Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effectiveness of a mobile application for tracking symptoms and enhancing symptom management among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in Bangkok, Thailand: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Duangrat Kaveenuntachai, Supawan Jaiboon, Bualuang Sumdaengrit, Chureeporn Silaguntsuti, Arveewan Vittayatigonnasak, Pornchan Sailamai
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):178-190. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study evaluated the effectiveness of a mobile application in tracking symptoms and improving symptom management and quality of life (QoL) among breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in Thailand.
Methods
A non-randomized controlled trial was used, with 25 participants in the intervention group and 25 in the control group. Research instruments included a demographic data form, the NCI-PRO-CTCAE Items-Thai-Thailand version 1.0, and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Core Questionnaire and Breast Cancer-Specific Module.
Results
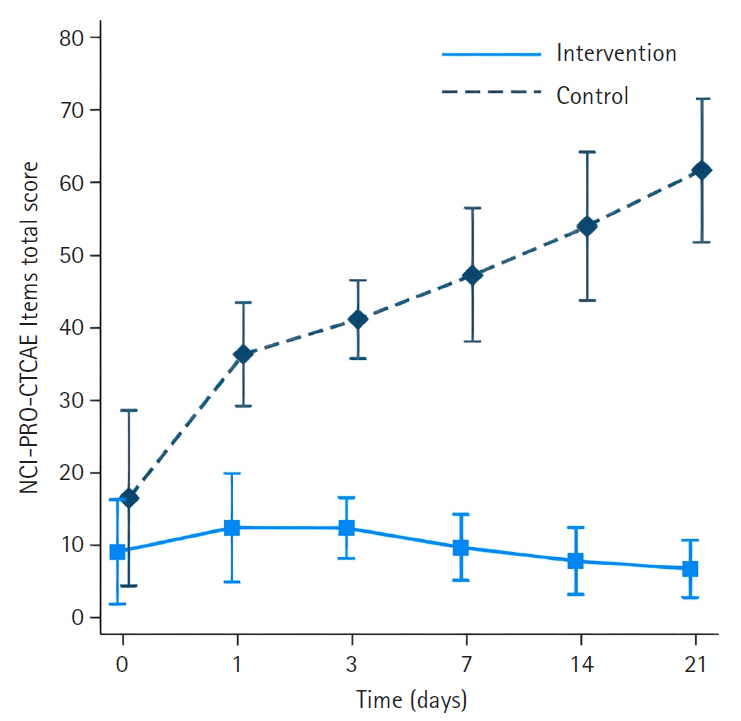
The intervention group had significantly less severe side effects than the control group, with mean differences of –23.33 (95% confidence interval [CI], –27.82 to –18.83) on day 1, –28.18 (95% CI, –33.22 to –23.14) on day 3, –34.63 (95% CI, –40.18 to –29.08) on day 7, –42.56 (95% CI, –48.72 to –36.40) on day 14, and –51.31 (95% CI, –58.13 to –44.48) on day 21 (p<.001 for all). On day 21, participants in the intervention group reported significantly higher scores in the Global Health QoL and Functional Scales compared to the control group (p<.001). Additionally, intervention group participants reported lower scores on the Symptom Scales and higher scores on the Functional Scales than those in the control group (p<.001).
Conclusion
The ChemoPro application helped manage chemotherapy-related symptoms and was associated with improved symptom monitoring and QoL. Nonetheless, the study was limited by a small sample size and restriction to Android users. Future research with larger and more diverse populations is recommended before broader implementation in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
Saúl Eduardo Contreras-Sánchez, Svetlana V. Doubova, Rocío Grajales-Álvarez, Ricardo Villalobos-Valencia, Abdel Karim Dip-Borunda, José Gustavo Nuñez-Cerrillo, Alma Diana Huerta-López, Álvaro José Montiel-Jarquín, Arturo García-Galicia, Enrique Isay Talam
BMC Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
- 4,258 View
- 215 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
- Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):418-431. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify factors influencing oncofertility and to explore the oncofertility experiences of patients with gynecological cancer using quantitative and qualitative methods, respectively. Methods: An explanatory sequential mixed-methods study was conducted. The quantitative study involved 222 patients with gynecological cancer recruited from online cafes and hospitals. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics 28. For qualitative research, eight patients with gynecological cancer were interviewed. Data were analyzed using theme analysis method. Results: Oncofertility performance was quantitatively assessed in 40 patients (18.0%). Factors that significantly affected oncofertility were fertility preservation awareness (odds ratio [OR] = 14.97, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 4.22~53.08), number of children planned before cancer diagnosis (OR = 6.08, 95% CI: 1.89~19.62; OR = 5.04, 95% CI: 1.56~16.29), monthly income (OR = 3.29, 95% CI: 1.23~8.86), social support (OR = 1.08, 95% CI: 1.01~1.17), and anxiety (OR = 0.79, 95% CI: 0.66~0.95). Qualitative results showed three theme clusters and eight themes: (1) themes for determinant factors affecting oncofertility selection: ‘desire to have children’ and ‘special meaning of the uterus and ovaries;’ (2) themes for obstructive factors affecting oncofertility selection: ‘fertility preservation fall behind priorities,’ ‘confusion caused by inaccurate information,’ and ‘my choice was not supported;’ (3) themes for support factors affecting oncofertility selection: ‘provide accurate and reasonable information about oncofertility,’ ‘addressing the healthcare gap,’ and ‘need financial support for oncofertility.’ Conclusion: Financial support, sufficient information, social support, and anxiety-relief interventions are required for oncofertility in patients with gynecological cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital health interventions for oncofertility in female patients: a systematic review
Juyoung Ha, Minji Kim, Hyojin Park
Women's Health Nursing.2025; 31(2): 119. CrossRef
- Digital health interventions for oncofertility in female patients: a systematic review
- 2,168 View
- 121 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of an App-Based Self-Management Program for Exercise Practice of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Suyoun Maeng, Jungok Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):250-265. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an app-based self-management program based on the transtheoretical model (TTM) for breast cancer survivors’ exercise practice, as well as to investigate the program’s effects on the stage of change for exercise, exercise self-efficacy, exercise decisional balance, exercise amount, and body composition.
Methods
This non-randomized controlled study included 52 participants (26 in each of the experimental and control groups, respectively). An app-based self-management program based on the TTM was conducted with the experimental group for a 12-week period. The program comprised three components: individual coaching for each stage of change for exercise based on TTM, amount of exercise and body composition monitoring, and online self-help meetings.
Results
Compared with the control group, the experimental group had significantly higher stages of change for exercise (p < .001), exercise self-efficacy (p < .001), exercise decisional balance (p = .002), exercise amount (p < .001), and body composition (body weight [p = .006], body mass index [p = .005], and body fat percentage [p = .010]) immediately and four weeks after the intervention.
Conclusion
An appbased self-management program based on the TTM improves exercise behaviors in breast cancer survivors and provides physical benefits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a mobile health coaching intervention on symptom experience, self-management, and quality of life in breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Ji Young Kim, Su Jin Jung
Medicine.2025; 104(12): e41894. CrossRef
- Effects of a mobile health coaching intervention on symptom experience, self-management, and quality of life in breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
- 4,171 View
- 212 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The Experience of Gynecologic Cancer in Young Women: A Qualitative Study
- Sung-Jin Kim, Hyunjeong Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):115-128. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to understand the experiences of women under 40 years of age with gynecologic cancer.
Methods
Semi-structured individual in-depth interviews were conducted with 14 Korean female patients aged 21~39 years with gynecologic cancer. The data were analyzed using Corbin and Strauss' grounded theory approach, including open coding, context analysis, and integrating categories.
Results
Grounded theory analysis revealed nine categories and a core category of ‘the journey to find my life after losing the life as a typical woman.’ The categories that emerged as the conditions are ‘Unwelcomed guest, cancer,’ ‘Completely devastated life as an ordinary woman,’ ‘Uncertain future,’ ‘Losing my physical characteristics as a woman,’ and ‘Life tied with treatments.’ The actions/interactions were ‘Decrease of interpersonal relationships,’ ‘A lonely battle to overcome alone,’ and ‘The power to overcome hardships.’ The consequence was ‘Live my own life.’ Conclusion: This study contributes to the development of a substantive theory of the experience of gynecologic cancer in young women, which has been on the rise in recent years. The study’s results are expected to be used as a basis for providing nursing care to help young women with gynecologic cancer adapt to their disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mediating Effects of Negative Affect and Cancer Coping in the Relationship between Perceived Stress and Health-Related Quality of Life among Gynecological Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Yeon-woo Kim, Sunki Kim, Hye-Ja Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(3): 266. CrossRef - Exploring the Disease Experience in Women with PCOS: A Qualitative Content Analysis
Miok Kim, Su Jeong Yi
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3243. CrossRef - ORGAN LOSS AS A TRIGGER OF IDENTITY CRISIS IN WOMEN WITH MALIGNANT TUMORS OF THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (literature review)
Valentyn BELYAK, Rostyslav BILOBRYVKA
Ukrains kyi Visnyk Psykhonevrolohii.2025; : 123. CrossRef - Illness Experiences of Young Adult Thyroid Cancer Patients Receiving Radioactive Iodine Treatment
Hyeon Ae Lee, Sue Kyung Sohn
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(4): 195. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 418. CrossRef
- The Mediating Effects of Negative Affect and Cancer Coping in the Relationship between Perceived Stress and Health-Related Quality of Life among Gynecological Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,669 View
- 82 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
- Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):245-260. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the effects of an advanced practice nurse-led psychoeducational program on distress, anxiety, depression, coping with cancer (CWC), health promotion behavior (HPB), and quality of life (QOL) among colorectal cancer survivors.
Methods
This study was designed as a quasi-experimental study with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest. The participants were survivors of colorectal cancer who underwent follow-up care. There were 39 survivors: 19 in the experimental group and 20 in the control group. The experimental group performed a psychoeducational program for 120 minutes per session, once a week for a total of six weeks, while the control group received routine education and counseling. Distress, anxiety, depression, CWC, HPB, and QOL were investigated before, immediately after, and 4 weeks after the intervention. The data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN ver. 24.0, using repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
There were significant interactions between time and group for distress and anxiety. In addition, CWC interacted with the total of CWC and interpersonal coping, and QOL interacted with the total of QOL and functional status. However, there were no significant differences in the depression or HPB scores.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, we expect that this program can be used as an effective intervention for colorectal cancer survivors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tailored psychoeducation for multiple myeloma patients: a step toward enhancing quality of life and health outcomes
Yoorin Cho, Yang Sook Yoo
Health Education Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a mobile-based return to work program for decent return to work, fatigue, stress, and quality of working life among cancer survivors
Kisook Kim, Hyohyeon Yoon
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2025; 19(2): 713. CrossRef - Elevating Elderly Cancer Care: A Systematic Review of Advanced Practice Nursing’s Role in Senior Oncology Patients’ Quality of Life
Cristian-David Useche-Guerrero, María-de-los-Ángeles Merino-Godoy, Eva-María Barroso-Márquez, Emilia Isabel Martins Teixeira da Costa, Rafaela Camacho Bejarano, Francisco-Javier Gago-Valiente, Rizal Angelo Grande
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Psycho-education Interventions on Colorectal Cancer Patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
XiaoYing Zhang, HuangQin Liu, LiYing Lin, Huimin Xiao
Journal of Cancer Education.2023; 38(5): 1413. CrossRef - How should the healthcare system support cancer survivors? Survivors’ and health professionals’ expectations and perception on comprehensive cancer survivorship care in Korea: a qualitative study
Su Jung Lee, Dal-Lae Jin, Young Ae Kim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Seok-Jun Yoon
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Survivorship Care and Roles of Oncology Nurses
Eun Young Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 121. CrossRef
- Tailored psychoeducation for multiple myeloma patients: a step toward enhancing quality of life and health outcomes
- 1,948 View
- 93 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- The Development of a Tool for Assessment of Spiritual Distress in Cancer Patients
- Jin Sook Kim, Il-Sun Ko, Su Jin Koh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):52-65. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was conducted to develop a scale to measure spiritual distress in cancer patients.
Methods
A total of 69 preliminary items for the spiritaul distress assessment tool (SDAT) were compiled, based on a literature review, selection of empirically relevant items through concept analysis of hybrid models, confirmation of content validity by experts, cognitive interviews, and a pretest. Self-administered questionnaires were collected between April 1 and July 31, 2018, from 225 cancer patients at four medical institutions and one nursing home. The data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, convergent and discriminant validity, and Pearson correlation for criterion validity. Reliability was tested by Cronbash’s α coefficient.
Results
The final version of the SDAT consisted of 20 items. Five-factors, loss of peace, burden of family, avoidance of confronting death, guilt and remorse, regret for not being able to apololgize and forgive were extracted, and showed 62.8% of total variance. The factors were confirmed through convergent and discriminant validity. Criterion validity was confirmed by functional assessment chronic illness therapy spiritual well-being scale 12 (FACIT-Sp12). The overall Cronbach’s α was .91, and the coefficients of each subscale ranged from .78~.83.
Conclusion
The SDAT for cancer patients is valid and reliable. It is suggested that the tool can be used to measure spiritual distress in cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a measurement of doctor-patient communication quality scale
Jiayi Shao, Minhui Wen, Yuqing Zhang, Liping Zhang, Jiangjie Sun
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity and reliability of the integrated palliative care outcome scale (IPOS) in Korea: a multicenter study of terminally ill cancer patients
So-Jung Park, Yujin Park, Mira Han, Sun-Hyun Kim, In Cheol Hwang, Go-un Woo, Yoo Jeong Lee, Young Sung Kim, Hyun Jung Jho, Yoon Jung Chang
BMC Palliative Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Family caregivers’ perceived value of caring for older patient: A hybrid model of concept analysis
Seon-Hye Heo, Hye-Ryoung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(2): 152. CrossRef - Spiritual Distress in Patients with Dyspnea: A Review of Measurement Tools
Leah McCann Klug
Illness, Crisis & Loss.2023; 31(4): 736. CrossRef
- Development of a measurement of doctor-patient communication quality scale
- 2,438 View
- 77 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- The Lived Experience of Body Alteration and Body Image with Regard to Immediate Breast Reconstruction among Women with Breast Cancer
- Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):245-259. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21028
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to explore the lived experience of body alteration and body image with regard to immediate breast reconstruction among women with breast cancer.
Methods
Data were collected from July to December 2020 through individual in-depth interviews with 15 women who had undergone immediate breast reconstruction due to breast cancer. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis.
Results
The following four theme clusters emerged. First, “revalued meaning of breasts due to cancer” illustrated the fact that cancer removal surgery brought the participants to reconsider the meaning of their breasts. Second, “had no choice but breast reconstruction” demonstrated the participants’ decision-making process of not wanting to lose breasts. Third, “unsatisfied breasts despite reconstruction” portrayed the distress due to the unexpected surgical outcomes. Finally, “restarted everyday routines with the altered body” described the healing process of the participants by accepting their changed body.
Conclusion
In Korea, where family-centeredness and fidelity are highly valued, women perceived their breasts not only as a symbol of femininity but as the mediator connecting the self to family. Despite the distress related to imperfect breasts, the participants were thankful for their reconstructed breasts. Breast reconstruction helped them return to daily life as the psychological trauma of breast cancer was healed. The participants rebuilt their body image by accepting their scarred new body. This may allow health professionals to provide constructive and culturally appropriate counseling in advance by providing insight into women’s perception of their body image with regard to breast reconstruction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
Hyeng Sook Yoon, Eunjung Ryu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100820. CrossRef - Categorising Subjective Perceptions of Middle-Aged Breast Cancer Patients Using Q Methodology
Min-Jeung Shim, Song-Yi Lee, Oh-Sun Ha
Healthcare.2024; 12(18): 1873. CrossRef - Body Acceptance Scale for Women with Breast Cancer: Development and Validation of a Measurement
Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2023; 39(5): 151486. CrossRef - Influence of body image on quality of life in breast cancer patients undergoing breast reconstruction: Mediating of self‐esteem
Yunhee Jang, Mihyeon Seong, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(17-18): 6366. CrossRef - Body acceptance in women with breast cancer: A concept analysis using a hybrid model
Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 62: 102269. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis on the prepectoral single-stage breast reconstruction
Jiameng Liu, Xiaobin Zheng, Shunguo Lin, Hui Han, Chunsen Xu
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(7): 5659. CrossRef
- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
- 2,513 View
- 86 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Applying Extended Theory of Planned Behavior for Lung Cancer Patients Undergone Pulmonary Resection: Effects on Self-Efficacy for Exercise, Physical Activities, Physical Function, and Quality of Life
- Yeonjung Lim, Haejung Lee, Do Hyung Kim, Yeong Dae Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):66-80. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.66
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: This study aims to examine the effects of nursing interventions based on the Extended Theory of Planned Behavior (ETPB) regarding self-efficacy for exercise (SEE), physical activity (PA), physical function (PF), and quality of life (QOL) in patients with lung cancer who have undergone pulmonary resection.
Methods: This quasi-experimental study was conducted between July 2015 and June 2018 in two university-affiliated hospitals. The intervention included pre-operative patient education, goal setting (action and coping planning), and feedback (behavior intention and perceived behavioral control). The intervention group (IG) (n=51) received nursing interventions from the day before surgery to 12 months after lung resection, while the comparison group (CG) (n=36) received usual care. SEE, PA, PF (dyspnea, functional status, and 6-minute walking distance [6MWD]), and QOL were measured before surgery and at one, three, six, and 12 months after surgery. Data were analyzed using the χ2 test, Fisher’s exact test, Mann-Whitney U test, t-test, and generalized estimation equations (GEE).
Results: There were significant differences between the two groups regarding SEE (χ2=13.53,
p =.009), PA (χ2=9.51,p =.049), functional status (χ2=10.55,p =.032), and 6MWD (χ2=15.62,p =.004). Although there were no time or group effects, the QOL mental component (Z=-2.78,p =.005) of the IG was higher than that of the CG one month after surgery. Interventions did not affect dyspnea or the QOL physical component.Conclusion The intervention of this study was effective in improving SEE, PA, functional status, and 6MWD of lung cancer patients after lung resection. Further extended investigations that utilize ETPB are warranted to confirm these results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- [Retracted] Dynamic Changes and Influencing Factors for the Quality of Life in Nursing Care after Lung Cancer Resection
Shuzhen Hu, Aihong Fang, Mohammad Farukh Hashmi
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on influence factors of public participation willingness in substation project based on integrated TPB-NAM model
Xin Ma, Junpeng Li, Fuli Guo, Caocao Cui, Tengfei Chen, Fan Xv, Wenbin Wang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- [Retracted] Dynamic Changes and Influencing Factors for the Quality of Life in Nursing Care after Lung Cancer Resection
- 2,542 View
- 105 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Incidence of Colon Cancer Related to Cigarette Smoking and Alcohol Consumption in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: Prospective Cohort Study
- Ahra Jo, Heeyoung Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):713-723. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.713
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the impact of cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption on the incidence of colon cancer in adults with metabolic syndrome.
Methods This study employed a longitudinal study design and utilized secondary data drawn from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES). The data of a sample of 2,327 adults with metabolic syndrome tracked every two years from 2001 to 2014 were used in this study. Statistical data analyses of the frequency, number of cases per 100,000 person-years, log-rank test, Kaplan-Meier curve, and Cox's proportional hazards regression were performed using IBM SPSS statistics version 24.
Results During the observation period, the number of colon cancer cases was 46, and the total person-years were 252,444. The incidence of colon cancer was higher in current, over 10 pack-year smokers when compared to non-smokers (hazard ratio=3.38, 95% confidence interval=1.09~8.42).
Conclusion Excessive and long-term smoking should be avoided to prevent colon cancer, especially in adults with metabolic syndrome, since it might exacerbate the risk factors of colon cancer. Particularly, health professionals need to provide individualized smoking cessation interventions to those at high risk of colon cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genetic correlation, and causal relationships between 3 solid cancer types and human traits
Claudia Cava, Ehsan Nazemalhosseini Mojarad, Isabella Castiglioni
Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ribosomal Protein L9 Maintains Stemness of Colorectal Cancer via an ID-1 Dependent Mechanism
Eun-Hye Jeon, So-Young Park, Keon Uk Park, Yun-Han Lee
Journal of Cancer Prevention.2024; 29(2): 25. CrossRef - Unhealthy lifestyle factors and the risk of colorectal cancer: a Mendelian randomization study
Xingyuan Li, Zewen Chang, Jiaqi Wang, Ke Ding, Shengqi Pan, Hanqing Hu, Qingchao Tang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between WHO First-Step Analgesic Use and Risk of Breast Cancer in Women of Working Age
Hyun Sook Oh, Hwa Jeong Seo
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(2): 323. CrossRef - RPL27 contributes to colorectal cancer proliferation and stemness via PLK1 signaling
So-Young Park, Daekwan Seo, Eun-Hye Jeon, Jee Park, Byeong-Churl Jang, Jee Kim, Seung-Soon Im, Jae-Ho Lee, Shin Kim, Chi Cho, Yun-Han Lee
International Journal of Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Time to Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Adults with Hyperglycemia: Using a Community-Based Cohort Study
Ihn-Sook Jeong, Chan-Mi Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12090. CrossRef - Effects of Nutritious Meal Combined with Online Publicity and Education on Postoperative Nutrition and Psychological State in Patients with Low Rectal Cancer After Colostomy
Lijuan Qu, Mei Zhou, Yi Yu, Kaili Li, Deepika Koundal
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Burden of Cancer Due to Cigarette Smoking and Alcohol Consumption in Korea
Yoon-Sun Jung, Seok-Jun Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3493. CrossRef - Effect and Prognosis Factors of Combining Laparoscopic Radical Resection of Colon Adenocarcinoma with Docetaxel Therapy in Treating Middle and Advanced Colon Adenocarcinoma
Qi Gao, Caifeng Zhang, Zhichao Dong, Yan Guo, Li Zhang, Sudipta Roy
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Cuproptosis-Related genes in the prognosis of colorectal cancer and their correlation with the tumor microenvironment
Weiqiang Wu, Jingqing Dong, Yang Lv, Dongmin Chang
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Motivational Factors for Smoking Behaviors in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
Moonkyoung Park, Baram Kang, Ahyun Ryu, YueLin Li, Rhayun Song
Patient Preference and Adherence.2021; Volume 15: 2847. CrossRef
- Genetic correlation, and causal relationships between 3 solid cancer types and human traits
- 1,510 View
- 21 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- The Effects of Utilizing Smartphone Application Peer Support on Health Behavior and Body Mass Index among Breast Cancer Survivors
- Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Hyun Yul Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):550-561. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.550
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to identify the effects of utilizing Smartphone Application Peer Support (SAPS) on health behavior and body mass index (BMI) among overweight or obese breast cancer survivors (BCS).
