Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
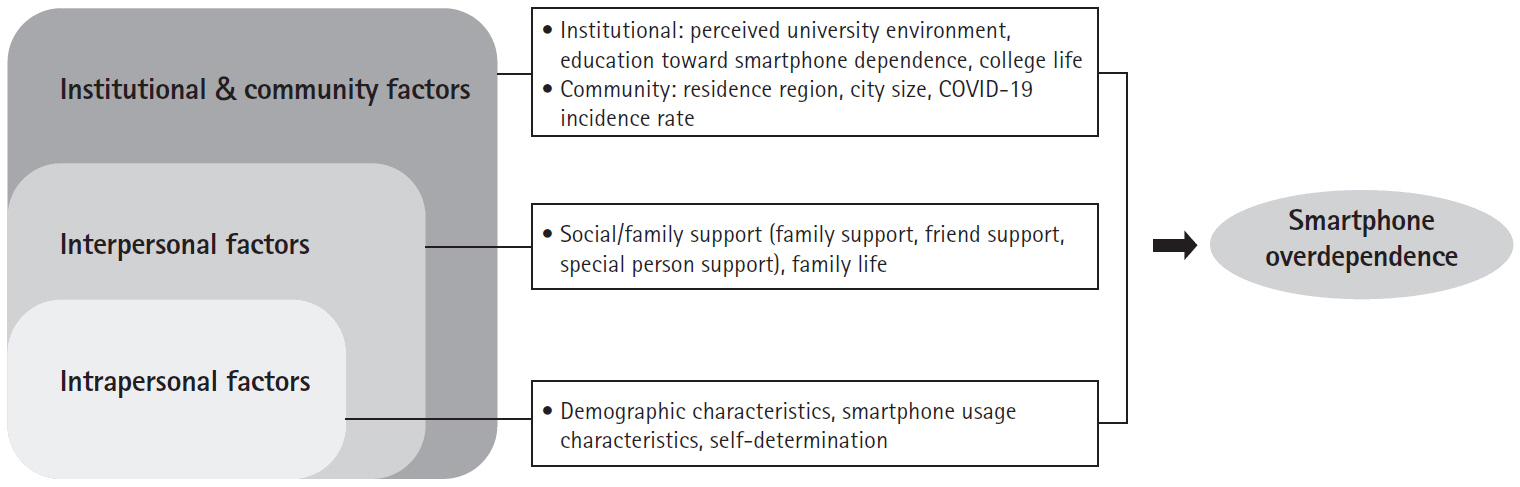
- Factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students: an ecological model: a descriptive study
- Jeong Soon Yu, Myung Soon Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):64-80. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24092
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study investigated the factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students using an ecological model and descriptive research.
Methods
Data were collected from 482 students at 13 universities in the six regions in South Korea from October 20, 2020, to March 25, 2021. Data analysis involved descriptive statistics, the chi-square test, the independent samples t-test, analysis of variance, and hierarchical multiple regression.
Results
The significant ecological factors influencing smartphone overdependence included self-awareness of smartphone overdependence (β=.33, p<.001), autonomy (β=–.25, p<.001), average daily smartphone usage time (β=.18, p<.001), gender (β=.15, p=.001), college year (β=.15, p=.020), forming relationships with others as a motivation for smartphone use (β=–.15, p=.008), friend support (β=.14, p=.006), and age (β=–.12, p=.047). The model explained 34.9% of the variance.
Conclusion
The study emphasized the role of personal and interpersonal factors, in smartphone overdependence among university students. Tailored intervention strategies are necessary to address smartphone overdependence, considering the unique characteristics of students’ environments. A significant aspect of this study is that it provides an explanation of the multidimensional factors contributing to smartphone overdependence among university students, including intrapersonal, interpersonal, and environmental influences.
- 3,715 View
- 195 Download

- Development of the Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students
- Seoyoung Yoon, Hye-Ah Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):340-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students (HCPES-NS) and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
The HCPES-NS was constructed following the DeVellis guidelines. The initial items were written based on a literature review and individual in-depth interviews. Content validity was verified through an expert panel review. To confirm the validity and reliability of the scale, a survey was conducted with 449 nursing students enrolled in 12 nursing colleges. Data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, concurrent validity, and reliability tests.
Results
Factor analysis showed that the HCPES-NS consists of 15 items on five subdomains: clinical site atmosphere, interpersonal relationship, alternative online practicum contents, provision of learning information, and clinical performance facilitation. A higher score indicated a more positive perception of the clinical practicum environment. The concurrent validity of the HCPES-NS was confirmed by its positive correlation with the Clinical Learning Environment Scale (r = .77). The Cronbach’s α reliability of the HCPES-NS was .84.
Conclusion
The HCPES-NS is both valid and reliable. This scale reflects the clinical practicum environment and includes an online practicum factor. It may be used effectively by faculty members and educators to evaluate nursing students’ perceptions of clinical practicum environments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Ui Rim Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 355. CrossRef
- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
- 2,961 View
- 96 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Moderating Effect of Organizational Justice on the Relationship between Self-Efficacy and Nursing Performance in Clinical Nurses
- Ju-Ra Kim, Yukyung Ko, Youngjin Lee, Chun-Ja Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):511-521. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22076
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the moderating effect of organizational justice on the relationship between self-efficacy and nursing performance among clinical nurses.
Methods
In January 2021, a cross-sectional survey was conducted with 224 clinical nurses recruited from a university-affiliated hospital in Suwon, South Korea. Participants completed online-based, self-report structured questionnaires. Collected data were analyzed using multiple regression and a simple model of PROCESS macro with a 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval.
Results
Self-efficacy and organizational justice were found to be significant predictors of nursing performance. These two predictors explained the additional 34.8% variance of nursing performance in the hierarchical regression model, after adjusting the other covariates. In addition, organizational justice moderated the relationship between self-efficacy and nursing performance among the clinical nurses. In particular, at low self-efficacy level, participants with high organizational justice had higher nursing performance compared to those with low organizational justice.
Conclusion
Enhancing organizational justice can be used as an organizational strategy for improving the organizational culture in terms of distribution, procedure, and interaction. Ultimately, these efforts will contribute to the improvement of nursing performance through a synergistic effect on organizational justice beyond nurses’ individual competency and self-efficacy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Balancing efficiency and fairness in an output-based agency relationship: an empirical investigation of the cognitive factors favouring a win–win situation
Filippo Ferrari
Evidence-based HRM: a Global Forum for Empirical Scholarship.2025; 13(5): 866. CrossRef - Work-family balance mediates self-efficacy and subjective well-being among nurses in Chinese intensive care units: A cross-sectional study
Lating Zhang, Xianzhen Jin, Na Cheng, Ruhua Wang, Xinhui Liang, Haiyan Fan, Xue Jiang
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 82: 151932. CrossRef - Relationship between resilience and self-efficacy among Iranian nurses: a cross-sectional study during the post-Corona era
Saeed Ghasempour, Ali Abbasi, Mohammad Hasan Basirinezhad, Ali Dadgari, Hossein Ebrahimi
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Nurse Collaboration and Nurse-Physician Collaboration on Nursing Performance in Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Patient Safety Management Activities
JaHyun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 343. CrossRef - The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Nurses’ Well-Being: Does Digital Competence Matter?
Yali Li, Qi Jing, Taiwen Feng, Xiaoling Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 385. CrossRef
- Balancing efficiency and fairness in an output-based agency relationship: an empirical investigation of the cognitive factors favouring a win–win situation
- 2,304 View
- 116 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Prenatal Education for Environmental Health Behavior Using Cartoon Comics
- Hyun Kyoung Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Mirim Kim, Seohwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):478-488. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21083
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and examine the effects of a prenatal program on environmental health behavior using cartoon comics among Korean pregnant women.
