Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Variables associated with compliance with standard precautions among hospital nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Song Hee Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Chang Seop Lee, Young Man Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):1-26. Published online February 27, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to identify variables associated with standard precautions compliance among hospital nurses and to comprehensively examine their effect sizes.
Methods
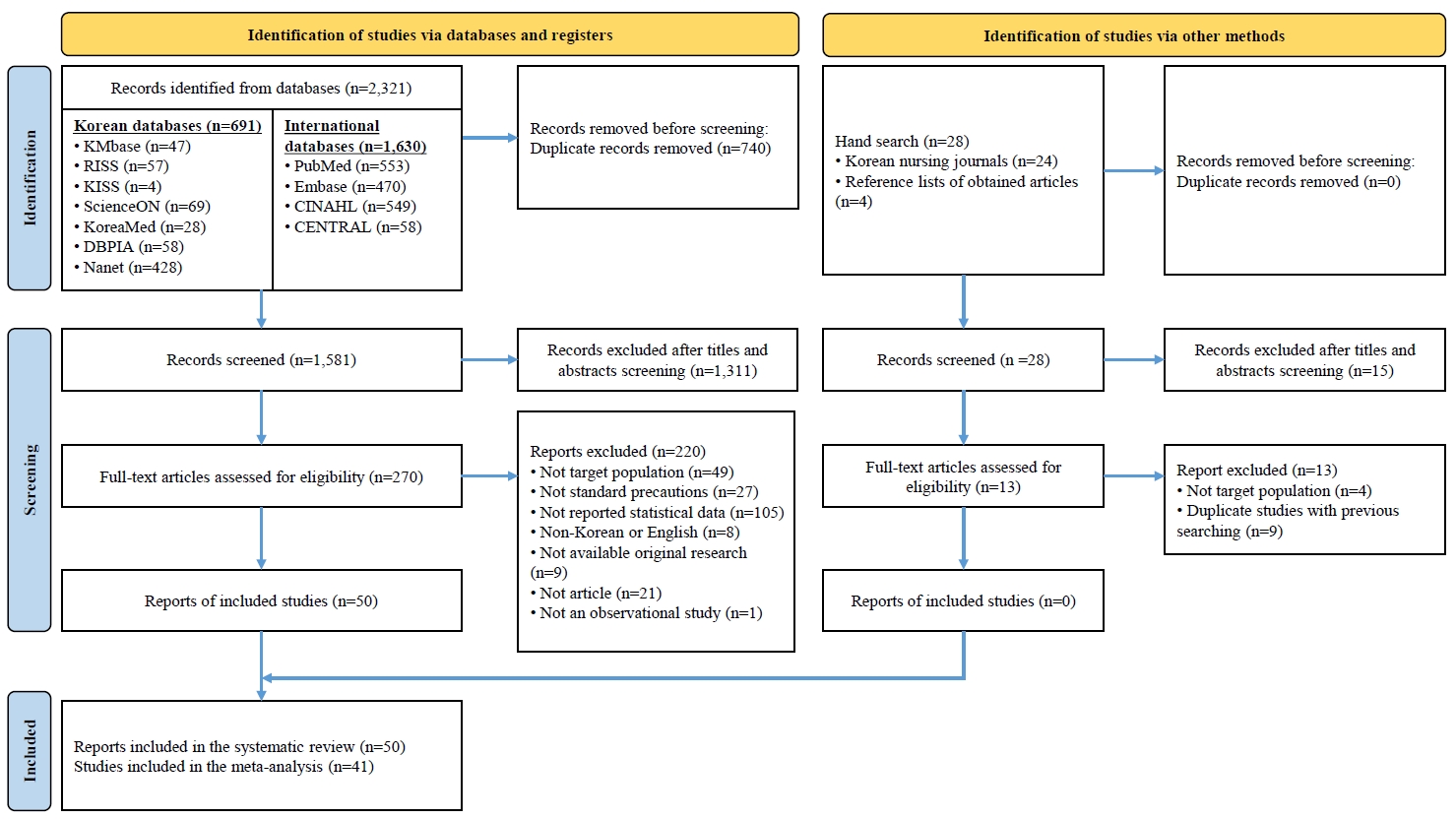
A systematic review and meta-analysis were reported in accordance with the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Studies published in English or Korean were retrieved from KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, Nanet, DBpia, PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, and CENTRAL. Data collection was conducted from July 6 to July 16, 2024. To ensure a comprehensive search, no restrictions were placed on the publication period, and studies published up to June 2024 were included in the literature search. Analyses were performed using R ver. 4.4.1.
Results
Of the 2,321 studies screened, 50 were included in the systematic review and 41 were included in the meta-analysis. Variables were categorized according to the ecological model. Among individual-level factors, variables with medium correlation effect sizes (ESr ≥.30) included self-efficacy (ESr=.41; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.24 to 0.56), perceived barriers (ESr=−.35; 95% CI, −0.59 to −0.05), cues to action (ESr=.34; 95% CI, 0.07 to 0.57), and perceived benefits (ESr=.30; 95% CI, 0.13 to 0.46). Among organizational factors, organizational culture for infection control (ESr=.47; 95% CI, 0.39 to 0.54) and patient safety culture (ESr=.44; 95% CI, 0.35 to 0.53) demonstrated medium effect sizes. Other statistically significant variables with small effect sizes were also identified. No variables were identified within the interpersonal, community, or public policy domains.
Conclusion
This study identified self-efficacy and organizational culture for infection control as key determinants of compliance with standard precautions. Strengthening these factors may reduce healthcare-associated infections and promote safer nursing care (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42024566518).
- 10 View
- 1 Download

- Variables influencing digital health literacy in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jin Hwa Park, Eun Ju Mun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):651-667. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to synthesize existing evidence on digital health literacy (DHL) among older adults and to estimate the associations between related influencing factors through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Methods
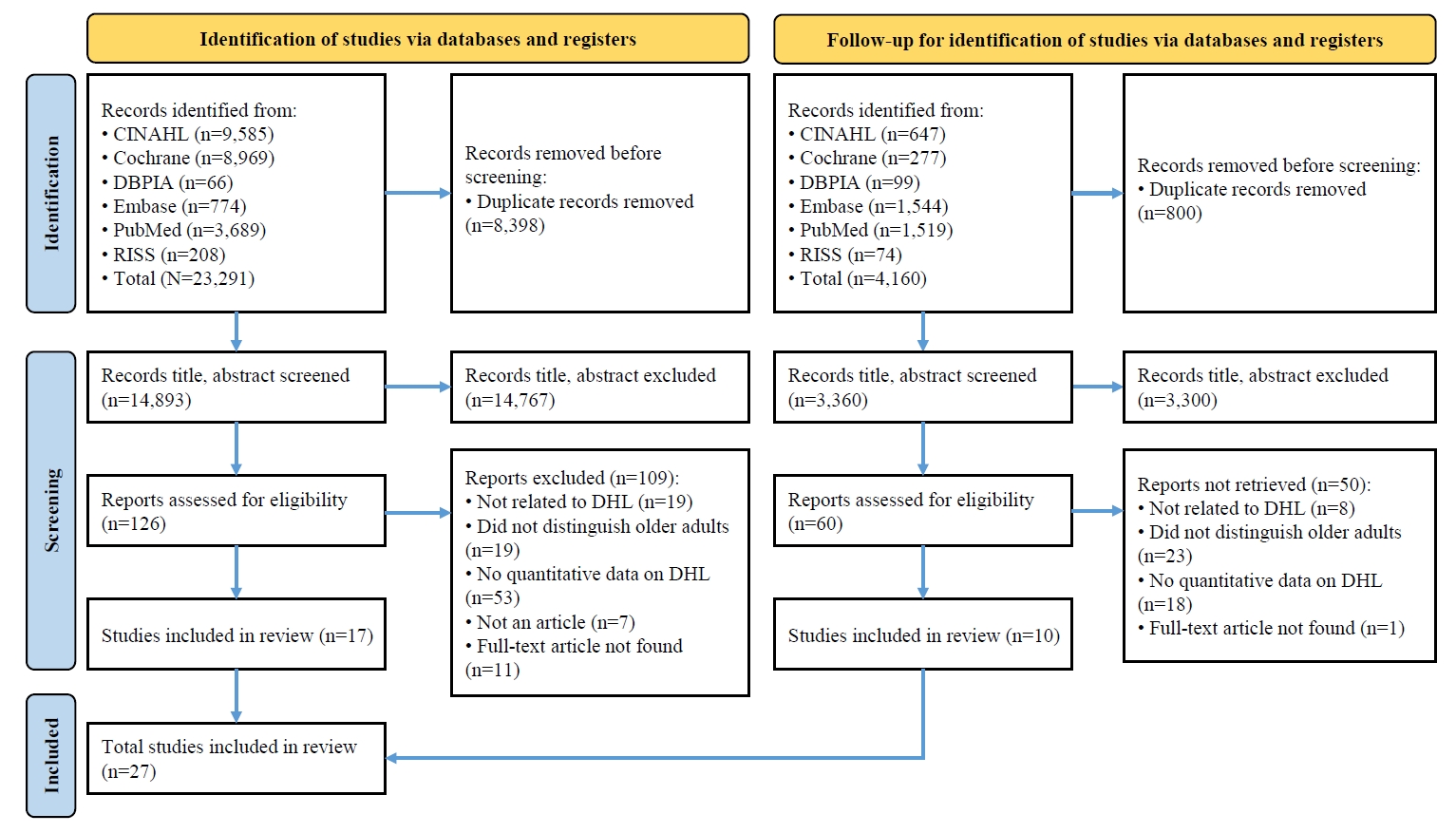
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Literature searches were performed across PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, RISS, and DBPIA. The search and screening process was conducted from December 24, 2023, to March 31, 2025. Effect sizes (ESr) using correlation coefficient for each variable were calculated, and meta-analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel and R version 4.3.1.
Results
Forty-seven variables were identified, including two demographic, six physical, six behavioral, 23 psychosocial, and 10 cognitive factors. Meta-analysis results showed that physical, behavioral, psychosocial, and cognitive factors had significant effects on DHL. Among these, digital information level (ESr=.62; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55 to 0.69) within the cognitive domain and technophobia (ESr=−.55; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.40) within the psychosocial domain demonstrated the largest ESr.
Conclusion
Among factors influencing DHL, digital information level and technophobia showed the strongest associations. These findings suggest that improving DHL in older adults requires a dual approach targeting both cognitive and psychosocial dimensions—enhancing digital information skills while reducing technophobia—to effectively support digital engagement and health empowerment in this population (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42023487486).
- 1,385 View
- 157 Download

- Risk factors for the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hyerim Ji, Sun-Kyung Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):634-650. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25072
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
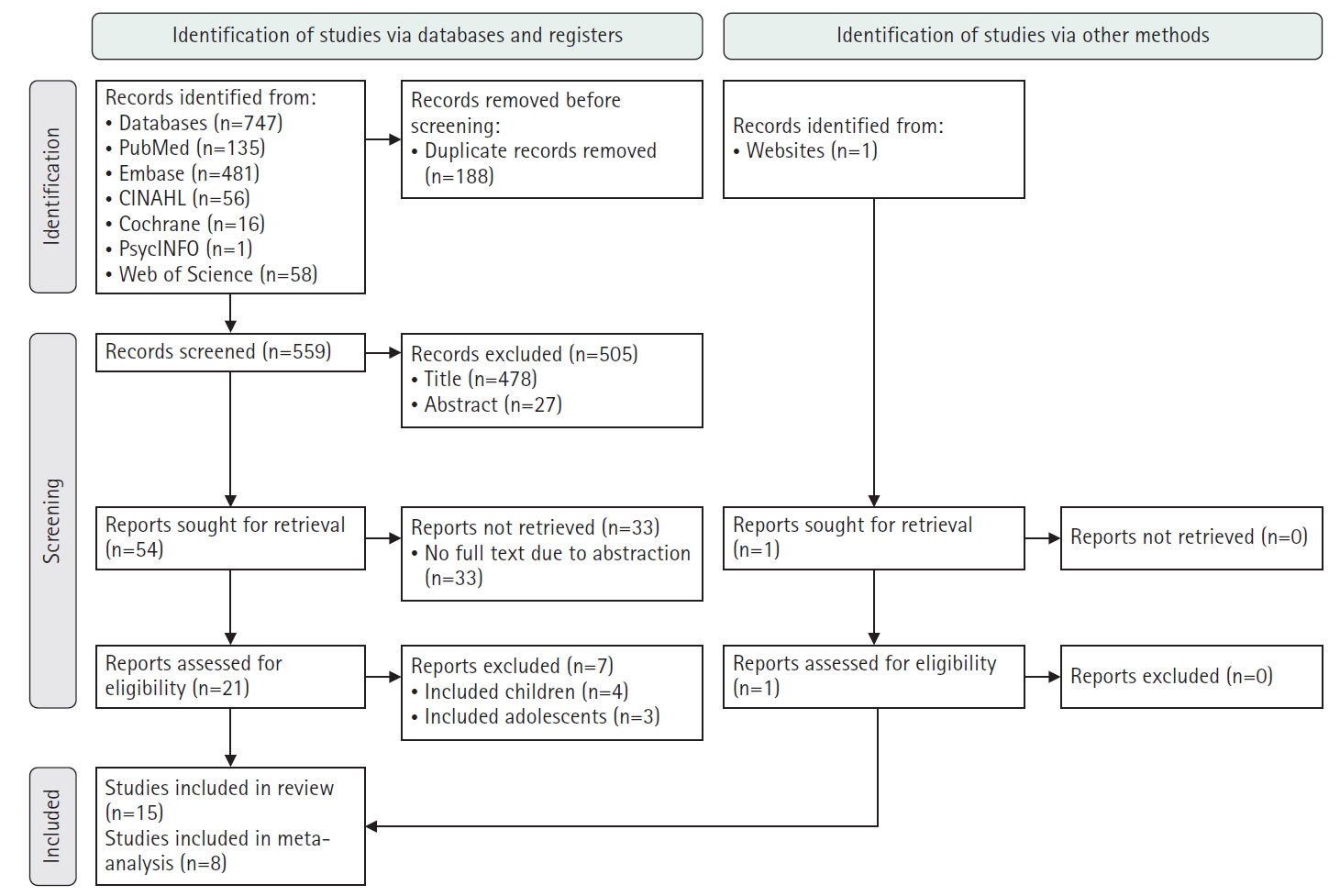
A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies were retrieved from international databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science) and Korean databases (RISS, KoreaMed, KMbase, KISS, and DBpia). Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model with the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment to account for the limited number of studies and heterogeneity.
Results
Fifteen studies were included in the review, and eight were eligible for meta-analysis. From the systematic review, 21 risk factors for DKA readmission were identified and categorized into five domains: demographic, socioeconomic, diabetes-related, comorbidity, and health-behavioral factors. In the meta-analysis, significant risk factors included low income, psychiatric disorders, and discharge against medical advice.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that DKA readmissions result from the complex interplay of multiple clinical and social factors. By identifying these risk factors and suggesting risk-stratification criteria, the findings may support the development of tailored interventions, such as self-management education, integrated mental health care, structured discharge planning, and coordinated post-discharge follow-up.
- 1,316 View
- 193 Download

- Effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to reduce internalized stigma in people with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Soyoung Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Myung-Sun Hyun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):1-18. Published online February 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24072
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study systematically reviewed and analyzed the effects of non-pharmacological interventions on internalized stigma among people with severe mental illness.
Methods
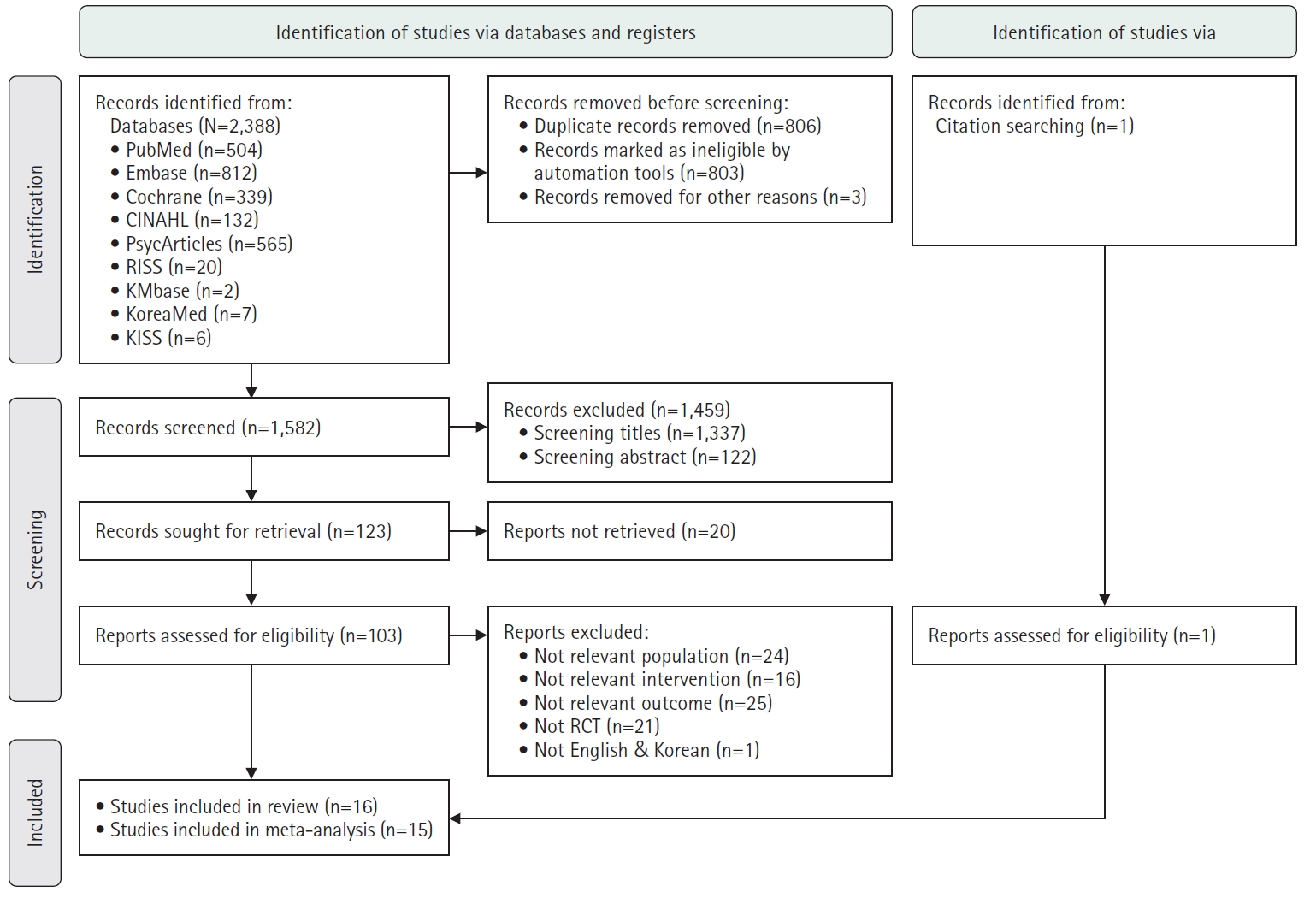
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted following the Cochrane Intervention Research Systematic Review Manual and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis guidelines. This study targeted people with severe mental illness as the population, interventions aimed at reducing internalized stigma, comparisons with control groups, and internalized stigma as the outcome. A literature search was performed across multiple databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycArticles, RISS, KMbase, and KoreaMed. The risk of bias was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool. Effect sizes were computed using Hedges’s g, and subgroup analyses were conducted with Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software version 4.0.
Results
Of 2,388 papers, 15 were included in the meta-analysis. The overall effect size (Hedges’s g) of the intervention was –0.60 (95% confidence interval, –1.01 to –0.19), indicating a statistically significant reduction in internalized stigma (Z=–2.88, p=.004). Subgroup analyses revealed that the intervention type (p=.008) and session length (p=.011) were significant moderators influencing the effectiveness of the interventions.
Conclusion
Tailoring interventions by considering variables such as the intervention type and session length could enhance the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions for reducing internalized stigma among people with severe mental illness (PROSPERO: CRD42023418561).
- 4,779 View
- 354 Download

- Effects of Non-Pharmacological Interventions on Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients Underwent Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sojeong Jo, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):311-328. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24019
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
In this study a systematic review and meta-analysis investigated the impact of non-pharmacological interventions on major adverse cardiac events (MACE) in patients with coronary artery disease who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Methods
A literature search was performed using PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health Literature databases up to November 2023. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool. Effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals were calculated using R software (version 4.3.2).
Results
Eighteen randomized studies, involving 2,898 participants, were included. Of these, 16 studies with 2,697 participants provided quantitative data. Non-pharmacological interventions (education, exercise, and comprehensive) significantly reduced the risk of angina, heart failure, myocardial infarction, restenosis, cardiovascular-related readmission, and cardiovascular-related death. The subgroup meta-analysis showed that combined interventions were effective in reducing the occurrence of myocardial infarction (MI), and individual and group-based interventions had significant effects on reducing the occurrence of MACE. In interventions lasting seven months or longer, occurrence of decreased by 0.16 times, and mortality related to cardiovascular disease decreased by 0.44 times, showing that interventions lasting seven months or more were more effective in reducing MI and cardiovascular disease-related mortality.
Conclusion
Further investigations are required to assess the cost-effectiveness of these interventions in patients undergoing PCI and validate their short- and long-term effects. This systematic review underscores the potential of non-pharmacological interventions in decreasing the incidence of MACE and highlights the importance of continued research in this area (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42023462690).
