System for nurses during the study period. Among the performed tasks, monitoring of oxygen saturation and measuring of vital signs were considered high-priority. From the focus group interview, three main themes and eleven sub-themes were generated. The three main themes are “Experiencing eventfulness in isolated settings,” “All-around player,” and “Reflections for solutions.” Conclusion: During the COVID-19 pandemic, it is imperative to ensure adequate staffing levels, compensation, and educational support for nurses. The study further propose improving guidelines for emerging infectious diseases and patient classification systems to improve the overall quality of patient care. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Nursing Care for Patients With COVID-19 Using International Classification for Nursing Practice–Based Nursing Records
Sumi Sung, Hyesil Jung, Youlim Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(2): 127. CrossRef - Burnout among Nurses in COVID-19 Designated Units Compared with Those in General Units Caring for Both COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Patients
Kyung Ah Woo, Eun Kyoung Yun, JiSun Choi, Hye Min Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 374. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of the Functional Ingredients and Physiological Activities of Taraxacum coreanum Nakai
In-Seo Yoo, Ae-Jung Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2023; 21(4): 719. CrossRef
- Exploring Nursing Care for Patients With COVID-19 Using International Classification for Nursing Practice–Based Nursing Records
- 2,044 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Influence of Learning Presence of Non-Face-to-Face Class Experience in Nursing Students on Academic Achievement: Mediating Effect of Learning Flow and Moderated Mediation of Digital Literacy
- Eui Jeong Ryu, Keum Seong Jang, Eun A Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):278-290. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the mediating effect of learning flow and the moderated mediation effect of digital literacy on the effect of the learning presence of non-face-to-face class experience in nursing students on academic achievement.
Methods
Participants were 272 nursing students from six universities in two different cities. A self-report questionnaire was used to measure learning presence, learning flow, digital literacy, and academic achievement. Analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 and SPSS PROCESS Macro (4.0).
Results
The mediating effect of learning flow on the effect of learning presence on academic achievement was 0.42, and the moderated mediation index of digital literacy was 0.17. Learning flow showed a mediating effect on the relationship between learning presence and academic achievement. Digital literacy had a moderated mediation effect on the relationship between learning presence and academic achievement that was mediated by learning flow.
Conclusion
The intensity of the mediating effect of nursing students’ learning presence on academic achievement through learning flow increases as the level of digital literacy increases. These results suggest that educational programs considering the level of learning presence, learning flow, and digital literacy are required to promote the academic achievement of nursing college students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between freshmen’s perceived social support and learning flow: the chain mediating role of perceived stress and depression
Ye Lin, Xixi Wang, Zhengmei Zhou, Yan Li, Li Liu, Yuanyuan Zhang, Zijiao Zhou, Xiaona Li
BMC Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
Shin Hyang Kim, Jong Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 358. CrossRef - The influence of nursing students’ digital literacy on academic achievement in a blended learning environment: Parallel multiple mediation effects of learning presence
Ja Hyeon Ha, Eun Ju Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 452. CrossRef - Study on the Attitudes toward Artificial Intelligence and Digital Literacy of Dental Hygiene Students
Seon-Ju Sim, Ji-Hye Kim, Min-Hee Hong, Su-Min Hong, Myung-Jin Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(3): 171. CrossRef - The influence of e-learning digital literacy on cognitive flexibility and learning flow in nursing students
Jeongim Lee, Su Ol Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(2): 87. CrossRef - The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Nurses’ Well-Being: Does Digital Competence Matter?
Yali Li, Qi Jing, Taiwen Feng, Xiaoling Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 385. CrossRef - Relationship between learning flow and academic performance among students: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis
Zhang Jinmin, Fang Qi
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The relationship between freshmen’s perceived social support and learning flow: the chain mediating role of perceived stress and depression
- 2,651 View
- 186 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Willingness to Use and Appropriate Payable Cost for Visiting Nurse Service for the Elderly in the Community
- Soyoung Seo, Soong-nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):105-119. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to measure willingness to use (WTU) and appropriate payable cost of visiting nurse service for the elderly and explore their impact factors.