Methods
This study used a non-equivalent control group pre-test/post-test design. The program used cartoon comics to explore environmental health behaviors during pregnancy. The program consisted of the following four components: environmental toxicants during pregnancy, avoiding particulate matter during pregnancy, environmental toxicants during baby care, and making a healthy environment for children. In total, 35 pregnant women participated in the study: 18 in the experimental group and 17 in the control group. Data collection and program adaptation were conducted between November 3, 2020 and January 19, 2021. The effect of the prenatal education program was evaluated by t-test and repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
Learning experience (t = - 2.35, p = .025), feasibility (t = - 2.46, p = .019), satisfaction (t = - 2.23, p = .032) were higher in the experimental group than in the control group in the first post-test. Feasibility (t = - 2.40, p = .022) was higher in the experimental group than in the control group in the second post-test. Repeated-measures ANOVA showed significant interactions between time and group in environmental susceptibility (F = 9.31, p < .001), self-efficacy (F = 3.60, p = .033), and community behavior (F = 5.41, p = .007).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the need for a prenatal education program to promote environmental health perceptions and behavior during pregnancy. We suggest a prenatal class adopting the creative cartoon comics to promote the maternal environmental health behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a diabetes-themed cartoon-based education on disease knowledge and physical activity among Japanese children: a preliminary randomized controlled trial
Yasuhiro Suzuki, Daichi Sugawara, Mika Oki, Hirofumi Takahashi, Takaaki Matsuda, Hiroaki Suzuki, Hitoshi Shimano, Yasushi Hada, Kenji Suzuki
Clinical Pediatric Endocrinology.2026; 35(1): 74. CrossRef - The effect of DECO-MOM mobile application for a prenatal environmental health program on environmental health behaviors: a pilot test
Hae Kyung Jo, Hyun Kyoung Kim
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a quasi-experimental sexual and reproductive health literacy (SRHL) programme for marriage immigrants in South Korea: focus on Vietnamese women
Heeran Chun, Young Sook Lee, Hyeran Yoon
BMJ Public Health.2025; 3(2): e002473. CrossRef - The effects of a YouTube prenatal program on social support, environmental health behavior, and content satisfaction: a quasi-experimental research design
Geum Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Hye Young Min
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Examining the Effectiveness of Interactive Webtoons for Premature Birth Prevention: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Sun-Hee Kim, Jennie C De Gagne
JMIR Research Protocols.2024; 13: e58326. CrossRef - Development and effects of a webtoon education program on preventive self-management related to premature labor for women of childbearing age: a randomized controlled trial
Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 250. CrossRef - The effects of environmental prenatal program on environmental health perception and behavior using internet-based intervention in South Korea: A non-randomized controlled study
Hyun Kyoung Kim, Geum Hee Jeong, Hye Young Min, George Vousden
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0277501. CrossRef
- Effects of a diabetes-themed cartoon-based education on disease knowledge and physical activity among Japanese children: a preliminary randomized controlled trial
- 1,544 View
- 40 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Identifying Trajectories of Behavioral Problems in Children with Allergic Diseases: Secondary Data Analysis of the 5th to 7th Panel Study of Korean Children
- Miseon Son, Eunsun Ji
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):822-836. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20177
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify latent classes of behavioral problem trajectories in children with allergic diseases and investigate their predictors.
Methods
This study used data from the 5th to 7th Panel Study of Korean Children. The participants included 840 children aged 4~6 years with allergic diseases. Statistical analyses were conducted using latent class growth analysis and multinomial logistic regression.
Results
The trajectories of both internalizing and externalizing behavioral problems in children with allergic diseases were classified into five groups, that is deteriorative, recovering, changing 1 (decreasing-increasing), changing 2 (increasing-decreasing), and low state persistent group. For the internalizing behavioral problems, predictors were temperament, father’s education, family interaction, and disconnection in peer interaction. For the externalizing behavioral problems, predictors child’s gender, temperament, marital conflict, parenting stress, family interaction, and parenting environment.
Conclusion
Deteriorative group has high-risk behavioral problems in children with allergic diseases. We suggest to provide interventions considering latent problem trajectories based on ecological environments for allergic children.
- 961 View
- 11 Download

- The Effects of Hospitals’ Family Friendly Management on Married Female Nurses’ Retention Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Work-Family Interface
- Jin Hwa Lee, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):386-397. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study examined the effect of hospitals’ family-friendly management on married female nurses’ retention intention. The focus was the mediating effects of the work-family interface (work-family conflict, work-family enrichment and work-family balance).
Methods This study was a cross-sectional study. The participants were 307 nurses working at five public and five private hospitals with more than 200 beds in Seoul. Data were collected using structured questionnaires from September 10 to September 17, 2018 and analyzed with SPSS 24.0. Data were analyzed using an independent t-test, a one-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation coefficients, and multiple regression following the Baron and Kenny method and Sobel test for mediation.
Results There were significant correlations among family-friendly management, the work-family interface, and retention intention. Work-family conflict showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention. Work-family enrichment showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention. Work-family balance showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention.
Conclusion These findings indicate that both hospitals’ family-friendly management and nurses’ work-family interface are important factors associated with nurses’ retention intention. Therefore, hospitals should actively implement family-friendly management for nurses and establish strategies to enhance nurses’ work-family interface for effective human resource management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How parenting-related characteristics influence parenting stress among nurses with young children in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Minhwa Hwang, Nagyeong Lee, Gunjeong Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Retention Intention of Female Nurses Raising Young and School-Age Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ha Neul Lee, Suyon Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 504. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of Instruments Measuring Dyadic Communication and Environment in Dementia Care: A Systematic Review
Sohyun Kim, Wen Liu, Patricia Heyn
The Gerontologist.2023; 63(1): 52. CrossRef - Disaster Preparedness and Associated Factors Among Emergency Nurses in Guangdong Province, China: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study
Jia Wang, Xinglan Sun, Sihui Lu, Fen Wang, Meijuan Wan, Hanxi Chen, Yibing Tan
Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Causes and Effects of Burnout Experienced by Insurance Review Nurses: Focus Group Interview
Eun Sil Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Myoung Hee Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 545. CrossRef - Nurses’ Clinical Work Experience during Pregnancy
Hyunjung Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jiyeon Ha
Healthcare.2020; 9(1): 16. CrossRef
- How parenting-related characteristics influence parenting stress among nurses with young children in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 1,244 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Environment Factors Affecting Childhood Obesity: Voices from Students, Parents, and Teachers with Photograph
- Eunok Park, Hyo Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):254-262. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.254
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to explore the environmental factors affecting childhood obesity using photovoice from the perspectives of students, parents, and teachers in the community.
Methods Six school students, seven parents, and seven school teachers completed an assignment requiring them to take 24 pictures and participate in group discussions. After training session, the participants were asked to take pictures associated with food and physical activity environments related to childhood obesity at home, school, and within their communities for two weeks and to submit the pictures with records. Each group had four sessions for discussion.
Results School cafeteria, convenience stores near schools, instant food and fast food joints, food delivery, and high-calorie snacks comprised the food environmental factors. Lack of physical activity classes at school, commuting by car, barriers to physical activity, and use of smart-phone were environmental factors that inhibited physical activity.
Conclusion To reduce childhood obesity, the creation of a supportive environment for encouraging the consumption of healthy foods and enhancing physical activity should be considered. Modifications of and improvement to the obesogenic environment might be a good strategy to prevent and reduce childhood obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of Eating Traits Scale for Adult in Republic of Korea
Youngwon Kim, Eunok Park
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 339. CrossRef - Experiences of Male Nursing Students in Women's Health Nursing Practicum: A Mixed-Methods Study Using Photovoice
Na Won An, Na Kyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(2): 104. CrossRef - A participatory practice study for the improvement of sub-regional health vulnerabilities: a qualitative study
Jeehee Pyo, Haneul Lee, Yangwha Kang, Jaewook Oh, Minsu Ock
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Eating propensity of adult women: An exploratory study
Eunok Park, Youngwon Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2020; 37(5): 69. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of Eating Traits Scale for Adult in Republic of Korea
- 1,447 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version Scale of the Clinical Learning Environment, Supervision and Nurse Teacher Evaluation Scale (CLES+T)
- Sun-Hee Kim, So Yeon Yoo, Yae Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):70-84. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.70
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher evaluation scale (CLES+T) that measures the clinical learning environment and the conditions associated with supervision and nurse teachers.
Methods The English CLES+T was translated into Korean with forward and back translation. Survey data were collected from 434 nursing students who had more than four days of clinical practice in Korean hospitals. Internal consistency reliability and construct validity using confirmatory and exploratory factor analysis were conducted. SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 22.0 programs were used for data analysis.
Results The exploratory factor analysis revealed seven factors for the thirty three-item scale. Confirmatory factor analysis supported good convergent and discriminant validities. The Cronbach's alpha for the overall scale was .94 and for the seven subscales ranged from .78 to .94.