- 3,018 View
- 218 Download

- Factors Related to Emotional Leadership in Nurses Manager: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Se Young Jang, Chan Mi Park, Eun Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):119-138. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24026
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify research trends related to emotional leadership among nurse managers by conducting a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. This study sought to derive insights that could contribute to improving emotional leadership in nursing practice.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Databases including PubMed, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, Scopus, Web of Science, Research Information Sharing Service, Koreanstudies Information Service System, Korean Medical Database, KoreaMed, ScienceON, and DBpia were searched to obtain papers published in English and Korean. Literature searches and screenings were conducted for the period December 1, 2023 to December 17, 2023. The effect size correlation (ESr) was calculated for each variable and the meta-analysis was performed using the statistical software SPSS 29.0, R 4.3.1.
Results
Twenty-five (four personal, six job, and fifteen organizational) relevant variables were identified through the systematic review. The results of the meta-analysis showed that the total overall effect size was ESr = .33. Job satisfaction (ESr = .40) and leader-member exchange (ESr = .75) had the largest effect size among the job and organizational-related factors.
Conclusion
Emotional leadership helps promote positive changes within organizations, improves organizational effectiveness, and increases member engagement and satisfaction. Therefore, it is considered an important strategic factor in improving organizational performance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emotional leadership in health care: A dire need illuminated by pivotal resource cuts
Jacqueline Hoare
South African Journal of Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Emotional leadership in health care: A dire need illuminated by pivotal resource cuts
- 3,722 View
- 193 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of Health Education Using Virtual Reality for Adolescents: A Systematic Review and MetaAnalysis
- SoMi Park, ChaeWeon Chung, Gaeun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):177-190. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of health interventions using virtual reality (VR) on improving knowledge, attitudes, and skills; and inducing behavioral change among adolescents.
Methods
This study is a systematic review and meta-analysis following PRISMA guidelines. We searched Cochrane, MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, Scopus, Web of Science, and Korean databases between database inception and April 10, 2021. Based on heterogeneity, a random- or fixed-effects model was used, as appropriate, to calculate effect sizes in terms of the standardized mean difference (SMD) and odds ratio (OR). Studies were selected if they verified the effects of health education using VR on adolescents; there was an appropriate control group; and if the effects of education were reported in terms of changes in knowledge, attitudes, skills, or behaviors.
Results
This analysis included six studies (n = 1,086). The intervention groups showed greater responses in knowledge and attitudes (SMD = 0.57, 95% confidence interval (CI) [0.12 to 1.02]), skills related to health behavior (SMD = -0.45, 95% CI [-0.71 to -0.19]), and behavioral change after 12 months (OR = 2.36, 95% CI [1.03 to 5.41]).
Conclusion
The results confirm the effectiveness of health interventions using virtual reality (VR). Although the analysis include a small number of studies, a case can be made for health interventions using VR to be utilized as educational methods and strategies to prevent risky behaviors among adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Implementation of a Childcare-Based Obesity Prevention Program for Vulnerable Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for School Nurses
Jiyoung Park, Gill ten Hoor, Seohyun Won, Gahui Hwang, Sein Hwang, Siew Tiang Lau
The Journal of School Nursing.2025; 41(5): 579. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Virtual Reality Intervention for Reducing Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors in Female Adolescents: A Pilot Study
SoMi Park, Yun Jeong Hwang, ChaeWeon Chung
Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Chinese nurses’ perspectives on child-friendly healthcare practice assessment: a qualitative study
Wei Xiao Huang, Mei Chan Chong, Li Yoong Tang, Xiao Xia Liu, Mei Fang, Yun Yun Shen, Xiao Li Guo
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing anatomy education with virtual reality: integrating three-dimensional models for improved learning efficiency and student satisfaction
Shuliang Niu, Jinlong Zhang, Jiang Lin, Binbin Wang, Jie Yan
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Implementation of a Childcare-Based Obesity Prevention Program for Vulnerable Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for School Nurses
- 4,496 View
- 103 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of Digital Health Interventions on Psychotic Symptoms among Persons with Severe Mental Illness in Community: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Eunjin Oh, Moonhee Gang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):69-86. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of digital health interventions on the psychotic symptoms among people with severe mental illness in the community.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Cochrane Intervention Research Systematic Review Manual and PRISMA. A literature search was conducted of published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for digital health interventions from January 2022 to April 2022. RevMan software 5.3 was used for quality assessment and meta-analysis.
Results
A total 14 studies out of 9,864 studies were included in the review, and 13 were included in meta-analysis. The overall effect size of digital health interventions on psychotic symptoms was - 0.21 (95% CI = - 0.32 to - 0.10). Sub-analysis showed that the reduction of the psychotic symptoms was effective in the schizophrenia spectrum group (SMD = - 0.22; 95% CI = - 0.36 to - 0.09), web (SMD = - 0.41; 95% CI = - 0.82 to 0.01), virtual reality (SMD = - 0.33; 95% CI = - 0.56 to - 0.10), mobile (SMD = - 0.15; 95% CI = - 0.28 to - 0.03), intervention period of less than 3 months (SMD = - 0.23; 95% CI = - 0.35 to - 0.11), and non-treatment group (SMD = - 0.23; 95% CI = - 0.36 to - 0.11).
Conclusion
These findings suggest that digital health interventions alleviate psychotic symptoms in patients with severe mental illnesses. However, well-designed digital health studies should be conducted in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Mobile App-Based Psychosocial Intervention for Personal and Clinical Recovery for People With Psychosis
Dowon You, Narae Jeong
Korean Journal of Schizophrenia Research.2024; 27(1): 1. CrossRef
- A Review of Mobile App-Based Psychosocial Intervention for Personal and Clinical Recovery for People With Psychosis
- 2,733 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of Leadership Styles of Nursing Managers on Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Yunjeong Cho, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Man Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):479-498. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22039
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine effect sizes of leadership styles of nursing managers on turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Participants were nurses working in hospitals. The intervention involved nursing managers’ leadership styles; the outcome assessed was nurses’ turnover intention. This was an observational study design. Eleven databases were searched to obtain articles published in Korean or English. Of the 14,428 articles reviewed, 21 were included in systematic review and meta-analysis. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and R software programs were used.
Results
The total effect size r (ESr) was - 0.25 (95% confidence interval: - 0.29 to - 0.20). Effect sizes of each leadership style on turnover intention were as follows: ethical leadership (ESr = - 0.34), transformational leadership (ESr = - 0.28), authentic leadership (ESr = - 0.23), transactional leadership (ESr = - 0.21), and passive avoidant leadership (ESr = 0.13). Ethical leadership was the most effective style in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Conclusion
Positive leadership styles of nurse managers effectively decrease turnover intention of hospital nurses, and negative leadership styles of nurse managers effectively increase turnover intention of hospital nurses. The ethical leadership style is the most effective in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses; however, it requires careful interpretation as its effects are reported by only two studies. This study contributes to addressing the high turnover rate of hospital nurses and developing positive leadership styles of nurse managers in hospital settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
Inji Ha, Heeok Park, Ji Hun Joung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 35. CrossRef - Influence of Leadership Styles on Turnover Intentions in Technology Startups
Sheeza Fayyaz, Saima Majeed
Journal of Professional & Applied Psychology .2025; 6(1): 36. CrossRef - Protecting Workers From Rude Customers to Enhance Organizational Identification in Emotional Labor Environments: A Study With Call Center Agents
Hyojeong Kim, Nagesh N Murthy, Anurag Agarwal, Kwangtae Park
Production and Operations Management.2025; 34(10): 3250. CrossRef - Humanistic nursing care management strategies: from formulation to implementation
Jing Lv, Yajie Su, Hongmei Tang, Xiaolin Jiang, Xiaojuan Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - When Leadership Drives Nurses Away: Empirical Research Qualitative on High Turnover Rates Reasons
Saleem Al‐Rjoub
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between different leadership styles of nursing managers and nurses’ turnover intention in hospitals: an integrative review
Alicia Jimenez-Caceres, Anna Agusti-Boada, Conxi Caro-Benito, Olga Monistrol
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Structured Subjective Readiness in Situational Leadership: Validating the 4D Model as an Associative Predictor
Dino Giergia, Nikola Drašković, Mario Fraculj
Administrative Sciences.2025; 15(12): 488. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Leader-Member Exchange on the Ethical Leadership of Nursing Unit Managers and Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses: A Nationwide Survey using Proportional Quota Sampling
Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Nara Han, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of Resilience, Nursing Managers’ Empowering Leadership on Turnover Intention among New Nurses: Mediating role of Transition Shock
Hyun Jin Jung, Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 212. CrossRef - Investigation of the relationship between nurses' perception of toxic leadership and their organizational trust levels and turnover intentions
Sultan Türkmen Keskin, Meltem Özduyan Kiliç
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2024; 80(5): 1859. CrossRef - The structural relationship of job stress, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention among youth sports education leaders in Korea
Myung Kyu Jung, Tae Gyeom Jung, Min Woo Jeon, Ji Hae Lee
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Patient Safety Management System, Leadership, and Communication Types on Nurse’ Patient Safety Management Activities
Eunji Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 367. CrossRef - Nursing-sensitive Indicators in East Asian Hospitals: A Scoping Review
Jae Jun Lee, Won Jin Seo, Dong Ah Park, Hwa Yeong Oh, Seung Eun Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2024; 30(2): 88. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurses Turnover in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review
Abdulmajeed M. Albalawi, Glezzeelyne P. Pascua, Sameer A. Alsaleh, Walaa Sabry, Sitti Nursa Ahajan, Jeseela Abdulla, Amal Abdulalim, Suad S. Salih, Sulaiman Al Sabei
Nursing Forum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Unit Managers’ Authentic Leadership, Transformational Leadership, and Transactional Leadership on Turnover Intention in Advanced Beginner Nurses: Mediation Effects of Positive Psychological Capital
Eun Jeong Kim, Eungyung Kim, Son Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 409. CrossRef - Factors related to the organizational silence of Korean nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kyungja Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 302. CrossRef
- The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
- 7,754 View
- 491 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Patient Safety Management Activities of Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis
- Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):363-377. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22022
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to test a hypothetical model of Korean nurses’ patient safety management activities using meta-analytic path analysis.
Methods
A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-analytic path analysis were conducted following the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Seventy-four studies for the meta-analysis and 92 for the meta-analytic path analysis were included. The R software program (Version 3.6.3) was used for data analysis.
Results
Four variables out of 49 relevant variables were selected in the meta-analysis. These four variables showed large effect sizes (ESr = .54) or median effect sizes (ESr = .33∼.40) with the highest k (number of studies) in the individual, job, and organizational categories. The hypothetical model for the meta-analytic path analysis was established using these variables and patient safety management activities. Twelve hypothetical paths were set and tested. Finally, the perception of the importance of patient safety management and patient safety competency directly affected patient safety management activities. In addition, self-efficacy, the perception of the importance of patient safety management, patient safety competency, and patient safety culture, indirectly affected patient safety management activities.
Conclusion
Self-efficacy, the perception of the importance of patient safety management, patient safety competency, and the organization’s patient safety culture should be enhanced to improve nurses’ patient safety management activities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and validation of patient safety educational booklet to empower anesthesia process owners to improve safety compliance before, during and after anesthesia
Fatemeh Asadi, Azam Saei, Shanam Sedigh Maroufi, Jamileh Abolghasemi
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a patient safety management protocol for nurses in long-term care hospitals
Soon-Ock Kim
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Clinical Nurses' Patient Safety Competency, Psychological Safety, and Nursing Unit Manager's Safety-Specific Transformational Leadership on Intention to Report Near Misses
Young hyun Cho, Seung Eun Lee, Mi Jeong Kwak, Hyun Joo Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2025; 31(2): 60. CrossRef - The influencing factors of pediatric nurses’ perception of patient safety culture and partnership with patients’ parents on patient safety nursing activities in South Korea: a descriptive study
Seo Jin Lee, Young Ran Han
Child Health Nursing Research.2024; 30(4): 255. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Nurse Collaboration and Nurse-Physician Collaboration on Nursing Performance in Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Patient Safety Management Activities
JaHyun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 343. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Job Satisfaction between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture and Their Safety Nursing Activities
I Jung Han, Young Ran Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 46. CrossRef - The Effects of Professional Autonomy, Job Satisfaction, and Perceived Patient-Safety Culture on Nurses' Patient-Safety Management Activities: A Cross-Sectional Study
Bokja Koak, Junglim Seo, Eunji Song, Haneul Shin, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 117. CrossRef
- Development and validation of patient safety educational booklet to empower anesthesia process owners to improve safety compliance before, during and after anesthesia
- 3,900 View
- 196 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Effect of Auriculotherapy on Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sun Yeob Choi, Yeo Ju Kim, Bomi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):4-23. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of auriculotherapy on musculoskeletal pain in adults.
Methods
A total of 885 studies were retrieved from nine databases (PubMed, Scopus, CINAHL, Web of Science, Ovid Medline, Cochrane Library, RISS, KMbase, and KISS). Sixteen studies were selected for meta-analysis, which satisfied the inclusion criteria and the evaluation of risk of bias. Demographic data, auriculotherapy types, intervention characteristics, auricular points, and outcomes related to pain (subjective pain scale, and amount of analgesic) were extracted from all included studies. The effect size of auriculotherapy was analyzed through comprehensive meta analysis 3.0, and the presence of publication bias was analyzed through a funnel plot and Egger’s regression.
Results
The results of the meta-analysis (n = 16) revealed that the auriculotherapy was significantly superior to the control group on present pain in adults (Hedges’ g = - 0.35, 95% Confidence Interval [CI] = - 0.55~- 0.15). According to the results of subgroup analysis, the effect size of auricular acupuncture therapy (Hedges’ g = 0.45, 95% CI = - 0.75~- 0.15) was higher than the auricular acupuncture (Hedges’ g = 0.27, 95% CI = - 0.53~0.00): the longer the intervention period, the greater the effect size.
Conclusion
In this study, auriculotherapy demonstrates a significant reduction in musculoskeletal pain in adults. Therefore, it is necessary to refine the curriculum to include auriculotherapy as a nursing intervention to relieve musculoskeletal pain in adults and encourage its use in clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Nurses’ Perceived Stress, Sleep Quality, and Presenteeism
Hyunseo Sim, Younghee Park
Holistic Nursing Practice.2025; 39(1): 15. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Pain and Stress in Nursing College Students With Cervical Pain: A Single-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial
Yuna Cho, Eunmi Cho, Eunseol Cho, Yeonju Chae, Eunkyung Choi, Hyeongyeong Yoon
Pain Management Nursing.2025; 26(1): e59. CrossRef - Effect of Auriculotherapy on Stress: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunyeob Choi, Bomi Kim
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2025; 43(4): 336. CrossRef - Comparative Effectiveness of Ear and Body Acupressure for Postoperative Pain in Elderly Women Following Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Trial
Fatemeh Ghanbari, Nahid Rejeh, Tahereh Bahrami, Hooman Yahyazadeh, Kiarash Saatchi
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2025; 31(11): 987. CrossRef - Estratégias de adaptação dos profissionais de enfermagem com dor musculoesquelética no trabalho hospitalar: uma revisão sistemática
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptation strategies for nurses with musculoskeletal pain in hospital work: a systematic review
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estrategias de adaptación de los profesionales de Enfermería con dolor musculoesquelético en el trabajo hospitalario: revisión sistemática
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adapting and Evaluating a Theory-Driven, Non-Pharmacological Intervention to Self-Manage Pain
Jennifer Kawi, Chao Hsing Yeh, Lauren Grant, Johannes Thrul, Hulin Wu, Paul J. Christo, Lorraine S. Evangelista
Healthcare.2024; 12(10): 969. CrossRef - The State of 21st Century Acupuncture in the United States
Clasina Smith, Bill Reddy, Charis Wolf, Rosa Schnyer, Korina St John, Lisa Conboy, Jen Stone, Lixing Lao
Journal of Pain Research.2024; Volume 17: 3329. CrossRef - The effects of auricular acupressure on blood pressure, stress, and sleep in elders with essential hypertension: a randomized single-blind sham-controlled trial
Bomi Kim, Hyojung Park
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2023; 22(6): 610. CrossRef
- Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Nurses’ Perceived Stress, Sleep Quality, and Presenteeism
- 3,064 View
- 126 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- The Effects of Programs on Body-Image Improvement in Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Hyun Jung Yun, Kyoungsan Seo, Dallong Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):597-616. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study’s objective was to investigate the effects of programs that improve adolescents’ body image, using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A literature search was performed in eleven electronic databases, using preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis guidelines. Population characteristics, contents of the programs, and measured outcomes were systematically reviewed from 21 selected studies. To estimate the size of the effects, meta-analysis was conducted using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software.
Results
The contents of the programs that aimed to improve body image included physical, psychological, interpersonal, and sociocultural interventions. Sixteen studies were meta-analyzed to estimate the effect size of body-image improvement programs. Results showed that the program for body-image improvement had significant effects on body satisfaction (effect size [ES] = 0.56, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.23 to 0.89), and body dissatisfaction (ES = - 0.15, 95% CI = - 0.23 to - 0.08).
Conclusion
The program for body image improvement in adolescents includes a combination of physical, psychological, interpersonal relationship, and socio-cultural dimensions. The program that seeks to improve body image appears to be effective at increasing body satisfaction, and at reducing body dissatisfaction in adolescents. Thus, it is necessary to develop and apply multidimensional programs for adolescents to have a positive body image. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 청소년의 신체상과 행복감 간의 관계: 가족 의사소통으로 조절된 자아존중감의 매개역할*
종일 여
Journal of Family Relations.2025; 30(1): 55. CrossRef
- 청소년의 신체상과 행복감 간의 관계: 가족 의사소통으로 조절된 자아존중감의 매개역할*
- 2,886 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of 2% Chlorhexidine Bathing on the Incidence of Hospital-Acquired Infection and Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Adult Intensive Care Unit Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jisu Seo, Rhayun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):414-429. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21046
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This systematic review and meta-analysis analyzed the effects of 2% chlorhexidine bathing on the incidence of hospital-acquired infection (HAI) and multidrug-resistant organisms (MDRO) in adult intensive care units.
Methods
PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane library, and RISS database were systematically searched, and 12 randomized studies were included in the analysis. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis version 3.0 was used to calculate the effect size using the odds ratio (OR) and a 95% confidence interval (CI). Subgroup analysis was performed according to the specific infection and intervention types.
Results
In general, 2% chlorhexidine bathing has a significant effect on the incidence of HAI (OR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.40~0.86) and MDRO (OR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.34~0.79). Subgroup analyses show 2% chlorhexidine bathing is effective in bloodstream infections (OR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.39~0.66) but not for urinary tract infections, ventilator-associated pneumonia infections, and Clostridium difficile infections. Moreover, 2% chlorhexidine bathing alone or its combination with other interventions has a significant effect on the incidence of HAI and MDRO (OR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.38~0.92).
Conclusion
This meta-analysis reveals that 2% chlorhexidine bathing significantly reduces the incidence of HAI and MDRO in intensive care units. The effect of 2% chlorhexidine bathing on pediatric patients or patients at general wards should be further assessed as a cost-effective intervention for infection control. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of bathing with two percent chlorhexidine gluconate every other day on healthcare-associated infections in the medical intensive care unit
Shu-Fen Hsu, Pei-Jung Yu, Hsing-Yu Yang, Te-Yu Wu
Infection Prevention in Practice.2026; : 100521. CrossRef - Implementation of 2% Chlorhexidine Bathing to Reduce Healthcare-Associated Infections Among Patients in the Intensive Care Unit
Hsu-Liang Chang, Tzu-Ying Liu, Po-Shou Huang, Chin-Hwan Chen, Chia-Wen Yen, Hui-Zhu Chen, Shin-Huei Kuo, Tun-Chieh Chen, Shang-Yi Lin, Po-Liang Lu
Microorganisms.2025; 13(1): 65. CrossRef - Can chlorhexidine gluconate baths reduce fungal colonisation in intensive care unit patients?
Teresa Nascimento, João Inácio, Daniela Guerreiro, Patrícia Patrício, Luís Proença, Cristina Toscano, Priscila Diaz, Helena Barroso
Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in central line-associated bloodstream infections in pediatric intensive care units: a single-center study
Yu Gyoung Bak, Won Kyoung Jhang
Archives of Pediatric Critical Care.2024; 2(2): 96. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Antibiotic Resistance Trends and Treatment Options for Hospital-Acquired Multidrug-Resistant Infections
Walter Y Agyeman, Aakash Bisht, Ankit Gopinath, Ameer Haider Cheema, Keyur Chaludiya, Maham Khalid, Marcellina Nwosu, Srujana Konka, Safeera Khan
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of bathing with two percent chlorhexidine gluconate every other day on healthcare-associated infections in the medical intensive care unit
- 2,236 View
- 232 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis on the Outcome Variables of Nursing Unit Managers’ Transformational Leadership: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):757-777. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20205
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the outcome variables of nursing unit managers’ transformational leadership and to test a hypothetical model using meta-analytic path analysis.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. Data analysis, conducted using R version 3.6.2 software, included 49 studies for the meta-analysis and 119 studies for meta-analytic path analysis.
Results
In the meta-analysis, four out of 32 outcome variables were selected. These four variables were empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment, which showed larger effect sizes than the median and more than five k. The hypothetical model for the meta-analytic path analysis was established by using these four variables and transformational leadership. A total of 22 hypothetical paths including nine direct effects and 13 indirect effects were set and tested. The meta-analytic path analysis showed that transformational leadership had direct effects on the four variables. Finally, eight direct effects, 12 indirect effects, and six mediating effects were statistically significant, and the hypothetical model was verified.