Methods
The study included 752 participants selected from data that were completed in 2017 for the elderly aged over 60 nationwide. Logit and Tobit regression analysis were performed to confirm the influencing factors.
Results
The study found that 39.1% of the elderly in the community were WTU the visiting nurse service, and they reported that the cost per visit was 12,650 Korean Won. The factors influencing WTU were having less than moderate subjective health status (OR = 1.63, p = .011), being part of a social participating groups (OR = 1.50, p = .046), or participation in senior health promotion programs (SHPPs) (OR = 1.96, p = .003). The cost was also influenced by less than moderate subjective health status (β = 4.37, p = .021), being part of a social participating groups (β = 4.41, p = .028), or participation in SHPPs (β = 4.87, p = .023). Additionally, elderly people living alone who were used as covariates were highly WTU (OR = 2.20, p = .029).
Conclusion
This study provides evidence to predict demand for visiting nurse service and reflects consumer value in setting the service cost. This is the first study to derive cost from consumers' perspective regarding the service for the elderly. As it is the result of an open-ended survey, follow-up studies are needed to estimate more reliable and reasonable results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
Dong-ah Choi, Yun-jeong Song, Andy Hong
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2024; 59(5): 147. CrossRef
- Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
- 2,860 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effectiveness of the Infectious Disease (COVID-19) Simulation Module Program on Nursing Students: Disaster Nursing Scenarios
- Won Ju Hwang, Jungyeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):648-660. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an emerging infectious disease (COVID-19) simulation module for nursing students and verify its effectiveness.
Methods
A one-group pretest–posttest quasi-experimental study was conducted with 78 under-graduate nursing students. A simulation module was developed based on the Jeffries simulation model. It consisted of pre-simulation lectures on disaster nursing including infectious disease pandemics, practice, and debriefings with serial tests. The scenarios contained pre-hospital settings, home visits, arrival to the emergency department, and follow-up home visits for rehabilitation.
Results
Disaster preparedness showed a statistically significant improvement, as did competencies in disaster nursing. Confidence in disaster nursing increased, as did willingness to participate in disaster response. However, critical thinking did not show significant differences between time points, and neither did triage scores.
Conclusion
The developed simulation program targeting an infectious disease disaster positively impacts disaster preparedness, disaster nursing competency, and confidence in disaster nursing, among nursing students. Further studies are required to develop a high-fidelity module for nursing students and medical personnel. Based on the current pandemic, we suggest developing more scenarios with virtual reality simulations, as disaster simulation nursing education is required now more than ever. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The development of disaster preparedness education for public: a scoping review
Ling Guo, Mingwang Fang, Li Liu, Haiyan Chong, Wen Zeng, Xiuying Hu
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sustainable Disaster Nursing Education Through Functional Exercises and Simulation: Effects on Knowledge, Problem-Solving, and Learning Outcomes
Myongsun Cho, Miyoung Kwon
Sustainability.2025; 17(20): 9165. CrossRef - The effect of repeated simulation-based disaster education on nursing students’ self-efficacy in disaster response
Ebru Konal Korkmaz, Aynur Uysal Toraman
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Implementation of a Mobile-Integrated Simulation for COVID-19 Nursing Practice: A Randomized Controlled Pretest–Posttest Experimental Design
Sun-Hwa Lee, Jeong-Sil Choi
Healthcare.2024; 12(4): 419. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Simulation-Based Disaster Nursing Education Program for Nursing Students Using Standardized Patients
Yeon Mi PARK, Won Ju HWANG
Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 32(1): e314. CrossRef - Enhancing Disaster Triage Competencies through Simulation-Based Training: An Interventional Study among Undergraduate Nursing Students
Amal Hamdi, Abdulellah Al Thobaity
Sustainability.2023; 15(21): 15513. CrossRef - Development and testing effectiveness of a simulation program to control COVID-19 infections in nursing students
Kino Kang, Mihae Im, Miyoung Jang, Jaewoon Lee, Okjong Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(2): 54. CrossRef - Implementation and Evaluation of a Virtual Reality-Based Cognitive Assessment and Rehabilitation Simulation Course in Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Pre-Post Study