Conclusion The findings suggest that the 33-items Korean CLES+T is an appropriate instrument to measure Korean nursing students'clinical learning environment with good validity and reliability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research progress of measuring tools for nursing students’ clinical learning environment
Yun Xu, Qing Wang, Qi Wei
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Learning Environment, Supervision, and Nurse Teacher Evaluation (CLES + T) Scale: Saudi Arabic Version—A Cross‐Sectional Validation Study of Nursing Interns and Students
Naif Hamdi Alanazi, Martin Cerveny
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing career identity in relation to the clinical practice learning environment, satisfaction, and stress among nursing students in the Republic of Korea: a comparative survey
Se Young Im, Min Ha Park, Hyeon Seok Kang, Sung Min Cho, Hye Won Lim, Myung Kyung Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of the Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students
Seoyoung Yoon, Hye-Ah Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 340. CrossRef - Personal Factors and Clinical Learning Environment as Predictors of Nursing Students' Readiness for Practice: A Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
Taewha Lee, Su Jeong Lee, Yea Seul Yoon, Hyunju Ji, Sookhee Yoon, SangA Lee, Yoonjung Ji
Asian Nursing Research.2023; 17(1): 44. CrossRef - Clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher (CLES+T) scale: Translation and validation of the Arabic version
Khadija Guejdad, Ali Ikrou, Camilla Strandell-Laine, Redouane Abouqal, Jihane Belayachi
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 63: 103374. CrossRef - The clinical learning environment, supervision and future intention to work as a nurse in nursing students: a cross-sectional and descriptive study
Juxia Zhang, Linda Shields, Bin Ma, Yuhuan Yin, Jiancheng Wang, Rong Zhang, Xueke Hui
BMC Medical Education.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of the Nursing Profession Self-Efficacy Scale: A Methodological Study
Jina Oh, Haeryun Cho, Yae Young Kim, So Yeon Yoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 1080. CrossRef - Are Traditional and Simulated Clinical Environments Meeting Nursing Students’ Learning Needs?
Kim Leighton, Suzan Kardong-Edgren, Gregory E. Gilbert
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2021; 59: 85. CrossRef - Clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher scale (CLES+T): Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version
Rong Zhao, Lu Xiao, Roger Watson, Yanhua Chen
Nurse Education Today.2021; 106: 105058. CrossRef - Testing the measurement invariance of the Korean clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher (CLES+t) scale
Sun-Hee Kim, Yae Young Kim, So Yeon Yoo
Nurse Education Today.2021; 107: 105140. CrossRef - Exploratory Factor Analysis of the Indonesian Version of the Clinical Learning Environment, Supervision, and Nurse Teacher Scale (CLES + T)
Christine L. Sommers, Ian Ruddy Mambu, Lisa McKenna, Sonia Reisenhofer, Julie McCaughan
Journal of Nursing Measurement.2021; 29(1): E39. CrossRef - The Clinical Learning Environment, Supervision and the Nurse Teacher Evaluation Scale: Turkish Version
Emine Iyigun, Sevinc Tastan, Hatice Ayhan, Berrin Pazar, Yasemin Eda Tekin, Halise Coskun, Mikko Saarikoski
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural Model of Professional Socialization of Nursing Students With Clinical Practice Experience
Soo-yeon Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Journal of Nursing Education.2020; 59(3): 133. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of a Korean Version of Nursing Student Perceptions of Dishonesty Scale
Hee-Yeong Woo, Jeongwon Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(2): 176. CrossRef - Nursing Students' Practice Experience on Community Visiting Nursing
Jae-Hyun Ha, Jeong-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(1): 43. CrossRef - The clinical learning environment, supervision and nurse teacher scale (CLES+T): psychometric properties measured in the context of postgraduate nursing education
Dorota Ozga, Aleksandra Gutysz-Wojnicka, Bogumił Lewandowski, Beata Dobrowolska
BMC Nursing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating clinical placements in Saudi Arabia with the CLES+T scale
Norah A. Al-Anazi, Dalyal Alosaimi, Isabelita Pandaan, Denis Anthony, Sue Dyson
Nurse Education in Practice.2019; 39: 11. CrossRef
- Research progress of measuring tools for nursing students’ clinical learning environment
- 2,686 View
- 82 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- A Study on the Disturbing Factors Which Work against Therapeutic Atmosphere and Environment on Hospital Wards as Perceived by Patients and Nurses
- Young Hae Kim, Myoung Eun Han
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):178-188. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF As a descriptive survey, this study was attempted to get basic data necessary to recognize the factors that disturb the therapeutic atmosphere of hospital wards as perceived by nurses and hospitalized patients, to identify differences between the perceptions of the nurses and of patients. The subjects, 159 patients in Pusan National Hospital and 68 nurses working there were sampled between March 18 and April 13, 1996. The tool used to measure the disturbing factors was an amended form of the one developed by Kim, Mae Ja(1983). The differences between each subject's score for each factor were analyzed using means and SD, and the highest 3 items above the mean score for each factor were collected and compared. The results are described below : 1. Subject's perception of main disturbing factors : patients reported that the main factors were 'loss of role and economic trouble', 'the prognosis of disease', 'the change of daily life' but nurses replied that the main factors were 'the prognosis of disease', 'the communication trouble with the medical team and interpersonal relationships'. 'The change of daily life' was not a perceived factor by nurses, but ranked third by patients. 2. Subject's perception degree of each disturbing factor : (1) among the items related to interpersonal relationship, the patient group reported that the worst disturbance was due to severely ill patients in the same room' but the nurse group regarded 'greed to monopolize wheelchairs or other supplies' as the worst disturbance. (2) among the items related to physical factors, the patient group regarded 'limitations to wash their body, physical pain and limitations in physical activity' as the worst disturbance, but the nurse group regarded 'physical pain', and 'limitations to activity or change of appearance' as the worst disturbance. (3) among the items related to the change of daily activity, the patient group regarded 'the boredom of hospitalization or in favorable diet' as the worst disturbance, but the nurse group regarded 'too much noise or unclean room' as the worst disturbance. (4) among the items related to the communication trouble with medical team, the patient group regarded 'the ignorance of their disease due to poor information, the inability to understand the language of the medical team or the difficulty in seeing physician in time' as the worst disturbance, but the nurse group regarded 'the inability to trust physicians and physician's poor attention to patients' as the worst disturbance.
- 419 View
- 0 Download

- Fatigue and its Related Factors in Patients on Hemodialysis
- Hye Ryoung Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(1):53-72. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.1.53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Purpose of this study was to identify characteristics of fatigue and the relationship between fatigue and related factors in patients on hemodialysis. This study was a survey study using a cross-sectional design. The subjects for this study were 101 patients on hemodialysis who were registered in the six hemodialysis clinics among a total of eleven clinics in Seoul. The period of data collection was from February 28, 1995 to May 2, 1995. Data were collected through an interview with a structured packet and the physiological data. The tools used in this study were the Visual Analogue Scale-Fatigue developed by Lee et al(1990) and translated by Lee (1991), the fatigue interview schedule developed by this reseacher, Zung's self rating depression scale (Zung, 1965), the self-efficacy scale developed by Sherer et al(1982) and the Norbeck Social Support Questionnaire (NSSQ) translated by Oh (1984). The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics (mean, standard deviation, frequency, range), Pearson correlation coefficients and Stepwise multiple regression. The results were as follows: 1. Characteristics of Fatigue of hemodialysis patients: 1) 79 of 101 hemodialysis patients complained fatigue. 2) The mean fatigue score as measured by the VAS-F was 36.2mm. 3) The mean duration of fatigue was 2.9 hours 2. Characteristics of fatigue related factors: 1) The physiologic factor which included Hgb, Hct, BUN, creatinine, potassium and inter-dialytic weight gain deviated from normal range. 2) The psychological factor which included depression and self-efficacy was about the same level as for patients with other chronic diseases. 3) The environmental factor which included social support had wide variation. 3. The relationship between fatigue and related factors: 1) Interdialytic weight gain in the physiological factor was the only valuable with fatigue (p<.05) 2) The relationship between fatigue and the psychological factor of depression showed a positive and strong correlation (p<.05). According to the findings of this study, fatigue was highly correlated with the depression, This indicates that nurses should try to assess and control psychological factors when patients complain of fatigue rather than just considering physiological factors. Nursing has to develop effective nursing interventions to reduce fatigue in patients with chronic diseases using the relationship between fatigue and physiological, psychological and environmental factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Dialysate Flow Rate on Dialysis Adequacy and Fatigue in Hemodialysis Patients
Sun Mi Cha, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 642. CrossRef
- The Effect of Dialysate Flow Rate on Dialysis Adequacy and Fatigue in Hemodialysis Patients
- 697 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Indoor Environment Management Education for Prevention of Allergic Asthma
- Jee Won Park, Yong Soon Kim, Young Shin Song
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):1017-1023. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.1017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The objective of this research is to provide the indoor environment management education program for the asthma patients and their families and then analyze the effectiveness in education preventing allergic asthma.
