Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Successful aging among the elderly with mild cognitive impairment facing the crisis of old age: a grounded theory study
- Haeyun Shin, Suhye Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):301-316. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Methods
The participants were 15 older adults with mild cognitive impairment who had experienced successful aging. Data were collected from January to October 2021 through individual deep, unstructured interviews. Data analysis was performed using Charmaz’s grounded theory method. In addition, the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research checklist was used to ensure the quality of the study.
Results
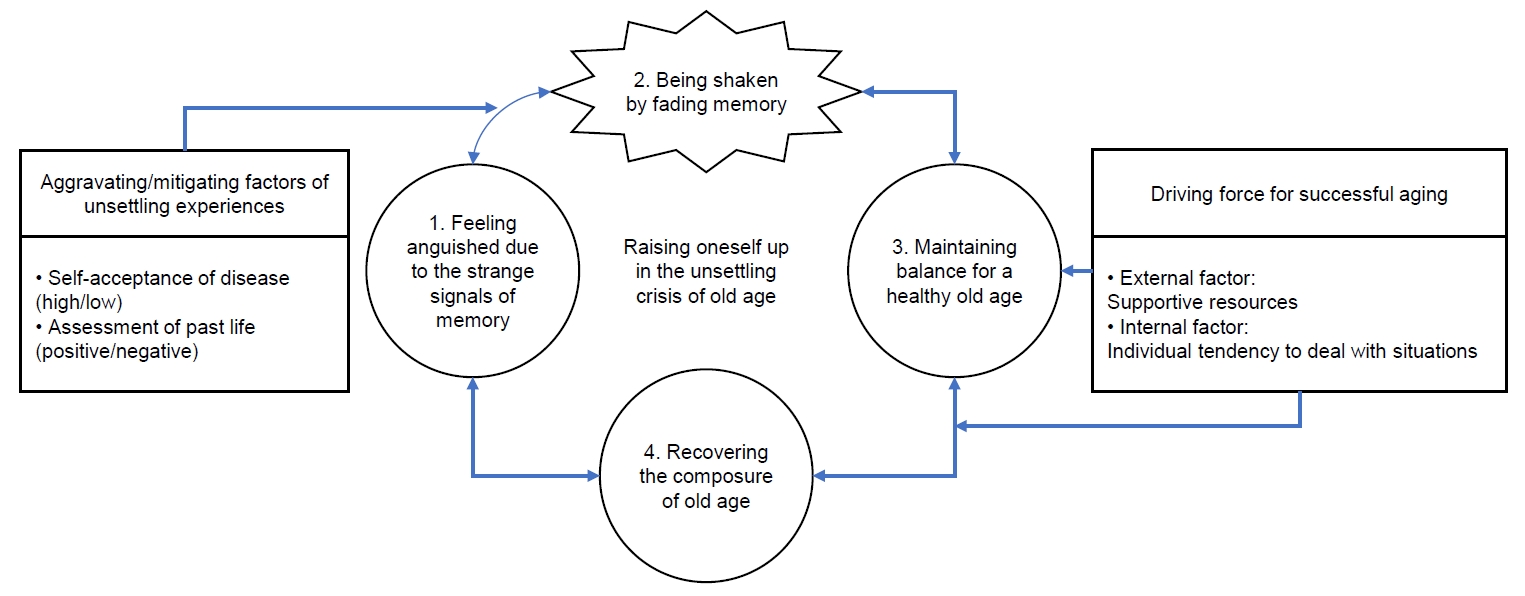
The key category representing experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment was “raising oneself up in the unsettling crisis of old age.” Four stages were derived: “feeling anguished due to the strange signals of memory,” “being shaken by fading memory,” “maintaining balance for a healthy old age,” and “recovering the composure of old age.”
Conclusion
Participants tried to successfully achieve aging while implementing their own plans and strategies in the midst of the challenges of old age, when the mind and body were unsettled by mild cognitive impairment. The results of this study provide a deep understanding of experiences of successful aging in older adults with mild cognitive impairment, potentially contributing to the development and implement of nursing intervention programs to promote the successful pursuit of aging in this population.
- 2,254 View
- 113 Download

- Nomogram for predicting changes in cognitive function in community dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment based on Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data: a retrospective study
- Hyuk Joon Kim, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):50-63. Published online February 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify factors associated with normal cognitive reversion and progression to dementia in older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) residing in the community and to develop a nomogram.
Methods
This longitudinal study used secondary data from the Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data (2006–2018). The study included 1,262 participants aged 60 or older, with initial Mini-Mental State Examination scores ranging from 18 to 23. Data were analyzed using the Rao-Scott chi-square test, panel binary logistic regression, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve in Stata ver. 17.0 (Stata Corp.).
Results
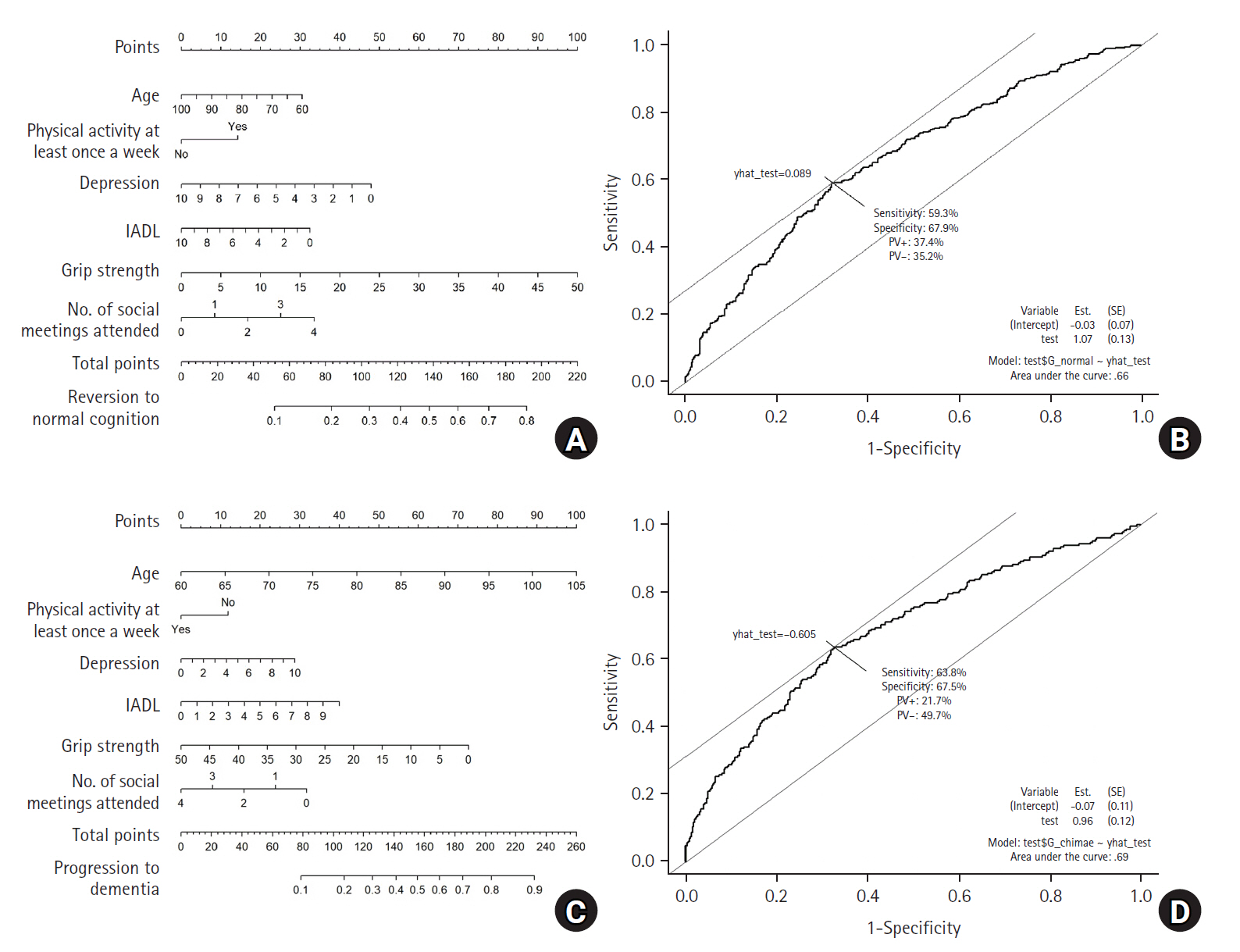
The rate of reversion from MCI to normal cognition was 37.0% after 2 years and 32.9% after 12 years. The rate of progression to dementia was 18.0% after 2 years and 30.2% after 12 years. In the nomogram for reversion to normal cognition, the most significant influences were grip strength, depression, number of meetings, age, and regular exercise, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of .66. In contrast, in the nomogram for progression to dementia, the most significant influences were age, grip strength, instrumental activities of daily living, number of social meetings attended, depression, and regular exercise, with an AUC of .69.
Conclusion
These nomograms can serve as an effective intervention tool for preventing dementia in the field of community health care since they can serve as a visual technique for presenting information on risk to individuals with MCI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Functions and Cognitive Functions Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Primary Care
Nan Hu, Wupeng Yin, Rabeya Illyas Noon, Noof Alabdullatif
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(6): 908. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Nomogram Predicting Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Sook Kyoung Park, Hyuk Joo Kim, Young-Me Lee, Hye Young Kim
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Emotional Labor on Burnout in Nurses: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Social Intelligence and Emotional Intelligence
Kyung Ran Lee, Jeoung Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(1): 22. CrossRef
- The Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Functions and Cognitive Functions Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Primary Care
- 3,509 View
- 212 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- An Investigation of the Cumulative Effects of Depressive Symptoms on the Cognitive Function in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging
- Eunmi Kim, Jinkyung Oh, Iksoo Huh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):453-467. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the cumulative effects of depressive symptoms on cognitive function over time in community-dwelling older adults. Methods: Data were investigated from 2,533 community-dwelling older adults who participated in the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA) from the 5th (2014) to the 8th wave (2020). The association between cumulative depressive symptoms and cognitive function was identified through multiple regression analysis. Results: When the multiple regression analysis was conducted from each wave, the current depressive symptoms scores and cognitive function scores were negatively associated, regardless of the waves (B5th = - 0.26, B6th = - 0.26, B7th = - 0.26, and B8th = - 0.27; all p < .001). Further, when all the previous depressive symptoms scores were added as explanatory variables in the 8th wave, the current one (B8th = - 0.09, p < .001) and the previous ones (B5th = - 0.11, B6th = - 0.09, and B7th = - 0.13; all p < .001) were also negatively associated with the cognitive function score. The delta R2 , which indicates the difference between the model’s R2 with and without the depressive symptoms scores, was greater in the model with all the previous and current depressive symptoms scores (6.4%) than in the model with only the current depressive symptoms score (3.6%). Conclusion: Depressive symptoms in older adults have a long-term impact. This results in an accumulated adverse effect on the cognitive function. Therefore, to prevent cognitive decline in older adults, we suggest detecting their depressive symptoms early and providing continuous intervention to reduce exposure to long-term depressive symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic identification and quantification of factors and their interactions with age, sex, and panel wave influencing cognitive function in Korean older adults
Eunmi Kim, Jinkyung Oh, Jungsoo Gim, Iksoo Huh
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Systematic identification and quantification of factors and their interactions with age, sex, and panel wave influencing cognitive function in Korean older adults
- 2,261 View
- 56 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Motivational Interviewing Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program Based on Self-Determination Theory for Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Jun Hee Jang, Hye Sook Min
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):191-207. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22093
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a motivational interviewing pulmonary rehabilitation program based on self-determination theory to maintain pulmonary rehabilitation-related health behaviors in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The program was developed by reviewing the literature on pulmonary rehabilitation guidelines, drawing on the self-determinism theory to establish its contents, recruiting experts to test its validity, and conducting a preliminary survey.
Methods
A quasi-experimental design was used to confirm the effect of the program. The participants were outpatients diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at three general hospitals in Busan. There were 33 subjects: 15 in the experimental group and 18 in the control group. The experimental group performed a motivational interviewing pulmonary rehabilitation program which comprised 11 sessions delivered over 10 weeks. The outcomes were measured using basic psychological needs, dyspnea, 6-minute walking distance, and functional status. Intervention effects were analyzed using repeated-measures ANOVA.
Results
The analysis revealed significant differences between the experimental and control groups in competence among the subdomains of basic psychological needs, dyspnea during exercise, and functional status.
Conclusion
The developed program affects physical conditions and can be applied as an effective clinical nursing intervention to continuously improve the pulmonary rehabilitation behavior of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Enhee Jo, Ju-Young Park, Young Jun Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 315. CrossRef
- Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 2,574 View
- 133 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Virtual Reality Program for Alleviating Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia Patients
- Seon-Min Park, Seung-Yi Choi, Jung-Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):121-133. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the impact of a virtual reality intervention program based on psychological needs on behavioral and psychological symptoms, apathy, and quality of life (QOL) in patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment living in nursing facilities.
Methods
This study is nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design of quasi-experimental study. The study collected data from November 18, 2020 to July 24, 2021 from patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment (30 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group) at three nursing facilities in G city using self-reporting and caregiver-informant reporting methods. The analysis employed the chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, paired t-test, independent t-test, Wilcoxon signed rank test, Mann–Whitney U, repeated measures ANOVA, GEE, using SPSS/WIN 27.0.
Results
The severity of behavioral and psychological symptoms (Wald χ2 = 2.68, p = .102) and the care burden of caregivers (Wald χ2 = 1.72, p = .190) were not significant and was no significant time and group interaction effect (Wald χ2 = 0.63, p = .426, Wald χ2 = 0.52, p =. 471). The difference in apathy and QOL score were statistically significant for the group-time interaction (F = 43.65, p < .001; F = 4.35, p= .041).
Conclusion
The virtual reality intervention program of this study shows a positive effect on the apathy reduction and QOL of patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment residing in nursing facilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for elderly dementia patients based on virtual reality technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jun Wen, Hong Yan, Siyu Wang, Jialan Xu, Zitong Zhou
Ageing Research Reviews.2024; 93: 102135. CrossRef - Development of the “living well” concept for older people with dementia
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for elderly dementia patients based on virtual reality technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 2,135 View
- 104 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Influences of Autonomic Function, Salivary Cortisol and Physical Activity on Cognitive Functions in Institutionalized Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: Based on Neurovisceral Integration Model
- Minhee Suh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):294-304. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate objectively measured physical activity (PA) in institutionalized older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and to elucidate the influence of autonomic nervous function, salivary cortisol, and PA on cognitive functions based on neurovisceral integration model.
Methods
Overall cognitive function was evaluated using the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) and executive function was evaluated using semantic verbal fluency test and clock drawing test. Actigraph for PA, HRV and sAA for autonomous function, and the geriatric depression scale for depression were used. Saliva specimens were collected in the morning for sAA and cortisol.
Results
Ninety-eight older adults from four regional geriatric hospitals participated in the study. They took 4,499 steps per day on average. They spent 753.93 minutes and 23.12 minutes on average in sedentary and moderate-to-vigorous activity, respectively. In the multiple regression analysis, lower salivary cortisol level (β = - .33, p = .041) and greater step counts (β = .37, p = .029) significantly improved MMSE score. Greater step count (β = .27, p = .016) also exerted a significant influence on verbal fluency, and greater sAA (β = .35, p = .026) was significantly associated with a better clock drawing test result.
Conclusion
Salivary cortisol, sAA and physical activity were significantly associated with cognitive functions. To prevent older adults from developing dementia, strategies are needed to increase their overall PA amount by decreasing sedentary time and to decrease salivary cortisol for cognitive function, and to maintain their sympathetic nervous activity for executive function. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between physical activity levels, sedentary time, and mild cognitive impairment in older adults
Wei Chen, Lei Zhang, Palida Abulizi, Ting Zou, Xuan Xiang, Ruikai Wu, Xiaohui Zhou
Frontiers in Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Rest-activity circadian rhythm in hospitalized older adults with mild cognitive impairment in Korea and its relationship with salivary alpha amylase: an exploratory study
Minhee Suh, Jihye Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(4): 306. CrossRef - Circadian Rhythm Changes in Healthy Aging and Mild Cognitive Impairment
Ahmadreza Keihani, Ahmad Mayeli, Fabio Ferrarelli
Advanced Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in stress pathways as a possible mechanism of aerobic exercise training on brain health: a scoping review of existing studies
Cristina Molina-Hidalgo, Chelsea M. Stillman, Audrey M. Collins, Daniel Velazquez-Diaz, Hayley S. Ripperger, Jermon A. Drake, Peter J. Gianaros, Anna L. Marsland, Kirk I. Erickson
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between physical activity levels, sedentary time, and mild cognitive impairment in older adults
- 1,719 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Prediction Models of Mild Cognitive Impairment Using the Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing
- Hyojin Park, Juyoung Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):191-199. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to compare sociodemographic characteristics of a normal cognitive group and mild cognitive impairment group, and establish prediction models of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI).
Methods
This study was a secondary data analysis research using data from “the 4th Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing” of the Korea Employment Information Service. A total of 6,405 individuals, including 1,329 individuals with MCI and 5,076 individuals with normal cognitive abilities, were part of the study. Based on the panel survey items, the research used 28 variables. The methods of analysis included a c2-test, logistic regression analysis, decision tree analysis, predicted error rate, and an ROC curve calculated using SPSS 23.0 and SAS 13.2.
Results
In the MCI group, the mean age was 71.4 and 65.8% of the participants was women. There were statistically significant differences in gender, age, and education in both groups. Predictors of MCI determined by using a logistic regression analysis were gender, age, education, instrumental activity of daily living (IADL), perceived health status, participation group, cultural activities, and life satisfaction. Decision tree analysis of predictors of MCI identified education, age, life satisfaction, and IADL as predictors.
Conclusion
The accuracy of logistic regression model for MCI is slightly higher than that of decision tree model. The implementation of the prediction model for MCI established in this study may be utilized to identify middle-aged and elderly people with risks of MCI. Therefore, this study may contribute to the prevention and reduction of dementia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nomogram for predicting changes in cognitive function in community dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment based on Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data: a retrospective study
Hyuk Joon Kim, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 50. CrossRef - Development of a neural network-based risk prediction model for mild cognitive impairment in older adults with functional disability
Deyan Liu, Yuge Tian, Min Liu, Shangjian Yang
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding Cognitive Trajectories in Middle-Aged and Older Cancer Survivors: An Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging
Mi Sook Jung, Munkyung Park, Kyeongin Cha, Xirong Cui, Nondumiso Satiso Dlamini, Ah Rim Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 507. CrossRef - Cognitive Dysfunction Prediction Model with Lifelog Dataset based on Random Forest and SHAP
Myeongjin Lee, Jongun Lee, Hanjun Lee
The Journal of Korean Institute of Information Technology.2024; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Sociodemographic Factors Predict Incident Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Brief Review and Empirical Study
Shuyi Jin, Chenxi Li, Jiani Miao, Jingyi Sun, Zhenqing Yang, Xingqi Cao, Kaili Sun, Xiaoting Liu, Lina Ma, Xin Xu, Zuyun Liu
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2023; 24(12): 1959. CrossRef - Characteristics and Factors Associated with Cognitive Decline of Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Eul Hee Roh
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(3): 179. CrossRef - Detection and Intervention of Subjective Cognitive Decline in Pre-Alzheimer’s Disease
雅红 何
International Journal of Psychiatry and Neurology.2022; 11(04): 65. CrossRef - Influencing Factors of Subjective Cognitive Impairment in Middle-Aged and Older Adults
Min Roh, Hyunju Dan, Oksoo Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11488. CrossRef
- Nomogram for predicting changes in cognitive function in community dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment based on Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data: a retrospective study
- 2,859 View
- 40 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients
- Jung Ran Lee, Pok Ja Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):375-385. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.375
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and test a structural model for chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment of breast cancer patients based on a literature review and Hess and Insel's chemotherapy-related cognitive change model.
Methods The Participants consisted of 250 patients who were ≥19 years of age. The assessment tools included the Menopause Rating Scale, Symptom Experience Scale, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Everyday Cognition, and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast Cancer. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs.