Methods A nonequivalent control group with a non-synchronized design was utilized and 36 participants (experimental group 14, control group 22) were recruited from August 2017 to September 2018. Participants were 40~65 years old, overweight or obese, had completed primary cancer treatment within the 12 months prior to the study, and had not done regular exercise during the last 6 months. The 3-month SAPS consisted of exercise and diet education (once p/2 weeks), peer support (once p/week), and self-monitoring using smartphone applications (5 times p/week). All participants underwent assessments at baseline, right after SAPS, and at 3 months after SAPS. Data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA.
Results At the completion of SAPS significant differences were found between groups in motivation for exercise (t=-3.24,
p =.005), physical activity (t=-4.15,p <.001), total calorie intake (t=3.42,p =.002), calories from fat (t=-3.01,p =.005), intake of vegetables (t=-2.83,p =.008), and BMI (t=5.21,p <.001). Significant differences in BMI (t=4.13,p <.001) remained up to 3 months after SAPS completion. No significant differences was shown between groups in self-efficacy for exercise, either immediately after or 3 months after SAPS.Conclusion The SAPS has the potential to improve motivation for exercise, health behavior, and BMI of BCS. However, special efforts are required to encourage participants to complete the intervention and maintain long-term effects for future trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- EHealth intervention for quality of life in long-term breast cancer survivors: randomized controlled trial
Gustavo Adolfo Pimentel-Parra, Nelia Soto-Ruiz, Paula Escalada-Hernández, Leticia San Martín-Rodríguez, Cristina García-Vivar
JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Mobile App–Based Dietary Interventions Among Cancer Survivors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Krista Ching Wai Chung, Naomi Takemura, Wendy Wing Tak Lam, Mandy Man Ho, Antoinette Marie Lee, Wynnie Yuen Yee Chan, Daniel Yee Tak Fong
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2025; 13: e65505. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an App-Based Self-Management Program for Exercise Practice of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
Suyoun Maeng, Jungok Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 250. CrossRef - Effects of an integrated lifestyle intervention for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
Su Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 73: 102714. CrossRef - User evaluation of a mobile education application for the management of metabolic syndrome among cancer survivors
Ji-Su Kim, Minhae Kim, Yeji Seo
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 63: 102276. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Digital Health on the Quality of Life of Long-Term Breast Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review
Gustavo Adolfo Pimentel-Parra, M. Nelia Soto-Ruiz, Leticia San Martín-Rodríguez, Paula Escalada-Hernández, Cristina García-Vivar
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2023; 39(4): 151418. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - Effects of smart-care services program for breast cancer survivors
Bok Yae Chung, Sung Jung Hong
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 95. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Peer‐supported lifestyle interventions on body weight, energy intake, and physical activity in adults: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Siew Lim, Wai Kit Lee, Andy Tan, Mingling Chen, Chau Thien Tay, Surbhi Sood, Stephanie Pirotta, Lisa J. Moran, Meena Daivadanam, Ljoudmila Busija, Helen Skouteris, Mamaru A. Awoke, Briony Hill
Obesity Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Application and evaluation of mobile nutrition management service for breast cancer patients
Ji Hee Choi, Seon-Joo Park, Hee Kwon, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 83. CrossRef
- EHealth intervention for quality of life in long-term breast cancer survivors: randomized controlled trial
- 1,533 View
- 25 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- The Development and Evaluation of a Health Literacy-Adapted Self-Management Intervention for Elderly Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
- Yoon Sun Kim, Young Sook Tae, Kwuy-Im Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):472-485. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.472
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of an adapted health literacy self-management intervention for elderly cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Methods The intervention in this study was systematically developed through the six stages of Intervention Mapping Protocol and was based on Fransen et al's causal pathway model. A quasi-experimental trial was conducted on a total of 52 elderly patients (26 in an experimental group and 26 in a control group) undergoing chemotherapy in Korea. The intervention consisted of seven sessions over 5 weeks. The experimental tool for this study was an adapted health literacy self-management intervention, which was designed to promote a reduction in the symptom experience and distress of elderly cancer patients through the promotion of self-management behavior. To develop efficient educational materials, the participants’ health literacy was measured. To educate participants, clear communication and the teach-back method were used. In addition, for the improvement of self-efficacy, four sources were utilized. For the promotion of self-management behavior, five self-management skills were strengthened. Data were collected before and after the intervention from June 4 to September 14, 2018. The data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN 21.0.
Results Following the intervention, self-management knowledge and behavior and, self-efficacy significantly improved in experimental group. Symptom experience and distress decreased in the experimental group compared to the control group.
Conclusion The self-management intervention presented in this study was found to be effective in increasing self-management knowledge and behavior and, self-efficacy, and ultimately in reducing symptom experience and distress for elderly patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
Gi Won Choi, Hee Jung Kim, Yujin Park, Ha Na Jeong, Sun Ju Chang
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(6): 724. CrossRef - The Effect of Group Education Reflecting Unmet Needs on Knowledge of Chemotherapy for Patients and Their Families Undergoing Chemotherapy: A One Group Pre-Post Design
Seyoung Lee, Hoyoung Kim, Nayeon Kim, Misun Yi, Ayoung Lee, Seonmi Cho, Minsun Nam, Juhee Cho
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(1): 42. CrossRef - Health Information Seeking Pathways and Factors Influencing Health Literacy Among Cancer Patients: Based on Data from the 2nd Korean Health Panel 2021
Yun-La Hur, Eun-Jeong Hong
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 155. CrossRef - The Effects of Chemotherapy Education Reflecting Educational Needs on Self-Care Knowledge and Performance in Female Cancer Patients: A Non-Equivalent Control Group Pretest-Posttest Design
Jin Hee Jun, Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 103. CrossRef - Effectiveness of teach‐back for chronic kidney disease patient education: A systematic review
Hemamali M. H. Jagodage, Amanda McGuire, Charrlotte Seib, Ann Bonner
Journal of Renal Care.2024; 50(2): 92. CrossRef - Effects of Telephone-based Self-care Intervention for Gynecologic Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Boyeon Lee, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 216. CrossRef - Analysis of Telephone Counseling of Patients in Chemotherapy Using Text Mining Technique
Seoyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Heiyoung Kang, Jeehye Bae, Kayoung Sim, Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 46. CrossRef - Evaluating a theory-based intervention for improving eHealth literacy in older adults: a single group, pretest–posttest design
Sun Ju Chang, Kyoung-eun Lee, Eunjin Yang, Hyunju Ryu
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the teach-back method among cancer patients: a systematic review of the literature
Seonhwa Choi, Jahyun Choi
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(12): 7259. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
- 2,939 View
- 90 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients
- Jung Ran Lee, Pok Ja Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):375-385. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.375
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and test a structural model for chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment of breast cancer patients based on a literature review and Hess and Insel's chemotherapy-related cognitive change model.
Methods The Participants consisted of 250 patients who were ≥19 years of age. The assessment tools included the Menopause Rating Scale, Symptom Experience Scale, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Everyday Cognition, and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast Cancer. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs.
Results The modified model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were χ 2=423.18 (
p <.001), χ 2/df=3.38, CFI=.91, NFI=.91, TLI=.89, SRMR=.05, RMSEA=.09, and AIC=515.18. Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment was directly influenced by menopausal symptoms (β=.38,p =.002), depression and anxiety (β=.25,p =.002), and symptom experiences (β=.19,p =.012). These predictors explained 47.7% of the variance in chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety mediated the relations among menopausal symptoms, symptom experiences, and with chemotherapy related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety (β=-.51,p =.001), symptom experiences (β=-.27,p =.001), menopausal symptoms (β=-.22,p =.008), and chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (β=-.15,p =.024) had direct effects on the quality of life and these variables explained 91.3%.Conclusion These results suggest that chemotherapy-related toxicity is highly associated with cognitive decline and quality of life in women with breast cancer. Depression and anxiety increased vulnerability to cognitive impairment after chemotherapy. Nursing intervention is needed to relieve chemotherapy-related toxicity and psychological factor as well as cognitive decline for quality of life in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of social support on cognitive function in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: The chain-mediating role of fatigue and depression
Yuanqi Ding, Qingmei Huang, Fulei Wu, Yang Yang, Ling Wang, Xuqian Zong, Xiaoyan Yu, Changrong Yuan
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100743. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 418. CrossRef - Relationships Between Chemotherapy-Related Cognitive Impairment, Self-Care Ability, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nan Wu, Ze Luan, Zijun Zhou, He Wang, Shiyuan Du, Yulu Chen, Xinxin Wang, Jiong Li, Xin Peng
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2024; 40(5): 151690. CrossRef - Effects of different exercise interventions on chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer: a study protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
Yu Dong, Hao Huang, Aiping Wang
BMJ Open.2024; 14(4): e078934. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Impact of discriminant factors on the comfort-care of nurses caring for trans-arterial chemoembolisation patients
Myoung Soo Kim, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(9): 7773. CrossRef - Brain morphological alterations and their correlation to tumor differentiation and duration in patients with lung cancer after platinum chemotherapy
Pin Lv, Guolin Ma, Wenqian Chen, Renyuan Liu, Xiaoyan Xin, Jiaming Lu, Shu Su, Ming Li, ShangWen Yang, Yiming Ma, Ping Rong, Ningyu Dong, Qian Chen, Xin Zhang, Xiaowei Han, Bing Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Clinical Study
Teresa Paolucci, Aristide Saggino, Francesco Agostini, Marco Paoloni, Andrea Bernetti, Massimiliano Mangone, Valter Santilli, Raoul Saggini, Marco Tommasi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8585. CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,795 View
- 23 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Experiences of Ego Integrity Recovery in Elderly Cancer Patients: Grounded Theory Approach
- Han-Gyo Choi, Hye-Ah Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):349-360. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.349
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to derive a substantive theory on lived experiences of elderly cancer patients.
Methods The data were collected from February to March 2018 through in-depth personal interviews with 14 elderly cancer patients. The collected data were analyzed based on Corbin and Strauss's grounded theory.
Results The core category was “the journey to find balance in daily lives as a cancer patient by recovering disturbed ego integrity.” The core phenomenon was “shattered by suffering from cancer,” and the causal conditions were “physical change” and “limitations in daily life.” The contextual conditions were “decreased self-esteem,” “feelings of guilt toward the family,” and the sense of “economic burden.” The participants’ action and interaction strategies were “maintaining or avoiding social relations,” “seeking meaning of the illness,” “falling into despair,” and “strengthening the willingness to battle the cancer.” The intervening conditions were “support from health care providers and family,” “dissatisfaction with health care providers,” “spiritual help from religion,” and “the improvement or worsening of health conditions.” The consequences were “having a new insight for life,” “living positively along with cancer illness,” and “the loss of willingness to live.” A summary of the series of processes includes the “crisis stage,” “reorganizing stage,” and the “ego integration stage.”
Conclusion This study explored the holistic process of ego integrity impairment and the recovery experience of elderly cancer patients. This study is expected to be used as a basis for the development of nursing interventions that can support patients when coping with all stages of their cancer illness trajectory.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decision-making experiences regarding kidney transplant among older adults in South Korea: A qualitative descriptive study
Hye Jin Chong, Min Kyeong Jang, Hyun Kyung Kim
Patient Education and Counseling.2024; 119: 108044. CrossRef - Living experiences of older patients with cancer amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A phenomenological study
Yong Hwan Hyeon, Kyoung Ja Moon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 54. CrossRef - Relationship between Communication Competence, Empathy and Geriatric Nursing Practice of Nurses Caring for Elderly Cancer Patients at a General Hospital: Focusing on Veterans Hospital
Eun Sil Park, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 94. CrossRef - Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
Dasom Im, Jeehye Pyo, Haneul Lee, Hyeran Jung, Minsu Ock
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(2): 100. CrossRef - Decision-Making Experience of Older Patients with Cancer in Choosing Treatment: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Se Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 418. CrossRef - Identifying optimal care coordination strategies for older adults with cancer
Han-Gyo Choi, Hye-Ah Yeom
Geriatric Nursing.2021; 42(6): 1349. CrossRef - Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on the Lived Experience of Illness among Older Females with Cancer in South Korea
Miseon Bang, Suhye Kwon, Seonnyeo Kim, Haeyun Shin, Eunyoung Seo
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(2): 110. CrossRef - Experiences of Inpatients Living with Lung Cancer in South Korea
Hae Ok Kim, Hyeon Jeong Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Good Nursing Experience of Patients with Cancer in a Korean Cancer Hospital
Eunyoung E. Suh, Hye Jin Yoo, Jeong Hee Hong, In Gak Kwon, Hyunju Song
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(3): 51. CrossRef
- Decision-making experiences regarding kidney transplant among older adults in South Korea: A qualitative descriptive study
- 1,427 View
- 25 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of Mobile Navigation Program in Colorectal Cancer Patients based on Uncertainty Theory
- Kyengjin Kim, Wanju Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):274-285. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.274
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to examine the effects of a mobile navigation program on uncertainty, resilience, and growth through uncertainty in colorectal cancer patients.
Methods To verify the effectiveness of the mobile navigation program, 61 participants diagnosed with colorectal cancer undergoing surgery were selected. A nonequivalent control group nonsynchronized design was used to evaluate the program. Uncertainty was measured using the Korean version of the Uncertainty in Illness Scale, resilience was measured using the Korean version of the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale, and growth through uncertainty was measured using the Growth through Uncertainty Scale.
Results Compared with the control group, patients in the mobile navigation program group showed significant differences in scores for uncertainty (F=7.22,
p =.009) and resilience (F=4.31,p =.042), but not for growth through uncertainty (F=2.76,p =.102).Conclusion These results suggest that the mobile navigation program has positive effects on decreasing uncertainty and increasing resilience among colorectal cancer patients. The mobile navigation program could play a significant role in assisting colorectal cancer patients in regard to the continuity and usability of the program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing and Evaluating a Mobile Application Self-management Program for Patients with Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators
Eunhee Jo, Rahyeon Hwang, Jeong-Lim Ryu, Chunja Yoo
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Design and Validity of a Patient Navigation Program for Adults with Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
Gloria Mabel Carrillo González, Jorge Esteban García, Lina Marcela Zuluaga
Aquichan.2026; 25(4): 1. CrossRef - Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Sooyoung Kwon, Ji Min Kim, Jun Yong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2025; 13: e60905. CrossRef - Feasibility and Acceptability of a Mobile App Intervention to Promote Self‐Efficacy and Resilience Among Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Hsin‐Tien Hsu, Chih‐Ning Yu, Wan‐Na Sun, Tyng‐Yeu Liang, Shih‐Feng Weng, Erica Yu, Yi‐Fen Hsu
Psycho-Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Video-based Education Program for Cerebral Angiography on Patients’ Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Sung-Hyun Tark, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2024; 30(1): 76. CrossRef - Influence of Illness Uncertainty on Health Behavior in Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease: A Path Analysis
Hyesun Jeong, Yesul Lee, Jin Sup Park, Yoonju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 162. CrossRef - The Influence of Uncertainty in Illness and Coping on Quality of Life in Colorectal Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
Jin Ah Kim, Juyoun Yu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 63. CrossRef - Development of a nurse navigation program for cancer pain
Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh, Mi Jang, Sunsil Kang
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 11(7): 100528. CrossRef - Mobile App for Gynecologic Cancer Support for Patients With Gynecologic Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy in China: Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Huicong Lin, Mingzhu Ye, Yanjuan Lin, Fuhong Chen, Sally Chan, Hongxia Cai, Jiemin Zhu
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2023; 25: e49939. CrossRef - Effects of an interactive coaching intervention on quality of life and psychological factors for colorectal cancer survivors: A single group pre and posttest design
Jaehee Yoon, HyunHae Lee, Heesook Son
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 66: 102413. CrossRef - The Development of a Mobile Application for Older Adults for Rehabilitation Instructions After Hip Fracture Surgery
YoungJi Ko, Jong-Moon Hwang, Seung-Hoon Baek
Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Essential Role of Theory in Nursing Research for Advancement of Nursing Science
Soyoung Yu, Ju-Eun Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(4): 391. CrossRef - A multi‐centre randomized controlled trial of mobile gynaecological cancer support program for patients with gynaecological cancer undergoing chemotherapy: Study protocol
Huicong Lin, Sally Wai‐chi Chan, Mingzhu Ye, Yanlong Wang, Hongli Liu, Min Li, Shengjie Liu, Jiemin Zhu
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(5): 2539. CrossRef - The Relationships among Social Support, Bowel Function Symptoms and Uncertainty in Rectal Cancer Patients
Kyungmi Lee, Semi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 421. CrossRef
- Developing and Evaluating a Mobile Application Self-management Program for Patients with Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators
- 1,823 View
- 38 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

- Family Surrogates' Decision Regret and Psychological Stress about End-of-Life Cancer Treatments: Path Analysis
- Su Hyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):578-587. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.578
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to understand the mechanisms of decision regret and stress of family surrogates' end-of-life decision making using an exploratory path model. In particular, the research identified the direct effects of perceptions of uncertainty and effective decisions on decision regret and stress, and examined the indirect effects of being informed, having clear values, and being supported for decision regret and the stress of end-of-life decision making through the mediating variables of perceptions of uncertainty and effective decisions.
Methods Data were collected from 102 family surrogates who had participated in end-of-life decision making for patients with terminal cancer in a tertiary hospital.
Results Perception of effective decisions was a significant direct predictor of decision regret, and uncertainty was a significant predictor of stress among the participants. Being informed, having clear values, and being supported had a significant indirect influence on decision regret through the perception of effective decisions among family surrogates. However, only having clear values had a significant indirect influence on stress through the perception of uncertainty. The model explained 63.0% of decision regret and 20.0% of stress among the participants and showed a good fit with the data, χ2=12.40 (df=8,
p =.134), TLI=.97, and RMSEA=.07.Conclusion Nurses can support family surrogates in end-oflife decision-making processes to decrease their decision regret by providing information about end-of-life care choices, clarifying personal values, and supporting the decision-making process, and to relieve their stress by facilitating the clarification of personal values.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Acceptance of Death and Symptom Control/Quality of Care Among Terminal Cancer Patients Under Inpatient Hospice Care: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
Jae Hyuck Lee, Yoo Jeong Lee, So Jung Park, Young Min Park, Chung Woo Lee, Sun Wook Hwang, Min Seok Seo, Sun Hyun Kim, Hong Yup Ahn, In Cheol Hwang
American Journal of Hospice and Palliative Medicine®.2026; 43(2): 165. CrossRef - Dying matters – innovating spaces to foster end-of-life discussions with applied theatre
Michael Koon Boon Tan, Ashley Barnes
Arts & Health.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Family Surrogate Decisional-Regret Trajectories
Fur-Hsing Wen, Chia-Hsun Hsieh, Po-Jung Su, Wen-Chi Shen, Ming-Mo Hou, Wen-Chi Chou, Jen-Shi Chen, Wen-Cheng Chang, Siew Tzuh Tang
Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.2024; 67(3): 223. CrossRef - The attitudes about life-sustaining treatment among cardiac surgery ICU patients and their families
Si Sun, Hao Zhang, XiaoYan Xiong
Frontiers in Surgery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Participation and Influencing Factors in the Decision-Making of Life-Sustaining Treatment: A Focus on Deceased Patients with Hematologic Neoplasms
Jae Eun Jang, Jeong Moon Ryu, Min Hee Heo, Do Eun Kwon, Ji Yeon Seo, Dong Yeon Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2023; 26(2): 69. CrossRef - Decisional-Regret Trajectories From End-of-Life Decision Making Through Bereavement
Fur-Hsing Wen, Chia-Hsun Hsieh, Ming-Mo Hou, Po-Jung Su, Wen-Chi Shen, Wen-Chi Chou, Jen-Shi Chen, Wen-Cheng Chang, Siew Tzuh Tang
Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.2023; 66(1): 44. CrossRef - We Want More Than Life-Sustaining Treatment during End-of-Life Care: Focus-Group Interviews
Mirinae Kim, Minju Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(9): 4415. CrossRef - Family's Perception of Proxy Decision Making to Authorize Do Not Resuscitate Order of Elderly Patients in Long Term Care Facility: A Q-Methodological Study
Hyeon Jin Cho, Jiyeon Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 15. CrossRef - A Mixed Method Study for Exploring the Difficulties in End-of-Life Care and End-of-Life Care Competency in Nurses Who Take Care of Cancer Patients
Lae Hee Kim, Su Yeon Kim, Shin Kim, Hyun A Kim, Hwa Jeong Yang, Kyoung Min Lee, Su Yeon Lee, Kyung Hee Lee, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(2): 98. CrossRef - Life-Sustaining Treatment in End-Stage Liver Disease Patients: Patients’ Decisions and Results
Hyun Jung Jung, Jeong Yun Park
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2020; 23(2): 85. CrossRef - The Relationship among Attitudes toward the Withdrawal of Life-sustaining Treatment, Death Anxiety, and Death Acceptance among Hospitalized Elderly Cancer Patients
YeonMi Seo, Sujin Shin
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 142. CrossRef - Reversals in Decisions about Life-Sustaining Treatment and Associated Factors among Older Patients with Terminal Stage of Cardiopulmonary Disease
Jung-Ja Choi, Su Hyun Kim, Shin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(3): 329. CrossRef
- Patient Acceptance of Death and Symptom Control/Quality of Care Among Terminal Cancer Patients Under Inpatient Hospice Care: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,826 View
- 53 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Psychosocial Adjustment in Korean Colorectal Cancer Survivors
- Hyejin Sun, Jia Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):545-553. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.545
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The increasing survival rate of colorectal cancer demands various nursing interventions and continuous care for patients to adapt to their psychosocial daily lives. The purpose of this study was to identify factors associated with psychosocial adjustment in colorectal cancer survivors.