METHODS
A pre-post single group quasi-experimental design was used to provide an education program about correct indoor environment management to a total of 58 households (29 patient households and 29 normal households). The performance rate of correct indoor environment management procedure, amount of house dust mite antigen, allergy subjective symptoms score and knowledge score about indoor environment management were compared before and after the education to test the effectiveness of the education.
RESULTS
Home-visit education in this research had effects in improving subject households' performance rate of indoor environment management procedures, reducing the amount of house dust mite antigen - an important inducing factor of allergy, and reducing perceived subjective symptoms of allergy.
- 543 View
- 0 Download

- Correlation between Personality, Family Dynamic Environment and Suicidal attempt among Korean Adolescents Population
- Hyun Sil Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(2):231-242. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.2.231
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to identify the rate of suicidal attempts, investigate difference of rate of suicidal attempts between students and delinquents, and examine correlation between personality, family dynamics, environment, and suicidal attempts among Korean adolescents. METHOD: Data were collected through questionnaire surveys. Internal consistencies for this questionnaire ranged from 0.63 to 0.88. The subject used in this study consisted of 922(delinquent : 367, student : 555), using the proportional stratified random sampling method. Statistical methods employed were Chi-square and t-test. RESULTS: 1) The rate of suicidal attempts were 10.8%, and the highest peak age of suicidal attempt was 17-18 year old (16.9%).2) Delinquents(19.6%) showed a higher rate of suicidal attempts than students (5.1%). Among the students, girls (43.3%) showed a higher rate of suicidal attempt than boys (19.1%). Whereas, boys (80.9%) showed a higher rate of suicidal attempt than girls (56.7%) among delinquents.3) Those who attempt suicide have more familial problem such as incest, psychosis, depression, attempted suicide, committed suicide, and alcoholism in their family. They also have more dysfunctional family dynamics, environment, and maladaptive personalities than non-attempters. CONCLUSIONS: Suicide and suicidal behaviors are multifaceted events. For suicide prevention, independent assessments of variables such as familial problems, personality, family dynamics, and environment must be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associated Factors of Depression and Suicidal Behaviors among Korean Adolescents: Web-based Survey of the Korea Youth Risk Behavior in 2015~2017
Hyun-A Choi, Hyejin Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(3): 292. CrossRef - Peer victimization and adolescents’ suicidal ideation and suicide attempts: A moderated mediation model
Wenya Peng, Dongping Li, Xian Li, Jichao Jia, Yanhui Wang, Jiale Xiao
Children and Youth Services Review.2020; 112: 104888. CrossRef - Longitudinal reciprocal effects between peer relationship difficulties and aggressive behaviors in Korean adolescents
Soyoun Kim, Choong Rai Nho
Children and Youth Services Review.2017; 83: 41. CrossRef - A review of school-based suicide prevention interventions in South Korea, 1995–2015
Jung Won Kong, Jung Woo Kim
Children and Youth Services Review.2016; 69: 193. CrossRef - Risk Factors Related to Suicidal Ideation and Attempted Suicide
Sung Suk Chung, Kyoung Hwa Joung
The Journal of School Nursing.2012; 28(6): 448. CrossRef - Interpersonal Relationships and Suicide Probability among Korean Adolescents
Hee Sook Kim, Wan Ju Park, Gyeong Ran Park, Mi Hyang Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(1): 11. CrossRef - Factors on the Suicidal Attempt by Gender of Middle and High School Student
Sanggu Yi, Yunjeong Yi, Hye-Sun Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(5): 652. CrossRef - An ecological understanding of youth suicide in South Korea
Seung-yeon Lee, Jun Sung Hong, Dorothy L. Espelage
School Psychology International.2010; 31(5): 531. CrossRef
- Associated Factors of Depression and Suicidal Behaviors among Korean Adolescents: Web-based Survey of the Korea Youth Risk Behavior in 2015~2017
- 719 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The Influence of a Family Dynamic Environment, Personality, and Smoking on Delinquent Behavior Among Korean Adolescents
- Hyun Sil Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(4):641-655. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.4.641
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to determine the important factors on juvenile delinquency and to examine relationships between sex, age, the family environment, the personality of adolescents, smoking, and juvenile delinquency.
Methods
Data collection was done through questionnaire surveys. The subjects for this study consisted of 1,948 adolescents delinquents : 784, students : 1,164 in Korea, using proportional stratified random sampling method. Statistical methods employed were chi-square, t-test and path analysis. Results: The results of this study were as follows : 1. The delinquent adolescents were reared in a more dysfunctional family environment, and had a higher maladaptive personality than the other student adolescents. 2. The delinquent adolescents showed the larger amount of smoking than the student adolescents. The cause of increased smoking tendency among delinquents simply were 'for social relation', 'for diversion', 'for nicotine addiction', whereas 'for tension relieving' among non-delinquent adolescents. 3. The most powerful contributors on delinquent behavior were antisocial personality tendencies, smoking, sex, strength of parent- child relationships, and the age of the adolescents in this order.
Conclusions
Our cross-sectional findings indicate that smoking was one of the most powerful contributing variables to delinquent behavior, but family environment, personality, sex and age of adolescents were also proved to be strong exogenous variables to smoking in adolescents.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of family function and oral health concern on the oral health impact profile(OHIP) in the adolescents
Kyung-Hee Lee, Hea-Shoon Lee
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2015; 15(4): 583. CrossRef - Smoking Behavior and Predictors of Smoking Initiation in Childhood and Early Adolescence
Sunhee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 376. CrossRef - Construction of the Structural Equation Model on Substance Use in Adolescents
Jeongyee Bae, Panuncio Rosel
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 446. CrossRef
- The Effect of family function and oral health concern on the oral health impact profile(OHIP) in the adolescents
- 770 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Study on the Development and Effectiveness of Parent Role Education Program
- Kyung Ja Han, Kyung Sook Bang, Mi Kyung Kwon, Jung Soo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):417-431. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.417
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the maternal role education program for primiparas in mother-infant interaction, childrearing environ- ment, and infant development. METHOD: A Non-equivalent control group time-series design was used. For the intervention group, programmed parenting education focusing on mother-infant interaction, home environment for infant development, and parent counseling and support was provided via home visits or telephone for twelve months.
RESULT
Significant differences were found in the mother-infant interaction feeding scale at one and three months, but no differences were found in the teaching scale at six and twelve months between the intervention and control groups. Also, the difference in childrearing environment (HOME) between the two groups was significant at three, six, twelve months. In addition, the intervention group showed higher GQ in the Griffiths mental development scale at three and six months. In multiple regression analysis, 22.6% to 43.6% of infant development was explained by HOME, mother-infant interaction, and previous development. CONCLUSION: The maternal role education program proved to be effective in promoting mother-infant interaction, organizing the childrearing environment, and fostering infant development.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of an Early Nursing Intervention Program for Infants' Development and Mother's Child Rearing in Poverty
Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 796. CrossRef
- Effects of an Early Nursing Intervention Program for Infants' Development and Mother's Child Rearing in Poverty
- 670 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Job Satisfaction among ICU nurses according to the Preference and Perception of Work Characteristics
- Rha Yun Song, Yeon Ok Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):431-440. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.431
-
 Abstract
Abstract
The purposes of this study were to determine the factors that influence job satisfaction for ICU nurses and to analyze group differences in job satisfaction based on the nurses' preference and perception of the work environment with an enhanced professional role. A total of 231 nurses who had been working in Intensive Care Units at least for 6 months at selected university hospitals participated in the study while head nurses or those with administrative positions were excluded. The study participants had an average of 33 months of clinical experience with an age range of 23 to 40 years. The data were analyzed by utilizing SPSSWIN and the results are as follows. 1) Hierarchical multiple regression analysis showed that work characteristics defined by Job characteristics theory and nurses' preference/ perception of ideal work environment together explained 33% of variance in job satisfaction. Skill variety, task identity and autonomy as well as individual perception of work environment were significant variables for explaining job satisfaction. Job satisfaction was not significantly related to age, marital status, education, and clinical experience. 2) The groups classified by nurses' preference and perception of work environment were significantly different in their job satisfaction. Nurses with high preference and high perception showed significantly higher general and specific job satisfaction than other nurses. The nurses who showed high preference but perceived their work environment as not reflecting ideal job characteristics reported the lowest job satisfaction among the groups. In conclusion, the role of individual preference and perception of the work environment in explaining the relationship between the redesign of work environment and job satisfaction was supported by the study. The preferences of nurses to the innovative work characteristics should be considered in the process of enhancing job characteristics to lead job satisfaction and low turn over and ultimately to improve quality of care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- KoreanWorkEnvironmentScales forClinicalNurses
Jong‐Kyung Kim, Se‐Young Kim, Mi Yu, Myung Ja Kim, Kyoung‐A Lee
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2015; 12(1): 54. CrossRef - Predictors of life satisfaction of Korean nurses
Haejung Lee, Sunkyung Hwang, Jeongsoon Kim, Barbara Daly
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2004; 48(6): 632. CrossRef
- KoreanWorkEnvironmentScales forClinicalNurses
- 655 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Professional Nursing Practice Environment and Its Impact on Nurses' Task Motivation
- So Young Kang, Young Rhan Um, Sung Suk Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(2):353-361. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.2.353
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was aimed at (a) describing professional nursing practice environments embedded in nursing care units and (b) examining its relationships to nurses' task motivation.
