Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Soo Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):269-284. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This methodological study was conducted to develop a scale to measure communication self-efficacy in nurses and examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
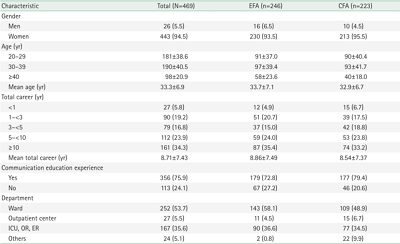
We selected 54 initial items from literature reviews and interviews with 10 clinical nurses. Thirty-two preliminary items were derived from consultations with 10 experts. To verify the scale’s factor structure, we conducted exploratory factor analysis (EFA), and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) among 469 nurses. Data were analyzed using item analysis, EFA, CFA, discriminant validity, convergent validity, and internal consistency using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 29.0 (IBM Corp.) and IBM SPSS AMOS ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp.).
Results
The scale consisted of 18 items with three factors (ability to apply therapeutic communication skills, crisis management capabilities, and communication competence), which explained 46.1% of the total variance. Convergent validity and discriminant validity were confirmed for the factors. CFA supported the fit of the measurement model comprising three factors (standardized root mean square residual=.04, root mean square error of approximation=.03, goodness of fit index=.92, Tucker-Lewis index=.97, comparative fit index=.98, normed fit index=.89, critical N=216). Internal consistency was confirmed by a Cronbach’s α coefficient of .91.
Conclusion
The communication self-efficacy scale for nurses is expected to measure communication self-efficacy among nurses. It will be useful for improving nurses’ professional communication abilities.
- 3,574 View
- 272 Download

- Effect of an Integrated Stress Management program on the Stress Symptoms on the Stress Symptoms, Progressive Muscle Relaxation Method
- Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):289-302. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.289
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The main purpose of this study was to identify the effects of integrated stress management program on the stress symptoms of psychophysiological patients, especially patients with peptic ulcer. The study employed a quasi -experimental design using two different experiential groups. The samples in the integrated stress management program participated in autogenic training with biofeedback, discussions on effective coping method, cognitive, behavioral, and emotional management. They were also provided with an educational booklet on stress management and an tape on progressive muscle relaxation. Exch session lasted one hour and the program consisted of seven sessions over four weeks. The other group was only given an tape on progressive muscle relaxation. The data were collected from May 20 to september 25, 1996 A total 47 patients from ore university hospital located in Seoul participated, experiment group 1 (integrated stress management training) had 23 subjects and experiment group 2(progressive muscle relaxation training) had 24 subjects. The effects of these programs were measured by the stress symptom scale developed by Kogan(1991) which was translated by Lee(1892) and the healing status of the ulcer evaluated by a physician The data were analyzed using Chi-square test, t-test, ANOVA, repeated measure ANOVA. The result are as follows : 1. The integrated stress management group reported a significantly lower stress symptom score than the group given the progressive muscle relaxation only. 2. The integrated stress management group showed a significantly improved ulcer status as compared to the group given a progressive muscle relaxation only. In conclusion, it was found that the integrated stress management program was more effective in decreasing self-reported stress and physiological symptoms among patients with peptic ulcer as compared to the progressive muscle relaxation group. Based on this finding, the following suggestions can be made. 1. It is necessary to broaden the scope of nursing Practice for psychophysiological patients so nurses can include stress management as part of Patient care. 2. It is necessary to develop stress management Program for other patients whose symptoms are know to be related to stress. 3. It is necessary to replicated this study with a larger sample in different settings.
- 473 View
- 4 Download

- Nursing Need of Patients with Chronic Illness: A Primary Study for Development for the Nursing Center of Chronic Illness
- Pyoung Sook Lee, So In Kim, Soon Yong Kim, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Young Joo Park, Ho Shin Rhu, Sung Ok Chang, Kuem Sun Han, Min Hyun Suk
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(2):165-175. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.2.165
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this descriptive study was to identify the nursing needs of patients with chronic illness. METHOD: The subjects of this study were 636 patients with chronic illness, 323 general nurses, and 106 public health nurses. The instruments used for this study were questionnaires including perceived functions of nursing from the center for chronic illness, preference to placement, intention to use, needs to receive services from the center for chronic illness, strategies management for nursing, and nursing needs of chronically ill patients. RESULTS: The mean of perceived functions for nursing from the center were 3.1(0.5) in public health nurses, 2.9 (0.59) in general nurses, and 2.4(1.33) in chronically ill patients. Regards of needs to receive on services of the nursing centers were, the regularly physical examination, for health educational services which was perceived highest request amongst chronically ill patients. We found the means of each specific need as 2.2(0.6), for physical health, 2.1(0.7), for psychosocial health, and 1.8(0.6) for spiritual health. CONCLUSION: From the results of this study, it is suggested that establishing a nursing center for chronically ill patients consider physical, psychosocial, for spiritual health needs of chronically ill patients. It is also a consideration that direct care for symptom management and health education in the nursing center be implemented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decision supporting method for chronic disease patients based on mining frequent pattern tree
Hoill Jung, Kyung-Yong Chung, Young-Ho Lee
Multimedia Tools and Applications.2015; 74(20): 8979. CrossRef - Relaxation Therapy for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review
Seong-Hi Park, Kuem Sun Han, Chang-Bum Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(3): 182. CrossRef - Preferences for Care near the End of Life according to Chronic Patients' Characteristics
Seonyoung Yun, Jiyeon Kang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(2): 207. CrossRef
- Decision supporting method for chronic disease patients based on mining frequent pattern tree
- 783 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Construct a Structural Model for Health Promoting Behavior of Chronic Illness
- Sook Ja Lee, So In Kim, Pyoung Sook Lee, Soon Yong Khim, Eun Sook Park, Young Joo Park, Ho Shin Ryu, Sung Ok Chang, Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(1):62-76. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.1.62
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was designed to construct a structural model for health promoting behavior of patients with chronic disease. The hypothetical model was developed based on the literature review and Pender's health promotion model.
METHOD
Data was collected by questionnaires from 1748 patients with chronic disease in General Hospital from December 1999 to July 2000 in Seoul. The disease of subject were cardiac disease included hypertension peptic ulcer, pulmonary disease included COPD and asthma, DM, and chronic kidney disease. Data analysis was done with SAS 6.12 for descriptive statistics and PC-LISREL 8.13 Program for Covariance structural analysis.
RESULTS
1. The fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate, it was modified by excluding 4 path and including free parameters to it. The modified model with path showed a good fitness to the empirical data (x2=591.83, p<.0001, GFI=0.97, AGFI= 0.94, NNFI=0.95, RMSR=0.01, RMSEA=0.05). 2. The perceived benefits, perceived barriers, self-efficacy, self-esteem, and the plan for action were found to have significant direct effect on health promoting behavior of chronic disease. 3. The health concept, health perception, emotional state, social support were found to have indirect effects on health promoting behavior of chronic disease.