Conclusion
Nursing unit managers can use the transformational leadership to improve empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment of nurses. This study empirically showed the importance of transformational leadership of nursing managers. This finding will be used as evidence to develop strategies for enhancing transformational leadership, empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment in nursing science and practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Strategies Employed by Nursing Managers Within a Transformational Approach: A Qualitative Study
Gholamhossein Mahmoudirad, Ayob Akbari, Suja P. Davis
Nursing Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Using Behaviour Diagnostics to Identify Enablers and Barriers to Optimise Nurse and Midwife Manager Leadership Time
Julie Considine, Philippa Blencowe, Naida Lumsden, Jordana Schlieff, Judy Currey, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Leadership Development in Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Patrícia Costa, Joana Pereira Sousa, Tiago Nascimento, Paulo Cruchinho, Elisabete Nunes, Filomena Gaspar, Pedro Lucas
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(5): 160. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Managers’ Ethical Leadership on Clinical Nurse Empowerment, Performance, and Organizational Commitment
Jihun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Nursing Research.2025; 33(4): e400. CrossRef - Transformational Leadership, Psychological Empowerment, and Organizational Citizenship Behaviors among Nursing Workforce: A Single Mediation Analysis
Ibrahim Abdullatif Ibrahim, Ahmed Hashem El-Monshed, Marwan Altheeb, Mohamed Gamal El-Sehrawy, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan
Journal of Nursing Management.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Personal and organisational attributes that support transformational leadership in acute healthcare: scoping review
Julie Considine, Jenny Dempster, Nga Man Wendy Wong, Noelleen Kiprillis, Leanne Boyd
Australian Health Review.2024; 48(3): 274 . CrossRef - Leadership styles and transformational leadership skills among nurse leaders in Qatar, a cross‐sectional study
Amer Al‐Thawabiya, Kalpana Singh, Badriya Abdulla Al‐Lenjawi, Albara Alomari
Nursing Open.2023; 10(6): 3440. CrossRef - Effects of Leadership Styles of Nursing Managers on Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yunjeong Cho, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Man Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 479. CrossRef - Patient Safety Management Activities of Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis
Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(4): 363. CrossRef - Nurses' ethical leadership and related outcome variables: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Myoung Hee Seo
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2308. CrossRef
- Strategies Employed by Nursing Managers Within a Transformational Approach: A Qualitative Study
- 2,809 View
- 127 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Characteristics of Aerobic Exercise as Determinants of Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sun Hee Lee, Young Ran Chae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):740-756. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect on blood pressure (BP) and heart rate (HR) according to aerobic exercise characteristics in adults with hypertension using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
The related researches were selected from PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane library, CINAHL, PsycINFO, SPORTDiscus and 5 domestic databases up to September 4, 2019. To estimate the effect size, random effect models were used to derive weighted mean differences (WMD) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) of aerobic exercise on BP and HR.
Results
A total of 37 RCTs with 1,813 samples were included. Aerobic exercise was found to significantly reduce systolic BP (WMD, - 8.29 mmHg; 95% CI, - 10.12 to - 6.46), diastolic BP (WMD, - 5.19 mmHg; 95% CI, - 6.24 to - 4.14) and HR (WMD, - 4.22 beats/min; 95% CI, - 5.36 to –3.09). In detail, systolic BP and diastolic BP were significantly decreased in all groups of exercise types, frequency and duration. Systolic BP and diastolic BP were significantly decreased in the moderate and vigorous-intensity group. Exercise characteristics with the most dramatical change in systolic BP were water-based training, moderate-intensity, 3 times a week and 8 to 11 weeks of duration. In diastolic BP, the greatest effect size was over 24 weeks of exercise.
Conclusion
Moderate aerobic exercise, especially water-based exercise can be an important part of lifestyle modification for hypertensive patients. Also, it can be recommended in a variety of clinical settings for lowering BP and HR. However, there is insufficient evidence that low-intensity exercise is effective in lowering BP. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermogenic supplement attenuates post-exercise hypotension after aerobic exercise in normotensive young adults without affecting heart rate variability
Douglas Cavalcante Silva, Reabias de Andrade Pereira, Gustavo da Silva Félix, Marizângela Ferreira de Souza, Glêbia Alexa Cardoso, George Celso Souza Côrtes de Araújo, Marcos Antonio Pereira dos Santos, Alexandre Sérgio Silva
Sport Sciences for Health.2025; 21(4): 3317. CrossRef - Improving cardiovascular autonomic function in postmenopausal women with hypertension: a pilot study of supervised versus home-based aerobic exercise
Cengizhan Gungor, Ezgi Akyildiz Tezcan, Önder Murat Özerbil, Abdullah Tuncez
Blood Pressure Monitoring.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of 17 Factors Potentially Related to Hypertension Control in the Siberian Urban Sample
A. N. Ryabikov, E. V. Mazdorova, E. S. Mazurenko, D. V. Malyutina, M. Yu. Shapkina
Kardiologiia.2025; 65(8): 31. CrossRef - Effect of exercise based on ACSM recommendations on blood pressure and heart rate in hypertensive patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Jiu Chen, Wenlai Cui, Jun Xie, Ratko Peric
PLOS Global Public Health.2024; 4(12): e0003743. CrossRef - Physical Activity Intensity and Risk of Dementia
Angelique G. Brellenthin, Duck-chul Lee, Elizabeth C. Lefferts, Wesley K. Lefferts, Ryan J. Dougherty, Youngwon Kim
American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2024; 66(6): 948. CrossRef - Effects of aerobic exercise on blood pressure in patients with hypertension: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized trials
Bahareh Jabbarzadeh Ganjeh, Sheida Zeraattalab-Motlagh, Ahmad Jayedi, Mojtaba Daneshvar, Zahra Gohari, Reyhane Norouziasl, Shadi Ghaemi, Maryam Selk-Ghaffari, Navid Moghadam, Ramin Kordi, Sakineh Shab-Bidar
Hypertension Research.2024; 47(2): 385. CrossRef - The Western and Chinese exercise training for blood pressure reduction among hypertensive patients: An overview of systematic reviews
Kelvin Tsoi, Amy Lam, Joshua Tran, Ziyu Hao, Karen Yiu, Yook‐Chin Chia, Yuda Turana, Saulat Siddique, Yuqing Zhang, Hao‐Min Cheng, Ji‐Guang Wang, Kazuomi Kario
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2024; 26(12): 1327. CrossRef - Does regular exercise help significantly reduce blood pressure in adults diagnosed with hypertension within the general population?
Jesse Schmidt, Nikhil Vatti, Nicole Tenegra
Evidence-Based Practice.2023; 26(3): 25. CrossRef - Physical Activity and Hypertension
Peter Hayes, Alexandra Ferrara, Aoife Keating, Kathryn McKnight, Andrew O'Regan
Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Thermogenic supplement attenuates post-exercise hypotension after aerobic exercise in normotensive young adults without affecting heart rate variability
- 5,455 View
- 135 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- A Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Mind-Body Therapy on Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Eun Hui Choi, Moon Ja Kim, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):385-400. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19224
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Previous randomized controlled trials (RCT) found that mind-body therapy can improve the health outcomes of patients with irritablebowel syndrome (IBS). The purpose of this meta-analysis was to identify the combined effects of mind-body therapy on patients’ IBSsymptoms, quality of life, anxiety, and depression.
Methods
A systematic literature search was conducted using various databases such asPubMed, EMBASE, CINAHL CENTRAL, DBpia, RISS, and KISS. The primary outcome variables were IBS symptoms and quality of life; the secondaryoutcome variables were anxiety and depression. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis version 3.0 was used to analyze the extracted data.The effect size was calculated using standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results
Eleven final RCTs wereused for this meta-analysis. Mind-body therapy was found to have a significant effect on the IBS patients’ symptoms (SMD, -0.63; 95% CI,-0.77 to -0.48), quality of life (SMD, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.40 to 1.66), anxiety (SMD, -0.28; 95% CI, -0.47 to -0.09), and depression (SMD,-0.31; 95% CI, -0.06 to -0.12).
Conclusion
This meta-analysis reveals that mind-body therapy significantly improves IBS patients’ symptoms,quality of life, anxiety, and depression. The results suggest that, in the future, appropriate mind-body therapy should be applied toKoreans suffering from IBS. Moreover, the therapy’s long-term effects should be assessed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of walking exercise on cognitive and physical functions: meta-analysis of older adults
Mi Jin Lee, Hee Ju Ro, Jung Kee Choi, So Yeon Kim
Forest Science and Technology.2024; 20(2): 201. CrossRef - Effects of Non-Pharmacological Interventions on Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients Underwent Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sojeong Jo, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 311. CrossRef - The Effect of Laughter Therapy on Physical and Mental Health: Systematic Review
Elif ÜNER, Ayşe SEZER BALCI, Hasibe KADIOĞLU
Halk Sağlığı Hemşireliği Dergisi.2022; 4(3): 251. CrossRef - RESEARCH ARTICLE: Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback: Managing Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction by Improving Autonomic Homeostasis
Richard Gevirtz
Biofeedback.2022; 50(4): 100. CrossRef - Effects of Korean forest healing programs on stress in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
So-Yeon Kim, Jungkee Choi
Forest Science and Technology.2021; 17(4): 206. CrossRef
- Effects of walking exercise on cognitive and physical functions: meta-analysis of older adults
- 1,991 View
- 25 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of First Assisted Reproductive Technologies on Anxiety and Depression among InfertileWomen: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ju-Young Ha, Seon-Hwa Ban, Hae-Jung Lee, Misoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):369-384. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze anxiety and depression among infertile women at different time points during the firstIn Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) treatment through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
Seven out of 3,011 studies were included for meta-analysis. To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performedusing the RevMan 5.3 program. We compared the measurement outcomes at three time points: before the start of treatment (T0), cancellationof treatment after pregnancy detection (T2), one to six months after treatment (T3). The effect size used was the standardizedmean difference (SMD).
Results
In comparing the different time points of the pregnant women from their cycle, significantly lower levelsof depression were found at T2 than at T0. In non-pregnant women, anxiety at T2 and depression at T2 and T3 were significantly higherthan those at T0. At T2 and T3, the non-pregnant women reported higher levels of anxiety and depression compared with the pregnantwomen.
Conclusion
Anxiety and depression in infertile women undergoing the first IVF or ICSI are associated with the time points andpregnancy status after treatment. These findings suggest that attention should be paid to helping infertile women prepare for and copewith treatment and treatment failure. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Stress on Each of the Stages of the IVF Procedure: A Systematic Review
Anastasia Tsambika Zanettoullis, George Mastorakos, Panagiotis Vakas, Nikolaos Vlahos, Georgios Valsamakis
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 726. CrossRef - An Integrative Review of Psychosocial Intervention Programs for Infertile Females
Youjin Shin, Soo-Hyun Nam
STRESS.2023; 31(4): 158. CrossRef - The dynamics of mental health measures of pre- and postpartum women undergoing assisted reproductive technology
Maria E. Blokh, Varvara O. Anikina, Svetlana S. Savenysheva, Maria I. Levintsova
Journal of obstetrics and women's diseases.2023; 72(1): 17. CrossRef
- Effect of Stress on Each of the Stages of the IVF Procedure: A Systematic Review
- 1,385 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Related to Persistent Postoperative Pain after Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jaewon Bae, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):159-177. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.159
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed at identifying factors related to persistent postoperative pain after cardiac surgery and estimating their effect sizes.
Methods
The literature search and selection was conducted in four different databases (CINAHL, Cochrane Library, PubMed, and PQDT) using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Statement. A total of 14 studies met the inclusion criteria and were systematically reviewed. For the meta-analysis, R was used to analyze 30 effect sizes of for both individual and operative factors as well as publication biases from a total of nine studies.
Results
The meta-analysis revealed that persistent postoperative pain after cardiac surgery was related to one individual factor (gender) and two operative factors (acute postoperative pain and use of the internal mammary artery). Operative factors (OR=5.26) had a larger effect size than individual factors (OR=1.53).
Conclusion
Female gender, acute pain after surgery, and use of the internal mammary artery are related factors to persistent postoperative pain. The development of interventions focusing on modifiable related factors, such as acute postoperative pain, may help to minimize or prevent PPP after cardiac surgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pain-Friendly Strategies: Nursing Intervention in Postoperative Myocardial Revascularization
Debora Milena Alvarez Yañez, Gloria Carvajal Carrascal
Revista de Investigación e Innovación en Ciencias de la Salud.2025; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Prognostic factors for chronic post‐surgical pain after lung and pleural surgery: a systematic review with meta‐analysis, meta‐regression and trial sequential analysis
P. R. D. Clephas, S. E. Hoeks, P. M. Singh, C. S. Guay, M. Trivella, M. Klimek, M. Heesen
Anaesthesia.2023; 78(8): 1005. CrossRef - Regional anesthesia in coronary artery bypass grafting: a narrative review
Viktor A. Koriachkin, Maksim A. Dzhopua, Beka S. Ezugbaia, Vaagn A. Avetisian, Dmitriy V. Zabolotskiy, Vladimir A. Evgrafov
Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Management.2023; 17(3): 161. CrossRef
- Pain-Friendly Strategies: Nursing Intervention in Postoperative Myocardial Revascularization
- 1,593 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of Autogenic Training for Stress Response: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Eunju Seo, Soukyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):361-374. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of autogenic training on stress responses through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods A systematic search was conducted using eight core electronic databases (Embase, CENTRAL, Medline, CINAHL, PsycInfo, DBpia, KISS, and RISS). To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performed using RevMan 5.3.5 program.
Results A total 21 studies out of 950 studies were included in the review, and 11 were included for meta-analysis. These studies showed that autogenic training decreased anxiety and depression, and increased the high frequency of heart rate variability. Calculations to understand the effect of autogenic training on anxiety, through a meta-analysis, observed a reduction effect of anxiety score by 1.37 points (n=85, SMD=-1.37: 95% CI -2.07 to -0.67), in the studies on short-term intervention targeting healthy adults. On the other hand, similar calculations to understand the effect of autogenic training on depression observed, a reduction effect on the depression score by 0.29 point (n=327, SMD=-0.29: 95% CI -0.50 to -0.07), in the studies on long term intervention targeting the patient group.
Conclusion Autogenic training is effective for adults’ stress management, and nurses will be able to effectively perform autogenic training programs for workers’ stress relief at the workplace.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A peer-led group intervention based on relaxation (soRELAX) to improve well-being and mental health in nursing students: A mixed method pilot study
Maria Pilar Ramirez Garcia, Jérôme Leclerc-Loiselle, Christine Genest, Etienne Paradis-Gagné, Caroline Larue, Marikim Poitras-Crête, Sylvie Corbeil, Camille Saseville
Journal of Professional Nursing.2025; 57: 8. CrossRef - Effects of Autogenic Training on Pain Modulation in Burning Mouth Syndrome: A Preliminary Study
Keita Takizawa, Kana Ozasa, Kohei Shimizu, Noboru Noma
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Strengthening psychological resilience: The effectiveness of autogenic training of community pharmacists
Dragana Jocic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2024; 81(11): 696. CrossRef - Ampliación del Informe de Sanidad: Evidencia Sobre la Seguridad y Eficacia del Entrenamiento Autógeno
Juan Manuel Guiote, Miguel Angel Vallejo Pareja, Blanca Mas
Papeles del Psicólogo - Psychologist Papers.2024; 45(3): 172. CrossRef - Autogenic Training in Mental Disorders: What Can We Expect?
Dagmar Breznoscakova, Milana Kovanicova, Eva Sedlakova, Maria Pallayova
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(5): 4344. CrossRef - The effects of online enactive education on secondary school students
Deborah R. Vivo
The Journal of Educational Research.2023; 116(4): 230. CrossRef - Self-reported symptom burden in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS): A narrative review of observational and interventional studies
Iris Knoop, Federica Picariello, Emma Jenkinson, Nicholas Gall, Claudia Chisari, Rona Moss-Morris
Autonomic Neuroscience.2023; 244: 103052. CrossRef - Efficacy of Individualized Sensory-Based mHealth Interventions to Improve Distress Coping in Healthcare Professionals: A Multi-Arm Parallel-Group Randomized Controlled Trial
Hannes Baumann, Luis Heuel, Laura Louise Bischoff, Bettina Wollesen
Sensors.2023; 23(4): 2322. CrossRef - The Effect of Autogenic Training in a Form of Audio Recording on Sleep Quality and Physiological Stress Reactions of University Athletes—Pilot Study
Kamila Litwic-Kaminska, Martyna Kotyśko, Tadeusz Pracki, Monika Wiłkość-Dębczyńska, Błażej Stankiewicz
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 16043. CrossRef - Combined effect of autogenic relaxation and aerobic exercise on postmenopausal hypertension: A randomized clinical trial
Shreen R Aboelmagd, Afaf M Botla, Hossam ELdine Hussein, Sahar M. Ali, Nehad A. Abo-Zaid
International journal of health sciences.2022; 6(S10): 2314. CrossRef - Temporomandibular Myofascial Pain Syndrome—Aetiology and Biopsychosocial Modulation. A Narrative Review
Paulina Golanska, Klara Saczuk, Monika Domarecka, Joanna Kuć, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 7807. CrossRef - To stress or not to stress: Brain-behavior-immune interaction may weaken or promote the immune response to SARS-CoV-2
Eva M.J. Peters, Manfred Schedlowski, Carsten Watzl, Ulrike Gimsa
Neurobiology of Stress.2021; 14: 100296. CrossRef - Non‐pharmacologic treatment of insomnia in primary care settings
Laura Hrehová, Kamal Mezian
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Single Session of Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Produced Greater Increases in Heart Rate Variability Than Autogenic Training
I-Mei Lin, San-Yu Wang, Sheng-Yu Fan, Erik Peper, Sui-Pi Chen, Ching-Yu Huang
Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback.2020; 45(4): 343. CrossRef - A Multimodal Stress-Prevention Program Supplemented by Telephone-Coaching Sessions to Reduce Perceived Stress among German Farmers: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial
Marita Stier-Jarmer, Cornelia Oberhauser, Dieter Frisch, Götz Berberich, Thomas Loew, Carina Schels-Klemens, Birgit Braun, Angela Schuh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9227. CrossRef
- A peer-led group intervention based on relaxation (soRELAX) to improve well-being and mental health in nursing students: A mixed method pilot study
- 4,007 View
- 182 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Effects of Reminiscence Therapy on Depressive Symptoms in Older Adults with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Kyungsoo Kim, Jia Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):225-240. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.225
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of reminiscence therapy on depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from January 2000 to January 2018 were searched through Research Information Sharing Service (RISS), Korean Studies Information Service System (KISS), Korean Medical Database (KMbase), KoreaMed, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), and Ovid MEDLINE. Two researchers independently performed the search, selection, and coding. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis 3.0 was used for meta-analysis, and Review Manager program 5.3 was used for quality assessment.
Results Out of the 1,250 retrieved articles, 22 RCTs were selected for analysis. The overall effect size of reminiscence therapy for mitigating depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia was -0.62 (95% Cl: -0.92 to -0.31). The effect size was greater in older adults under 80, those with less disease severity, and those for whom the therapy session lasted less than 40 minutes.
Conclusion Reminiscence therapy is an effective non-pharmacological therapy to improve depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia. Because its effectiveness is also influenced by age, disease severity, and application method, it is necessary to consider treatment designs based on individual characteristics as well as methodological approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Group reminiscence therapy interventions in non-clinical older adults: A systematic review
Ali Eryılmaz, Emre Yıldırım, Hacer Yıldırım Kurtulus, Murat Yıldırım
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 63: 35. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Influence of Garden Therapy on Memory Decline and Depression in Older Adults with Cognitive Impairments
Chohye Youn, Minji Kang, Hyejin Kim, Hyeyoon Kim, Jiyun Choi, Suyeon Lee, Juyoung Lee
Journal of Environmental Science International.2025; 34(3): 125. CrossRef - Mental health and treatment challenges in older adults
Ken Laidlaw, Georgina Charlesworth, Sunil Bhar
Nature Reviews Psychology.2025; 4(11): 737. CrossRef - Effects of reminiscence interventions on depression and anxiety: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Martin Pinquart
Aging & Mental Health.2024; 28(5): 717. CrossRef - Effects of reminiscence therapy on quality of life and life satisfaction of the elderly in the community: a systematic review
Eunyoung Shin, Myeongshin Kim, Seyoon Kim, Sohyune Sok
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcultural Pilot Study of the Efficacy of Reminiscence Therapy for Mexican and Spanish Older Adults with Different Levels of Cognitive Decline
Alba Villasán-Rueda, Antonio Sánchez-Cabaco, Manuel Mejía-Ramírez, Rosa Marina Afonso, Eduardo Castillo-Riedel
Journal of Cross-Cultural Gerontology.2023; 38(4): 371. CrossRef - Cross-cultural effects of reminiscence therapy on life satisfaction and autobiographical memory of older adults: a pilot study across Mexico and Spain
Alba Villasán Rueda, Antonio Sánchez Cabaco, Manuel Alejandro Mejía-Ramírez, Rosa Marina Afonso, Eduardo Castillo-Riedel
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of group reminiscence therapy based on Chinese traditional festival activities (CTFA-GRT) on loneliness and perceived stress of rural older adults living alone in China: a randomized controlled trial
Shasha Li, Yanyan Dai, Yuqiu Zhou, Jiayuan Zhang, Chiteng Zhou
Aging & Mental Health.2022; 26(7): 1377. CrossRef - Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms and Associated Factors in Community-Dwelling Persons at the First Time of Dementia Diagnosis
Gijung Jung, Jia Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 7765. CrossRef
- Group reminiscence therapy interventions in non-clinical older adults: A systematic review
- 2,554 View
- 57 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Telemonitoring Intervention in Children and Adolescents with Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Youjin Jung, Jimin Kim, Dong Ah Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):389-406. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.389
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This review aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of telemonitoring (TM) in the management of children and adolescents with asthma.
Methods We searched Ovid-MEDLINE, Ovid-EMBASE, CENTRAL (Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials), CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), and 5 domestic databases to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published through December 2017. Two reviewers independently selected relevant studies, assessed methodological quality and extracted data. We performed a meta-analysis of TM versus usual care and summarized the intervention characteristics of included studies.