Method Using the Nursing Work Index Revised (NWI-R) and the Work Preference Inventory (WPI), a descriptive study was conducted with a sample of 320 registered nurses on 26 nursing care units in one University hospital in Korea.
Result Mean scores were 12.9 on a 5-20 score range of an autonomous environment scale, 7.3 on a 3-12 score range of a collaborative environment, and 15.8 on a 7-28 score range of control over nursing practice. Nurses' age, educational level, job position, working period at the hospital and employment status were significantly related to the degree of a professional practice environment. The extent to which a professional practice environment accounted for task motivation was 19.5%.
Conclusion There is a certain degree of professionalism in the workplace environment that nurses perceived within the nursing care units. When nurses care for patients, the degree of task motivation depends on the work environment supporting the professional nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Unit-level Nurse Practice Environment on Nurse Turnover Intention in the Small and Medium Sized Hospitals
Jeong Ok Kwon, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(4): 414. CrossRef - Construct Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Practice Environment Scale of Nursing Work Index for Korean Nurses
Eunhee Cho, Mona Choi, Eun-Young Kim, Il Young Yoo, Nam-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(3): 325. CrossRef - Predictors of the Clinical Competence in New Graduate Nurses
Youn-Wha Shin, Haejung Lee, Yeonjung Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(1): 37. CrossRef
- Impact of Unit-level Nurse Practice Environment on Nurse Turnover Intention in the Small and Medium Sized Hospitals
- 813 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Burnout in Clinical Nurses based on CS-CF Model
- Hyun-Jung Kim, Young-Hee Yom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(3):259-269. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.3.259
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct and test a structural equation modeling on burnout of clinical nurses based on CS-CF model.
Methods A survey using a structured questionnaire was conducted with 557 clinical nurses. Data were analyzed using structural equation modeling.
Results The modified hypothetical model yielded the following χ2=289.70,
p <.001, RMSEA=.09, GFI=.93, TLI=.91, CFI=.94, PCFI=.65, AIC=363.21, SRMR=.05 or less and showed good fit indices. Nursing work environment, patient safety culture and resilience showed indirect effects on burnout while compassion fatigue and compassion satisfaction had direct effects.Conclusion Results of this study suggest that compassion fatigue must be decreased and compassion satisfaction has to be increased, while burnout is lowered by enhancing the clinical nursing work environment, patient safety culture and resilience. In addition, more variables and longitudinal studies are necessary to validate the clear cause-and-effect relationship between the relevant variables.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Paediatric nurses' burnout, quality of life and perceived patient adverse events during the COVID‐19 pandemic: Testing an integrated model using structural equation modelling
Haitham Khatatbeh, Tariq Al‐Dwaikat, Jehad Rababah, András Oláh, Annamária Pakai
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2024; 33(1): 255. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study of Psychological Distress, Professional Quality of Life, Effort-Reward Imbalance, and Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Suk-Jung Han, Soon-Youl Lee, Sie-Eun Kim
Healthcare.2023; 11(19): 2695. CrossRef - Effects of Job Stress, Social Support, and Infection Control Fatigue on Professional Quality of Life among Nurses in Designated COVID-19 Hospitals
Minyoung Shin, Woojoung Joung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(5): 603. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Coping Strategies, Compassion Satisfaction, and Compassion Fatigue During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ebtsam Aly Abou Hashish, Amal Diab Ghanem Atalla
SAGE Open Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between secondary traumatic stress and burnout in critical care nurses: The mediating effect of resilience
Yun Jeong Jeong, Sujin Shin
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2023; 74: 103327. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Nurses' Responses to Violence on Burnout: The Moderating Role of Positive Psychological Capital
Haejun Choi, Sujin Shin, Seungji Kim, Sungran Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(4): 406. CrossRef - Influence of the subfactors of self‐compassion on burnout among hospital nurses: A cross‐sectional study in South Korea
Mi Heui Jang, Yoo Mi Jeong, Geuna Park
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(4): 993. CrossRef - Developing a structural equation model from Grandey's emotional regulation model to measure nurses' emotional labor, job satisfaction, and job performance
Won Ju Hwang, Eun Hee Park
Applied Nursing Research.2022; 64: 151557. CrossRef - Influence of Emotional Intelligence and Professional Self-concept on Compassion Competence in Psychiatric Nurses
Hye Suk Im, Won Hee Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(4): 259. CrossRef - A Path Model for Burnout in Community Mental Health Professionals
Jin-Joo Chang, Sung-Hee Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(18): 9763. CrossRef - Effect of Nurse's Character for Care and Sense of Coherence on Professional Quality of Life Among Oncology Nurses
Gie-Ok Noh, Gyeonga Kang, In Gak Kwon, Sang Hee Kim, Yoon Jung Kim, Jeong Hye Kim, Eun Young Park, Jeong-Sook Park, Han Jong Park, Kwuy-Im Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(1): 52. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Burnout among Tertiary Hospital Nurses during the COVID-19 Outbreak
Geun-Hee Kim, Jun Ok You, Mira Lee, Yunju Choi, Yoon Mi Lee, Ji Hye Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(4): 390. CrossRef - The Influence of Burnout on Patient Safety Management Activities of Shift Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Compassion Satisfaction
I Seul Ryu, JaeLan Shim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(22): 12210. CrossRef - Association between nursing work environment and compassion satisfaction among clinical nurses
Jihyun Baek, Hyeonmi Cho, Kihye Han, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2020; 28(2): 368. CrossRef - Analysis of Research on Compassion Satisfaction among Nurses
Soon-Neum Lee, Jung-A Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 599. CrossRef - Perceptions of Medical Personnel toward Burnout using Q Methodology
Eun Ja Yeun, Young Mi Kwon, Young Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(1): 57. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Practice Environment, Compassion Fatigue and Compassion Satisfaction on Burnout in Clinical Nurses
Mi Young Han, Min Sook Lee, Ju Young Bae, Young Suk Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(2): 193. CrossRef - Effect of Empathy, Resilience, Self-care on Compassion Fatigue in Oncology Nurses
Ho Jin Cho, Myun Sook Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(4): 373. CrossRef - Effects of Work Stress, Compassion Fatigue, and Compassion Satisfaction on Burnout in Clinical Nurses
Jung-Min Lee, Young-Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(5): 689. CrossRef
- Paediatric nurses' burnout, quality of life and perceived patient adverse events during the COVID‐19 pandemic: Testing an integrated model using structural equation modelling
- 1,374 View
- 17 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Nursing Productivity of Nurses in Korea
- Se Young Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Heon Man Lim, Mi Young Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, Kyoung A Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(1):20-29. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.1.20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to propose and test a predictive model that could explain and predict nursing productivity.
Methods A survey using a structured questionnaire was conducted with 360 nurses in Korea. The data were analyzed using SPSS Windows 18.0 and AMOS 19.0 program.
Results Based on the constructed model, burnout and organizational commitment were found to have direct effects on nurses' turnover intention and nursing productivity. While nursing work environment was found to have indirect effects on nurses' turnover intention and nursing productivity.