CONCLUSION
The derived model in this study is considered appropriate in explaining and predicting health promoting behavior of patients with chronic disease. Therefore, it can effectively be used as a reference model for further studies and suggested implication in nursing practice.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting the health promoting behaviors of office male workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: Using Pender’s health promotion model
Jeong Hyo Seo, Hee Kyung Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 412. CrossRef - The intervention effects of the Clean Diet program on the health promotion attitudes and the physiological indices of an elderly
So-Hong Shin, Hyun-Sil Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(6): 495. CrossRef - Implementation of U-Healthcare System for Chronic Disease Management
Geun-Teak Ryu, Hun Choi
Journal of the Institute of Electronics and Information Engineers.2014; 51(1): 233. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health-Promoting Behaviors in People Living with HIV
Young Mi Park, Gisoo Shin, Jiyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 234. CrossRef - A Predictive Model on Health Promotion Behavior in Women who Immigrate for Marriage
Namok Jeong, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 695. CrossRef - A Predictive Model of Health Promotion Behavior in Obese School-Age Children
Mi Suk Jeon, Hyeon-Ok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 264. CrossRef - Testing and Developing the Health Promotion Model in Low-Income, Korean Elderly Women
Kyung Rim Shin, Younhee Kang, Hyo Jung Park, Myoung Ok Cho, Margaret Heitkemper
Nursing Science Quarterly.2008; 21(2): 173. CrossRef - Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
Yun Hee Shin, Hea Kung Hur, Nola J. Pender, Hee Jung Jang, Moon-Sil Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2006; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Test of the health promotion model as a causal model of commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean adults with chronic disease
YunHee Shin, SangKyun Yun, Nola J. Pender, HeeJung Jang
Research in Nursing & Health.2005; 28(2): 117. CrossRef
- Factors affecting the health promoting behaviors of office male workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: Using Pender’s health promotion model
- 797 View
- 8 Download
- 9 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Health Promoting Behaviors in Patients with Chronic Respiratory Disease
- Young Joo Park, So In Kim, Pyoung Sook Lee, Soon Yong Khim, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Ho Shin Ryu, Sung Ok Chang, Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):477-491. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was designed to construct a structural model for health promoting behavior in patients with chronic respiratory disease. A hypothetical model was developed based on the literature review. METHOD: Data was collected by questionnaires from 235 patients with chronic respiratory disease in a General Hospital in Seoul. Data analysis was done using SAS 6.12 for descriptive statistics and the PC-LISREL 8.13 Program for Covariance Structural Analysis. RESULT: The results are as follows : 1. The fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate. It was modified by excluding 2 path and including free parameters and 3 path to it. The modified model with path showed a good fitness to the empirical data(X2=80.20, P=0.05, GFI=0.95, AGFI=0.88, NNFI=0.95, NFI=0.96, RMSR=0.01, RMSEA =0.06). 2. The perceived benefits, self-efficacy, and a plan of action were found to have significant direct effects on the health promoting behavior in patients with chronic respiratory disease. 3. The health perception, self-esteem, and activity related to affect were found to have indirect effects on the health promoting behavior in patients with chronic respiratory disease. CONCLUSION: The modified model of this study is considered appropriate in explaining and predicting health promoting behavior in patients with chronic respiratory disease. Therefore, it can effectively be used as a reference model for further studies and suggested direction in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Predictive Model of Health Promotion Behavior in Obese School-Age Children
Mi Suk Jeon, Hyeon-Ok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 264. CrossRef - Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
Yun Hee Shin, Hea Kung Hur, Nola J. Pender, Hee Jung Jang, Moon-Sil Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2006; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Test of the health promotion model as a causal model of commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean adults with chronic disease
YunHee Shin, SangKyun Yun, Nola J. Pender, HeeJung Jang
Research in Nursing & Health.2005; 28(2): 117. CrossRef - Using methodological triangulation for cultural verification of commitment to a plan for exercise scale among Korean adults with chronic diseases
YunHee Shin, Nola J. Pender, SangKyun Yun
Research in Nursing & Health.2003; 26(4): 312. CrossRef
- A Predictive Model of Health Promotion Behavior in Obese School-Age Children
- 727 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Influencing Factors on Social Adaptation of Chronic Mental Illness
- Pyoung Sook Lee, Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(2):340-340. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.2.340
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to investigate the factors influencing social adaptation of chronic mental illness. The subjects of this study were 190 patients, over the age of 20 with chronic mental illness diagnosed by a physician, and living in Seoul, Korea during May, 2000 to December 2000. The instruments for this study were the social adaptation scale by Wallace (1979), the self-esteem scale by Rogenberg (1965), social support scale by ParkJiWon (1985), coping behavior scale by Shirley Zeitlin (1978), self efficacy scale by Sherer et. al (1982), and Rand mental health inventory(1979). The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression. The results of this study are as follows: 1. The level of social adaptation showed moderate (M=3.43). 2. The social adaptation showed significant positive correlation with self-esteem (r=0.39, p=0.00), self-efficacy (r=0.31, p=0.00), social support (r=0.47, p=0.00), self-productive coping (r=0.14, p=0.05), self-flexible coping (r=0.22, p=0.00), environment-active coping (r=0.21, p=0.00), and environment-flexible coping (r=0.14, p=0.04). The social adaptation showed significant negative correlation with anxiety (r=-0.16, p=0.02), and emotional problems (r=-0.18, p=-0.00). 3. The stepwise multiple regression analysis revealed that the most powerful predictor of social adaptation was social support (21%). A combination of social support, depression, behavioral controllability, self-efficacy, and environmental coping behavior accounted for 39% of the variance in social adaptation in chronic mental illness. From the results of this study, it is suggested to develop and apply a social adaptation training program for chronic mental illness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Survey on Community dwelling Mentally Ill Patients Who could not be Accessed by a Community Health Center
Jeong-Suk Reu, Myung-Hee Kim, Chu-Young Jeong
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(2): 91. CrossRef
- A Survey on Community dwelling Mentally Ill Patients Who could not be Accessed by a Community Health Center
- 722 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Structural Model Based on Pender's Model for Quality of Life of Chronic Gastric Disease
- Eun Sook Park, So In Kim, Pyoung Sook Lee, Soon Yong Khim, Sook Ja Lee, Young Joo Park, Ho Shin Ryu, Sung Ok Chang, Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(1):107-125. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.1.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to construct a structural model for quality of life of chronic gastric disease. The hypothetical model was developed based on the literature review and Pender's health promotion model. Data were collected by questionnaires from 459 patients with chronic gastric disease in a General Hospital from July 1999 to August 2000 in Seoul. Data analysis was done with SAS 6.12 for descriptive statistics and PC-LISREL 8.13 Program for Covariance structural analysis. The results are as follows : 1. The fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate, thus it was modified by excluding 1 path and including free parameters and 2 path to it. The modified model with path showed a good fitness to the empirical data (Chi2=934.87, p<.0001, GFI=0.88, AGFI=0.83, NNFI=0.86, RMSR =0.02, RMSEA=0.07). 2. The perceived barrier, health promoting behavior, self-efficacy, and self-esteem were found to have significant direct effects on the quality of life. 3. The health concept, health perception, emotional state, and social support were found to have indirect effects on quality of life of chronic gastric disease. In conclusion, the derived model in this study is considered appropriate in explaining and predicting quality of life of chronic gastric disease. Therefore it can effectively be used as a reference model for further studies and suggested direction in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
Yun Hee Shin, Hea Kung Hur, Nola J. Pender, Hee Jung Jang, Moon-Sil Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2006; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Structural Model for Quality of Life of Patients With Chronic Cardiovascular Disease in Korea
Kuem Sun Han, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Young-Joo Park, Kang Hyun Cheol
Nursing Research.2005; 54(2): 85???96. CrossRef - Test of the health promotion model as a causal model of commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean adults with chronic disease
YunHee Shin, SangKyun Yun, Nola J. Pender, HeeJung Jang
Research in Nursing & Health.2005; 28(2): 117. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in People with Chronic Illness in Korea
KuemSun Han, PyoungSook Lee, SookJa Lee, EunSook Park
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2003; 35(2): 139. CrossRef - Using methodological triangulation for cultural verification of commitment to a plan for exercise scale among Korean adults with chronic diseases
YunHee Shin, Nola J. Pender, SangKyun Yun
Research in Nursing & Health.2003; 26(4): 312. CrossRef
- Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
- 696 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Influencing Factors on Symptoms of Stress of Middle Aged Women
- Kuem Sun Han, Pyoung Sook Lee, Yong Mi Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1427-1436. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1427