Guichen Li, Lan Gao, Huiru Yin, Yong Jia, Xueyan Zhang, Huimin Tian, Lufang Zheng, Yiming Qiu, Xin Li, Li Chen
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2023; 81: 101430. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Education for Caring Patients with COVID-19
Min Hye Lee, Eun-Young Noh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 397. CrossRef - Effectiveness of multiple scenario simulations of acute and critical care for undergraduate nursing students: A quasi-experimental design
Yu-Ling Chang, Ming-Ju Hsieh, Tsui-Hsia Feng, Shu-Ting Shang, Yun-Fang Tsai
Nurse Education Today.2022; 118: 105526. CrossRef - Systematic Bibliometric Analysis of Research Hotspots and Trends on the Application of Virtual Reality in Nursing
Junqiang Zhao, Yi Lu, Fujun Zhou, Ruping Mao, Fangqin Fei
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fourth Industrial Revolution and Nursing Research
Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 1. CrossRef
- The development of disaster preparedness education for public: a scoping review
- 2,853 View
- 70 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Nurses’ Performance of Care in COVID-19 Wards
- Yoon Sun Kim, Mi-Ae Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):678-688. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing nurses’ performance of care in COVID-19 wards.
Methods
The participants were 132 nurses who worked in COVID-19 wards at three hospitals, and were recruited from April 1 to May 31, 2021. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-test, ANOVA, and multiple regression analysis with SPSS/WIN 24.0 program.
Results
Nursing performance was significantly and positively correlated with ethical sensitivity (r = .75, p < .001), nursing professionalism (r = .67, p < .001), and social support (r = .67, p < .001). Nursing professionalism was positively correlated with ethical sensitivity (r = .64, p < .001) and social support (r = .55, p < .001). Multiple regression analysis for nursing performance revealed that the most significant factor was ethical sensitivity (β = .47, p < .001). Ethical sensitivity, nursing professionalism, and social support explained 66.0% of total variance in nursing performance.
Conclusion
Ethical sensitiviy, nursing professionalism, and social support significantly influence nurses’ performace of care in COVID-19 wards. It suggests that intervention programs should be directed at improving nurses’ ethical sensitivity, bolstering social support, and enhancing nursing professionalism. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Knowledge on Standard Precautions, Nursing Professionalism, and Organizational Culture for Infection Control on Hospital Nurses’ Performance with Guidelines for Standard Precautions
Jiwon Kim, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 225. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Infection Control Practices of Nurses at University Hospitals
Mi Hyang Lee, Sun Hwa Jun
Healthcare.2022; 10(8): 1517. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Anxiety of Nursing Students in Clinical Practice during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Gun Ja Jang, Shin Jeong Park, Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(4): 363. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Post-traumatic Growth of Nurses at Nationally Designated Infectious Disease Hospital
Ji Eun Oh, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 499. CrossRef
- The Influence of Knowledge on Standard Precautions, Nursing Professionalism, and Organizational Culture for Infection Control on Hospital Nurses’ Performance with Guidelines for Standard Precautions
- 1,956 View
- 40 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Nurses’ Experience with Caring for COVID-19 Patients in a Negative Pressure Room Amid the Pandemic Situation
- Eun-Young Noh, Young Jun Chai, Hyun Jeong Kim, Eunjin Kim, Yeon-Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):585-596. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to explore nurses’ experience with caring for COVID-19 patients in a negative pressure room amid the spread of the pandemic.
Methods
This study was a qualitative research, and focus group interviews were used to collect data. Three focus groups comprising 19 nurses were interviewed from February 17 to 25, 2021. All interviews were recorded and transcribed verbatim with the consent of the participants. The verbatim transcripts were scrutinized using thematic analysis.
Results
Two main themes emerged from the analysis: ‘Struggling in an isolated space’ and ’Limitations of nursing infrastructure and system’. The nurses caring for COVID-19 patients experienced anxiety and fear about the infection, physical exhaustion, emotional burnout, and a sense of duty as a nurse. They also acknowledged the lack of guidelines, increased task and burden, limitations of nursing care, and the demand for improving the limitations of the nursing system.