Conclusion This structural equational model is a comprehensive theoretical model that explains the related factors and their relationship with nursing productivity. Comprehensive organizational interventions to improve nursing productivity should focus on improving the nursing work environment. Findings from this study can be used to design appropriate strategies to decrease nurse turnover in Korea. Further studies are needed to prospectively verify these causal relationships with larger samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Mi-So Shim, Seoyoung Baek, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Youngjin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 295. CrossRef - Effect of Job Embeddedness on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Long Term Care Hospitals: The Mediating Effect of Nursing Work Environment
Sun Mi Ha, Yeong Ju Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 439. CrossRef - A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis on the Outcome Variables of Nursing Unit Managers' Transformational Leadership: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 757. CrossRef - Clinical nurses’ beliefs, knowledge, organizational readiness and level of implementation of evidence-based practice: The first step to creating an evidence-based practice culture
Jae Yong Yoo, Jin Hee Kim, Jin Sun Kim, Hyun Lye Kim, Jung Suk Ki, Tim Schultz
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(12): e0226742. CrossRef - Relationship among Nursing Professionalism, Nursing Work Environment, and Patient Safety Nursing Activities in General Hospital Nurses
Mi-Aie Lee, Sunjoo Kang, Hye Sun Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(4): 317. CrossRef - Influence of Emotional Intelligence, Communication, and Organizational Commitment on Nursing Productivity among Korean Nurses
Hyo Geun Geun, Eunok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(2): 226. CrossRef - Impact of Burnout on Organizational Outcomes, the Influence of Legal Demands: The Case of Ecuadorian Physicians
Paola Ochoa
Frontiers in Psychology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Social Capital and Job Engagement on Nursing Performance: Focused on the Mediating effects of Organizational Citizenship Behavior
Mi Soon Ko, Hyunsook Zin Lee, Myung Suk Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 42. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Social capital between Transformational leadership and Organizational Commitment of Nurses in Hospitals
Soon-gu Kim, Young-sook Seo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 282. CrossRef - Relationship of between Task Performance, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Contribution of Dental Hygienists
Jun-Yeong Kwon, Su-Young Lee
Journal of dental hygiene science.2016; 16(4): 302. CrossRef - A Path Analysis of Variables Influencing customer orientation of Hospital Nurses
Eun-Su Do, Young-Sook Seo
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(1): 275. CrossRef - Nurses' Perception of Organizational Commitment, Nursing Work Environment, and Social Support in a General Hospital
Sook Bin Im, Mi Young Lee, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Clinical Nurses' Experience of Positive Organizational Culture
Young-Hee Yom, Sang Mi Noh, Kyung Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(5): 469. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Intensive Care Units Nursing Workload
Mohammad Karim Bahadori, Ramin Ravangard, Mehdi Raadabadi, Seyed Masod Mosavi, Mohammad Gholami Fesharaki, Fardin Mehrabian
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Hospital Nurses' Recognition of the Team System and Effects on the Nursing Organizational Team System
Kwang-ok Park, Sung Hee Park, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(4): 414. CrossRef
- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
- 1,531 View
- 10 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Individual and Environmental Factors Influencing Questionable Development among Low-income Children: Differential Impact during Infancy versus Early Childhood
- Gyungjoo Lee, Linda McCreary, Mi Ja Kim, Chang Gi Park, Soo Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(7):1039-1049. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.7.1039
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose From the holistic environmental perspective, individual and environmental influences on low-income children's questionable development were identified and examined as to differences in the influences according to the child's developmental stage of infancy (age 0-35 months) or early childhood (age 36-71 months).
Methods This study was a cross-sectional comparative design using negative binominal regression analysis to identify predictors of questionable development separately for each developmental stage. The sample was comprised of 952 children (357 in infancy and 495 in early childhood) from low-income families in South Korea. Predictors included individual factors: child's age and gender; proximal environmental influences: family factors (family health conditions, primary caregiver, child-caregiver relationship, depression in primary caregiver) and institution factors (daycare enrollment, days per week in daycare); and distal environmental influences: income/resources factors (family income, personal resources and social resources); and community factors (perceived child-rearing environment). The outcome variable was questionable development.
Results Significant contributors to questionable development in the infancy group were age, family health conditions, and personal resources; in the early childhood group, significant contributors were gender, family health conditions, grandparent as a primary caregiver, child-caregiver relationships, daycare enrollment, and personal resources.
Conclusion Factors influencing children's questionable development may vary by developmental stage. It is important to consider differences in individual and environmental influences when developing targeted interventions to ensure that children attain their optimal developmental goals at each developmental stage. Understanding this may lead nursing professionals to design more effective preventive interventions for low-income children.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between home motor affordances and motor skills in daycare and non-daycare attending children
Saeed Valadi
Early Child Development and Care.2022; 192(10): 1599. CrossRef - Recursos ambientais, tipos de brinquedos e práticas familiares que potencializam o desenvolvimento cognitivo infantil
Leiziane Pereira, Sabrina da Conceição Guedes, Rosane Luzia de Souza Morais, Juliana Nogueira Pontes Nobre, Juliana Nunes Santos
CoDAS.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A PRÁTICA DO ENFERMEIRO NA CONSULTA DE PUERICULTURA NA ESTRATÉGIA SAÚDE DA FAMÍLIA
Daniele de Souza Vieira, Nathanielly Cristina Carvalho de Brito Santos, João Agnaldo do Nascimento, Neusa Collet, Beatriz Rosana Gonçalves de Oliveira Toso, Altamira Pereira da Silva Reichert
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Affordances in the home environment for motor development: Validity and reliability for the use in daycare setting
Alessandra Bombarda Müller, Nadia Cristina Valentini, Paulo Felipe Ribeiro Bandeira
Infant Behavior and Development.2017; 47: 138. CrossRef
- Association between home motor affordances and motor skills in daycare and non-daycare attending children
- 1,129 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Multisensory Stimulation Using Familiarity: Persons with Dementia in Long-term Care Facility in Korea
- Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(4):528-538. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.528
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to examine the effects of multisensory stimulation (MSS) using familiarity on persons with dementia (PWDs) residing in nursing homes in Korea.
Methods A nonequivalent control group with pre and posttests was used. Fifty one PWDs were included if they: 1) were over 65 yr old, 2) were diagnosed with dementia, 3) had no visual or speech impairments, 4) were able to communicate, and 5) had spent more than one month in a nursing home. The experimental group (n=25) received a 55 min MSS program twice a week for 10 weeks. The outcome variables included were cognition, activities of daily living, grip strength, depression, wandering, and aggressive behaviors. Repeated ANOVA was used for data analysis.
Results There were no significant differences in demographics or the main variables at pretest. Cognition, depression, wandering, and aggressive behaviors were significant over time between the two groups. Grip strength was only significant when accounting for interaction between group and time.
Conclusion An intervention of MSS using familiarity was marginally effective in improving cognition, depression, wandering, and aggression. Future study is suggested with a larger sample and longer treatment to retest the effects of MSS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of multisensory environment/stimulation therapy on adults with cognitive impairment and/or special needs: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Meret Helbling, Marie‐Laure Grandjean, Murali Srinivasan
Special Care in Dentistry.2024; 44(2): 381. CrossRef - Personally tailored activities for improving psychosocial outcomes for people with dementia in long-term care
Ralph Möhler, Stella Calo, Anna Renom, Helena Renom, Gabriele Meyer
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomization controlled and nonrandomized controlled studies on nurse‐led nonpharmacological interventions to improve cognition in people with dementia
Yujin Suh, Sumi Lee, Go‐Eun Kim, JuHee Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3155. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological Intervention for Wandering Behavior in Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Yoojin Kim, Eunhee Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 321. CrossRef - A pragmatic trial testing a tailored non pharmacologic therapies on nocturnal behavioral and psychological symptoms associated with dementia
Thierry Bautrant, Caroline Franqui, Hossein Clément, Maurice Rabault, Faima Masseboeuf, Manon Pastore, Magali Pardo, Yannick Brandi, Nicolas Drouin, Anne-Daphnée Brice, Michel Grino
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 43: 85. CrossRef - The Development of Wholeness Program for Effects Dementia-Buffering Testing of the Demented Elderly
Hye-Jeon Hong
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(1): 405. CrossRef - Personally tailored activities for improving psychosocial outcomes for people with dementia in long-term care
Ralph Möhler, Anna Renom, Helena Renom, Gabriele Meyer
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of an educational tooth-brushing program using priming in an elderly population with dementia residing in nursing homes
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Jung-Soo Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(3): 149. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological interventions for agitation in dementia: systematic review of randomised controlled trials
Gill Livingston, Lynsey Kelly, Elanor Lewis-Holmes, Gianluca Baio, Stephen Morris, Nishma Patel, Rumana Z. Omar, Cornelius Katona, Claudia Cooper
British Journal of Psychiatry.2014; 205(6): 436. CrossRef
- Effects of multisensory environment/stimulation therapy on adults with cognitive impairment and/or special needs: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- 1,329 View
- 30 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Impact of Pro-environmental Behavior on Dysmenorrhea
- Hyun Kyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(2):236-244. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose In this study the impact of pro-environmental behavior, well-being oriented behavior, and use of cloth menstrual pads on dysmenorrhea in Korean female adults was examined according to the theory of reasoned action.
Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted with 195 Korean female adults. Data were collected from June to August, 2010 using self-report questionnaires. Data were analyzed using t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficients, multiple regression, and logit regression with STATA 10.0.