Results Of the 3,095 articles identified, 8 RCTs (9 articles) were included in this review. The type of TM intervention of included studies was varying across studies (transmitted data, transmission frequency, data review, etc.). The pooled asthma control score was not significantly different between TM and usual care (standardized mean difference 0.04, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.20~0.28). Another pooled analysis demonstrated no statistically significant difference in asthma exacerbation between TM and usual care (odds ratio 0.95, 95% CI 0.43~2.09). Overall, the pooled results from these studies revealed that TM did not lead to clinically significant improvements in health outcomes, but some studies in our analysis suggested that TM increased patient medication adherence and intervention adherence.
Conclusion The current evidence base does not demonstrate any differences between TM intervention and usual care, but TM intervention might be considered a promising strategy for the delivery of self-management support for children and adolescents with asthma. Further well-designed studies are needed to assess the effects on clinical outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Telemedicine in chronic lung disease management: progress and prospects
Hee-Young Yoon, Jin Woo Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2026; 41(1): 31. CrossRef - Impact of Telemedicine on Asthma Control and Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Julen Garcia Gerriko, Tregony Simoneau, Jonathan M. Gaffin, Marina Ortúzar Menéndez, Alejandro Fernandez-Montero, Laura Moreno-Galarraga
Children.2025; 12(7): 849. CrossRef - Visitas virtuales en pediatría: experiencias, preferencias y expectativas de pacientes y cuidadores
Miren Ibarzabal Arregi, Tregony Simoneau, Jonathan M. Gaffin, María Gimeno Castillo, Isabel Castro Garrido, Claudia María Chaverri Reparaz, Laura Moreno-Galarraga
Anales de Pediatría.2025; 103(4): 503993. CrossRef - Pediatric virtual visits: experiences, preferences, and expectations of patients and caregivers
Miren Ibarzabal Arregi, Tregony Simoneau, Jonathan M. Gaffin, María Gimeno Castillo, Isabel Castro Garrido, Claudia María Chaverri Reparaz, Laura Moreno-Galarraga
Anales de Pediatría (English Edition).2025; 103(4): 503993. CrossRef - Effectiveness of eAsthmaCare on Symptoms, Childhood Asthma Control Test, and Lung Function among Asthmatic Children
Tzu-Ning Wen, Hsueh-Chun Lin, Kuo-Wei Yeh, Jing-Long Huang, Li-Chi Chiang
Journal of Medical Systems.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Real‐time effects of COVID‐19 pandemic lockdown on pediatric respiratory patients
Michal Cahal, Israel Amirav, Nir Diamant, Moria Be'er, Omri Besor, Moran Lavie
Pediatric Pulmonology.2021; 56(6): 1401. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Effects of Virtual Reality Simulation on Nursing Students Caring for Children with Asthma
Kyung-Ah Kang, Shin-Jeong Kim, Myung-Nam Lee, Mikang Kim, Sunghee Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(22): 8417. CrossRef - Effects of a Virtual Reality Simulation and a Blended Simulation of Care for Pediatric Patient with Asthma
Mikang Kim, Sunghee Kim, Woo Sook Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(4): 496. CrossRef
- Telemedicine in chronic lung disease management: progress and prospects
- 2,388 View
- 43 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacologic Interventions in Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Pok-Ja Oh, You Lim Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):123-142. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of non-pharmacologic interventions in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN).
Methods PubMed, Cochrane Library CENTRAL, EMBASE, CINAHL, and several Korean databases (Until August 2017) were searched. The main search strategy combined terms for peripheral neuropathy and presence of neoplasms. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane's Risk of Bias tool for randomized studies and the Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non-randomized studies. To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performed using the Rev Man 5.3 program of the Cochrane Library random-effects models were used in the analyses.
Results Twenty-two studies with a total of 954 participants met the inclusion criteria. Of the 22 studies, 12 were used to estimate the effect size of the non-pharmacologic interventions. The non-pharmacologic interventions used in patients with CIPN were exercise, acupuncture, massage, and foot bath. The acupuncture significantly reduced CIPN symptoms and signs (d=-0.71) and CIPN pain (d=-0.73) (
p <.001). Massage and foot bath were also effective in reducing CIPN symptoms (d=-0.68; 95% CI=-1.05, -0.30;p <.001; I2=19%).Exercis-es were effective in improving muscle strength and endurance(d=-0.55) and quality of life (d=-2.96), but they were not significantly effective in improving CIPN.Conclusion Although these results provide little evidence of the effectiveness of acupuncture, massage, and foot bath in the treatment of CIPN, they suggest that these interventions can reduce CIPN symptoms in patients with cancer. However, the findings of this study should be interpreted with caution as there is a relative lack of data in this field, and additional well-designed studies are needed. PROSPERO registration: CRD42017076278.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effectiveness and Safety of Nurse-Led Auricular Acupressure on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Among Patients With Breast Cancer
Mi Sook Jung, Mijung Kim, Eun Hee Sohn, Jin Sun Lee
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(2): E64. CrossRef - Effects of acupuncture-related intervention on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and quality of life: An umbrella review
Mei-Ling Yeh, Chin-Che Hsu, Matthew Lin, Chuan-Ju Lin, Jaung-Geng Lin
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2025; 89: 103131. CrossRef - Effects of Swanson theory-based auricular acupressure on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, and broader health-related outcomes in patients with breast cancer: A randomized controlled trial
Yuanyuan Mi, Ying Chen, Jing Li, Xinxin Liu, Zhengrong Li, Quanlian Ye, Jinli Guo, Yuanfei Liu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100729. CrossRef - Traditional herbal medicine for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis with association rule analysis
Eun Hye Kim, Hayun Jin, Su Hyeon Lee, Seong Woo Yoon
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Acupuncture-related interventions improve chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mei-Ling Yeh, Ru-Wen Liao, Pin-Hsuan Yeh, Chuan-Ju Lin, Yu-Jen Wang
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Intervention on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms in Cancer Patients: A Meta-analysis
Nan Wu, Hongshi Cao, Shiyuan Du, Yulu Chen, Xinxin Wang, Jiong Li, Xin Peng
Cancer Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture/electroacupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Li-Xia Pei, Yue Yi, Jing Guo, Lu Chen, Jin-Yong Zhou, Xiao-Liang Wu, Jian-Hua Sun, Hao Chen
Acupuncture in Medicine.2023; 41(2): 73. CrossRef - Effects of Footbath on Postoperative Pain and Sleep Quality in Patients With Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease: A Randomized Controlled Study
Seher Ünver, Ülkü Çolakoğlu, Ahmet Tolgay Akıncı
Journal of Neuroscience Nursing.2023; 55(4): 125. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological therapy for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Xia Zhang, Ao Wang, Miaowei Wang, Guo Li, Quan Wei
BMC Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Manual Therapy on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Eunsang Lee, Hyunjoong Kim
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - The impact of peripheral neuropathy symptoms, self-care ability, and disturbances to daily life on quality of life among gynecological cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a cross-sectional survey
Sohee Mun, Hyojung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 296. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Mobile Application-based Self-Management Program for Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 258. CrossRef - Treatment and diagnosis of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: An update
Allison D. Desforges, Chance M. Hebert, Allyson L. Spence, Bailey Reid, Hemangini A. Dhaibar, Diana Cruz-Topete, Elyse M. Cornett, Alan David Kaye, Ivan Urits, Omar Viswanath
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 147: 112671. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in children and adolescent cancer patients
Nicolette Tay, E-Liisa Laakso, Daniel Schweitzer, Raelene Endersby, Irina Vetter, Hana Starobova
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case Report of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Treated with Modified
Guibi-tang
Su Bin Park, Jee-Hyun Yoon, Eun Hye Kim, Seong Woo Yoon
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2022; 43(3): 451. CrossRef - Kanser Tedavisi Alan Çocuklarda Kemoterapiyle İlişkili Periferik Nöropatinin Değerlendirilmesinde Hemşirenin Rolü
Bilge ÖZDEMİR, Gülçin ÖZALP GERÇEKER
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektronik Dergisi.2022; 15(3): 369. CrossRef - Non-Pharmacological Self-Management Strategies for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in People with Advanced Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Megan Crichton, Patsy M. Yates, Oluwaseyifunmi Andi Agbejule, Amy Spooner, Raymond J. Chan, Nicolas H. Hart
Nutrients.2022; 14(12): 2403. CrossRef - The Effects of Foot Reflexology on the Physical Symptoms of Cancer Patients
Young-Ran Yeun, Yi-Sub Kwak, Hye-Young Kim
Exercise Science.2021; 30(1): 8. CrossRef - A Case Report of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Treated with Warm Needling
Jee-Hyun Yoon, Su Bin Park, Jee Young Lee, Eun Hye Kim, Seong Woo Yoon
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2021; 42(2): 114. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-Acupressure on Peripheral Neuropathy, Disturbance in Daily Activity, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients undergoing Chemotherapy
Su Young Kim, Jeong Sook Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 129. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise on Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yu Hyeon Choe, Da Hye Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 458. CrossRef - Effects of pain neuroscience education on kinesiophobia in patients with chronic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hyunjoong Kim, Seungwon Lee
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2020; 9(4): 309. CrossRef - Prescribing for persistent cancer pain: focus on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
Martin Galligan
Journal of Prescribing Practice.2020; 2(4): 176. CrossRef - Effects of Nonpharmacological Interventions in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: An Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Jie Hao, Xiaoshu Zhu, Alan Bensoussan
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical study on concurrent use of electro-acupuncture or Chuna manual therapy with pregabalin for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: safety and effectiveness (open-labeled, parallel, randomized controlled trial, assessor-blinded)
Jin-Hyun Lee, Tae jin Cho, Min Geun Park, Ji-Hoon Kim, Sung Kyu Song, Shin-Young Park, Yun-Young Sunwoo, Ilkyun Lee, Tae-Yong Park
Medicine.2020; 99(3): e18830. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in People with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Eun Sook Choi, Jin Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(2): 81. CrossRef - Acupuncture therapy improves health-related quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Po-Chun Hsieh, Mei-Chen Yang, Yao-Kuang Wu, Hsin-Yi Chen, I-Shiang Tzeng, Pei-Shan Hsu, Chang-Ti Lee, Chien-Lin Chen, Chou-Chin Lan
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2019; 35: 208. CrossRef - Acupuncture for the Relief of Chronic Pain: A Synthesis of Systematic Reviews
Carole A. Paley, Mark I. Johnson
Medicina.2019; 56(1): 6. CrossRef - Evidence, safety and recommendations for when to use acupuncture for treating cancer related symptoms: a narrative review
Stephen Birch, Myeong Soo Lee, Terje Alraek, Tae-Hun Kim
Integrative Medicine Research.2019; 8(3): 160. CrossRef - Physiotherapy management of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy in a gynecological condition through clinical reasoning process: A case study
K. M. Amran Hossain, Mohammad Anwar Hossain, Feroz Ahmed Mamin, Ehsanur Rahman, Nasrin Afroz, Nusrat Jahan Sonia, Shati Aziz Khan
Edorium Journal of Disability and Rehabilitation.2018; 4(2): 1. CrossRef - Research Trend about Complementary and Alternative Therapy in Korea using Text Network Analysis
Hae Ree Sung, Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim, Jeong Sig Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(2): 61. CrossRef - Síntesis de la evidencia científica en acupuntura
Juan Muñoz-Ortego, Jorge Vas, Betina Nishishinya Aquino, Beltrán Carrillo, Alberto Pérez Samartín, Cristina Verástegui, Rafael Cobos
Revista Internacional de Acupuntura.2018; 12(4): 97. CrossRef
- The Effectiveness and Safety of Nurse-Led Auricular Acupressure on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Among Patients With Breast Cancer
- 3,362 View
- 81 Download
- 32 Crossref

- Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):143-163. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate effects of psychoeducational intervention for cancer survivors.
Methods Ten databases were searched. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of the studies, data extraction and assessment. The risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane Collaboration's tool. To estimate the effect size, meta-analysis of the studies was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and RevMan programs.
Results Of 18,781 publications identified, 35 met inclusion criteria, and 25 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychoeducational intervention. Effect sizes (standardized mean difference [SMD]) were heterogeneous and random effects models were used in the analyses. Psychoeducational intervention was effective for quality of life (n=2,410, ES=0.23; 95% CI: 0.09~0.37), coping and self-efficacy (n=179, ES=0.68; 95% CI: 0.26~1.11), anxiety (n=1,786, ES=-0.26; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.15), depression (n=1,910, ES=-0.28; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.18), and psychological distress (n=2,242, ES=-0.31; 95% CI: -0.46~-0.17). Subgroup analysis showed that counseling was the most effective intervention for quality of life, and behavioral therapy was an effective intervention for all positive and negative outcomes. Publication bias was not detected except for psychological distress.
Conclusion Psychoeducational intervention appears to be effective in improving quality of life and coping and self-efficacy, and it is effective in reducing psychological symptoms in cancer survivors. Behavioral therapy, especially, is commonly effective in improving psychosocial outcomes. However, low-quality evidence, variability in the designs of existing studies, and publication bias suggest that additional high-quality trials should be conducted in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
Safa Elkefi, Corina T. Lelutiu-Weinberger, Jean-Marie Bruzzese, Alicia K. Matthews
Discover Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Group‐Based Support Interventions for Adolescents and Young Adults With Lymphoma: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Dalnim Cho, Sairah Ahmed, Stella Snyder, Juliet Kroll, Minxing Chen, Michael Roth, Kathrin Milbury
Psycho-Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mind Health of Persons with Cancer: Psycho-Oncology and Nursing
Park Eun Young
Journal of Clinical Psychooncology.2025; 11(1): 24. CrossRef - Psychosocial interventions for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease and their caregivers: a scoping review
Juyeon Oh, Jiwon An, Kyongok Park, Youngok Park
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of telemedicine psychoeducational interventions for adults with non‐oncological chronic disease: A systematic review
Carmen Sánchez‐Gutiérrez, Eugenia Gil‐García, Adriana Rivera‐Sequeiros, José M. López‐Millán
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(5): 1267. CrossRef - Cancer-Related Psychological Distress in Lymphoma Survivor: An Italian Cross-Sectional Study
Giulia Agostinelli, Barbara Muzzatti, Samantha Serpentini, Michele Spina, Maria Antonietta Annunziata
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 245. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Physical Function and Depression in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jinhyang YANG, Changwan KANG, Hye-Won PARK, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 396. CrossRef - Development of A Nurse-Led Educational Intervention Program in Managing the Nutrition Impact Symptom Cluster in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma following the Medical Research Council Framework
Wenli Xiao, Carmen W Chan, Jinnan Xiao, Cho L Wong, Ka M Chow
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 653. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Education and Support: A Model for Use in the Ambulatory Care Setting
Terri Jabaley, Patricia Rizzo, Nina Grenon, Clare Sullivan, Janet Bagley, Maritza Nassif, Renee Siegel, Meghan Underhill-Blazey
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 24(4): E43. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Chronic Pain Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hee-Sook Kang, Sung-Dong Hwang, Sang-Eun Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(3): 271. CrossRef
- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
- 2,108 View
- 35 Download
- 12 Crossref

- A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Imagery
- Won Oak Oh, Min Hyun Suk
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(2):265-276. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.2.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was to identify the trends and contents of imagery interventions and to evaluate the effects of imagery interventions by using meta-analysis. METHOD: The materials used for this study were 15 imagery intervention studies carried out from Jan. 1995 to Dec. 2001. The studies were analyzed and evaluated in different categories: 1) types of dependent variables 2) types of imagery 3) interval of imagery 4) total duration of imagery 5) sample characteristics 6) intervention method. RESULT: 1) Behavioral imagery was more prevalent than dynamic imagery. There were wide variations in duration, and interval of interventions. Imagery intervention had moderate effects on psychological variables (state of anxiety, depression & and stress etc.) and had moderate to large effects on physiological variable(pulse rate, cortisol etc.). Behavioral imagery had larger effects than dynamic imagery. Imagery applied to the public had larger effect on decreasing the state of anxiety and stress than applied to the patients. But imagery applied to the patients had a larger effect on decreasing depression than applied to the public. The imagery intervention method by using the individual approach had greater effect than group approach method. CONCLUSION: These results of this study will be used to guide the development of imagery interventions to nursing practice. Also, various types of imagery interventions need to be developed based on the characteristics of nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Korean hospice nursing interventions using the Nursing Interventions Classification system: A comparison with the USA
Sung‐Jung Hong, Eunjoo Lee
Nursing & Health Sciences.2014; 16(4): 434. CrossRef - The Effect of Guided Imagery on Stress and Fatigue in Patients with Thyroid Cancer Undergoing Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Mi Hye Lee, Dong-Hee Kim, Hak Sun Yu
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - The Effects of P6 Acupressure and Guided Imagery on Nausea, Vomiting, Retching and Anorexia of the Patients with Thyroid Cancer Undergoing Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Mi Kyung Kang, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2013; 13(4): 184. CrossRef - Analysis of Nursing Interventions Performed by Gynecological Nursing Unit Nurses Using the Nursing Interventions Classification
Sung-Jung Hong, Sung Hee Lee, Hwa Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 275. CrossRef
- Korean hospice nursing interventions using the Nursing Interventions Classification system: A comparison with the USA
- 686 View
- 4 Download
- 4 Crossref

- A Meta-Analysis of Explanatory Variables of Health Promotion Behavior
- Young Joo Park, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Ho Shin Ryu, Jae Won Lee, Sung Ok Chang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):836-846. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.836
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This Meta-Analysis of 18 studies was conducted to determine the magnitude of th relationship between health promotion behavior and each of explanatory variables. The studies were measured using Health Promoting Life Style(HPLP) developed by Walker and others based on Pender's definiton of health promoting behavior. The sample was collected by searching for The Journal of Korean Academy Nursing Society, The Journal of Korean Women's Health Nursing Academic Society,The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Adult Nursing, Journal of Korean Community Nursing, The Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing, The Journal of Korean Nursing Administration Academic Society, The Korean Journal of Child Health Nursing, The Journal of Korean Psychiatric Academic Society, the dissertations for mater degree or doctoral dissertations for the period from 1980 to 1998. The explanatory variables measured more than 2 times in studies were self-efficacy, perceived health status, self-esteem, internal, powerful- others and chance dimensions of health locus of control, perceived benefits, hardiness, wellbeing and clinical demensions of health concepts, and quality of life(life satisfaction). Effect sizes were calculated by unweighted mean r, weighted mean r by sample size and weighted mean r by quality index score after homogeneity test. The mean r effect size indicator range of each predictor variable were as follows; quality of life (0.50- 0.52), self-efficacy(0.46-0.47), hardiness (0.42-0.44), self-esteem(0.41-0.43), health locus of control- internal(0.32-0.34), health locus of control- powerful others (0.25-0.31), perceived health status(0.18-0.19) and clinical dimensions of health concepts (0.16-0.17).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the Intention of COVID-19 Infection Preventive Behaviors Among Hemodialysis Patients in Korea: A Cross-sectional Study
Su In Ham, Kyu Eun Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(2): 142. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Health-promoting Behaviors Among Nurses in South Korea: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Based on Pender's Health Promotion Model
Myung Jin Choi, Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 188. CrossRef - The Influence of Dispositional Optimism and Food-related Lifestyle on Health Promoting Behavior in Middle-Aged Early Onset Stroke Patients
Jung Hee Choi, Wan Ju Park
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(1): 34. CrossRef - Structural Equation Model of Elementary School Students’ Quality of Life Related to Smart Devices Usage Based on PRECEDE Model
Jin-Pyo Lee, Yang-Sook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4301. CrossRef - Influence of Perceived Health Status, Perceived Barrier, Cultural Acculturation on Empowerment in Married Migrant Women
Yong-Sook EO, Yeon Hee LEE
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2020; 32(5): 1308. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promoting Behavior in Postpartum Women at Sanhujoriwon
Hyekyung Choi, Namok Jung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(2): 135. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behaviors, Disease Prevalence between One-person women and Multiple households women in Korea
Eun-gyeong Kim, Sook-kyoung Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(3): 483. CrossRef - Qualitative study on experience of health behavior among Korean low-income breast cancer survivors
Young-Sun Rhee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(5): 3188. CrossRef - Association of Dental Caries with Health Lifestyle in Adults
Soo-Kyung Kim
Journal of dental hygiene science.2015; 15(3): 333. CrossRef - An Efficacy of Social Cognitive Theory to Predict Health Behavior A Meta-Analysis on the Health Belief Model Studies in Korea
Byoungkwan Lee, 김채린, 윤문영, 김민희, 손영곤, 이상록
Journal of Public Relations.2014; 18(2): 163. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health-Promoting Behaviors in People Living with HIV
Young Mi Park, Gisoo Shin, Jiyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 234. CrossRef - Pathway Analysis on the Influence of Health Promoting Behavior(HPB) and Depression Cognitive Scale(DCS) on Smoking Cessation Thoughts and Intention to Quit Smoking of College Students who Smoke
Hee-Jeong Kim, Se-Jin Ju, Gyeong-Suk Kim, Mi-Ok Kim, Yu Mi, Jeong-Hyeon Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(4): 1830. CrossRef - Factors influencing health-promoting behaviors in Korean breast cancer survivors
Myungsun Yi, Jeongeun Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2013; 17(2): 138. CrossRef - A Study of Relations Between a Health Promoting Behaviors and Self-efficacy of Conscripted Policemen
Young Jin Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(2): 778. CrossRef - A Predictive Model on Health Promotion Behavior in Women who Immigrate for Marriage
Namok Jeong, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 695. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Youth Health Risk Behaviors by Region: Focused on Metropolitan Areas, Medium Sized and Small City Areas, and Rural Areas
Eunok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 14. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the Intention of COVID-19 Infection Preventive Behaviors Among Hemodialysis Patients in Korea: A Cross-sectional Study
- 754 View
- 7 Download
- 16 Crossref

- A Meta-Analysis of Effects of Relaxation Therapy on Anxiety and Blood Pressure
- Hee Seung Kim, Hae Hiang Song, So Eun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):282-292. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A meta-analysis of 14 quasi-experimental studies was conducted to compare the effect of size on various relaxation therapies applied to patients and health volunteer students. These studies were selected from theses, dissertations and papers that have been done between 1982 to 1993. Also They have a randomized or nonequivalent control group in a pre test-post test design. The studies were evaluated in different ways; 1) types of relaxation therapy, 2) total amount of time of relaxation therapy, and 3) types of outcome variables. For a group of homogenious studies, the weighted mean effect size and standard error were estimated. Some findings are summarized as follows : 1. Jacobson relaxation therapy had a larger effect on systolic and diastolic blood pressures than on state anxiety. 2. For the total time of relaxation therapy, (longer than 60 minutes) had a much larger effect in decreasing systolic and diastolic blood pressures than in the case of a time period shorter than 60 minutes. 3. Relaxation therapy applied to surgery patients also had a larger effect in decreasing state anxiety than when applied to other patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Abdominal Breathing on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Peripheral Skin Temperature and Saturation Oxygen of Pregnant Women in Preterm Labor
Soon-Bok Chang, Hee-Sook Kim, Yun-Hee Ko, Choon-Hee Bae, Sung-Eun An
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(1): 32. CrossRef
- Effects of Abdominal Breathing on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Peripheral Skin Temperature and Saturation Oxygen of Pregnant Women in Preterm Labor
- 726 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Self-Efficacy as a Predictor of Self-Care in Persons with Diabetes Mellitus: Meta-Analysis
- Hyang Yeon Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(5):1087-1102. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.5.1087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Diabetes mellitus, a universal and prevalent chronic disease, is projected to be one of the most formidable worldwide health problems in the 21st century. For those living with diabetes, there is a need for self-care skills to manage a complex medical regimen. Self-efficacy which refers to one's belief in his/her capability to monitor and perform the daily activities required to manage diabletes has found to be related to self-care. The concept of self-efficacy comes from social cognitive theory which maintains that cognitive mechanism mediate the performance of behavior. The literature cities several research studies which show a strong relationship between self-efficacy and self-care behavior. Meta-analysis is a technique that enables systematic review and quantitative integration of the results from multiple primary studies that are relevant to a particular research question. Therefore, this study was done using meta-analysis to quantitatively integrate the results of independent research studies to obtain numerical estimates of the overall effect of a self-efficacy with diabetic patient on self-care behaviors. The research proceeded in three stages : 1) literature search and retrieval of studies in which self-efficacy was related to self-care, 2) coding, and 3) calculation of mean effect size and data analysis. Seventeen studies which met the research criteria included study population of adults with diabetes, measures of self-care and measures of self-efficacy as a predictive variable. Computation of effect size was done on DSTAT which is a statistical computer program specifically designed for meta-analysis. To determine the effect of self-efficacy on self-care practice homogeneity tests were conducted. Pooled effect size estimates, to determine the best subvariable for composite variables, metabolic control variables and component of self-efficacy and self-care, indicated that the effect of self-efficacy composite on self-care composite was moderate to large. The weighted mean effect size of self-efficacy composite and self-care composite were +.76 and the confidence interval was from +.66 to +.86 with the number of subjects being 1,545. The total for this meta-analysis result showed that the weighted mean effect sizes ranged from +.70 to +1.81 which indicates a large effect. But since reliabilities of the instruments in the primary studies were studies were low or not stated, caution must be applied in unconditionally accepting the results from these effect sizes. Meta-analysis is a useful took for clarifying the status of knowledge development and guiding decision making about future research and this study confirmed that there is a relationship between self-efficacy and self-care in patients with diabetes. It, thus, provides support for nurses to promote self-efficacy in their patients. While most of the studies included in this meta-analysis used social cognitive theory as a framework for the study, some studies use Fishbein and Ajzen's attitude model as a model for active self-care. Future research is needed to more fully define the concept of self-care and to determine what it is that makes patients feel competent in their self-care activities. The results of this study showed that self-efficacy can promote self-care. Future research is needed with experimental design to determine nursing interventions that will increase self-efficacy.
