Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to reduce internalized stigma in people with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Soyoung Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Myung-Sun Hyun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):1-18. Published online February 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24072
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study systematically reviewed and analyzed the effects of non-pharmacological interventions on internalized stigma among people with severe mental illness.
Methods
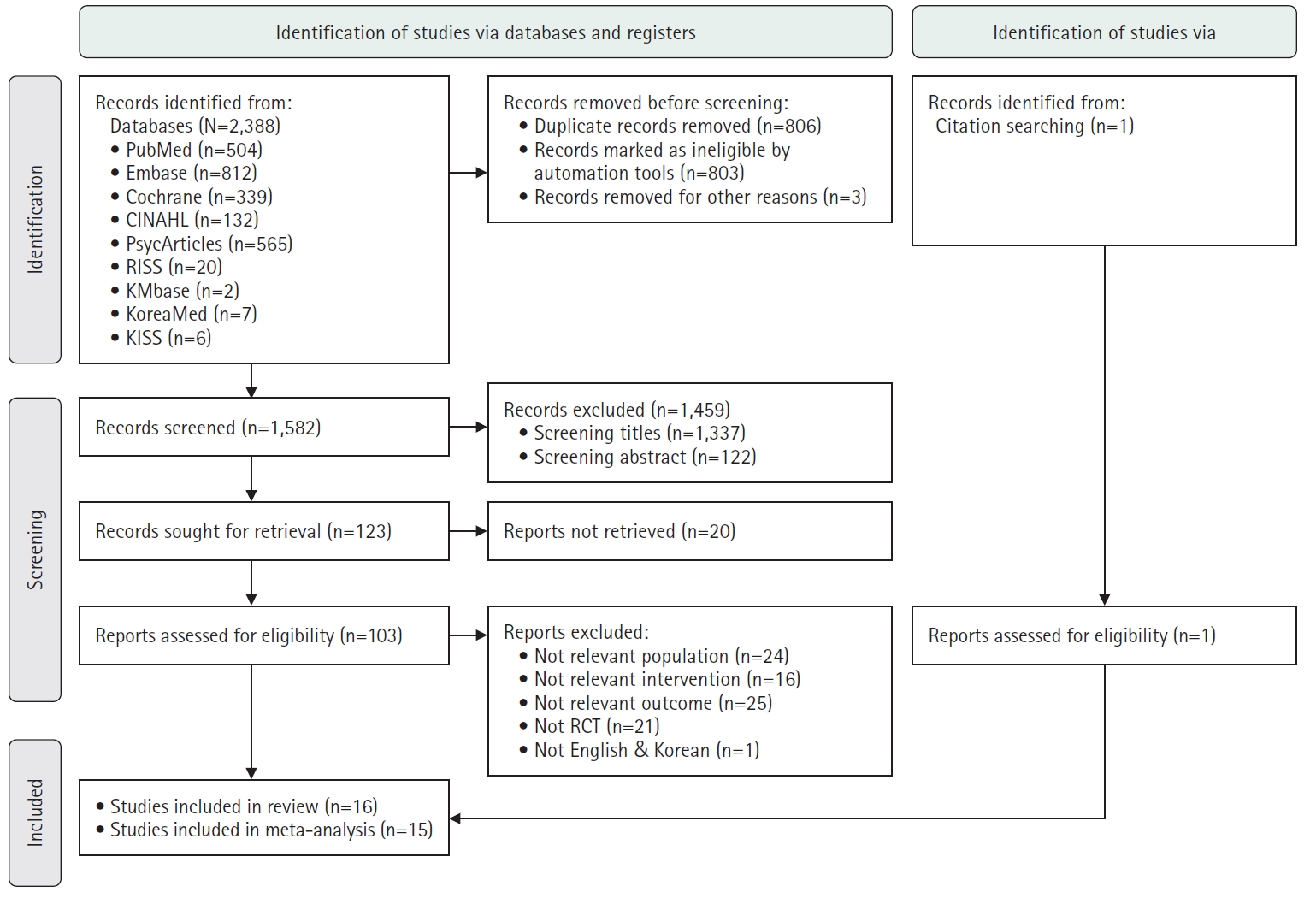
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted following the Cochrane Intervention Research Systematic Review Manual and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis guidelines. This study targeted people with severe mental illness as the population, interventions aimed at reducing internalized stigma, comparisons with control groups, and internalized stigma as the outcome. A literature search was performed across multiple databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycArticles, RISS, KMbase, and KoreaMed. The risk of bias was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool. Effect sizes were computed using Hedges’s g, and subgroup analyses were conducted with Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software version 4.0.