Results Pro-environmental behavior explained 48% of well-being oriented behavior. Well-being oriented behavior explained 10% of cloth pad use. Use of cloth pad explained 4% of dysmenorrhea and 5% of menstrual pain. The path through well-being oriented behavior had a significant effect from pro-environmental behavior to cloth pad use.
Conclusion Use of cloth pad was significantly related with well-being oriented behavior, pro-environmental behavior, social influence, dysmenorrhea, and menstrual pain. The results of this study suggest that pro-environmental strategies can help health care providers diminish clients' menstrual symptoms. Nursing intervention can support pro-environmental behavioral strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proposal of Mobile Application Service for a Sustainable Menstrual Experience
Min-Ju Park, Woo-Jeong Chon
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2022; 23(10): 1929. CrossRef - Effects of a dietary modification intervention on menstrual pain and urinary BPA levels: a single group clinical trial
SoMi Park, ChaeWeon Chung
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Behavior of Reducing Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Breastfeeding Mothers
Sun Hyang Kim, Eun-Young Jun
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 423. CrossRef - Health behaviors related to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and the associated factors of adolescent Korean girls
SoMi Park, ChaeWeon Chung
Women & Health.2018; 58(8): 915. CrossRef - Relationship between Menstrual Distress and Sleep Disturbance in Middle-school Girls
Se Yeong Park, SoMi Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 392. CrossRef
- Proposal of Mobile Application Service for a Sustainable Menstrual Experience
- 895 View
- 5 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Work-related Stress and Risk Factors among Korean Employees
- Eun Sook Choi, Yeongmi Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(4):549-561. Published online August 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.549
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Work-related stress and risk factors among Korean employees were identified in this study.
Methods Data were obtained from employees aged 20 to 64 using the Korean Working Conditions Survey 2006 (KWCS). Multiple logistic regression analysis using SAS version 9.1 was performed to examine risk factors of work-related stress by gender.
Results The age-adjusted prevalence of work-related stress among male and female employees was 18.4% and 15.1% respectively. After adjustments for multiple variables among both male and female employees, there was a significant relationship between work-related stress and risk factors including education, company size, work time, ergonomic risks, biological·chemical risks, and job demands. The significant variables for male employees were housework load, occupational class, and shift work, and for female employees, type of employment.
Conclusion There is a need to develop and support intensive stress management programs nationally giving consideration to work-related stress associated with working time, physical working environment, and job demands. Based on gender specific approaches, for male employes, stress management programs should be developed with consideration being given to occupational class and shift work. For stress management programs for female employees, consideration needs to be given to permanent employment status, specifically those in small companies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Occupational Stress on the Psychological Well-Being of Healthcare Workers: Basis for Stress Management Interventions
LOVELY V. ECHALAR
International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology (IJISRT).2024; : 391. CrossRef - The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 38. CrossRef - Associations of extended work, higher workloads and emotional work demands with sleep disturbance among night-shift workers
Bo Min Jeon, Su Hyun Kim
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological stress, smoking, and hazardous drinking behaviors in South Korea: findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyunjoon Lee, Harold H. Lee, Augustine Kang, Yoojin Cha, Don Operario
Journal of Substance Use.2021; 26(1): 13. CrossRef - Job Stress and Cardiometabolic Lifestyle Modification Behaviors Among Workers in High-risk and Low-risk Workplaces
Jiyeon Jung, Jina Choo, Sooyeon Park, Jihyun Moon, Songwhi Noh
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2021; 63(6): e346. CrossRef - Sex and Gender Differences in Occupational Hazard Exposures: a Scoping Review of the Recent Literature
A. Biswas, S. Harbin, E. Irvin, H. Johnston, M. Begum, M. Tiong, D. Apedaile, M. Koehoorn, P. Smith
Current Environmental Health Reports.2021; 8(4): 267. CrossRef - Effects of a Yoga Program in Reducing Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Workers of Small Workplaces: A Pilot Test
Won Ju Hwang, Jin Ah Kim, Ji Sun Ha
Sustainability.2020; 12(23): 10038. CrossRef - Impacts of family status and gender on the relationships between job demands, job control, and distress
Sehoon Kim, Hyounju Kang, Boreum Ju
European Journal of Training and Development.2019; 43(3-4): 322. CrossRef - Relationship between stress-related psychosocial work factors and suboptimal health among Chinese medical staff: a cross-sectional study
Ying-Zhi Liang, Xi Chu, Shi-Jiao Meng, Jie Zhang, Li-Juan Wu, Yu-Xiang Yan
BMJ Open.2018; 8(3): e018485. CrossRef - Association of stress, depression, and suicidal ideation with subjective oral health status and oral functions in Korean adults aged 35 years or more
Young Sun Kim, Han-Na Kim, Jung-Ha Lee, Se-Yeon Kim, Eun-Joo Jun, Jin-Bom Kim
BMC Oral Health.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating Role of Psychological Capital in Relationship between Occupational Stress and Turnover Intention among Nurses at Veterans Administration Hospitals in Korea
Hee-Yun Yim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Yoonhyung Cho, JinHee Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Association between supervisors’ behavior and wage workers’ job stress in Korea: analysis of the fourth Korean working conditions survey
Shin Uk Kang, Byeong Jin Ye, ByoungGwon Kim, Jung Il Kim, Jung Woo Kim
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Job Stress with Health-promoting Behaviors and Health Status in Clinical Nurses
Jung-Suk Kim, Chun-Ja Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 311. CrossRef - The psychosocial status of the family members of rheumatoid arthritis patients in Korea
Sang Wan Chung, You Jung Ha, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, Yeong Wook Song
Rheumatology International.2016; 36(5): 719. CrossRef - A Study on the Characteristics of Injured Workers Rate and Work Environment of Male Workers for over 40 years
Kil-Yong Choi, Kyung-Soo Yang
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2016; 10(1): 131. CrossRef - Effects of an internet-based lifestyle intervention on cardio-metabolic risks and stress in Korean workers with metabolic syndrome: A controlled trial
Chun-Ja Kim, Elizabeth A. Schlenk, Se-Won Kang, Jae-Bum Park
Patient Education and Counseling.2015; 98(1): 111. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Job Satisfaction of Road Freight Transportation Industry Workers by Type of Employment
Heon Jong YOO, Seung Bum AHN
Journal of Korean Society of Transportation.2015; 33(4): 368. CrossRef - Effect of Obesity and Psychological Stress on Oral Health
Soo-Hwa Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of dental hygiene science.2015; 15(2): 119. CrossRef - Association Night-Shift and Long Working-Hours Effects on Subjective Insomnia in Korean Workers: The Third Korean Working Conditions Survey
Chae-Bong Kim, Tae-Young Jung, Seoung-Min Han
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(1): 41. CrossRef - Under and Over Employment and Working Conditions
Kyung Yong Rhee, Se Wook Song, Young Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene.2014; 24(4): 536. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of the Metabolic Syndrome in the Korean Workforce
Dae Ryong KANG, Yeongmi HA, Won Ju HWANG
Industrial Health.2013; 51(3): 256. CrossRef - Health Status and Affecting Factors related to Job among Korean Women Employees
Eun-Young Hong, Sang-Dol Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(9): 4107. CrossRef - Influence of task demands on occupational stress: Gender differences
Susana García Herrero, Miguel Ángel Mariscal Saldaña, Javier García Rodriguez, Dale O. Ritzel
Journal of Safety Research.2012; 43(5-6): 365. CrossRef - Analysis on Stress and Dietary Attitudes of Male Employees
Mi-Ae Lee, Eun-Ju Lee, Hye-Kyung Soh, Bong-Soon Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(3): 337. CrossRef - Spirituality and Stress Responses in Small Industry Employees
Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 220. CrossRef - Health Behaviors by Job Stress Level in Large-Sized Company with Male and Female Workers
Hyunju Park, Hye-Sun Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 852. CrossRef
- The Effect of Occupational Stress on the Psychological Well-Being of Healthcare Workers: Basis for Stress Management Interventions
- 1,938 View
- 5 Download
- 26 Crossref

- The Effects of an Environmental Education with Newspaper in Education (NIE) on the Environmental Concern and Practice
- Ki-Wol Sung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(6):891-901. Published online December 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.6.891
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an environmental education program using newspaper articles in education (NIE) and to evaluate changes in concern and practice for environmental protection after NIE.
Methods The design was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants were university students in nursing, of which 31 were assigned to the experimental group and 43 to the control group. The education was carried out for 2 hr, once a week for 7 weeks. Data were analyzed with SPSS WIN 14 program, and included χ2 test, independent t-test, and repeated measure ANOVA.
Results NIE showed significant differences in the changes of attitude toward environment (F=4.461, p=.036).