Methods A cross-sectional descriptive study with face-to-face interviews was conducted of 156 colorectal cancer survivors after surgery visiting an outpatient cancer clinic at a tertiary hospital in S city, Korea. Posttraumatic growth, health-promoting behavior, length of treatment, difficulty in activities of daily living, and having a stoma were entered into the linear regression model.
Results The strongest factor influencing the level of psychosocial adjustment was health-promoting behavior (β=.33,
p <.001), followed by difficulty in activities of daily living (β=-.24,p =.001), posttraumatic growth (β=.20,p =.004), and having a stoma (β=-.19,p =.004).Conclusion Nursing interventions for psychosocial adjustment in colorectal cancer survivors need to include the contents for posttraumatic growth, as well as health-promoting behavior, and activities of daily living.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences of colorectal cancer patients in Australia: a qualitative study on specialised nursing and supportive care
Karina T. Rune, Jared Ardern, Cindy Davis
Supportive Care in Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationships between stigma, coping styles, self-care and post-traumatic growth among colorectal cancer patients with permanent enterostomy: A cross-sectional study
Meida Zhang, Yiming Li
Heliyon.2025; 11(10): e38902. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Daily Living and Ostomy Self‐Care Management in Ostomates: A Mixed Methods Study
Elif Budak Ertürk, Hacer Ari, Çiğdem Üstündağ, Esra Yilmaz, Ülkü Topdemir
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(7): 2677. CrossRef - Psychosocial adjustment and influencing factors in patients with newly diagnosed colorectal cancer: A latent profile analysis
Chen Yuan, Jingyue Xie, Lu Cui, Qianqian Du, Xinxin Li, Xiaoxuan Wang, Jianfei Liu, Xiaodan Wu, Meifen Zhang
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 75: 102818. CrossRef - Correlated factors of posttraumatic growth in patients with colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Dingyuan Wei, Xue Wang, Mengxing Wang, Jiayan Wang, Fangping Chen, Luyang Jin, Xuemei Xian
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2025; 12(1): 96. CrossRef - The Trajectory of Adjustment Outcomes Among New Ostomy Patients
Carol Stott, Julia Kittscha, Lisa Graaf, Ian Whiteley, Colleen Mendes, Deb Day, Brenda Christiansen, Jill Fairhall, Jenny Duggan, Joan Walsh, Karen Cole, Mark Murtagh, Greg Fairbrother
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2025; 52(2): 126. CrossRef - Predictors of psychosocial adjustment and its subdomains in young adults with hematologic malignancy: A cross-sectional study
Seul Gi Lee, Sung Reul Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 70: 102571. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Stress, Disability Acceptance, and Quality of Life of People With Physical Disabilities in South Korea: Focused on the Psychosocial Adaptation Model
Hyun-Ju Ju, Uibin Lee, Yein Kim, Debra A. Harley
Journal of Applied Rehabilitation Counseling.2024; 55(2): 143. CrossRef - ‘That gave me a lot of comfort, that he would ask my opinion about how we wanted to talk about this’: A qualitative analysis of clinical communication experiences of ostomy patients
Braidyn S Lazenby, Ashley Guidry, Erin E Donovan, René Dailey, Srinivas Joga Ivatury
BMJ Open.2024; 14(2): e079362. CrossRef - Social isolation profiles and conditional process analysis among postoperative enterostomy patients with colorectal cancer
Yuan Liao, Xuelan Liu, Xinyu Wu, Chun Li, Yu Li
BMC Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Elevating Elderly Cancer Care: A Systematic Review of Advanced Practice Nursing’s Role in Senior Oncology Patients’ Quality of Life
Cristian-David Useche-Guerrero, María-de-los-Ángeles Merino-Godoy, Eva-María Barroso-Márquez, Emilia Isabel Martins Teixeira da Costa, Rafaela Camacho Bejarano, Francisco-Javier Gago-Valiente, Rizal Angelo Grande
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Posttraumatic growth in colorectal cancer survivors: A systematic review
Zhiming Wang, Xuan Chen, Junrui Zhou, Alice Yuen Loke, Qiuping Li
Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy.2023; 30(4): 740. CrossRef - Adjustment to an Ostomy
Julia Kittscha, Greg Fairbrother, Vida Bliokas, Val Wilson
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2022; 49(5): 439. CrossRef - Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 245. CrossRef - Factors associated with psychosocial adjustment in working-age colorectal cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Wenjie Zou, Yiheng Zhang, Lizhen Gong, Meng Zhang, Xiaoyu Wu, Jingyue Xie, Meifen Zhang
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 9(6): 100057. CrossRef - Moderating Effect of Posttraumatic Growth on the Relationship Between Social Support and Quality of Life in Colorectal Cancer Patients With Ostomies
Hyerang Kim, Heesook Son
Cancer Nursing.2021; 44(3): 251. CrossRef - Health promoting lifestyle behaviors and associated predictors among clinical nurses in China: a cross-sectional study
Wen Zeng, Shaomei Shang, Qian Fang, Shan He, Juan Li, Yuanrong Yao
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Experiences of colorectal cancer patients in Australia: a qualitative study on specialised nursing and supportive care
- 1,380 View
- 14 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Psychoeducational Approach to Distress Management of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer
- Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Yong Sik Jung, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):669-678. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.669
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of integrated psychoeducational program for distress management of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer.
Methods A quasi-experimental trial was conducted. The participants consisted of 47 female patients with breast cancer assigned to an intervention group (n=25) and control group (n=22). The intervention group participated in integrated psychoeducational program, consisting of individual face-to-face education and telephone-delivered health-coaching sessions. Data were collected at three time points: pre-intervention (T1), post-intervention (T2), and 6-month follow-up (T3). Study instruments were Distress thermometer, Supportive Care Needs Survey Short Form 34 and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast.
Results Compared with the control group, breast cancer patients in the intervention group reported lower distress and supportive care needs than the control group. The intervention group reported higher quality of life (QOL) overall and higher emotional well-being than the control group.
Conclusion These findings indicate that the integrated psychoeducational program is an effective intervention for reducing distress and supportive care needs and increasing QOL of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer. Oncology nurses need to provide psychoeducational intervention to support patients with breast cancer in managing their distress and helping them adjust to their life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Tailored Psychoeducational Intervention for Patients With Advanced Cancer in Indonesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nurul Huda, Made Satya Nugraha Gautama, Wan Nishfa Dewi, Agung Waluyo, Hsiu Ju Chang, Malissa Kay Shaw
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2025; 57(5): 848. CrossRef - Evidence on the benefits of mind-body Qigong exercise in women with breast cancer
Michel Marcos Dalmedico, Jackson Adriano Canavarro Ribeiro, Juliana Londero Silva Avila, Prisley Pereira de Oliveira, Paula Karina Hembecker, Sergio Ossamu Ioshii
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Distress and Influencing Factors in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Yu Jin Jeong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 311. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions for Patients with Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis
Kyu-Sic Hwang, Kuy-Haeng Lee, Chan-Mo Yang, Hye-Jin Lee, Sang-Yeol Lee
Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience.2023; 21(1): 118. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Adjustment to life with metastatic cancer through psychodrama group therapy: A qualitative study in Turkey
Songül Kamışlı, Bahar Gökler
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(2): 488. CrossRef - Integration of longitudinal psychoeducation programmes during the phases of diagnosis, management and survivorship of breast cancer patients: A narrative review
Athena Michaelides, Constantina Constantinou
Journal of Cancer Policy.2020; 23: 100214. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer
Kavitha Konnakkaparambil Ramakrishnan, Sreekumar Damodaran
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2020; 7(28): 1368. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef - Uncertainty and unmet care needs before and after surgery in patients with gastric cancer: A survey study
Ji Yea Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Sanghee Kim, Woo Jin Hyung
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(2): 427. CrossRef - Effects of Different Exercise Interventions on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Tetiana Odynets, Yuriy Briskin, Valentina Todorova
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,836 View
- 41 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the Coping and Adaptation Processing Scale–Short-Form in Cancer Patients
- Chi Eun Song, Hye Young Kim, Hyang Sook So, Hyun Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):375-388. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.375
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to assess the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Coping and Adaptation Processing Scale-Short-Form in patients with cancer.
Methods The original scale was translated into Korean using Brislin's translation model. The Korean Short-Form and the Functional Assessment Cancer Therapy-General were administered to 164 Korean patients with cancer using convenience sampling method. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0. Construct validity, criterion validity, test-retest reliability, and internal consistency reliability of the Korean Coping and Adaptation Processing Scale-Short-Form were evaluated.
Results Exploratory factor analysis supported the construct validity with a four-factor solution that explained 60.6% of the total variance. Factor loadings of the 15 items on the four subscales ranged .52~.86. The four-subscale model was validated by confirmatory factor analysis (Normed χ 2=1.38 (
p =.013), GFI=.92, SRMR=.02, RMSEA=.05, TLI=.94, and CFI=.95), and criterion validity was demonstrated with the Functional Assessment Cancer Therapy-General. Cronbach's alpha for internal consistency of the total scale was .83 and ranged .68~.81 for all subscales, demonstrating sufficient test-retest reliability.Conclusion The Korean version showed satisfactory construct and criterion validity, as well as internal consistency and test-retest reliability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Colombian validation of the short-form coping and adaptation processing scale in caregivers
Carolina Gutiérrez-López, Gustavo Ordoñez-Sierra, Ricardo Borda Hernández, Marcia Andrea Quiñonez-Mora
International Journal of Nursing Studies Advances.2026; 10: 100497. CrossRef - Disease Activity and Psychosocial Factors Associated with Heath-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Crohn’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study
YoonJi Roh, Hye-Ah Yeom
Healthcare.2026; 14(4): 432. CrossRef - Risk factors for inadequate and excessive gestational weight gain during pregnancy among women
Ju Sun Cho, Sook Jung Kang
Midwifery.2025; 144: 104345. CrossRef - A cross-sectional study of Malaysian low-income drug addict wives: Relationship between family impact, coping and mental wellbeing
Haikal Anuar Adnan, Zarinah Arshat, Nurul Saidatus Shaja’ah Ahmad Shahril
F1000Research.2025; 11: 683. CrossRef - Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
Hyeng Sook Yoon, Eunjung Ryu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100820. CrossRef - North Korean defectors with PTSD and complex PTSD show alterations in default mode network resting-state functional connectivity
Byung-Hoon Kim, Jiwon Baek, Ocksim Kim, Hokon Kim, Minjeong Ko, Sang Hui Chu, Young-Chul Jung
BJPsych Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Coping and adaptation of adults with cancer: the art of nursing care
Lina Marcela Cepeda-Trujillo, Jesús Miguel Mosquera-Aguirre, Daniela Yurani Rojas-Atehortua, Alix Yaneth Perdomo-Romero
Aquichan.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - A cross-sectional study of Malaysian low-income drug addict wives: Relationship between family impact, coping and mental wellbeing
Haikal Anuar Adnan, Zarinah Arshat, Nurul Saidatus Shaja’ah Ahmad Shahril
F1000Research.2022; 11: 683. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Psychometric Testing of the Chinese Version of the Coping and Adaptation Processing Scale-Short Form in Adults With Chronic Illness
Xiyi Wang, Leiwen Tang, Doris Howell, Jing Shao, Ruolin Qiu, Qi Zhang, Zhihong Ye
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A Simple Framework of Smart Geriatric Nursing considering Health Big Data and User Profile
Shijie Li, Yongchuan Tang, Mirian C. D. Pinheiro
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Psychosocial Adjustment in Hemodialysis Patients
Kang Sun Lee, Hye Young Kim, Myung Ha Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(1): 38. CrossRef
- Colombian validation of the short-form coping and adaptation processing scale in caregivers
- 2,081 View
- 46 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Symptom Distress and Coping in Young Korean Breast Cancer Survivors: The Mediating Effects of Social Support and Resilience
- Ji Hyun Lee, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):241-253. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the mediating effect of social support and resilience on the relationship between symptom distress and coping in young Korean breast cancer survivors.
Methods A purposive sample of 209 young breast-cancer survivors (mean age 39.9) was recruited for a cross-sectional survey, and the data were collected between June and October 2015. The instruments used in this study were the Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale-Short Form, the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support, 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale, and Cancer Coping Questionnaire. The collected data were then analyzed using the SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 programs.
Results Symptom distress was found to have a significant indirect effect on coping (beta=-.32,
p =.002), but not a significant direct effect (beta=.06,p =.577). Additionally, based on the values obtained for the squared multiple correlation, symptom distress, social support, and resilience were found to explain 46.4% of the total variance of coping.Conclusion Based on the results of this study, it can be suggested that in order to enhance young breast cancer survivors’ ability to cope with the distress they commonly feel, intervention methods that strengthen resilience and provide social support should be developed and made available to them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sexual well-being in cancer care services: the role of body image and coping strategies
Judith Partouche-Sebban, Saeedeh Rezaee Vessal, Youssef Souak, Aymen Ammari, Alain Toledano
Journal of Services Marketing.2026; : 1. CrossRef - How Online Patient-Provider Communication Alleviates Psychological Distress Among Patients with Chronic Diseases: The Role of Perceived Patient-Centered Communication and Adaptive Coping Strategies
Bingqing Ling, Yu Zheng
Health Communication.2025; 40(8): 1559. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Not Returning to Work Among Breast Cancer Survivors
Leni Merdawati, Hui-Chen Lin, Chieh-Hsin Pan, Hui-Chuan Huang
Workplace Health & Safety.2025; 73(5): 216. CrossRef - Factors affecting resilience among young breast cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Hye Young Min, Yoonjung Kim, Hae Jeong An
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 75: 102837. CrossRef - Latent classes of health‐promoting lifestyle in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in China: A cross‐sectional survey
Meixuan Song, Qiuyao He, Juan Yang, Jinyu Zhang
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Postmastectomy Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Sajad Ahmad Salati, Lamees Alsulaim, Mariyyah H Alharbi, Norah H Alharbi, Thana M Alsenaid, Shoug A Alaodah, Abdulsalam S Alsuhaibani, Khalid A Albaqami
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the CALM intervention on resilience in Chinese patients with early breast cancer: a randomized trial
Shaochun Liu, Runze Huang, Anlong Li, Sheng Yu, Senbang Yao, Jian Xu, Lingxue Tang, Wen Li, Chen Gan, Huaidong Cheng
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(20): 18005. CrossRef - Perceived social support and depressive symptoms in Chinese patients with ovarian cancer and the mediating role of resilience:a cross-sectional study
Xiaoyan Pang, Fangmei Li, Lei Dou, Yichang Tian, Yi Zhang
Current Psychology.2023; 42(24): 20485. CrossRef - Resilience-related Breast Cancer: A Concept Analysis
Fitria Endah Janitra, Nur Aini, Anggi Lukman Wicaksana
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing.2023; 13(1): 31. CrossRef - Factors influencing the coping strategies of liver cancer patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolization
Su‐Chih Chen, Shu‐Fang Wu, Tsae‐Jyy Wang, John Rosenberg, Yu‐Ying Lu, Shu‐Yuan Liang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived social support and coping style as mediators between resilience and health-related quality of life in women newly diagnosed with breast cancer: a cross-sectional study
Kaina Zhou, Fan Ning, Xiao Wang, Wen Wang, Dongfang Han, Xiaomei Li
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - A Mobile Healing Program Using Virtual Reality for Sexual Violence Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Mi‐ran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2021; 18(1): 50. CrossRef - Factors related to the resilience and mental health of adult cancer patients: a systematic review
Saori Tamura, Kumi Suzuki, Yuri Ito, Akiko Fukawa
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(7): 3471. CrossRef - Resilience in women with breast cancer: A systematic review
Ibane Aizpurua-Perez, Joana Perez-Tejada
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 49: 101854. CrossRef - Individual resilience in adult cancer care: A concept analysis
Dan Luo, Manuela Eicher, Kate White
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 102: 103467. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Effects of cyclic adjustment training delivered via a mobile device on psychological resilience, depression, and anxiety in Chinese post-surgical breast cancer patients
Kaina Zhou, Jin Li, Xiaomei Li
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2019; 178(1): 95. CrossRef
- Sexual well-being in cancer care services: the role of body image and coping strategies
- 1,975 View
- 22 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Impact of Uncertainty on the Quality of Life of Young Breast Cancer Patients: Focusing on Mediating Effect of Marital Intimacy
- Yeong Kyong Oh, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):50-58. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the mediating effect of marital intimacy on the impact of uncertainty on the quality of life (QoL) of young breast cancer patients.
Methods This study used a pathway analysis with 154 young breast cancer cases in their early diagnosis stage at a medical center in Korea. Data were collected from November 2016 to February 2017 and analyzed using correlation analysis and pathway analysis.
Results Uncertainty, marital intimacy, and 4 sub-scales of QoL showed a significant correlation. Marital intimacy was directly affected by uncertainty (b=-.39,
p =.013) and 4 sub-scales of QoL were also affected by uncertainty. Among the 4 sub-scales of QoL, physical well-being (PWB) (b=.17,p =.026), social well-being (SWB) (b=.49,p =.010), and functional well-being (FWB) (b=.38,p =.009) were affected by marital intimacy but emotional well-being (EWB) was not affected by it. The mediating effect of marital intimacy on the impact of uncertainty on QoL was confirmed. Marital intimacy showed a significant indirect effect on PWB (b=-.07,p =.024), SWB (b=-.19,p =.008), and FWB (b=-.15,p =.005), and it means that marital intimacy has a partial mediating effect on the impact of uncertainty on PWB, SWB, and FWB.Conclusion Effects of uncertainty on QoL was mediated by marital intimacy of young breast cancer patients in their early diagnosis stage. It suggests that marital intimacy needs to be considered in providing nursing intervention for young breast cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incertidumbre en mujeres diagnosticadas con cáncer de mama: estudio transversal
Rosa Herminia Pastuña-Doicela, Olivia Inés Sanhueza-Alvarado
Escola Anna Nery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Uncertainty in women diagnosed with breast cancer: a cross-sectional study
Rosa Herminia Pastuña-Doicela, Olivia Inés Sanhueza-Alvarado
Escola Anna Nery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body change stress, sexual function, and marital intimacy in korean patients with breast cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: A cross-sectional study
Hyesoon Lee, Hyeon Gyeong Yoon
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(5): 100228. CrossRef - Factors influencing the supportive care needs of female patients with genital cancer in South Korea
Yu-Jung Son, Keum-Hee Nam, JaeLan Shim
Medicine.2023; 102(51): e36650. CrossRef - An explanatory model of quality of life in high-risk pregnant women in Korea: a structural equation model
Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(4): 302. CrossRef - Impacts of Uncertainty and Social Support on the Quality of Life of Breast Cancer Survivors after Chemotherapy: Based on Self-help Group Participants
Hyenam Hwang, Yoonshin Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(4): 177. CrossRef - A hermeneutic phenomenological study on the disease experience among young women with breast cancer
Jeonghee Ahn, Kyoung-eun Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(10): 100310. CrossRef - Psychological variables associated with quality of life in patients with head and neck cancer: the role of body image distress
Silvia Cerea, Maria Sansoni, Giovanni Scarzello, Elena Groff, Marta Ghisi
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(11): 9127. CrossRef - Relationships among sexual function, marital intimacy, type D personality and quality of life in patients with ovarian cancer, with spouses
Ju‐Hee Nho, Sung Reul Kim, Won Ku Choi
European Journal of Cancer Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationships among Social Support, Bowel Function Symptoms and Uncertainty in Rectal Cancer Patients
Kyungmi Lee, Semi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef - Effects of uncertainty and spousal support on infertility-related quality of life in women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies
Hye Shin Lee, Sunjoo Boo, Jeong-Ah Ahn, Ju-Eun Song
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 72. CrossRef - Impact of Psycho-Social Factors on Fatigue among Breast Cancer Patients Who Are Currently Undergoing Radiotherapy
Hyesun Park, Kisook Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(17): 6092. CrossRef - Health care Utilization of Cancer patient Women at Nursing Hospital
Hye-Sun Park, Kyung-Sook Park
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2018; 19(11): 2139. CrossRef
- Incertidumbre en mujeres diagnosticadas con cáncer de mama: estudio transversal
- 1,334 View
- 14 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):143-163. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate effects of psychoeducational intervention for cancer survivors.
Methods Ten databases were searched. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of the studies, data extraction and assessment. The risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane Collaboration's tool. To estimate the effect size, meta-analysis of the studies was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and RevMan programs.