Conclusion
The results of this study demonstrate that nurses caring for COVID-19 patients encounter physical and emotional problems within the limited healthcare system. The study suggests that comprehensive interventions are needed for nurses. Furthermore, detailed guidelines, strengthening of nursing personnel, and improvements to the nursing system are vital to effectively cope with the pandemic. The government and medical institutions should be aware of the needs of nurses and what they are going through, and make efforts to improve the quality of life of healthcare workers and create a safe healthcare environment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth among Nurses in COVID-19 Isolation Wards in Tertiary Hospitals
Ye Seul Im, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 233. CrossRef - Experiences of Person‐Centred Care Among Nurses in COVID‐19 Wards: A Qualitative Study
Myoungsuk Kim, Yongmi Lee, Hyun‐Ju Kang
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Non-Contact Nursing Experiences of Clinical Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 446. CrossRef - Nurses’ intention to care of COVID-19 patients in hospitals dedicated to infectious disease in South Korea: application of the theory of planned behavior and verification of the moderating effect of ethical nursing competence
Mira Mo, Seongmi Moon, Eun Kyeung Song
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses' perceptions of medical service robots in negative‐pressure isolated wards and in general wards: A cross‐sectional survey
Jung Hwan Lee, In Ho Han, Jong Hwan Park, Kye‐Hyung Kim, Jaehyun Hwang, Dong Hwan Kim, Jae Il Lee, Kyoung Hyup Nam
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Korean Hospital Nurses’ Experiences with COVID-19: A Meta-Synthesis of Qualitative Findings
Suk-Jung Han, Hee-Jung Hong, Bok-Soon Shin
Healthcare.2024; 12(9): 903. CrossRef - Improving Emerging Infectious Disease Control Based on the Experiences of South Korean Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Systematic Review
Ha-Young Park, In-Sun Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Need for Information and Communication Technology during COVID-19: An Exploratory Study Using Nurses’ Activity Diaries
Hyeongsuk Lee, Dongmin Lee, Seungmin Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2023; 29(3): 256. CrossRef - Factors Influencing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Control Practices of Nurses Caring for COVID-19 Patients in South Korea: Based on Health Belief Model
Dain Jeong, Young Eun
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 3223. CrossRef - Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 584. CrossRef - Experiences of Psychiatric Nurses Working in a Closed Psychiatric Unit during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 374. CrossRef - Experiences of Caring for Cohort-Isolated Patients among Nurses in Locked Psychiatric Units
Hyeran An, Kyungmi Kim, Jongeun Lee, Sunhwa Won
Healthcare.2023; 11(19): 2650. CrossRef - Effect of Anxiety and Calling on Professional Quality of Life in COVID-19 Dedicated Nurses in Korea
Minjung Moon, Kyoungsan Seo
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1797. CrossRef - Critical role of information and communication technology in nursing during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A qualitative study
Hye Jin Yoo, Hyeongsuk Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(8): 3677. CrossRef - Correlation between COVID-19 and Nurses’ Job Stress and Burnout
Seyoung Yun, Song Vogue Ahn
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2022; 2(2): 202. CrossRef - Experience of Nurses in Charge of COVID-19 Screening at General Hospitals in Korea
Boo Young Ha, Yun-Sook Bae, Han Sol Ryu, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 66. CrossRef - Frontline nurses' burnout and its associated factors during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea
Eun-Young Noh, Yeon-Hwan Park, Young Jun Chai, Hyun Jeong Kim, Eunjin Kim
Applied Nursing Research.2022; 67: 151622. CrossRef - Emergency nurses' attitudes, perceptions about personal protective equipment and willingness to care for COVID‐19 patients: A descriptive, cross‐sectional study
Ha‐Ra Jang, Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2514. CrossRef - Clinical Field and Alternative Clinical Practice Experience in a Pandemic Situation of Nursing Students Who Have Experienced Clinical Practice before COVID-19
Hyeran An, Sunnam Park, Jongeun Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(20): 13372. CrossRef - Fourth Industrial Revolution and Nursing Research
Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 1. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experience in COVID-19 Patient Care
Soojin Chung, Mihyeon Seong, Ju-young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(2): 142. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth among Nurses in COVID-19 Isolation Wards in Tertiary Hospitals
- 1,954 View
- 26 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref

- A Phenomenological Study of the Lived Experience of Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in Korea
- Hee Oh, Na Kyoung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):561-572. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to understand nurses’ lived experiences of caring for patients with COVID-19.