Conclusion Findings suggest that this NIE in environmental education was effective in changing students' attitudes toward the environment. Therefore this NIE is recommended for inclusion in education for university students in nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Newspaper Reading in Families with School-Age Children: Relationship between Parent–Child Interaction Using Newspaper, Reading Motivation, and Academic Achievement
Naya Choi, Jiyeon Sheo, Suji Jung, Jisu Choi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(21): 14423. CrossRef - Nursing Students' Environmental Consciousness and Medical Waste Related Knowledge and Attitudes
Jae-Hyun Ha, Hyun Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(2): 174. CrossRef
- Newspaper Reading in Families with School-Age Children: Relationship between Parent–Child Interaction Using Newspaper, Reading Motivation, and Academic Achievement
- 1,029 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Wandering Behavior in Korean Elders with Dementia Residing in Nursing Homes
- Jun-Ah Song, Young Mi Lim, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):29-28. Published online February 28, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study investigated various factors relatied to wandering behavior of Korean elders with dementia (KED).
Methods A sample of 160 ambulatory residents with dementia from 14 long term care facilities was used to examine demographic, individual, cognitive, physical health, and environmental characteristics by comparing wanderers (N=108) to nonwanders (N=52). Subjects were evaluated by Korean versions of the Mini-mental State Exam (K-MMSE), the Physical and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (K-PIADL), and the Revised Algase Wandering Scale Nursing Home version (KRAWS-NH) along its six dimensions. Demographic and environmental data were also obtained. Independent sample t-tests, Chi-square test, Fisher's Exact tests, and ANCOVAs were used to examine differences between wanderers and nonwanders.
Results Wanderers were significantly (p<.05) older and had more limitations in K-PADL and K-IADL. The degree of overall wandering and certain features of wandering were significantly different (p<.05) by total number of residents in the facility, type of bedroom (i.e., "Ondol"), and color of bedroom and living-room walls (i.e., sky blue).
Conclusion Findings of this study may be useful in understanding wandering behavior of KEDs and thus developing more culturally specific management strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors Associated with Missing Incidents among Persons Living with Dementia: A Scoping Review
Hector Perez, Antonio Miguel Cruz, Noelannah Neubauer, Christine Daum, Aidan K. Comeau, Samantha Dawn Marshall, Elyse Letts, Lili Liu
Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement.2024; 43(3): 370. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological Intervention for Wandering Behavior in Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Yoojin Kim, Eunhee Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 321. CrossRef - A Relationship between Depression and Wandering in Community-Dwelling Elders with Dementia
Jae Gwon Jeong, Jun Ah Song, Kun Woo Park
Dementia and Neurocognitive Disorders.2016; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Validation of the Measure of Unmet Need For Dementia Family Caregivers For Korean Sample
Kyeonga Yoon, 손의성
Korean Journal of Gerontological Social Welfare.2015; null(70): 197. CrossRef - The Long-term Care Utilization of the Elderly with Dementia, Stroke, and Multimorbidity in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Soonman Kwon, Hongsoo Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(1): 90. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Dysphagia Assessment Tool and an Intervention Program for the Elderly in the Long-Term Care Facilities
Chi-Young Kim, Young-Mi Lee, Eun-Ho Ha
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(2): 685. CrossRef - Relationship between familiar environment and wandering behaviour among Korean elders with dementia
Gwi‐Ryung Son Hong, Jun‐Ah Song
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2009; 18(9): 1365. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Observable Indicators of Nursing Home Care Quality Evaluation Instrument
Jia Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 474. CrossRef
- Risk Factors Associated with Missing Incidents among Persons Living with Dementia: A Scoping Review
- 1,152 View
- 8 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Study on Exercise Behavior, Exercise Environment and Social Support of Middle-Aged Women
- Myoung-Ae Choe, Yang Sook Hah, Keum Soon Kim, Myungsun Yi, Jung-An Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):101-110. Published online February 28, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify exercise environments and social support associated with exercise behaviors in middle-aged women
Methods Subjects were 207 women aged between 41 and 59 yr in an urban community. The research instruments utilized in this study were exercise stages, exercise environments, exercise partners and social support scale. Subjects were given a self-report questionnaire. Data was analyzed using the SPSS Win program.
Results The subjects were in the stages of precontemplation (3.4%), contemplation (25.1%), preparation (40.6%), action (5.8%), and maintenance (25.1%). Subjects who engaged in regular exercise were 30.9%. The mean score of the exercise environment was 6.34. The mean score of social support was 21.28, and 65.7% of subjects had exercise partners. The score of the exercise environment was significantly associated with the exercise stage (p=.01). The number of exercise partners of regular exercise groups was significantly greater than that of non-regular exercise groups (p=.00). The score of social support of regular exercise groups was significantly greater than that of non-regular exercise groups (p=.00). The score of social support was significantly associated with the exercise stage (p=.00).
Conclusion Exercise environments and social support need to be considered in planning exercise programs to improve exercise behavior among middle-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of tai chi, ba duan jin, and walking on the mental health status of urban older people living alone: the mediating role of social participation and the moderating role of the exercise environment
Baoyuan Wu, Guoyan Xiong, Peng Zhang, Xiujie Ma
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention (LSI) Program on Health, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Middle-Aged Women
Su-Jin Jung, Seung-Ok Lee, Min-Jun Choi, Jun Heo, Soo-Wan Chae, Baik-Hwan Cho
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2022; 12(3): 127. CrossRef - Exploratory study on obesity among middle-aged women in rural areas based on the Socio-ecological Model
Heui Sug Jo, Jong Sun Lee, Su Mi Jung, Yuliya Dronina, Yu Kyung Park, Yang Jun Park
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2021; 38(5): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Health Status and Type of Health Management on Depression in Middle-Aged Women
Myung Sill Chung, Yeon Ha Kim, Kyung Choon Lim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2018; 24(3): 250. CrossRef - A Structural Analysis for Psychosocial Variables related to Sick Role Behavioral Compliance in Hemodialysis Patients
Young-Mun Cho
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(4): 415. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Perceived Health Status of Multiracial/Ethnic Midlife Women in the United States
Young Ko, Wonshik Chee, Eun-Ok Im
Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic & Neonatal Nursing.2016; 45(3): 378. CrossRef - Sex differences in social cognitive factors and physical activity in Korean college students
Jin Yi Choi, Ae Kyung Chang, Eun-Ju Choi
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2015; 27(6): 1659. CrossRef - Converged Influencing Factors on the Stages of Change of Exercise in Middle Aged Women
Hyea-Kyung Lee, Eun-Hee Shin, Yeon-Kyung Kim
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2015; 6(5): 187. CrossRef - Relationship between Expectations Regarding Aging and Physical Activity among Middle Aged Adults in Urban Areas: Based on the Pender's Health Promotion Model
Sung-Hye Cho, MoonKi Choi, JuHee Lee, Hyewon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 14. CrossRef - Effects of Social support based walking program on community
Hyun Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(7): 357. CrossRef - Construction of a Physical Activity Model for the Elderly
Nam-Hee Kim, Hyoung-Sook Park, Myunghan Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(1): 27. CrossRef - The Comparison between Physical Activity and Health Related Factors of the Korean Male Adult
Jisu Kim, Gyeongnam Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2012; 14(3): 166. CrossRef - Physical Activities and Related Factors among Low-income Middle-aged People
Seong-Mi Moon
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(1): 38. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Active Participation in Health Promotion Programs at a Public Health Center
Yeun-Ju Park, Hyun-Hee Park, So-Yeon Ryu
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2010; 35(3): 287. CrossRef - The Effects of Breast Self-examination Program Enriched Environmentally among Healthy Women
Kyung-Yeon Park, So Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 105. CrossRef - The Association Between Apolipoprotein E Genotype and Lipid Profiles in Healthy Woman Workers
Kieun Moon, Sook Hee Sung, Youn-Koun Chang, Il-Keun Park, Yun-Mi Paek, Soo-Geun Kim, Tae-In Choi, Young-Woo Jin
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2010; 43(3): 213. CrossRef - Health Promotion and Related Factors Among Korean Goose Mothers
Chiyoung Cha
Asian Nursing Research.2010; 4(4): 205. CrossRef - A Study on Exercise Performance and Its Relating Factors in Middle-aged Women
Sung-Jae Oh, Jeung-Im Kim, Young-Ran Chae
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 348. CrossRef
- Effects of tai chi, ba duan jin, and walking on the mental health status of urban older people living alone: the mediating role of social participation and the moderating role of the exercise environment
- 1,228 View
- 3 Download
- 18 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