Results
Of 2,388 papers, 15 were included in the meta-analysis. The overall effect size (Hedges’s g) of the intervention was –0.60 (95% confidence interval, –1.01 to –0.19), indicating a statistically significant reduction in internalized stigma (Z=–2.88, p=.004). Subgroup analyses revealed that the intervention type (p=.008) and session length (p=.011) were significant moderators influencing the effectiveness of the interventions.
Conclusion
Tailoring interventions by considering variables such as the intervention type and session length could enhance the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions for reducing internalized stigma among people with severe mental illness (PROSPERO: CRD42023418561).
- 4,874 View
- 355 Download

- Effect of Digital Health Interventions on Psychotic Symptoms among Persons with Severe Mental Illness in Community: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Eunjin Oh, Moonhee Gang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):69-86. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of digital health interventions on the psychotic symptoms among people with severe mental illness in the community.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Cochrane Intervention Research Systematic Review Manual and PRISMA. A literature search was conducted of published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for digital health interventions from January 2022 to April 2022. RevMan software 5.3 was used for quality assessment and meta-analysis.
Results
A total 14 studies out of 9,864 studies were included in the review, and 13 were included in meta-analysis. The overall effect size of digital health interventions on psychotic symptoms was - 0.21 (95% CI = - 0.32 to - 0.10). Sub-analysis showed that the reduction of the psychotic symptoms was effective in the schizophrenia spectrum group (SMD = - 0.22; 95% CI = - 0.36 to - 0.09), web (SMD = - 0.41; 95% CI = - 0.82 to 0.01), virtual reality (SMD = - 0.33; 95% CI = - 0.56 to - 0.10), mobile (SMD = - 0.15; 95% CI = - 0.28 to - 0.03), intervention period of less than 3 months (SMD = - 0.23; 95% CI = - 0.35 to - 0.11), and non-treatment group (SMD = - 0.23; 95% CI = - 0.36 to - 0.11).
Conclusion
These findings suggest that digital health interventions alleviate psychotic symptoms in patients with severe mental illnesses. However, well-designed digital health studies should be conducted in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Mobile App-Based Psychosocial Intervention for Personal and Clinical Recovery for People With Psychosis
Dowon You, Narae Jeong
Korean Journal of Schizophrenia Research.2024; 27(1): 1. CrossRef
- A Review of Mobile App-Based Psychosocial Intervention for Personal and Clinical Recovery for People With Psychosis
- 2,856 View
- 90 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of an Integrated Health Management Program for Psychiatric Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
- Yun Bock Kwak, Ji Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):261-277. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed an integrated health management program for metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients and examined its effects on self-efficacy, healthy lifestyle, physiological indicators, knowledge of metabolic syndrome, attitudes toward healthy behavior, and social support.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pretest posttest design was used. The participants were 65 psychiatric patients with metabolic syndrome in psychiatric rehabilitation centers, with 33 in the experimental group and 32 in the control group. The experimental group participants engaged in daily mobile application and walking exercises three times a week for more than 40 minutes over 8 weeks, while those in the control group were provided education booklets. The outcomes were measured using self-report questionnaires, anthropometrics, and blood analyses. Intervention effects were analyzed using the independent t-test, Mann—Whitney U test, ANCOVA, and Ranked ANCOVA.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant increase in self-efficacy (F = 8.85, p = .004, ηp2 = .13) and knowledge of metabolic syndrome (t = 2.60, p = .012, d = 0.60) compared to the control group. Additionally, the experimental group demonstrated a significant decrease in waist circumference (Z = - 2.34, p = .009, d = 0.58) and body mass index (Z = - 1.91, p = .028, d = 0.47) compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The integrated health management program for psychiatric patients with metabolic syndrome is effective in improving self-efficacy and knowledge of metabolic syndrome and decreasing physiological indicators such as waist circumference and body mass index. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- User evaluation of a mobile education application for the management of metabolic syndrome among cancer survivors
Ji-Su Kim, Minhae Kim, Yeji Seo
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 63: 102276. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Web-Based Self-Management Program for Korean Adult Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on the Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skills Model
Seohyeon Hwang, Woori Na, Dayoung Oh, Cheongmin Sohn
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(12): 6915. CrossRef - Effect of Patient Safety Training Program of Nurses in Operating Room
Peijia Zhang, Xin Liao, Jie Luo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(4): 378. CrossRef
- User evaluation of a mobile education application for the management of metabolic syndrome among cancer survivors
- 2,729 View
- 110 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Nurse Staffing and Health Outcomes of Psychiatric Inpatients: A Secondary Analysis of National Health Insurance Claims Data
- Suin Park, Sohee Park, Young Joo Lee, Choon-Seon Park, Young-Chul Jung, Sunah Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):333-348. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The present study investigated the association between nurse staffing and health outcomes among psychiatric inpatients in Koreaby assessing National Health Insurance claims data.