- 489 View
- 3 Download

- A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of a Self-Efficacy Promoting Program
- Bo Kyoung Cha, Hae Kyung Chang, Jung Nam Sohn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(6):934-944. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.6.934
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the effects of a self-efficacy promoting program and analyze its components.
Method The material used for this study were 18 self-efficacy promoting program studies carried out from Jan. 1980 to Oct. 2003. The studies were analyzed in different categories: 1) types of dependent variables 2) sample characteristics 3) types of experimental treatment conditions 4) types of self-efficacy source and 5) total amount of time.
Result 1) The weighted mean of a self-efficacy promoting program ranged from 1.383 to 0.015 2) for the experimental treatment condition, exercise had a much larger effect in increasing general self-efficacy and self-care than education 3) the studies using 3 sources had a much larger effect in increasing self-care than the studies using 4 sources 4) a time period longer than 900 minutes had a much larger effect in increasing specific self-efficacy, general self-efficacy and self-care than in a time period shorter than 900 minutes. 5) effect size of specific self-efficacy was significantly higher than general self-efficacy.
Conclusion These results can be used to guide the development of a self-efficacy promoting program for nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effectiveness of the information-motivation-behavioral skills model-based intervention on preventive behaviors against respiratory infection among community-dwelling older adults
Min Hye Lee, Yeon-Hwan Park
Patient Education and Counseling.2021; 104(8): 2028. CrossRef - The Effects of Group Motivational Interviewing Compliance Therapy on Drug Attitude, Medicine Application Self-efficacy and Medicine Application in Psychiatric Patients
Dawoon Lee, Sungjae Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(4): 391. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of the Empowering A Self-Efficacy (EASE) Program for Children with Epilepsy
Hana Yoo, Hee-Soon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 54. CrossRef
- The effectiveness of the information-motivation-behavioral skills model-based intervention on preventive behaviors against respiratory infection among community-dwelling older adults
- 772 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A Meta-analysis of the Effects of Smoking Prevention Programs in Korea
- Eun Ok Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(6):1004-1013. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.6.1004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this paper was to describe the characteristics of smoking prevention programs in Korea, to estimate overall effect size of Korean smoking prevention programs, and to investigate effect size variations by program modality and instruction method.
Method Meta-analysis was performed on21 programs in 20 studies.
Result The estimation of overall effect size for knowledge and attitude was not possible because effect sizes were not homogeneous in this meta-analysis. However, effect sizes of studies that were socially influential programs or active/interactive methods were larger than information-oriented programs or passive/non-interactive methods in the pictures. The effects for behavioral outcomes were generally not as positive and not statistically significant. Q statistics showed that variations among effect sizes within program modality and instruction method classifications were heterogeneous.
Conclusion The results from this meta-analysis support the continued use of socially influential programs and active/interactive methods for smoking prevention programs. Because behavioral effect might be the fundamental objective of smoking prevention programs, the present results indicate that smoking prevention programs should consider adopting more effective programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Staged Smoking Prevention Program for Primary School Children
Jae-Hee Kim, Yu-Jeong Lee, Seong-Mi Kang, Yu-Mi Oh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(8): 5131. CrossRef - Influence of Depression, Anxiety and Stress-Coping Aspect upon Smoking Desire of Undergraduates, according to Their Lifestyles
Sung-Sik Ahn, Chun-Sook Kim, Sung-Hwan Choi
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2012; 6(1): 205. CrossRef - A Meta-Analysis on the Effectiveness of Computer-Based Education in Nursing
Kook Hee Roh, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Healthcare Informatics Research.2010; 16(3): 149. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of Effects on Adolescent Smoking Cessation Programs in Korea
Younkyoung Kim, Inhyae Park, Jeong-Soo Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 204. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Staged Smoking Prevention Program for Primary School Children
- 701 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Meta-Analysis of the Research Findings Concerning Functional Relationships of Explanatory Variables to Hope
- Dal Sook Kim, Weon Hee Moon, Seong Yoon Ahn, Hyun Sook Oh, Kyung Hee Kwon, Moon Kyoung Park, Hyeon Sook Choi, Mee Ok Lee, Young Ju Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(5):673-684. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.5.673
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to meta-analyze the relationships of major concepts, which were made by synthesizing similar explanatory variables into more comprehensive concepts, to hope.
Method The relevant researches from Jan 1980 to Dec 2003, performed in adults or adult patients, were collected. Using the SAS program, meta-analysis were done with the input data of the number of subjects, the correlation coefficients provided from most of the studies or a few transformed correlation coefficients from F value. In order to get the analysis to be done in homogeneous status of the data regarding each relationship of each major concept to hope(p>0.05), heterogeneous data were eliminated in repeating Q-test.
Result The major variable regarding relationship to self/transcendental being/life(spiritual wellbeing & self esteem) and social support(social support & family support) have very large positive effects on hope(D̅=1.72, D̅=1.27). The negative effect of the variable regarding captive state(uncertainty in illness, perceived unhealthiness status, & fatigue) and positive effect of coping(approach coping) on hope are in the level between moderate to large(D̅=-0.61,D̅=0.78). All the effects of the major concepts on hope were verified as significant statistically(p=.000). The Fail -Safe numbers showed the significant effects of the three major concepts except coping on hope were reliable.
Conclusion The results can be a guide to advance hope theory for nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- What Determines the Health-related Quality of Life of Vietnamese Migrant Workers in Korea?
Jihyon Pahn, Heesuk Kim, Youngran Yang
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2023; 34: 147. CrossRef - Hope Enhancement Program for Increased Hope, Self-Efficacy, and Quality of Life for Mentally Ill Persons in Day Hospitals
Ju Hyun Park, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(3): 260. CrossRef - The Effects of Tai Chi Exercise on Hope, Dependency, and Perceived Health Status of Elderly Women
Yong Ju Park, Ja Ok Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2014; 21(2): 106. CrossRef - Impact Factors for Health of Family Caregivers of Hospice Patients
Bok Yae Chung, Hyeon Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(2): 75. CrossRef
- What Determines the Health-related Quality of Life of Vietnamese Migrant Workers in Korea?
- 783 View
- 4 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Breastfeeding Interventions on Breastfeeding Rates at 1, 3 and 6 Months Postpartum: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):713-730. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.713
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to evaluate the effects of breastfeeding intervention on breastfeeding rates.
Methods Based on the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA), a systematic search was conducted using eight core electronic databases and other sources including gray literature from January 9 to 19, 2017. Two reviewers independently select the studies and assessed methodological risk of bias of studies using the Cochrane criteria. The topics of breastfeeding interventions were analyzed using descriptive analysis and the effects of intervention were meta-analyzed using the Review Manager 5.2 software.
Results A total of 16 studies were included in the review and 15 were included for meta-analysis. The most frequently used intervention topics were the importance of good latch-on and frequency of feeding and determining adequate intake followed. The pooled total effect of breastfeeding intervention was 1.08 (95% CI 1.03~1.13). In the subgroup analysis, neither pre-nor post-childbirth intervention was effective on the breastfeeding rates at 1, 3, and 6 months, and neither group nor individual interventions had an effect. Only the 1 month breastfeeding rate was found to be affected by the individual intervention with the persistent strategies 1.21 (95% CI 1.04~1.40).
Conclusion Effective breastfeeding interventions are needed to help the mother to start breastfeeding after childbirth and continue for at least six months. It should be programmed such that individuals can acquire information and specific breastfeeding skills. After returning home, there should be continuous support strategies for breastfeeding as well as managing various difficulties related to childcare.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond Intentions: The Breastfeeding Intention-Practice Gap in Tunisia- A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Initiation and Continuation among Post-Partum Women
Narjes karmous, Omar Oualha, Anouar Drira, Abdelwaheb Masmoudi, Badreddine Bouguerra, Abdennour Karmous
F1000Research.2025; 14: 881. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Breastfeeding Duration in Tunisia: A Cross-Sectional Analysis Highlighting the Role of Early Initiation
Narjes karmous, Omar Oualha, Anouar Drira, Abdelwaheb Masmoudi, Badreddine Bouguerra, Abdennour Karmous
F1000Research.2025; 14: 881. CrossRef - Postpartum Breastfeeding Practices and Attitudes in Parents: A Randomized Study to Evaluate the Effects of Individual and Group Breastfeeding Education of Mothers and Fathers
Yeşim Yeşil, Hafize Öztürk Can
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Social policies and breastfeeding duration in South Korea: A survival analysis of the national data
Jung Hee Yeo, Eun-Young Kim
Midwifery.2022; 107: 103282. CrossRef - Information Resource Network Analysis of Factors Influencing Breastfeeding Planning and Duration
Eunyoung Lee, Insook Cho, Seong Jin Cho, Eunju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 232. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Breastfeeding Behavior of First-Time Mothers
Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2021; 25(3): 184. CrossRef - The Relationship of Previous Breastfeeding Experiences and Factors Affecting Breastfeeding Rates: A Follow-Up Study
Jun-Yan Li, Yi Huang, Hao-Qi Liu, Jing Xu, Lu Li, Sharon R. Redding, Yan-Qiong Ouyang
Breastfeeding Medicine.2020; 15(12): 789. CrossRef - Effects of galactagogue herbal tea containing Chrysanthemum indicum as the main component on milk production in postpartum rats
Jiyoung Choi, Yunjung Lee, Sunuk Choi, Eunju Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(5): 445. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventions incorporating behaviour change techniques to promote breastfeeding among postpartum women
Angelos P. Kassianos, Emma Ward, Antonio Rojas-Garcia, Allison Kurti, Fiona C. Mitchell, Dian Nostikasari, Jamie Payton, Julian Pascal-Saadi, Claire Adams Spears, Caitlin Notley
Health Psychology Review.2019; 13(3): 344. CrossRef
- Beyond Intentions: The Breastfeeding Intention-Practice Gap in Tunisia- A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Initiation and Continuation among Post-Partum Women
- 2,458 View
- 20 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Stimulation-Oriented Interventions for Behavioral Problems among People with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Eun Young Kim, Sung-Dong Hwang, Eun Joo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(4):475-489. Published online August 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.4.475
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate the effects of stimulation-oriented interventions for behavioral problems among people with dementia.
Methods Based on the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA), a literature search was conducted using seven electronic databases, gray literature, and other sources. Methodological quality was assessed using the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) for randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Data were analyzed using R with the ‘meta’ package and the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA 2.0) program.
Results Sixteen studies were included for meta-analysis to investigate the effect of stimulation-oriented interventions. The quality of individual studies was rated as ‘++’ for eight studies and ‘+’ for the rest. The effect sizes were analyzed according to three subgroups of interventions (light, music, and others); Hedges’ g=0.04 (95% CI: -0.38~0.46), -0.23 (95% CI: -0.56~0.10), -0.34 (95% CI: -0.34~0.00), respectively. To explore the possible causes of heterogeneity (I2=62.8%), meta-regression was conducted with covariates of sample size, number of sessions, and length of session (time). No moderating effects were found for sample size or number of sessions, but session time showed a significant effect (Z=1.96, 95% CI: 0.00~0.01). Finally, a funnel plot along with Egger's regression test was performed to check for publication bias, but no significant bias was detected.
Conclusion Based on these findings, stimulation-oriented interventions seem to have a small effect for behavioral problems among people with dementia. Further research is needed to identify optimum time of the interventions for behavioral problems among dementia patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Horticultural Therapy on Korean Elderly with Dementia: A Meta-analysis
Kyung Ja Kang, Mi-Jung Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(4): 352. CrossRef - Effect of aquatic exercise on gait in persons with chronic stroke: a meta-analysis study in Korea
Dong-Jin Lee, Sung-Hyoun Cho
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2019; 8(2): 112. CrossRef
- Effects of Horticultural Therapy on Korean Elderly with Dementia: A Meta-analysis
- 1,497 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Correlates of Cognitive Impairment of Rheumatic Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- JinA Mo, JiSuk Park, HyunSoo Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(1):1-18. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to synthesis the results of research on relationships of cognitive impairment with multi-dimensional correlates of rheumatic disease through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Methods For the study purpose, 23 studies were selected through a systematic process of searching the literature.
Results The study results showed that among general characteristics, age and education were the variables having a significant relationship with cognitive impairment. Among health risk factors, obesity appeared to have a significant positive relationship with cognitive impairment. For past history, diabetes and hypertension were shown to have a significant positive relationship with cognitive impairment. It was noted also that aPL, one of the physiological factor, had significant association with cognitive impairment. None of the medication related factors had a significant relationship with cognitive impairment. Results showed that among disease related factors, disease activity had the highest relationship with cognitive impairment. Depression, among psychological factors, was the only variable having a significant relationship with cognitive impairment.
Conclusion The findings indicate that the variables strongly impacting on cognitive impairment in rheumatic disease are depression and disease activity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Cognitive Impairment among Iraqi Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Zahraa Hussein Altemimi, Faiq I. Gorial
Medical Journal of Babylon.2024; 21(2): 324. CrossRef - Temporal Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Indices and Factors of Metabolic Syndrome Development in Patients With Rheumatic Disease
HyunSoo Oh, JiSuk Park, JiYoung Kim, SungKyung Jang, Yeona Ryu, YeoJu Jeong, SuYeon Kwon, SoHyun Suh, HaYoung Lee, DaHee Choi, HanNa Lee, GaWon Cho, WhaSook Seo
Orthopaedic Nursing.2023; 42(4): 251. CrossRef - Correlates of cognitive impairment in patients with chronic kidney failure on haemodialysis: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
HyunSoo Oh, JinA Mo, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2019; 75(5): 962. CrossRef - Comparisons of the Incidence and Critical Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients With a Rheumatic Disease or Gout
HyunSoo Oh, JiSuk Park, YoungSub Yoon, WhaSook Seo
Orthopaedic Nursing.2019; 38(3): 201. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Cognitive Impairment among Iraqi Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- 1,171 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Family Support Programs for Caregivers of People with Dementia - Caregiving Burden, Depression, and Stress: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Seyeon Park, Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):627-640. Published online October 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.627
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The objective of this systematic review was to assess the effects of family support programs on caregiving burden, depression, and stress in family caregivers of people with dementia.
Methods A literature search was conducted of electronic databases to identify randomized controlled studies with family support programs done between 2000 and 2014. Studies published in English and/or Korean were included for the analysis with search strategies adapted from the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group. Studies were rated for quality assessment by two independent reviewers using the appraisal checklist developed by Cochrane Reviews and Dissemination. Of 8,334 articles identified in the literature search, full texts of 76 articles that met the inclusion criteria were reviewed and 38 were found to include relevant outcomes.
Results Results from selected studies were pooled in statistical meta-analysis using Review Manager Software and heterogeneity between combined studies was assessed using the Chi-square test. Meta-analysis showed that the effect sizes of family caregiver support programs were small to medium for categories of caregiving burden (Hedge's g= - 0.17, 95% CI= - 0.30~ - 0.04), depression (Hedge's g= - 0.30, 95% CI= - 0.40~ - 0.20), and stress (Hedge's g= - 0.39, 95% CI= - 0.52~ - 0.25).
Conclusion The review results indicate that a support programs can assist family care-givers in reducing their psycho-emotional distress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the presence of a family member with dementia on the prevalence of depression: a comparison based on household income level
Min Hui Moon, Suk Woong Kang, Min Hyeok Choi
International Journal for Equity in Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Reitman Centre CARERS program for supporting dementia family caregivers: a pre–post intervention study
Joel Sadavoy, Sima Sajedinejad, Mary Chiu
International Psychogeriatrics.2022; 34(9): 827. CrossRef - Caregiver Burden among Caregivers of Patients with Mental Illness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Choy Qing Cham, Norhayati Ibrahim, Ching Sin Siau, Clarisse Roswini Kalaman, Meng Chuan Ho, Amira Najiha Yahya, Uma Visvalingam, Samsilah Roslan, Fairuz Nazri Abd Rahman, Kai Wei Lee
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2423. CrossRef - Evaluating the Effectiveness of Community-Based Dementia Caregiver Intervention on Caregiving Burden, Depression, and Attitude Toward Dementia: A Quasi‐experimental Study
Su Jung Lee, Hyun-Ju Seo, IL Han Choo, Seong Min Kim, Jeong Min Park, Eun-Young Yang, Yu Mi Choi
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2022; Volume 17: 937. CrossRef - Loss and Grief in the Context of Dementia Caregiving
Olimpia Paun, Dimitra Loukissa, Marianne G. Chirica, Horace M. Nowell
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2022; 60(10): 7. CrossRef - Korean Family Caregivers' Experiences With Managing Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Keeping Harmony in Daily Life
Jiyeon Kim, Jun-Ah Song, Sua Jung, Hongjin Cheon, Jiyeon Kim
Research in Gerontological Nursing.2022; 15(3): 141. CrossRef - Health Promotion Behavior among Older Korean Family Caregivers of People with Dementia
Aram Cho, Chiyoung Cha
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4123. CrossRef - A systematic review of interventions for family caregivers of the elderly with dementia in Korea
Seonghee Jeong, Jeonghae Hwang, Doonam Oh
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 306. CrossRef - An empowerment program for family caregivers of people with dementia
Heun Keung Yoon, Gwang Suk Kim
Public Health Nursing.2020; 37(2): 222. CrossRef - Horticultural Therapy Programs Enhancing Quality of Life and Reducing Depression and Burden for Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia
Yong Hyun Kim, Chul Soo Park, Hwa-Ok Bae, Eun Ji Lim, Kyung Heui Kang, Euy Sun Lee, Su Hyeon Jo, Moo Ryong Huh
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2020; 23(3): 305. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study of the Research on Caregiver Depression: Using Bibliometrics and LDA Topic Modeling
Soyoung Choi, JooYoung Seo
Issues in Mental Health Nursing.2020; 41(7): 592. CrossRef - The Effects of a Support Program for Family Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia on Empowerment and Attitudes toward Dementia
So Yoon Kim, Seonghee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 103. CrossRef - Behavioural Changes in Dementia and their Impact on Professional Caregivers: A Grounded Theory Approach
Katie Appleton, Antonina Pereira
Dementia.2019; 18(4): 1479. CrossRef - The Effects of Group Occupational Therapy Including Education Programs on Depression, Anxiety, and Participation of Activities in People With Dementia
Min-Joo Ham, Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2018; 26(4): 97. CrossRef - Shifting of Centricity: Qualitative Meta Synthetic Approach on Caring Experience of Family Members of Patients with Dementia
Young Mi Ryu, Mi Yu, Seieun Oh, Haeyoung Lee, Haejin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 601. CrossRef - Effects of a Dementia Family Education Program for Dementia Recognition, Burden, and Depression in Caregivers of Elders with Dementia
Sun-A Lee, Hee-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(1): 14. CrossRef - Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on Caring Experience of Spouses of Elderly People with Dementia at Home
Hye-Young Jang, Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 367. CrossRef - The voices of family caregivers of seniors with chronic conditions: a window into their experience using a qualitative design
Suzette Brémault-Phillips, Jasneet Parmar, Melissa Johnson, Arlene Huhn, Anna Mann, Victoria Tian, Lori-Ann R. Sacrey
SpringerPlus.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Conceptualization of an evidence-based smartphone innovation for caregivers and persons living with dementia
Melvyn W.B. Zhang, Sally Chan, Olivia Wynne, Sarah Jeong, Sharyn Hunter, Amada Wilson, Roger C.M. Ho
Technology and Health Care.2016; 24(5): 769. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Caregiving Satisfaction among Family Caregivers of Patients with Dementia
Yunhee Lee, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2016; 18(3): 117. CrossRef
- Impact of the presence of a family member with dementia on the prevalence of depression: a comparison based on household income level
- 2,196 View
- 34 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Effects of Dietary and Physical Activity Interventions on Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-analysis
- Guna Lee, Hye-Young Choi, Sook-Ja Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):483-494. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.483
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study identified effects of dietary and physical activity interventions including dietary interventions or physical activity interventions alone or combined dietary-physical activity interventions to improve symptoms in metabolic syndrome including abdominal obesity, high triglycerides, low high density lipoprotein cholesterol, elevated blood pressure, and elevated fasting glucose through meta-analysis.