Results Of 18,781 publications identified, 35 met inclusion criteria, and 25 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychoeducational intervention. Effect sizes (standardized mean difference [SMD]) were heterogeneous and random effects models were used in the analyses. Psychoeducational intervention was effective for quality of life (n=2,410, ES=0.23; 95% CI: 0.09~0.37), coping and self-efficacy (n=179, ES=0.68; 95% CI: 0.26~1.11), anxiety (n=1,786, ES=-0.26; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.15), depression (n=1,910, ES=-0.28; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.18), and psychological distress (n=2,242, ES=-0.31; 95% CI: -0.46~-0.17). Subgroup analysis showed that counseling was the most effective intervention for quality of life, and behavioral therapy was an effective intervention for all positive and negative outcomes. Publication bias was not detected except for psychological distress.
Conclusion Psychoeducational intervention appears to be effective in improving quality of life and coping and self-efficacy, and it is effective in reducing psychological symptoms in cancer survivors. Behavioral therapy, especially, is commonly effective in improving psychosocial outcomes. However, low-quality evidence, variability in the designs of existing studies, and publication bias suggest that additional high-quality trials should be conducted in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
Safa Elkefi, Corina T. Lelutiu-Weinberger, Jean-Marie Bruzzese, Alicia K. Matthews
Discover Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Group‐Based Support Interventions for Adolescents and Young Adults With Lymphoma: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Dalnim Cho, Sairah Ahmed, Stella Snyder, Juliet Kroll, Minxing Chen, Michael Roth, Kathrin Milbury
Psycho-Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mind Health of Persons with Cancer: Psycho-Oncology and Nursing
Park Eun Young
Journal of Clinical Psychooncology.2025; 11(1): 24. CrossRef - Psychosocial interventions for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease and their caregivers: a scoping review
Juyeon Oh, Jiwon An, Kyongok Park, Youngok Park
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of telemedicine psychoeducational interventions for adults with non‐oncological chronic disease: A systematic review
Carmen Sánchez‐Gutiérrez, Eugenia Gil‐García, Adriana Rivera‐Sequeiros, José M. López‐Millán
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(5): 1267. CrossRef - Cancer-Related Psychological Distress in Lymphoma Survivor: An Italian Cross-Sectional Study
Giulia Agostinelli, Barbara Muzzatti, Samantha Serpentini, Michele Spina, Maria Antonietta Annunziata
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 245. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Physical Function and Depression in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jinhyang YANG, Changwan KANG, Hye-Won PARK, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 396. CrossRef - Development of A Nurse-Led Educational Intervention Program in Managing the Nutrition Impact Symptom Cluster in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma following the Medical Research Council Framework
Wenli Xiao, Carmen W Chan, Jinnan Xiao, Cho L Wong, Ka M Chow
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 653. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Education and Support: A Model for Use in the Ambulatory Care Setting
Terri Jabaley, Patricia Rizzo, Nina Grenon, Clare Sullivan, Janet Bagley, Maritza Nassif, Renee Siegel, Meghan Underhill-Blazey
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 24(4): E43. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Chronic Pain Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hee-Sook Kang, Sung-Dong Hwang, Sang-Eun Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(3): 271. CrossRef
- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
- 2,108 View
- 35 Download
- 12 Crossref

- An Analytical Review on Fatigue of Cancer Patients
- Yun Jung Lee, Dal Sook Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):897-905. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.897
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to discuss and address the state of the knowledge development and the nature of knowledge regarding fatigue. METHOD: This study analyzed the 63 fatigue related articles published from 1990 to 2001. The analysis schema was 'Alternative linkages among philosophy, theory, and method for nursing science' (Kim, 1993). RESULT: The 63 articles had been studied only within 5 types among all 96 types of linkages. Most of the articles (59 among 63 articles) had been studied within scientific realism and deductive logic. Fifty-three articles among 59 articles were the type of explanatory and predictive theory, grasping reality by the etic method on the controlled setting. CONCLUSION: This study suggests more development of knowledge regarding fatigue with various logics, especially with discovery logic such as inductive and retroductive or methods in multiple designs on various subjects under various philosophy needed for nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends in Research on Caregivers Hospitalized Children in Korea-Focus on Knowledge Type
In-soo Kwon, Yeong-mi Seo, Ji-youn Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(3): 101. CrossRef - Trends of Doctoral Dissertations in Nursing Science: Focused on Studies Submitted Since 2000
Hyunsook Shin, Kyung-Mi Sung, Seok Hee Jeong, Dae-Ran Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 74. CrossRef
- Trends in Research on Caregivers Hospitalized Children in Korea-Focus on Knowledge Type
- 738 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Longitudinal Study on the Calorie and Protein Intakes and Food Choices in Gastrectomy Patients who Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy
- Myung Hee Jun, Soo Gyung Wang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(2):206-218. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.2.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to investigate nutrient and food choices in gastric cancer patients receiving Cisplatin after surgery. Ten patients were followed from the fist day of the first cycle to the last date of the 6th the cycle of the chemotherapy. The subjects kept daily self record of dietary intake and the period of nausea/vomiting during 6 cycles. Using Computer Aided Nutritional Analysis Program, the degree of Calorie, carbohydrate, protein, fat and fluid intakes according the chemotherapy period. The reseacher developed food intake rating scale, and then three dietitians analysed the oral intakes according to the type of foods. As the results of this study, during the chemotherapy cancer patients are intakes much fewer calorie, protein and fluids than recommended dietary allowance. Oral intake was worsen as treatment proceed. During the chemotherapy periods most of the patients choose fruits, vegitables, steam rice, porridge, yogurt and the beam soup to overcome nausea and vomiting. In order to promote oral intake for chemotherapy patients, the researcher strongly suggest that indiviual food preform should be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- 684 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of Educational Program of Manual Lymph Massage on the Arm Functioning and the Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients
- Eun Sook Lee, Sung Hyo Kim, Sun Mi Kim, Jeong Ju Sun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(7):1390-1400. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.7.1390
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of EPMLM(educational program of manual lymph massage) on the arm functioning and QOL(quality of life) in breast cancer patients with lymphedema.
Method Subjects in the experimental group(n=20) participated in EPMLM for 6 weeks from June to July, 2005. The EPMLM consisted of training of lymph massage for 2 weeks and encourage and support of self-care using lymph massage for 4 weeks. The arm functioning assessed at pre-treatment, 2weeks, and 6weeks using Arm functioning questionnaire. The QOL assessed at pre-treatment and 6 weeks using SF-36. The outcome data of experimental group was compared with control group(n=20). The collected data was analyzed by using SPSS 10.0 statistical program.
Result The arm functioning of experimental group was increased from 2 weeks after(W=.224, p=.011) and statistically differenced with control group at 2 weeks(Z=-2.241, p=.024) and 6 weeks(Z=-2.453, p=.013). Physical function of QOL domain increased in experimental group(Z=-1.162, p=.050), also statistically differenced with control group(Z=-2.182, p= .030) at 6weeks.
Conclusion The results suggest that the educational program of manual lymph massage can improve arm functioning and physical function of QOL domain in breast cancer patients with lymphedema.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Domestic Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD)-related Research Trend
Ji-Hyun Mun, Min-Hee Kim
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2022; 24(5): 636. CrossRef - Changes in Upper Extemity Sensation and the Quality of Life for Patients Following Mastectomy
Suk Jeong Lee, Young Mi Park, Jiyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(3): 229. CrossRef
- Analysis of Domestic Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD)-related Research Trend
- 854 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of a Comprehensive Rehabilitation Program for Mastectomy Patients
- Ok Hee Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(5):809-819. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.5.809
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of a comprehensive rehabilitation program on physical function, immune response, fatigue and quality of life in mastectomy patients.
Method The subjects included fifty-five patients with breast cancer (27 in the control group and 28 in the experimental group). The subjects in the experimental group participated in a comprehensive rehabilitation program for10 weeks, which was composed of 1 session of education, 2 sessions of stress management, 2 sessions of exercise, and 1 session of peer support group activity per week.
Result The results revealed anincrease in shoulder extension, abduction, external rotation, and internal rotation of the affectedupper extremity, and in shoulder extension and abduction of the healthy upper extremity. Also an increase in quality of life and a decrease in fatigue were significantly higher in the experimental group than the control group. However, the results revealed that the natural killer cell ratio of the experimental group increased but there was no significant difference from that of the control group.
Conclusion The 10-week comprehensive rehabilitation program showed a large affirmative effect on physical function, fatigue and quality of life of breast cancer patients after a mastectomy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Comprehensive Care Program for Ovarian Cancer Survivors
Kyung-Hye Hwang, Ok-Hee Cho, Yang-Sook Yoo
Clinical Nursing Research.2016; 25(2): 192. CrossRef - Review of Rehabilitation Programs for Cancer survivors
Jong Hee Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(12): 307. CrossRef - Effect of a 12-week walking exercise program on body composition and immune cell count in patients with breast cancer who are undergoing chemotherapy
Ji Jeong Kim, Yun A Shin, Min Hwa Suk
Journal of Exercise Nutrition & Biochemistry.2015; 19(3): 255. CrossRef - Effects of BeHaS Exercise Program on Flexibility, Grip Strength, Stress and Self-esteem in Breast Cancer Survivors
Sun Young Park, Jong Im Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(3): 171. CrossRef - Relationships among Pain, Upper Extremity Function, and Anxiety in the Breast Cancer Survivors
Jeong-Sun Lim, Jong-Im Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(1): 37. CrossRef - Effects of Laughter Therapy on Depression, Quality of Life, Resilience and Immune Responses in Breast Cancer Survivors
Eun A Cho, Hyun Ei Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(3): 285. CrossRef - Developing a Rehabilitation Model of Breast Cancer Patients Through Literature Review and Hospital Rehabilitation Programs
Bok-Yae Chung, Yu Xu
Asian Nursing Research.2008; 2(1): 55. CrossRef
- The Effect of Comprehensive Care Program for Ovarian Cancer Survivors
- 811 View
- 24 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the Cancer Stigma Scale
- Hyang Sook So, Myeong Jeong Chae, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(1):121-132. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose In this study the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Cancer Stigma Scale (KCSS) was evaluated.
Methods The KCSS was formed through translation and modification of Cataldo Lung Cancer Stigma Scale. The KCSS, Psychological Symptom Inventory (PSI), and European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire - Core 30 (EORTC QLQ-C30) were administered to 247 men and women diagnosed with one of the five major cancers. Construct validity, item convergent and discriminant validity, concurrent validity, known-group validity, and internal consistency reliability of the KCSS were evaluated.
Results Exploratory factor analysis supported the construct validity with a six-factor solution; that explained 65.7% of the total variance. The six-factor model was validated by confirmatory factor analysis (Q (χ2/df)= 2.28, GFI=.84, AGFI=.81, NFI=.80, TLI=.86, RMR=.03, and RMSEA=.07). Concurrent validity was demonstrated with the QLQ-C30 (global:
r =-.44; functional:r =-.19; symptom:r =.42). The KCSS had known-group validity. Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the 24 items was .89.Conclusion The results of this study suggest that the 24-item KCSS has relatively acceptable reliability and validity and can be used in clinical research to assess cancer stigma and its impacts on health-related quality of life in Korean cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Roles of Cancer Stigma and Resilience in the Relationship Between Type D Personality and Quality of Life Among Patients with Breast Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sujin Kim, Sunki Kim, Hye-Ja Park
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2026; : 103122. CrossRef - Assessing cancer-related fatigue: Validation of the Korean version of the cancer fatigue scale among cancer survivors
Haneul Lee, Eun Young Park, Kwang-Hi Park
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100657. CrossRef - Return-to-Work Support Needs and Influencing Factors Among Korean Young Adult Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Kisook Kim, Hyohyeon Yoon
Oncology Nursing Forum.2025; 52(2): 151. CrossRef - Stigma and quality of life in lung cancer patients: The mediating effect of distress and the moderated mediating effect of social support
Hyewon Lim, Hyunmi Son, Gyumin Han, Taehwa Kim
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 11(6): 100483. CrossRef - Assessment tools for stigma in breast cancer patients based on COSMIN guidelines: a systematic review
Xue‐Mei Xie, Jing Gao, Ding‐Xi Bai, Huan Chen, Yue Li
Supportive Care in Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of childhood maltreatment on the prosocial behavior of Chinese university students: a chain mediation analysis
Hui Zhou, Jiajia Ruan, Junyi Xie, You Wang, Xueling Yang
Current Psychology.2024; 43(23): 20722. CrossRef - Stigma in Mexican patients with Lung Cancer: Psychometric Properties of the Cataldo Lung Cancer Stigma Scale (CLCSS) - Brief version
Joel Flores-Juárez, Oscar Galindo-Vázquez, Patricia Ortega-Andeane, Ana Fresán-Orellana, Xolyanetzin Montero-Pardo, Tania Estapé, Marisol Arroyo-Hernández, Luis Antonio Cabrera-Miranda, Oscar Arrieta
Palliative and Supportive Care.2024; 22(6): 2084. CrossRef - Disease Perception, Stigma, Distress, Physical Symptom Experience and Quality of Life in Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Cross-Sectional Study
Eun-Hee Lee, Dongwon Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 494. CrossRef - Social stigma associated with cancer in the Newfoundland and Labrador population: an exploratory study
Sevtap Savas, Mercy Winsor, Eric Y. Tenkorang, Charlene Simmonds, Teri Stuckless
Journal of Psychosocial Oncology Research & Practice.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of the Cancer Fatigue Scale in Patients with Cancer
Haneul Lee, Eun Young Park, Ji Hyun Sung
Healthcare.2023; 11(12): 1796. CrossRef - The mediating effect of resilience on happiness of advanced lung cancer patients
Sunwha Cho, Eunjung Ryu
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(11): 6217. CrossRef - Structural Equation Model of the Quality of Working Life among Cancer Survivors Returning to Work
Ju Hyun Jin, Eun Ju Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 37. CrossRef - Turkish version of the cancer stigma scale: validity and reliability study
Birsen Paltun, Nurgül Bölükbaş
Psychology, Health & Medicine.2021; 26(sup1): 37. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Stigma and Distress among Cancer Patients: The Mediating Effect of Self-blame
Kyung Mi Yang, Myeong Jeong Chae, Hyang Sook So
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 89. CrossRef
- Mediating Roles of Cancer Stigma and Resilience in the Relationship Between Type D Personality and Quality of Life Among Patients with Breast Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
- 1,706 View
- 30 Download
- 15 Crossref

- The Relationships among Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV), Non-Pharmacological Coping Methods, and Nutritional Status in Patients with Gynecologic Cancer
- Haerim Lee, Smi Choi-Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):731-743. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.731
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) can cause severe malnutrition. However, relationships between CINV levels, nonpharmacological coping methods, and nutritional status of female cancer patients have rarely been investigated. Therefore, this study aimed to analyze their relationships in gynecologic cancer patients.
Methods Participants receiving a highly and moderately emetogenic chemotherapy were recruited. The level of CINV was assessed using a numeric rating scale. Coping methods were determined using multiple-choice self-report questionnaires and categorized into seven types for statistical analysis. Nutritional status was evaluated using biochemical and anthropometric parameters.
Results Among all the 485 patients, 200 eligible inpatients were included. Despite the administration of prophylactic antiemetics, 157 patients (78.5%) still experienced CINV, and several used nonmedically recommended coping methods, such as just enduring the symptom or rejecting food intake. A total of 181 patients (90.5%) had nutritional disorders. Although the level of CINV was indirectly related to the occurrence of nutritional disorders, patients who rejected food (b=1.57,
p =.023) and did not use physical measures (b= -1.23,p =.041) as coping methods were under the high risk of nutritional disorders.Conclusion Korean gynecologic cancer patients had high levels of CINV and were at high risk of nutritional disorders, which may be related to the use of nonscientific coping methods, possibly due to cultural backgrounds and lack of proper nutritional program. Therefore, developing a culturally appropriate educational program for the cancer patients with CINV is urgently needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perceived food literacy in women with gynecologic cancer receiving chemotherapy
Sakine Yılmaz, Yadigar Ordu, Elif Hançer
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of sleep quality components in patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolisation: a cross-sectional study
Ji Young Park, Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Mi Ryu
Supportive Care in Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Jinekolojik Kanser Hastası ve Ailesinin Psiko-Sosyal Bakımında Sağlık Profesyonelinin Rolü
Elif BALKAN, Ümran OSKAY
Bandırma Onyedi Eylül Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri ve Araştırmaları Dergisi.2023; 5(1): 74. CrossRef - Effects of Continuous Nutrition Care on Nutritional Status and Dietary Habits of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Surgery
Jina Son, Ha I Kang, Eun young Jung, Hae won Ryu, Kyung-Ha Lee
Clinical Nutrition Research.2023; 12(2): 99. CrossRef - Dietary strategies for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: A systematic review
Devanshi Gala, Hattie H. Wright, Bekhinkosi Zigori, Skye Marshall, Megan Crichton
Clinical Nutrition.2022; 41(10): 2147. CrossRef - Effect of Auricular Acupressure on Nausea, Vomiting, and Retching in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy
Nayeon Shin, Jummi Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(3): 227. CrossRef
- Perceived food literacy in women with gynecologic cancer receiving chemotherapy
- 1,652 View
- 36 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Cancer-Specific Posttraumatic Growth Inventory
- Young-Mi Jung, Jin-Hee Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):319-331. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.319
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a scale to evaluate posttraumatic growth in patients with cancer and to examine the validity and reliability of the scale.
Methods A literature review, semi-structured patient interviews and an expert panel consultation produced a 27 preliminary item questionnaire. Participants were 150 cancer patients recruited to test the reliability and validity of the preliminary scale. Data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, convergent validity and internal consistency.
Results Item reduction and exploratory factor analysis led to 23 items, grouped into five subscales which were labelled new possibilities (6 items), coping skills (5 items), preciousness of life (5 items), relating to others (4 items), and personal strength (3 items). Convergent validity was evaluated by total correlation with the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General (r=.45,
p <.001). The final scale demonstrated satisfactory internal consistency (Cronbach's a =.94).Conclusion Findings from this study indicate that the Cancer-Specific Posttraumatic Growth Inventory has validity and reliability and is considered to be appropriate for assessing posttraumatic growth in patients with cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transcultural adaptation and Mexican validation of the posttraumatic growth inventory (PTGI-X-Mx) in a palliative oncology population
Leticia Ascencio Huertas, Fernando Austria Corrales, Claudia Iveth Astudillo García, Carlos Alejandro García Benitez, Silvia Allende-Pérez
Palliative and Supportive Care.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Efecto de un nuevo modelo de gestión de la organización de enfermería basado en la investigación apreciativa en pacientes con tumores ginecológicos en el periodo perioperatório
Chuntao Fang, Jing Yang
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a new nursing organization management mode constructed by appreciative inquiry on gynecological tumor patients in the perioperative period
Chuntao Fang, Jing Yang
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Coping, Family Support, and Posttraumatic Growth in Female Genital Cancer Patients
Hee Nam An, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Post-Traumatic Growth in Patients with Breast Cancer Based on a Model of Post-Traumatic Growth
Hee Yeon Park, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(2): 65. CrossRef - Psychometric property of an instrument 1: content validity
Eun-Hyun Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(1): 10. CrossRef - Impact of Posttraumatic Growth and Health Promoting Behavior on Quality of Life in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Mi-Ae Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(1): 32. CrossRef - The Development and Validation of a Perceived Nursing Support Scale for Mothers of Preterm Infants
Mihae Im, Jina Oh
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(5): 317. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth of Gynecologic Oncology Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sun Jeong Yun, Hye Young Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 409. CrossRef - Psychosocial Adjustment in Korean Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyejin Sun, Jia Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 545. CrossRef - Development of a revised model of posttraumatic growth in the contexts of leisure and sport
Se-Hyuk Park
Korean Journal of Sport Science.2018; : 237. CrossRef
- Transcultural adaptation and Mexican validation of the posttraumatic growth inventory (PTGI-X-Mx) in a palliative oncology population
- 2,210 View
- 47 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Decision Making Experience on Breast Reconstruction for Women with Breast Cancer
- Myungsun Yi, Woo Joung Joung, Eun Young Park, Eun Jin Kwon, Haejin Kim, Ji Young Seo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(6):894-904. Published online December 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.894
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore decision making experiences of Korean women with breast cancer who underwent breast reconstruction with/after a mastectomy.
Methods Data were collected during 2015-2016 through individual in-depth interviews with 10 women who had both mastectomy and breast reconstruction, and analyzed using phenomenological method to identify essential themes on experiences of making a decision to have breast reconstruction.
Results Five theme clusters emerged. First, “expected loss of sexuality and discovery of autonomy” illustrates various aims of breast reconstruction. Second, “holding tight to the reputation of doctors amid uncertainty” specifies the importance of a trust relationship with their physician despite a lack of information. Third, “family members to step back in position” describes support or opposition from family members in the decision making process. Fourth, “bewilderment due to the paradox of appearance-oriented views” illustrates paradoxical environment, resulting in confusion and anger. Lastly, “decision to be made quickly with limited time to oneself” describes the crazy whirling process of decision making.
Conclusion Findings highlight aims, worries, barriers, and facilitators that women with breast cancer experience when making a decision about breast reconstruction. Deciding on breast reconstruction was not only a burden for women in a state of shock with a diagnosis of breast cancer, but also an opportunity to decide to integrate their body, femininity, and self which might be wounded from a mastectomy. These findings will help oncology professionals provide effective educational counselling before the operation to promote higher satisfaction after the operation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
Hyeng Sook Yoon, Eunjung Ryu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100820. CrossRef - Influence of body image on quality of life in breast cancer patients undergoing breast reconstruction: Mediating of self‐esteem
Yunhee Jang, Mihyeon Seong, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(17-18): 6366. CrossRef - Effects of decision aids on breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials
Shu Yang, Lin Yu, Chunmiao Zhang, Mengmeng Xu, Qi Tian, Xuan Cui, Yantong Liu, Shuanghan Yu, Minglu Cao, Wei Zhang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(7-8): 1025. CrossRef - “Struggling to Accept the New Breast as Part of My Body” – The Challenge of Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Women With Breast Cancer
Jeehee Han, Juhye Jin, Sanghee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Sue Kim
Cancer Nursing.2022; 45(4): 262. CrossRef - Do COVID-19–Related Treatment Changes Influence Fear of Cancer Recurrence, Anxiety, and Depression in Breast Cancer Patients?