Methods
The dataset included 70,136 patients aged 19 years who were inpatientsin psychiatric wards for at least two days in 2016 and treated for mental and behavioral disorders due to use of alcohol; schizophrenia,schizotypal and delusional disorders; and mood disorders across 453 hospitals. Nurse staffing levels were measured in three ways: registerednurse-to-inpatient ratio, registered nurse-to-adjusted inpatient ratio, and nursing staff-to-adjusted inpatient ratio. Patient outcomesincluded length of stay, readmission within 30 days, psychiatric emergency treatment, use of injected psycholeptics for chemical restraint,and hypnotics use. Relationships between nurse staffing levels and patient outcomes were analyzed considering both patient and systemcharacteristics using multilevel modeling.
Results
Multilevel analyses revealed that more inpatients per registered nurse, adjusted inpatientsper registered nurse, and adjusted inpatients per nursing staff were associated with longer lengths of stay as well as a higher risk of readmission.More adjusted inpatients per registered nurse and adjusted inpatients per nursing staff were also associated with increased hypnoticsuse but a lower risk of psychiatric emergency treatment. Nurse staffing levels were not significantly associated with the use of injectedpsycholeptics for chemical restraint.
Conclusion
Lower nurse staffing levels are associated with negative health outcomes of psychiatricinpatients. Policies for improving nurse staffing toward an optimal level should be enacted to facilitate better outcomes for psychiatricinpatients in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Association Between Nurse Staffing and Conflict and Containment in Acute Mental Health Care: A Systematic Review
Samuel Woodnutt, Simon Hall, Paula Libberton, Jane Ball, Chiara Dall'Ora, Peter Griffiths
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Relative Associations of Communication Competence, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Commitment with Nursing Work Performance among Psychiatric Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
Hyungsim Yang, Seong Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(4): 483. CrossRef - Comprehensive Symptom Prediction in Inpatients With Acute Psychiatric Disorders Using Wearable-Based Deep Learning Models: Development and Validation Study
Minseok Hong, Ri-Ra Kang, Jeong Hun Yang, Sang Jin Rhee, Hyunju Lee, Yong-gyom Kim, KangYoon Lee, HongGi Kim, Yu Sang Lee, Tak Youn, Se Hyun Kim, Yong Min Ahn
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024; 26: e65994. CrossRef - Changing the focus of adverse incident reporting in mental health nursing
Samuel Woodnutt
Mental Health Practice.2024; 27(2): 20. CrossRef - Factors associated with readmissions in psychiatric inpatient care: a prospective cohort study based on hospital registers
Marianna Virtanen, Laura Peutere, Mikko Härmä, Annina Ropponen
BMC Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Workload and psychosocial risks among nurses in mental health and psychiatry in Chile
Daniela Fuentes‐Olavarría, Matías E. Rodríguez‐Rivas, Javiera Romo‐Neira
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 869. CrossRef - NEAT: Nurse Effort Assessment Tool—Human Factors Considerations in Designing for Appropriate Staffing
Scott Good, Michael W. Boyce, Leigh V. Evans, Mark Sevilla
Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting.2024; 68(1): 1680. CrossRef - Developing nurse‐sensitive outcomes in acute inpatient mental health settings—A systematic review
Irene Ngune, Helen Myers, Amanda Cole, Peter Palamara, Robina Redknap, Michael Roche, Diane Twigg
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(17-18): 6254. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef - Time to readmission in psychiatric inpatients with a therapeutic leave
Tiziana Ziltener, Julian Möller, Lukas Imfeld, Roselind Lieb, Undine E. Lang, Christian G. Huber
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2021; 144: 102. CrossRef - Physical Comorbidity According to Diagnoses and Sex among Psychiatric Inpatients in South Korea
Suin Park, Go-Un Kim, Hyunlye Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4187. CrossRef
- The Association Between Nurse Staffing and Conflict and Containment in Acute Mental Health Care: A Systematic Review
- 7,234 View
- 119 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Difficulties in Caring for Psychiatric Patient as Experienced by Non-Psychiatric Nurses
- Jaewon Joung, Mi Young Jang, Jihyun Shim, Yoonhi Ko, Sung Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(1):49-59. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify non-psychiatric nurses' difficulties in caring for patients with mental illness.