Results The modified model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were χ 2=423.18 (
p <.001), χ 2/df=3.38, CFI=.91, NFI=.91, TLI=.89, SRMR=.05, RMSEA=.09, and AIC=515.18. Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment was directly influenced by menopausal symptoms (β=.38,p =.002), depression and anxiety (β=.25,p =.002), and symptom experiences (β=.19,p =.012). These predictors explained 47.7% of the variance in chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety mediated the relations among menopausal symptoms, symptom experiences, and with chemotherapy related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety (β=-.51,p =.001), symptom experiences (β=-.27,p =.001), menopausal symptoms (β=-.22,p =.008), and chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (β=-.15,p =.024) had direct effects on the quality of life and these variables explained 91.3%.Conclusion These results suggest that chemotherapy-related toxicity is highly associated with cognitive decline and quality of life in women with breast cancer. Depression and anxiety increased vulnerability to cognitive impairment after chemotherapy. Nursing intervention is needed to relieve chemotherapy-related toxicity and psychological factor as well as cognitive decline for quality of life in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of social support on cognitive function in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: The chain-mediating role of fatigue and depression
Yuanqi Ding, Qingmei Huang, Fulei Wu, Yang Yang, Ling Wang, Xuqian Zong, Xiaoyan Yu, Changrong Yuan
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100743. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 418. CrossRef - Relationships Between Chemotherapy-Related Cognitive Impairment, Self-Care Ability, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nan Wu, Ze Luan, Zijun Zhou, He Wang, Shiyuan Du, Yulu Chen, Xinxin Wang, Jiong Li, Xin Peng
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2024; 40(5): 151690. CrossRef - Effects of different exercise interventions on chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer: a study protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
Yu Dong, Hao Huang, Aiping Wang
BMJ Open.2024; 14(4): e078934. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Impact of discriminant factors on the comfort-care of nurses caring for trans-arterial chemoembolisation patients
Myoung Soo Kim, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(9): 7773. CrossRef - Brain morphological alterations and their correlation to tumor differentiation and duration in patients with lung cancer after platinum chemotherapy
Pin Lv, Guolin Ma, Wenqian Chen, Renyuan Liu, Xiaoyan Xin, Jiaming Lu, Shu Su, Ming Li, ShangWen Yang, Yiming Ma, Ping Rong, Ningyu Dong, Qian Chen, Xin Zhang, Xiaowei Han, Bing Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Clinical Study
Teresa Paolucci, Aristide Saggino, Francesco Agostini, Marco Paoloni, Andrea Bernetti, Massimiliano Mangone, Valter Santilli, Raoul Saggini, Marco Tommasi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8585. CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,794 View
- 23 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of Low-intensity Exercise on Functional Ability in Hospitalized Elderly
- Rhayun Song, Yeon Ok Suh, Young Rhan Um, Kyung Ja June, Beverly L Roberts
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):807-819. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.807
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of the study was to identify the effects of 12-week low-intensity exercise program on muscle strength, flexibility, balance, and cognitive characteristics related to the performance of activity of daily living(ADL). A total of 16 patients who were admitted to the medical unit of a general hospital in ChoongChung province were recruited eight for the exercise group and eight for the comparison group. Four levels of low-intensity exercise from 'ROM on bed' to 'exercise while walking' were then applied to the exercise group according to their physical condition. During hospitalization, patients in the exercise group performed each level of the prescribed exercise with the researchers until they felt. comfortable doing it independently. The researchers also visited the patients' homes after discharge to make sure they could perform the exercise with Theraband in their living environment. The exercise group was contacted by phone once a week to assess the frequency and intensity in which they performed the exercise as well as their physical condition. The subjects in the comparison group participated in measurements for the study without performing the exercise and were contacted by phone after discharge, in a matched time frame with the exercise group, to assess physical condition. Muscle strength, flexibility, balance, cognitive characteristics, and performance of ADL for the two groups were compared at the pretest and the posttest after the low-intensity exercise program by utilizing SPSSWIN and the results are as follows : 1) At the posttest, measurments of muscle strengths showed that the strength of the dorsal flexor in the exercise group was significantly higher than in the comparison group. 2) Objective balance for the exercise group was significantly better than for the comparison group as measured by 'standing on one foot' and Tinetti gait and balance control. 3) The exercise group showed significantly higher task self-efficacy than the comparison group. 4) Perceived exertion for ADL for the exercise group was significantly lower than for the comparison group. 5) Improvement of performance of ADL without assistance was significantly for the exercise group than the comparison group. The findings suggest that a low-intensity exercise program would be useful for the elderly who show decline in their physical functioning due to hospitalization by partly improving physical strength, task self-efficacy, and performance of ADL. Directions for further research on issues of motivating people to exercise as well as of standardizing various types of exercise were discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Basic Physical Capability Scale for Older Adults
Eun-Ok Song, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(1): 21. CrossRef - A study on the effects of exercise motivation of the elderly people on euphoria
Ah-Ra Oh, Eun-Surk Yi
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2017; 13(4): 387. CrossRef
- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Basic Physical Capability Scale for Older Adults
- 664 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Effect of Walking Exercise Program on Cardiorespiratory Function and Flexibility in Elderly Women
- Yun Hee Shin, Young Hee Choi
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(2):372-386. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.2.372
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recently, the ratio of elderly in the population are fastly growing due to socio-economical development and the better medical service. Proportionally, the health problems in elderly are increasing, too. Medical professionals must try so that the elderly have the better life through health promotion and disease prevention as well as disease treatment. This study evaluated the effect of walking exercise program on the cardiorespiratory function and the flexibility in the elderly women. The design of research was one group pretest -posttest design. The subjects were eleven elderly women over sixty years old to live in K-city, Kyonggi-do. The type of exercise was walking, which was the most popular exercise in questionnaire. The exercise intensity was 40%~60% of the target heart-rate by Karvonen's method and maintained by the heart-rate monitor. The exercise period was five weeks and the exercise frequency was three times per week. The exercise duration was forty minites at first and gradually increased up to a hour. In order to evaluate the effect of walking exercise, we measured VO2 max, resting heart-rate, systolic/diastolic blood pressure, FVC, FEV1, the flexibility before and after the five week's exercise program. The data are analyzed by the paired t-test and Wilcoxon signed rank test using SAS package. The results are as follows: 1) The hypothesis that cardiorespiratory function will be improved was partly supported. In VO2 max(p=0.0001), resting heart-rate(p=0. 0030), systolic/diastolic blood-pressure (p=0.0387/p=0.0024), there was significant difference. FVC and FEV1 were increased after the exercise, but there were no significant difference. 2) The hypothesis that the flexibility will be improved was supported. There was significant difference in the flexibility (p=0.0140). As the further study, it is necessary to reevaluate the effect with more refined design. We also need to try meta-analysis about the results of previous studies obtained in the experimental setting and compare our result obtained in the field setting with them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 여성 노인과 여가 스포츠
재윤 배
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2024; 63(3): 403. CrossRef - Effect of a Home-based Exercise Program on Elderly Women’s Health
Hyo-Lyun Roh, Dae-Hee Lee
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2012; 24(5): 449. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Therapy on Physical Functions in the Elderly
Sook Hee Jung, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 252. CrossRef
- 여성 노인과 여가 스포츠
- 624 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effect of Circumvaginal Muscle Exercise on Sexual Function in Married Women
- Young Sook Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(1):148-164. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.1.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effect of circumvaginal muscle (CVM) exercises to improve sexual function in married women has not been investigated by currently acceptable research methods, nor have appropriate instruments and techniques to carry out such investigation been available. The purpose of this research was to study the effect of CVM exercise on sexual function, and of measuring CVM function after CVM exercises. The research tools used were a modified Derogatis Sexual Function Inventory questionnare and a pressure sensitive intravaginal balloon device. This research was conducted in Kwangju-city and Chonnam province, Korea from July, 1994 to July, 1995. The research used a non-equivalent control pre-post test quasi-experimental design. Forty-five healthy married female volunteers, aged 30?8, and were randomly assigned by age using the matching fixed-length blocks to two groups. The experimental group consisted of 21 women who were assigned a 25 -minute per day CVM home exercise program for six weeks. The control group of 24 women did not do the CVM home exercises. The CVM home exercise was developed by Dougherty (1989a) and adopted to Korea by Lee (1993). Data were analyzed by x2-test, Paired t-test, Spearman product-moment correlation using SAS/PC+. The results are summarized as follows: 1. There were no significant differences in the characteristics of the subjects between the exper imental and control groups before the CVM home exercises. 2. Hypothesis 1 that married women who participated in CVM home exercises would have higher mean scores on the sexual function (SF) than in those who did not participate in home exercise was supported. 3. Hypothesis 2 that married women who participated in CVM home exercises would have higher vaginal pressure on SF than in those who did not participate in home exercises was supported (mean maximum pressure, t= -7.338, P<.0001, peak maximum pressure, t=-11.164, P<.0001). 4. Hypothesis 3 that the more often (number of days) and the more frequent (numbers of times per day) that married women do CVM home exercise, the higher their mean scores on SF and vaginal pressures was supported (r =0.233, P<.01; r=0.352, P<.05). A six week CVM home exercise program using a tape recording showed that SF can be improved. Results of this study showed that married women who exercise on a regular basis for six weeks improve their sexual function and increase the mean vaginal pressure and peak maximum pressure (tested by electronic monitor). In conclusion, CVM exercise is effective in increasing SF.
- 408 View
- 0 Download

- Factors Influencing Functional Status in People with Chronic Lung Disease
- Eui Geum Oh, Cho Ja Kim, Won Hee Lee, So Sun Kim, Bo Eun Kwon, Yeon Soo Chang, Ji Yeon Lee, Young Jin Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):643-653. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.643
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to identify factors that influence the functional status of chronic lung disease patients. METHOD: A descriptive, correlational study design was used. The study was conducted at the outpatient respiratory clinic of the large university hospital in Korea. A convenience sample of 128 chronic lung patients (age = 64.2 yrs; 106 COPD, 17 bronchiectasis, 5 DILD) with mean FEV1 64.4 % predicted. Functional status was measured with SIP. Physical variables (FEV1% predicted, dyspnea, fatigue, pulmonary symptom distress), psychological variables (mood, stress), and situational variable (sleep quality) were examined. Dyspnea was measured by the BDI, fatigue was measured with the MFI. Mood was measured with the modified Korean version of POMS. Sleep quality was measured with the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Potential independent variables for the regression were age, gender, years since diagnosis, FEV1% predicted, dyspnea, fatigue, pulmonary symptom distress, stress, and sleep quality. RESULT: In general, functional status was relatively good. In regression analysis, functional status were significantly influenced by dyspnea, mood, age and fatigue. These variables explained 70 % of the variances in functional status. CONCLUSION: The results suggest that psychophysiologic symptom management should be a focus to enhance the functional status in this group.
- 428 View
- 2 Download

- The Effect of the Dan-Jun Breathing Exercise Program on pulmonary function and psychological Health of Women in Midlife
- Kyung Sun Hyun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(4):459-469. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.4.459
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was to examine the effects of the Dan-Jun Breathing Exercise Program on pulmonary function and psychological health promotion of women in midlife. METHOD: Experimental group(20) was matched to control group(20) according to age, education, religion and marital status. The Dan-Jun Breathing Exercise Program was carried out for 80 minutes a day, 3 times a week for 12 weeks. FVC and FEV1.0/FVC(%) were measured by using the Health Management System developed by the Korean Physical Science Institution. The scores of depression, anxiety and hostility were measured by the Korean Manual of Symptoms-Checklist -90 revision. RESULT: 1) FVC of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group, FEV1.0/FVC(%) was not higher than that of the control group. 2) The scores for depression, anxiety and hostility in the experimental group were lower than those of the control group. 3) FVC of 6 weeks and 12 weeks experiment in the experimental group was higher than that of pre-experimental group. CONCLUSION: The Dan-Jun Breathing Exercise Program promotes the Pulmonary function and psychological health of women in midlife.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Trend on Aromatherapy for Korean Middle-aged Women
Hee-Jung Yong, Hyun Hee Jang, Sung Nae Lee, Soo-Yeon Kim, Young-Sam Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2017; 15(1): 113. CrossRef
- Research Trend on Aromatherapy for Korean Middle-aged Women
- 739 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study on the Development of the Korean Family Functioning Scale
- In Sook Lee, Young Sook Park, Mi Soon Song, Eun Ok Lee, Hesook Suzie Kim, Youn Hwan Park, Kyong Won Choi, Young Ran Chin, Dae Hee Kim, Hyeon Sook Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(3):395-405. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.3.395
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to develop the instrument to measure family functioning for Korean family with a chronic ill child, and to test the validity and reliability of the instrument. METHOD: The items of instrument were consisted based on researchers' previous study of concept analysis of the Korean family functioning. Twenty six item scale was developed with six domains. In order to test reliability and validity of the scale, data were collected from the 231 families, who have a child with a chronic illness. Data was collected between August and September in 2001 in a General Hospital in Seoul, Korea. RESULT: The results were as follows:As a result of the item analysis, 24 items were selected from the total of 26 items, excluding items with low correlation with total scale. Six factors were evolved by factor analysis. Six factors explained 61.4% of the total variance. The first factor 'Affective bonding' explained 15.4%, 2nd factor 'External relationship' 11.8%, 3rd factor 'Family norm' 10.5%, 4th factor 'Role and responsibilities' 8.3%, 5th factor ' Communication' 7.9%, and the 6th factor 'Financial resource' explained 7.3%. Cronbach's alpha coefficient of this scale was .87 and Guttman spilt- half coefficient was .84. CONCLUSION: The study support the reliability and validity of the scale. There were distinct differences in dimensions of family functioning scales developed in the U. S.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The father’s attachment to the fetus and related factors in late pregnancy: a longitudinal study using a path analysis model
Marie Tabayashi, Tomoharu Sato, Tae Kawahara, Akemi Yamazaki
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing self-management behaviors in older people with multiple chronic conditions based on the individual and family self-management theory: A cross-sectional study
Youngji Seo, Sunyoung Jung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(3): 332. CrossRef - Do spouse burden of care, family resilience, and coping affect family function in gynecologic cancer in Korea?: a cross-sectional study
Minkyung Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 197. CrossRef - Family functioning according to clusters of family management styles in Korean families of children with chronic atopic disease: A cross-sectional study
YeoJin Im, Sunyoung Jung
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 109: 103674. CrossRef - Factors Related to Dementia Worry: Comparing Middle-Aged and Older Adults in South Korea
So Im Ryu, Yeon-Hwan Park
Research in Gerontological Nursing.2019; 12(6): 299. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Korea Midlife Family Resilience Scale(KMFRS)
Hea Rhan Park, Gwee-Yeon Jeon
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2014; 23(6): 1013. CrossRef - Infants' Temperament and Health Problems according to Maternal Postpartum Depression
Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 444. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Social Isolation in Older Adults using Senior Welfare Centers
Yeon-Hwan Park, Hee Sun Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 712. CrossRef - To Holroyd E (2005) Commentary on Lee et al. (2004)
Insook Lee, Eun‐Ok Lee, Hesook Suzie Kim, Young Sook Park, Misoon Song, Youn Hwan Park
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2006; 15(5): 654. CrossRef
- The father’s attachment to the fetus and related factors in late pregnancy: a longitudinal study using a path analysis model
- 941 View
- 18 Download
- 9 Crossref

- A Survey on Functional Status among Low-Income Older Adults Living at Home
- Kyung Ja June, Yoon Mi Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(5):749-758. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.5.749
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of the study was to analyze the functional status of low income elderly living at home according to their socio-economic factors, sensory function, health status, medical service utilization, commodity and types of chronic disease.
METHOD
Functional status was defined by the level of mobility, ADL and IADL categorized as independently functional, mildly impaired, moderately disabled, and severely disabled. The data was collected by home-visit interviews with 567 community dwelling adults who were 65 years of age or more with low a income status subsidized by government in ChonAn.
RESULTS
9.9% of community dwelling older adults were severely disabled, and 44.4% were moderately disabled in their functional status. There were significant differences in the functional status by age, education, religion, and types of family structure. The older adults with hearing impairment or dental problems had a significantly higher rate of severe disability. Self-rated health status and medical service utilization were also significant factors to the differences in functional status. The functional status of older adults was also significantly related to the presence of chronic health problems such as chronic back pain, stroke, and Alzheimer-dementia.
CONCLUSION
The results confirmed that community dwelling older adults with low income status were more functionally disabled in comparison to general older adults at national level, while the relating factors to their functional status seemed similar to other studies on older adults. Further studies were suggested to look into functional status longitudinally and focus on the changes of functional status by managing modifiable influencing factors.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Case Management using Resident Assessment Instrument-Home Care (RAI-HC) in Home Health Services for Older People
Kyung Ja June, Ji Yun Lee, Jong Lull Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 366. CrossRef
- Effects of Case Management using Resident Assessment Instrument-Home Care (RAI-HC) in Home Health Services for Older People
- 720 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development of an Urban Community Based Comprehensive Service Model for Bed-Ridden Elderly
- Keum Soon Kim, Moon Ja Suh, Nam Ok Cho, In Ja Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(4):656-668. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.4.656
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study aims to identify the ADL and IADL of bed-ridden elderly. Also it is used to show fuctional status, and to investigate the content and the level of nursing services provided. METHOD: The subjects were 191 elderly who received visiting nurse service through public health centers in the Seoul Metopolitan and Chungnam Province. Data collection was conducted by public health center nurses during four months in 2000. Result: As for daily living activities, 100% of subjects had at least one difficulty in ADL and IADL. Among them, only 0.5% had moderate disabilities and 99.5% had severe disabilities by HFS, 27.9% were in a semi bed-ridden state and 72.1% were completely bed-ridden by JABC. The major service provided was a visiting nurse service which was preferable to the social welfare service. In the visiting nurse service, there was no significant difference according to the elderlys' functional status. In addition there was no standadization about the qualification of the visiting nurse, and single entry point for the nursing service. CONCLUSION: The researchers urgently suggest that a community based comprehensive service model has to be developed to respond to the needs of the elderly in Korea.
- 444 View
- 0 Download

- Effects of Exercise on Cardiopulmonary Functions and Shoulder Joint Functioning in Breast Cancer Patients undergoing Radiation Therapy after Breast Surgery
- Young Ran Chae, Myoung Ae Choe
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):454-466. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.454
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of exercise program on cardiopulmonary functions and shoulder joint functioning in breast cancer patients who under- went radiation therapy after surgery. METHOD: Subjects in the experimental group(N=12) participated in an exercise program for eight weeks. The Exercise program consisted of shoulder stretching, arm weight training, and walking on treadmill. Maximal oxygen uptake(o2max), maximal running time, shoulder joint range of motion, and shoulder functional assessment were determined before and after the exercise program. Baseline sociodemographic and medical data were compared between experimental group and control group using the Fisher's exact test and Mann- Whitney U test. For effects of the exercise program, repeated measures ANOVA were used. RESULT: 1) Following the exercise program for eight weeks, both o2 max and maximal running time tended to increase in experimental group comparing with the control group. 2) Shoulder abduction, extension and flexion of the operated upper extremity in the experimental group comparing with control significantly increased after the exercise program(p<0.05). 3) Shoulder flexion of the normal upper extremity in the experimental group comparing with control significantly increased after the exercise program(p<0.05). CONCLUSION: The
results
suggest that the exercise program for breast cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy after breast surgery can improve shoulder functions and increase cardiopulmonary functions, which are maximal oxygen uptake and maximal running time.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Short-term effects of a new resistance exercise approach on physical function during chemotherapy after radical breast cancer surgery: a randomized controlled trial
Ming Huo, Xin Zhang, Jialin Fan, Hao Qi, Xuemei Chai, Minghui Qu, Yuqi Shan, Hualong Xie, Chao Wang
BMC Women's Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pre-post analysis of a social capital-based exercise adherence intervention for breast cancer survivors with moderate fatigue: a randomized controlled trial
Sue Kim, Yun Hee Ko, Yoonkyung Song, Min Jae Kang, Hyojin Lee, Sung Hae Kim, Justin Y. Jeon, Young Up Cho, Gihong Yi, Jeehee Han
Supportive Care in Cancer.2020; 28(11): 5281. CrossRef - Effects of Resistance Exercise using Elastic Band on Range of Motion, Function and Shoulder Pain among Patients with Rotator Cuff Repair
Jae Ok Sim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(5): 491. CrossRef - The Effect of a PNF Technique Program after Mastectomy on Lymphedema Patients’ Depression and Anxiety
Kyungjin Ha, Seungjun Choi
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2014; 26(7): 1065. CrossRef - Effects of a Rehabilitation Program on Quality of Life, Cardiopulmonary Function and Fatigue During Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer Patients
Jung-Hwa Do, Jun-Hyuk Seong, Jun-Su Ahn, Young-Ki Cho
Physical Therapy Korea.2012; 19(1): 56. CrossRef - Exercise interventions for upper-limb dysfunction due to breast cancer treatment
Margaret L McNeely, Kristin Campbell, Maria Ospina, Brian H Rowe, Kelly Dabbs, Terry P Klassen, John Mackey, Kerry Courneya
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2010;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of comprehensive group rehabilitation for women with early breast cancer in South Korea
Ok‐Hee Cho, Yang‐Sook Yoo, Nam‐Cho Kim
Nursing & Health Sciences.2006; 8(3): 140. CrossRef
- Short-term effects of a new resistance exercise approach on physical function during chemotherapy after radical breast cancer surgery: a randomized controlled trial
- 815 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The Effects of Planned Exercise Program on Metabolism, Cardiopulmonary Function and Exercise Compliance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Ae Ran Hwang, Ji Soo Yoo, Chun Ja Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(1):20-30. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.1.20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to identify the effects of a planned exercise program based on Bandura's self efficacy model on metabolism, and the exercise compliance in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. The study design was a nonequivalent pre-test post-test control design. Thirty four type 2 diabetes mellitus patients, who received follow-up care regularly through the diabetic out-patient clinic, were randomly sampled for this study. Twenty patients were assigned to the experimental group and fourteen patients were assigned to the control group. In the experimental group, a planned exercise program is composed of an individualized exercise prescription for 12 weeks, an individual education, and even a telephone coach program. In the case of the control group, they were instructed to continue with their usual schedules. The data collection period was from March 1999 to February 2000 Data were analyzed using SPSS/WINDOW 10.0program. The results were as follows. 1. In the experimental group, the level of fasting blood sugar has significantly decreased from 188.20 mg/dl to 155.55 mg/dl after planned exercise program (F= 16.86, p=.000). For lipid metabolism, body fat per cutaneous decreased from 27.16% to 26.57% after planned exercise program. The score of self efficacy has increased from 64.20 to 66.65 after planned exercise program and it was statistically significant (F=4.850, p=.040) The functional vital capacity has increased from 3.28 liter to 3.37 liter and it was statistically significant(F=7.300, p=.020). 2. In an after effect of a planned exercise program, 35 percent of the subjects who participated in a planned exercise program continued to exercise for another six months. In conclusion, the planned exercise program can improve cardiopulmonary function, glucose, and lipid metabolism. This program was show a positive effect on the self efficacy and exercise compliance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Exercise Intervention in Reducing Body Weight and Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ji-Eun Jang, Yongin Cho, Byung Wan Lee, Ein-Soon Shin, Sun Hee Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 302. CrossRef - Analysis of Reported Study on Intervention Programs for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Gab-Sun Song, Ho-Jin Kim, Jum-Yi Jun
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(9): 541. CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition and Exercise Modification Therapy on Metabolism Efficiency of Middle-aged Women Through Convergence
Su-In Chea, Sang-Nam Nam, In-Dong Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(5): 393. CrossRef - Effects of a Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Intervention With Psychobehavioral Strategies for Korean Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Chun-Ja Kim, Dae-Jung Kim, Hyung-Ran Park
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2011; 26(2): 117. CrossRef - Effects of a problem‐solving counseling program to facilitate intensified walking on Koreans with type 2 diabetes
Haejung LEE, Myoung‐Soo KIM, Kyung‐Yeon PARK, Hyoung‐Sook PARK, In‐Joo KIM
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2011; 8(2): 129. CrossRef - Application of the Transtheoretical Model
Chun-Ja Kim, Bom-Taeck Kim, Sun-Mi Chae
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2010; 25(4): 323. CrossRef - Utility of a Web-based Intervention for Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
CHUN-JA KIM, DUCK-HEE KANG
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2006; 24(6): 337. CrossRef - The impact of a stage-matched intervention to promote exercise behavior in participants with type 2 diabetes
Chun-Ja Kim, Ae-Ran Hwang, Ji-Soo Yoo
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2004; 41(8): 833. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Exercise Intervention in Reducing Body Weight and Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 756 View
- 3 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The Effects of a Cardiac Rehabilitation Program on Health Behavior Compliance, Cardiovascular Function, and Quality of Life for the Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease
- Hyun Sook Jo, Kwang Joo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):560-570. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.560
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study is aimed at developing a cardiac rehabilitation program and enlightening the effects of the program on patient's health behavior compliance, cardiovascular functional capacity, and quality of life. Using a quasi-experimental approach the nonequivalent control group pretest - posttest design was accepted for this study. The subjects of this study consisted of 55 patients with ischemic heart disease at the Cardiac Center of 'G' Hospital located in Inchon from May 1, 1998 to April 30, 1999. The patients were divided into two groups: the experimental group, which participated in the cardiac program with 30 patients and 25 patients of a control group were not involved in the program. There were two phases in the cardiac rehabilitation program: the first phase was a team approach education. It focused on reducing the risk of ischemic heart problems. The second phase was individual training by using a home based exercise program, which was comprised of 8 weeks, three sessions per week, 40-60 minutes per session, and followed by consultation. Every session involved 20-40 minutes of aerobic exercise at 40-60% of heart rate reserve, 11~13 RPE and 10 minutes of warm-up and 10 minutes of cool-down exercises. The experimental tools for the study were the health behavior compliance scale developed by Lee, Yoon-hee (1992), and quality of life scale developed by McGirr et al.(1990). RPPsubmax were measured by the treadmill. The collected data was processed by SPSS and analyzed by X2test and t-test. The results of this study were as follows: 1. The health behavior compliance in experimental group was significantly increased (t=5.091, p=.000) when compared to the control group. 2. RPPsubmax also decreased significantly in the experimental group when compared to the control group(t=-2.109, p=.040). 3. The quality of life significantly improved in the experimental group (t=3.853, p=.000) as compared to the control group. As the above results of this study revealed, the effectiveness of the cardiac rehabilitation program of the study was confirmed. It increased the health behavior compliance for reducing the risk of further coronary events, enhanced the cardiovascular functional capacity, and eventually improved the patient's quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of a Self-management Program based on Prothrombin INR Monitoring for Patients with Cardiac Valve Replacement
Hyun Rye Jeon, Jeong Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 554. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Web-based Education Program to Prevent Secondary Stroke
Chul-Gyu Kim, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(1): 47. CrossRef - Factors explaining Quality of Life in Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease
In Sook Park, Rhayun Song, Sukhee Ahn, Hee Young So, Hyun Li Kim, Kyung Ok Joo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 866. CrossRef
- Development and Application of a Self-management Program based on Prothrombin INR Monitoring for Patients with Cardiac Valve Replacement
- 641 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effect of Dance Therapy on Pulmonary and Cognitive Function in the Elderly
- Young Ran Lee, Sook Ja Yu
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1273-1283. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1273
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to explore the effects of dance therapy on pulmonary and cognitive functions in the elderly. The design of this study was a non-equivalent pre-post test experiment. The subjects consisted of elderly persons living in a facility located in Kyoungi-Do. Fifty eight subjects had normal cognition, sensory function and resting blood pressure. They underwent tests of pulmonary and cognitive function as baseline data before dance therapy, and at 6th week and at the end of 12nd week after following dance therapy. Twenty seven elderly persons were assigned to the experimental group and participated with the dance therapy. This therapy was based on the Marian Chace's dance therapy and Korean traditional dance with music. The dance therapy consisted of 50 minutes session, 3 times a week for 12 weeks. One session consisted of warming-up, expression, catharsis, sharing and closing stage. the intensity of the dance therapy was at the 40% of age-adjusted maximum heart rates. Data were analyzed with mean, standard deviation, Chi-square test, unpaired t-test, repeated measures ANOVA, and Bonferroni multiple regression using SAS program. The results were as follows: 1. Pulmonary function(forced expiratory volumn at one second and forced vital capacity) of the experimental subjects significantly increased over time more than that of the control subjects. 2. The experimental group had significantly higher score for pulmonary function than the control group at the 12nd week after dance therapy. 3. Cognitive function of the experimental subjects significantly increased over time more than that of the control subjects. 4. The experimental group had significantly higher score for cognitive function than the control group at the 6th week and 12nd week after dance therapy. The findings showed the dance therapy could be effective in improving the pulmonary and cognitive function of the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of High-Intensity Aerobic Exercise on the Pulmonary Function among Inactive Male Individuals
Arwa Rawashdeh, Nedal Alnawaiseh
Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal.2018; 11(2): 735. CrossRef - Effects of high intensity aerobic exercise on treadmill on maximum-expiratory lung capacity of elderly women
Joonsung Park, Dongwook Han
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2017; 29(8): 1454. CrossRef
- The Effect of High-Intensity Aerobic Exercise on the Pulmonary Function among Inactive Male Individuals
- 661 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Study on the Effect of Self-Management and Relaxation Training through Biofeedback on Influencing the Stress Response and Immune Functions
- Soowoo Lee, Keum Soon Kim, Sung Hoi Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):855-869. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.855
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to test the effectiveness of self-management relaxation training through biofeedback and progressive muscle relaxation methods. The effectiveness of the experimental methods was tested by measuring the degree of symptoms of stress(SOS), the McNair's profile of Mood STates(POMS), the levels of ephinephrine, norepinephrine, pulse rate, blood pressure and natural killer cells. The subjects of this study were sixty six nursing students divided into four groups two groups were the biofeedback and progressive muscle relaxation groups, the other two groups served as control groups. One was a group of sophomores with no experience at all, the other a junior group without self-management or relaxation training. This study was condicted for eight weeks of clinical practice from April, 26th 1998 to June, 20th 1998. Biofeedback training was done with software developed by J&J company(1-410 form for abdominal respiration training). Progressive muscle relaxation training was done with an audiotape recorded according to Jacobson's Theory. The data were analyzed with frequencies, means, and analysis of cobariance using the SPSS program and the significance level of statistics was 5%. The results of the study are : 1) The importance of clinical practice stress reduction is shown in that the level of symptoms of stress in the experimental groups in clinical practice was higher than in the group receiving only a lecture. 2) The relaxation training methods of biofeeback and progressive muscle relaxation were effective in reducing the symptoms of stress under the clinical practice stress conditions. 3) The effectiveness of the biofeedback training relaxation method to reduce symptoms of stress was higher than that of progressive muscle relaxation. 4) The relaxation training methods of biofeedback and progressive muscle relaxation were effective in reducing stressful mood states. 5) The relaxation training methods of bioffedback and progressive muscle relaxation were not effective in reducing epinephrine and norepinephrine levels. 6) The relaxation training methods of biofeedback and progressive muscle relaxation were effective in increasing the number of natural killer cells. 7) The relaxation training methods of biofeedback and progressive muscle relaxation were effective in decreasing high systolic and diastolic values of blood pressure and high pulse rates. In summary, the relaxation methods of biofeedback and progressive muscle relaxation in reducing clinical practice stress were effective in lowering the level of symptoms of stress and the profile of stressful mood states. They were also effective in lowering high blood pressure and pulse rates. The relaxation methods were effective in increasing the number of natural killer cells as part of the immune function. However, relaxation methods were not effective symptoms of stress was more effective than the progressive muscle relaxation method.