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify the influencing factor on Symptoms of Stress of Middle Aged Women. The subjects of this study were 35 middle aged women who lives in Seattle, Washington in U.S, and 74 middle aged women who lives in Seoul. Data collection was performed at the University of Washington and Seoul from Oct. 1998 to May. 1999. Data collected through 4 types of questionnaires : SOS, Ways of Coping, Mood Status, Perceived Stress. The results of this study are as follows: 1. The stress symptoms showed positive correlation with emotion-oriented coping, mood status, and perceives stress. 2. Stepwised multiple regression analysis revealed that most powerful predictor of Stress Symptoms was mood status. A combination of perceived stress, mood status and ways of coping account for 64% of the variance in Symptoms of stress in Middle aged women. From the results of the study, the following recommendations are presented as follow: 1. It is necessary to replicate this study with a larger sample. 2. It is necessary to develop a stress management program focused on ways of coping, mood status, perceived stress for middle aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Menopausal stage transitions and associations with overall and domain-specific perceived stress in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Sang Won Jeon, Junhee Park, Byungtae Seo, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Maturitas.2025; 200: 108660. CrossRef - The relationship between psychological distress, depressive symptoms, emotional eating behaviors and the health-related quality of life of middle-aged korean females: a serial mediation model
Jihyun Oh, Sunghee Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Forest Therapy on Health Promotion among Middle-Aged Women: Focusing on Physiological Indicators
Bum-Jin Park, Chang-Seob Shin, Won-Sop Shin, Chung-Yeub Chung, Si-Hyung Lee, Dong-Jun Kim, Youn-Hee Kim, Chang-Eun Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4348. CrossRef - The Effect of walking exercise on the improvement of housewives' Self-esteem, Stress, Depression in terms of convergence
Hae-Mi Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(12): 453. CrossRef - Development of the Perceived Stress Inventory: A New Questionnaire for Korean Population Surveys
Eon Sook Lee, Ho Cheol Shin, Jun Hyung Lee, Yun Jun Yang, Jung Jin Cho, Gwiyeoroo Ahn, Yeong Sook Yoon, Eunju Sung
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2015; 36(6): 286. CrossRef - Study of on Academic Stress Responses According to Sasang Constitutions of Oriental Medicine College Students
Jun-Yong Chang, Kyoung-Shin Kim, Byoung-Soo Kim
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2012; 23(3): 77. CrossRef
- Menopausal stage transitions and associations with overall and domain-specific perceived stress in middle-aged Korean women
- 800 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- A study of Stress Reaction, Symptoms of Stress, Health Promoting Behavior, and Quality of Life in Korean Immigrant Middle Aged Women
- Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):606-618. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.606
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify the level of Symptoms of Stress, Stress Reaction, Health Promoting Behavior, and Quality of Life in Korean Immigrant Middle Aged Women. The subjects of this study were 33 middle aged women who live in Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Data collection was performed at the U.W from Oct. 1998 to May. 1999. Data collection time was one hour and data was collected through 4 types of questionnaires : SOS, Health Promoting Behaviors, Quality of Life and Demographic data form, and the Physiologic Stress Profile was collected by J&J I-410 biofeedback equipment. The data was analyzed by descriptive statistics and the pearson correlation coefficient using the SAS program. The results of this study are as follows: 1. The level of physiological stress reaction and stress symptoms showed high level and quality of life showed low in general. 2. The Stress Reaction and Symptoms of Stress showed significant negative correlation with health promoting behavior, quality of life in the middle aged women. 3. The health promoting behavior showed significant positive correlation with quality of life in the middle aged women. In conclusion, the physiological stress reaction, symptoms of stress, and health promoting behavior were major influencing factor to quality of life in Korean Immigrant Women. From the results of the study, the following recommendations are presented as follow: 1. It is suggested that the study for developing the health promotion program focused on stress self-regulation for Korean immigrant women. 2. It is suggested that the comparative study for Korean immigrant women and Women in Korea. 3. It is necessary to broaden the scope of nursing practice for middle aged healthy women, so nurses can include a health promotion program focused on stress self-regulating as part of nursing care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bio-social determinants of health-related quality of life of middle aged (45–59 years) population in India
Aarti Nagarkar, Snehal Kulkarni, Rashmi Gadkari
Post Reproductive Health.2020; 26(1): 19. CrossRef - Predictors of Health-Related Quality of Life Among Low-Income Midlife Women
Ok Kyung Ham
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2011; 33(1): 63. CrossRef - A study on the Health Status, Social Support and Acculturative Stress of Filipino Marriage-Migrant Women
Ae-Hwa Jaung, Hye-Jin Kim, Hyun-Ja Jeong
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(12): 5509. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Locus of Control, Depression, Wellbeing, and Health Promoting Lifestyle Profile II in Middle Aged Korean and Korean-American Women
Eun Hee Lee, Ae Young So, Kyung Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 157. CrossRef - Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women
Hye-Sook Shin, Jia Lee, Kyung-Hee Lee, Young-A Song
Asian Nursing Research.2007; 1(1): 61. CrossRef
- Bio-social determinants of health-related quality of life of middle aged (45–59 years) population in India
- 660 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- A Study of Factors Influencing Health Promoting Behavior and Quality of life in the Elderly
- Eun Sook Park, Soon Ja Kim, So In Kim, Young Ja Chun, Pyoung Sook Lee, Haeng Ja Kim, Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):638-649. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.638
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to investigate the factors influencing health promoting behavior and quality of life in the elderly, to provide the basic data for health promoting intervention in order to improve quality of life. The subjects of this study were 51 elderly person over the age of 65, living in Seoul, Korea, during the period from November, 1997 to January, 1998. The instruments for this study were the health promoting behavior scale developed by Walker et (1987), the quality of life scale by RoyouJa(1988), the health concept scale by Laffrey(1986), the perceived health states scale by Lawston et al. (1992), the health value scale by Walston et al.(1978), the self esteem scale by Rogenberg(1965) and self efficacy scale by Sherer(1982). The instruments of this using descriptive statistics, t-test, Person correlation coefficients ANOVA and stepwise multiple regression. The results of this study are as follows; 1. The health promoting behavior showed significant positive correlation with health concept perception of health status, self esteem, internal health locus of control, self efficacy and quality of life in the elderly. 2. The quality of life showed significant positive correlation with health concept, perception of health status, self esteem, internal health locus of control, self efficacy in the elderly. 3. Stepwise multiple regression analysis revealed that the most powerful predictor of health promoting behavior was quality of life. A combination of quality of life, health concept, perceived health status, self esteem, internal health locus of control, and self esteem, internal health locus, and self efficacy accounted for 46% of the variance in health promoting behavior in the elderly. 4. Stepwise multiple regression analysis revealed that the most powerful predictor of quality of life in the elderly was self esteem. A combination of self esteem. health concept, perceived health status, health promoting behavior and self efficacy account for 56% of the variance in quality of life in the elderly. From the results of the study, the following recommendations are presented as follow : 1. Development of a health promoting program to improve quality of life in the elderly. 2. In developing the health promoting, the above major influencing factors be considered. 3. It is suggested that an education specialist in practice in the community be include in the program development.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effectiveness of Psychological Treatments in Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Angela Guarino, Cristina Polini, Giuseppe Forte, Francesca Favieri, Ilaria Boncompagni, Maria Casagrande
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 209. CrossRef - The Effects of Neighborhood Environment on Elderly’s Walking Time and Quality of Life : A Case Study of Nokbeon-Dong in Seoul
Hyo-Sook Park, Kyung-Hwan Lee
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2019; 54(2): 109. CrossRef - The Impact of Poverty on Self-Rated Health in Philippines: A Mediated Moderation Model of Health Behaviors and Family and Friend Support
Jae Woo Kim, Dohyeong Kim, Eun Woo Nam
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(1): 24. CrossRef - Health Status and Factors related to Health Behaviors of Older Adults Using a Senior Center
Ji-Yeon Ha, Yeon-Hwan Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(4): 428. CrossRef - Correlation of Quality of Life in the Health Condition of Korean Elderly: Perceived, Physical, Mental Health Status
Soo-Jin Yu, Chang-Yeol Kang, Young-Ran Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(2): 47. CrossRef - Health Status and Health-promoting Lifestyle for Living Donors after Kidney Donation Through Survey
Min Kyung Nam, Doo In Lee, Oh Jung Kwon
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2014; 28(3): 144. CrossRef - A Study on Health Behavior and Quality of Life of Married Immigrant Women
Min-Sook Seo, Kyung-Sook Park, Hyung Moo Park, Hyun-Ok Park
The Journal of Korean Society of Menopause.2013; 19(2): 112. CrossRef - Correlation analysis of factors and the geriatric oral health-related quality of life in Gumi
Han-Na Kim, In-Young Ku, Seon-Jeong Moon
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2012; 12(5): 1039. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Low Income Korean Aged
Hye-Ryoung Kim, Kasil Oh, Kyong-Ok Oh, Sun-Ock Lee, Sook-Ja Lee, Jeong-Ah Kim, Hoa-Yun Jun, Jung-Hee Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 694. CrossRef - Comparison of Health‐Promoting Behaviors of Noninstitutionalized and Institutionalized Older Adults in Korea
Sook‐Young Kim, Eun‐Young Jeon, Sohyune R. Sok, Kwuy‐Bun Kim
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2006; 38(1): 31. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in People with Chronic Illness in Korea
KuemSun Han, PyoungSook Lee, SookJa Lee, EunSook Park