Methods
The phenomenological research method was used. The study participants were 16 Korean nurses who had experiences in caring for patients with COVID-19 in clinical settings. Data was collected using one-on-one in-depth interviews, from June 30 to September 30, 2020. During the interview, the quarantine rules were observed.
Results
The study derived four themes clusters and thirty-eight sub themes. Four theme clusters were identified, i.e., ‘a repetitive sense of crisis’, ‘enduring a drastic change,’ ‘sacrifice of personal life,’ and ‘pride in nursing’. The nurses’ experiences of caring for patients with COVID-19 were an uneasy, unfamiliar, and threatening experiences for an individual, but it is an opportunity for a nursing organization to renew. Accordingly, it was found that nurses faithfully fulfill their individual roles with a vocation and responsibility.
Conclusion
The study provides an in-depth understanding of the situational, psychological, and environmental aspects of challenges facing nurses in the pandemic situation. Based on the findings, institutional follow-up measures should be provided to establish support systems for better nursing care. In addition, studies are needed to track nurses' experiences in the prolonged COVID-19 situation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Death Attitude, Self-esteem, and Perceived Risk of Respiratory Infectious Diseases on Death Anxiety among Nurses in COVID-19 Wards
Yeon Hee Jeong, Hun Ha Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(1): 5. CrossRef - Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(2): 236. CrossRef - Development of Standard Operating Procedures for Infectious Disease Disaster Response in Healthcare Institutions
Kyungah Woo, Sungmo Jung, HyeMin Byun, Keunhee Yoo, Eunkyoung Yun
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2025; 31(1): 46. CrossRef - Experiences of Person‐Centred Care Among Nurses in COVID‐19 Wards: A Qualitative Study
Myoungsuk Kim, Yongmi Lee, Hyun‐Ju Kang
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses’ Experience of Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in Residential Treatment Centers: A Qualitative Study
Jung Hwan Heo, Heeje Yun, Yeong Hun Park
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 226. CrossRef - Terminal Care Performance of Nurses Caring for COVID‐19 Patients: A Cross‐Sectional Descriptive Study
Juyeon Oh, Dong‐Hee Kim, Yujin Kim
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experiences of Nurses Working as Helpers in a Dedicated COVID-19 Ward of a Certified Tertiary Hospital
Eun Hyang Park, Hee Kyung Chang
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(2): 93. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Non-Contact Nursing Experiences of Clinical Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 446. CrossRef - The lived experiences of operating room nurses from the surgery on COVID-19 patients: a phenomenological study
Behzad Imani, Mehrnush Mostafayi, Shirdel Zandi
Perioperative Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Delphi Study on the Changes in Work, Organizational Culture, and Health Issues of Nurses at Tertiary Hospitals in South Korea during the COVID‐19 Pandemic
MiRa Yun, WonJong Kim, Boas Yu, Eun-Hi Choi, Paolo C. Colet
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses’ Experiences with the Use of Electronic Nursing Record: A Qualitative Study
Yul Hee LEE, Min Sun KIM, Hee Jung KIM
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2024; 24(3): 110. CrossRef - Nurses’ healthy behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic and related factors
Eun-Kyoung Lee, Ji-Soo Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(1): 39. CrossRef - Nurses’ intention to care of COVID-19 patients in hospitals dedicated to infectious disease in South Korea: application of the theory of planned behavior and verification of the moderating effect of ethical nursing competence
Mira Mo, Seongmi Moon, Eun Kyeung Song
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety among nurses in caring for COVID-19 patients: a qualitative study
Sri Eka Wahyuni, Budi Anna Keliat, Herni Susanti, Besral Besral
Healthcare in Low-resource Settings.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving Emerging Infectious Disease Control Based on the Experiences of South Korean Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Systematic Review
Ha-Young Park, In-Sun Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Influences of Organizational Culture, Nursing Workplace Spirituality, and Nurses’ Perceived Health Status on Quality of Nursing Work Life according to Nursing Clinical Ladder