Soo Yeon Kim, Sue Kim
Cancer Nursing.2022; 45(2): E628. CrossRef - A Decision Tree Model for Breast Reconstruction of Women with Breast Cancer: A Mixed Method Approach
Eun Young Park, Myungsun Yi, Hye Sook Kim, Haejin Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3579. CrossRef - The Lived Experience of Body Alteration and Body Image with Regard to Immediate Breast Reconstruction among Women with Breast Cancer
Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E Suh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 245. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life Among Breast Cancer Patients Following Immediate Breast Reconstruction
A Young Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Korean Translation and Psychometric Evaluation of Korean Version EORTC QLQ-BRECON23
Soo-Kyung Bok, Youngshin Song, Ancho Lim, Hyunsuk Choi, Hyunkyung Shin, Sohyun Jin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9163. CrossRef - Operation Experiences of Women with Breast Cancer
Hyeon-Young Kim, Sun Hwa Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(2): 129. CrossRef - “Waiting for breast reconstruction”: An interpretative phenomenological analysis of heterosexual couples’ experiences of mastectomy for breast cancer
Kristopher Lamore, Cécile Flahault, Léonor Fasse, Aurélie Untas
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2019; 42: 42. CrossRef - Breast reconstruction statistics in Korea from the Big Data Hub of the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service
Jae-Won Kim, Jun-Ho Lee, Tae-Gon Kim, Yong-Ha Kim, Kyu Jin Chung
Archives of Plastic Surgery.2018; 45(05): 441. CrossRef
- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
- 1,218 View
- 13 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth in Survivors of Breast Cancer
- Jin-Hee Park, Yong-Sik Jung, Youngmi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):454-462. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.454
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Posttraumatic growth (PTG) is defined as 'positive psychological change experienced as a result of a struggle with highly challenging life circumstances'. The purpose of this study was to identify the level of PTG and its correlates in Korean patients with breast cancer.
Methods A sample of 120 participants was recruited from outpatients, who had successfully completed primary treatment of breast cancer at a university hospital., Data were collected from June to December, 2014 using Posttraumatic Growth Inventory, lllness Intrusiveness Rating Scale, Cancer Coping Questionnaire, Revised Life Orientation Test and The Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support.
Results Total score for the PTG was 79.18±17.54 in patients surviving breast cancer. Bivariate analyses indicated that PTG was positively associated with having a religion, perceived social support, greater optimism, cancer coping, and illness intrusiveness. Results of the regression analysis showed that cancer coping (β=.29,
p =.001), optimism (β=0.28,p =.001) and illness intrusiveness (β=0.17,p =.037) were statistically significant in patients' PTG.Conclusion The research findings show that the variables of cancer coping, optimism and illness intrusiveness significantly explain PTG and these psychological variables can be used to provide improvement in PTG for patients with breast cancer
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The influence of locus of control, coping strategies and time perspective on post-traumatic growth in survivors with primary breast cancer
Alexandra-Cristina Paunescu, Marina Kvaskoff, Cyrille Delpierre, Lidia Delrieu, Guillemette Jacob, Myriam Pannard, Marie Préau
BMC Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Do caregivers of traumatic brain injury survivors experience post-traumatic growth? A mixed-methods study exploring the positive experiences of informal caregivers
Molly Hillyard, Ryan Westley, Jade Kettlewell, Melissa Brunner
Brain Impairment.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Post-traumatic growth and its influencing factors in first-episode stroke patients: a cross-sectional study
Minli Hu, Yue Ban, Zhihui Li, Yu He, Liping Deng, Xiaohua Xie
BMC Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Resilience in Patients with Multiple Myeloma: A Cross-Sectional Study
Hae-Lyeon Jeon, Hye-Ah Yeom
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(1): 41. CrossRef - Post-traumatic Growth Experiences of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Grounded Theory Approach
Seung-Kyoung Yang, Young-Suk Park, Eun-Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(2): 79. CrossRef - Social Reintegration Experiences of Young Adult Cancer Survivors
Ji Seong Yi, Song Yi Lee
Behavioral Sciences.2024; 14(11): 1101. CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model for Posttraumatic Growth among Cured Patients with COVID-19
Soo Young An, Heejung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 309. CrossRef - Effects of Post Traumatic Growth on Successful Aging in Breast Cancer Survivors in South Korea: The Mediating Effect of Resilience and Intolerance of Uncertainty
Su Jeong Yi, Ku Sang Kim, Seunghee Lee, Hyunjung Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(21): 2843. CrossRef - Pathways to post-traumatic growth in Korean female cancer patients: the mediation effects of coping strategies and resilience
Sumi Choi, Dongil Kim, Ahyoung Cho, Sohyun An, Changhyun Kim, Inhwa Yoo
European Journal of Psychotraumatology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural Equation Model for Psychosocial Adjustment of Breast Cancer Survivors Based on Family Resilience Model
Jiyoung Seo, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(2): 178. CrossRef - Cancer coping, healthcare professionals’ support and posttraumatic growth in brain-tumor patients
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
Psychology, Health & Medicine.2022; 27(4): 780. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Post-Traumatic Growth in Patients with Breast Cancer Based on a Model of Post-Traumatic Growth
Hee Yeon Park, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(2): 65. CrossRef - Factors influencing posttraumatic growth in ovarian cancer survivors
Jeong Min Oh, Yoonjung Kim, Yeunhee Kwak
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(4): 2037. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Supportive Care Needs of Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyekyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 60. CrossRef - Factors associated with post-traumatic growth in male patients with rectal cancer: A cross-sectional study
Yuri Kim, Yoonjung Kim, Yeunhee Kwak
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102028. CrossRef - A Structural Model on the Post-Traumatic Growth of Police Officers
Seung Woo Han, Eun Suk Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(3): 348. CrossRef - Stacking Ensemble Technique for Classifying Breast Cancer
Hyunjin Kwon, Jinhyeok Park, Youngho Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2019; 25(4): 283. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth in Cancer Survivors
Jeong-Sook Park, You-Jeong Kim, Young-Seun Ryu, Mi-Hyang Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - The relationship between cancer‐related worry and posttraumatic growth in adolescent and young adult cancer survivors
Glynnis A. McDonnell, Alice W. Pope, Tammy A. Schuler, Jennifer S. Ford
Psycho-Oncology.2018; 27(9): 2155. CrossRef - The Influence of Spiritual Well-Being, Self-Esteem, and Perceived Social Support on Post-Traumatic Growth among Breast Cancer Survivors
Eun Young Seo, Suhye Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(4): 232. CrossRef
- The influence of locus of control, coping strategies and time perspective on post-traumatic growth in survivors with primary breast cancer
- 1,541 View
- 16 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Effect of Cancer Symptoms and Fatigue on Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Depression in People with Gastrointestinal Cancer
- Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):420-430. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.420
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test a hypothetical model of chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (CRCI) and depression in people with gastrointestinal cancer.
Methods A purposive sample of 198 patients undergoing chemotherapy was recruited from November 2014 to July 2015. The instruments were Everyday Cognition (ECog), Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F), and M. D. Anderson Symptom Inventory-Gastrointestinal Cancer Module. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation, and path analysis.
Results CRCI was directly affected by cancer symptoms (β=.19,
p =.004) and fatigue (β=.56,p <.001)(R 2=47.2%). Depression was directly affected by fatigue (β=.48,p <.001) and CRCI (β=.27,p <.001). However, The impact of cancer symptoms on depression was confirmed through the mediating effect of CRCI.Conclusion Results indicate that in patients with gastrointestinal cancer undergoing chemotherapy along with the direct physiologic effects (fatigue, symptoms) of cancer treatment may have altered cognitive function leading to depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Low Back Pain and Its Influencing Factors among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
Hyun Ju Uhm, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(2): 95. CrossRef - Factors affecting the quality of life of gastric cancer survivors
Jahyun Choi, Sanghee Kim, Mona Choi, Woo Jin Hyung
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(4): 3215. CrossRef - Attitudes About Coping With Fatigue in Patients With Gastric Cancer
Eun Ja Yeun, Misoon Jeon
Gastroenterology Nursing.2020; 43(1): 97. CrossRef - Symptom Distress and Depression in Patients with Recurrent Gynecologic Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy: Mediating Effect of Resilience
Eun Jung Yang, Ho Sihn Ryu
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(1): 28. CrossRef - Computerized programs for cancer survivors with cognitive problems: a systematic review
Yoonjung Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2019; 13(6): 911. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Depression following Chemotherapy in Women with Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee, Hyun Ah Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(2): 66. CrossRef - Symptom Clusters and Quality of Life in Subjects With COPD
Kyeung Eun Lim, Sung Reul Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim, So Ri Kim
Respiratory Care.2017; 62(9): 1203. CrossRef
- Low Back Pain and Its Influencing Factors among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
- 1,088 View
- 14 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Frequency, Intensity and Daily Life Distress of Urinary Dysfunction in Women with Cervical Cancer after Radical Hysterectomy
- Nami Chun, Gie Ok Noh, Hyun Ju Song, Sang Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):400-408. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.400
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to identify frequency, intensity of urinary dysfunction and daily life distress in women after a radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
Methods One hundred and fifty seven women who had undergone a radical hysterectomy and one hundred and sixty five women as healthy controls completed questionnaires on intensity of urinary dysfunction and daily life distress caused by urinary dysfunction.
Results Women with cervical cancer showed higher frequency of urinary dysfunction than healthy controls. Major urinary dysfunction for women with cervical cancer in order of frequency were night-time incontinence (odds ratio=10.39,
p <.001), difficulty in starting urination, weak urine stream and sense of incomplete emptying of bladder. The highest score on intensity was difficulty in starting urination, followed by urgency, weak urine stream, daytime frequency and sense of incomplete emptying. Night-time incontinence was the urinary symptom causing the most daily life distress for cervical cancer women followed by difficulty in starting urination, urgency, sense of incomplete emptying, and night-time frequency.Conclusion Results suggest that nurses should address the potential postoperative urinary complications and develop long term interventions to decrease urinary dysfunction and daily life distress for women who have had a radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of pelvic floor muscle function (PFMF) in cervical cancer patients with Querleu–Morrow type C hysterectomy: a multicenter study
Shiyan Wang, Lei Gao, Hongwu Wen, Yunong Gao, Qiubo Lv, Hongyu Li, Sumei Wang, Yanlong Wang, Qing Liu, Jinsong Han, Haibo Wang, Yi Li, Na Yu, Qing Wang, Tingting Cao, Sha Wang, Huaxin Sun, Zhiqi Wang, Xiuli Sun, Jianliu Wang
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2022; 305(2): 397. CrossRef - Association of pelvic floor function with postoperative urinary incontinence in cervical cancer patients after the radical hysterectomy
Shiyan Wang, Runzhi Wang, Hongwu Wen, Yunong Gao, Qiubo Lv, Hongyu Li, Sumei Wang, Yanlong Wang, Qing Liu, Jinsong Han, Haibo Wang, Yi Li, Qing Wang, Tingting Cao, Sha Wang, Huaxin Sun, Zhiqi Wang, Xiuli Sun, Jianliu Wang
Neurourology and Urodynamics.2021; 40(1): 483. CrossRef - Influence of Urinary Dysfunction on Quality of Life in Women with Cervical Cancer after Radical Hysterectomy
Nami Chun, Gie-Ok Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 150. CrossRef - Symptom Distress and Depression in Patients with Recurrent Gynecologic Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy: Mediating Effect of Resilience
Eun Jung Yang, Ho Sihn Ryu
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(1): 28. CrossRef
- Evaluation of pelvic floor muscle function (PFMF) in cervical cancer patients with Querleu–Morrow type C hysterectomy: a multicenter study
- 1,112 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Structural Equation Model on Resilience of Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
- Jeong Ha Yang, Ok Soo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):327-337. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct and test a structural equation model on resilience of breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy.
Methods Participants were 204 patients with breast cancer who received chemotherapy treatment. They participated in a structured interview, which included social support, depression, symptom experience, self-efficacy, hope, resilience, and infection prevention behaviors. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 20.0 and AMOS 18.0.
Results Lower depression (γ=-.33,
p =.020) and symptom experience (γ=-.31,p =.012) and higher self-efficacy (γ=.32,p =.005) and hope (γ=.48,p =.016) were influenced by higher social support. Greater resilience was influenced by lower symptom experience (β=-.18,p =.016), higher self-efficacy (β=.49,p =.023), and higher hope (β=.46,p =.012), and these predictors explained 66.7% of variance in resilience. Greater resilience (β=.54,p =.009) made an impact on greater infection prevention behaviors. Resilience mediated the relations of symptom experience (β=-.10p =.013), self-efficacy (β=.27,p =.006) and hope (β=.25,p =.009) with infection prevention behaviors. These predictors explained 24.9% of variance in infection prevention behaviors.Conclusion The findings of the study suggest that breast cancer patientsw ith greater resilience who are receiving chemotherapy participate in increased infection prevention behaviors. Further research should be conducted to seek intervention strategies that improve breast cancer patients' resilience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Structural Equation Model of Resilience in Patients Undergoing Lung Cancer Surgery During the Acute Survival Phase: A Cross-Sectional Study
Miri Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 174. CrossRef - Understanding Intention Triggers in Early Autism Screening Promotion: The Role of Narrative and Framing
Lingfei Wang, Will Grant, Xinyi Jin, Guoyan Wang
Health Communication.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Effects of Telephone-based Self-care Intervention for Gynecologic Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Boyeon Lee, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 216. CrossRef - Adaptación a la enfermedad, resiliencia y optimismo en mujeres con cáncer de mama
Marlen Simancas Fernández, Carla Zapata Rueda, Gonzalo Galván Patrignani, Jose Carlos Celedón Rivero, Juan Hernández Padilla
Revista Colombiana de Psiquiatría.2023; 52(4): 280. CrossRef - Adaptation to the disease, resilience and optimism in woman with breast cancer
Marlen Simancas Fernández, Carla Zapata Rueda, Gonzalo Galván Patrignani, Jose Carlos Celedón Rivero, Juan Hernández Padilla
Revista Colombiana de Psiquiatría (English ed.).2023; 52(4): 280. CrossRef - Positive personal resources and psychological distress during the COVID-19 pandemic: resilience, optimism, hope, courage, trait mindfulness, and self-efficacy in breast cancer patients and survivors
Francesca Chiesi, Deborah Vizza, Moira Valente, Rosy Bruno, Chloe Lau, Maria Rosita Campagna, Melania Lo Iacono, Francesco Bruno
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(8): 7005. CrossRef - A menopausal transition model based on transition theory
Jisoon Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 210. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Resilience in Patients With Lung Cancer
Jie Zhang, Yizhen Yin, Anni Wang, Hui Li, Juan Li, Silan Yang, Yuchen Wu, Jingping Zhang
Cancer Nursing.2021; 44(6): 465. CrossRef - Mediator Roles of Social Support and Hope in the Relationship Between Body Image Distress and Resilience in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Treatment: A Modeling Analysis
Hsin-Tien Hsu, Chiung-Hui Juan, Jyu-Lin Chen, Hsiu-Fen Hsieh
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Structure Equation Modeling for Resilience in Patients with Breast Cancer
Dong Rim Hyun, So Yeun Jun, Chang Wan Jun, Sue Kyung Sohn
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(2): 87. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Resilience among Korean adolescents and young adult survivors of childhood cancer
Yoon Jung Shin, Eui Geum Oh
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 53: 101977. CrossRef - Self-efficacy, Hope as Mediators Between Positive Coping and Resilience Among Patients With Gastric Cancer Before the First Chemotherapy
Xiaoting Wu, Haibo Xu, Xiaomin Zhang, Shiyu Han, Liuna Ge, Xiaohui Li, Xinqiong Zhang
Cancer Nursing.2021; 44(1): 79. CrossRef - The relationship between resilience, anxiety and depression among patients with mild symptoms of COVID‐19 in China: A cross‐sectional study
Jie Zhang, Zhen Yang, Xiao Wang, Juan Li, Lili Dong, Fusheng Wang, Yifei Li, Ruihong Wei, Jingping Zhang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4020. CrossRef - Relationship between Self-efficacy and Resilience among Patients with Colorectal Cancer with Stoma: Mediating Effects of Family Support and Medical Staff Support
Mi Na Yun, Kyoung Mi Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(6): 599. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Resilience and Its Predictors Among Chinese Liver Cancer Patients Undergoing Transarterial Chemoembolization
Caixia Li, Huijuan Lu, Wei Qin, Xiaorong Li, Jingxian Yu, Fang Fang
Cancer Nursing.2019; 42(5): E1. CrossRef - Resilience in Koreans With Cancer
Shin-Young Lee, Haeok Lee, Jacqueline Fawcett, Jeong-Hwan Park
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2019; 21(5): 358. CrossRef - Examining spiritual support among African American and Caucasian Alzheimer's caregivers: A risk and resilience study
Scott E. Wilks, Wanda R. Spurlock, Sandra C. Brown, Bettina C. Teegen, Jennifer R. Geiger
Geriatric Nursing.2018; 39(6): 663. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Resilience in Hospitalized Patients with Stroke
Jong Kyung Lee, Ji Yeong Yun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(4): 385. CrossRef - Effects of a Group Coaching Program on Depression, Anxiety and Hope in Women with Breast Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
So Ryoung Seong, Moon-kyung Cho, Jeeyoon Kim, Yeo Ok Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(3): 188. CrossRef
- A Structural Equation Model of Resilience in Patients Undergoing Lung Cancer Surgery During the Acute Survival Phase: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,540 View
- 23 Download
- 21 Crossref

- A Study on the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors based on Social Network Analysis
- Sun Young Kwon, Ka Ryeong Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(1):50-58. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the knowledge structure of cancer survivors.
Methods For data, 1099 articles were collected, with 365 keywords as a Noun phrase extracted from the articles and standardized for analyzing. Co-occurrence matrix were generated via a cosine similarity measure, and then the network analysis and visualization using PFNet and NodeXL were applied to visualize intellectual interchanges among keywords.
Results According to the result of the content analysis and the cluster analysis of author keywords from cancer survivors articles, keywords such as 'quality of life', 'breast neoplasms', 'cancer survivors', 'neoplasms', 'exercise' had a high degree centrality. The 9 most important research topics concerning cancer survivors were 'cancer-related symptoms and nursing', 'cancer treatment-related issues', 'late effects', 'psychosocial issues', 'healthy living managements', 'social supports', 'palliative cares', 'research methodology', and 'research participants'.
Conclusion Through this study, the knowledge structure of cancer survivors was identified. The 9 topics identified in this study can provide useful research direction for the development of nursing in cancer survivor research areas. The Network analysis used in this study will be useful for identifying the knowledge structure and identifying general views and current cancer survivor research trends.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Self-Assessment, TAilored Information, and Lifestyle Management for Cancer Patients’ Returning to Work (START): A Multi-center, Randomized Controlled Trial
Danbee Kang, Ka Ryeong Bae, Yeojin Ahn, Nayeon Kim, Seok Jin Nam, Jeong Eon Lee, Se Kyung Lee, Young Mog Shim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Seung Yeop Oh, Mison Chun, Jaesung Heo, Juhee Cho
Cancer Research and Treatment.2023; 55(2): 419. CrossRef - Web-Based Research Trends on Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Over the Last 5 Years: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling Study
Hyun-Yong Kim, Kyung-Ah Kang, Suk-Jung Han, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(2): e32309. CrossRef - Network analysis based on big data in social media of Korean adolescents’ diet behaviors
JongHwi Song, SooYeun Yoo, JunRyul Yang, SangKyun Yun, YunHee Shin, Girish C. Melkani
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0273570. CrossRef - An Overview of Cognitive Reserve in Aging Based on Keyword Network Analysis
Jihyun Kim, Mi So Kim
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of research on metabolic syndrome in cancer survivors using topic modeling and social network analysis
Ji-Su Kim, Hyejin Kim, Eunkyung Lee, Yeji Seo
Science Progress.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Identification of the Knowledge Structure on the Resilience of Caregivers of People with Dementia using a Text Network Analysis
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 66. CrossRef - Research Topics and Trends in Interprofessional Education in Nursing
Kisook Kim, Ki-Seong Lee
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(10): 554. CrossRef - Social Determinants of Health of Multicultural Adolescents in South Korea: An Integrated Literature Review (2018~2020)
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Hyeyeon Lee, Mikyung Lee, Sookyung Kim, Kennedy Diema Konlan
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(4): 430. CrossRef - A Network Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in End-of-Life Care and Nursing
Kisook Kim, Seung Gyeong Jang, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(1): 313. CrossRef - Research Trends on Factors Influencing the Quality of Life of Cancer Survivors: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling Approach
Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Sun Hyoung Bae, Hee-Jun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(4): 231. CrossRef - Knowledge Structure of Nursing Studies on Heart Failure Patients in South Korea through Text Network Analysis
Seang Ryu, Hyunyoung Park, Yun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 409. CrossRef - Semantic Network Analysis of Iussues Related to Mental Illness in Korea Media: Focusing on the Five Major Media from 2016 to 2018
Sun Joo Park, Na Ri Shin, Seung Hye Kim, Su Bin Park, Chul Eung Kim
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2020; 59(1): 72. CrossRef - Identification of the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors’ Return to Work and Quality of Life: A Text Network Analysis
Kisook Kim, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9368. CrossRef - Using Text Network Analysis for Analyzing Academic Papers in Nursing
Chan Sook Park
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2019; 16(1): 12. CrossRef - Identification of Knowledge Structure of Pain Management Nursing Research Applying Text Network Analysis
Chan Sook Park, Eun-Jun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 538. CrossRef - Exploring the Knowledge Structure of Nursing Care for Older Patients With Delirium
Jung Eun Choi, Mi So Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(5): 216. CrossRef - A Comparison of Hospice Care Research Topics between Korea and Other Countries Using Text Network Analysis
Eun-Jun Park, Youngji Kim, Chan Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 600. CrossRef - The Network Analysis of Nursing Diagnoses for Children Admitted in Pediatric Units Determined by Nursing Students
Mikyung Moon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(3): 223. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Articles Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration for 3 Years (2013~2015): The Application of Text Network Analysis
Tae Wha Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, GyeongAe Seomun, Miyoung Kim, Jee-In Hwang, Soyoung Yu, Seok Hee Jeong, Min Jung, Mikyung Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 101. CrossRef - Social Network Analysis on Mapping the Knowledge Structure of Dementia Research
Jung-Hee Han, Young-Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(2): 69. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Self-Assessment, TAilored Information, and Lifestyle Management for Cancer Patients’ Returning to Work (START): A Multi-center, Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,196 View
- 4 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
- Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(1):19-28. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the mediating effect of psychological distress in the relationship between chemotherapy related cognitive impairment (CRCI) and quality of life (QOL) in people with cancer.