Methods Data were collected from eighteen general medical-surgical nurses working at a university hospital in Seoul, Korea. This study involved two focus group discussions and three in-depth individual interviews. All interviews were recorded and transcribed as they were spoken, and data were analyzed using qualitative content analysis.
Results General medical-surgical nurses experienced difficulties in 3 categories, 9 subcategories, 27 codes. The three categories were ‘nurse’ related factors, ‘patient’ related factors, ‘resource’ related factors. The nine categories were ‘unpreparedness’, ‘nursing barriers due to stigma’, ‘undervaluing and avoidance of psychiatric nursing’, ‘eroding into the trap of a vicious cycle’, ‘facing unapproachable patients’, ‘dealing with unhelpful family members’, ‘burdening already overburdened staff’, ‘obstructive environment’, and ‘isolation of staff with heavy responsibilities’.
Conclusion The results of this study indicate the need to develop psychiatric mental health education programs for non-psychiatric nurses. Education about psychiatric mental health and support from institutions for non-psychiatric nurses can reduce their negative attitude toward psychiatric patients and difficulties in caring for psychiatric patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Auditory hallucinations simulation in mental health nursing education: a scoping review
Mauro Parozzi, Mattia Bozzetti, Paolo Ferrara, Stefano Mancin, Anne Destrebecq, Marco Sguanci, Andrea Gazzelloni, Claudia Fantuzzi, Maura Lusignani, Stefano Terzoni
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2025; 20(1): e175. CrossRef - Effects of a Narrative Therapy Training Program Utilizing MetaverseZEP for Psychiatric Mental Health Nurses
Jina Shin, Hee Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(1): 79. CrossRef - “It felt real”: Nursing students’ experiences of mental health simulation utilizing service users as standardized patients
Jiyoung Kim, Suyoun Ahn, Jaewon Joung
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2025; 107: 101794. CrossRef - Daily experiences of non‐psychiatric nurses in acute psychiatric wards
Mphedziseni Esther Rangwaneni, Ndidzulafhi Selina Raliphaswa, Mary Maluleke, Thingahangwi Cecilia Masutha
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A model for the involvement of service users as instructors into the psychiatric nursing curriculum in Korea: A qualitative study on participation experience
Suyoun Ahn, Soyoung Shin, Jaewon Joung
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 917. CrossRef - ‘We are working in specialty units’—An exploratory qualitative study
Mphedziseni Esther Rangwaneni, Ndidzulafhi Selina Raliphaswa, Mary Maluleke, Vusiwana Patricia Letlalo, Thingahangwi Cecilia Masutha, Duppy Manyuma, Langanani Makhado, Tinyiko Nelly Rikhotso
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Educational Needs for Psychiatric Nursing Competencies among Non-Psychiatric Nurses
Min-Ki Son, Suk-Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(2): 146. CrossRef - The Process of Home-Visiting Nurses Supporting People with Mental Disorders
Fumi Ohtake, Maiko Noguchi-Watanabe, Kumiko Morita
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(21): 6965. CrossRef - Investigation of the Relationship Between Psychiatry Visit and Suicide After Deliberate Self-harm: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hye Hyeon Kim, Chanyoung Ko, Ji Ae Park, In Han Song, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41261. CrossRef - Effects of a mental health nursing simulation for general ward nurses: A pilot study
Min‐Yeong Lee, Yun‐Jung Choi
Nursing Open.2023; 10(5): 3432. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Depression Attitude Questionnaire: Korean Version
Kyung Mi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(3): 318. CrossRef - Affecting Factors on Discriminatory Behavior toward Mentally Disabled in the Nursing Students
Jeong-Eon PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(4): 969. CrossRef - Experiences of Psychiatric Nurses Who Care for Patients with Physical and Psychological Violence: A Phenomenological Study
In Ok Sim, Kyoung Min Ahn, Eun Jeong Hwang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(14): 5159. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of Korean version Competency Assessment Tool-Mental Health
Hyun Mee Cho, Jeong Won Han, Eun Joung Choi, Hyo Eun Jeong, Bo Ram Hong, Eun Yong Kim
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(2): 143. CrossRef - Influence of Symptom Awareness and Nursing Competency on the Burden of Nursing Care for Patients with Mental Illness by General Ward Nurses
Seung Hee Kim, Kuem Sun Han
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2020; 29(3): 264. CrossRef - A constructivist grounded theory of generalist health professionals and their mental health work