Hyun Sook Lee, Ju Hyun Jin, Ju Ri Lee, Hye Jin Kim, Yeon Jae Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(1): 31. CrossRef - The COVID-19 Pandemic Experience of A Cohort of Quarantined University Hospital Nurse Managers
Soon-Youl Lee, Suk Jung Han, Hee Jung Hong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(2): 205. CrossRef - Parenting Experience of Shift Nurses With Elementary School-Aged Children During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Phenomenological Study
Jeung-Im Kim, Mi-Youn Jang, A-Ri Song, Jung-Eun Yu, Myung-Sook Baik
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2023; 27(3): 154. CrossRef - Development of a Reward Scale for Hospital Nurses
Sun Hee Kim, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(5): 525. CrossRef - Treatment of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and cross‐infection in dental clinics in Korea
Na‐Young Lee, Han‐Na Kim
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2023; 21(2): 438. CrossRef - Influence of Job Stress and Resilience on Burnout of Clinical Nurses Working in Small and Medium-Sized Hospital: Focusing on Comparing National Safety Hospital and COVID-19 Dedicated Hospital
Su-Young Jang, Young Ko
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(2): 65. CrossRef - Beyond the case numbers: Social determinants and contextual factors in patient narratives of recovery from COVID-19
Danielle Hitch, Elle Deféin, Melanie Lloyd, Bodil Rasmussen, Kimberley Haines, Eleanor Garnys
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health.2023; 47(1): 100002. CrossRef - Experiences of Caring for Cohort-Isolated Patients among Nurses in Locked Psychiatric Units
Hyeran An, Kyungmi Kim, Jongeun Lee, Sunhwa Won
Healthcare.2023; 11(19): 2650. CrossRef - Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 584. CrossRef - Experiences of Psychiatric Nurses Working in a Closed Psychiatric Unit during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 374. CrossRef - Burnout among Nurses in COVID-19 Designated Units Compared with Those in General Units Caring for Both COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Patients
Kyung Ah Woo, Eun Kyoung Yun, JiSun Choi, Hye Min Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 374. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Organizational Commitment of Nurses at an Infectious Disease Hospital of COVID-19
Su Hee Moon, Min Hye Kim, Doo Young Kim, Yoon Ji Ryu, Soo Joung Lee, Jin Nyoung Jang, Mi Yeoul Jung, Yoon Ju Cho, Hyo Jeong Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(2): 39. CrossRef - The COVID-19 Correspondence Work Experience of Community Health Practitioners
Jae-Hyun Ha, Hyun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(2): 139. CrossRef - Exploring the Experiences of Nurse Managers during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hyunjin Jang, Eun-Mi An, Ki-Eun Kim, Yoounjoong Jung, Youjung Choi, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 460. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nursing Intention for Patients with Emerging Infectious Diseases among Nurses in Hospitals Dedicated to COVID-19: A Focus on the Mediating Effects of Job Crafting
Yu Na Lim, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 105. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experiences of Care for Patients in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection Wards during the Early Stages of the Pandemic
Nanhui Kim, Youngran Yang, Junhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(1): 109. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Educational Needs and Nursing Intention Regarding COVID-19 Patient Care among Undergraduate Nursing Students
Eun-Joo Ji, Eun-Kyung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15671. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Post-traumatic Growth of Nurses at Nationally Designated Infectious Disease Hospital
Ji Eun Oh, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 499. CrossRef
- Effects of Death Attitude, Self-esteem, and Perceived Risk of Respiratory Infectious Diseases on Death Anxiety among Nurses in COVID-19 Wards
- 3,604 View
- 91 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref

- A Concept Analysis of Quality Nursing Care
- I Gede Juanamasta, Yupin Aungsuroch, Joko Gunawan
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):430-441. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21075
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to perform a concept analysis of quality nursing care.