Methods Articles on metabolic syndrome X published from 1988 to 2013 were searched through electronic databases, Google Scholar, and reference reviews. Methodological quality was assessed by the checklist, SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network).
Results In the meta-analysis, there were 9 articles reporting 13 interventions with 736 participants. Using random effect models, the dietary and/or physical activity interventions showed a lower mean difference in waist circumference ( - 1.30 cm, 95% CI: - 2.44~ - 0.15,
p =.027). The combined dietary-physical activity interventions showed a lower mean difference in waist circumference ( - 2.77 cm, 95% CI: - 4.77~ - 0.76,p =.007) and systolic blood pressure ( - 5.44 mmHg, 95% CI: - 10.76~ - 0.12,p =.044). Additionally, interventions of over 24 weeks yielded a lower mean difference in waist circumference ( - 2.78 cm, 95% CI: - 4.69~ - 0.87,p =.004) and diastolic blood pressure ( - 1.93 mmHg, 95% CI: - 3.63~ - 0.22,p =.026).Conclusion The findings indicate that dietary and/or physical activity interventions for metabolic syndrome reduce central obesity with no adverse effects. This finding provides objective evidences for dietary and physical activity management on metabolic syndrome as an efficient intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and associated factors of normal-weight central obesity among community-dwelling adults 18 years and older in Mongolia
Karl Peltzer, Supa Pengpid
BMC Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Scoping review of research trends in genetic factors related to metabolic syndrome in Koreans: using the data from Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES)
Minyeong Kim, Subin Kim, Dayeon Shin
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 131. CrossRef - Diyabet Riski, Aktivite Düzeyleri ile Akdeniz Tipi Beslenme Davranışları İlişkisi
İbrahim Topuz, Sercan Gümüş, Sebahat Gözüm
Etkili Hemşirelik Dergisi.2025; 18(2): 193. CrossRef - Immune Microenvironment Dysregulation: A Contributing Factor to Obesity-Associated Male Infertility
Rui Feng, Dexin Cheng, Wei Zhang, Jiayun Zhang, Sixiang Chen, Yan Xia
Biomedicines.2025; 13(6): 1314. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Blended Self-Management Program for Metabolic Syndrome in Patients With Rheumatic Diseases
BoAe Im, HyunSoo Oh, SooHyun Kim, HyeSun Jeong, WhaSook Seo
Health Education & Behavior.2024; 51(4): 625. CrossRef - Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
Miseon Seo, Eun-Young Jun, Hyunjin Oh
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychosocial Determinants of Recommended Lifestyle Behaviors among Hypertensive Patients: An Integrative Literature Review
Wachira Suriyawong, Tsui-Sui Annie Kao, Lorraine B. Robbins, Jiying Ling, Leapetswe Malete
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2023; 45(5): 455. CrossRef - 노인 대사증후군에 효과적인 중재: 체계적 문헌고찰과 메타분석
서현 이, 슬 구, 유미 서, 선화 반
Public Health Weekly Report.2023; 16(48): 1633. CrossRef - Association between green tea consumption and metabolic syndrome among Korean adults: results from the Health Examinees study
Hyeonjin Cho, Sunwoo Han, Jiwon Jeong, Hyein Jung, Sangah Shin
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(1): 70. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis study
D. G. Corona, W. Vena, A. Pizzocaro, G. Rastrelli, C. Sparano, A. Sforza, L. Vignozzi, M. Maggi
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 46(11): 2195. CrossRef - Determination of Factors Inhibiting the Physıcal Activity Status of Nursing Students in the Covid-19 Pandemic
Tuba Bülbül, Betül Tosun, Ezgi Dirgar
International Journal of Disabilities Sports and Health Sciences.2022; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - Impact of motivational interviewing as a follow-up to an exercise intervention among women with or at risk for metabolic syndrome: A randomized controlled trial
Kameron B Suire, Ashley Peart, Jan Kavookjian, Danielle D Wadsworth
SAGE Open Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral and cognitive benefits of physical exercise in a mouse model of midlife metabolic syndrome
Farida El Gaamouch, Hsiao-yun Lin, Qian Wang, Wei Zhao, Jiangping Pan, Kalena Liu, Jean Wong, Clark Wu, Chongzhen Yuan, Haoxiang Cheng, Weiping Qin, Ke Hao, Bin Zhang, Jun Wang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender Differences of Health Behaviors in the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome for Middle-Aged Adults: A National Cross-Sectional Study in South Korea
Jaehee Yoon, Jeewuan Kim, Heesook Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3699. CrossRef - A Technology-Mediated Interventional Approach to the Prevention of Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Gaeun Kim, Ji-Soo Lee, Soo-Kyoung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(2): 512. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome and Functional Fitness Abilities
Laura Gallardo-Alfaro, Maria del Mar Bibiloni, Emma Argelich, Escarlata Angullo-Martinez, Cristina Bouzas, Josep A. Tur
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(24): 5840. CrossRef - Effects of BeHaS Program on Health Behavior, Physiologic Index and Self-Esteem of the Elderly Living Alone with Metabolic Syndrome Based on Community Based Participatory Research
Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim, Keumok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Lina Lee, Si Wan Choi, Bon Jeong Ku
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 571. CrossRef - Dietary Fat Intake and Metabolic Syndrome in Older Adults
Alicia Julibert, Maria del Mar Bibiloni, David Mateos, Escarlata Angullo, Josep A. Tur
Nutrients.2019; 11(8): 1901. CrossRef - Metabolic fitness in relation to genetic variation and leukocyte DNA methylation
M. Caspers, S. Blocquiaux, R. Charlier, J. Lefevre, K. De Bock, M. Thomis
Physiological Genomics.2019; 51(1): 12. CrossRef - Effects of a Self-Care Reinforcement Program for Socially Vulnerable Elderly Women with Metabolic Syndrome in Korea
Mikyung Park, Kiwol Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(3): 271. CrossRef - Flavonoids and Insulin-Resistance: From Molecular Evidences to Clinical Trials
Benedetta Russo, Fabiana Picconi, Ilaria Malandrucco, Simona Frontoni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(9): 2061. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Status of Chinese Workers and Their Physical Profiles, Lifestyle Scores, and Nutrient Intakes
Chao Wang, Hokyung Ryu
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(1): 63. CrossRef - Physical activity, mediating factors and risk of colon cancer: insights into adiposity and circulating biomarkers from the EPIC cohort
Krasimira Aleksandrova, Mazda Jenab, Michael Leitzmann, Bas Bueno-de-Mesquita, Rudolf Kaaks, Antonia Trichopoulou, Christina Bamia, Pagona Lagiou, Sabina Rinaldi, Heinz Freisling, Marion Carayol, Tobias Pischon, Dagmar Drogan, Elisabete Weiderpass, Paula
International Journal of Epidemiology.2017; 46(6): 1823. CrossRef - Association between siesta (daytime sleep), dietary patterns and the presence of metabolic syndrome in elderly living in Mediterranean area (MEDIS study): The moderating effect of gender
E.N. Georgousopoulou, N. Naumovski, D.D. Mellor, S. Tyrovolas, S. Piscopo, G. Valacchi, N. Tsakountakis, A. Zeimbekis, V. Bountziouka, E. Gotsis, G. Metallinos, D. Tyrovola, J. Kellett, A. Foscolou, J.-A. Tur, A.-L. Matalas, C. Lionis, E. Polychronopoulos
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2017; 21(10): 1118. CrossRef - metabolic syndrome: some results and prospects for solving the problem
Чу, Syaoyan Chu, Киргизова, Oksana Kirgizova
Бюллетень Восточно-Сибирского научного центра Сибирского отделения Российской академии медицинских наук.2016; 1(5): 187. CrossRef - Prevalence of Central Obesity among Adults with Normal BMI and Its Association with Metabolic Diseases in Northeast China
Peng Zhang, Rui Wang, Chunshi Gao, Lingling Jiang, Xin Lv, Yuanyuan Song, Bo Li, Pratibha V. Nerurkar
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(7): e0160402. CrossRef
- Prevalence and associated factors of normal-weight central obesity among community-dwelling adults 18 years and older in Mongolia
- 2,004 View
- 34 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Effects of Nursing Interventions for Fall Prevention in Hospitalized Patients: A Meta-analysis
- Yoon Lee Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):469-482. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.469
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify which nursing interventions are the most effective in fall prevention for hospitalized patients.
Methods From 3,675 papers searched, 34 were selected for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Number of fallers, falls, falls per 1,000 hospital-days, and injurious falls, fall protection activity, knowledge related to falls, and self-efficacy about falls were evaluated as outcome variables. Data were analyzed using the Comprehensive Meta Analysis (CMA) 2.2 Version program and the effect sizes were shown as the Odd Ratio (OR) and Hedges's g.
Results Overall effect size of nursing interventions for fall prevention was OR=0.64 (95% CI: 0.57~0.73,
p <.05) and Hedges's g= - 0.24. The effect sizes (OR) of each intervention ranged from 0.34 to 0.93, and the most effective nursing intervention was the education & environment intervention (OR=0.34, 95% CI: 0.28~0.42,p <.001), followed by education intervention (OR=0.57, 95% CI: 0.50~0.67,p =.001). Subgroup analyses showed that multifaceted interventions (OR=0.76, 95% CI: 0.73~0.79,p <.001) were more effective than unifactorial interventions, and that activities for prevention of falls (OR=0.08, 95% CI: 0.05~0.15,p <.001) showed the largest effect size among outcome variables.Conclusion Falls in hospitalized patients can be effectively prevented using the nursing interventions identified in this study. These findings provide scientific evidence for developing and using effective nursing interventions to improve the safety of hospitalized patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristics and Effects of Fall Prevention Interventions among the Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review
Jeong Ha Park, Hee Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 65. CrossRef - Internet-Delivered Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hyunjung Kim, Younjae Oh, Sun Ju Chang
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(6): e35260. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Turkish Version of the Self- Awareness of Falls in Elderly Scale Among Elderly Inpatients
Fatma Birgili, Seda Kılınç, Nezihe Bulut Uğurlu
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(7): 69. CrossRef - Validity of the Morse Fall Scale and the Johns Hopkins Fall Risk Assessment Tool for fall risk assessment in an acute care setting
Young Ju Kim, Kyoung‐Ok Choi, Suk Hyun Cho, Seok Jung Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2022; 31(23-24): 3584. CrossRef - An Educational Intervention to Improve Staff Collaboration and Enhance Knowledge of Fall Risk Factors and Prevention Guidelines
Kimberly A. DiGerolamo, Mei Lin Chen-Lim
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2021; 57: 43. CrossRef - Trends of Nursing Research on Accidental Falls: A Topic Modeling Analysis
Yeji Seo, Kyunghee Kim, Ji-Su Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 3963. CrossRef - Analysis of Fall Incident Rate among Hospitalized Korean Children Using Big Data
Eun Joo Kim, Anna Lee
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2021; 61: 136. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on the King's Goal Attainment Theory for Fall High-Risk Elderly Patients in Long-Term Care Hospital
Bom Mi Park, Ho Sihn Ryu, Kyeung Eun Kwon, Chun Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(2): 203. CrossRef - Use of the Nursing Outcomes Classification for Falls and Fall Prevention by Nurses in South Korea
Eunjoo Lee
International Journal of Nursing Knowledge.2019; 30(1): 28. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Self-Awareness of Falls in Elderly Scale Among Elderly Inpatients
Meei-Ling Shyu, Hui-Chuan Huang, Mei-Jung Wu, Hsiu-Ju Chang
Clinical Nursing Research.2018; 27(1): 105. CrossRef - The effectiveness of intervention programs for preventing patients from falls
Jana Horová, Iva Brabcová, Jitka Krocová
Kontakt.2017; 19(2): e105. CrossRef - Effect of Strength Exercise on Patient Fall Prevention Program: Focusing on the Fall High Risk Group Elderly Patients
Hyun-Ok Lee, Byung-Hwa Lee, Chang-Hee Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(4): 338. CrossRef - The Effect of Pediatric Inpatient Fall Prevention Education on Caregivers' Fall-related Knowledge and Preventive Behaviors
So Yeon Park, Hyeon Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2017; 23(4): 398. CrossRef
- Characteristics and Effects of Fall Prevention Interventions among the Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review
- 4,028 View
- 108 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder among School-aged Children in Korea: A Meta-Analysis
- Wan-Ju Park, Shin-Jeong Park, Sung-Dong Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(2):169-182. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was a meta-analysis designed to identify effects of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) interventions in alleviating main symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among school-aged children in Korea.
Methods Examination of several databases including Research Information Sharing Service, Korean Studies Information Service System, Data Base Periodical Information Academic and hand-searched article references, resulted in identification of 1,298 studies done between 2000 and 2013 of which 21 met the inclusion criteria. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis version 2.0 was used to analyze effect sizes, explore possible causes of heterogeneity, and check publication bias with a funnel plot and its trim-and-fill analysis.
Results Overall effect size of CBT intervention was large (g=1.08) along with each outcome of self-control (g=1.26), lack of attention (g=1.02), social skills (g=0.92), and hyperactivity (g=0.92). For heterogeneity, moderator analysis was performed, but no significant differences were found between the RCT (Randomized Controlled Trials) group and the NRCT (Non RCT) group. Also, meta-regression was performed using sample size, number of sessions, and length of session as predictors, but no statistically significant moderators were found. Finally, a funnel plot along with trim-and-fill analysis was produced to check for publication bias, but no significant bias was detected.
Conclusion Based on these findings, there is clear evidence that CBT intervention has significant positive effects on the main symptoms of school-aged children suffering ADHD. Further research is needed to target diverse age groups with ADHD along with more RCT studies to improve the effectiveness of the CBT intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- CBT, parent training, and combined approaches for children with ADHD: A randomized study
Burcu Hafiz Ahmet, Alperen Bıkmazer, Vahdet Gormez
Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice.2026; 99(1): 149. CrossRef - Towards Understanding the Effect of Serious Games on Attention, Adherence, and Behavior for Children with ADHD
Jonathan Wang Liu, Mahmood Jasim, Jeong-Heon Song, So-Hwi Ha, Jun-Su Kim, Dayoung Kim, Hyunsuk Lee, Byeong Il Kim, Hee-Tae Jung
ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction.2026; 33(1): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sensory integration therapy in children, focusing on Korean children: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Seri Oh, Jong-Sik Jang, A-Ra Jeon, Geonwoo Kim, Mihwa Kwon, Bahoe Cho, Narae Lee
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(7): 1260. CrossRef - Trends in South Korean Medical Device Development for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Narrative Review
Yunah Cho, Sharon L Talboys
JMIR Biomedical Engineering.2024; 9: e60399. CrossRef - Self-management training vs. neurofeedback interventions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Results of a randomized controlled treatment study
Ann-Kathrin Korfmacher, Oliver Hirsch, Mira-Lynn Chavanon, Björn Albrecht, Hanna Christiansen
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of hippotherapy on children with cerebral palsy: systematic review and meta-analysis
Kwon-Hoi Kim, Suk-Min Lee
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2020; 9(1): 55. CrossRef - Effect of aquatic exercise on gait in persons with chronic stroke: a meta-analysis study in Korea
Dong-Jin Lee, Sung-Hyoun Cho
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2019; 8(2): 112. CrossRef - Risk and protective factors for the development of ADHD symptoms in children and adolescents: Results of the longitudinal BELLA study
Anne Wüstner, Christiane Otto, Robert Schlack, Heike Hölling, Fionna Klasen, Ulrike Ravens-Sieberer, Kenji Hashimoto
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0214412. CrossRef - A Meta Analysis on Variables related to Death Anxiety of Elderly in Korea
Sinhyang Kim, Kyung Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(2): 156. CrossRef - A Meta-analysis of Intervention Studies on the Effects of Self Management and Education in Adult Asthmatic Patients
Chae-Bong Kim, Min-Kyung Han, Mi-Seon Jeong, Bo-Young Choi, Kil-Yong Choi, Moo-Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(3): 175. CrossRef - Effects of a Social Skills Training Program on Problem Behaviors, Social Skill, and Peer Relationship in Children using a Community Child Center at Vulnerable Area
Myeong-Hui Choe, Yong-Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2015; 24(3): 156. CrossRef - Clinical Application of the Korean Personality Rating Scale for Children in Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Woon Yoon, Kee-Jeong Park, Kukju Kweon, Hyo-Won Kim
Journal of the Korean Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.2015; 26(3): 217. CrossRef
- CBT, parent training, and combined approaches for children with ADHD: A randomized study
- 3,329 View
- 49 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Predictive Validity of the Braden Scale for Pressure Ulcer Risk: A Meta-analysis
- Seong-Hi Park, Yu-Sun Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(6):595-607. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.595
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The Braden Scale is one of the most intensively studied risk assessment scales used in identifying the risk of developing pressure sore. However, not all studies show that the predictive validity of this scale is sufficient. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the Braden Scale for predicting pressure ulcer development.
Methods Articles published 1946 and 2013 from periodicals indexed in Ovid Medline, Embase, CINAHL, KoreaMed, NDSL and other databases were selected, using the following keywords: 'pressure ulcer'. The QUADAS-II was applied to assess the internal validity of the diagnostic studies. Selected studies were analyzed using meta-analysis with MetaDisc 1.4.
Results Thirty-eight diagnostic studies with high methodological quality, involving 17,934 patients, were included. Results of the meta-analysis showed that the pooled sensitivity and specificity of the Braden Scale were 0.74 (95% CI: 0.72-0.76), 0.75 (95% CI: 0.74-0.76) respectively. However the predictive validity of the Braden Scale has limitation because there was high heterogeneity between studies.
Conclusion The Braden Scale's predictive validity of risk for pressure ulcer is interpreted as at a moderate level. However there is a limitation to the interpretation of the results, because of high heterogeneity among the studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Pressure Injury Machine Learning Prediction Model and Integration into Clinical Practice: A Prediction Model Development and Validation Study
Ju Hee Lee, Jae Yong Yu, So Yun Shim, Kyung Mi Yeom, Hyun A Ha, Se Yong Jekal, Ki Tae Moon, Joo Hee Park, Sook Hyun Park, Jeong Hee Hong, Mi Ra Song, Won Chul Cha
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 191. CrossRef - The Interrater Agreement for the Assessment of Pressure Ulcer Risk Using the Braden Scale and the Classification of Pressure Ulcers by Nurses in A Medium-Sized Hospital
Hyung-Ju Na, Sung-Hee Yoo, Young-Ran Kwon, Min-Jeng Ahn
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(1): 35. CrossRef - A prediction tool for hospital‐acquired pressure ulcers among surgical patients: Surgical pressure ulcer risk score
Fazila Aloweni, Shin Yuh Ang, Stephanie Fook‐Chong, Nurliyana Agus, Patricia Yong, Meh Meh Goh, Lisa Tucker‐Kellogg, Rick Chai Soh
International Wound Journal.2019; 16(1): 164. CrossRef - Predictive Validity of Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Scales among Patients in a Trauma Intensive Care Unit
Ja Eun Choi, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 26. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on Illness Experience of Patients with Pressure Ulcer
Misoo Yoo, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(5): 515. CrossRef
- Development of a Pressure Injury Machine Learning Prediction Model and Integration into Clinical Practice: A Prediction Model Development and Validation Study
- 3,385 View
- 26 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of Dignity Interventions on Psychosocial and Existential Distress in Terminally ill Patients: A Meta-analysis
- Pok Ja Oh, Sung-Rae Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(5):471-483. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.471
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to evaluate the effects of dignity interventions on depression, anxiety and meaning of life in terminally ill patients.