Methods A purposive sample of 130 patients undergoing chemotherapy was recruited for the cross-sectional survey design. Data were collected from November 2014 to June 2015. The instruments were K-MMSE (Korean Mini-Mental State Examination), Everyday Cognition (ECog), Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS), and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General (FACT-G). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation, and multiple regression using Baron and Kenny steps for mediation.
Results The mean score for objective cognitive function was 27.95 and 69.32 for perceived cognitive decline. Overall quality of life was 91.74. The mean score was 17.52 for psychological distress. The prevalence was 56.2% for anxiety and 63.1% for depression, and 20.0% for CRCI. There were significant correlations among the variables, objective cognitive function and self-reported cognitive decline, psychological distress, and quality of life. Psychological distress was directly affected by CRCI. (R2=29%). QOL was directly affected by CRCI. Psychological distress and CRCI effected QOL (R2=43%). Psychological distress had a partial mediating effect (β= -.56,
p <.001) in the relationship between self-reported cognitive decline and quality of life (Sobel test: Z= -5.08,p <.001).Conclusion Based on the findings of this study, nursing intervention programs focusing on managing cognitive decline, and decreasing psychological distress are highly recommended to improve quality of life in cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Physical Activity with Dementia Risk in Cancer Survivors: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Su Kyoung Lee, Minji Han, Sangwoo Park, Sun Jae Park, Jihun Song, Hye Jun Kim, Jaewon Kim, Hyeokjong Lee, Hyun-Young Shin, Kyae Hyung Kim, Sang Min Park
Cancer Research and Treatment.2026; 58(1): 48. CrossRef - Self-disclosure in Adult Patients With Cancer
Hyungran Lee, Younhee Jeong
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(4): 289. CrossRef - NYHA classification deterioration and quality of life in heart failure inpatients: A chain mediation analysis of cognitive impairment and depression
Jin Yang, You Pu, Mingjun He, Tianyi Wang, Ting Ye, Yunman Huang, Yunfeng Di, Xianqin Zhang, Zheng Yang
Heart & Lung.2025; 73: 95. CrossRef - Disease Perception, Stigma, Distress, Physical Symptom Experience and Quality of Life in Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Cross-Sectional Study
Eun-Hee Lee, Dongwon Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 494. CrossRef - Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 polymorphism is associated with chemotherapy‐related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer who receive chemotherapy
Senbang Yao, Wen Li, Shaochun Liu, Yinlian Cai, Qianqian Zhang, Lingxue Tang, Sheng Yu, Yanyan Jing, Xiangxiang Yin, Huaidong Cheng
Cancer Medicine.2023; 12(5): 5209. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Colon Cancer Survivorship in Patients Who Have Received Adjuvant Chemotherapy
Meghana Kesireddy, Laura Tenner
Clinical Colorectal Cancer.2023; 22(4): 361. CrossRef - Predictors of cognitive impairment in patients undergoing ileostomy for colorectal cancer: a retrospective analysis
Jing Xu, Yuelan Yang, Die Hu
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15405. CrossRef - Symptom Experience, Social Support, and Quality of Life in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies Undergoing Chemotherapy
Ga Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song, Mi-Ae You, Jin-Hee Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 29. CrossRef - Effect of Ambulatory Chemotherapy (Portable Infusion Pump Use) Video Education on Knowledge, Self-efficacy and Anxiety of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Young Park, Young A Park, You Hee Son, Myung Jin Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 193. CrossRef - A pilot retrospective study of comprehensive nursing care on psychological disorder in colorectal cancer undergoing chemotherapy
Zhou-Yi Zhang, Rui Wang, Li Zhang, Ming-Li Gu, Xiu-E Guan
Medicine.2022; 101(28): e29707. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Depression on the Relationship between Cognitive Function and the Activities of Daily Living in Post-stroke Patient
Ji Eun Kim, Hwee Wee
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(4): 309. CrossRef - A serial multiple mediator model of sense of coherence, coping strategies, depression, and quality of life among gynecologic cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy
Hee Sun Kim, Ju-Hee Nho, Joo-Hyun Nam
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102014. CrossRef - Impact of changes in perceived attentional function on postsurgical health-related quality of life in breast cancer patients awaiting adjuvant treatment
Mi Sook Jung, Moira A. Visovatti, Eun Hee Sohn, Hwa-Seung Yoo, Mijung Kim, Je Ryong Kim, Jin Sun Lee
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing quality of life in patients with multiple myeloma
Hee-Young Kang, Eun-Young Choi
Contemporary Nurse.2019; 55(2-3): 109. CrossRef - The role of depression in the relationship between cognitive decline and quality of life among breast cancer patients
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung, Sun Hyoung Bae
Supportive Care in Cancer.2019; 27(7): 2707. CrossRef - A Longitudinal Path Analysis of Symptom, Fatigue and Quality of life in Patients with Colorectal Cancer during Chemotherapy
Eun Hee Kim, Soon Rim Suh
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(3): 200. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Cognitive Function in Patients with Stomach Cancer
Yeoung Ji Yu, Seung Hee Ahn, Yong Ae Cho, Eunjung Ryu, Eun-Ju Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(4): 241. CrossRef - Serum lipid changes following the onset of depressive symptoms in postmenopausal women
Jane E. Persons, Jennifer G. Robinson, Martha E. Payne, Jess G. Fiedorowicz
Psychiatry Research.2017; 247: 282. CrossRef - Development of the Cognitive Function Scale for Breast Cancer Patients
Bok Yae Chung, Eun Hee Choi, Gyung Duck Kim, Kyung Hae Kim, Hye Sun Byun
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(1): 12. CrossRef
- Association of Physical Activity with Dementia Risk in Cancer Survivors: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
- 1,390 View
- 21 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Effects of Lifestyle Intervention on Fatigue, Nutritional Status and Quality of Life in Patients with Gynecologic Cancer
- Hyunjin An, Ju-Hee Nho, Sunyoung Yoo, Hyunmin Kim, Minji Nho, Hojeong Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):812-822. Published online December 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.812
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of lifestyle intervention on the development of fatigue, nutritional status and quality of life of patients with gynecologic cancer.
Methods A nonequivalent control group quasi-experimental design was used. Participants were 49 patients with gynecologic cancer. They were assigned to the experiment group (n=24) or the control group (n=25). The lifestyle intervention for this study consisted of physical activity, nutritional education, telephone call counseling, health counseling, monitoring for lifestyle, and affective support based on Cox's Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior and was implemented for six weeks.
Results Significant group differences were found for fatigue (
p =.037), nutritional status (p =.034) and social/family well-being (p =.035) in these patients with gynecologic cancer.Conclusion Results indicate that this lifestyle intervention is effective in lessening fatigue, and improving nutritional status and social/family well-being. Therefore, nurses in hospitals should develop strategies to expand and provide lifestyle interventions for patients with cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Postoperative Dietary Intervention in Patients with Gastric Cancer who Underwent Gastrectomy: Quasi-Experimental Study Design
Dahye KIM, Myung Kyung LEE
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2025; 41(1): 151797. CrossRef - Health-Related Behaviors of Middle-Aged Cancer Survivors: A Comparative Study with Matched Non-Cancer Controls Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI–VII (2013–2018) Data
Mi Lee KIM, Ju Ri JEONG, Yu Ri CHOE
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2025; 25(1): 20. CrossRef - Analysis of Educational Needs Related to Chemotherapy among Patients with Solid Tumors
Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(2): 89. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Interventions for Lower Limb Lymphedema in Patients with Gynecologic Cancer
Soon Yang Jang, Ji Hyeon Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2025; 28(1): 40. CrossRef - Effects of a Customized Diet Education Program Using a Mobile Instant Messenger for People Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: A Feasibility Test
Hyun-Jung Lee, Hee-Young Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(4): 367. CrossRef - Effects of an integrated lifestyle intervention for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
Su Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 73: 102714. CrossRef - Literature Review on Lifestyle Intervention Program for Adults in Korea
Keun-Young Yang
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(8): 1815. CrossRef - Effect of a Hospital-To-Home Transitional Intervention Based on an Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior for Adult Patients with Stroke
Su-Jin Cho, Sung Reul Kim, Kyung-Hee Cho, Nah-Mee Shin, Won-Oak Oh
Journal of Community Health Nursing.2023; 40(4): 273. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Attitudes About Coping With Fatigue in Patients With Gastric Cancer
Eun Ja Yeun, Misoon Jeon
Gastroenterology Nursing.2020; 43(1): 97. CrossRef - Health-related Quality of Life and Its Related Factors among Cancer Survivors and General Adults: Focusing on Lifestyle Behaviors and Mental Health
Eun A Song, Youngran Kweon, Yoon Young Hwang, Minjeong An
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 385. CrossRef - Deriving the Components of Lifestyle-Related Occupational Therapy Intervention Program for the Elderly: Through the Delphi Technique
Yun-Chan Shin, Da-Sol Park, Eun-Hye Cho, Kyung-A Won, Dae-Sung Han, Jung-Ran Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2020; 28(1): 45. CrossRef - Theoretical evaluation of Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior for health promotion in adult
women
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Gi Wook Ryu
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 120. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Characteristics of Cancer Patients and Cancer Survivors
So Young Baek, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 11. CrossRef - The Effects of Stress and Stress Coping on Life Quality in Cancer Patients and Caregivers: A Dyadic Analysis Using an Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Eun-Jung Kim, Jeong Won Han
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(3): 135. CrossRef - The Effects of Integrated Intervention Program for Community Dwelling Cancer Patients' Quality of Life, Depression and Self Care Agency
Young Sil Kang, In Soo Kwon, Eunyoung Hong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(3): 445. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Postoperative Dietary Intervention in Patients with Gastric Cancer who Underwent Gastrectomy: Quasi-Experimental Study Design
- 1,381 View
- 37 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Disturbance in ADL from Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy and Quality of Life in Cancer Patients: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
- Kyung Yeon Kim, Seung Hee Lee, Jeong Hye Kim, Pok Ja Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):661-670. Published online October 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.661
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the mediation of psychological distress in the relationship between disturbance in ADL from chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy and quality of life in order to provide a basis for planning nursing interventions to improve the quality of life in cancer patients.
Methods A purposive sample of 130 patients treated with chemotherapy were recruited in the cross-sectional survey design. Data were collected using self-report questionnaires. The instruments were the Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Assessment Tool (CIPNAT), Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS), and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General (FACT-G).
Results The mean score for disturbance in ADL from chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy was 3.30. Overall quality of life was 2.48. The mean score was 1.04 for psychological distress. The prevalence was 35.4% for anxiety and 47.7% for depression. There were significant correlations among the three variables, disturbance in ADL from chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy, psychosocial distress, and quality of life. Psychosocial distress had a complete mediating effect (β= -.74,
p <.001) in the relationship between disturbance in ADL from chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy and quality of life (Sobel test: Z= -6.11,p <.001).Conclusion Based on the findings of this study, nursing intervention programs focusing on disturbance of ADL management, and decrease of psychological distress are highly recommended to improve quality of life in cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of distress among individuals with cancer reporting physical problems
McKinzey Dierkes, Yilin Cai, Victoria Trotta, Patricia Policicchio, Sijin Wen, Gwendolyn Dzwil, Nicholas Davis, Nicole L. Stout
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Quality of Life in Cancer Patients Experiencing Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN) : Scoping review
Minah Cho, Injung Hyun, Jiyeon Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(2): 75. CrossRef - Sex differences of the association between handgrip strength and health-related quality of life among patients with cancer
Jihye Kim, Yujin Kim, Jae Won Oh, San Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Mobile Application-based Self-Management Program for Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 258. CrossRef - The impact of peripheral neuropathy symptoms, self-care ability, and disturbances to daily life on quality of life among gynecological cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a cross-sectional survey
Sohee Mun, Hyojung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 296. CrossRef - The mediation and interaction of depressive symptoms in activities of daily living and active aging in rural elderly: A cross-sectional survey
Xuelian Fu, Yinli Su, Chunyan Zeng, Liqiong Liu, Yang Guo, Yuanyuan Wu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Sleep Quality, and Quality of Life following Chemotherapy in Stomach Cancer Patients: a Prospective Study
Pok Ja Oh, Jin Lee, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(2): 72. CrossRef - Changes in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, disturbance in activities of daily living, and depression following chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer: A prospective study
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee, Sook-Kyoung Kim, Jeong-Hye Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 44: 101676. CrossRef - Effects of aroma self-foot reflexology on peripheral neuropathy, peripheral skin temperature, anxiety, and depression in gynaecologic cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: A randomised controlled trial
Gie Ok Noh, Kyung Sook Park
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2019; 42: 82. CrossRef - Oxaliplatin-induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Symptoms, Distress and Quality of Life among Korean Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Hye Jeong Jung, Soo jung Ahn, Yoo Ri Yang, Kyoung A Kim, Sang Joon Shin, Min Kyu Jung, Sang Hui Chu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(4): 204. CrossRef - Neuropathic symptoms, physical and emotional well-being, and quality of life at the end of life
Cindy Tofthagen, Constance Visovsky, Sara Dominic, Susan McMillan
Supportive Care in Cancer.2019; 27(9): 3357. CrossRef - Dolor neuropático en pacientes oncológicos en tratamiento con bortezomib
S. Expósito Vizcaíno, J. Casanova-Mollà, L. Escoda, S. Galán, J. Miró
Neurología.2018; 33(1): 28. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Sleep and Quality of Life among Patients with Gastric Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy
Hyemi Kim, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(3): 176. CrossRef - Neuropathic pain in cancer patients treated with bortezomib
S. Expósito Vizcaíno, J. Casanova-Mollà, L. Escoda, S. Galán, J. Miró
Neurología (English Edition).2018; 33(1): 28. CrossRef - Predicting health-related quality of life in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: a structural equation approach using the self-control model
Yu-Ri Park, Eun-Young Park, Jung-Hee Kim
BMC Health Services Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Assessment Tool (CIPNAT)
Sevinç Kutlutürkan, Elif Sözeri Öztürk, Fatma Arıkan, Burcu Bayrak Kahraman, Keziban Özcan, Mürvet Artuk Uçar
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2017; 31: 84. CrossRef
- Predictors of distress among individuals with cancer reporting physical problems
- 1,186 View
- 21 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Empowerment Scale for Woman with Breast Cancer
- Sun Hwa Shin, Hyojung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):613-624. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.613
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a scale to evaluate empowerment in woman with breast cancer and to examine the validity and reliability of the scale.
Methods The development process for the initial items included a literature review, interviews, and construction of a conceptual framework. The identified items were evaluated for content validity by experts, resulting in 3 factors and 48 preliminary items. Participants were 319 women with breast cancer recruited to test reliability and validity of the preliminary scale. Data were analyzed using item analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, criterion related validity, internal consistency and test-retest reliability.
Results The final scale consisted of 30 items and 3 factors. Factors, including 'intrapersonal factor' (14 items), 'interactional factor' (8 items), and 'behavioral factor' (8 items), were drawn up after confirmatory factor analysis. Goodness of fit of the final research model was very appropriate as shown by χ2/df=1.86, TLI=.90, CFI=.92, SRMR=.06, and RMSEA=.05. Criterion validity was evaluated by total correlation with the Cancer Empowerment Questionnaire .78. Cronbach's alpha for total items was .93 and test-retest reliability was .69.
Conclusion Findings from this study indicate that the scale can be used in the development of nursing interventions to promote the empowerment of women having breast cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of depression and empowerment on medication adherence in patients with breast cancer: a descriptive survey
Sookyung Jeong, Eun Jeong Kim
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Which Chemotherapy-Related Terms Were Difficult for Cancer Patients, and Who Would Have the Most Difficulties?
Mangyeong Lee, Nayeon Kim, Ho-Young Kim, Ayoung Lee, Junghee Yoon, Juhee Cho
Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 57(3): 669. CrossRef - Empowerment mediates the impact of upper extremity function on posttraumatic growth in breast cancer survivors
Chaewon Yun, Yujin Jeong
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100708. CrossRef - Patient Empowerment in Cancer Care
Soo Hyun Kim, Yu Hyeon Choe, Da Hye Kim
Cancer Nursing.2024; 47(6): 471. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Health Empowerment Scale for North Korean Women Defectors
Semi Lim, Younhee Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 80. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the Health Care Empowerment Questionnaire (K-HCEQ)
Semi Lim, Kyungmi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(2): 131. CrossRef - Effects of a partnership‐based, needs‐tailored self‐management support intervention for post‐treatment breast cancer survivors: A randomized controlled trial
Soo Hyun Kim, Yu Hyeon Choe, Young Up Cho, Seho Park, Moon Hee Lee
Psycho-Oncology.2022; 31(3): 460. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of the Empowerment of Patients With Coronary Artery Disease Using a Hybrid Model
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
Advances in Nursing Science.2022; 45(1): E31. CrossRef - Application of empowerment education in health education for cancer patients
Yan PENG, Lin HAN, Fang-Fang AN, Li LI, Yue-Li HOU
Journal of Integrative Nursing.2021; 3(1): 46. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of the Coronary Artery Disease Empowerment Scale (CADES) in Korea
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin, Kyungmi Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2021; 30(8): 1241. CrossRef - Design of a randomized controlled trial of a partnership-based, needs-tailored self-management support intervention for post-treatment breast cancer survivors
Soo Hyun Kim, Yu Hyeon Choe, Ah Reum Han, Gwui Jeong Yeon, Gyeong Hee Lee, Bo Gyeong Lee, Young Up Cho, Seho Park, Moon Hee Lee
BMC Cancer.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Clinical Competency Scale for Nursing Students
Bo Young Kim, Myeong Jeong Chae, Yun Ok Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(2): 220. CrossRef - Development and Validity Testing of an Arthritis Self-Management Assessment Tool
HyunSoo Oh, SunYoung Han, SooHyun Kim, WhaSook Seo
Orthopaedic Nursing.2018; 37(1): 24. CrossRef - Patient empowerment: a systematic review of questionnaires measuring empowerment in cancer patients
Nanna Bjerg Eskildsen, Clara Ruebner Joergensen, Thora Grothe Thomsen, Lone Ross, Susanne Malchau Dietz, Mogens Groenvold, Anna Thit Johnsen
Acta Oncologica.2017; 56(2): 156. CrossRef
- Effect of depression and empowerment on medication adherence in patients with breast cancer: a descriptive survey
- 1,344 View
- 18 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Prevalence and Characteristics of Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong-Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):118-128. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.118
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Evidence suggests that some patients with breast cancer experience cognitive difficulties following chemotherapy. This longitudinal study was done to examine the prevalence of cognitive impairment and trajectory of cognitive function over time in women with breast cancer, who received adjuvant chemotherapy.
Methods Participants were 137 patients with breast cancer. They completed neuropsychological tests and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Cognitive Function before adjuvant therapy (pretest), toward the end of adjuvant therapy (posttest), and 6 months after the completion of adjuvant therapy (follow-up test). Of the patients, 91 were treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and 46 patients who did not receive chemotherapy made up the comparison group. A reliable-change index and repeated-measure ANOVA were used for statistical analyses.
Results At the posttest point, over 30% of patients showed complex cognitive impairment and reported greater difficulty in subjective cognitive function. At the follow-up test point, 22.0% of patients exhibited complex cognitive impairment and 30.8% of patients complained of subjective cognitive impairment. Repeated-measure ANOVA showed significant decreases after receiving chemotherapy followed by small improvements 6 months after the completion of chemotherapy in cognitive domains of change for attention and concentration, memory, executive function, and subjective cognitive function.