Methods
Walker and Avant’s concept analysis method was used to carry out this study.
Results
The defining attributes identified were as follows: caring, the nurse-patient relationship, and patient needs. Antecedents included patient characteristics, individual factors (age, education, knowledge, competence, and experience), job position, and environmental factors. The consequences of quality nursing care have significant influence on both patients and nurses.
Conclusion
The findings can aid researchers in obtaining a better understanding of quality nursing care, and stakeholders can consider the factors related to quality nursing care and its consequences to improve the nursing process. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- CPD focus: importance of listening in developing therapeutic relationships
Sophie Louise Waters
Mental Health Practice.2025; 28(3): 37. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the quality of nursing care scale among hospital nurses: a bifactor exploratory structural equation modeling analysis
Chiu-Shu Fang, Cheng-Hsien Li, Shu-Ching Ma, Fang-Ming Hwang, Maria Manuela Martins, Fan-Hao Chou
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of high-quality nursing on surgical site wound infections after colostomy in patients with colorectal cancer
Yu Cheng, Yuan-Xing Chen
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2024; 16(12): 3835. CrossRef - Emergency room nurses' caring ability and its relationship with patient safety outcomes: A cross-sectional study
Leodoro J. Labrague
International Emergency Nursing.2024; 72: 101389. CrossRef - Prevalence of burnout and its determinants among Indonesian nurses: a multicentre study
I. Gede Juanamasta, Yupin Aungsuroch, Joko Gunawan, Michael Joseph Dino, Rapin Polsook
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Current trends and issues in quality care and patient safety: A discussion with ChatGPT
Joko Gunawan
Journal of Healthcare Administration.2023; 2(1): 1. CrossRef - The ethical principles and caring behavior of Indonesian nurses
Ilkafah Ilkafah, Anestasia Pangestu Mei Tyas, Rini Rachmawaty
Healthcare in Low-resource Settings.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - L’expérience des soins des personnes qui vivent une transplantation hépatique. Recherche phénoménologique descriptive au sein d’un hôpital académique belge
Ivo Manuel Mateus Alves, Chantal Cara, Thierry Gustot, Hélène Lefebvre, Dan Lecocq
Recherche en soins infirmiers.2023; N° 152(1): 42. CrossRef - Strategies and challenges in addressing ethical issues in the hospital context: A phenomenological study of nurse team leaders
Ni Made Nopita Wati, I Gede Juanamasta, Jutharat Thongsalab, Jintana Yunibhand
Belitung Nursing Journal.2023; 9(2): 139. CrossRef - Causal Modelling of Factors Influencing Quality of Nursing Care in China
Xiaolu Xue, Wipada Kunaviktikul, Kulwadee Abhicharttibutra, Orn-Anong Wichaikhum
Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research.2023; 27(3): 417. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Indonesian Version of the McCloskey/Mueller Satisfaction Scale
I. Gede Juanamasta, Yupin Aungsuroch, Mary L. Fisher, Nursalam, Jose Luis Santos
Journal of Nursing Management.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - The Therapeutic Nurse–Patient Relationship in Hemodialysis: A Pilot Mixed-Method Study on the Perceived Quality of Nurses’ Attitudes and Caring Behaviors
Claudia Camedda, Gloria Bici, Camilla Elena Magi, Alice Guzzon, Yari Longobucco
Nursing Reports.2023; 13(3): 990. CrossRef - Translation and validation study of the Indonesian version of the practice environment scale of the nursing work index
I Gede Juanamasta, Yupin Aungsuroch, Mary L. Fisher, Siluh Nyoman Alit Nuryani, Ni Nyoman Ayuningsih
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2023; 10(4): 511. CrossRef
- CPD focus: importance of listening in developing therapeutic relationships
- 9,553 View
- 367 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