- 503 View
- 1 Download

- The Predictive Model of Adolescent Women's Depression
- Young Joo Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Jung Nam Sohn, Suk Hee Cheon, Hyun Jung Shin, Young Nam Chung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):829-840. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.829
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was condicted to construct a hypothetical model of depression in Korean adolescent women and validate the fit of the model to the empiricla data. The data were collected from 345 high school girls in Seoul, from May 1 to June 30, 1998. The instruments were the Body Mass Index, Physical Satisfaction Scale, Family Adaptatibility and Cohesion Evaluation Scale III, Family Satisfaction Scale, CES-D and School Adaptation Scale. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics with the pc-SAS program. The Linear Structural Relationship(LISREL) modeling process was used to find the best fit model which would predict the causal relationships among the variables. The overall fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate [X2=69.6(df=17, p=.000), GFI=0.95, AGFI=0.90, RMR=0.087, NNFI=0.86, NFI=0.90]. The predictable variables, especially menstrual symptoms, physical symptoms and family function, had a significant direct effect on depression, but school life adaptation did not have a significant direct effect. These variables explained 18.1% of the total variance.
- 532 View
- 0 Download

- Effects of Rehabilitation Program on Functional Recovery in Stroke Patients
- Yeon Ok Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(3):665-678. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.3.665
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Stroke is a major cause of death and long-term disability. Because muscle weakness is one of the most prominent consequences of stroke, it was considered important to determine whether exercise if order to improve muscle strength and range of motion could have an effect in limiting the learned disuse of the affected side. The purpose of the study was to identify the effects of an 8 week rehabilitation program on physical and cognitive ability in stroke patients. A total of 18 patients who were admitted to the oriental medicine unit of a K medical center in Seoul were recruited : Ten for the experimental group and eight for the control group. The rehabilitation program consisted of three level's of active and passive exercises for prevention of muscle contracture and at range of motion. Muscle strength, flexibility of the upper and lower extremity, perceived balance, functional independence, depression, and quality of life for the two groups were compared at the pretest and 4 and 8 weeks after the rehabilitation program. The results are as follows: 1) When measuring muscle strengths of shoulder abduction and elbow flexion, hip flexion and knee extensor, ankle dorsi-flexor and muscle strength of knee flexor. Muscle strength of knee flexor for the experimental group was significantly higher than the comparison group at the 4 weeks. 2) Muscle strength and flexibility of the ankle dorsi-flexor for the experimental group was significantly better than for the control group at 8 weeks. 3) Functional independence, perceived balance, and Tinetti balance for the experimental group as measured at 4 and 8 weeks were better than for the control group. Also, there were changes over time in physical balance and functional ability, but there was no significant differences between the groups. 4) The experimental group showed a higher quality of life and lower depression than the control group at 8 weeks. 5) Muscle strength and flexibility of ankle dorsi-flexor were significantly changer over time and an interaction between group and time. The findings suggested that the rehabilitation program would improve the physical and psychological status of the stroke patients. Thus, the gains in actual or perceived ability to perform physical activities was marked.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Group Rehabilitation Gymnastics for Stroke Patients
Sun-Houng Kim, Nam-Eun Moon, Mi-Yang Jeon, Hyeon-Cheol Jeong
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2022; 11(2): 207. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Hybrid Walking Rehabilitation Robot, DDgo Pro
Jung-Yup Kim, Ji-Yong Kim, Hyeong-Sic Kim, Kiwon Park
International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing.2020; 21(11): 2105. CrossRef - Effects of Bilateral Passive Range of Motion Exercise on the Function of Upper Extremities and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Acute Stroke
Hyun Ju Kim, Yaelim Lee, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2014; 26(1): 149. CrossRef
- Effects of Group Rehabilitation Gymnastics for Stroke Patients
- 811 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Model Development of Change of Family Functioning with Chronic Illness
- Eun Ok Lee, He Sook Kim, Young Sook Park, Misoon Song, Insook Lee, Yeon Hwan Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(3):467-484. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.3.467
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The main objectives of this study were to investigate the concept of family function from the perspective of the contemporary Korean family, and to construct model of change of family function whit chronic illness. The hybrid model approach was applied in which three phases(theoretical phase, empirical phase, and analytic phase) of concept development were explored for family functioning. The study was conducted from 1997 to 1998. In empirical phase, two groups of purposive samples were drawn : normal family group composed of six families without ill family member, and ill family group composed of seven families of which wives have rheumatoid arthritis. Only families with child(or children)in primary or secondary schools were included in the study. The results were as follows: In theoretical phase, six dimensions of family concept were emerged : affective, structural, control, cognitive, financial, and reproductive dimension. In order to analyze the Korean normal family function in middle class with middle-age women, financial and reproductive dimension were not included. In empirical phase, five dimensions(affective, structural, control, cognitive, and external relationship) were fond from the normal family data. External relationship dimension is very important factor as a resource of the support, especially when their parents or siblings had no help or support to them. In the affective dimension, Korean family emphasized harmony and balance rather than affective expression harmony and balance rather than affective expression between couples and between parents and children. They also showed common goals of the families to solve their problems to control the family members. The priority of the goals was getting into the higher education of their children or helping their unhealthy parents or family members. Six dimension(affective, structural, control, cognitive, external relationship, and financial) of family functions were emerged from the ill family data. From the analysis of ill family data, types of restructuring house chore after wives illness were developed : (a) negociated, (b) accomodated, and (c) isolated, enduring types. Although the dimensions of family functioning identified in this study are similar to the conceptualizations that exist in the western literature, there where distinct differences in the nature of major themes and subconcepts under these family function dimensions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of the Japanese Version FFS (Family Functioning Scale): Reliability and Validity for Family on Child-Fostering Phase
Mitsuko Kanzaki, Chifumi Otaki, Kazue Maeda, Taeko Hori, Akemi Take, Hiroko Otsuka, Taeko Noguchi, Sumiko Maehara
Journal of Japan Academy of Nursing Science.2012; 32(1): 50. CrossRef - To Holroyd E (2005) Commentary on Lee et al. (2004)
Insook Lee, Eun‐Ok Lee, Hesook Suzie Kim, Young Sook Park, Misoon Song, Youn Hwan Park
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2006; 15(5): 654. CrossRef
- Development of the Japanese Version FFS (Family Functioning Scale): Reliability and Validity for Family on Child-Fostering Phase
- 749 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Comparision of Group and Individual Social Support on Burden and Family Functioning in Families with Asthmatic Children
- Hoa Yun Jun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):418-428. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.418
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The main purpose of this study was to identify the effects of group social support and individual social support on the reduction of burden and improvement in family functioning of families with asthmatic children. The design of this study was a randomized pre-posttest quasi-experimental design to compare the two experimental groups. The theoretical framework for this study was derived from the study of burden in family caregivers by Suh and Oh(1993) based on the main effect model of social support theories. The data were collected from February 12, 1998 to May 29, 1998 at the pediatric out patient department of a university hospital located in Suwon city. The sample consisted of 39 family members who were identified as families with asthmatic children, Eighteen subjects were randomly assigned to the group social support group and 21 were assigned to the individual social support group. Group and individual social support members were seen for 60 to 90 minutes, four times over one to three weeks. The instruments used in this study were the Burden Scale developed by Suh and Oh(1993), the Visual Analogue Scale, and the Family Adaptability Cohesion Evaluation Scale(FACES-III) developed by Olson, Portner, and Lavee(1985). The collected data were analyzed using Mann-Whitney test, x2-test, Wilcoxon sign rank test, t-test, ANOVA(Scheff), pearson correlation coefficient, multiple regression, and social support process and content analysis. The results are as follow ; 1. There was no significant difference before the experimental treatment among the subjects in the group social support group and individual social support group for general characteristics, burden, or family functioning. 2. Hypothesis 1 ; "There will be a greater reduction on the burden score of the group social support group compared to the individual social support group" was not statistically significant(U=174.5, p=.683). The burden scores showed a significant decrease after participation in social support as compared to before participation for both groups. However there was a tendency for more reduction in the burden scores for the group social support than for individual social support. 3. Hypothesis 2 ; "There will be a greater improvement in the family functioning scores for the group social support group compared to the individual social support group" was not statistically significant(U=153.0, p=.309). There was a tendency toward improvement in the family functioning scores of the group social support as compared to that of the individual social support. 4. According to the length of the treatment period, families with asthmatic children displayed affirmative responses, and the families set up a self-help group of mothers with asthmatic children n order to share their experiences, to get information and to solve their problems. In conclusion, it was found that group social support was the more effective nursing intervention for reducing burden and for improving family functioning of families with asthmatic children.
- 381 View
- 0 Download

- The Effect of a Hand Massage Program on Anxiety and Immune Function in Clients with Cataract Surgery under Local Anesthesia
- Kyung Sook Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(1):97-106. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.1.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to investigate the effect of a hand massage program on anxiety and immune function in patients during cataract surgery. The hand massage program, in this study, consisted of hand massage and hand-holding. The subjects were sixty-three patients, thirty for the experimental and thirty-three for the control group, who were admitted at Kang Nam St. Mary's Hospital for cataract surgery. This study was carried out from December 10, 1997 to February 26, 1998. The level of anxiety as measured by the Visual Analogue Scale, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and pulse rate were measured before, after hand massage, and after hand-holding. Epinephrine, norepinephrine, cortisol, blood sugar levels, neutrophil, lymphocyte, and natural killer cell percentages also were measured before hand massage and five minutes before the end of the operation. Data were analyzed by t-test, ANCOVA, repeated measure ANOVA, and Bonferroni multiple comparisons. The results were as follows : 1) After hand massage, psychological anxiety levels decreased significantly compare with before hand massage in the experimental group, not in the control group. After hand holding, there were significant decrease in both groups. 2) There were no significant differences on systolic blood pressure, diastorlc blood pressure, and pulse rates in both groups. 3) The hand massage program decreased epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cortisol significantly in the experimental group and increased epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cortisol in the control group. 4) There were no differences in blood sugar levels, neutrophil and lymphocyte percentages in white blood cells after the hand massage program. However, natural killer cells in lymphocytes were significantly increased in the experimental group. These findings indicate that a hand massage program could be a effective nursing intervention in decreasing the psychological and physiological anxiety levels and improving immune function in clients having cataract surgery under local anesthesia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
Yun Kyeong Lee, Mihae Im, Haeryun Cho
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1404. CrossRef - Effects of Extremity Massage on Preoperative Anxiety: A Three-Arm Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial on Phacoemulsification Candidates
Moloud Farmahini Farahani, Masoomeh Noruzi Zamenjani, Morteza Nasiri, Soheila Shamsikhani, Zahra Purfarzad, Mehdi Harorani
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2020; 35(3): 277. CrossRef - The Effects of Hand Massage in Patients Who Underwent Transradial Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Sil Shin, Myung-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(4): 465. CrossRef - Effects of the Provision of Information on Anxiety in Patients during Outpatient Surgery: A Systematic Review
Ae-Ri Jung, In-Sook Lee
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2016; 13(1): 48. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Hand Massage Combined with Analgesics on Pain Control in Patients with Terminal Cancer
Yunmi Lee, Hosoon Yoon, Sungwoon Lee, Young Mi Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(4): 296. CrossRef - Effect of Music Therapy on Vital Signs, Anxiety, Cortisol and Pain of Cataract Surgery Patients in Elderly
Jung-Hae Park, Kwang-Hi Park
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(8): 549. CrossRef - The Effect of Hand Holding and Nei-Guan Acupressure on Anxiety and Pain under Local Anesthetic Patients during Surgery
Sun Hee Park, Hee Jung Jang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(11): 378. CrossRef - Effect of Aroma Hand Massage on Anxiety and Immune Function in Patients with Gynecology Surgery under Local Anesthesia
Yun Ah Kim, Mi Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(2): 126. CrossRef - Relational and Health Correlates of Affection Deprivation
Kory Floyd
Western Journal of Communication.2014; 78(4): 383. CrossRef - Analysis of Studies on Hand Massage Published in Korea: On the Effects of Sleep, Pain, Anxiety and Depression
In-Ja Kim, Yu-Na Cho
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Effects of Foot Reflexology on Fatigue, Sleep and Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jeongsoon Lee, Misook Han, Younghae Chung, Jinsun Kim, Jungsook Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(6): 821. CrossRef - Effects of Hand Holding on Self-esteem and Assertiveness in Women Patients with Depression
Mi-Hae Sung, Mi Young Choi, Ok Bong Eum
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 154. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Foot Reflexology on Stress, Fatigue and Blood Circulation in Premenopausal Middle-Aged Women
Soo Hyun Jang, Kye Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 662. CrossRef - The effects of handholding on anxiety in cataract surgery patients under local anaesthesia
Jung‐Soon Moon, Kyung‐Sook Cho
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2001; 35(3): 407. CrossRef
- An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
- 854 View
- 6 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Needs for Home Care Nursing in the Vulnerable Elderly
- Ji Hyun Lee, Younhee Jeong, Geum Ja Park, Sook Hee Kwon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(2):201-207. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.2.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine the subjects' health status according to the needs of visiting health and the function of the family in home care nursing.
Sample and Method The data collection period was from 07/01/04 to 10/31/04 and the subjects were 488 of those above 60 years of age staying at home or living alone who registered at a visiting health service of public health center at an urban area in Korea. This survey was carried out by visiting health nurses and participation was agreed on by the elderly people.
Results The extent of the subjects' total health status to the general characteristics had differences according to the age, sex, monthly income, perceived health status, known functional disorder, and yes-or-no for disease. At all health status domains, visiting health need care in the group I was very lower than one in II, III, or IV groups. Also the severe dysfunctional family was lower than lightly dysfunctional family and normal functional family in all health status domains.
Conclusion Nurses must provide their characteristics considered nursing intervention for the elderly who have high visiting health needs and severe dysfunctional family with vulnerable health care.
- 605 View
- 11 Download

- Effects of a Postpartum Back Pain Relief Program for Korean Women
- Hyun Ei Oh, Young Sook Lee, Mi Jung Shim, Jin Sun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(2):163-170. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.2.163
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Despite the high prevalence of back pain and its subsequent effects in post-partum women, intervention programs are scarce. The purpose of this study was to test the effects of a back-pain-reducing program on post-partum women who experienced low-back pain during pregnancy.
Methods A non-equivalent control-group pretest-posttest design was used. Pregnant women who attended a hospital for prenatal check-ups and experienced back pain participated in an intervention program (n=27), and the results were compared with women in a control group from another hospital (n=25).
Results At 8 weeks post-partum, the pain intensity, functional limitations were lower in the intervention group than in the control group. However, differences in mean change of the pain intensity and functional limitations between 36 and 39 weeks of gestation and at 8 weeks post-partum were not statistically significant between the groups. Moreover, the flexibility, post-partum functional status, and post-partum depression did not differ significantly between the groups.
Conclusions A back-pain-relief program in this study was not effective to reduce the back-pain intensity in post-partum women and to decrease the associated functional limitations. The implications for nursing practice and directions for future research are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Educating women to prevent and treat low back and pelvic girdle pain during and after pregnancy: a systematized narrative review
Sabine Vesting, Annelie Gutke, Liesbet de Baets
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes and outcomes measurements used in intervention studies of pelvic girdle pain and lumbopelvic pain: a systematic review
Francesca Wuytack, Maggie O’Donovan
Chiropractic & Manual Therapies.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Power Analysis in Experimental Designs with t test Analysis
Jeong-Hee Kang, Kyung-Sook Bang, Sung-Hee Ko
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2009; 15(1): 120. CrossRef
- Educating women to prevent and treat low back and pelvic girdle pain during and after pregnancy: a systematized narrative review
- 959 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Family Functioning and Quality of Life of the Family Care-giver in Cancer Patients
- Kuem Sun Han, Soon Yong Khim, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Young Joo Park, Jeong Hwa Kim, Kwang Mi Lee, Hyun Chul Kang, Ji Won Yoon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(6):983-991. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.6.983
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship among quality of life, family coherence, family hardiness, and family resources of the family care-giver caring for a cancer patient.
Method Data was collected by questionnaires from 137 families with a cancer patient at a General Hospital and Government Cancer Hospital. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression.
Results The score of quality of life showed a significant positive correlation with the score of the level of family sense of coherence, family hardiness, and family resources. The most powerful predictor of quality of life was sense of coherence and the variance was 30%. A combination of sense of coherence and family resources account for 34 % of the variance in quality of life of the family care-giver caring for a cancer patient.
Conclusion The results showed that family sense of coherence, hardiness, and family resources were significant influencing factors on the quality of life of the family care-giver caring for a cancer patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The development and validation of the short-form Family Inventory of Resources for Management among families of older people with dementia: instrument development and cross-sectional study
Yuxin Li, Chang Zan, Sanmei Chen, Shengnan Tang, Qiongqiong Zhang, Yijia Pan, Yu Sheng, Qingyan Wang
BMC Geriatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Do spouse burden of care, family resilience, and coping affect family function in gynecologic cancer in Korea?: a cross-sectional study
Minkyung Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 197. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-efficacy and Depression on Sense of Family Coherence in Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy and Primary Caregivers in Day Care Wards: Using the Method Actor-partner Interdependence Model
Eun-Hee Do, Eun Joung Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(4): 214. CrossRef - Influence of Hospital Nurse Staffing Levels on the Colorectal Cancer Evaluation Grades, Mortality, and Length of Stay
Yunmi Kim, Se Young Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(5): 479. CrossRef - The Lived Experience of Suffering of Family with Cancer Patients: Parse’s Human Becoming Research Method
Ye-Sook Choi
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(2): 127. CrossRef - Quality of Life of Family Members Living with Cancer Patients
Hyo Jung Lee, Eun-Cheol Park, Seung Ju Kim, Sang Gyu Lee
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(16): 6913. CrossRef - Burden and Quality of Life in Terminal Cancer Patient's Family Caregivers in the area of Jeollanam-do
Eun-Young Yang, Young A Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 3954. CrossRef - Family Caregivers’ Quality of Life, Depression and Anxiety according to Symptom Control in Hospice Patients
Yun Hee Kim, Seung Hun Lee, Ho Seop Lim, Young Jin Choi, Yun Jin Kim, Sang Yeoup Lee, Jeong Gyu Lee, Dong Wook Jeong, Kyoung Hwa Yu
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2015; 18(4): 314. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth in Family Caregivers of Patients with Cancer
Soon Ock Choi
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life of Family Caregivers of Patient with Lung Cancer
Ju-Young Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 129. CrossRef
- The development and validation of the short-form Family Inventory of Resources for Management among families of older people with dementia: instrument development and cross-sectional study
- 908 View
- 7 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of Constraint-Induced Movement Using Self-Efficacy Enhancing Strategies on the Upper Extremity Function of Chronic Hemiplegic Patients
- Jiyeon Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(2):403-414. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.2.403
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of constraint-induced (CI) movement using self-efficacy on U/E function of chronic hemiplegic patients. CI movement discourages the use of the unaffected U/E, combined with intensive training of the affected U/E.