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2003; 35(2): 139. CrossRef - HEALTH-PROMOTING BEHAVIORS OF Older Adults Compared to Young and Middle-Aged Adults in Korea
Mee Ock Gu, Young Eun
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2002; 28(5): 46. CrossRef
- The Effectiveness of Psychological Treatments in Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 892 View
- 4 Download
- 12 Crossref

- The Relationship of Perceived Stress, Ways of Coping, and Stress Response of Nursing Students
- Na Sun Ha, Kuem Sun Han, Jung Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):358-368. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.358
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This was designed to identify the relationship of perceived stress, ways of coping, and stress response in student nurses. The subjects of this study were 320 student nurses from two universities and three junior colleges located in Seoul. The data were collected from November 28 to December 10, 1997 by a questionnaire survey method. The instruments for this study were the perceived stress scale developed by Levenstein(1993), ways of coping scale developed by Lazarus and Folkman(1984), and the stress response scale developed by Choi(1991). The data were analyzed by SAS program, using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation coefficient, and ANOVA. The results are summarized as follows : 1. The mean score for the level of perceived stress was 2.55. 2. The mean score for the level of problem oriented coping was 1.61 and the mean score for the level of emotional oriented coping was 1.37. 3. The mean score for the level of stress response was 3.74. Stress was classified into nine factors and the order of scoring for the most frequent was; assignments(3.98), as a nurse(3.97), interpersonal relationship(3.88). 4. The relationship between perceived stress and stress response revealed a positive significant correlation(r=0.23, p=0.0001). 5. The relationship between emotional oriented coping and stress response revealed a positive significant correlation(r=0.22, p=0.0001). 6. The relationship between perceived stress and emotional oriented coping revealed a positive significant correlations(r=0.13, p=0.020). In conclusion, this study revealed that the level of perceived stress and ways of coping were important factors influencing the stress response of student nurses. Therefore, in consideration of perceived stress, ways of coping should be included in the development of a stress management program for student nurses. Further research with an expanded area and subjects is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Smartphone Addiction and Intolerance of Uncertainty on Mental Health in Nursing Students: Mediating Effects of Resilience
Jeong Mi Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(3): 296. CrossRef - The Relationship of Communication Competence, Professional Self-Concept and Stress in Clinical Practice of Nursing Students
Min-Ah Kang, Soo-Kyoung Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(4): 452. CrossRef - Impact of Nursing Students' Emotional Labor on Burnout during Nursing Practice in a Hospital: Moderating Effect of Emotional Intelligence
So-Young Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 77. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Leadership and Stress Coping on College Life Adjustment in Nursing Students
Hyo-Jin Won
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(1): 123. CrossRef - The Relationship between Anxiety, Anger and Fatigue among Stress factor of Nursing Students in Clinical Practice
San-Young Han, Young-Mee Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(2): 554. CrossRef - An Analysis Study on stress factor of Emergency medical Students during preparing Examination for Korea Registered licence
Ji-Yeon Jung, Jong-Geun Yun, Jin-Hwan Oh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(1): 194. CrossRef - Experience on Delivery Room Practice of Male Nursing Students
Ok Bun Jung, Hyun Joo Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(1): 64. CrossRef
- Effects of Smartphone Addiction and Intolerance of Uncertainty on Mental Health in Nursing Students: Mediating Effects of Resilience
- 880 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Family Functioning and Quality of Life of the Family Care-giver in Cancer Patients
- Kuem Sun Han, Soon Yong Khim, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Young Joo Park, Jeong Hwa Kim, Kwang Mi Lee, Hyun Chul Kang, Ji Won Yoon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(6):983-991. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.6.983
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship among quality of life, family coherence, family hardiness, and family resources of the family care-giver caring for a cancer patient.
Method Data was collected by questionnaires from 137 families with a cancer patient at a General Hospital and Government Cancer Hospital. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression.
Results The score of quality of life showed a significant positive correlation with the score of the level of family sense of coherence, family hardiness, and family resources. The most powerful predictor of quality of life was sense of coherence and the variance was 30%. A combination of sense of coherence and family resources account for 34 % of the variance in quality of life of the family care-giver caring for a cancer patient.
Conclusion The results showed that family sense of coherence, hardiness, and family resources were significant influencing factors on the quality of life of the family care-giver caring for a cancer patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The development and validation of the short-form Family Inventory of Resources for Management among families of older people with dementia: instrument development and cross-sectional study
Yuxin Li, Chang Zan, Sanmei Chen, Shengnan Tang, Qiongqiong Zhang, Yijia Pan, Yu Sheng, Qingyan Wang
BMC Geriatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Do spouse burden of care, family resilience, and coping affect family function in gynecologic cancer in Korea?: a cross-sectional study
Minkyung Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 197. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-efficacy and Depression on Sense of Family Coherence in Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy and Primary Caregivers in Day Care Wards: Using the Method Actor-partner Interdependence Model
Eun-Hee Do, Eun Joung Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(4): 214. CrossRef - Influence of Hospital Nurse Staffing Levels on the Colorectal Cancer Evaluation Grades, Mortality, and Length of Stay
Yunmi Kim, Se Young Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(5): 479. CrossRef - The Lived Experience of Suffering of Family with Cancer Patients: Parse’s Human Becoming Research Method
Ye-Sook Choi
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(2): 127. CrossRef - Quality of Life of Family Members Living with Cancer Patients
Hyo Jung Lee, Eun-Cheol Park, Seung Ju Kim, Sang Gyu Lee
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(16): 6913. CrossRef - Burden and Quality of Life in Terminal Cancer Patient's Family Caregivers in the area of Jeollanam-do
Eun-Young Yang, Young A Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 3954. CrossRef - Family Caregivers’ Quality of Life, Depression and Anxiety according to Symptom Control in Hospice Patients
Yun Hee Kim, Seung Hun Lee, Ho Seop Lim, Young Jin Choi, Yun Jin Kim, Sang Yeoup Lee, Jeong Gyu Lee, Dong Wook Jeong, Kyoung Hwa Yu
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2015; 18(4): 314. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth in Family Caregivers of Patients with Cancer
Soon Ock Choi
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life of Family Caregivers of Patient with Lung Cancer
Ju-Young Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 129. CrossRef
- The development and validation of the short-form Family Inventory of Resources for Management among families of older people with dementia: instrument development and cross-sectional study
- 910 View
- 7 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of Assertive Training on Interpersonal Relations, Social Behavior, and Psychiatric Symptoms in Patients with a Mental Disorder
- Kuem Sun Han, Hee Su Im, Bo Kyum Yang, Hae Kyung Chung, Yong Jin Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(5):896-903. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.5.896
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of an assertive training program on interpersonal relations, and psychiatric symptoms in patients with a mental disorder.
Method The study employed a quasi experimental design. The subjects included44 patients with a mental disorder, 20 in the experimental group, and 24 in the control group. Data was collected using structured questionnaires over a 3 month period.
Results There were greater significant increases in scores of interpersonal relations and content of communication in the experimental group than the control group. Also, there was a greater significant decrease in the score of psychiatric symptoms in the experimental group than the control group.
Conclusion Assertive training has an effect on increasing content of communication and decreasing psychiatric symptoms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Psychosocial Rehabilitation Programs on the Levels of Self-Efficacy for Mentally Disabled Persons
Hyun Sook Park, Sung-Woo Bae, Yi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 704. CrossRef
- The Effects of Psychosocial Rehabilitation Programs on the Levels of Self-Efficacy for Mentally Disabled Persons
- 818 View
- 12 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Perceived Stress, Ways of Coping, and Health Promoting Behavior in Patients with Chronic Cardiovascular Disease
- Kuem Sun Han, Eun Young Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(5):702-711. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.5.702
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship among perceived stress, ways of coping, and health promoting behaviors in patients with chronic cardiovascular disease(CCVD).
Method Data was collected by questionnaires from 436 patients with CCVD in a General Hospital in Seoul. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression.
Result The health promoting behavior showed a significant positive correlation with self-efficacy and social support. Also, the health promoting behavior showed a significant negative correlation with perceived stress and symptoms of stress. The stepwise multiple regression analysis revealed that the most powerful predictor of health promoting behaviors was symptoms of stress.
Conclusion A combination of symptoms of stress, social support, self-efficacy, and perceived stress account for 41% of the variance in health promoting behaviors of patients with CCVD. Data from this study suggest that symptoms of stress, social support, ways of coping, and perceived stress are significant influencing factors on health promoting behaviors of patients with CCVD.