Conclusion These results suggest that chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer may be associated with objective and subjective cognitive impairments. Further studies are needed to explore the potential risk factors and predictor of chemotherapy-related cognitive changes. Also nursing interventions for prevention and intervention of cognitive impairments should be developed and tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Brain network deficits in breast cancer patients after early neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A longitudinal MRI study
Jing Yang, Yongchun Deng, Daihong Liu, Yong Tan, Meng Lin, Xiaoyu Zhou, Jing Zhang, Hong Yu, Yixin Hu, Yu Tang, Shixi Jiang, Jiuquan Zhang
Journal of Neuroscience Research.2023; 101(7): 1138. CrossRef - Frailty and its associated factors among older adults with cancer undergoing chemotherapy as outpatients: A cross-sectional study
Misun Jeon, Hyoeun Jang, Arum Lim, Sanghee Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 60: 102192. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Distinct sleep disturbance and cognitive dysfunction profiles in oncology outpatients receiving chemotherapy
Vivian Huang, Lynda Mackin, Kord M. Kober, Steven M. Paul, Bruce A. Cooper, Yvette P. Conley, Marilyn J. Hammer, Jon D. Levine, Christine Miaskowski
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(11): 9243. CrossRef - Measurement, outcomes and interventions of cognitive function after breast cancer treatment: A narrative review
Miaomiao Jia, Xiaojun Zhang, Liyuan Wei, Jinnan Gao
Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology.2021; 17(4): 321. CrossRef - Improving preoperative breast reconstruction consultations: a qualitative study on the impact of personalised audio-recordings
Josipa Petric, Bahara Sadri, Phillipa van Essen, Nicola Ruth Dean
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on Neurologic and Cognitive Dysfunction in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy with Resting State fMRI
Fenshan Zheng, Peiying Cao, Jie Zhou, Chunyu Li, John Norris
World Neurosurgery.2021; 149: 388. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Fatigue following Chemotherapy in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Prospective Controlled Study
Pok-Ja Oh, Sun Mi Moon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 126. CrossRef - Computerized programs for cancer survivors with cognitive problems: a systematic review
Yoonjung Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2019; 13(6): 911. CrossRef - Cancer treatment effects on cognition and depression: The moderating role of physical activity
Margaret F. Bedillion, Emily B. Ansell, Gwendolyn A. Thomas
The Breast.2019; 44: 73. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Depression following Chemotherapy in Women with Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee, Hyun Ah Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(2): 66. CrossRef - Mulheres Submetidas à Quimioterapia e suas Funções Cognitivas
Camila Vasconcelos Carnaúba Lima, Raner Miguel Ferreira Póvoa
Psicologia: Ciência e Profissão.2017; 37(4): 970. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-induced prospective memory impairment in breast cancer patients with different hormone receptor expression
Wen Li, Chen Gan, Yue Lv, Shanghu Wang, Huaidong Cheng
Medicine.2017; 96(13): e6514. CrossRef - Altered network efficiency of functional brain networks in patients with breast cancer after chemotherapy
Han Xuan, Chen Gan, Wen Li, Zhonglian Huang, Longsheng Wang, Qianqian Jia, Zhendong Chen, Huaidong Cheng
Oncotarget.2017; 8(62): 105648. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - Effect of Cancer Symptoms and Fatigue on Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Depression in People with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 420. CrossRef - A review of traditional Korean medical treatment for cancer-related cognitive impairment
Hye-Yoon Lee, Jung-Eun Kim, Mikyung Kim, Joo-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Medicine.2016; 37(3): 74. CrossRef - Cognitive outcome after radiotherapy in brain tumor
Thomas Durand, Marie-Odile Bernier, Isabelle Léger, Hervé Taillia, Georges Noël, Dimitri Psimaras, Damien Ricard
Current Opinion in Oncology.2015; 27(6): 510. CrossRef - Changes of Symptom Distress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Adjuvant Therapy
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(2): 67. CrossRef
- Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1,412 View
- 12 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Cortisol and Immune Parameters in Patients with Cancer: A Meta-analysis
- Pok Ja Oh, Eun-su Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):446-457. Published online August 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.446
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to evaluate the effects of psychosocial interventions on cortisol and immune response in adult patients with cancer.
Methods MEDLINE via PubMed, Cochrane Library CENTRAL, EMBASE, CINAHL and domestic electronic databases were searched. Twenty controlled trials (11 randomized and 9 non-randomized trials) met the inclusion criteria with a total of 862 participants. Methodological quality was assessed using the Cochrane's Risk of Bias for randomized studies and the Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non randomized studies. Data were analyzed using the RevMan 5.2.11 program of Cochrane library.
Results Overall, study quality was moderate to high. The weighted average effect size across studies was -0.32 (95% CI [-0.56, -0.07],
p =.010, I2=45%) for cortisol concentration, -0.62 (95%CI [-0.96,-0.29],p <.001, I2=0%) for T lymphocyte (CD3) and -0.45 (95%CI [-0.74, -0.16],p =.003, I2=0%) for Th lymphocyte (CD4) numbers. Psychosocial interventions were not effective for Tc lymphocyte (CD4), NK cell, monocyte, and cytokine response.Conclusion Although these results provide only small evidence of successful immune modulation, they support the conclusion that psychosocial interventions can assist cancer patients in reducing emotional distress and improving immune response.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Depression and Cancer (literature review)
A. N. Blinkov
V.M. BEKHTEREV REVIEW OF PSYCHIATRY AND MEDICAL PSYCHOLOGY.2020; (2): 16. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of psychosocial interventions on survival time in patients with cancer
P.J. Oh, S.R. Shin, H.S. Ahn, H.J. Kim
Psychology & Health.2016; 31(4): 396. CrossRef - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Primary Insomnia: A Meta-analysis
Ji-Hyun Kim, Pok-Ja Oh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 407. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - Effects of Non-pharmacological Interventions on Primary Insomnia in Adults Aged 55 and Above: A Meta-analysis
Ji Hyun Kim, Pok Ja Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(1): 13. CrossRef - The Effect of a Community-Based Self-Management Program for Patients at Thyroid Cancer-Diagnosis Stage : a Pilot Study
Hyera Yoo, Sunjoo Boo, Mison Chun, Eun Mi Jo
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(3): 582. CrossRef - Effects of Dignity Interventions on Psychosocial and Existential Distress in Terminally ill Patients: A Meta-analysis
Pok Ja Oh, Sung-Rae Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 471. CrossRef
- Depression and Cancer (literature review)
- 1,324 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of a Progressive Walking Program on Physical Activity, Exercise Tolerance, Recovery, and Post-Operative Complications in Patients with a Lung Resection
- Inah Kim, Haejung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):381-390. Published online August 15, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.381
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of a Progressive Walking program (PW) on physical activity, exercise tolerance, recovery, and post-operative complications for patients with a lung resection.
Methods A nonequivalent control group non-synchronized design was utilized and 37 participants with a lung resection (22 for control group, 15 for experimental group) were recruited at A university hospital from December 2012 to August 2013. The PW consisted of preoperative education, goal setting, and feedback, provided to the experimental group, and usual care to the control group. Data were analyzed using the SPSS WIN 18.0.
Results A higher proportion of patients in the experimental group showed adequate levels of physical activity (
p = .001), shorter period of chest tube retention (≤ 7 days;p = .011), and shorter stay in the hospital (≤ 10 days;p = .036) than patients in the control group. Patients in the experimental group reported longer 6-minute walking distance (p = .032) and lower levels of dyspnea (p = .049) than patients in the control group. The PW did not influence the occurrence of pulmonary complications.Conclusion The findings of this study suggest that the PW could be a useful strategy for improving patients’ post-operative health and reducing cost after lung resection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of patient-based self-assessed fatigue intervention on early postoperative ambulation following gynaecological oncology surgery: a randomised controlled non-inferiority trial
Qian Du, Bo Chen, Xiaohong Zhang, Hong He, Xiaomin Qin, Lin Li, Junyi Du, Xindi He, Shaoyong Xu, Huang Xiaojie
BMJ Open.2024; 14(7): e078461. CrossRef - Walking to a better future? Postoperative ambulation after cesarean delivery and complications: A prospective study
Offra Engel, Einat Haikin Herzberger, Yael Yagur, Anat Hershko Klement, Ami Fishman, Naama Constantini, Tal Biron Shental
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2022; 157(2): 391. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Exercise after Lung Cancer Surgery: A Systematic Review in PubMed Database
Ui Min Jerng
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2021; 31(1): 149. CrossRef - Applying Extended Theory of Planned Behavior for Lung Cancer Patients Undergone Pulmonary Resection: Effects on Self-Efficacy for Exercise, Physical Activities, Physical Function, and Quality of Life
Yeonjung Lim, Haejung Lee, Do Hyung Kim, Yeong Dae Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(1): 66. CrossRef - Preoperative exercise training for patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Vinicius Cavalheri, Catherine Granger
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of a Standardized Preoperative Education Program on Stomach Cancer Patients undergoing Gastrectomy
Min Ah Yun, So Sun Kim, SangHee Kim, Sung Hoon Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(2): 85. CrossRef
- Effects of patient-based self-assessed fatigue intervention on early postoperative ambulation following gynaecological oncology surgery: a randomised controlled non-inferiority trial
- 1,147 View
- 14 Download
- 6 Crossref

- An Analysis of Cancer Survival Narratives Using Computerized Text Analysis Program
- Dal Sook Kim, Ah Hyun Park, Nam Jun Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(3):328-338. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.3.328
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to explore experiences of persons living through the periods of cancer diagnosis, treatment, and self-care.
Methods With permission, texts of 29 cancer survival narratives (8 men and 21 women, winners in contests sponsored by two institutes), were analyzed using Kang's Korean-Computerized-Text-Analysis-Program where the commonly used Korean-Morphological-Analyzer and the 21st-century-Sejong-Modern-Korean-Corpora representing laymen's Korean-language-use are connected. Experiences were explored based on words included in 100 highly-used-morphemes. For interpretation, we used 'categorizing words by meaning', 'comparing use-rate by periods and to the 21st-century-Sejong-Modern-Korean-Corpora', and highly-used-morphemes that appeared only in a specific period.
Results The most highly-used-word-morpheme was first-person-pronouns followed by, diagnosis·treatment-related-words, mind-expression-words, cancer, persons-in-meaningful-interaction, living and eating, information-related-verbs, emotion-expression-words, with 240 to 0.8 times for layman use-rate. 'Diagnosis-process', 'cancer-thought', 'things-to-come-after-diagnosis', 'physician·husband', 'result-related-information', 'meaningful-things before diagnosis-period', and 'locus-of-cause' dominated the life of the diagnosis-period. 'Treatment', 'unreliable-body', 'husband · people · mother · physician', 'treatment-related-uncertainty', 'hard-time', and 'waiting-time represented experiences in the treatment-period. Themes of living in the self-care-period were complex and included 'living-as-a-human', 'self-managing-of-diseased-body', 'positive-emotion', and 'connecting past · present · future'.
Conclusion The results show that the experience of living for persons with cancer is influenced by each period's own situational-characteristics. Experiences of the diagnosis and treatment-period are negative disease-oriented while that of the self-care period is positive present-oriented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors to improve distress and fatigue in Cancer survivorship; further understanding through text analysis of interviews by machine learning
Kyungmi Yang, Jina Kim, Mison Chun, Mi Sun Ahn, Eunae Chon, Jinju Park, Mijin Jung
BMC Cancer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Workplace Experiences of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Survey of an Online Community
Ka Ryeong Bae, Sun Young Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(4): 208. CrossRef
- Factors to improve distress and fatigue in Cancer survivorship; further understanding through text analysis of interviews by machine learning
- 963 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Path Analysis on Factors Influencing Second Primary Cancer Screening Practices in Stomach, Colon, and Breast Cancer Survivors
- Young Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(2):139-148. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.2.139
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to identify the factors influencing second primary cancer (SPC) screening practice by examining the relationships of physical symptoms, knowledge and attitudes regarding SPC screening, perceived risk, primary cancer type, and demographic factors of cancer survivors.
Methods Participants were 308 survivors of stomach, colon, or breast cancer recruited from 2 university hospitals in Korea. Data were collected using a questionnaire and analyzed using IBM SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 18.0.
Results The proportion of participants taking all cancer screenings according to national guidelines was 40%. They had moderate knowledge and a relatively positive attitude regarding SPC screening and high cancer risk perception. The participants had taken fewer SPC screenings after than before cancer diagnosis. The factors influencing cancer risk perception were age, physical symptoms, knowledge regarding SPC and primary cancer type (stomach). The factors influencing SPC screening practice were age, gender, economic status, knowledge regarding SPC screening, and primary cancer types (colon).
Conclusion It is important for clinical professionals to recognize that survivors of cancer are susceptible to another cancer. Education on SPC screening for these survivors should focus on communicating with and encouraging them to have regular cancer screenings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Integrated Supportive Care Nursing Competence Scale for Cancer Survivors
Eun-Jung Bae, Yun-Hee Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(7): 755. CrossRef - Health Behaviors of Cancer Survivors According to the Employment Status and Occupation: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ka Ryeong Bae, Wi-Young So, Su Jung Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2974. CrossRef - Survivors’ health competence mediates the association between wearable activity tracker use and self-rated health: HINTS analysis
Steven De La Torre, Donna Spruijt-Metz, Albert J. Farias
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2022; 16(6): 1268. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Health Check-up and Cancer Screening Participation among Family Caregivers of Patients with Dementia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Bomgyeol Kim, Yejin Lee, Jin-Won Noh, Tae Hyun Kim
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Supportive Care Needs of Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyekyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 60. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life among Cancer Survivors: Based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) for 2019
Hee Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(2): 109. CrossRef - Colorectal cancer screening practices among cancer survivors five years after diagnosis
Adeline Monet, Rajae Touzani, Anne-Déborah Bouhnik, Marc-Karim Bendiane, Julien Mancini
Journal of Public Health.2021; 29(4): 805. CrossRef - An Integrated TK-TD Model for Evaluation of Radix Aconitikusnezoffii (RAK)
Xin Miao, Ren Bu, Yang Liu, Bing Li, Xiaofei Zhang, Haiyan Xing, Gang Li
Pharmacology.2020; 105(11-12): 669. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Characteristics of Cancer Patients and Cancer Survivors
So Young Baek, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 11. CrossRef - Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening Behavior in Female Cancer Survivors: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2012
Eun-Ae Lee, Jinyoung Shin, Eun-Joo Hwang, Jung-Woong Lee
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2017; 38(3): 116. CrossRef - The necessity of analysis of cancer survivor concept in Korea
Jiyoung Kim
Journal of Comprehensive Nursing Research and Care.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Factors Related to the Non-Practice of Cancer Screening in Cancer Survivors: Based on the 2007-2012 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Song-Ei Yang, Nam-Kyung Han, Sun-Mi Lee, Tae-Hyun Kim, Woojin Chung
Health Policy and Management.2015; 25(3): 162. CrossRef
- Development of Integrated Supportive Care Nursing Competence Scale for Cancer Survivors
- 1,145 View
- 4 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Quality of Life in Patients with Breast Cancer on Hormone Therapy
- Eunkyung Hwang, Myungsun Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):108-117. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to identify degrees of pain, menopause symptoms, and quality of life, and to identify factors influencing quality of life of patients with breast cancer who were on hormone therapy.
Methods A cross-sectional survey design was utilized. Data were collected using questionnaires from 110 patients with breast cancer who had been on hormone therapy for 3 months or more and were being treated at a university hospital in Seoul. Data were analyzed using χ2-test, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient and multiple linear regression.
Results Mean age of the participants was 53.56 (SD=6.67) and 54 (51.4%) had stage 0 or I at the time of diagnosis. Most of the participants reported having pain and menopause symptoms (88.2% and 95.5% respectively). The mean score for quality of life was 87.84±21.17. Pain, menopause symptoms and quality of life had strong correlations with each other (
p <.005). Quality of life was explained by menopause symptoms (β= -.71), economic status (β=.20) and occupation (β=.16).Conclusion The results of the study suggest that menopause symptoms should be incorporated into oncologic nursing care to improve quality of life of patients with breast cancer on hormone therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
Soo Hyun Kim, Yu Hyeon Choe, Jingyeong Choi, Ji Young Park, Eun Yi
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(1): E47. CrossRef - Effects of Functional Glide on lymphedema, Handgrip strength, and Quality of Life in Patients with Breast Cancer
Hyunah Lee, Dongkwon Seo
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2024; 13(4): 524. CrossRef - Traditional Korean Medicine Treatment for Sequelae After Tamoxifen in Breast Cancer Patients: Two Case Reports
Jung-min Yang, Jae-woo Yang, Ji-hoon Oh, Woo-seok Hwang
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2023; 44(1): 53. CrossRef - Impacts of Uncertainty and Social Support on the Quality of Life of Breast Cancer Survivors after Chemotherapy: Based on Self-help Group Participants
Hyenam Hwang, Yoonshin Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(4): 177. CrossRef - Factors associated with the quality of work life among working breast cancer survivors
Juhyun Jin
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 9(2): 97. CrossRef - Perceived New Normal and Inner Strength on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy
Sujin Ha, Eunjung Ryu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(4): 377. CrossRef - Unmet Needs and Quality of Life of Cancer Patients and Their Families: Actor–Partner Interdependence Modeling
Yubeen Jang, Younhee Jeong
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 874. CrossRef - Photovoice-Based Assessment of Weight Management Experiences of Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Tamoxifen
Jung Suk Park, Jeong-Won Han, Jin Hyuk Choi, Kyoung Chun Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4359. CrossRef - Effects of Illness Perception and Health Beliefs on the Quality of Life of Breast Cancer Patients in the Yanbian Area of China
Fenshan Zheng, Ogcheol Lee, Jie Zhou, Chunyu Li
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 135. CrossRef - Effects of Menopausal Symptoms and Depression on the Quality of Life of Premenopausal Women With Breast Cancer in Korea
Jeong Ae Han, So Young Choi, Seonah Lee
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2019; 30(1): 8. CrossRef - Pain and Menopause Symptoms of Breast Cancer Patients with Adjuvant Hormonal Therapy in Korea: Secondary Analysis
Myungsun Yi, Eunkyung Hwang
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2018; 5(3): 262. CrossRef - Predictors of the quality of life in Chinese breast cancer survivors
Juan Xia, Zheng Tang, Qinglong Deng, Renren Yang, Jiwei Wang, Jinming Yu
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2018; 167(2): 537. CrossRef - How Menopause Symptoms and Attitude Impact Korean Women's Quality of Life After Adjuvant Treatment for Breast Cancer
Moonhee Gang, Mi Sook Jung, Sunyoung Park, Younghee Park, Kyongok Oh
Cancer Nursing.2017; 40(6): E60. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire-Specific for Breast Cancer Patients on Hormone Therapy
Younglan Kim, Yul Ha Min
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(2): 136. CrossRef - Effect of Abdominal Skin Massage and Warming Therapy on the Pain and Anxiety in Breast Cancer Patients who Underwent Hormone Injections
Jin Hee Jun, Youn Ok Lee, Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(4): 226. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Inner Strength Questionnaire
Suhyeon Choi, Eunjung Ryu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(1): 38. CrossRef - Changes of Supportive Care Needs and Quality of Life in Patients with Breast Cancer
Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Yong-Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(4): 217. CrossRef - Effects of Trogopterorum Faeces on the Apoptostic Cell Death in Breast Cancer Cells
Yu-Rim Song, Ji-Eun Kim, Seung-Jeong Yang, Kyung-Mi Park, Su-Jung Jung, Seong-Hee Cho
The Journal of Oriental Obstetrics and Gynecology.2015; 28(1): 46. CrossRef - Fatigue, Sleep Disturbance, and Quality of Life among Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
Ran Young Kim, Hyojung Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(2): 188. CrossRef
- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
- 1,206 View
- 2 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Effect of PLISSIT Model Sexual Health Enhancement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer and Their Husbands
- Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(5):681-689. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.681
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine effects of the Permission, Limited Information, Specific Suggestions, Intensive Therapy (PLISSIT) model sexual health enhancement program on, and development in, sexual function, sexual distress, marital intimacy, and subjective happiness of women with gynecologic cancer and their husbands.
Methods The comprehensive program (4 session, 90 minutes per session) was developed based on the PLISSIT model. Participants were 43 couples, 21 assigned to the experimental group who attended the 4-week program, and 22 to the control group. Sexual function, sexual distress, marital intimacy, subjective happiness of the women, marital intimacy, subjective happiness of husbands were determined by a questionnaire that was completed by the participants before and after the program. The control group received the intervention post experiment. Chi-square test, t-test, Fisher's exact test were used to test the effectiveness of the program.
Results Post intervention results showed significant differences between the groups for sexual function, sexual distress, and marital intimacy in the women and for subjective happiness in the husbands.