Method A non-equivalent pretest-posttest design was used. Study subjects were 40 hemiplegic patients conveniently selected from 2 different community health centers. The experimental subjects participated in the CI movement program for 6 hours daily over a period of two weeks. The exercises for affected U/E consisted of warming up, main exercise and ADL practice. To encourage the participants' behaviors self-efficacy enhancing strategies were used, which included performance accomplishment, vicarious experience, verbal persuasion and emotional arousal.
Result After 2 weeks of treatment, the grip power, pinch power, wrist flexion/extension, elbow flexion, and shoulder flexion/extension were significantly higher in the experimental subjects than in the control subjects. However, there was no significant difference in hand functions of the two groups.
Conclusion The above results show that the constraint-induced movement using self-efficacy could be an effective nursing intervention for improving U/E function of chronic hemiplegic patients. Long term studies are needed to determine the lasting effects of constraint-induced movement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Self Efficacy and Quality of Life of Stroke Patients
Serpil TOPÇU, Sıdıka OĞUZ
Hemşirelik Bilimi Dergisi.2021; 4(3): 114. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Self Efficacy and Quality of Life of Stroke Patients
- 697 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Functional Status of Stroke Patients among Different Long-Term Care Settings
- Eun Young Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):372-378. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.372
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to measure the functional status of stroke patients cared for in different long-term care settings.
Method We assessed all stroke patients in two home health care agencies, four nursing homes and one geriatric hospital in Korea (n=171) using the Resident Assessment Instrument (RAI), which comprises Activity of Daily Living (ADL), urine incontinence, bowel incontinence, a Cognitive Performance Scale (CPS),and being understood and understanding others. Data was collected by face-to-face surveys with patients.
Results The mean ADL score, urine incontinence score, bowel incontinence score, CPS, and being understood score and understanding others score were lowest for the patients receiving home health care, and highest for the patients in nursing homes. Low scores described poor and high scores good functional status. The results showed significant differences in physical and cognitive function scores between the three groups of patients.
Conclusion This study suggests that there may be large differences between the patients in these three types of long-term care settings. These findings can be used to help develop and implement efficient long-term care programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and potential determinants of musculoskeletal disease symptoms among care workers in long‐term care facilities in South Korea
Myung‐Sook Park, Mi Yu, Su‐Jeong Yu, Kyung‐Ja Kang, Hyun‐Mi Seo
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2014; 11(3): 211. CrossRef - The Long-term Care Utilization of the Elderly with Dementia, Stroke, and Multimorbidity in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Soonman Kwon, Hongsoo Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(1): 90. CrossRef
- Prevalence and potential determinants of musculoskeletal disease symptoms among care workers in long‐term care facilities in South Korea
- 751 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Care Dependency in Patients with Dementia
- Eun Joo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(6):705-712. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.6.705
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore factors that influence care dependency of institutionalized patients with dementia.
Method This study utilized descriptive correlational design. The convenience sample was composed of 110 residents with dementia of two long-term care facilities in Korea. Stepwise multiple regression was used to identify significant factors influencing care dependency in patients with dementia. Care dependency was measured using the Care Dependency Scale, Korean version(CDS-K). Cognition was measured by the MMSE-K. Functional disability was measured by the PULSES Profile. Behavioral dysfunction was measured by the modified E-BEHAVE AD.
Result Care dependency was significantly influenced by cognition, functional disability, behavioral dysfunction, and duration of dementia. This regression model explained 61% of the variances in care dependency. Cognition explained 37% of the variances, and functional disability explained 21% of the variances.
Conclusion Results of this study suggest that professional caregivers intervene more effectively in caring for their patients with dementia by recognizing the patients cognitive, functional, behavioral disability, and its periodic change. Individually, remaining abilities-focused intervention should be applied to enhance patient to be dependent and to prevent unnecessary independency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of care dependency in nursing home residents with moderate to severe dementia: A cross-sectional study
Marinda Henskens, Ilse M. Nauta, Katja T. Drost, Maarten V. Milders, Erik J.A. Scherder
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2019; 92: 47. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Care Burden among Family Caregivers for Elders with Dementia: Focusing on Family Caregivers using a Support Center for Dementia
Kyung Choon Lim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Perceptions regarding Purpose in Life and Good Death on Caring Behaviors of Formal Caregivers of Community-dwelling Older Adults with Dementia
Chun-Gill Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(2): 57. CrossRef - Perceived oral health awareness in dementia and dementia-suspected depending on KMME
Eun Sook Kim, Min-Hee Hong
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2015; 15(2): 217. CrossRef - The Long-term Care Utilization of the Elderly with Dementia, Stroke, and Multimorbidity in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Soonman Kwon, Hongsoo Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(1): 90. CrossRef - Relationships Among Cognition, Activities of Daily Living and Depression in Persons With Decreased Memory
Min Suk Kim, Soon Young Yoon, Eun Young Oh
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(3): 404. CrossRef
- Predictors of care dependency in nursing home residents with moderate to severe dementia: A cross-sectional study
- 841 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of Upper Extremity Exercise Training Using Biefeedback and Constraint-induced Movement on the Upper Extremity Function of Hemiplegic Patients
- Keum Soon Kim, Ji Yeon Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(5):591-600. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.5.591
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of exercise training using biofeedback and constraint-induced movement on the upper extremity function of hemiplegic patients.
Method A non-equivalent pretest-posttest design was used. Study subjects were a conveniently selected group of 40 hemiplegic patients(20 experimental subjects, 20 control subjects) who have been enrolled in two community health centers. After biofeedback training the subjects of experimental group were given constraint-induced movement, involving restraint of unaffected U/E in a sling for about 6 hours in a day over a period of two weeks, while at the same time intensively training the affected U/E. Outcomes were evaluated on the basis of the U/E motor ability(hand function, grip power, pinch power, U/E ROMs), and motor activity(amount, quality).
Result 1. After 2 weeks of treatment, the motor abilities of affected U/E(hand function, grip power, pinch power, ROMs of wrist flexion, elbow flexion and shoulder flexion/extension) were significantly higher in subjects who participated in exercise training than in subjects in the control group with no decrement at 4-week follow-up. However, there was no significant difference in wrist extension between experimental or control group. 2. After 2 weeks of treatment, the amount of use and the quality of motor activity of affected U/E were significantly higher in subjects who participated in exercise training than in subjects in the control group with no decrement at 4-week follow-up.
Conclusion The above results state that exercise training using biofeedback and constraint-induced movement could be an effective intervention for improving U/E function of chronic hemiplegic patients. Long-term studies are needed to determine the lasting effects of constraint-induced movement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Can Short-Term Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy Combined With Visual Biofeedback Training Improve Hemiplegic Upper Limb Function of Subacute Stroke Patients?
Hyun Seok, Seung Yeol Lee, Jihoon Kim, Jungho Yeo, Hyungdong Kang
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2016; 40(6): 998. CrossRef - The Effects of Weight-Bearing Exercise on Upper Extremity Activities Performance in the Female Stroke Patients
SungEun Lee, SungHyoun Cho, Kyoung Kim
International Journal of Contents.2013; 9(1): 65. CrossRef - The Effects of Rehabilitation Training Using Video Game on Improvement Range of Motion for Upper-Extremity, Shoulder Pain and Stress in Stroke Patients with Hemiplegia
Pil-Suck Buyn, Mi-Young Chon
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(1): 46. CrossRef
- Can Short-Term Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy Combined With Visual Biofeedback Training Improve Hemiplegic Upper Limb Function of Subacute Stroke Patients?
- 697 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Comparison of Maternal Self-esteem, Postpartal Depression, and Family Function in Mothers of Normal and of Low Birth-weight Infants
- Young Mee Ahn, Jung Hyun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(5):580-590. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.5.580
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The study investigates the degree of maternal self-esteem, postpartal depression, and family function in mothers of normal and of low birth-weight infants.
Method A retrospective cohort design was applied to compare the variables of interest between a group of 73 mothers with normal birth weight infants and a group of 45 mothers with low birth-weight infants, using the maternal self-report inventory(MSRV), Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale(EPDS) and Family APGAR(FAPGAR).
Result The total mean score was 82.57 for MSRV, 8.45 for EPDS, and 6.83 for FAPGAR with no differences between two groups. A positive correlation was found between MSRV and FAPGAR, while a negative correlations between MSRV and EPDS, and FAPGAR and EPDS. Regardless of the direction of the relationship, the degrees of the correlations were stronger in low birth-weight mothers group than in normal group.
Conclusion No differences in MSRV, EPDS and FAPGAR between the normal and the low birth-weight group considered as beneficial effects of the follow-up management which low birth-weight group was engaged in. This suggested the early intervention(follow-up) for the family with risk factor(low birth-weight) could reduce negative outcomes such as the impaired maternal self-esteem and family function, and the occurrence of postpartal depression, retrospectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Longitudinal Relationship Study of Depression and Self-Esteem in Postnatal Korean Women Using Autoregressive Cross-Lagged Modeling
Jeong-Won Han, Da-Jung Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(10): 3743. CrossRef - Effects of Kangaroo Care on Physical Development and Adaptation of External Environment of Prematurity, and Maternal Role Confidence who Delivered Premature Infants
Ji-Won Lee, Yong-Sook Eo, Jung Hwa Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(12): 128. CrossRef - The Correlation between Maternal Adult Attachment Style and Postpartum Depression and Parenting Stress
Sung Yong Park, Sun Mi Kim, Baik Seok Kee, Doug Hyun Han, Churl Na, Gwang Jun Kim, Min Young Park, Na Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2015; 54(4): 515. CrossRef - Effects of Self Efficacy, Body Image and Family Support on Postpartum Depression in Early Postpartum Mothers
Ji-Won Lee, Yong-Sook Eo, Eun-Hye Moon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 4011. CrossRef - Effects of Music Therapy and Phone Counseling on Postpartum Depression and Maternal Identity in High Risk Women
Hae Won Kim, Sun OK Kim, Hye Gyung Kim, Hyang Ran Jeon
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(1): 63. CrossRef - Effects of Postpartum Depression and Temperament of Infant on Child-care Stress among Mothers of Newborn Infants
Hye-Jin Kwon, Kyung-Hee Kim, Mi-Hye Choi, Ju-Yeon Cho, Young-Mi Ahn, Ki-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 69. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Postpartum Depression of Vietnamese Marriage Immigrant Women and Korean Women
Eun Young Choi, Eun Hee Lee, Jung Sook Choi, Sun Ha Choi
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(1): 39. CrossRef - Kangaroo Care on Premature Infant Growth and Maternal Attachment and Post-partum Depression in South Korea
H. Y. Ahn, J. Lee, H.-J. Shin
Journal of Tropical Pediatrics.2010; 56(5): 342. CrossRef - Postpartum Depressive Score and Related Factors Pre- and Post-delivery
Sun Ok Lee, Jung Hee Yeo, Suk Hee Ahn, Hyeon Sook Lee, Hyun Joo Yang, Mi Jung Han
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 29. CrossRef - Subjective Sleep Quality in Depressed and Non-Depressed Mothers During the Late Postpartum Period
Eun-Jung Cho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(2): 108. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an e-Learning Program for Mothers of Premature Infants
Nae-Young Lee, Young-Hae Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 152. CrossRef
- Longitudinal Relationship Study of Depression and Self-Esteem in Postnatal Korean Women Using Autoregressive Cross-Lagged Modeling
- 755 View
- 2 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effects of a Short-term Home-based Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program in Patients with Chronic Lung Disease
- Eui Geum Oh, Sun Hee Kim, Hee Ok Park, So Yon Bang, Chun Hwa Lee, So Hee Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(5):570-579. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.5.570
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study is to exam the effects of a short-term pulmonary program on lung function, exercise tolerance, and quality of life in chronic lung patients.
Method Randomized controlled pre-post test design was used. The outcome measures were forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1, % predicted), 6 min walking distance (6MWD), Borg score after 6MWD, and Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire (CRDQ). Experimental group performed the 4-week home-based pulmonary rehabilitation program composed of inspiratory muscle training, upper and lower extremity exercise, relaxation, and telephone visit. Patients in control group were only given education about self-management strategies. Thirty four patients with moderate-to-severe respiratory impairment were recruited, and 28 patients (19 in experiments, 15 in control) completed the study.
Result Significant improvements in lung function, exercise tolerance, and health related quality of life were found only in the experiment group.
Conclusion This study yielded evidence for the potential and beneficial effects of home-based pulmonary rehabilitation program in patients with moderate to severe chronic lung disease. The program could be adequately utilized for improvement of health related quality of life in chronic lung patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Embedding Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in the Home and Community Setting: A Rapid Review
Túlio Medina Dutra de Oliveira, Adriano Luiz Pereira, Giovani Bernardo Costa, Liliane P. de Souza Mendes, Leonardo Barbosa de Almeida, Marcelo Velloso, Carla Malaguti
Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Home based Pulmonary Rehabilitation in COPD Patients: Randomized Controlled Trials
Min Hee Ahn, Ja Yun Choi, Yun Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(2): 82. CrossRef - Developing a Home-based Self-management Support Intervention for Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Hee-Young Song
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2015; 18(2): 75. CrossRef
- Embedding Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in the Home and Community Setting: A Rapid Review
- 797 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Relationships among Loneliness, Social Support,and Family Function in Elderly Korean
- Ok Soo Kim, Sung Hee Baik
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(3):425-432. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.3.425
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To examine the relationships among loneliness, social support, and family function in elderly Korean.
Method The sample for this study were 290 elderly Korean who were at least 60 years of age. Data were collected by interview using the translated Korean versions of the Revised University of California Los Angels Loneliness Scale(RULS), Family APGAR, and Social Support Questionnaire 6.
Result Subjects were moderately lonely and had moderately functional families. Means for social support were 1.42 for network size and 4.09 for satisfaction. Subjects who lived with their spouses had a larger number of network members than who did not live with spouses. However, living with spouses was not associated with social support satisfaction. The level of loneliness was related negatively to the level of social support network, social support satisfaction and family function in this study. Social support satisfaction and Family function were the significant predictor of loneliness.
Conclusion The number of social supporter and satisfaction and family function should be considered in nursing intervention to decrease the level of loneliness in older adults. Further studies and efforts will be needed to reduce the level of loneliness in older adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on the determination of the factors affecting the happiness levels of older individuals during the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkish society
Nurşen Çomaklı Duvar, Ahmet Kamil Kabakuş, Neslihan İyit, Ömer Alkan, Boshra A. Arnout
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0316000. CrossRef - Living alone, widowhood, and loneliness among older males and females: longitudinal evidence from South Korea
Yuri Han, Robert Rudolf
Asian Population Studies.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Basic Psychological Need Satisfaction and Frustration Scale Among Cancer Survivors in Korean Healthcare Contexts
Hyun-E Yeom, Jungmin Lee
Healthcare.2024; 12(24): 2535. CrossRef - Family Function, Loneliness, Emotion Regulation, and Hope in Secondary Vocational School Students: A Moderated Mediation Model
Pan Yun, Han Xiaohong, Yang Zhongping, Zhao Zhujun
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Perception of Aging Symptoms as a Mediator and Moderator on the Relationship between Family Function and Stress in Middle-Aged Adults
Hyun-E Yeom, Kyoung Ok Ju
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(2): 175. CrossRef - Gender Difference in the Relationship Among Family Function, Health Behavior, and Stress in Midlife
Hyun-E Yeom, Jungmin Lee
The International Journal of Aging and Human Development.2020; 91(4): 476. CrossRef - Consideration of the Psychological and Mental Health of the Elderly during COVID-19: A Theoretical Review
Kunho Lee, Goo-Churl Jeong, JongEun Yim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 8098. CrossRef - Influence of home care services on caregivers' burden and satisfaction
Eun‐Young Kim, Hyun‐E Yeom
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2016; 25(11-12): 1683. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Suicidal Ideation of the Low-income Elderly Living Alone
Hee Chong Baek, Jinhwa Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(3): 180. CrossRef - A Study on the Patients Who Attempted Suicide with Drug Intoxication
Jung-Su Han, Seong-Woo Yun, Sung-Soo Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(4): 1863. CrossRef - Impact of Family Support and Social Support on Hopelessness among Rural Elderly People
Sun An Kim
Journal of Agricultural Extension & Community Development.2012; 19(3): 581. CrossRef - The effects of relationships with their children on the elderly's attitudes toward dating and remarriage
Yeong Sug Yi
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2012; 21(4): 695. CrossRef - Analysis of the Influence of Physical Function and Social Support on Depressive Symptom in the Community Elderly Using the Structural Equation Model
Eun-Sook Shin, In-Sun Kwon, Young-Chae Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(11): 4995. CrossRef - Ageing Experiences of Nurses with Overseas Employment: Focusing on the Korean Nurses Dispatched to Germany in the 1960s and 1970s
Hack-Sun Kim, Sun-Woo Hong, Kyung-Sook Choi, Ae-Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(2): 185. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Life Satisfaction of Korean Older Adults Living with Family
Sohyune R. Sok
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2010; 36(3): 32. CrossRef - Effect of Tai Chi Exercise on Loneliness, Sleep Pattern, and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living in Elderly Women
Young-Ju Park, In-Hyae Park
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(2): 151. CrossRef - Relationship of Peer Relationships, Perceived Parental Rearing Attitudes, Self-reported Attachment Security, to Loneliness in Upper Elementary School-age Children
So-Hyun Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 401. CrossRef - Quality of Life of Korean and Korean American Older Adults: A Comparison
Sook-Young Kim, Eun-Young Jeon, Sohyune R. Sok, Hye Kyung Oh, Kwuy-Bun Kim
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2009; 35(6): 28. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Social Isolation in Older Adults using Senior Welfare Centers
Yeon-Hwan Park, Hee Sun Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 712. CrossRef - Aging, Health, and Physical Activity in Korean Americans
Kyung-Choon Lim, Jeanie S. Kayser-Jones, Catherine Waters, Grace Yoo
Geriatric Nursing.2007; 28(2): 112. CrossRef
- A study on the determination of the factors affecting the happiness levels of older individuals during the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkish society
- 1,020 View
- 17 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Effects of Electric Stimulation and Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise in Women with Vaginal Rejuvenation Women
- Jung Bok Lee, So Young Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):713-722. Published online October 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.713
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of pelvic floor muscle exercise using electric stimulation and biofeedback on maximum pressure of vaginal contraction, vaginal contraction duration and sexual function in women who have had vaginal rejuvenation.
Methods The research design was a non-equivalent control group non-synchronized design study. Participants in this study were women who had vaginal rejuvenation at C obstetrics and gynecology hospital. The 15 participants in the experimental group were given pelvic floor muscle exercise using electric stimulation and biofeedback and the 15 participants in the control group received self pelvic floor muscle exercise.
Results For maximum pressure of vaginal contraction, the experimental group showed a statistically significant increase compared to than the control group (t=5.96,
p <.001). For vaginal contraction duration, the experimental group also showed a statistically significant increase compared to the control group (t=3.23,p =.003). For women's sexual function, the experimental group showed a significant increase when compared to the control group in total sexual function scores (t=3.41,p =.002).Conclusion The results indicate that pelvic floor muscle exercise with electric stimulation and biofeedback after vaginal rejuvenation is effective in strengthening vaginal contraction pressure, vaginal contraction and that it also positively functions to increase women's sexual function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of pelvic organ prolapse and various options for its correction on female sexual function: A review
Nataliya M. Podzolkova, Vasilii В. Osadchev, Olga L. Glazkova, Kirill V. Babkov, Yulia V. Denisova
Gynecology.2023; 25(1): 31. CrossRef
- The effect of pelvic organ prolapse and various options for its correction on female sexual function: A review
- 1,197 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Muscle Strength Training on Urinary Incontinence and Physical Function: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Long-term Care Facilities
- Hyekyung Kang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):35-45. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to determine whether muscle strength training programs have an impact on improving symptoms of urinary incontinence (UI) and physical function among elderly women with UI who reside in long-term care facilities.
Methods A randomized controlled trial was conducted. Participants had to be over 65 years, score over 15 score on the mini-mental state examination, and be able to walk alone or with an assistant. Seventy residents were randomly allocated to either the training group (n=35) or control group (n=35). The program consisted of 50 minutes, twice a week for 8 weeks, and included Kegel's exercise, Thera-band training and indoor walking. Main outcomes were UI symptoms, peak vaginal pressure and physical functions measured with timed up and go test (TUG), one leg standing test (OLST), activities of daily living (ADL) and grip strength. Changes in outcome measurements were calculated from baseline to 4 weeks and to 8 weeks using repeated measures ANOVA.
Results There were significant differences in peak vaginal pressure (
p <.001), TUG (p <.001), OLST (p =.012) and grip strength (p <.001) in the interaction between groups and time.Conclusion Future studies are suggested to confirm the effect of muscle strength training in long-term care facilities where elderly women with UI reside.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interventions for treating urinary incontinence in older women: a network meta-analysis
Giovana Vesentini, Nicole O'Connor, Mélanie Le Berre, Ashraf F Nabhan, Adrian Wagg, Sheila A Wallace, Chantale Dumoulin
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - What is the impact of a multi‐component exercise intervention on the cure rate of urinary incontinence among older women living in the community?
Rachele Ricci, Pinar Avsar, Zena Moore, Tom O'Connor, Linda Nugent, Declan Patton
Lifestyle Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Multisite Study on the Effect of a Urinary Incontinence Self-Management Program on Community-Dwelling Older Women in Korea
Sunah Park, Aeyoung So
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2024; 51(1): 61. CrossRef - The Sustainable Care Model for an Ageing Population in Vietnam: Evidence from a Systematic Review
Loi Tan Nguyen, Phouthakannha Nantharath, Eungoo Kang
Sustainability.2022; 14(5): 2518. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Muscle Strength of the Elderly Without Activity Restrictions By Gender
Myoungjin Kwon, Moonkyoung Park, Hyun Joo Kim, Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 43. CrossRef - Long-Term Effects of a Self-management Program for Older Women With Urinary Incontinence in Rural Korea
Aeyoung So, Jennie C. De Gagne, Sunah Park
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(1): 55. CrossRef - Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women
Chantale Dumoulin, Licia P Cacciari, E Jean C Hay-Smith
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of an Exercise Program for Preventing Urinary Incontinence among Community-Dwelling Elderly Females Living Alone
Mi Sook Song, Sunjoo Boo
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 247. CrossRef - The Development of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Medical Devices for The Treatment of Non-implantable Urinary Incontinence
Jae-Yong Lee, Chang-Doo Lee, Ki-Jin Kwon
The Transactions of the Korean Institute of Electrical Engineers P.2015; 64(3): 175. CrossRef
- Interventions for treating urinary incontinence in older women: a network meta-analysis
- 1,692 View
- 46 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Prevalence and Characteristics of Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong-Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):118-128. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.118
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Evidence suggests that some patients with breast cancer experience cognitive difficulties following chemotherapy. This longitudinal study was done to examine the prevalence of cognitive impairment and trajectory of cognitive function over time in women with breast cancer, who received adjuvant chemotherapy.
Methods Participants were 137 patients with breast cancer. They completed neuropsychological tests and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Cognitive Function before adjuvant therapy (pretest), toward the end of adjuvant therapy (posttest), and 6 months after the completion of adjuvant therapy (follow-up test). Of the patients, 91 were treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and 46 patients who did not receive chemotherapy made up the comparison group. A reliable-change index and repeated-measure ANOVA were used for statistical analyses.