- 499 View
- 3 Download

- Influencing Factors on File-up Stress of Family Caregivers with a Family Member having a Chronic Mental Illness
- Kuem Sun Han, Pyoung Sook Lee, Eun Sook Park, Young Joo Park, Ho Shin Rhyu, Hyun Chul Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(3):586-594. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.3.586
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the factors influencing file-up family stress in the family with a family member having a chronic mental illness.
Method Data was collected by questionnaires from 365 families with a member having a chronic mental illness, in an outpatient clinic of a General Hospital and Government Psychiatric Hospital in Seoul. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression.
Result The score of file-up stress showed a significantly negative correlation with the score of level of hardiness (r=-.31, p=.00), family support (r=-.13, p=.00), family cohesion (r=-.25, p=.00), and sense of coherence (r=-.26, p=.00). The most powerful predictor of file-up stress was family hardiness and the variance was 11.1%. A combination of hardiness, family support, and sense of coherence account for 14.8 % of the variance in file-up stress of the family with a member having a chronic mental illness.
Conclusion This study suggests that family support, hardiness, cohesion, and sense of coherence are significant influencing factors on file-up stress inthe family with a member having a chronic mental illness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concerns for Older Adult Patients with Acute Hip Fracture
Jun-Il Yoo, Young-Kyun Lee, Kyung-Hoi Koo, Young-Jin Park, Yong-Chan Ha
Yonsei Medical Journal.2018; 59(10): 1240. CrossRef - File-up Stress, Family Hardiness and Mental Health Status in Family Caregivers Caring for Elderly Dementia
Kuem Sun Han, Hee Su Lim
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2016; 24(4): 309. CrossRef
- Concerns for Older Adult Patients with Acute Hip Fracture
- 747 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Symptom Management of the Patients with Chronic Fatigue
- Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):333-343. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to construct a structural model for symptom management of life of the patients with chronic fatigue. The hypothetical model was developed based on the literature review and Self-regulating Model.
Method Data were collected by questionnaires from 252 patients with chronic fatigue in the 8 community from December 2002 to April 2003 in Seoul. Data analysis was done with SAS for descriptive statistics and PC-LISREL Program for Covariance structural analysis.
Result The fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate, thus it was modified by excluding 4 path and including free parameters and 3 path to it. The modified model with path showed a good fitness to the empirical data(χ2=318.11, p=0.0, GFI= .98, AGFI= .98, NNFI= .95, RMSR= .03, RMSEA= .05). The symptoms of stress, self-efficacy, and present fatigue level were found to have significant direct effect on symptom management of the patients with chronic fatigue. The ways of coping, perceived stress, and fatigue symptom were found to have indirect effects on symptom management of the patients with chronic fatigue.
Conclusion The derived model is considered appropriate in explaining and predicting symptom management of the patients with chronic fatigue. Therefore, it can effectively be used as a reference model for further studies and suggested direction in nursing practice.
- 621 View
- 0 Download

- Prediction on the Negative Outcomes of Anger in Female Adolescents
- Young Joo Park, Kuem Sun Han, Hyun Jeong Shin, Hyun Chul Kang, Sook Hee Chun, So Hyun Moon, Young Sik Lee, Hun Soo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(1):172-181. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.1.172
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to construct a structural model for explaining negative outcomes of anger in female adolescents.
Method Data was collected by questionnaires from 199 female adolescents ina female high school in Seoul. Data analysis was done with SAS for descriptive statistics and a PC-LISREL Program for Covariance structural analysis.
Result The fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate, thus it was modified by excluding 7 paths and adding free parameters to it. The modified model withthe paths showed a good fit to the empirical data(χ2 =5.62, p=.69, GFI=.99, AGFI=.97, NFI=.99, NNFI=1.01, RMSR=.02, RMSEA=.00). Trait anger, state anger, and psychosocial problems were found to have a significant direct effect on psychosomatic symptoms. State anger, psychosocial problems, and learning behaviorswere found to have direct effects on depression of female adolescents.
Conclusion The derived modelis considered appropriate for explaining and predicting negative outcomes of anger in female adolescents. Therefore, it can effectively be used as a reference model for further studies and is a suggested direction in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Suicide Prevention Program Applied on Psychodrama among Female High School Students
Gyeong Ran Park, Hee Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(3): 269. CrossRef - Effect of Life Stress and Anger Expression in College Students on Suicidal Ideation
Eun-Young Chin, Sung-Sup So, Myung-In Lee
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(8): 409. CrossRef - Suicidal Ideation in Adolescents: An Explanatory Model Using LISREL
Young-Joo Park, Hosihn Ryu, KuemSun Han, Jung Hye Kwon, Han Kyeom Kim, Hyun Cheol Kang, Ji-Won Yoon, Suk-Hee Cheon, Hyunjeong Shin
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2010; 32(2): 168. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a School-based Anger Management Program (SAMP) for Adolescents
Young-Joo Park, Ho-Sihn Ryu, Keum-Sun Han, Jung Hye Kwon, HanKyeom Kim, Yoon Jung Cho, Hyun-Cheol Kang, Suk-Hee Cheon, Ji-Won Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 145. CrossRef - Anger Expression Type and Mental Health in Middle Aged Women
Il-Rim Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 602. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Suicide Prevention Program Applied on Psychodrama among Female High School Students
- 704 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Drinking Pattern, Problem Related Drinking, Perceived Stress, Ways of Coping, and Symptoms of Stress of the Female University Students
- Seung Hee Yang, Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(7):1057-1064. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.7.1057
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship among problem related drinking, perceived stress, ways of coping, and symptoms of stress of the college women.
Method Data was collected by questionnaires from 436 the College Women in S City. It was analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation coefficients.
Result Three point forty -four of the subject had problem-related drinking, 92.43% were experienced alcohol drinking. The level of perceived stress(M=1.48) showed moderate, and symptoms of stress(M=1.34) showed below. The problem-related drinking showed significant positive correlation with perceived stress(r=.10, p=.03), emotion-oriented coping(r=.13, p=.00), and symptoms of stress(r=.23, p=.03).
Conclusion Data from this study suggest that perceived stress, ways of coping, and symptoms of stress are significant influencing factors on problem-related drinking in the Female University Students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in Drinking Scores according to Stress and Depression in Unmarried Women
Hyo Jung Kim, Chae Weon Chung
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2016; 13(1): 10. CrossRef - A Comparative Analysis of Drinking Attitudes and Behavior among College Students in Busan
Ji-Eun Kang, Han-Seok Choi, Ji-Ho Choi, Soo-Hwan Yeo, Seok-Tae Jung, Mihyang Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2014; 25(1): 19. CrossRef - Development of an Assessment Tool for Drinking Motives and Problem Drinking in Female University Students
Seoung Uk Wie, Moon Hee Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(4): 225. CrossRef - Self-reported Realities of Health Behavior of Undergraduate Students After Web-based Health Promotion Education: Qualitative Content Analysis
Joo Hyun Kim, Eun Young Park, Kyung Choon Lim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2012; 18(3): 413. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Drinking Behavior in Female University Students
Hyun-Sook Ryu, Min-Ja Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(3): 307. CrossRef - The Relationship between Alcohol Use and Drinking Problems Among College Students
Mi Ra Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(10): 4619. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of a Drinking Refusal Self-Efficacy Questionnaire-Revised (DRSEQ-R) in Korean College Students
Young-Ran Tak, Ji-Yeon An, Hae-Young Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 344. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of a Drinking Refusal Self-Efficacy Questionnaire-Revised (DRSEQ-R) in Korean College Students
Young-Ran Tak, Ji-Yeon An, Hae-Young Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 344. CrossRef
- Differences in Drinking Scores according to Stress and Depression in Unmarried Women
- 737 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Workload Analysis of a Visiting Nursing Service based on a Health Center in Seoul
- Ho Sihn Ryu, Eun Sook Park, Young Joo Park, Kuem Sun Han, Ji Young Lim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(7):1018-1027. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.7.1018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study focused on analysing the workload of visiting nurses based on a health center.
Method A Prospective descriptive analysis of self-records for workload data from 115 visiting nurses during 4 weeks was done. In addition, a cross-sectional analysis of linked data to grasp the priority of visiting nursing services from 155 visiting nurses at the 25 health centers in Seoul.
Result Time allocation that was performed on all nursing workload of visiting nurses was identified as follows: First, the inside workload of the health center took up 60% of all visiting nurse activities. Second, providing direct nursing care(caseload) took up 25%. Third, outside nursing activities excluding the caseload provided in the health center took up 15% of all working time. Fourth, the core works to have a high priority among visiting nursing activities were family health assessment, planning and evaluation of a visiting nursing program, personal health assessment, and so forth.