Methods PubMed, Cochrane Library CENTRAL, EMBASE, CINAHL and several Korean databases were searched. The main search strategy combined terms indicating dignity intervention, presence of terminal illness and study design. Methodological quality was assessed using Cochrane's Risk of Bias for randomized studies and Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non randomized studies. Data were analyzed by the RevMan 5.2.11 program of Cochrane Library.
Results Twelve clinical trials met the inclusion criteria with a total of 878 participants. Dignity intervention was conducted for a mean of 2.2 weeks, 2.8 sessions and an average of 48.7 minutes per session. Effect sizes were heterogeneous and subgroup analysis was done. Dignity interventions had a significant effect on depression (ES=-1.05,
p <.001, I2=15%) and anxiety (ES=-1.01,p <.001, I2=0). For meaning of life, dignity interventions were effective (ES=-1.64,p =.005) and effect sizes were still heterogeneous.Conclusion Results support findings that dignity interventions can assist terminal ill patients in reducing emotional distress and improving meaning of life. Further well-designed dignity studies will lead to better understanding of the effects of treatments on spiritual well-being.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of dignity therapy on meaning in life scores of cancer patients in palliative care
Michelle Uchida Miwa, Carlos Eduardo Paiva, Ana Julia Sucupira Ferreira, Miguel Julião, Harvey Max Chochinov, Welinton Yoshio Hirai, Ricardo dos Reis, Bianca Sakamoto Ribeiro Paiva
Palliative and Supportive Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of meaning in life and individual characteristics on dignity in patients with advanced cancer in China: a cross-sectional study
Xiaocheng Liu, Zhili Liu, Qinqin Cheng, Nuo Xu, Hui Liu, Wenjuan Ying
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(5): 2319. CrossRef - Effectiveness of dignity therapy for patients with advanced cancer: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials
Yanfei Li, Xiuxia Li, Liangying Hou, Liujiao Cao, Guanghua Liu, Kehu Yang
Depression and Anxiety.2020; 37(3): 234. CrossRef - Mechanisms Behind Religiosity and Spirituality’s Effect on Mental Health, Quality of Life and Well-Being
Mario Fernando Prieto Peres, Helder H. Kamei, Patricia R. Tobo, Giancarlo Lucchetti
Journal of Religion and Health.2018; 57(5): 1842. CrossRef
- Effect of dignity therapy on meaning in life scores of cancer patients in palliative care
- 1,185 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Review of Meta-analysis Research on Exercise in South Korea
- Youngshin Song, Moonhee Gang, Sun-Ae Kim, In-Soo Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(5):459-470. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.459
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the quality of meta-analysis regarding exercise using Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR) as well as to compare effect size according to outcomes.
Methods Electronic databases including the Korean Studies Information Service System (KISS), the National Assembly Library and the DBpia, HAKJISAand RISS4U for the dates 1990 to January 2014 were searched for 'meta-analysis' and 'exercise' in the fields of medical, nursing, physical therapy and physical exercise in Korea. AMSTAR was scored for quality assessment of the 33 articles included in the study. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-test, ANOVA and χ2-test.
Results The mean score for AMSTAR evaluations was 4.18 (SD=1.78) and about 67% were classified at the low-quality level and 30% at the moderate-quality level. The scores of quality were statistically different by field of research, number of participants, number of databases, financial support and approval by IRB. The effect size that presented in individual studies were different by type of exercise in the applied intervention.
Conclusion This critical appraisal of meta-analysis published in various field that focused on exercise indicates that a guideline such as the PRISMA checklist should be strongly recommended for optimum reporting of meta-analysis across research fields.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of sensory integration therapy in children, focusing on Korean children: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Seri Oh, Jong-Sik Jang, A-Ra Jeon, Geonwoo Kim, Mihwa Kwon, Bahoe Cho, Narae Lee
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(7): 1260. CrossRef - A Methodological Quality Evaluation of Meta-Analyses on Nursing Home Research: Overview and Suggestions for Future Directions
In-Soo Shin, Juh-Hyun Shin, Dong-Eun Jang, Jiyeon Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(1): 505. CrossRef - Methodological Quality Assessment of Meta-Analyses in the Field of Korean Occupational Therapy Using the Korean Journal of Occupational Therapy
Yoo-Im Choi, Se-Yun Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2020; 28(3): 71. CrossRef - Methodological Qualitative Evaluation of Meta-analysis Studies in Sport Management
Sanghyun Park, Minseok Kwag
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(1): 247. CrossRef - Evaluation of methodological quality of meta-analysis studies in early childhood education
PARK SEO-HYUN
Korean Journal of Early Childhood Education.2018; 38(5): 131. CrossRef - The Feature of the Program components in the Meta Analysis Research: Evidence Based Program Development Perspective
In Hae Seo, Kong Gye-Soon
Korean Journal of Social Welfare Studies.2018; 49(3): 247. CrossRef - Trends in Evidence-based Nursing Research in South Korea
Seang Ryu, Sun Weon Yun, Yun Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(4): 385. CrossRef - A Quality Assessment of Systematic Review of Oriental Medicine in South Korea
Yun-Young Kim, Hye Sun Hyun
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(10): 549. CrossRef - Methodological Quality of Meta-Analyses on the Elderly in Korea
송영신, 김선애, 강문희
Korean Journal of Local Government & Administration Studies.2014; 28(4): 349. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of sensory integration therapy in children, focusing on Korean children: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1,185 View
- 3 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Cortisol and Immune Parameters in Patients with Cancer: A Meta-analysis
- Pok Ja Oh, Eun-su Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):446-457. Published online August 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.446
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to evaluate the effects of psychosocial interventions on cortisol and immune response in adult patients with cancer.
Methods MEDLINE via PubMed, Cochrane Library CENTRAL, EMBASE, CINAHL and domestic electronic databases were searched. Twenty controlled trials (11 randomized and 9 non-randomized trials) met the inclusion criteria with a total of 862 participants. Methodological quality was assessed using the Cochrane's Risk of Bias for randomized studies and the Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non randomized studies. Data were analyzed using the RevMan 5.2.11 program of Cochrane library.
Results Overall, study quality was moderate to high. The weighted average effect size across studies was -0.32 (95% CI [-0.56, -0.07],
p =.010, I2=45%) for cortisol concentration, -0.62 (95%CI [-0.96,-0.29],p <.001, I2=0%) for T lymphocyte (CD3) and -0.45 (95%CI [-0.74, -0.16],p =.003, I2=0%) for Th lymphocyte (CD4) numbers. Psychosocial interventions were not effective for Tc lymphocyte (CD4), NK cell, monocyte, and cytokine response.Conclusion Although these results provide only small evidence of successful immune modulation, they support the conclusion that psychosocial interventions can assist cancer patients in reducing emotional distress and improving immune response.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Depression and Cancer (literature review)
A. N. Blinkov
V.M. BEKHTEREV REVIEW OF PSYCHIATRY AND MEDICAL PSYCHOLOGY.2020; (2): 16. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of psychosocial interventions on survival time in patients with cancer
P.J. Oh, S.R. Shin, H.S. Ahn, H.J. Kim
Psychology & Health.2016; 31(4): 396. CrossRef - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Primary Insomnia: A Meta-analysis
Ji-Hyun Kim, Pok-Ja Oh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 407. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - Effects of Non-pharmacological Interventions on Primary Insomnia in Adults Aged 55 and Above: A Meta-analysis
Ji Hyun Kim, Pok Ja Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(1): 13. CrossRef - The Effect of a Community-Based Self-Management Program for Patients at Thyroid Cancer-Diagnosis Stage : a Pilot Study
Hyera Yoo, Sunjoo Boo, Mison Chun, Eun Mi Jo
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(3): 582. CrossRef - Effects of Dignity Interventions on Psychosocial and Existential Distress in Terminally ill Patients: A Meta-analysis
Pok Ja Oh, Sung-Rae Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 471. CrossRef
- Depression and Cancer (literature review)
- 1,324 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Diagnostic Accuracy of Infrared Thermometer when Identifying Fever in Children
- Young Joo Park, Seong-Hi Park, Chang-Bum Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(6):746-759. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.746
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Infrared thermometers are increasingly used as a convenient, non-invasive assessment method for febrile children. However, the diagnostic accuracy of the infrared thermometer for children has been questioned, particularly in relation to sensitivity and specificity. The aim of this study was to evaluate diagnostic accuracy of infrared thermometers in febrile children.
Methods Articles published between 1966 and 2012 from periodicals indexed in the Ovid Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane, KoreaMed, NDSL, KERIS and other databases were selected, using the following keywords: 'infrared thermometer'. The QUADAS-II was applied to assess the internal validity of the diagnostic studies. Selected studies were analyzed using meta-analysis with MetaDisc 1.4.
Results Nineteen diagnostic studies with high methodological quality, involving 4,304 children, were included. The results of meta-analysis showed that the pooled sensitivity, specificity and AUC (Area Under the Curve) of infrared tympanic thermometers in children over 1 year were 0.80 (95% CI 0.78, 0.81), 0.94 (95% CI 0.93, 0.95) and 0.95 respectively. However the diagnostic accuracy of infrared tympanic thermometers in children with hyperthermia was low.
Conclusion The diagnostic accuracy of infrared tympanic thermometer was similar to axillary and rectal thermometers indicating a need for further research to substantiate these findings in children with hyperthermia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Accuracy of Non-Contact Forehead Infrared Thermometer Measurement in Children: An Observational Study
Yeon-Mi Kim, Myung-Roul Jang, Ju-Ryoung Moon, Goeun Park, Ye-Jin An, Jeong-Meen Seo
Children.2022; 9(9): 1389. CrossRef - Axillary temperature measurements based on smart wearable thermometers in South Korean children: comparison with tympanic temperature measurements
Younglee Choi, Hye Young Ahn
Child Health Nursing Research.2022; 28(1): 62. CrossRef - Smart Patch for Skin Temperature: Preliminary Study to Evaluate Psychometrics and Feasibility
Heejung Kim, Sunkook Kim, Mingoo Lee, Yumie Rhee, Sungho Lee, Yi-Rang Jeong, Sunju Kang, Muhammad Naqi, Soyun Hong
Sensors.2021; 21(5): 1855. CrossRef - Role of materiovigilance in COVID era
Ahmad Najmi, Shilpa Kaore, Balakrishnan Sadasivam, Avik Ray
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 10(7): 2722. CrossRef - Force protection in contingency operations: an evaluation of temperature monitoring in Sierra Leone
Catherine Cole, C Turnbull, W Eardley, P Hunt
Journal of the Royal Army Medical Corps.2016; 162(3): 176. CrossRef
- Clinical Accuracy of Non-Contact Forehead Infrared Thermometer Measurement in Children: An Observational Study
- 2,423 View
- 27 Download
- 5 Crossref

- A Quality Assessment of Meta-Analyses of Nursing in South Korea
- Jung-Hee Kim, Ae-Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(6):736-745. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.736
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to assess the quality of meta-analyses on nursing published in South Korea.
Methods Relevant meta-analyses were identified through searches of the National Assembly Library, KISS (Korean Studies Information Service System), and the DBpia and RISS4U databases from 1990 to May 2013. Quality assessments were conducted using AMSTAR, a validated tool for assessing the quality of systematic reviews.
Results Forty-two meta-analyses were included in this study. Twenty-nine published between 1990 and 2010, and 13, between 2011 and May 2013. Two high quality studies and 11 moderate quality studies were published in the latter period. The mean score for the reviews was 5.61 (range 3-10); 11 studies were rated as low quality, 29 as moderate quality, and two as high quality.
Conclusion Although an improvement in the quality of meta-analyses conducted by nursing researchers in South Korea was observed across the study period, the study results indicate a need to use of more rigorous research methods when conducting systematic reviews or meta-analyses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies on extended reality-based pediatric nursing simulation program development
Eun Joo Kim, Ji Young Lim, Geun Myun Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(1): 24. CrossRef - Methodological Quality Assessment of Meta-Analyses in the Field of Korean Occupational Therapy Using the Korean Journal of Occupational Therapy
Yoo-Im Choi, Se-Yun Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2020; 28(3): 71. CrossRef - Methodological Qualitative Evaluation of Meta-analysis Studies in Sport Management
Sanghyun Park, Minseok Kwag
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(1): 247. CrossRef - Recent Research Trends in Meta-analysis
In-Soo Shin
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(2): 79. CrossRef - Trends in Evidence-based Nursing Research in South Korea
Seang Ryu, Sun Weon Yun, Yun Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(4): 385. CrossRef - A Quality Assessment of Systematic Review of Oriental Medicine in South Korea
Yun-Young Kim, Hye Sun Hyun
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(10): 549. CrossRef - The Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses on the Effectiveness of Non-pharmacological Cancer Pain Management
Youngshin Song, Minhye Oh, Seyeon Park, Myouyun Park, Kyoungok Kim, Ukyoung Lee, Myonghwa Park
Pain Management Nursing.2015; 16(5): 781. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Interventions for Fall Prevention in Hospitalized Patients: A Meta-analysis
Yoon Lee Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 469. CrossRef - Review of Meta-analysis Research on Exercise in South Korea
Youngshin Song, Moonhee Gang, Sun-Ae Kim, In-Soo Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 459. CrossRef
- A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies on extended reality-based pediatric nursing simulation program development
- 1,220 View
- 2 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Meta- analysis of Psychosocial Interventions to Reduce Pain in Patients with Cancer
- Pok Ja Oh, Suk Jung Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(5):658-668. Published online October 15, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.658
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of psychosocial interventions on pain in cancer patients.
Methods Eight studies published between 1980 and 2012 in Korean and ten studies published between 2002 and 2012 in English met the inclusion criteria with a total of 1539 participants. Methodological quality assessed by Cochrane's Risk of Bias for randomized studies and Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non randomized studies. The data were analyzed by the RevMan 5.2 program of Cochrane library.
Results Overall, study quality was moderate to high. Effect sizes were heterogeneous and subgroup analysis was done. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) were effective for pain (ES= -0.35; 95% CI= -0.56, -0.13). Pain education studies measured with NRS and VAS were effective for pain (ES= -0.77; 95% CI= -1.01, -0.52). Publication bias was not detected.
Conclusion This study support the use of psychosocial interventions administered to cancer patients for their pain management. However, more well-designed studies are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Good Nursing Experience of Patients with Cancer in a Korean Cancer Hospital
Eunyoung E. Suh, Hye Jin Yoo, Jeong Hee Hong, In Gak Kwon, Hyunju Song
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(3): 51. CrossRef - Managing Cancer Pain, Monitoring for Cancer Recurrence, and Mitigating Risk of Opioid Use Disorders: A Team-Based, Interdisciplinary Approach to Cancer Survivorship
Eric R. Goodlev, Sandra Discala, Beth D. Darnall, Molly Hanson, Alison Petok, Michael Silverman
Journal of Palliative Medicine.2019; 22(11): 1308. CrossRef - Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(2): 143. CrossRef - The Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses on the Effectiveness of Non-pharmacological Cancer Pain Management
Youngshin Song, Minhye Oh, Seyeon Park, Myouyun Park, Kyoungok Kim, Ukyoung Lee, Myonghwa Park
Pain Management Nursing.2015; 16(5): 781. CrossRef - Setting a Health Policy Research Agenda for Controlling Cancer Burden in Korea
Sung-In Jang, Kyoung-Hee Cho, Sun Jung Kim, Kwang-Sig Lee, Eun-Cheol Park
Cancer Research and Treatment.2014; 47(2): 149. CrossRef
- Good Nursing Experience of Patients with Cancer in a Korean Cancer Hospital
- 1,483 View
- 13 Download
- 5 Crossref

- A Meta-analysis of the Effect of Walking Exercise on Lower Limb Muscle Endurance, Whole Body Endurance and Upper Body Flexibility in Elders
- Kook-Hee Roh, Hyeoun-Ae Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(4):536-546. Published online August 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.536
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine whether walking exercise improved physical function in elderly people using meta-analysis.
Methods Medical and nursing literature databases were searched to identify the studies on the effectiveness of walking exercise on physical function. In the databases, there were 16 articles reporting 21 interventions. Overall effect sizes for three outcome variables, elders' physical function in lower limb muscle endurance, whole body endurance and upper body flexibility, were calculated. Effects of study characteristics on outcome variables were analyzed.
Results The meta-analysis showed that walking exercise generally had positive effects on CST (chair stand test), 6MW (6 min walking), and SRT (standing or sitting reach test) with overall weighted effect sizes of 1.06, 0.41 and 0.29 respectively. This study also showed that the chronic disease status of the elders, intervention methods, and type of residence had different effects on CST, 6MW and SRT.
Conclusion The results indicate that walking exercise improves physical function in elders. Walking exercise which can be done at any time and any location is indeed a very effective exercise for elderly people.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Protein Intake and Physical Activity on Hand Grip Strength in the Older Adults Aged over 65 Years of Age: Using Data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Do-Yeon Kim, Byung-Sun Choi
Korean Journal of Geriatrics & Gerontology.2025; 26(1): 23. CrossRef - Objectively measured the impact of ambient air pollution on physical activity for older adults
Jiali Cheng, Yin Wu, Xiaoxin Wang, Hongjun Yu
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of walking exercise on cognitive and physical functions: meta-analysis of older adults
Mi Jin Lee, Hee Ju Ro, Jung Kee Choi, So Yeon Kim
Forest Science and Technology.2024; 20(2): 201. CrossRef - A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Walking Exercise on Depression
Jonghwa Lee, Youngho Kim
The Asian Journal of Kinesiology.2023; 25(4): 12. CrossRef - Effect of Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercise Training on Depressive Symptoms, Quality of Life, and Muscle Strength in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Ahmad Mahmoudi, Farahnaz Amirshaghaghi, Reza Aminzadeh, Ehsan Mohamadi Turkmani
Biological Research For Nursing.2022; 24(4): 541. CrossRef - Multimorbidity and associations with clinical outcomes in a middle-aged population in Iran: a longitudinal cohort study
Maria Lisa Odland, Samiha Ismail, Sadaf G Sepanlou, Hossein Poustchi, Alireza Sadjadi, Akram Pourshams, Tom Marshall, Miles D Witham, Reza Malekzadeh, Justine I Davies
BMJ Global Health.2022; 7(5): e007278. CrossRef - Effects of a Physical Exercise Program on Physiological, Psychological, and Physical Function of Older Adults in Rural Areas
Sunmi Kim, Eun-Jee Lee, Hyeon-Ok Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8487. CrossRef - Comparison of the Effects of Education Only and Exercise Training Combined with Education on Fall Prevention in Adults Aged 70 Years or Older Residing in Elderly Residential Facilities
Chahwa Hong, Haejung Lee, Misoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 173. CrossRef - The Effects of Forest Healing Anti-aging Program on Physical Health of the Elderly: A Pilot Study
Ji-Eun Baek, Ho-jin Shin, Sung-Hyeon Kim, Jae Yeon Kim, Sujin Park, Si-Yoon Sung, Hwi-young Cho, Suk-Chan Hahm, Min-Goo Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Physical Medicine.2021; 16(2): 81. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life in the Korean Seniors with Lower Education Level: Focusing on Physical Activity Types
Hye Young Choi, Guna Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(3): 292. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior‐based multifaceted intervention on patient activation and osteoarthritis symptoms
Yang Heui Ahn, Ok Kyung Ham
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Sand Exercise Program on Balance Capability, Extremity Muscle Activity, and Inflammatory Markers in Older Women
Sung-Soo Lee, Yong-Seok So
Exercise Science.2019; 28(2): 131. CrossRef - Physical activity in older age: perspectives for healthy ageing and frailty
Jamie S. McPhee, David P. French, Dean Jackson, James Nazroo, Neil Pendleton, Hans Degens
Biogerontology.2016; 17(3): 567. CrossRef - Literature Review for the Effects of Physical Activity on Musculoskeletal Outcomes in Community-dwelling Older Adults
Kyung Choon Lim, Jeung-Im Kim, Young Ran Chae
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(4): 297. CrossRef
- Effects of Protein Intake and Physical Activity on Hand Grip Strength in the Older Adults Aged over 65 Years of Age: Using Data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,306 View
- 25 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Effect of Kegel Exercise to Prevent Urinary and Fecal Incontinence in Antenatal and Postnatal Women: Systematic Review
- Seong-Hi Park, Chang-Bum Kang, Seon Young Jang, Bo Yeon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(3):420-430. Published online June 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.420
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to review the literature to determine whether intensive pelvic floor muscle training during pregnancy and after delivery could prevent urinary and fecal incontinence.
Methods Randomized controlled trials (RCT) of low-risk obstetric populations who had done Kegel exercise during pregnancy and after delivery met the inclusion criteria. Articles published between 1966 and 2012 from periodicals indexed in Ovid Medline, Embase, Scopus, KoreaMed, NDSL and other databases were selected, using the following keywords: 'Kegel, pelvic floor exercise'. The Cochrane's Risk of Bias was applied to assess the internal validity of the RCT. Fourteen selected studies were analyzed by meta-analysis using RevMan 5.1.
Results Fourteen RCTs with high methodological quality, involving 6,454 women were included. They indicated that Kegel exercise significantly reduced the development of urinary and fecal incontinence from pregnancy to postpartum. Also, there was low clinical heterogeneity.