Results At the posttest point, over 30% of patients showed complex cognitive impairment and reported greater difficulty in subjective cognitive function. At the follow-up test point, 22.0% of patients exhibited complex cognitive impairment and 30.8% of patients complained of subjective cognitive impairment. Repeated-measure ANOVA showed significant decreases after receiving chemotherapy followed by small improvements 6 months after the completion of chemotherapy in cognitive domains of change for attention and concentration, memory, executive function, and subjective cognitive function.
Conclusion These results suggest that chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer may be associated with objective and subjective cognitive impairments. Further studies are needed to explore the potential risk factors and predictor of chemotherapy-related cognitive changes. Also nursing interventions for prevention and intervention of cognitive impairments should be developed and tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Brain network deficits in breast cancer patients after early neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A longitudinal MRI study
Jing Yang, Yongchun Deng, Daihong Liu, Yong Tan, Meng Lin, Xiaoyu Zhou, Jing Zhang, Hong Yu, Yixin Hu, Yu Tang, Shixi Jiang, Jiuquan Zhang
Journal of Neuroscience Research.2023; 101(7): 1138. CrossRef - Frailty and its associated factors among older adults with cancer undergoing chemotherapy as outpatients: A cross-sectional study
Misun Jeon, Hyoeun Jang, Arum Lim, Sanghee Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 60: 102192. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Distinct sleep disturbance and cognitive dysfunction profiles in oncology outpatients receiving chemotherapy
Vivian Huang, Lynda Mackin, Kord M. Kober, Steven M. Paul, Bruce A. Cooper, Yvette P. Conley, Marilyn J. Hammer, Jon D. Levine, Christine Miaskowski
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(11): 9243. CrossRef - Measurement, outcomes and interventions of cognitive function after breast cancer treatment: A narrative review
Miaomiao Jia, Xiaojun Zhang, Liyuan Wei, Jinnan Gao
Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology.2021; 17(4): 321. CrossRef - Improving preoperative breast reconstruction consultations: a qualitative study on the impact of personalised audio-recordings
Josipa Petric, Bahara Sadri, Phillipa van Essen, Nicola Ruth Dean
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on Neurologic and Cognitive Dysfunction in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy with Resting State fMRI
Fenshan Zheng, Peiying Cao, Jie Zhou, Chunyu Li, John Norris
World Neurosurgery.2021; 149: 388. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Fatigue following Chemotherapy in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Prospective Controlled Study
Pok-Ja Oh, Sun Mi Moon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 126. CrossRef - Computerized programs for cancer survivors with cognitive problems: a systematic review
Yoonjung Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2019; 13(6): 911. CrossRef - Cancer treatment effects on cognition and depression: The moderating role of physical activity
Margaret F. Bedillion, Emily B. Ansell, Gwendolyn A. Thomas
The Breast.2019; 44: 73. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Depression following Chemotherapy in Women with Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee, Hyun Ah Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(2): 66. CrossRef - Mulheres Submetidas à Quimioterapia e suas Funções Cognitivas
Camila Vasconcelos Carnaúba Lima, Raner Miguel Ferreira Póvoa
Psicologia: Ciência e Profissão.2017; 37(4): 970. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-induced prospective memory impairment in breast cancer patients with different hormone receptor expression
Wen Li, Chen Gan, Yue Lv, Shanghu Wang, Huaidong Cheng
Medicine.2017; 96(13): e6514. CrossRef - Altered network efficiency of functional brain networks in patients with breast cancer after chemotherapy
Han Xuan, Chen Gan, Wen Li, Zhonglian Huang, Longsheng Wang, Qianqian Jia, Zhendong Chen, Huaidong Cheng
Oncotarget.2017; 8(62): 105648. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - Effect of Cancer Symptoms and Fatigue on Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Depression in People with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 420. CrossRef - A review of traditional Korean medical treatment for cancer-related cognitive impairment
Hye-Yoon Lee, Jung-Eun Kim, Mikyung Kim, Joo-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Medicine.2016; 37(3): 74. CrossRef - Cognitive outcome after radiotherapy in brain tumor
Thomas Durand, Marie-Odile Bernier, Isabelle Léger, Hervé Taillia, Georges Noël, Dimitri Psimaras, Damien Ricard
Current Opinion in Oncology.2015; 27(6): 510. CrossRef - Changes of Symptom Distress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Adjuvant Therapy
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(2): 67. CrossRef
- Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1,411 View
- 12 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Mediating Effect of Self-efficacy in the Relationship between Anger and Functional Health of Homeless Men
- Su In Park, Sunah Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):361-370. Published online August 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the mediation of self-efficacy in the relationship between anger and the functional health of homeless men in order to provide a basis for planning nursing interventions to improve the functional health of homeless persons.
Methods The participants were 137 homeless men who lived in homeless shelters or visited one center serving free meals for homeless persons in Seoul. Data were collected using self-report questionnaires and analyzed with the SPSS-WIN 20.0 program. The instruments were the Functional Health Pattern Screening Assessment Tool (FHPAST), Self-efficacy Scale (SES), and State-trait Anger Expression Inventory-Korean version (STAXI-K).
Results The mean score for functional health was 2.41. Overall self-efficacy was 70.82. state anger was 16.53, trait anger was 19.54, and anger expression was 25.31. There were signigicant correlations among the 3 variables, functional health, self-efficacy, and anger. Also, self-efficacy had a complete mediating effect in the relationship between anger and functional health.
Conclusion Based on the findings of this study, health management programs focusing on anger management and self-efficacy improvement are highly recommended to promote functional health in homeless persons.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing satisfaction with medical services in medically underserved populations: an analytical cross-sectional study at a free medical clinic in the Republic of Korea
Joo Hyun Kim, Yeon Jeong Heo, Jae Bok Kwak, Samil Park, Curie Ahn, So Hee Ahn, Bumjo Oh, Jung Sik Lee, Jun Hyun Lee, Ho Young Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2025; 16(2): 181. CrossRef - The Urban Poor Patients’ Experience of Visiting a Free Clinic
Joo Hyun Kim, Yeon Jeong Heo, Jae Bok Kwak, So Hee Ahn, Bumjo Oh, Jung Sik Lee, Ho-Young Lee
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2023; 8(2): 137. CrossRef - Association between post‐traumatic stress symptoms and functional health among internally displaced people in Myanmar
Go‐Un Kim, Eunyoung Jung, Mi‐So Shim, Gwang Suk Kim
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 29(4): 555. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Functional Health of Patients with Chronic Insomnia based on Theory of Unpleasant Symptoms
Eun Kyoung Han, Sunah Kim, In-Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(2): 165. CrossRef - A Phenomenology Study of the Lived Experience of Homeless Persons
Jin Ju Kim, Eunyoung Park, Myungsun Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(1): 88. CrossRef - Comparing anger, anger expression, life stress and social support between Korean female nursing and general university students
Won Hee Jun, Gyungjoo Lee
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2017; 73(12): 2914. CrossRef - Anger expression, self‐efficacy and interpersonal competency of Korean nursing students
W.‐H. Jun
International Nursing Review.2016; 63(4): 539. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy in the Relationship between Internalized Stigma and Treatment Adherence of Community Dwelling Patients with Mental Illness
Jin Hee Kim, Hyunjoo Na
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Trait Anger, Anger Expression, Positive Thinking and Gratitude in College Students
Won-Hee Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(1): 28. CrossRef
- Factors influencing satisfaction with medical services in medically underserved populations: an analytical cross-sectional study at a free medical clinic in the Republic of Korea
- 1,016 View
- 4 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effect of PLISSIT Model Sexual Health Enhancement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer and Their Husbands
- Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(5):681-689. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.681
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine effects of the Permission, Limited Information, Specific Suggestions, Intensive Therapy (PLISSIT) model sexual health enhancement program on, and development in, sexual function, sexual distress, marital intimacy, and subjective happiness of women with gynecologic cancer and their husbands.
Methods The comprehensive program (4 session, 90 minutes per session) was developed based on the PLISSIT model. Participants were 43 couples, 21 assigned to the experimental group who attended the 4-week program, and 22 to the control group. Sexual function, sexual distress, marital intimacy, subjective happiness of the women, marital intimacy, subjective happiness of husbands were determined by a questionnaire that was completed by the participants before and after the program. The control group received the intervention post experiment. Chi-square test, t-test, Fisher's exact test were used to test the effectiveness of the program.
Results Post intervention results showed significant differences between the groups for sexual function, sexual distress, and marital intimacy in the women and for subjective happiness in the husbands.
Conclusion Results indicate that the sexual health enhancement program is effective in improving sexual function, lowering sexual distress, increasing marital intimacy, and subjective happiness in women with gynecologic cancer and their husbands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Sexual Education Program on Sexual Function and Genital Self-image, Sexual Quality of Life among Primiparous Women
Athar Rasekh Jahromi, Hanie Jafari, Parvin Adedi, Mojgan Javadnoori, Solmaz Mohammadi, Vahid Rahmanian, Safieh Jamali
Current Womens Health Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a sexual health enhancement program for women with breast cancer: A quasi-experimental study
Hye Sook Kim, Chaewon Yun
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 76: 102852. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in Pregnant Women With Preterm Labor
So Jin Lee, Ju-Hee Nho, Eun Jee Lee, Dong Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(2): 87. CrossRef - The effectiveness of couple-based interventions on the marital outcomes of women with genital and breast cancer and their partners: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hamideh Zahedi, Zohreh Alizadeh-Dibazari, Mojgan Mirghafourvand, Mohammad Hasan Sahebihagh, Mina Hosseinzadeh
BMC Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility and effectiveness of communication tools for addressing intimacy and sexuality in patients with cancer: a systematic review
Susanne A. M. Arends, Carlijn E. van Rossum, Corien M. Eeltink, Jantien E. Robertus, Linda J. Schoonmade, Anneke L. Francke, Irene P. Jongerden
Supportive Care in Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Sexual Counseling Based on PLISSIT and EX-PLISSIT Models on Sexual Function, Satisfaction, and Quality of Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sevil Cicek Ozdemir, Aliye Dogan Gangal, Ayten Senturk Erenel
Archives of Sexual Behavior.2024; 53(9): 3485. CrossRef - The Effect of Sexual Counseling Based on EX‑PLISSIT Model on Improving the Sexual Function of Married Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Maryam Shami, Ali Montazeri, Seyedeh Tahereh Faezi, Zahra Behboodi Moghadam
Sexuality and Disability.2023; 41(2): 451. CrossRef - The Effect of Post-Operative Sexual Counseling Carried out with PLISSIT Model on Sexual Function and Sexual Satisfaction in Gynecologic Cancers
Çiğdem BİLGE, Ergül ASLAN
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2023; 13(3): 623. CrossRef - The effect of a psycho-educational intervention on sexuality of women with acute coronary syndromes: a randomized controlled trial
Fatemeh Soleimaninejad, Razieh Lotfi, Mehdi Mousavi, Majid Taghizadeh, Kourosh Kabir
Sexual and Relationship Therapy.2023; 38(2): 277. CrossRef - Sexual health outcomes of PLISSIT-based counseling versus grouped sexuality education among Iranian women with breast cancer: A randomized clinical trial
Effat Merghati Khoei, Rhoghieh Kharaghani, Elham Shakibazadeh, Soghrat Faghihzadeh, Noura Aghajani, Jeffrey E. Korte, Mina Esmkhani
Sexual and Relationship Therapy.2022; 37(4): 557. CrossRef - Effects of the Better Model Based Counseling on Sexuality of Women with Breast Cancer
Zeynep Ozkan Olcer, Umran Oskay
International Journal of Sexual Health.2022; 34(1): 41. CrossRef - The effect of PLISSIT based counseling model on sexual function, quality of life, and sexual distress in women surviving breast cancer: a single-group pretest–posttest trial
Zohreh Keshavarz, Elham Karimi, Samira Golezar, Giti Ozgoli, Maliheh Nasiri
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Sexual Health Improvement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Soon Yang Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 163. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - The Effect of the PLISSIT Model on Sexual Functions: A Systematic Review
Serap KIRICI, Emel EGE
Bandırma Onyedi Eylül Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri ve Araştırmaları Dergisi.2021; 3(3): 199. CrossRef - Sexual Health Outcomes of PLISSIT-based Counseling versus Grouped Sexuality
Education among Iranian Women with Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Medical & Clinical Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - PLISSIT Interventions and Sexual Functioning: Useful Tools for Social Work in Palliative Care?
Michael R. Bennett
Journal of Social Work in End-of-Life & Palliative Care.2019; 15(4): 157. CrossRef - Effect of a Web-Based Sexual Health Enhancement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer and Their Husbands
Ju-Hee Nho, Yeon Hee Kim, Hye-Ji Kook
International Journal of Sexual Health.2019; 31(1): 50. CrossRef - Oncology Nurses' Knowledge Regarding Fertility Preservation for Patients with Cancer
Miok Kim, Ju-Hee Nho, Aeran Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 315. CrossRef - The Influence of Ex-PLISSIT (Extended Permission, Limited Information, Specific Suggestions, Intensive Therapy) Model on Intimacy and Sexuality of Married Women with Multiple Sclerosis
Fatemeh Daneshfar, Zahra Behboodi-Moghadam, Zohreh Khakbazan, Seyed Massood Nabavi, Nahid Dehghan Nayeri, Sogand Ghasemzadeh, Ali Montazeri
Sexuality and Disability.2017; 35(4): 399. CrossRef - Development of a Web-based Sexual Health Program for Women Undergoing Treatment for Gynecologic Cancer and Their Partners
Ju-Hee Nho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(2): 104. CrossRef - The effectiveness of the Permission, Limited Information, Specific suggestions, Intensive Therapy (PLISSIT) model based sexual counseling on the sexual function of women with Multiple Sclerosis who are sexually active
Zohreh Khakbazan, Fatemeh. Daneshfar, Zahra Behboodi-Moghadam, Seyed Massood Nabavi, Sogand Ghasemzadeh, Abbas Mehran
Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders.2016; 8: 113. CrossRef - Comments on female sexual dysfunction with cervical cancer in Republic of Korea
Gyeong-Eun Heo, Tae-Hee Kim, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Jun-Mo Kim
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2016; 294(1): 209. CrossRef - Reply to letter to the editor by J.-M. Kim et al. on "Sexual function and quality of life in women with cervical cancer before radiotherapy: a pilot study" by Grion et al.
R. C. Grion, Luiz Francisco Baccaro, A. F. Vaz, L. Costa-Paiva, D. M. Conde, A. M. Pinto-Neto
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2016; 294(1): 211. CrossRef - Interventions for sexual dysfunction following treatments for cancer in women
Bridget Candy, Yuan Chi, Lisa Graham-Wisener, Louise Jones, Michael King, Anne Lanceley, Victoria Vickerstaff, Adrian Tookman
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Lifestyle Intervention on Fatigue, Nutritional Status and Quality of Life in Patients with Gynecologic Cancer
Hyunjin An, Ju-Hee Nho, Sunyoung Yoo, Hyunmin Kim, Minji Nho, Hojeong Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(6): 812. CrossRef
- The Effect of Sexual Education Program on Sexual Function and Genital Self-image, Sexual Quality of Life among Primiparous Women
- 3,072 View
- 22 Download
- 26 Crossref

- An Introduction to Logistic Regression: From Basic Concepts to Interpretation with Particular Attention to Nursing Domain
- Hyeoun-Ae Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(2):154-164. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.154
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this article is twofold: 1) introducing logistic regression (LR), a multivariable method for modeling the relationship between multiple independent variables and a categorical dependent variable, and 2) examining use and reporting of LR in the nursing literature.
Methods Text books on LR and research articles employing LR as main statistical analysis were reviewed. Twenty-three articles published between 2010 and 2011 in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing were analyzed for proper use and reporting of LR models.
Results Logistic regression from basic concepts such as odds, odds ratio, logit transformation and logistic curve, assumption, fitting, reporting and interpreting to cautions were presented. Substantial shortcomings were found in both use of LR and reporting of results. For many studies, sample size was not sufficiently large to call into question the accuracy of the regression model. Additionally, only one study reported validation analysis.
Conclusion Nursing researchers need to pay greater attention to guidelines concerning the use and reporting of LR models.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Examining the effect of farm and farmers' characteristics and input allocation on potato production
Ardi Rumallang, Muslim Salam, Letty Fudjaja, Pipi Diansari, Baharuddin Patandjengi, Rahim Darma, A. Nixia Tenriawaru, Heliawaty, Akhsan, Rahmadanih, Rida Akzar, Muhammad Ridwan, Hamed Noralla Bakheet Ali
Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sikkim Himalayas using an ensemble machine learning approach
Indrajit Poddar, Ranjan Roy
Discover Geoscience.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Sociodemographic Characteristics of Internationally Educated Nurses Associated With Successful Outcomes in Canada: Quantitative Analysis
Nasrin Alostaz, Jiajie Mo, Margaret Walton‐Roberts, Ruth Chen, Maria Pratt, Olive Wahoush
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025; 81(7): 3753. CrossRef - The development of classification-based machine-learning models for the toxicity assessment of chemicals associated with plastic packaging
Md Mobarak Hossain, Kunal Roy
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2025; 484: 136702. CrossRef - Development of a predictive model for severe peripartum hemorrhage in placenta accreta spectrum cases under neuraxial anesthesia: a multicenter retrospective analysis
Yanan Li, Liang Li, Xiao Song, Fanqing Meng, Meiling Zhang, Yarong Li, Ran Chu
Therapeutic Advances in Reproductive Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative Credit Risk Assessment: Leveraging Social Media Data for Inclusive Credit Scoring in Indonesia’s Fintech Sector
Andry Alamsyah, Aufa Azhari Hafidh, Annisa Dwiyanti Mulya
Journal of Risk and Financial Management.2025; 18(2): 74. CrossRef - Machine Learning as a Tool for Assessment and Management of Fraud Risk in Banking Transactions
Antonio Dichev, Silvia Zarkova, Petko Angelov
Journal of Risk and Financial Management.2025; 18(3): 130. CrossRef - MLP-SVM: a hybrid approach for improving the performance of the classification model for health-related documents from social media using multi-layer perceptron and support vector machine
Etana Fikadu, Teklu Urgessa, Mrinal Das
Discover Applied Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Armed conflict and household food insecurity: impacts and coping strategies in the conflict-affected rural settings of Tigray, Ethiopia
Hafte Gebreselassie Gebrihet, Yibrah Hagos Gebresilassie
Cogent Social Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Employing Binary Logistic Regression in Modeling the Effectiveness of Agricultural Extension in Clove Farming: Facts and Findings from Sidrap Regency, Indonesia
Hasim Hasim, Muslim Salam, Andi Amran Sulaiman, Muhammad Hatta Jamil, Hari Iswoyo, Pipi Diansari, Ariady Arsal, Andi Nixia Tenriawaru, Akhsan Akhsan, Ahmad Imam Muslim
Sustainability.2025; 17(6): 2786. CrossRef - Harnessing Socio-Spatial Dynamics for Pandemic Resilience: Evidence from Kozhikode, India
Shahana Usman Abdulla, Bimal Puthuvayi
One Health.2025; 20: 101052. CrossRef - A supervised learning approach for recommending medical specialists in the healthcare sector for the Afaan Oromo context
Etana Fikadu, Mrinal Das, Teklu Urgessa, Krishnaraj Ramaswamy
Discover Computing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning-Based Ensemble Feature Selection and Nested Cross-Validation for miRNA Biomarker Discovery in Usher Syndrome
Rama Krishna Thelagathoti, Dinesh S. Chandel, Wesley A. Tom, Chao Jiang, Gary Krzyzanowski, Appolinaire Olou, M. Rohan Fernando
Bioengineering.2025; 12(5): 497. CrossRef - Unmooring tax compliance: The impact of information technology in the Zimbabwean small firms under presumptive taxation
Munyaradzi Duve, Daniel P. Schutte
Social Sciences & Humanities Open.2025; 11: 101422. CrossRef - Is Video Assistant Referee (VAR) a disadvantage for the strong and a protection for the weak? The case of Turkish Super League
Ümit Kuvvetli, Esin Firuzan, Ali Riza Firuzan
Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2025; 80: 102924. CrossRef - Factores que motivan la intención emprendedora de los estudiantes universitarios: caso Universidad Técnica de Machala
Julio César Cacay Cacay, Lenny Beatriz Capa Benítez
LATAM Revista Latinoamericana de Ciencias Sociales y Humanidades.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine learning techniques for stroke prediction: A systematic review of algorithms, datasets, and regional gaps
Afeez Adekunle Soladoye, Nicholas Aderinto, Mayowa Racheal Popoola, Ibrahim A. Adeyanju, Ayokunle Osonuga, David B. Olawade
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2025; 203: 106041. CrossRef - A Machine Learning Approach to the Prediction of Malaria in Under-five Children: Analysis of the 2021 Nigerian Malaria Indicator Survey
Sbongiseni Makhosonke Mthethwa, Sileshi Fanta Melesse
The Open Public Health Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Modelling of biological age in stable and acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Yujiao Wang, Ting Mu, Yufen Fu, Yuxin Wang, Guoping Li
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing undernutrition among children in Nepal: a comparative study of Composite Index of Anthropometric Failure (CIAF) using 2016 and 2022 demographic and health survey data
Ram Prasad Dhakal, Vijay Aryal, Pitambar Acharya
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the Impact of Infrastructure and Social Environment Predictors on Road Accidents in Switzerland Using Machine Learning Algorithms and Open Large-Scale Dataset
Alessandro Auzzas, Gian Franco Capra, Antonio Ganga
Urban Science.2025; 9(9): 343. CrossRef - Drivers of Integrated Soil Fertility Management Adoption Among Smallholder Farmers in Bure District, Ethiopia
Solomon Tadesse, Tekalign Assefa, Wafaa M. Abd El Rahim
Applied and Environmental Soil Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Career paths and university education: factors that determine the employment status of university graduates
Heily Consepción Portocarrero Ramos, Jonathan Alberto Campos Trigoso, Omer Cruz Caro, Yuri Reina Marín, Jorge Luis Maicelo Guevara, Einstein Sánchez Bardales, River Chávez Santos
Frontiers in Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Prevalence and Determinants Associated with Hypertension Among the Adult Population in Hawtat Bani Tamim Province
Mohammed Omar Musa Mohammed, Ahmed Saied Rahama Abdallah
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(10): 1467. CrossRef - Deep learning techniques used for the detection of fraudulent activities within the ethereum network
Khalid Alkhatib, Fares Al Ayoub, Qais Marji
Cluster Computing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Examining the prevalence of and factors associated with facility-based birth services in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional analysis using national data
Sanjoy Kumar Chanda, Meherab Hossain, Ashik Mondal, Antora Rahut, Md. Mehedi Hasan, Md. Shariful Islam
Discover Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses' Self‐Perceived Patient Safety Competencies: Associations With Work‐ and Education‐Related Factors in a Cross‐Sectional Study
Liisi Mägi, Kaja Põlluste, Margus Lember, Mariliis Põld, Mari Kangasniemi
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effective pulse shape discrimination for neutron and gamma-ray radiation using wavelet transform and logistic regression
Assem Abdelhakim, Ehab Elshazly, M.E. Hammad
Journal of Instrumentation.2025; 20(12): P12003. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of machine learning classification models utilizing GIS and key flood-causing factors for enhancing flood vulnerability assessment
Ahmed E. M. Al-Juaidi, Osman Taylan, Huseyin Toros
Environment, Development and Sustainability.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Landslide Occurrence and Mitigation Strategies: Exploring Community Perception in Kivu Catchment of Rwanda
Ma-Lyse Nema, Bachir Mahaman Saley, Arona Diedhiou, Assiel Mugabe
GeoHazards.2025; 7(1): 1. CrossRef - Informatics and measurement in healthcare: deep learning for diabetic patient readmission prediction
Shiva Saffari, Mahdi Bahaghighat
Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska.2025; 15(4): 56. CrossRef - Longitudinal Risk Analysis of Second Primary Cancer after Curative Treatment in Patients with Rectal Cancer
Jiun-Yi Hsia, Chi-Chang Chang, Chung-Feng Liu, Chia-Lin Chou, Ching-Chieh Yang
Diagnostics.2024; 14(13): 1461. CrossRef - MODELLING THE FACTORS AFFECTING CRASH OCCURRENCE AND FREQUENCY RESULTED FROM MOBILE PHONE USE WHILE DRIVING: EVIDENCE FROM AL-NAJAF, IRAQ
Firas Asad, Shaimaa Hadi
Kufa Journal of Engineering.2024; 15(2): 74. CrossRef - Factors That Affect Rural Financial Inclusion: A Case of Gambella Town, Gambell Peoples National Regional State, Ethiopia
Chuol Jock Ruey
KnE Social Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Learning strategies, self-efficacy beliefs and academic achievement of first-year preservice teachers: a person-centred approach
Henna Vilppu, Eero Laakkonen, Anu Laine, Marko Lähteenmäki, Riitta-Leena Metsäpelto, Mirjamaija Mikkilä-Erdmann, Anu Warinowski
European Journal of Psychology of Education.2024; 39(2): 1161. CrossRef - Landscape dynamics and its related factors in the Citarum River Basin: a comparison of three algorithms with multivariate analysis
Moh. Dede, Sunardi Sunardi, Kuok-Choy Lam, Susanti Withaningsih, Hendarmawan Hendarmawan, Teguh Husodo
Geocarto International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis in Terms of Environmental Awareness of Farmers’ Decisions and Attitudes: Reducing Pesticide Use and Risks
Ismail Bulent Gurbuz
Sustainability.2024; 16(11): 4323. CrossRef - Assessment of pedestrians’ red light violation behavior at signalized crosswalks in Kathmandu, Nepal
Deepak Raj Shah, Rojee Pradhananga
Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives.2024; 24: 101035. CrossRef - Financial Stress, Family, Marital, and Life Satisfaction of Turkish Families During Covid-19: What Did We Learn?