Conclusion The workload of a visiting nurse suggests that the caseload of visiting nurses in a health center needs to be increased. Also, our results will contribute to baseline data used to establish a proper visiting nurses infrastructure based on the demand of visiting nursing services.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimating need for Home Visiting Nurse from Public Health Centers
Hyun-Ji Bae, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2015; 12(1): 23. CrossRef - Job Performance and Self Confidence by Visiting Nurses who are engaged in the Consolidated Health Promotion Program in Gangwon-Province
Myung Soon Kwon, Soon Ok Yang, Sun Ok Eom
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(2): 190. CrossRef - The Effects of a Mobile Computerized System for Individual Tailored Home Care Services in a City
Nam Hee Park, Rang Jang, Jung Young Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(1): 71. CrossRef - Statistical Methods to Control Response Bias in Nursing Activity Surveys
Ji Young Lim, Chang Gi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 48. CrossRef - Task Analysis of Managers in the Customized Visiting Health Services
Young Ran Han, Young Rye Park, Young Hee Kim, Hee Chung Choi, Mi Ja Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(2): 165. CrossRef - Relations among the Decision Making Style, Self Leadership and Communication Competence of Visiting Nurses
Eun-Joo Kim, Ji-Young Lim, Kyung-Won Choi
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2011; 11(10): 324. CrossRef - Elders' Health Status, Quality of Life, and Satisfaction with Customized Home Visiting Health Service Depending on Connection to Volunteerism
Ji Eun Park, Chungnam Kim, Yunhee Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 448. CrossRef
- Estimating need for Home Visiting Nurse from Public Health Centers
- 769 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Perceived Stress, Mood State, and Symptoms of Stress of the Patient with Chronic Illness
- Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(1):87-94. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.1.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the factors influencing Symptoms of Stress in patients with chronic illness.
Method Data were collected by questionnaires from 1,748 patients with chronic disease in General Hospital in Seoul. Chronic diseases of were cardiac disease including hypertension, peptic ulcer, pulmonary disease included COPD and asthma, DM, and chronic kidney disease. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression.
Result 1. The level of symptoms of stress was moderate(M=2.17). 2. The score of symptoms of stress showed significantly positive correlation with the score of mood state(r=.58, p=.00), perceived stress(r=.57, p=.00), and ways of coping(r=.33, p=.00). The symptoms of stress showed significantly negative correlation with the score of social support(r=-.37, p=.00) and self-esteem(r=-.19, p=.00). 3. The most powerful predictor of symptoms of stress was mood state and the variance explained was 34%. A combination of mood state, ways of coping, perceived stress, social support, and duration of illness account for 45% of the variance in symptoms of stress of the patients with chronic illness.
Conclusion This study suggest that mood state, ways of coping, perceived stress, and social support are significantly influencing factors on symptoms of stress of the patients with chronic illness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of social support on subjective well-being of patients with chronic diseases in China: chain-mediating effect of self-efficacy and perceived stress
Zhenni Luo, Sisi Zhong, Siyu Zheng, Yun Li, Yan Guan, Weihong Xu, Lu Li, Siyuan Liu, Haozheng Zhou, Xuanhao Yin, Yibo Wu, Diyue Liu, Jiangyun Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting Unmet Healthcare Needs among Adults with Chronic Diseases
Ji-Young Han, Hyeon-Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(2): 131. CrossRef - A Correlational Study on the Knowledge, Stress and Self-care Performance among Tuberculosis Patients
Yun Mi Kim, Kyung Hee Yoo
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 366. CrossRef - Relationships of Depression Symptom, Self-Esteem, and Stress to Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Hypertension Registered to a Community Health Center
Mi Ni Choi, Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(2): 165. CrossRef - Relationship between emotional labor and occupational stress of dental counselor
Gey-Pyo Kim, Ji-Young Lee, Byeng-Chul Yu
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2013; 13(5): 727. CrossRef - The Relationship between Physical/Mental health and life stress of college students (Focusing on department of dental laboratory technology and dental hygiene)
Yeoun-Soo Kim, Sang-Hui Yu
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2013; 35(4): 405. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study of Factors associated with the Health Behavior of Working Elderly with Chronic Diseases
Dong Ok Kim, Soon-Nyung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(4): 395. CrossRef
- Influence of social support on subjective well-being of patients with chronic diseases in China: chain-mediating effect of self-efficacy and perceived stress
- 892 View
- 0 Download
- 7 Crossref

- A Structural Equation Model on Family Strength of Married Working Women
- Yeong Seon Hong, Kuem Sun Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):900-909. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.900
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of predictive factors related to family strength and develop a structural equation model that explains family strength among married working women.
Methods A hypothesized model was developed based on literature reviews and predictors of family strength by Yoo. This constructed model was built of an eight pathway form. Two exogenous variables included in this model were ego-resilience and family support. Three endogenous variables included in this model were functional couple communication, family stress and family strength. Data were collected using a self-report questionnaire from 319 married working women who were 30~40 of age and lived in cities of Chungnam province in Korea. Data were analyzed with PASW/WIN 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 programs.
Results Family support had a positive direct, indirect and total effect on family strength. Family stress had a negative direct, indirect and total effect on family strength. Functional couple communication had a positive direct and total effect on family strength. These predictive variables of family strength explained 61.8% of model.
Conclusion The results of the study show a structural equation model for family strength of married working women and that predicting factors for family strength are family support, family stress, and functional couple communication. To improve family strength of married working women, the results of this study suggest nursing access and mediative programs to improve family support and functional couple communication, and reduce family stress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of family beliefs and family strength on individual resilience and quality of life among young breast cancer survivors: A cross‐sectional study
Lin Tao, Xiaoxia Hu, Lan Fu, Xiaoxia Zhang, Hong Chen
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(11-12): 2616. CrossRef - Factors influencing quality of life in caregivers of adolescents with developmental disabilities
Joung Woo Joung
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2022; 13(4): 298. CrossRef - Developing a Prediction Model for Family Health in Families of Patients with Schizophrenia
Kuem Sun Han, Yeong Seon Hong, Hyuncheol Kang, Youn Hee Roh, Myung Sook Choi, Hee Jin Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(4): 309. CrossRef
- Effects of family beliefs and family strength on individual resilience and quality of life among young breast cancer survivors: A cross‐sectional study
- 1,146 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Depression Status of Academic High School Students in Seoul: Mediating Role of Entrapment
- Young-Joo Park, Nah-Mee Shin, Kuem Sun Han, Hyun Cheol Kang, Sook-Hee Cheon, Hyunjeong Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(5):663-672. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.663
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Purpose of this study was to investigate the status of depression in academic high school students and path analysis model for exploring the mediating role of entrapment to depression in relation to academic stress and perceived social support.
Methods Measurements were four reliable questionnaires measuring academic stress, social support, entrapment, and depression. Data were collected from students in 17 high schools in Seoul.
Results Students (n=5,346) completing the questionnaires indicated depression & entrapment from academic stress. Depression was more prevalent in girls, those whose parents' household income was less than two million won, who did not live with father or mother or both due to divorce, separation, or death, and those who smoked or used alcohol. Entrapment was more prevalent in students similar to cases of depression and in seniors. According to the proposed path model, 48.6% of depression was explained by academic stress, social support, and entrapment. The indirect effect of entrapment as a mediator between academic stress and depression was verified and larger than the direct effect of academic stress on depression.