Conclusion There is some evidence that for antenatal and postnatal women, Kegel exercise can prevent urinary and fecal incontinence. Therefore, a priority task is to develop standardized Kegel exercise programs for Korean pregnant and postpartum women and make efficient use of these programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrasound Quantitative Assessment of the Effects of Yoga on Early Postpartum Pelvic Organ Position Recovery
Qunfeng Li, Yanhong Liu, Yunli Liu, Qiongzhu Liu, Liping Jiang, Xinling Zhang
International Urogynecology Journal.2025; 36(1): 221. CrossRef - Reliability of Digital Palpation to Perineometeric Scoring for Assessment of Pelvic Floor Muscle Strength: A Comparative Study
Alisha Rai, Sanjeev Kumar Jain, Nidhi Sharma, Astha Lalwani, Sonika Sharma
Gynecology and Minimally Invasive Therapy.2025; 14(3): 223. CrossRef - The Effect of Kegel Exercises and Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy on the
Improvements of Stress Urinary Incontinence and Urge Incontinence in
Women with Normal Vaginal Delivery
Radnia Nahid, Bakhtiari Mahsa, Neda Alimohammadi, Moghadami Samar
Current Womens Health Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of self-reported ability to perform Kegel’s exercise pre- and post-coital penetration in postpartum women
Chidiebele Petronilla Ojukwu, Ginikachukwu Theresa Nsoke, Stephen Ede, Anne Uruchi Ezeigwe, Sylvester Caesar Chukwu, Emelie Morris Anekwu
Libyan Journal of Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, attitudes, and practice of pelvic floor dysfunction and pelvic floor ultrasound among women of childbearing age in Sichuan, China
Xiaoli Wu, Xiaohong Yi, Xiu Zheng, Zeling Chen, Junxi Liu, Xiong Dai
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Kegel Exercises on Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Young Gymnasts: A Prospective Cohort Study
Celia Rodríguez-Longobardo, Amelia Guadalupe-Grau, Miguel Ángel Gómez-Ruano, Olga López-Torres
Urogynecology.2023; 29(8): 670. CrossRef - Improving the Technique of Pelvic Floor Muscle Contraction in Active Nulliparous Women Attending a Structured High–Low Impact Aerobics Program—A Randomized Control Trial
Magdalena Piernicka, Monika Błudnicka, Damian Bojar, Jakub Kortas, Anna Szumilewicz
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5911. CrossRef - Comparison of postpartum incontinence outcomes after vacuum-assisted and forceps-assisted deliveries in a tertiary maternity unit
Li Shan Sng, Wan Hui Yip, Stella Yan Chai Hong, Stephanie Man Chung Fook-Chong, Wei Keat Andy Tan, Devendra Kanagalingam, Jason Shau Khng Lim
International Urogynecology Journal.2022; 33(6): 1529. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Pregnant Women in Jazan, Saudi Arabia Concerning Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
Sarra L Derrar, Fatimah H Dallak, Azhar Alfaifi, Rawan M Alessa, Khawlah A Abbas, Atyaf J Zurayyir, Ahmed A Altraifi, Ibrahim Gosadi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Structured teaching programme on knowledge regarding Pelvic floor muscle exercises in prevention of Urinary incontinence among premenopausal women admitted in selected hospital Bangalore
Christina Jose, Christina Rachel C., Della Mathew, Deva Prasanna, Dolma Lhakyi, Dona Elizabeth Mathew, Ethel Deenah Hazel, Grace Ninan, Indumathi Anbalagan, Jismi Thomas, Josmy Jose
Asian Journal of Nursing Education and Research.2021; : 307. CrossRef - What Is Fecal Incontinence That Urologist Need to Know?
HongWook Kim, Jisung Shim, Yumi Seo, Changho Lee, Youngseop Chang
International Neurourology Journal.2021; 25(1): 23. CrossRef - Effects of yoga on the intervention of levator ani hiatus in postpartum women: a prospective study
Qunfeng Li, Xinling Zhang
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2021; 33(11): 862. CrossRef - High-impact aerobics programme supplemented by pelvic floor muscle training does not impair the function of pelvic floor muscles in active nulliparous women
Magdalena Piernicka, Monika Błudnicka, Jakub Kortas, Barbara Duda-Biernacka, Anna Szumilewicz
Medicine.2021; 100(33): e26989. CrossRef - Development of an exercise attitude scale in Turkish for pregnant women: validity and reliability
Seyda Toprak Celenay, Esra Calik Var, Derya Ozer Kaya
Women & Health.2021; 61(9): 854. CrossRef - Predictors of pelvic muscle exercise on the self‐efficacy of women giving birth
Gisoo Shin, Hye Jin Kim, Miok Kim
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2020; 14(2): 67. CrossRef - Vaginal hyperlaxity syndrome: a new concept and challenge
Santiago Palacios
Gynecological Endocrinology.2018; 34(5): 360. CrossRef - Effect of Pila-dance to Ease Urinary Incontinence of Middle-aged Women
Hye-Jeon Hong
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(2): 431. CrossRef - Faecal incontinence: Current knowledges and perspectives
Alban Benezech
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology.2016; 7(1): 59. CrossRef - Effects of Prenatal Perineal Massage and Kegel Exercises on the Integrity of Postnatal Perine
Sevgul Dönmez, Oya Kavlak
Health.2015; 07(04): 495. CrossRef - A Study on Fecal Incontinence and Depression of Rural Women
Chunmi Kim, Hung Sa Lee, Eun Man Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(3): 198. CrossRef
- Ultrasound Quantitative Assessment of the Effects of Yoga on Early Postpartum Pelvic Organ Position Recovery
- 2,262 View
- 82 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Effects of Tai Chi on Fall Risk Factors: A Meta-Analysis
- Moonkyoung Park, Rhayun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(3):341-351. Published online June 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.341
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to analyze the effects of Tai Chi on fall-related risk factors through meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials published in English and Korean between 2000 and 2010.
Methods Using health related database and hand search of references and Google, 28 randomized studies were collected from doctoral dissertation and published peer reviewed articles. The Comprehensive Meta-analysis version 2.0 was used for the analysis.
Results The effect sizes for Tai Chi for 3 months were significant with ES=0.54 for static balance, ES=0.24 for dynamic balance, ES=0.69 for balance measured by scale, and ES=0.40 for flexibility, ES=0.48 for muscle strength, ES=0.71 for ADL, and ES=0.37 for fear of falling. Also, the effect sizes of Tai Chi for 6 months were significant for most fall-related variables. The 6 month data for flexibility was not analyzed since only one study was published.
Conclusion The analysis of studies of randomized clinical trials indicate that Tai Chi is effective in improving balance, flexibility, muscle strength, activities of daily living, and fear of falling when applied for 3 or 6 months. The findings provide the objective evidence to apply Tai Chi as a fall preventive intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global research on Chinese martial arts (1974–2025): A bibliometric and visualization-based analysis using Web of Science
Wei Chen, Syahrul Ridhwan Morazuki
Medicine.2025; 104(32): e43769. CrossRef - Effects of Tai-Chi and Running Exercises on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Biomarkers in Sedentary Middle-Aged Males: A 24-Week Supervised Training Study
Yi Wang, Xian Guo, Liangchao Liu, Minhao Xie, Wing-Kai Lam
Biology.2022; 11(3): 375. CrossRef - Mind-Body Therapies From Traditional Chinese Medicine: Evidence Map
Lissandra Zanovelo Fogaça, Caio Fabio Schlechta Portella, Ricardo Ghelman, Carmen Verônica Mendes Abdala, Mariana Cabral Schveitzer
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Tai Chi for improving balance and reducing falls: An overview of 14 systematic reviews
Dongling Zhong, Qiwei Xiao, Xili Xiao, Yuxi Li, Jing Ye, Lina Xia, Chi Zhang, Juan Li, Hui Zheng, Rongjiang Jin
Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine.2020; 63(6): 505. CrossRef - Exploring the Adaptability of Tai Chi to Stroke Rehabilitation
Inok Hwang, Rhayun Song, Sukhee Ahn, Myung-ah Lee, Peter M. Wayne, Min Kyun Sohn
Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 44(4): 221. CrossRef - The association between Tai Chi exercise and safe driving performance among older adults: An observational study
Sally Miller, Ruth E. Taylor-Piliae
Journal of Sport and Health Science.2018; 7(1): 83. CrossRef - Adapting Tai Chi for Upper Limb Rehabilitation Post Stroke: A Feasibility Study
Shujuan Pan, Dahlia Kairy, Hélène Corriveau, Michel Tousignant
Medicines.2017; 4(4): 72. CrossRef - The Effects of Tai Chi Practice With Asynchronous Music on Compliance and Fall-Related Risk Factors in Middle-Aged and Older Women: A Pilot Study
Yan Du, Penny Roberts, Qingwen Xu
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2017; 35(2): 142. CrossRef - The Effects of Exercise Intervention for Fall Prevention in Persons with Arthritis: A Meta Analysis
Chun Hee Lee, Heeok Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(6): 587. CrossRef - The correlation between white matter hyperintensity and balance disorder and fall risk: An observational, prospective cohort study
Dong‐Chao Shen, Shuo‐Lin Wu, Yu‐Zhi Shi, Shuo Wang, Yu‐Mei Zhang, Chun‐Xue Wang
Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine.2016; 2(3): 173. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Interventions for Fall Prevention in Hospitalized Patients: A Meta-analysis
Yoon Lee Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 469. CrossRef - The effects of Tai‐Chi in conjunction with thera‐band resistance exercise on functional fitness and muscle strength among community‐based older people
Shu‐Fen Lin, Huei‐Chuan Sung, Tzai‐Li Li, Tsung‐Cheng Hsieh, Hsiao‐Chin Lan, Shoa‐Jen Perng, Graeme D. Smith
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(9-10): 1357. CrossRef - Recent Literature
Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Global research on Chinese martial arts (1974–2025): A bibliometric and visualization-based analysis using Web of Science
- 1,328 View
- 2 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Meta-Analysis of Spiritual Intervention Studies on Biological, Psychological, and Spiritual Outcomes
- Pok-Ja Oh, Young-Hyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(6):833-842. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.6.833
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of spiritual intervention studies by examining biological, psychological, and spiritual outcomes.
Methods From electronic databases 2522 studies were retrieved, of which 21 studies met the inclusion criteria. These studies had 1411 participants. Two authors independently extracted data from the selected studies and assessed the methodological quality. The data were analyzed using the RevMan 5.1 program of the Cochrane library.
Results Overall effect size of spiritual intervention on spiritual and psychological (depression and anxiety) outcomes were moderate (d=-0.65 to d=-0.76,
p <.001). The effects on biological outcomes (pain and functional status) ranged from -0.51 to -0.39, respectively. No publication bias was detected as evaluated by a funnel plot. Spiritual intervention had a moderate effect on psychological and spiritual outcomes and a smaller effect on biological outcomes.Conclusion The results of this study suggest that spiritual intervention can relieve depression and anxiety. Further randomized controlled trials studies are needed to evaluate the effects of spiritual intervention on biological outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Interventions on Death Anxiety and Fear in Adults with Chronic Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Merve Gulbahar Eren, Kübra Üçgül, Havva Sert
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2025; 91(4): 2007. CrossRef - Effects of counselling and spiritual care program on anxiety in patients with chronic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Nader Salari, Mohsen Kazeminia, Alireza Abdi, Amir Abdolmaleki, Nasrin Abdoli, Masoud Mohammadi, Shamarina Shohaimi
Current Psychology.2023; 42(12): 9943. CrossRef - The development of a Cancer Pain Belief Modification Program for patients with oral cancer in China: a feasibility study
Rongna Wang, Xiaoyan Zheng, Xixi Su, Xiuyu Huang, Huangju Liu, Yulai Guo, Ji Gao
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Spiritual Well-being on Self-care Practices in People Undergoing Hemodialysis: The Mediating Effect of Hope
Bu Kyung Kim, Pok-Ja Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(6): 592. CrossRef - Abriendo nuevas puertas: Relevancia clínica de integrar la religión y la espiritualidad en la disciplina de la psicología
Orlando M. Pagan-Torres Ponce
Revista Puertorriqueña de Psicologia.2022; 33(2): 258. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Depression on the Relationship between Social Support, Spirituality and Burnout in Family Members of Patients with Cancer
Won-Hee Jun, Kyung-Sook Cha, Kee-Lyong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1727. CrossRef - Spirituality, religiousness, and mental health: A review of the current scientific evidence
Giancarlo Lucchetti, Harold G Koenig, Alessandra Lamas Granero Lucchetti
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(26): 7620. CrossRef - Analysis of Spiritual Care Experiences of Acute-Care Hospital Nurses
Ga Eon Lee, KyoungMi Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2020; 23(2): 44. CrossRef - The Effect of Religion Intervention on Life Satisfaction and Depression in Elderly with Heart Failure
Alireza Abdi, Askar Soufinia, Milad Borji, Asma Tarjoman
Journal of Religion and Health.2019; 58(3): 823. CrossRef - Initial Assessment and Care Planning in Palliative Hospice Care: Focus on Assessment Tools
Eun Ju Park, Su Jin Koh, Jae Kyung Cheon
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2019; 22(2): 67. CrossRef - Experience of Cancer Patients Receiving Spiritual Nursing Care in one Christian General Hospital
Eun Youngi Seo, Suhye Kwon, Youngkyoung Kim, ALeum Han
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 179. CrossRef - Complementary religious and spiritual interventions in physical health and quality of life: A systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials
Juliane Piasseschi de Bernardin Gonçalves, Giancarlo Lucchetti, Paulo Rossi Menezes, Homero Vallada, Gianni Virgili
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0186539. CrossRef - Panorama das pesquisas em ciência, saúde e espiritualidade
Alexander Moreira-Almeida, Giancarlo Lucchetti
Ciência e Cultura.2016; 68(1): 54. CrossRef - Spirituality is associated with better prostate cancer treatment decision making experiences
Michelle A. Mollica, Willie Underwood, Gregory G. Homish, D. Lynn Homish, Heather Orom
Journal of Behavioral Medicine.2016; 39(1): 161. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Spiritual Care Competence Scale
Mi Ja Chung, Youngrye Park, Young Eun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(6): 871. CrossRef - Influence of Self-esteem, Empathy and Existential Well-being on Spiritual Care Competence in Nursing Students
Jin Kim, Sookyung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(3): 328. CrossRef - Religious and spiritual interventions in mental health care: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
J. P. B. Gonçalves, G. Lucchetti, P. R. Menezes, H. Vallada
Psychological Medicine.2015; 45(14): 2937. CrossRef - The Effects of Spiritual Interventions in Patients With Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Pok-Ja Oh, Soo Hyun Kim
Oncology Nursing Forum.2014; 41(5): E290. CrossRef - Association between Spiritual Well-Being and Pain, Anxiety and Depression in Terminal Cancer Patients: A Pilot Study
Yong Joo Lee, Chul-Min Kim, John A. Linton, Duk Chul Lee, Sang-Yeon Suh, Ah-Ram Seo, Hong-Yup Ahn
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2013; 16(3): 175. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of Psychosocial Interventions to Reduce Pain in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Suk Jung Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 658. CrossRef - Effect of Intervention Programs for Improving Maternal Adaptation in Korea: Systematic Review
Hee Sun Kang, Soo Young Yeom, Eun-Young Jun
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2013; 19(3): 153. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Interventions on Death Anxiety and Fear in Adults with Chronic Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- 1,331 View
- 8 Download
- 21 Crossref

- A Meta-analysis of the Variables related to Depression in Korean Patients with a Stroke
- Eun-Young Park, In-Soo Shin, Jung-Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(4):537-548. Published online August 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.537
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to use meta-analysis to evaluate the variables related to depression in patients who have had a stroke.
Methods The materials of this study were based on 16 variables obtained from 26 recent studies over a span of 10 years which were selected from doctoral dissertations, master's thesis and published articles.
Results Related variables were categorized into sixteen variables and six variable groups which included general characteristics of the patients, disease characteristics, psychological state, physical function, basic needs, and social variables. Also, the classification of six defensive and three risk variables group was based on the negative or positive effect of depression. The quality of life (ES= -.79) and acceptance of disability (ES=-.64) were highly correlated with depression in terms of defensive variables. For risk variables, anxiety (ES= .66), stress (ES= .53) showed high correlation effect size among the risk variables.
Conclusion These findings showed that defensive and risk variables were related to depression among stroke patients. Psychological interventions and improvement in physical functions should be effective in decreasing depression among stroke patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stroke recurrence, uncertainty in illness, and self-efficacy as predictors of post-stroke depression in Korean survivors: a cross-sectional study
Jin-Gyeong Lee, Insook Lee
BMC Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Post-stroke depression risk prediction models in stroke patients: A systematic review
Xiang Zeng, Xiao Juan Chen
General Hospital Psychiatry.2025; 96: 132. CrossRef - The trajectory and influencing factors of disability acceptance in patients with hypertensive intracerebral haemorrhage: a protocol for prospective longitudinal cohort study in Heyuan City, China
Jia Zhang, Xi Liu, Zuolian Zhang
BMJ Open.2024; 14(1): e076314. CrossRef - Acceptance of disability in stroke: a systematic review
Mervyn Jun Rui Lim, Jaclyn Tan, Arturo Yong Yao Neo, Brandon Chin Jie Ng, Miho Asano
Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine.2024; 67(2): 101790. CrossRef - Unravelling the complex interactions between self-awareness, cognitive change, and mood at 6-months post-stroke using the Y-shaped model
Miranda Wheeler, Owen A. Williams, Louise Johns, Evangeline G. Chiu, Elitsa D. Slavkova, Nele Demeyere
Neuropsychological Rehabilitation.2023; 33(4): 680. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Music Therapy on Depression for Stroke Patients
Moonhyang Kim, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(4): 416. CrossRef - Relationships among Self-Care Competency, Presence of Depressive Symptom, and Health-Related Quality of Life of Korean Stroke Patients
Sohyune R. Sok, Eunji Yim, Hyebeen Sim, Hyun Jin Sim
Clinical Nursing Research.2021; 30(5): 670. CrossRef - Socioeconomic Factors Predicting Depression Differ in the Acute Stage and at 1 year After Ischemic Stroke or TIA
Ágnes Mirolovics, Magdolna Bokor, Balázs Dobi, Judit Zsuga, Dániel Bereczki
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2020; 29(11): 105241. CrossRef - Factors Associated to Returning Home in the First Year after Stroke
Seung Han Kim, Yong-Il Shin, Seung Chan Kim, Sung Hwa Ko, Deog Young Kim, Jongmin Lee, Min Kyun Sohn, Sam-Gyu Lee, Gyung-Jae Oh, Yang-Soo Lee, Min Cheol Joo, Eun Young Han, Junhee Han, Won Hyuk Chang, Ji Hong Min, Yun-Hee Kim
Brain & Neurorehabilitation.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of Social Psychological Factors related to Quality of Life in Stroke Patients
Young-Ok Yang, Minju Kim, Kyung-Yeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(4): 510. CrossRef - Recent Research Trends in Meta-analysis
In-Soo Shin
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(2): 79. CrossRef - The Effect of a Movie-Based Nursing Intervention Program on Rehabilitation Motivation and Depression in Stroke Patients
Hye Kyung Kwon, Sook Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - An analysis of depressive symptoms in stroke survivors: verification of a moderating effect of demographic characteristics
Eun-Young Park, Jung-Hee Kim
BMC Psychiatry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The convergent influence of Perceived Stress and the Empowerment on Rehabilitation motive of Stroke patients
Hyo-Jeong Kang, Suhye Kwon, Soon-Chul Youn
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(1): 291. CrossRef - Comparison of Motivation for Rehabilitation, Family Support and Adherence to Rehabilitation between Depressive and Non-depressive Stroke Patients
An Suk Park, Eun Ko, Hee Sun Kang
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(2): 138. CrossRef - The mediating effect of psychological distress on functional dependence in stroke patients
Hui‐Chuan Huang, Li‐Kai Huang, Chaur‐Jong Hu, Chien‐Hung Chang, Hsin‐Chien Lee, Nai‐Fang Chi, Meei‐Ling Shyu, Hsiu‐Ju Chang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2014; 23(23-24): 3533. CrossRef - The Effect of Functional Dependency and Stress on Health-related Quality of Life in Patients under Rehabilitation after Stroke
Ok-Hee Cho, Suyoung Choi, Jihyeun Song
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(2): 81. CrossRef - Social Welfare Approaches for Patients with Diabetes and Stroke
Been Yoo
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(3): 152. CrossRef
- Stroke recurrence, uncertainty in illness, and self-efficacy as predictors of post-stroke depression in Korean survivors: a cross-sectional study
- 1,132 View
- 7 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Meta Analysis of Variables Related to Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in School-Age Children
- Wan Ju Park, Ji Yeong Seo, Mi Ye Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(2):256-268. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.256
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to use meta-analysis to examine recent domestic articles related to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in school-age children.
Methods After reviewing 213 articles published between 1990 and 2009 from and cited in RISS, KISS, and DBpia, the researchers identified 24 studies with 440 research variables that had appropriate data for methodological study. SPSS 17.0 program was used. The outcome variables were divided into five types: Inattention, hyperactive impulsive, intrinsic, extrinsic, and academic ability variables.
Results Effects size of overall core symptoms was 0.47 which is moderate level in terms of Cohen criteria and effects size of overall negative variables related ADHD was 0.27 which is small level. The most dominant variable related to ADHD was obtained from hyperactive-impulsive (0.70). Also academic ability (0.45), inattention (0.37), and intrinsic variables (0.29) had a small effect whereas extrinsic variables (0.13) had little effect on descriptive ADHD study.
Conclusion The results reveal that ADHD core symptoms have moderate effect size and peripheral negative variables related ADHD have small effect size. To improve the reliability of the meta-analysis results by minimizing publication bias, more intervention studies using appropriate study designs should be done.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations between Dietary Intake and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Scores by Repeated Measurements in School-Age Children
Su-a Ryu, Yean-Jung Choi, Hyojin An, Ho-Jang Kwon, Mina Ha, Yun-Chul Hong, Soo-Jong Hong, Hyo-Jeong Hwang
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2919. CrossRef
- Associations between Dietary Intake and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Scores by Repeated Measurements in School-Age Children
- 1,098 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