Selda Coşkuner Aktaş, Birgül Çiçek
Journal of Family Issues.2024; 45(4): 1044. CrossRef - Logistic regression and other statistical tools in diagnostic biomarker studies
Dina Mohamed Ahmed Samir Elkahwagy, Caroline Joseph Kiriacos, Manar Mansour
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2024; 26(9): 2172. CrossRef - Machine learning applications in vadose zone hydrology: A review
Xiang Li, John L. Nieber, Vipin Kumar
Vadose Zone Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving dengue fever predictions in Taiwan based on feature selection and random forests
Chao-Yang Kuo, Wei-Wen Yang, Emily Chia-Yu Su
BMC Infectious Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A logit model approach to the examination of parents’ willingness to contribute towards the cost of senior high school education: The case of parents in Tamale, Ghana
William Kofi Nkegbe
Social Sciences & Humanities Open.2024; 9: 100832. CrossRef - PET radiomics-based lymphovascular invasion prediction in lung cancer using multiple segmentation and multi-machine learning algorithms
Seyyed Ali Hosseini, Ghasem Hajianfar, Pardis Ghaffarian, Milad Seyfi, Elahe Hosseini, Atlas Haddadi Aval, Stijn Servaes, Mauro Hanaoka, Pedro Rosa-Neto, Sanjeev Chawla, Habib Zaidi, Mohammad Reza Ay
Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine.2024; 47(4): 1613. CrossRef - Boosting Institutional Identity on X Using NLP and Sentiment Analysis: King Faisal University as a Case Study
Khalied M. Albarrak, Shaymaa E. Sorour
Mathematics.2024; 12(12): 1806. CrossRef - Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Hasil Belajar Statistika Mahasiswa melalui Pemodelan Regresi Logistik Biner
Filda Febrinita, Wahid Ibnu Zaman, Wahyu Dwi Puspitasari
Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika.2024; 4(1): 523. CrossRef - What made you do moonlighting? A tale from the Indonesian labor force survey
Padang Wicaksono, Dewi Kartika Sari, Reinaldy Sutanto
Cogent Social Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - CREDIT RISK ANALYSIS: AN ASSESSMENT OF THE PERFORMANCE OF SIX MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUES IN CREDIT SCORING MODELLING
Abba Bello Muhammad, Ishaq O. Olawoyin, Abubakar Yahaya, S. U. Gulumbe, Abdullahi. A. Muhammad, Iliyasu Abubakar Salisu
FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES.2024; 8(6): 163. CrossRef - Reliable water quality prediction and parametric analysis using explainable AI models
M. K. Nallakaruppan, E. Gangadevi, M. Lawanya Shri, Balamurugan Balusamy, Sweta Bhattacharya, Shitharth Selvarajan
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling the drivers of large herbivore distribution in human‐dominated southern African savannas
Dionísio V. Roque, Thomas Göttert, Ulrich Zeller, Valério A. Macandza
Ecosphere.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antecedents of Savings Behaviour Among Rural Households: A Holistic Approach
Mohd Abass Bhat, Geleta Demera Gomero, Shagufta Tariq Khan
FIIB Business Review.2024; 13(1): 56. CrossRef - The causal-effect model of input factor allocation on maize production: Using binary logistic regression in search for ways to be more productive
Muslim Salam, Rusli M. Rukka, Muh An-Nashrullah K. Samma, A. Nixia Tenriawaru, Rahmadanih, Ahmad Imam Muslim, Hamed Noralla Bakheet Ali, Muhammad Ridwan
Journal of Agriculture and Food Research.2024; 16: 101094. CrossRef - Sensing Biomechanical Alterations in Red Blood Cells of Type 1 Diabetes Patients: Potential Markers for Microvascular Complications
Riccardo Di Santo, Benedetta Niccolini, Alessandro Rizzi, Laura Bertini, Denise Pires Marafon, Maria Vaccaro, Federica Cristallo, Enrico Rosa, Linda Tartaglione, Laura Leo, Marco De Spirito, Gabriele Ciasca, Dario Pitocco
Biosensors.2024; 14(12): 587. CrossRef - Evaluating Rural Land Administration Institutional Efficiency from Modern Land Administration Systems Perspective: In Case of Awi Zone, North-Western Ethiopia
Dereje Shiferaw, Mihret Yeneneh, Teha Benti
Journal of Public Policy and Administration.2024; 8(3): 88. CrossRef - Predicting increments in heavy metal contamination in farmland soil
Jieh-Haur Chen, Meng-Fen Yeh, Jui-Pin Wang, Hsi-Hsien Wei
Environment, Development and Sustainability.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of Risk Factors Associated with the African Swine Fever Outbreaks in the Nizhny Novgorod Region of Russia, 2011–2022
Olga I. Zakharova, Andrey A. Blokhin, Ivan V. Yashin, Olga A. Burova, Denis V. Kolbasov, Fedor I. Korennoy, Jordi Casal
Transboundary and Emerging Diseases.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Determinants of bamboo processors' utilization level: The case of Bahir Dar city and Injibara town, Ethiopia
Tsadiku Setegne Dessie, Ahmed Mohammed Yimer, Mohammed Yimam Ali
Advances in Bamboo Science.2023; 5: 100043. CrossRef - Comprehensive breathing variability indices enhance the prediction of extubation failure in patients on mechanical ventilation
Qing Pan, Haoyuan Zhang, Mengting Jiang, Gangmin Ning, Luping Fang, Huiqing Ge
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2023; 153: 106459. CrossRef - A Survey on Machine Learning in Hardware Security
Troya Çağıl Köylü, Cezar Rodolfo Wedig Reinbrecht, Anteneh Gebregiorgis, Said Hamdioui, Mottaqiallah Taouil
ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems.2023; 19(2): 1. CrossRef - Machine learning facilitated structural activity relationship approach for the discovery of novel inhibitors targeting EGFR
Rekha Choudhary, Vinayak Walhekar, Amol Muthal, Dilip Kumar, Chandrakant Bagul, Ravindra Kulkarni
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.2023; 41(22): 12445. CrossRef - What Factors Influence Consumers to Buy Green Products? An Analysis through the Motivation–Opportunity–Ability Framework and Consumer Awareness
Gizem Yener, Arzu Secer, Pascal L. Ghazalian
Sustainability.2023; 15(18): 13872. CrossRef - Relationships between Health Education, Health Behaviors, and Health Status among Migrants in China: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on the China Migrant Dynamic Survey
Minji Kim, Hai Gu
Healthcare.2023; 11(12): 1768. CrossRef - Multi-View Learning to Unravel the Different Levels Underlying Hepatitis B Vaccine Response
Fabio Affaticati, Esther Bartholomeus, Kerry Mullan, Pierre Van Damme, Philippe Beutels, Benson Ogunjimi, Kris Laukens, Pieter Meysman
Vaccines.2023; 11(7): 1236. CrossRef - Stacked Generalization Architecture for Predicting Publisher Behaviour from Highly Imbalanced User-Click Data Set for Click Fraud Detection
Deepti Sisodia, Dilip Singh Sisodia
New Generation Computing.2023; 41(3): 581. CrossRef - Textual Feature Extraction Using Ant Colony Optimization for Hate Speech Classification
Shilpa Gite, Shruti Patil, Deepak Dharrao, Madhuri Yadav, Sneha Basak, Arundarasi Rajendran, Ketan Kotecha
Big Data and Cognitive Computing.2023; 7(1): 45. CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors for Poor Mental Health and Suicidal Ideation in the Nigerian Construction Industry
Janet M. Nwaogu, Albert P. C. Chan, Riza Yosia Sunindijo, Amos Darko, Jackie Y. Yang, Dauda Salihu
Journal of Construction Engineering and Management.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A comprehensive analysis for classification and regression of surface points based on geodesics and machine learning algorithms
Vahide Bulut
Engineering Computations.2023; 40(9/10): 2270. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Success of High-flow Nasal Cannula Treatment Applied to Respiratory Distress Patients with Hematologic Neoplasms
Eun Hee Kim, Dong Yeon Kim, Yang Sook Yoo
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(4): 185. CrossRef - Data Balancing Techniques for Predicting Student Dropout Using Machine Learning
Neema Mduma
Data.2023; 8(3): 49. CrossRef - Prevalence and severity of temporomandibular joint disorder in partially versus completely edentulous patients: A systematic review
Pragati Rawat, Deepesh Saxena, Pratiksha A. Srivastava, Abhinav Sharma, Arka Swarnakar, Aditya Sharma
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2023; 23(3): 218. CrossRef - An Explainable Hybrid Intelligent System for Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease
Annwesha Banerjee Majumder, Somsubhra Gupta, Dharmpal Singh, Sourav Majumder
Journal of Mines, Metals and Fuels.2023; : 687. CrossRef - Asset Management of Wastewater Interceptors Adjacent to Bodies of Water
Mohammad Damen Bani Fawwaz, Mohammad Najafi, Vinayak Kaushal
Water.2023; 15(23): 4176. CrossRef - Comparison of Machine Learning Strategies in Hazardous Asteroids Prediction
Yao Wang
Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology.2023; 39: 201. CrossRef - Healthcare predictive analytics using machine learning and deep learning techniques: a survey
Mohammed Badawy, Nagy Ramadan, Hesham Ahmed Hefny
Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analyzing physical and socio-economic factors for property crime incident in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Yeshimar Yigzaw, Asnake Mekuriaw, Tadesse Amsalu
Heliyon.2023; 9(2): e13282. CrossRef - Mapping and Prediction of Urban Growth using Remote Sensing, Geographic Information System, and Statistical Techniques for Tiruppur Region, Tamil Nadu, India
K. Elangovan, G. Krishnaraaju
Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing.2023; 51(8): 1657. CrossRef - Development of a predictive model for workers' involvement in workplace accidents in an underground coal mine
Kumar Arra, Yuga Raju Gunda, Suprakash Gupta
Sādhanā.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A review on the significance of body temperature interpretation for early infectious disease diagnosis
Nurul Izzati Darul Zaman, Yuan Wen Hau, Ming Chern Leong, Rania Hussien Ahmed Al-ashwal
Artificial Intelligence Review.2023; 56(12): 15449. CrossRef - Unraveling Structural Alerts in Marketed Drugs for Improving Adverse Outcome Pathway Framework of Drug-Induced QT Prolongation
Wulin Long, Shihai Li, Yujie He, Jinzhu Lin, Menglong Li, Zhining Wen
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6771. CrossRef - The Influence of Street Morphology on Thermal Environment Based on ENVI-met Simulation: A Case Study of Hangzhou Core Area, China
Jin Bao, Lihua Xu, Yijun Shi, Qiwei Ma, Zhangwei Lu
ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information.2023; 12(8): 303. CrossRef - An Asymmetric Ensemble Method for Determining the Importance of Individual Factors of a Univariate Problem
Jelena Mišić, Aleksandar Kemiveš, Milan Ranđelović, Dragan Ranđelović
Symmetry.2023; 15(11): 2050. CrossRef - Classification of WatSan Technologies Using Machine Learning Techniques
Hala Al Nuaimi, Mohamed Abdelmagid, Ali Bouabid, Constantinos V. Chrysikopoulos, Maher Maalouf
Water.2023; 15(15): 2829. CrossRef - A Study of R-R Interval Transition Matrix Features for Machine Learning Algorithms in AFib Detection
Sahil Patel, Maximilian Wang, Justin Guo, Georgia Smith, Cuixian Chen
Sensors.2023; 23(7): 3700. CrossRef - Determinants of viral load suppression among orphaned and vulnerable children living with HIV on ART in Tanzania
Amal Ally, Amon Exavery, John Charles, Levina Kikoyo, Remmy Mseya, Asheri Barankena, Rose Fovo, Akwila Temu
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Economic Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Organization and Cultivation of the Wheat Crop in Iraq Using Logistic Regression
Noor Amer Ali, Ali Darub Kassar Al-Hiyali, Muhammed Khalid Muhammed
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2023; 1158(9): 092001. CrossRef - An interpretable prediction model of illegal running into the opposite lane on curve sections of two-lane rural roads from drivers’ visual perceptions
Li He, Bo Yu, Yuren Chen, Shan Bao, Kun Gao, You Kong
Accident Analysis & Prevention.2023; 186: 107066. CrossRef - Explainable Artificial Intelligence of Multi-Level Stacking Ensemble for Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Particle Swarm Optimization and the Sub-Scores of Cognitive Biomarkers
Abdulaziz AlMohimeed, Redhwan M. A. Saad, Sherif Mostafa, Nora Mahmoud El-Rashidy, Sarah Farrag, Abdelkareem Gaballah, Mohamed Abd Elaziz, Shaker El-Sappagh, Hager Saleh
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 123173. CrossRef - Prediction of pine mistletoe infection using remote sensing imaging: A comparison of the artificial neural network model and logistic regression model
Ayhan Usta, Murat Yilmaz
Forest Pathology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydrogeochemical characterization of the groundwater of Lahore region using supervised machine learning technique
Sadia Ismail, M. Farooq Ahmed
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - TÜRK SİGORTACILIK SEKTÖRÜNDE UFRS 17’YE GEÇİŞ SÜRECİ VE SİGORTA ŞİRKETLERİNE OLASI ETKİLERİ
Gülcan ÇAĞIL, Cüneyt TUNÇ
Finansal Araştırmalar ve Çalışmalar Dergisi.2022; : 55. CrossRef - The effect of residential house rent on Urban households poverty status in Ethiopia: evidence from Wolkite town
Endalkachew Kabtamu Mekonen
Cogent Economics & Finance.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Local perception of watershed degradation in the upper Gibe basin, southwest Ethiopia: implications to sustainable watershed management strategies
Fekadu Mengistu, Engdawork Assefa
International Journal of River Basin Management.2022; 20(2): 235. CrossRef - Pliable lasso for the multinomial logistic regression
Theophilus Quachie Asenso, Hai Zhang, Yong Liang
Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods.2022; 51(11): 3596. CrossRef - Consumer choice for purchasing imported apparel goods and its effect on perceived saving in Debre Markos district, Amhara Ethiopia: A logistic regression analysis
Fasika Chekol, Yigardush Alimaw, Nitsuh Mengist, Ashebir Tsegaye
Cogent Social Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparison of neural and non-neural machine learning models for food safety risk prediction with European Union RASFF data
Alberto Nogales, Rodrigo Díaz-Morón, Álvaro J. García-Tejedor
Food Control.2022; 134: 108697. CrossRef - Assessing Landslide Susceptibility by Coupling Spatial Data Analysis and Logistic Model
Antonio Ganga, Mario Elia, Ersilia D’Ambrosio, Simona Tripaldi, Gian Franco Capra, Francesco Gentile, Giovanni Sanesi
Sustainability.2022; 14(14): 8426. CrossRef - The Impact of Coping Strategies and Individual Resilience on Anxiety and Depression among Construction Supervisors
Janet M. Nwaogu, Albert P. C. Chan
Buildings.2022; 12(12): 2148. CrossRef - Differences in levels of E. coli contamination of point of use drinking water in Bangladesh
Md. Masud Hasan, Zahirul Hoque, Enamul Kabir, Shahadut Hossain, Mentore Vaccari
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0267386. CrossRef - Analysis of the tendency of transition between segments of green consumer behavior with a Markov chain approach
Aries Susanty, Pradita Yusi Akshinta, M. Mujiya Ulkhaq, Nia Budi Puspitasari
Journal of Modelling in Management.2022; 17(4): 1177. CrossRef - DravidianCodeMix: sentiment analysis and offensive language identification dataset for Dravidian languages in code-mixed text
Bharathi Raja Chakravarthi, Ruba Priyadharshini, Vigneshwaran Muralidaran, Navya Jose, Shardul Suryawanshi, Elizabeth Sherly, John P. McCrae
Language Resources and Evaluation.2022; 56(3): 765. CrossRef - Staff resilience and coping behavior as protective factors for mental health among construction tradesmen
Janet Mayowa Nwaogu, Albert P.C. Chan, Mershack Opoku Tetteh
Journal of Engineering, Design and Technology .2022; 20(3): 671. CrossRef - Investigating Which Services are Effective on Recommendation of the Airline Companies
Seden DOĞAN, Emrah ÖZKUL, Gamze KAYA
Advances in Hospitality and Tourism Research (AHTR).2022; 10(1): 109. CrossRef - Nature, patterns, and determinants of seasonal outmigration in the north-eastern part of Ethiopia
Girma Senbetie Asefawu, Kumela Gudeta Nedessa
Norsk Geografisk Tidsskrift - Norwegian Journal of Geography.2022; 76(3): 177. CrossRef - Civil servants’ integrity in public sector: the case of Nepal
Rajan Khanal, Anil Kumar Gupta, Prakash C. Bhattarai
Heliyon.2022; 8(12): e12632. CrossRef - Development of a prediction models for chemotherapy-induced adverse drug reactions: A retrospective observational study using electronic health records
Jeongah On, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Sooyoung Yoo
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 56: 102066. CrossRef - Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) Model for Predicting Teratogenic Risk of Antiseizure Medications in Pregnancy by Using Support Vector Machine
Liyuan Kang, Yifei Duan, Cheng Chen, Shihai Li, Menglong Li, Lei Chen, Zhining Wen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferences for service bundles in the energy sector – a survey of German private households
André Hackbarth, Timo Tremml, Sabine Löbbe
International Journal of Energy Sector Management.2022; 16(6): 1214. CrossRef - Classification of imbalanced medical data: An empirical study of machine learning approaches
Shikha Mundra, Shounak Vijay, Ankit Mundra, Punit Gupta, Mayank Kumar Goyal, Mandeep Kaur, Supriya Khaitan, Abha Kiran Rajpoot, Valentina Emilia Balas
Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems.2022; 43(2): 1933. CrossRef - Development and validation of a predictive scoring system for in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 Egyptian patients: a retrospective study
Mohamed AbdelSalam Elgohary, Asmaa Ali, Thanaa A. El-Masry, Hani Faidah, Farkad Bantun, Ahmad M. Elkholy, Jaklin S. Fahim, Nabila N. Elgamal, Mohamed Emam Mohamed, Mohamed G. Seadawy, Amro M. Helal, Michel De Waard, Hesham M. Shishtawy, Maisra M. El-Bouse
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intelligent modeling of unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of hybrid cement-modified unsaturated soil with nanostructured quarry fines inclusion
Kennedy C. Onyelowe, Fazal E. Jalal, Mudassir Iqbal, Zia Ur Rehman, Kizito Ibe
Innovative Infrastructure Solutions.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Neutron/gamma pulse shape discrimination using short-time frequency transform
Assem Abdelhakim, Ehab Elshazly
Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing.2022; 111(3): 387. CrossRef - Paradox of Success-Mediated Conflicts: Analysing Attitudes of Local Communities Towards Successfully Reintroduced Tigers in India
Manjari Malviya, Sankar Kalyanasundaram, Ramesh Krishnamurthy
Frontiers in Conservation Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Simulation of Acute Pulmonary Hypertension in Beagle Dogs
Miao Wang, YaTing Hu, BinBin Guo, Hong Tang
International Heart Journal.2022; 63(3): 612. CrossRef - An Analytical Predictive Models and Secure Web-Based Personalized Diabetes Monitoring System
Radwa Marzouk, Ala Saleh Alluhaidan, Sahar A. El Rahman
IEEE Access.2022; 10: 105657. CrossRef - Practical Machine Learning Model to Predict the Recovery of Motor Function in Patients with Stroke
Jeoung Kun Kim, Zhihan Lv, Donghwi Park, Min Cheol Chang
European Neurology.2022; 85(4): 273. CrossRef - Analyzing Various Factors Affecting Farmers’ Willingness to Adopt Soil Erosion Control Measures in the Sebeya Catchment, Rwanda
Félicien Majoro, Umaru Garba Wali
Sustainability.2022; 14(19): 12895. CrossRef - Risk Factors Associated with Tuberculosis Among Men; A Study of South Africa
Muziwandile Nhlakanipho Mlondo, Sileshi Fanta Melesse, Henry G Mwambi
The Open Public Health Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence methods for improving the inventive design process, application in lattice structure case study
Masih Hanifi, Hicham Chibane, Remy Houssin, Denis Cavallucci, Naser Ghannad
Artificial Intelligence for Engineering Design, Analysis and Manufacturing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - TheImpacts of Apple-based Agroforestry Practices on the Livelihoods of Smallholder Farmers in Southern Ethiopia
Tesfaye Gebeyehu Admasu, Amene Afework Jenberu
Trees, Forests and People.2022; 7: 100205. CrossRef - Relation of Dietary n-3 and n-6 Fatty Acid Intakes to Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged People Depending on the Level of HbA1c: A Review of National Health and Nutrition Survey Data from 2014 to 2016
Seo-Woo Park, Do-Yeong Kim, Gyeong-Tae Bak, Dae-Sung Hyun, Sung-Kyung Kim
Medicina.2022; 58(8): 1017. CrossRef - Prevalence and factors associated with pre‐frailty and frailty among Korean older adults with heart failure
Youn‐Jung Son, Sang‐Wook Kim, Wang‐Soo Lee, Seung Yong Shin, Hoyoun Won, Jun Hwan Cho, Hyue Mee Kim, Joonhwa Hong, JiYeon Choi
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(10): 3235. CrossRef - An Ensemble Heart Disease Prediction Model Bagged with Logistic Regression, Naïve Bayes and K Nearest Neighbour.