Conclusion Considering levels of depression and entrapment demonstrated by these students, better mental health programs with diverse strategies should be developed for their psychological well-being.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on Awareness of Suicide and Suicide Prevention Among Community Youth
Jiyoung Kim, Young-Hoon Ko, Ho-Kyoung Yoon, Boram Chae, Rayoung Han, Nayoung Chae, Jongha Lee
Journal of the Korean Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.2024; 35(3): 210. CrossRef - The association mental health of adolescents with economic impact during the COVID-19 pandemic: a 2020 Korean nationally representative survey
Hanul Park, Kang-Sook Lee
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adolescent suicide in South Korea: Risk factors and proposed multi-dimensional solution
Chae Woon Kwak, Jeannette R. Ickovics
Asian Journal of Psychiatry.2019; 43: 150. CrossRef - Test anxiety and telomere length: Academic stress in adolescents may not cause rapid telomere erosion
Yaru Zou, Waiian Leong, Mingling Yao, Xuefei Hu, Sixiao Lu, Xiaowei Zhu, Lianxiang Chen, Jianjing Tong, Jingyi Shi, Eric Gilson, Jing Ye, Yiming Lu
Oncotarget.2017; 8(7): 10836. CrossRef - Effects of Anger and Entrapment on Psychological Health of High School Boys: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Social Support
Sun Yi Yang, Yun Hee Oh
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(4): 429. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Emotional and Behavioral Characteristics of High School Students
Kyoung Sun Park, Gyu Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2014; 27(2): 109. CrossRef - Depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among Vietnamese secondary school students and proposed solutions: a cross-sectional study
Dat Tan Nguyen, Christine Dedding, Tam Thi Pham, Pamela Wright, Joske Bunders
BMC Public Health.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors of heavy episodic drinking among Korean adolescents
S. S. Chung, K. H. Joung
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 20(8): 665. CrossRef - Relationships among Daily Hassles, Social Support, Entrapment and Mental Health Status by Gender in University Students
Suk-Hee Cheon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(3): 223. CrossRef - Effects of Adolescent Temperament and Parent-child Attachment on Depression
So-Youn Yim, Myoung-Ok Chae, Ja-Hyung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(4): 207. CrossRef
- Study on Awareness of Suicide and Suicide Prevention Among Community Youth
- 1,287 View
- 8 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Influencing Factors on Symptom Self Management in Patients with Chronic Mental Disorders
- Kuem Sun Han, Bo Gyum Yang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(1):127-135. Published online February 28, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.1.127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the factors influencing symptom self management (SSM) in the patient with a chronic mental disorder.
Method Data was collected by questionnaires from 204 chronic mental disorders in an outpatient clinic in a General Hospital and Public Mental Health Centers in Seoul and Kyunggi Province. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression.
Results The score of SSM showed a significantly positive correlation with the score of the level of self efficacy (SE) (r=.33, p=.00), social support (SS) (r=.27, p=.00), self care agency (SCA) (r=.36, p=.00) and daily living ability (DLA) (r=.34, p=.00). The score of DLA showed a significantly positive correlation with the score of level of SE (r=.46, p=.00), SS (r=.51, p=.00), and SCA (r=.52, p=.00). The most powerful predictor of SSM was SCA (14%). A combination of SCA, DLA, and SS account for 20 % of the variance in SSM.
Conclusion This study suggests that SCA, DLA, and SS are significant influencing factors on SSM in patients with chronic mental disorders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationships Among Demographic Factors, Stigma, Social Support, and Self-Management in Individuals With Bipolar Disorder in Remission
Chenchen Zhang, Meiying Xu, Hongwei Yu, Yuting Hua, Xiaoyan Wang, Xianan Nan, Jing Zhang
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2024; 62(7): 26. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an Integrated Health Management Program for Psychiatric Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Yun Bock Kwak, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 261. CrossRef - Effects of Basic Psychological Needs and Support of Health Professionals on Self Care Agency in Inpatients with Schizophrenia: Based on the Self-determination Theory
Jae Woon Lee, Jungho Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2020; 29(1): 33. CrossRef - The relationship of snack habits, oral health behavior and oral health status in psychiatric patients
Eun-Gyeong Lee
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2013; 13(6): 1023. CrossRef
- Relationships Among Demographic Factors, Stigma, Social Support, and Self-Management in Individuals With Bipolar Disorder in Remission
- 700 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Self Efficacy, Health Promoting Behaviors, and Symptoms of Stress among University Students
- Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(3):585-592. Published online June 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.3.585
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship between self efficacy (SE), health promoting behaviors (HPB) and symptoms of stress (SOS) among university students.
Method Data was collected by questionnaires from 369 university students in Seoul, Korea. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression.
Results The mean score for SE was 3.42, the mean score for HPB was 2.48, and the mean score for SOS was 2.31. The score of SOS showed a significantly negative correlation with the score of SE (r=-.24, p=.00) and HPB (r=-.13, r=.00). Also, SOS showed a significantly negative correlation with diet HPB (r=-.15, p=.00), spiritual growth HPB (r=-.17, p=.00), interpersonal relationship HPB (r=-.17, p=.00), and stress management HPB (r=-.10, p=.04). The most powerful predictor of SOS was SE and the variance was 10%. A combination of SE, diet, problems related to drinking, and responsibility for health HPB account for 16% of the variance in SOS among university students.
Conclusion This study suggests that SE and HPB are significant influencing factors on SOS among university students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Competitive and non-competitive school climate and students’ well-being
Márta Fülöp, Balázs András Varga, Nóra Sebestyén
Learning and Instruction.2025; 95: 102036. CrossRef - Development of a no-contact health promotion behavior program for the digital generation: A simplified one-group pretest/posttest design for nursing students
Myoung-Lyun Heo, Seung-Ha Kim, Chang-Sik Noh, Yang-Min Jang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(1): 84. CrossRef - The chain mediating roles of teacher−student relationships and perceived parental pressure between academic activities and self-efficacy in college students
Hui Wang, Zhiyi Li, Mengyao Yang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Self-concept and Self-efficacy on Well-being among College Students*
Soo-Min Cho, Sung-Doo Won
School Counselling and Sandplay.2024; 6(3): 51. CrossRef - Prolonged Social Media Use and Its Association with Perceived Stress in Female College Students
Atinuke G. Oyinbo, Karyn Heavner, Kelsey M. Mangano, Brenna Morse, Mazen El Ghaziri, Herpreet Thind
American Journal of Health Education.2024; 55(3): 189. CrossRef - Bidirectional reduction effects of perceived stress and general self-efficacy among college students: a cross-lagged study
Xinqiao Liu, Yan Li, Xiaojie Cao
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Academic Psychological Capital Resources on Student Engagement at Undergraduate Level: The Mediating Role of Faculty Support
Zınat SULTANA, Mahmud WAHID
Participatory Educational Research.2023; 10(6): 58. CrossRef - Dietary habits and nutrient intake status of university students according to obesity risk based on body mass index and percent body fat
Chae Hong Lee, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 714. CrossRef - Influence of Health Promotion Behaviors on College Life Adaptation in Maritime College Students
Hyunyoung PARK, Jeong Ok KO
THE JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2023; 35(5): 875. CrossRef - Ethnic Differences in Response to COVID-19: A Study of American-Asian and Non-Asian College Students
Yijun Zhao, Yi Ding, Hayet Chekired, Ying Wu, Qian Wang
Behavioral Sciences.2023; 13(4): 325. CrossRef - Asian American University Students’ Adjustment, Coping, and Stress during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Jacqueline Hwang, Yi Ding, Eric Chen, Cixin Wang, Ying Wu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(5): 4162. CrossRef - A Measure for Assessment of Beneficial and Harmful Fortitude: Development and Initial Validation of the Sisu Scale
Henttonen Pentti, Ilmari Määttänen, Makkonen Emilia, Honka Anita, Seppälä Vilja, Närväinen Johanna, Garcia-Velazquez Regina, Airaksinen Jaakko, Markus Jokela, Elisabet Emilia Lahti
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A measure for assessment of beneficial and harmful fortitude: development and initial validation of the Sisu Scale
Pentti Henttonen, Ilmari Määttänen, Emilia Makkonen, Anita Honka, Vilja Seppälä, Johanna Närväinen, Regina García-Velázquez, Jaakko Airaksinen, Markus Jokela, Emilia Elisabet Lahti
Heliyon.2022; 8(11): e11483. CrossRef - Transformational Leadership and Sick Leave: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Tobias Hauth, José M. Peiró, Juan M. Mesa
Journal of Leadership Studies.2022; 16(3): 6. CrossRef - Predictors of stress in college students during the COVID-19 pandemic