Conclusion Results indicate that the sexual health enhancement program is effective in improving sexual function, lowering sexual distress, increasing marital intimacy, and subjective happiness in women with gynecologic cancer and their husbands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Sexual Education Program on Sexual Function and Genital Self-image, Sexual Quality of Life among Primiparous Women
Athar Rasekh Jahromi, Hanie Jafari, Parvin Adedi, Mojgan Javadnoori, Solmaz Mohammadi, Vahid Rahmanian, Safieh Jamali
Current Womens Health Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a sexual health enhancement program for women with breast cancer: A quasi-experimental study
Hye Sook Kim, Chaewon Yun
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 76: 102852. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in Pregnant Women With Preterm Labor
So Jin Lee, Ju-Hee Nho, Eun Jee Lee, Dong Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(2): 87. CrossRef - The effectiveness of couple-based interventions on the marital outcomes of women with genital and breast cancer and their partners: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hamideh Zahedi, Zohreh Alizadeh-Dibazari, Mojgan Mirghafourvand, Mohammad Hasan Sahebihagh, Mina Hosseinzadeh
BMC Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility and effectiveness of communication tools for addressing intimacy and sexuality in patients with cancer: a systematic review
Susanne A. M. Arends, Carlijn E. van Rossum, Corien M. Eeltink, Jantien E. Robertus, Linda J. Schoonmade, Anneke L. Francke, Irene P. Jongerden
Supportive Care in Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Sexual Counseling Based on PLISSIT and EX-PLISSIT Models on Sexual Function, Satisfaction, and Quality of Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sevil Cicek Ozdemir, Aliye Dogan Gangal, Ayten Senturk Erenel
Archives of Sexual Behavior.2024; 53(9): 3485. CrossRef - The Effect of Sexual Counseling Based on EX‑PLISSIT Model on Improving the Sexual Function of Married Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Maryam Shami, Ali Montazeri, Seyedeh Tahereh Faezi, Zahra Behboodi Moghadam
Sexuality and Disability.2023; 41(2): 451. CrossRef - The Effect of Post-Operative Sexual Counseling Carried out with PLISSIT Model on Sexual Function and Sexual Satisfaction in Gynecologic Cancers
Çiğdem BİLGE, Ergül ASLAN
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2023; 13(3): 623. CrossRef - The effect of a psycho-educational intervention on sexuality of women with acute coronary syndromes: a randomized controlled trial
Fatemeh Soleimaninejad, Razieh Lotfi, Mehdi Mousavi, Majid Taghizadeh, Kourosh Kabir
Sexual and Relationship Therapy.2023; 38(2): 277. CrossRef - Sexual health outcomes of PLISSIT-based counseling versus grouped sexuality education among Iranian women with breast cancer: A randomized clinical trial
Effat Merghati Khoei, Rhoghieh Kharaghani, Elham Shakibazadeh, Soghrat Faghihzadeh, Noura Aghajani, Jeffrey E. Korte, Mina Esmkhani
Sexual and Relationship Therapy.2022; 37(4): 557. CrossRef - Effects of the Better Model Based Counseling on Sexuality of Women with Breast Cancer
Zeynep Ozkan Olcer, Umran Oskay
International Journal of Sexual Health.2022; 34(1): 41. CrossRef - The effect of PLISSIT based counseling model on sexual function, quality of life, and sexual distress in women surviving breast cancer: a single-group pretest–posttest trial
Zohreh Keshavarz, Elham Karimi, Samira Golezar, Giti Ozgoli, Maliheh Nasiri
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Sexual Health Improvement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Soon Yang Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 163. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - The Effect of the PLISSIT Model on Sexual Functions: A Systematic Review
Serap KIRICI, Emel EGE
Bandırma Onyedi Eylül Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri ve Araştırmaları Dergisi.2021; 3(3): 199. CrossRef - Sexual Health Outcomes of PLISSIT-based Counseling versus Grouped Sexuality
Education among Iranian Women with Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Medical & Clinical Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - PLISSIT Interventions and Sexual Functioning: Useful Tools for Social Work in Palliative Care?
Michael R. Bennett
Journal of Social Work in End-of-Life & Palliative Care.2019; 15(4): 157. CrossRef - Effect of a Web-Based Sexual Health Enhancement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer and Their Husbands
Ju-Hee Nho, Yeon Hee Kim, Hye-Ji Kook
International Journal of Sexual Health.2019; 31(1): 50. CrossRef - Oncology Nurses' Knowledge Regarding Fertility Preservation for Patients with Cancer
Miok Kim, Ju-Hee Nho, Aeran Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 315. CrossRef - The Influence of Ex-PLISSIT (Extended Permission, Limited Information, Specific Suggestions, Intensive Therapy) Model on Intimacy and Sexuality of Married Women with Multiple Sclerosis
Fatemeh Daneshfar, Zahra Behboodi-Moghadam, Zohreh Khakbazan, Seyed Massood Nabavi, Nahid Dehghan Nayeri, Sogand Ghasemzadeh, Ali Montazeri
Sexuality and Disability.2017; 35(4): 399. CrossRef - Development of a Web-based Sexual Health Program for Women Undergoing Treatment for Gynecologic Cancer and Their Partners
Ju-Hee Nho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(2): 104. CrossRef - The effectiveness of the Permission, Limited Information, Specific suggestions, Intensive Therapy (PLISSIT) model based sexual counseling on the sexual function of women with Multiple Sclerosis who are sexually active
Zohreh Khakbazan, Fatemeh. Daneshfar, Zahra Behboodi-Moghadam, Seyed Massood Nabavi, Sogand Ghasemzadeh, Abbas Mehran
Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders.2016; 8: 113. CrossRef - Comments on female sexual dysfunction with cervical cancer in Republic of Korea
Gyeong-Eun Heo, Tae-Hee Kim, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Jun-Mo Kim
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2016; 294(1): 209. CrossRef - Reply to letter to the editor by J.-M. Kim et al. on "Sexual function and quality of life in women with cervical cancer before radiotherapy: a pilot study" by Grion et al.
R. C. Grion, Luiz Francisco Baccaro, A. F. Vaz, L. Costa-Paiva, D. M. Conde, A. M. Pinto-Neto
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2016; 294(1): 211. CrossRef - Interventions for sexual dysfunction following treatments for cancer in women
Bridget Candy, Yuan Chi, Lisa Graham-Wisener, Louise Jones, Michael King, Anne Lanceley, Victoria Vickerstaff, Adrian Tookman
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Lifestyle Intervention on Fatigue, Nutritional Status and Quality of Life in Patients with Gynecologic Cancer
Hyunjin An, Ju-Hee Nho, Sunyoung Yoo, Hyunmin Kim, Minji Nho, Hojeong Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(6): 812. CrossRef
- The Effect of Sexual Education Program on Sexual Function and Genital Self-image, Sexual Quality of Life among Primiparous Women
- 3,073 View
- 22 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Meta- analysis of Psychosocial Interventions to Reduce Pain in Patients with Cancer
- Pok Ja Oh, Suk Jung Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(5):658-668. Published online October 15, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.658
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of psychosocial interventions on pain in cancer patients.
Methods Eight studies published between 1980 and 2012 in Korean and ten studies published between 2002 and 2012 in English met the inclusion criteria with a total of 1539 participants. Methodological quality assessed by Cochrane's Risk of Bias for randomized studies and Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non randomized studies. The data were analyzed by the RevMan 5.2 program of Cochrane library.
Results Overall, study quality was moderate to high. Effect sizes were heterogeneous and subgroup analysis was done. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) were effective for pain (ES= -0.35; 95% CI= -0.56, -0.13). Pain education studies measured with NRS and VAS were effective for pain (ES= -0.77; 95% CI= -1.01, -0.52). Publication bias was not detected.
Conclusion This study support the use of psychosocial interventions administered to cancer patients for their pain management. However, more well-designed studies are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Good Nursing Experience of Patients with Cancer in a Korean Cancer Hospital
Eunyoung E. Suh, Hye Jin Yoo, Jeong Hee Hong, In Gak Kwon, Hyunju Song
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(3): 51. CrossRef - Managing Cancer Pain, Monitoring for Cancer Recurrence, and Mitigating Risk of Opioid Use Disorders: A Team-Based, Interdisciplinary Approach to Cancer Survivorship
Eric R. Goodlev, Sandra Discala, Beth D. Darnall, Molly Hanson, Alison Petok, Michael Silverman
Journal of Palliative Medicine.2019; 22(11): 1308. CrossRef - Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(2): 143. CrossRef - The Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses on the Effectiveness of Non-pharmacological Cancer Pain Management
Youngshin Song, Minhye Oh, Seyeon Park, Myouyun Park, Kyoungok Kim, Ukyoung Lee, Myonghwa Park
Pain Management Nursing.2015; 16(5): 781. CrossRef - Setting a Health Policy Research Agenda for Controlling Cancer Burden in Korea
Sung-In Jang, Kyoung-Hee Cho, Sun Jung Kim, Kwang-Sig Lee, Eun-Cheol Park
Cancer Research and Treatment.2014; 47(2): 149. CrossRef
- Good Nursing Experience of Patients with Cancer in a Korean Cancer Hospital
- 1,483 View
- 13 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Posttraumatic Growth of Patients with Breast Cancer
- Sook Lee, Yeon Jung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(6):907-915. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.6.907
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose A diagnosis of breast cancer is one of the most traumatic events that threatens a woman's life, but while women adapt to and overcome these threats, they not only experience negative aspects, but also growth. The purpose of this study was to identify the many factors that affect growth, and to provide fundamental information for nursing interventions, which can help the women in their growth.
Methods The participants in this study were 131 married women patients with breast cancer, who were on medical treatment in one of two university hospitals, in Seoul and Chungnam. Data were collected for posttraumatic growth, self-esteem, cancer coping questionnaire, marital intimacy, and body image. The data were analyzed using the SPSS 19.0 program (IBM).
Results Interpersonal cancer coping, intrapersonal cancer coping (planning) and self-esteem accounted for 29.0% of posttraumatic growth.
Conclusion These findings indicate that in order to help the women's growth after the trauma of breast cancer, it is necessary to enhance their self-esteem, and to develop psycho-social nursing supportive programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Equation Model for Psychosocial Adjustment of Breast Cancer Survivors Based on Family Resilience Model
Jiyoung Seo, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(2): 178. CrossRef - Development and effects of a post-traumatic growth program for patients with breast cancer
Sung Hee Choi, Young Whee Lee, Hwa Soon Kim, Soo Hyun Kim, Eun-Hyun Lee, Eun Young Park, Young Up Cho
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 57: 102100. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth and Health Promotion Behavior in Patients with Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Spiritual Well-Being
Shunji Piao, Pok Ja Oh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(1): 33. CrossRef - The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy on the rate of acceptance and post-traumatic growth in colorectal cancer patients comorbid with stress
Ahmad kazemipour, Fazlolah mirderikvand, Kourosh amraei
Health Monitor Journal of the Iranian Institute for Health Sciences Research.2020; 19(5): 569. CrossRef - Post-traumatic Growth among Stroke Patients: Impact of Hope, Meaning in Life, and Social Support
Young-Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(6): 605. CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model of Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth of Earthquake Victims
Minyeong Kwak
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(3): 345. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth of Gynecologic Oncology Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sun Jeong Yun, Hye Young Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 409. CrossRef - The Influence of Spiritual Well-Being, Self-Esteem, and Perceived Social Support on Post-Traumatic Growth among Breast Cancer Survivors
Eun Young Seo, Suhye Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(4): 232. CrossRef - The Relationship between Post-Traumatic Growth, Trauma Experience and Cognitive Emotion Regulation in Nurses
Sook Lee, Mun Gyeong Gwon, YeonJung Kim
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2018; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - Posttraumatic growth in breast cancer survivors and their husbands based on the actor‐partner interdependence model
MyoSuk Lee, Kyunghee Kim, Changwon Lim, Ji‐Su Kim
Psycho-Oncology.2017; 26(10): 1586. CrossRef - Comparison of Perception of Successful Aging between Late Middle-aged Breast Cancer Survivors and Healthy Women
Eun Ja Kim, Nahyun Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(1): 48. CrossRef - Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, Posttraumatic Growth, and Quality of Life in Patients with Cancer according to Disease Characteristics
Jinho Choi, Sunyoung Lee, Byungduck An
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(2): 170. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-esteem and Problem Focused Coping on Post-traumatic Growth among Police Officers
Seung Woo Han, Eunsuk Choi
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 141. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth in Survivors of Breast Cancer
Jin-Hee Park, Yong-Sik Jung, Youngmi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 454. CrossRef - Factors Related to Posttraumatic Growth in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
Hyeon Ju Lee, Seong Sook Jun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(3): 247. CrossRef - Influencing Factors for Post-traumatic Growth in Patients with Breast Cancer
Sung-Hee Choi, Young-Whee Lee
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2016; 16(11): 499. CrossRef - The Effects of Posttraumatic Growth and Meaning in Life on Health Promotion Behavior in Cancer Patients
Sun-Hee Jang, Hae-Rang Lee, Hyung-Nam Yeu, Soon-Ock Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(2): 100. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth, Dyadic Adjustment, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors and Their Husbands
Seunghee Song, Eunjung Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 515. CrossRef - Changes of Self-efficacy, Depression, and Posttraumatic Growth in Survivors with Breast Cancer Participating Breast Cancer Prevention Volunteering
Myungsun Yi, Jieun Cha, Youngmi Ryu
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(4): 256. CrossRef - Effects of a Cancer-Overcome BeHaS Exercise Program on Post-trauma Risk and Anxiety in Breast Cancer Patients
Sun Ae Kim, Jong Im Kim, Sun Young Park
Journal of muscle and joint health.2014; 21(1): 27. CrossRef
- Structural Equation Model for Psychosocial Adjustment of Breast Cancer Survivors Based on Family Resilience Model
- 1,018 View
- 7 Download
- 20 Crossref

- A Meta-analysis of Chemotherapy related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(5):644-658. Published online October 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.644
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cognitive effects of chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer.
Methods Using several databases, prospective studies were collected up to August 2011. Of 2,106 publications identified, 12 met the inclusion criteria, and 8 studies were used to estimate the effect size of chemotherapy on cognitive impairment.
Results Twelve studies were done since 2005 and most of the research was performed in Europe or North America. Eight studies were used to generate effect size across the cognitive domains of attention/concentration, verbal and visual memory, executive function, visuospatial skill, language, and subjective cognitive function. Each of the cognitive domains showed small effect sizes (-0.02 ~ -0.26), indicating diminished cognitive function for the chemotherapy group compared with non-chemotherapy groups.
Conclusion Finding suggests that breast cancer patients who undergo chemotherapy may experience mild cognitive decline. Further study is needed to generate knowledge and guideline for interventions to address chemotherapy related cognitive impairment in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of smart-care services program for breast cancer survivors
Bok Yae Chung, Sung Jung Hong
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 95. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Fatigue following Chemotherapy in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Prospective Controlled Study
Pok-Ja Oh, Sun Mi Moon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 126. CrossRef - Effects of compensatory cognitive training intervention for breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a pilot study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ku Sang Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
Supportive Care in Cancer.2017; 25(6): 1887. CrossRef - Impact of Cognitive Function and Cancer Coping on Quality of Life among Women with Post-chemotherapy Breast Cancer
Yoon Jung Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(3): 182. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - QLU-C10D: a health state classification system for a multi-attribute utility measure based on the EORTC QLQ-C30
M. T. King, D. S. J. Costa, N. K. Aaronson, J. E. Brazier, D. F. Cella, P. M. Fayers, P. Grimison, M. Janda, G. Kemmler, R. Norman, A. S. Pickard, D. Rowen, G. Velikova, T. A. Young, R. Viney
Quality of Life Research.2016; 25(3): 625. CrossRef - The Impact of Cancer on Psychological and Social Outcomes
Daniel Sj Costa, Rebecca Mercieca‐bebber, Claudia Rutherford, Liam Gabb, Madeleine T King
Australian Psychologist.2016; 51(2): 89. CrossRef - Prevalence and Characteristics of Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong-Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 118. CrossRef
- The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
- 1,188 View
- 5 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Development and Effectiveness of Expressive Writing Program for Women with Breast Cancer in Korea
- Eun Young Park, Mungsun Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(2):269-279. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.2.269
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To develop a expressive writing program for women with breast cancer and to identify its effects on stress physical symptom, cancer symptom, anxiety, depression, and QOL.
Methods A non-equivalent control pre-post design was used. Participants were recruited from self-help groups in six hospitals and were assigned to the experimental group (29) or control group (29). Data were collected before, after, and at four weeks after the intervention program. Changes in the variables were evaluated to test effects of the developed program, using χ2-test, Fisher's exact test, repeated measures ANOVA, and paired t-test.
Results The expressive writing program was developed for women with breast cancer based on Pennebaker's expressive writing. Significant differences were found between the two groups for stress related to physical symptoms (
p <.00) and quality of life (p =.024). No significant differences were found in cancer symptoms, anxiety, or depression between the two groups.Conclusion The results indicate that the expressive writing program designed to express cancer-related deep thoughts and emotions helps in decreasing physical symptoms and improving QOL. Further studies are needed to identify the effect on emotions such as anxiety and depression for women with breast cancer with above average levels of anxiety and depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Remote Videoconferencing-based Expressive Writing Program on Posttraumatic Stress, Resilience, and Post-traumatic Growth among Traumatized Nurses
Nam Hee Chae, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(2): 152. CrossRef - Care Needs of Advanced Cancer Patients in a Long-term Care Hospital: Patient-Nurse Comparison
Hee-Jung Kang, Kyung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(4): 196. CrossRef - Can emotional expressivity and writing content predict beneficial effects of expressive writing among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy? A secondary analysis of randomized controlled trial data from China
Yanni Wu, Dongliang Yang, Biao Jian, Chaixiu Li, Liping Liu, Wenji Li, Xiaojin Li, Chunlan Zhou
Psychological Medicine.2023; 53(4): 1527. CrossRef - Development and effects of a post-traumatic growth program for patients with breast cancer
Sung Hee Choi, Young Whee Lee, Hwa Soon Kim, Soo Hyun Kim, Eun-Hyun Lee, Eun Young Park, Young Up Cho
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 57: 102100. CrossRef - Effect of Expressive Writing on Professional Quality of Life and Resilience among Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Danbi You, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 276. CrossRef - Effect of prolonged expressive writing on health outcomes in breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial
Yanni Wu, Liping Liu, Wanting Zheng, Chunrao Zheng, Min Xu, Xiaohong Chen, Wenji Li, Lijun Xie, Pengyan Zhang, Xiaoli Zhu, Chuanglian Zhan, Chunlan Zhou
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(2): 1091. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological therapies for depressive symptoms in breast cancer patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Liliana Coutiño-Escamilla, Maricela Piña-Pozas, Aurelio Tobías Garces, Brenda Gamboa-Loira, Lizbeth López-Carrillo
The Breast.2019; 44: 135. CrossRef - The Effects of Expressive Writing Interventions for Patients With Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Pok-Ja Oh, Soo Kim
Oncology Nursing Forum.2016; 43(4): 468. CrossRef - Does therapeutic writing help people with long-term conditions? Systematic review, realist synthesis and economic considerations
Olga P Nyssen, Stephanie JC Taylor, Geoff Wong, Elizabeth Steed, Liam Bourke, Joanne Lord, Carol A Ross, Sheila Hayman, Victoria Field, Ailish Higgins, Trisha Greenhalgh, Catherine Meads
Health Technology Assessment.2016; 20(27): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Expressive Writing Intervention on Health Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Chunlan Zhou, Yanni Wu, Shengli An, Xiaojin Li, Gozde Ozakinci
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(7): e0131802. CrossRef - Expressive writing interventions in cancer patients: a systematic review
Erin L. Merz, Rina S. Fox, Vanessa L. Malcarne
Health Psychology Review.2014; 8(3): 339. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Symptom Experiences of Breast Cancer Patients: Based on the Theory of Unpleasant Symptoms
HyoJin Kim, Sanghee Kim, Hyangkyu Lee, SangEun Oh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(1): 7. CrossRef - Written emotional disclosure for women with ovarian cancer and their partners: randomised controlled trial
Emily Arden‐Close, Yori Gidron, Louise Bayne, Rona Moss‐Morris
Psycho-Oncology.2013; 22(10): 2262. CrossRef - Effect of Depression and Anxiety on Symptoms in Thyroid Cancer Patients Undergoing Radioactive Iodine (I131) Therapy
Nami Chun
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(4): 297. CrossRef - The Relationships between Stigma, Distress, and Quality of Life in Patients with Lung Cancer
Jung Lim Lee, Keum Soon Kim
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(3): 237. CrossRef
- Effects of a Remote Videoconferencing-based Expressive Writing Program on Posttraumatic Stress, Resilience, and Post-traumatic Growth among Traumatized Nurses
- 1,821 View
- 17 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Illness Experience of Adolescents with Hematologic Malignancies
- Sun Young Son
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(5):603-612. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.603
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to describe the experience process of adolescents with hematologic malignancies. The question for the study was "What is the experience of adolescents with hematologic malignancies like?".
Methods The grounded theory methodology was used for this study. The data were collected through in-depth interview from 10 adolescents with hematologic malignancies. Data collection was done from January to June 2007. Theoretical sampling was used until the data reached saturation.
Results As a result of the analysis, "Reconstructing self-image from deviated and suspended life" was identified as the core category. And 11 subcategories were identified and they were integrated to the core category. 'Establishment of expanded and matured self' was identified as the consequence.
Conclusion The results of the study provide a frame for effective individualized nursing intervention strategies in helping adjustment of the adolescents with hematologic malignancies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and psychometric properties of the social adjustment scale for youth cancer survivors in South Korea
Sumi Oh, Hyejung Lee, Sue Kim, Sanghee Kim, Chuhl Joo Lyu, Chang Gi Park, Hyoung Jin Kang
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(7): 100241. CrossRef - Parents’ Perception of Self-Management Behaviors for Their Children With Spina Bifida in South Korea: A Qualitative Study
Hyun Jung Yun, Eun Kyoung Choi, Sang Won Han
Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 46(2): 73. CrossRef - Health-related Quality of Life of Children and Adolescents after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Yu Min Hwang, Kyung-Sook Bang
Child Health Nursing Research.2020; 26(4): 402. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth of Adolescents with Childhood Leukemia and their Parents
Sungsil Hong, Ho Ran Park, Sun Hee Choi
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(1): 9. CrossRef - Measurement Properties of Self-Report Questionnaires Measuring the Social Adjustment for Youth after Treatment of Childhood Cancer: Systematic Review
Su-Mi Oh, Sun-Young Park, Hye-Jung Lee, Ju Hee Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(1): 78. CrossRef - The Illness Adaptation Process of Patients Suffering from Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS): Doing My Best in Uncertainty
Ae-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(5): 472. CrossRef - Predictors of Resilience in Adolescents with Leukemia
Sung Sil Hong, Ho Ran Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 595. CrossRef - Impact of psychological and cancer-related factors on HRQoL for Korean childhood cancer survivors
Myung Ah Rhee, Kyong Mee Chung, Yuri Lee, Hana K. Choi, Jung Woo Han, Hyo Sun Kim, Sun Hee Kim, Yoon Jung Shin, Chuhl Joo Lyu
Quality of Life Research.2014; 23(9): 2603. CrossRef
- Development and psychometric properties of the social adjustment scale for youth cancer survivors in South Korea
- 1,012 View
- 4 Download
- 8 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