Annwesha Banerjee Majumder, Somsubhra Gupta, Dharmpal Singh
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2022; 2286(1): 012017. CrossRef - Motives for the introduction of agricultural innovations in Serbia with particular accent on beekeepers: The application of logistic regression
Lidija Madžar
Ekonomika poljoprivrede.2022; 69(1): 27. CrossRef - Predicting Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Using Machine Learning
Seonwoo Jung, Min-Keun Song, Eunjoo Lee, Sejin Bae, Yeon-Yong Kim, Doheon Lee, Myoung Jin Lee, Sunyong Yoo
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (QSAR) Model for the Severity Prediction of Drug-Induced Rhabdomyolysis by Using Random Forest
Yifan Zhou, Shihai Li, Yiru Zhao, Mingkun Guo, Yuan Liu, Menglong Li, Zhining Wen
Chemical Research in Toxicology.2021; 34(2): 514. CrossRef - Knowledge extraction from pointer movements and its application to detect uncertainty
Catia Cepeda, Maria Camila Dias, Dina Rindlisbacher, Hugo Gamboa, Marcus Cheetham
Heliyon.2021; 7(1): e05873. CrossRef - Predicting the Utilization of Mental Health Treatment with Various Machine Learning Algorithms
Meera Sharma, Sonok Mahapatra, Adeethyia Shankar, Xiaodi Wang
WSEAS TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTERS.2021; 19: 285. CrossRef - Talking about Sustainability: How the Media Construct the Public’s Understanding of Sustainable Food in Romania
Valentina Marinescu, Bianca Fox, Darie Cristea, Daniela Roventa-Frumusani, Ramona Marinache, Silvia Branea
Sustainability.2021; 13(9): 4609. CrossRef - TÜRK SİGORTACILIK SEKTÖRÜNDE UFRS 17’YE GEÇİŞ SÜRECİ VE SİGORTA ŞİRKETLERİNE OLASI ETKİLERİ
Cüneyt TUNÇ
Finansal Araştırmalar ve Çalışmalar Dergisi.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Unmet Healthcare Needs in Ireland: A Data Mining Approach
Dr. Anatoli Nachev
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology.2021; 10(3): 81. CrossRef - Performance analysis of Word Embeddings for Cyberbullying Detection
Subbaraju Pericherla, E Ilavarasan
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2021; 1085(1): 012008. CrossRef - The usage of logistic regression and artificial neural networks for evaluation and predicting property-liability insurers' solvency in Egypt
Eid Elghaly Hassan, Diping Zhang
Data Science in Finance and Economics.2021; 1(3): 215. CrossRef - Predicting the Safety Climate in Construction Sites of Saudi Arabia: A Bootstrapped Multiple Ordinal Logistic Regression Modeling Approach
Anas A. Makki, Ibrahim Mosly
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(4): 1474. CrossRef - Community participation in watershed management: analysis of the status and factors affecting community engagement in the upper Gibe basin, South West Ethiopia
Fekadu Mengistu, Engdawork Assefa
Journal of Environmental Planning and Management.2021; 64(2): 252. CrossRef - AGRICULTURAL INNOVATIONS, EXTENSION, FINANCE AND RURAL LOANS IN THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA:
THE CASE OF LOGISTIC REGRESSION
Lidija Madžar
Annals of the Polish Association of Agricultural and Agribusiness Economists.2021; XXIII(4): 129. CrossRef - An Approach Using Fuzzy Sets and Boosting Techniques to Predict Liver Disease
Pushpendra Kumar, Ramjeevan Singh Thakur
Computers, Materials & Continua.2021; 68(3): 3513. CrossRef - Does engagement with frontline health workers improve maternal and child healthcare utilisation and outcomes in India?
Anu Rammohan, Srinivas Goli, Shashi Kala Saroj, C. P. Abdul Jaleel
Human Resources for Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing risk factors associated with urban transit bus involved accident severity: a case study of a Middle East country
Mehrdad Nasri, Kayvan Aghabayk
International Journal of Crashworthiness.2021; 26(4): 413. CrossRef - Detecting Information on the Spread of Dengue on Twitter Using Artificial Neural Networks
Samina Amin, M. Irfan Uddin, M. Ali Zeb, Ala Abdulsalam Alarood, Marwan Mahmoud, Monagi H. Alkinani
Computers, Materials & Continua.2021; 67(1): 1317. CrossRef - Automatic Evaluation of Heart Condition According to the Sounds Emitted and Implementing Six Classification Methods
Manuel A. Soto-Murillo, Jorge I. Galván-Tejada, Carlos E. Galván-Tejada, Jose M. Celaya-Padilla, Huizilopoztli Luna-García, Rafael Magallanes-Quintanar, Tania A. Gutiérrez-García, Hamurabi Gamboa-Rosales
Healthcare.2021; 9(3): 317. CrossRef - Visual light perceptions caused by medical linear accelerator: Findings of machine-learning algorithms in a prospective questionnaire-based case–control study
Chao-Yang Kuo, Cheng-Chun Lee, Yuh-Lin Lee, Shueh-Chun Liou, Jia-Cheng Lee, Emily Chia-Yu Su, Yi-Wei Chen, Rongxiao Zhang
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0247597. CrossRef - Health-seeking behavior and waste management practices among women in major urban markets in Owerri, Nigeria
Cyprian Ezedike, Eudora Ohazurike, Faisal C Emetumah, Okechukwu O Ajaegbu
AIMS Public Health.2020; 7(1): 169. CrossRef - A cross-sectional study to determine factors affecting dental and medical students’ preference for virtual learning during the COVID-19 outbreak
Nosayba Al-Azzam, Lina Elsalem, Farai Gombedza
Heliyon.2020; 6(12): e05704. CrossRef - Machine Learning Algorithms in Cardiology Domain: A Systematic Review
Aleksei Dudchenko, Matthias Ganzinger, Georgy Kopanitsa
The Open Bioinformatics Journal.2020; 13(1): 25. CrossRef - Effect of Succession Planning on Leadership Elevation
Ammad Zafar, Ghazal Khawaja Hummayun Akhtar
Pakistan Journal of Applied Social Sciences.2020; 11(2): 21. CrossRef - Postpartum depression and its correlates in middle‐class women in Hunan, China
Ziyao Guan, Wenhui Bai, Chunxiang Qin, Mei Sun, Xiaoling Bai, Siyuan Tang
Asian Social Work and Policy Review.2020; 14(2): 107. CrossRef - A Regression Model for Predicting the Likelihood of Reporting a Crime Based on the Victim’s Demographic Variables and Their Perceptions Towards the Police
Malebogo Pulenyane, Tlhalitshi Volition Montshiwa
Statistics, Politics and Policy.2020; 11(2): 167. CrossRef - Gender differences in the relationships between sleep disturbances and academic performance among nursing students: A cross-sectional study
Ollyvia Freeska Dwi Marta, Shu-Yu Kuo, Jacqueline Bloomfield, Hsin-Chien Lee, Faqih Ruhyanudin, Mia Yuangi Poynor, Ageng Brahmadhi, Indah Dwi Pratiwi, Nur Aini, Erma Wahyu Mashfufa, Faizul Hasan, Hsiao-Yean Chiu
Nurse Education Today.2020; 85: 104270. CrossRef - Prediction of physical violence in schizophrenia with machine learning algorithms
Kevin Z. Wang, Ali Bani-Fatemi, Christopher Adanty, Ricardo Harripaul, John Griffiths, Nathan Kolla, Philip Gerretsen, Ariel Graff, Vincenzo De Luca
Psychiatry Research.2020; 289: 112960. CrossRef - Assessment of a Deep Learning Algorithm for the Detection of Rib Fractures on Whole-Body Trauma Computed Tomography
Thomas Weikert, Luca Andre Noordtzij, Jens Bremerich, Bram Stieltjes, Victor Parmar, Joshy Cyriac, Gregor Sommer, Alexander Walter Sauter
Korean Journal of Radiology.2020; 21(7): 891. CrossRef - Application of logistic regression analysis in prediction of groundwater vulnerability in gold mining environment: a case of Ilesa gold mining area, southwestern, Nigeria
K. A. N. Adiat, B. E. Akeredolu, A. A. Akinlalu, G. M. Olayanju
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Eco-Kansei design for retailing packaging: a current research progress
A Aprilia, T Djatna, N S Indrasti, Sugiarto
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2020; 472(1): 012046. CrossRef - Knowledge mining on the association between psychological capital and educational qualifications among hospitality employees
Donald Douglas Atsa’am, Ersin Kuset Bodur
Current Issues in Tourism.2020; 23(9): 1073. CrossRef - Predicting Dysfunctional Human–Dog Dyads
Rute Canejo-Teixeira, Pedro Armelim Almiro, Luís V. Baptista, Maria Manuela Grave Rodeia Espada Niza
Anthrozoös.2020; 33(6): 743. CrossRef - Entrepreneurship factor’s affecting the youth decision to continue their family farm
S F Ayu, M Nauly
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2020; 1542(1): 012052. CrossRef - Farmers’ Attitudes Towards the Use of Biomass as Renewable Energy—A Case Study from Southeastern Europe
Prespa Ymeri, Csaba Gyuricza, Csaba Fogarassy
Sustainability.2020; 12(10): 4009. CrossRef - AI Approaches towards Prechtl’s Assessment of General Movements: A Systematic Literature Review
Muhammad Tausif Irshad, Muhammad Adeel Nisar, Philip Gouverneur, Marion Rapp, Marcin Grzegorzek
Sensors.2020; 20(18): 5321. CrossRef - Logistic Regression and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator
Hyunyong Lee, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2020; 2(4): 142. CrossRef - A modular framework for estimating annual averaged power output generation of wind turbines
Benjamin Wacker, Johann V. Seebaß, Jan Chr. Schlüter
Energy Conversion and Management.2020; 221: 113149. CrossRef - Interest to continue farming among agricultural students who is a child of a farmer
S F Ayu, M Nauly
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2020; 454(1): 012027. CrossRef - Assessment of Teachers’ Knowledge about Tuberculosis at Primary School in Balad City
Wafaa S. Hasanain
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2020; 1591(1): 012001. CrossRef - A Comparative Assessment of Credit Risk Model Based on Machine Learning ——a case study of bank loan data
Yuelin Wang, Yihan Zhang, Yan Lu, Xinran Yu
Procedia Computer Science.2020; 174: 141. CrossRef - Machine Learning Algorithms in Cardiology Domain: A Systematic Review (Preprint)
Georgy Kopanitsa, Aleksei Dudchenko, Matthias Ganzinger
JMIR Medical Informatics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of child labour practices in Ghana
Lucy Twumwaah Afriyie, Bashiru I. I. Saeed, Abukari Alhassan
Journal of Public Health.2019; 27(2): 211. CrossRef - Mapping fecal pollution in rural groundwater supplies by means of artificial intelligence classifiers
S. Díaz-Alcaide, P. Martínez-Santos
Journal of Hydrology.2019; 577: 124006. CrossRef - A Hybrid Computational Intelligence Approach to Groundwater Spring Potential Mapping
Dieu Tien Bui, Ataollah Shirzadi, Kamran Chapi, Himan Shahabi, Biswajeet Pradhan, Binh Pham, Vijay Singh, Wei Chen, Khabat Khosravi, Baharin Bin Ahmad, Saro Lee
Water.2019; 11(10): 2013. CrossRef - Determinants of environmental conservation in Lake Tana Biosphere Reserve, Ethiopia
Zemenu Bires, Sahil Raj
Heliyon.2019; 5(7): e01997. CrossRef - Drivers of Cooperation Activity in Kosovo’s Agriculture
Shyhrete Muriqi, Maria Fekete-Farkas, Zsolt Baranyai
Agriculture.2019; 9(5): 96. CrossRef - Determinants of paying national health insurance premium with mobile phone in Ghana: a cross-sectional prospective study
Joseph Marfo Boaheng, Eugenia Amporfu, Daniel Ansong, Anthony Kofi Osei-Fosu
International Journal for Equity in Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Determining Factors Affecting Consumer’s Decision to Purchase Organic Chicken Meat
F Kaygisiz, BA Bolat, D Bulut
Brazilian Journal of Poultry Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Performance and cost-effectiveness of change burst metrics in predicting software faults
Malanga Kennedy Ndenga, Ivaylo Ganchev, Jean Mehat, Franklin Wabwoba, Herman Akdag
Knowledge and Information Systems.2019; 60(1): 275. CrossRef - Detection of Timestamps Tampering in NTFS using Machine Learning
Alji Mohamed, Chougdali Khalid
Procedia Computer Science.2019; 160: 778. CrossRef - Responding to the greatest challenges? Value creation in ecological startups
Andreas Kuckertz, Elisabeth S.C. Berger, Anja Gaudig
Journal of Cleaner Production.2019; 230: 1138. CrossRef - Sewer Pipes Condition Prediction Models: A State-of-the-Art Review
Mohammadreza Malek Mohammadi, Mohammad Najafi, Vinayak Kaushal, Ramtin Serajiantehrani, Nazanin Salehabadi, Taha Ashoori
Infrastructures.2019; 4(4): 64. CrossRef - TLUSBoost algorithm: a boosting solution for class imbalance problem
Sujit Kumar, Saroj Kr. Biswas, Debashree Devi
Soft Computing.2019; 23(21): 10755. CrossRef - Analysis between GPA and TOEFL Score For Postgraduate Student of Sports Education using Bivariate Logistic Regression
A Sofro, A Oktaviarina, E Mintarto, O Wiriawan
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2019; 1417(1): 012022. CrossRef - Suicidal ideation in systemic lupus erythematosus: NR2A gene polymorphism, clinical and psychosocial factors
R I Buji, N A Abdul Murad, L F Chan, T Maniam, M S Mohd Shahrir, M Rozita, A S Shamsul, R Mohamad Hussain, N Abdullah, R Jamal, N R Nik Jaafar
Lupus.2018; 27(5): 744. CrossRef - The use of geographic information system and 1860s cadastral data to model agricultural suitability before heavy mechanization. A case study from Malta
Gianmarco Alberti, Reuben Grima, Nicholas C. Vella, Hugo Rebelo
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(2): e0192039. CrossRef - Drivers of eco-innovation in the manufacturing sector of Nigeria
Maruf Sanni
Technological Forecasting and Social Change.2018; 131: 303. CrossRef - Spatial filtering pipeline evaluation of cortically coupled computer vision system for rapid serial visual presentation
Zhengwei Wang, Graham Healy, Alan F. Smeaton, Tomas E. Ward
Brain-Computer Interfaces.2018; 5(4): 132. CrossRef - Logistic Regression and Growth Charts to Determine Children Nutritional and Stunting Status: A Review
Margaretha Ohyver, Jurike V. Moniaga, Karina Restisa Yunidwi, Muhamad Irfan Setiawan
Procedia Computer Science.2017; 116: 232. CrossRef - Predictors of Unintentionally Severe Harm During Nonsuicidal Self‐Injury
Trevor J. Buser, Juleen K. Buser, Corrine C. Rutt
Journal of Counseling & Development.2017; 95(1): 14. CrossRef - Women’s opinion on the justification of physical spousal violence: A quantitative approach to model the most vulnerable households in Bangladesh
Raaj Kishore Biswas, Nusma Rahman, Enamul Kabir, Farabi Raihan, Fakir M Amirul Islam
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(11): e0187884. CrossRef - Well-testing model identification using time-series shapelets
Rouhollah Ahmadi, Babak Aminshahidy, Jamal Shahrabi
Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering.2017; 149: 292. CrossRef - Proposing stochastic probability-based math model and algorithms utilizing social networking and academic data for good fit students prediction
Muhammad Fahim Uddin, Jeongkyu Lee
Social Network Analysis and Mining.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Infrared assessment of knee instability in ACL deficient patients
Aleksandar Matić, Suzana Petrović Savić, Branko Ristić, Vladan B. Stevanović, Goran Devedžić
International Orthopaedics.2016; 40(2): 385. CrossRef - Binary Logistic Model for Estimation of Mode Shift into Delhi Metro
Vineet Chauhan, Hemant K. Suman, Nomesh B. Bolia
The Open Transportation Journal.2016; 10(1): 124. CrossRef - Analysis of the Factors Influencing the Use of Public Buses in Delhi
Hemant K. Suman, Nomesh B. Bolia, Geetam Tiwari
Journal of Urban Planning and Development.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Are predictors of future suicide attempts and the transition from suicidal ideation to suicide attempts shared or distinct: A 12-month prospective study among patients with depressive disorders
Lai Fong Chan, Azhar Shah Shamsul, Thambu Maniam
Psychiatry Research.2014; 220(3): 867. CrossRef
- Examining the effect of farm and farmers' characteristics and input allocation on potato production
- 12,111 View
- 218 Download
- 189 Crossref

- Effects on Salivation, Xerostomia and Halitosis in Elders after Oral Function Improvement Exercises
- Young Jin Kim, Kyung Min Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(6):898-906. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.6.898
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of Oral Function Improvement Exercises on salivation, xerostomia and halitosis in elderly people.
Methods The participants in the study were 48 female community-dwelling elders in D city. The Oral Function Improvement Exercises were given 3 times a week, for a total of 24 times from August to October 2011. Spitting method, Visual Analogue Scale, and halimeter (mBA-21) were used to evaluate the effects of Oral Function Improvement Exercises on salivation, xerostomia, and halitosis. The data were analyzed using χ2-test and t-test with the SPSS program.
Results The experimental group had significantly better salivation, and less xerostomia and halitosis than the control group.
Conclusion The results indicate that Oral Function Improvement Exercises were effective for salivation, xerostomia and halitosis in the elders. Therefore, it was suggested that Oral Function Improvement Exercise are applicable in a community nursing intervention program to improve the quality of life for elders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of halitosis according to herbal mouthwash containing Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract and saline mouthwash: A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study
Yu‐Rin Kim, Seoul‐Hee Nam
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2024; 22(3): 614. CrossRef - A Literature Review on the Causes and Treatments of Halitosis Related to Dental Prosthetics
Ji Su Jo, Jung Eun Lee, Su Young Lee
Korean Journal of Clinical Geriatrics.2023; 24(1): 17. CrossRef - A qualitative research on the needs for oral care according to the subjective oral health status of the elderly
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in concentration of VSCs after home oral care interventions based on community care in older adults
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Oral Care Interventions on Oral Health and Oral Health-related Quality of Life among Denture-wearing Older Adults
Chanhee Lim, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(1): 76. CrossRef - Effect of Oral Health Education Using a Mobile App (OHEMA) on the Oral Health and Swallowing-Related Quality of Life in Community-Based Integrated Care of the Elderly: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Ji-Yun Ki, Se-Rim Jo, Kyung-Sook Cho, Jung-Eun Park, Ja-Won Cho, Jong-Hwa Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11679. CrossRef - The Actual Status of Elderly Orofacial-Function Improvement Program in Seoul and Gyenggi-Area
Do-Seon Lim, Ju-hee Kim, So-yeon Lee, Im-Hee Jung
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(4): 267. CrossRef - Effectiveness of oral exercise on oral function among the elderly
BThanga Raj, B Sreelekha, A Manjula
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(4): 1896. CrossRef - Effects of oral health programmes on xerostomia in community‐dwelling elderly: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Kyoungsan Seo, Han‐Na Kim
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2020; 18(1): 52. CrossRef - Relationship among Oral Hygiene Management, Halitosis, Interpersonal Relationships and Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Elderly
Young Ran Chae, So Yean Kang, Eun Sook Nam, Hye Jin Hyun, Su Youn Park, Sun Hee Lee, Ju Young Lee, Doo Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(4): 229. CrossRef - Comparison of Extract Components and Saliva Secretion of Ixeridium dentatum and Pueraria lobata Ohwi
Na-Hee Jung, Jin-Hee Chang, Joo-Yeon Hong, Dong-Keon Kweon, Jung-Ah Han
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(4): 358. CrossRef - Effects of an Oral Self-care Program on the Elderly's Xerostomia and Oral Health-related Quality of Life
Ji Hyun Kim, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 382. CrossRef - Correlations between Xerostomia, Oral Health Quality of Life and Knowledge about Water Intake among Community-dwelling Older Adults
Hye Young Joung, Sang Bok Lee
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(2): 164. CrossRef - The effect of oral function improvement with oral exercise program by elderly people
Young-Soon Kim, Kyoung-hee Shin, Jeong-Ran Park, Soon-hee Chung, Hye Sook Choi
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2016; 16(4): 559. CrossRef - The Effect of Subjective Xerostomia and Salivary pH in Salivary Glands Stimulated by Laughter Therapy in Frail Elderly Women
Sun Young Lim, Kyem Ju Lee, Su Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(1): 72. CrossRef - Comparison of Effects according to Type of Oral Exercise Program for Elderly in Gangneung City
Sue-Hyang Lee, Jean-A Ryu, Ha-Eun Yu, Jin-Hee Lee, Sun-Jung Shin
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2016; 16(6): 424. CrossRef - A comparative study of the effects of intra and extra circumoral exercise for older people on oral health at nursing homes: a non‐equivalent trial
Mijung Nam, Dongchoon Uhm
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2016; 72(9): 2114. CrossRef - Change of salivary flow rate, xerostomia, and oral health-related quality of life after oral muscle massage
Eun-Ju Kim, Jung-Suk Kwag
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2015; 15(4): 679. CrossRef - Development of Mouthwash Products with Solid Fermented Oriental Medicinal Herb
Byung-Je Cho, Jun Young Hong, Mijeong Kim, Yeong Ok Song
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2014; 43(9): 1380. CrossRef
- Comparison of halitosis according to herbal mouthwash containing Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract and saline mouthwash: A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study
- 1,427 View
- 18 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Effectiveness of PLISSIT Model Sexual Program on Female Sexual Function for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
- Nami Chun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(4):471-480. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.471
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the Permission, Limited Information, Specific Suggestions, Intensive Therapy (PLISSIT) model sexual program on female sexual function for women with gynecologic cancer.
Methods The integrative 6-hr (two hours per session) program reflecting physical and psychosocial aspects of women's sexuality was developed based on Annon's PLISSIT model. Participants were 61 women with cervical, ovarian, or endometrial cancer. Of them, 29 were assigned to the experimental group and 32 to the control group. The women completed the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) including sexual desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain. Independent t-test and repeated measured ANOVA were used to test the effectiveness of the program.
Results Significant group differences were found on FSFI sub-domain scores including sexual desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, and satisfaction but not pain. Significant time differences were found on all domains except for pain in the experimental group repeated measured ANOVA.