Mírian Celly Medeiros Miranda David, Gilberto Ramos Vieira, Lívia Maria de Lima Leôncio, Letycia dos Santos Neves, Clécia Gabriela Bezerra, Marina Souza Barbosa de Mattos, Nataly Ferreira dos Santos, Flávio Henrique de Santana, Rodolfo Barbosa Antunes, Jo
Journal of Affective Disorders Reports.2022; 10: 100377. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-efficacy and Health Promoting Behaviors on Professional Quality of Life in University Hospital Nurses
Sun Hee Song, Soon Rim Suh, Jeong Mi Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(2): 147. CrossRef - Cross-sectional Associations between Lifestyle Factors and Obesity among Students in a University at Gyeonggi Province
Jin Hee Jeong, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(4): 402. CrossRef - Relationship between Saliva Factors Measured Using the SILL-HaⓇ Saliva Test System and Blood Cell Counts according to Perceived Stress Scale Scores in Female College Students
Sun-Mi Lee, Eun-Ha Jung, Mi-Kyoung Jun
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(3): 150. CrossRef - The Impact of Different Coping Styles on Psychological Distress during the COVID-19: The Mediating Role of Perceived Stress
Yi Ding, Xinchen Fu, Rude Liu, Jacqueline Hwang, Wei Hong, Jia Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(20): 10947. CrossRef - Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Related to Metabolic Syndrome in College Students: A Cross-Sectional Secondary Data Analysis
Insil Jang, Ji-Su Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(19): 3708. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promotion Behavior by Students of the College of Maritime Sciences
Younkyoung Kim, Nooree Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Marine Environment and Safety.2018; 24(7): 889. CrossRef - The Effects of a Cognitive Behavioral Intervention on Perceived Stress and Somatic Symptoms in College Students
Soohyun Nam, Boyoung Hwang
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2017; 25(3): 179. CrossRef - Health Related Lifestyle Behaviors among Undergraduate Medical Students in Patan Academy of Health Sciences in Nepal
Sudarshan Paudel, Krishna Bahadur GC, Dil Bahadur Bhandari, Lilanath Bhandari, Amit Arjyal
Journal of Biosciences and Medicines.2017; 05(09): 43. CrossRef - Body Esteem, Stress, and Health Promoting Behavior among Korean Adults in a Community
Minhee Hong, Youngrye Park, Eun Young Chen, Jeong Woo Yun, Mi Hwa Oh
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(1): 61. CrossRef - The Effects of the Motivation Management Program on Stress Response, Self-Efficacy and Subjective Well-Being among Female University Students with Academic and Career Stress
Ji-Hye Jang, Jung-Ho Kim, Mirihae Kim
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2017; 25(4): 317. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-efficacy and Self-directed Learning Readiness to Self-leadership of Nursing Student
Sun-Young Lee, Yun-Young Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(3): 309. CrossRef - A Study on the Relationship between Body Composition Analysis and CBC in University Students
Yoon-kyung Jo, Joon Yoon, Young-KuK Cho, Hyun-Ho Sung
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2016; 48(3): 269. CrossRef - Relationship between Stress Symptoms and Health Promoting Behaviors for University Students by the Type of Residence
Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 447. CrossRef - The Convergence Study of Life Stress and Health Clinic User Satisfaction in Female Students: focused on the one women's University
Jin Hee Lee
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(5): 89. CrossRef - The Metacognition, Self-efficacy and Self-leadership among Nursing Students
Heejung Wang, Sun-A Jung, Hyo-Eun Park, Hye-Sook Yoo, Yeonhee Bae, Jiyoung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 619. CrossRef - The Convergence Study of Self-Management and Self-efficacy on Health Promotion Activities of University Student
Sook Ryon Lee
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(1): 311. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Health Promoting Behaviors of Health-related and Health-unrelated Department University Students
Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(9): 6120. CrossRef - Influence on Health Promotion Behavior among Nursing students according to Health Information Seeking Behavior
Inn Oh Moon, Sook Kyoung Park, Eun-Gyeong Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(2): 231. CrossRef - The Effects of Health Department Undergraduates' Self-efficacy on Stress-coping Strategies : Focusing on multiple group analysis by grade and sex
Yu-Mi Baek
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(8): 5273. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promotion Behaviors of College Students
Hwanhui Sim, Misook Kim, Kyeongsook Jeong, Jeeun Heo, Eunjung Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(3): 97. CrossRef - Self-efficacy and stress coping method of students in the department of dental hygiene in some areas
So-Young Lee, Myeong-Ju Lee, Sun-Hwa Kwon
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2014; 14(1): 67. CrossRef - Influencing Factors in Self-Efficacy among College Students
Kyung Hee Yoo, Jin-Hyang Yang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(3): 435. CrossRef - Assessment of implicit self-esteem in bipolar manic and euthymic patients using the implicit association test
Jin Young Park, Vin Ryu, Ra Yeon Ha, Su Jin Lee, Won-Jung Choi, Kyooseob Ha, Hyun-Sang Cho
Comprehensive Psychiatry.2014; 55(3): 557. CrossRef - The Effect of an Educational Hand Washing Program on Knowledge, Attitude and Performance of Hand Washing in Undergraduates
Eun Hee Choi, In Sun Jang, Ji Youn Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2014; 27(1): 39. CrossRef - Development of a Scale to Measure Reproductive Health Promoting Behavior of Undergraduates
Ho Yoon Jo, Young Hae Kim, Hyun Mi Son
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(5): 29. CrossRef - The differences of dietary and health-related habits, depression, eating disorder and nutrient intake according to the life stress in nursing college students
Myung-Sook Park, Kyung-Ae Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(1): 344. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Practices of Health Behavior for Cancer Prevention in University Students
Youn Na Lee, In Soo Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(2): 109. CrossRef - Health Promotion Behavior according to Body Mass Index and Self-Perception of Body Weight in Female Nursing Students
Su Jeung Yu, Kyung-Sook Lee, Joo Hyun Kim, Kyung Choon Lim, Jin Sook Park
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(1): 60. CrossRef - Relationship between School Life Stress, Self-Esteem and Health Promoting Behaviors for Specialized High School Students
Sung-Ok Lee, Sun-Mi Lee, Jong-Lim Kim, Jeong-Sook Lee
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2013; 7(2): 11. CrossRef - Depression Cognition and Health Promoting Behaviors of Smoking and Non-smoking College Students
Mi-Ok Kim, Mi Yu, Se-Jin Ju, Kyeong-Suk Kim, Jung-Hyun Choi, Hee-Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(3): 35. CrossRef - Ethnographic Analysis on Health-related Behavioral Patterns of Male College Students in a Weight-control Program
Jeong Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(2): 241. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Dietary Habits, Life Habits, Physical Symptoms and Body Composition of University Students by Gender Differences in Incheon City
Jae-Seon Jang, Myung-Sun Hong
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2013; 26(4): 928. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Health Promotion Behavior of Fire Officers
Ja-Ok Kim, Ja-Sook Kim, A-Yong Park, Su-Jeong Han
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(3): 218. CrossRef - Effects of Self-esteem and Academic Stress on Depression in Korean Students in Health Care Professions
Jaeku Kang, Yu Kyung Ko, Hye-Kyung Lee, Kyung-hee Kang, Yera Hur, Keum-ho Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(1): 56. CrossRef - Effects of a Health Education Program based on Social Cognitive Theory on the Health Promotion of University Students with Metabolic Syndrome
Hee-Gerl Kim, Jinhwa Lee, Jiyun Kim, Hyunju Park, Hyun Sook Oh, Won Jae Lee, Eun Aae Kim, Hye Kyung Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(4): 451. CrossRef - Impact of Stress on Depression among University Students: Testing for Moderating Effect of Social Support
Young Rye Park, Eun Hee Jang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(5): 549. CrossRef - An Analysis of Factors Affecting Energy Drink Consumption in College Students
Haesun Yun, Su Hee Kim, Chung Yul Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(3): 1. CrossRef - Self-reported Realities of Health Behavior of Undergraduate Students After Web-based Health Promotion Education: Qualitative Content Analysis
Joo Hyun Kim, Eun Young Park, Kyung Choon Lim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2012; 18(3): 413. CrossRef - Relationships between Knowledge, Attitude and Preventive Health Behavior about Cancer in University Students
Ick-Jee Kim, Sang-Hee Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(1): 44. CrossRef - A study on the effect of self-efficacy and stress-coping method of dental hygienist
Young-Soon Won, So-Young Park, Jeong-Suk Kim
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2012; 12(5): 909. CrossRef - Health Knowledge, Health Promoting Behavior and Factors Influencing Health Promoting Behavior of North Korean Defectors in South Korea
Myoung-Ae Choe, Myungsun Yi, Jung-An Choi, Gisoo Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(5): 622. CrossRef - Development of a Structural Equation Model to estimate University Students' Depression
Kwang-Hi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 779. CrossRef
- Competitive and non-competitive school climate and students’ well-being
- 1,300 View
- 30 Download
- 57 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