Scott Brunero, Lucie M. Ramjan, Yenna Salamonson, Daniel Nicholls
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2018; 27(6): 1816. CrossRef - Care Burden for Mental Illness Patients, Attitude toward Mental Illness and Psychiatric Nursing Competency in Non-psychiatric Nurses
Mi Young Jang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(1): 55. CrossRef - Development of Health Assessment Tool for Middle-aged Adults in Long-term Care Settings
Yoon-Jin Park, Nam Cho Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Auditory hallucinations simulation in mental health nursing education: a scoping review
- 2,457 View
- 51 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Structural Equation Model for Caregiving Experience of Families Providing Care for Family Members with Mental Disorders
- In Ohg Oh, Sunah Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):97-106. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop and test a structural model for caregiving experience including caregiving satisfaction and caregiving strain in families providing care for family members with a mental disorder.
Methods The Stress-appraisal-coping model was used as the conceptual framework and the structural equation model to confirm the path that explains what and how variables affect caregiving experience in these families. In this hypothesis model, exogenous variables were optimism, severity of illness and uncertainty. The endogenous variables were self efficacy, social support, caregiving satisfaction and caregiving strain. Data were collected using structured questionnaires.
Results Optimism and caregiving self-efficacy had significant direct and indirect effects on caregiving satisfaction. Optimism, severity of illness and uncertainty had significant direct and indirect effects on caregiving strain. The modified path model explained effects of optimism on caregiving self-efficacy with social support in the path structure as a mediator. Also, there were direct and indirect effects of optimism and uncertainty on caregiving satisfaction with social support and caregiving self-efficacy in the path structure as a mediators.
Conclusion Results suggest the need to improve caregiving self-efficacy of these families, establish support systems such as a mental health professional support programs for caregiving self-efficacy. Optimism, severity of illness and uncertainty perceived by families need to be considered in the development of support programs in order to increase their effectiveness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of the Caring Competence Scale for Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Disorders
Won Hee Jun
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 32(5): 1248. CrossRef - Experience of Mental Healthcare Services by Family Caregivers of Patients With Mental Disorders
Ja-Yeon Nam, In-Seo Son, Tae-Hoon Kim, Yoon-Young Nam
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2024; 63(1): 38. CrossRef - Influence of Gratitude and Sense of Meaning in Life on Caregiving Self-Efficacy of Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Illness
Won Hee Jun
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2023; 45(12): 1104. CrossRef - Development of Discharge Nursing Service Model for Heart Failure Patients
Sung Hye Park, Ju Hee Lee, Yeon Soo Jang, Soo Young Han, Young Ah Kim, Eui Geum Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(2): 141. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Quality of Life of Family Caregivers of Stroke Patients: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Ji-Hye Lee, Mi Sook Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(4): 479. CrossRef - Uncertainty and Nursing Needs of Parents with Pediatric Cancer Patients in Different Treatment Phases: A Cross-Sectional Study
Mijeong Park, Eunyoung E. Suh, Soo-Young Yu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4253. CrossRef - Suffering Experience of Primary Caregivers of People with Mental Disabilities in Community Dwellings
Eun Joung Choi, Hyun Mee Cho, Eun Ju Cho, Minkyung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2020; 29(3): 218. CrossRef - A Review of Trend of Nursing Theories related Caregivers in Korea
Sung Hae Kim, Yoona Choi, Ji-Hye Lee, Da-El Jang, Sanghee Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2018; 12(1): 26. CrossRef - Effects of Family Burden, Resilience and Spiritual Well-being on the Quality of Life of Primary Caregivers of People with Mental Illness
Hyun Mee Joe, Eun Joung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(3): 226. CrossRef - Experiences of Caring for a Spouse with Schizophrenia
Gong Ju Chai, Eun Sook Nam
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(2): 133. CrossRef
- Development of the Caring Competence Scale for Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Disorders
- 1,249 View
- 20 Download
- 10 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