Conclusion The results indicate that the three-week PLISSIT model sexual program is effective in increasing sexual function for women with gynecologic cancer. Nurses may contribute to improving women's sexual function by utilizing the program. Strategies to relieve sexual pain need to be considered for greater effectiveness of the program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- “Maybe if this was addressed sooner, maybe things might be different in our relationship. I don’t know. But who knows?” Sexuality after TBI and its place in healthcare: A qualitative exploration of survivors’ experiences
Jill H. A. Hwang, Marina Downing, Jennie L. Ponsford
Neuropsychological Rehabilitation.2025; 35(5): 960. CrossRef - The Effect of Sexual Education Program on Sexual Function and Genital Self-image, Sexual Quality of Life among Primiparous Women
Athar Rasekh Jahromi, Hanie Jafari, Parvin Adedi, Mojgan Javadnoori, Solmaz Mohammadi, Vahid Rahmanian, Safieh Jamali
Current Womens Health Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a sexual health enhancement program for women with breast cancer: A quasi-experimental study
Hye Sook Kim, Chaewon Yun
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 76: 102852. CrossRef - Effect of PLISSIT model counseling on the sexual quality of life of infertile women: a randomized controlled trial
Reyhane Amini, Mahboube Taebi, Hatav Ghasemi Tehrani
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility and effectiveness of communication tools for addressing intimacy and sexuality in patients with cancer: a systematic review
Susanne A. M. Arends, Carlijn E. van Rossum, Corien M. Eeltink, Jantien E. Robertus, Linda J. Schoonmade, Anneke L. Francke, Irene P. Jongerden
Supportive Care in Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Educational programs and counseling models for improving postpartum sexual health: a narrative review
Tayebeh Darooneh, Giti Ozgoli, Zohreh Keshavarz, Malihe Nasiri
Sexual and Relationship Therapy.2024; 39(3): 1044. CrossRef - The Effect of Post-Operative Sexual Counseling Carried out with PLISSIT Model on Sexual Function and Sexual Satisfaction in Gynecologic Cancers
Çiğdem BİLGE, Ergül ASLAN
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2023; 13(3): 623. CrossRef - The effect of a psycho-educational intervention on sexuality of women with acute coronary syndromes: a randomized controlled trial
Fatemeh Soleimaninejad, Razieh Lotfi, Mehdi Mousavi, Majid Taghizadeh, Kourosh Kabir
Sexual and Relationship Therapy.2023; 38(2): 277. CrossRef - The Effect of BETTER-Based Sex Counseling on Sexual Quality of Life in Infertile Women: a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Farzaneh Dastaran, Raziyeh Maasoumi, Fatemeh Foroozanfard, Shima Haghani
Sexuality and Disability.2022; 40(4): 785. CrossRef - Relationships among sexual function, marital intimacy, type D personality and quality of life in patients with ovarian cancer, with spouses
Ju‐Hee Nho, Sung Reul Kim, Won Ku Choi
European Journal of Cancer Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sexual health and function in women with diabetes
Kirsty Winkley, Camilla Kristensen, Jackie Fosbury
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Sexual Health Improvement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Soon Yang Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 163. CrossRef - The effect of PLISSIT based counseling model on sexual function, quality of life, and sexual distress in women surviving breast cancer: a single-group pretest–posttest trial
Zohreh Keshavarz, Elham Karimi, Samira Golezar, Giti Ozgoli, Maliheh Nasiri
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - ´Tratamientos psicológicos para mejorar la vida sexual en mujeres supervivientes de cáncer ginecológico: revisión sistemática.
Karla Maricela Figueroa Espinoza
Psicooncología.2020; 17(2): 293. CrossRef - Sexual Health After Acute Myocardial Infarction: The Lived Experience of Women During the First-Year Post Discharge
Silvio Simeone, Assunta Guillari, Gianluca Pucciarelli, Filomena Stile, Gianpaolo Gargiulo, Mauro Esposito, Rosaria Alvaro, Teresa Rea
Sexuality and Disability.2020; 38(3): 547. CrossRef - Effects of Education About Rheumatoid Arthritis and Sexuality on the Sexual Problems of Women With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Tülay Kars Fertelli
Clinical Nursing Research.2020; 29(3): 189. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sexual counseling using PLISSIT model on sexual function of women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from a randomized controlled trial
Maryam Mehrabi, Razieh Lotfi, Mitra Rahimzadeh, Effat Merghati Khoei
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2019; 39(4): 626. CrossRef - The Effect of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Sexual Function in Infertile Women: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Maryam Sahraeian, Razieh Lotfi, Mostafa Qorbani, Mahbobeh Faramarzi, Fatemeh Dinpajooh, Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani
Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy.2019; 45(7): 574. CrossRef - PLISSIT Interventions and Sexual Functioning: Useful Tools for Social Work in Palliative Care?
Michael R. Bennett
Journal of Social Work in End-of-Life & Palliative Care.2019; 15(4): 157. CrossRef - Influence of Urinary Dysfunction on Quality of Life in Women with Cervical Cancer after Radical Hysterectomy
Nami Chun, Gie-Ok Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 150. CrossRef - The Influence of Ex-PLISSIT (Extended Permission, Limited Information, Specific Suggestions, Intensive Therapy) Model on Intimacy and Sexuality of Married Women with Multiple Sclerosis
Fatemeh Daneshfar, Zahra Behboodi-Moghadam, Zohreh Khakbazan, Seyed Massood Nabavi, Nahid Dehghan Nayeri, Sogand Ghasemzadeh, Ali Montazeri
Sexuality and Disability.2017; 35(4): 399. CrossRef - Comments on female sexual dysfunction with cervical cancer in Republic of Korea
Gyeong-Eun Heo, Tae-Hee Kim, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Jun-Mo Kim
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2016; 294(1): 209. CrossRef - Reply to letter to the editor by J.-M. Kim et al. on "Sexual function and quality of life in women with cervical cancer before radiotherapy: a pilot study" by Grion et al.
R. C. Grion, Luiz Francisco Baccaro, A. F. Vaz, L. Costa-Paiva, D. M. Conde, A. M. Pinto-Neto
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2016; 294(1): 211. CrossRef - The effectiveness of the Permission, Limited Information, Specific suggestions, Intensive Therapy (PLISSIT) model based sexual counseling on the sexual function of women with Multiple Sclerosis who are sexually active
Zohreh Khakbazan, Fatemeh. Daneshfar, Zahra Behboodi-Moghadam, Seyed Massood Nabavi, Sogand Ghasemzadeh, Abbas Mehran
Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders.2016; 8: 113. CrossRef - Sexual Health Care Attitudes and Practices of Nurses Caring for Patients with Cancer
Young Hee Chae, Young Ok Song, Soon Tae Oh, Won Hee Lee, Young Mi Min, Hyang Mi Kim, Seung A Lee, Young Sin Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(1): 28. CrossRef - The Effect of Face-to-Face With Telephone-Based Counseling on Sexual Satisfaction Among Reproductive Aged Women in Iran
Shirin Zargar Shoushtari, Poorandokht Afshari, Parvin Abedi, Hamed Tabesh
Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy.2015; 41(4): 361. CrossRef - Compare the Effectiveness of PLISSIT and Sexual Health Models on Women's Sexual Problems in Tehran, Iran: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Farnaz Farnam, Mohsen Janghorbani, Firoozeh Raisi, Effat Merghati-Khoei
The Journal of Sexual Medicine.2014; 11(11): 2679. CrossRef - Discussing Sexuality with Cancer Patients: Oncology Nurses Attitudes and Views
Umran Oskay, Gulbeyaz Can, Sukran Basgol
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2014; 15(17): 7321. CrossRef - Effect of PLISSIT Model Sexual Health Enhancement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer and Their Husbands
Ju-Hee Nho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 681. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of the Psychosocial Distress Nursing Intervention for Patients with Gynecological Cancer
Jeong-Sook Park, Yun-Jung Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(3): 219. CrossRef
- “Maybe if this was addressed sooner, maybe things might be different in our relationship. I don’t know. But who knows?” Sexuality after TBI and its place in healthcare: A qualitative exploration of survivors’ experiences
- 2,210 View
- 26 Download
- 30 Crossref

- Predictors of Sexual Desire, Arousal, Lubrication, Orgasm, Satisfaction, and Pain in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
- Nami Chun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(1):24-32. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to identify psychosocial factors that might be predictive of sexual desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain in women with gynecologic cancer.
Methods Two hundred and twelve women with cervical, ovarian, or endometrial cancer completed questionnaires on the Female Sexual Function Index including sexual desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain, and data on their psychosocial factors including body image, sexual attitude, sexual information, depression, and marital intimacy. Stepwise multivariable regression analysis was performed to explore psychosocial predictors of women's sexual function domains.
Results Predictors were identified as sexual attitude, depression, sexual information, and body image for sexual desire; sexual information, depression, and sexual attitude for sexual arousal; sexual information, marital intimacy, and depression for lubrication; sexual information, marital intimacy, depression, and body image for orgasm; marital intimacy, sexual information, sexual attitude, and depression for satisfaction; sexual information, depression, and marital intimacy for pain.
Conclusion The results indicate that women's sexual function needs to be approached to domains of female sexual function psychosocially as well as to general sexual function. These factors should be considered in future interventions to positively promote sexual function in women with gynecologic cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of factors influencing sexual dysfunction and the coping strategies adopted by cancer patients in selected hospitals of the city
Samina Mehaboob Mulani
i-manager’s Journal on Nursing.2022; 12(3): 28. CrossRef - Psychosexual Advantages of Physical Adaptation
Sujita Kumar Kar, Garima Singh
Journal of Psychosexual Health.2022; 4(3): 203. CrossRef - Influence of Urinary Dysfunction on Quality of Life in Women with Cervical Cancer after Radical Hysterectomy
Nami Chun, Gie-Ok Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 150. CrossRef - Sexual function, depression, and quality of life in patients with cervical cancer
Hyewoo Bae, Hyojung Park
Supportive Care in Cancer.2016; 24(3): 1277. CrossRef - Comparison of Distress and Body Image according to the Stages of Cancer Survivorship in Gynecological Cancer Patients
Jeong Sook Park, Hye Ran Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(1): 15. CrossRef - Factors Related to Female Sexual Dysfunction of North Korean Women Defectors
Young Sun Rhee, Hye Wan Ku, In Young Han
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(2): 55. CrossRef - Menopausal symptoms, sexual function, depression, and quality of life in Korean patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy
Hyojung Park, Hyeon Gyeong Yoon
Supportive Care in Cancer.2013; 21(9): 2499. CrossRef - Factors Influencing on Quality of Life in Gynecological Cancer Patients
Jeong-Sook Park, Yun-Jung Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(1): 52. CrossRef - A Study on the Predictive Factors of Sexual Function in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Jeong Sook Park, Soon Yang Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(2): 156. CrossRef - Effectiveness of PLISSIT Model Sexual Program on Female Sexual Function for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Nami Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 471. CrossRef
- Assessment of factors influencing sexual dysfunction and the coping strategies adopted by cancer patients in selected hospitals of the city
- 1,272 View
- 0 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Predictors of Nursing Service Need for Nursing Homes Residents
- Tae Wha Lee, Soon Yung Cho, Yoon Kyung Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(1):95-106. Published online February 28, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.1.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to explore the functional status of elderly residents and to analyze time use, and finally identify factors to predict nursing care needs in relation to functional status and health related variables. Methods: In this study a descriptive-correlational design was used. Functional status of participants was obtained through interviews, and nursing care time was examined using a 1 min time-motion study with a standardized instrument developed by Korea Long-Term Care Planning Committee (2005).
Methods In this study a descriptive-correlational design was used. Functional status of participants was obtained through interviews, and nursing care time was examined using a 1 min time-motion study with a standardized instrument developed by Korea Long-Term Care Planning Committee (2005).
Results The mean total functional score was 65 (range 28-125) and mean total nursing care time was 144.15 min per day. There were significant positive relationships between total nursing care time, marital status, back pain, dementia, and vision impairment. Multiple regression analyses showed that a liner combination of number of illnesses, types of primary disease, ADL, IADL, cognitive function, nursing demand, and rehabilitation demand explained 42.8% of variance of total nursing time. ADL (β=-.533) was the most significant predictor of nursing service need.
Conclusion Identifying factors that result in variations of service need has implications for adequate nursing service, estimation of optimum nurse to patient ratio, quality of care and patient safety.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Constipation among Korean older adults in long-term care facilities: A scoping review
Yuseon Jeong, Dukyoo Jung, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 4. CrossRef - The effect of registered nurses on nursing home residents’ outcomes, controlling for organizational and health care market factors
Juh Hyun Shin, In-Soo Shin
Geriatric Nursing.2019; 40(3): 296. CrossRef - A study on the nursing knowledge, attitude, and performance towards pressure ulcer prevention among nurses in Korea long‐term care facilities
Jung Y. Kim, Yun J. Lee
International Wound Journal.2019; 16(S1): 29. CrossRef - Nursing Homes of the Elderly in Asia: A comparison of Korea and Japan
Myung-Hee Jung
Journal of Industrial Distribution & Business.2018; 9(10): 15. CrossRef - Ego-Integrity Management of Residents in Nursing Homes: A Concept Analysis based on the Method by Walker and Avant
Sun Young Lim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(2): 97. CrossRef - Impact of the nursing home scale on residents’ social engagement in South Korea
Ju Young Yoon, Hongsoo Kim, Young-Il Jung, Jung-Hwa Ha
International Psychogeriatrics.2016; 28(12): 1965. CrossRef - Nursing home adjustment scale: a psychometric study of an English version
Ga Eon Lee, Ju Young Yoon, Barbara J. Bowers
Quality of Life Research.2015; 24(4): 993. CrossRef - The Long-term Care Utilization of the Elderly with Dementia, Stroke, and Multimorbidity in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Soonman Kwon, Hongsoo Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(1): 90. CrossRef - The Comparison of Functional Status and the Level of Health Care Needs in Elderly Koreans in Health Care Institutions
Hyun-Sil Kim, Young-Mi Jung, Hung-Sa Lee, Yoo-Hyang Cho, In-Young Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 386. CrossRef - Health Needs of the Elderly in Long-term Care Facilities: Using RAI-MDS-FC
Eun-Joo Bang, Soon-Young Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 263. CrossRef
- Constipation among Korean older adults in long-term care facilities: A scoping review
- 1,033 View
- 2 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of an Exercise Program on Frontal Lobe Cognitive Function in Elders
- Mee-Kyung Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(1):107-115. Published online February 28, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.1.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of an exercise program on frontal lobe cognitive function in seniors.
Methods The participants were 42 seniors using a health center in Seoul (experimental group) and 28 seniors using a facility for elders in Seoul (control group). The exercise program was carried out for 16 weeks from April to August 2007. The frontal lobe cognitive function, which includes short term memory, attention, immediate memory, delayed memory, verbal fluency and motor function, was measured by the Digit Span Forward test, Trail Making test, Immediate recall words test, Delayed recall words, Controlled oral word association test and Finger tapping test. The collected data were analyzed by Fisher's exact test, Chi-square, t-test, and ANCOVA using the SAS program.
Results The major findings of this study were as follows: Attention (p=.009), immediate memory (p=.005), delayed memory (p=.009), and verbal fluency (p=.004) improved after the exercise program.
Conclusion In this study, the exercise program was effective in improving frontal lobe cognitive function in elders. So it provides basic information for further nursing education on exercise programs which will be effective for prevention of early cognitive function decline in normally aging elders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cognitive decline in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura survivors: The role of white matter health as assessed by MRI
F. Hannan, J. Hamilton, C. J. Patriquin, K. Pavenski, M. T. Jurkiewicz, L. Tristao, A. M. Owen, P. K. Kosalka, S. C. L. Deoni, J. Théberge, J. Mandzia, S. H. S. Huang, J. D. Thiessen
British Journal of Haematology.2024; 204(3): 1005. CrossRef - Effectiveness of an Exercise Program for Older Adults Using an Augmented Reality Exercise Platform: A Pilot Study
Tae Sung Park, Myung-Jun Shin
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2023; 27(1): 73. CrossRef - Influence of collateral circulation on cerebral blood flow and frontal lobe cognitive function in patients with severe internal carotid artery stenosis
Wei Wei, Xingyang Yi, Jianghai Ruan, Xiaodong Duan, Hua Luo, Zhiyu Lv
BMC Neurology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of exercise on the structure of cognitive related brain regions: a meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging data
Guohua Zheng, Bingzhao Ye, Yuhui Zheng, Zhenyu Xiong, Rui Xia, Pingting Qiu, Jing Tao, Lidian Chen
International Journal of Neuroscience.2019; 129(4): 406. CrossRef - The effect of exercise combined with a cognitive-enhancement group training program on cognition and depression in the community-dwelling elderly
Hwan-hee Kim, Nam-hae Jung
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2018; 30(2): 335. CrossRef - The effect of exercise on cognitive function in the elderly : A systematic review and meta-analysis
Bok Yae Chung, Ji Young Han
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(5): 1375. CrossRef - Effect of Net-Step Exercise on Gait Ability, Depression, Cognitive Function and Activities of Daily Living in Older Adults
Eun Ja Lee, Jae Boone Yoo
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(2): 108. CrossRef - The Effects of an Exercise Program using a Resident Volunteer as a Lay Health Leader for Elders' Physical Fitness, Cognitive Function, Depression, and Quality of Life
Yeon-Hee Choi, Na-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(3): 346. CrossRef - Effects of a Cognition Activation Program for the Institutionalized Old-Old in Korea
Hung Sa Lee, Dohyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(4): 427. CrossRef - Long-term exercise treatment reduces oxidative stress in the hippocampus of aging rats
K. Marosi, Z. Bori, N. Hart, L. Sárga, E. Koltai, Z. Radák, C. Nyakas
Neuroscience.2012; 226: 21. CrossRef - The Effects of Exercise in the Frail Elderly
Young-Im Park, Kang-Yi Lee, Tae-Im Kim, Moung-Hee Jeon, Dong-Oak Kim, Ji-Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(1): 91. CrossRef - The Effects of a Cognitive Enhancement Group Training Program for Community-dwelling Elders
Young Ran Han, Mi Sook Song, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 724. CrossRef
- Cognitive decline in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura survivors: The role of white matter health as assessed by MRI
- 1,369 View
- 5 Download
- 12 Crossref

- A Structural Equation Model on Sexual Function in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
- Nami Chun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(5):639-648. Published online October 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.5.639
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to construct and test a structural equation model on sexual function in women with gynecologic cancer.
Methods The model was constructed and tested under the hypotheses that women's physical changes in sexual function after gynecologic cancer treatment did not automatically lead to sexual dysfunctions. Women's psychosocial factors were considered to be mediating variables. Two hundred twelve women with cervical, ovarian, and endometrial cancer were recruited and asked to complete a survey on their physical factors, psychosocial factors and sexual function. Data was analyzed using SPSS WIN 12.0 and Amos WIN 5.0.
Results Predictors of sexual function in the final model were sexual attitude affected by physical distress and couple's age, sexual information affected by physical distress and couple's age, depression affected by physical distress, and marital intimacy affected by physical distress. Tumor stage and time since last treatment directly affected women's sexual function without any mediating psychosocial variables. However, body image did not affect women's sexual function.
Conclusion Nursing professionals should develop a tailored educational program integrating both physical and psychosocial aspects, and apply it to women and their spouses in order to promote sexual function in women with gynecologic cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of a Sexual Health Improvement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Soon Yang Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 163. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Sexual Function of Pregnant Women
Eun Jung Oh, Moon Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(1): 73. CrossRef - Quality of Life by Stage of Cervical Cancer among Malaysian Patients
Mohammed Nawi Azmawati, Endut Najibah, Mohd Dali Ahmad Zailani Hatta, Ahmad Norfazilah
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2014; 15(13): 5283. CrossRef - Effect of PLISSIT Model Sexual Health Enhancement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer and Their Husbands
Ju-Hee Nho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 681. CrossRef - A Study on the Predictive Factors of Sexual Function in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Jeong Sook Park, Soon Yang Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(2): 156. CrossRef - Descriptive Study on Sexuality for Women with Gynecological Cancer
Ju Hee Nho, Young Sook Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(1): 17. CrossRef - Effect of Depression and Anxiety on Symptoms in Thyroid Cancer Patients Undergoing Radioactive Iodine (I131) Therapy
Nami Chun
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(4): 297. CrossRef - Effectiveness of PLISSIT Model Sexual Program on Female Sexual Function for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Nami Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 471. CrossRef - Predictors of Sexual Desire, Arousal, Lubrication, Orgasm, Satisfaction, and Pain in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Nami Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 24. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of a Sexual Health Improvement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
- 954 View
- 0 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Construction of an Explanatory Model of Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Jeongyee Bae, Kweonsik Min, Sukhee Ahn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(7):1080-1090. Published online December 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.7.1080
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Although concerns of female sexual dysfunction (FSD) are increasing in Korea, sexual dysfunction related factors are limited in research studies. The aim of this study was to develop an explanatory model that will further explain the continuously increasing female sexual dysfunction cases in Korea.
Methods Survey visits were conducted to four hundred and eighty five women, over 25 years of age and presently residing in either urban or rural areas. All of them were analyzed using a structured questionnaire. A total of 8 instruments were used in this model. The analysis of data was done with both SPSS WIN for descriptive statistics and AMOS 5.0 for covariance structure analysis.
Results As a result, variables that showed notably direct effects on FSD were: sexual concept (sexual attitude), sexual distress, and psychosocial health (depression, crisis, traumatic life events). On the other hand, variables such as age, educational level, economic status, and marital status showed indirect influences on health-promoting behaviors.
Conclusion By comprehensively addressing the factors related to sexual dysfunction, and comparing each influence, this study can contribute to designing an appropriate sexual dysfunction prevention strategy in tune with the particular characteristics and problems of a client.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unmet Needs and Sexual Distress of Gynecological Cancer Patients according to the Period after Initial Treatment
Yeon Hee Bae, Jeong Sook Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(4): 221. CrossRef - A Study on Sexual Function, Sexual Stress, and Quality of Life in Middle Aged Women Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Sunyoung Ahn, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(4): 393. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Sexual Function in Postmenopausal Married Women
Hye Young Kim, Eun Ko
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(4): 287. CrossRef - Factors influencing sexual function of middle-aged married Korean women
YoungJu Jee, YoungHae Kim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2015; 27(3): 819. CrossRef - Study of the Sexual Behaviors and Influential Factors Affecting Premenopausal Women with Breast Cancer: Application of the Method of Triangulation
Eun Ja Kim, Myung Ae Kim, Na Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(1): 72. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Illness Intrusiveness of the Sexual Life in Women with Overactive Bladder
Jeong Lim Cho, Eun Nam Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 62. CrossRef - Factors Related to Female Sexual Dysfunction of North Korean Women Defectors
Young Sun Rhee, Hye Wan Ku, In Young Han
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(2): 55. CrossRef - Relationship among Sexual Knowledge, Frequency, Satisfaction, Marital Intimacy and Levels of Depression in Stroke Survivors and Their Spouses
Jung-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 483. CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model on Sexual Function in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Nami Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 639. CrossRef
- Unmet Needs and Sexual Distress of Gynecological Cancer Patients according to the Period after Initial Treatment
- 850 View
- 0 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of Aerobic Exercise Using a Flex-band on Physical Functions & Body Image in Women Undergoing Radiation Therapy after a Mastectomy
- Hyang Sook So, In Sook Kim, Jung Han Yoon, Oh Jang Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(7):1111-1122. Published online December 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.7.1111
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study examined the effects of aerobic exercise using a flex band on the improvement of physical functions & body image in breast cancer women undergoing radiation therapy after a mastectomy.
Method Women with breast cancer(n = 26) were assigned to an experimental group(EG, n = 15) and control group(CG, n = 11). The E.G. participated in an aerobic exercise program with a 60% to 80% intensity of maximal heart rate for 25 minutes during the main exercise, 3 times per week, for 6 weeks. The EG did not exercise regularly for 3 months before participating in this program. The CG received no exercise treatment during the research period. Data were analyzed using the χ2-test and Mann-Whitney U test by the SPSS version 11.0 program at a 5% significant level.
Result Group analysis revealed that the EGwomen had significantly more improved cardiopulmonary functions, ROM of the affected shoulder joint, and body image compared to the CG.
Conclusion Aerobic exercise using a flex band may be an effective rehabilitative measure for mastectomy women with respect to cardio-pulmonary functions, ROM, & body image. Further studies are recommended to study early rehabilitation programs within 10 days post-operatively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exercise for women receiving adjuvant therapy for breast cancer
Anna C Furmaniak, Matthias Menig, Martina H Markes
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic Review of Exercise Effects on Health Outcomes in Women with Breast Cancer
ChaeWeon Chung, Seonheui Lee, ShinWoo Hwang, EunHee Park
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(3): 149. CrossRef
- Exercise for women receiving adjuvant therapy for breast cancer
- 1,040 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


