Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of an agro-healing program on depression, stress, and cognitive function in older adults: a quasi-experimental study
- Gyu Yeon Park, Kwang Ok Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):342-352. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
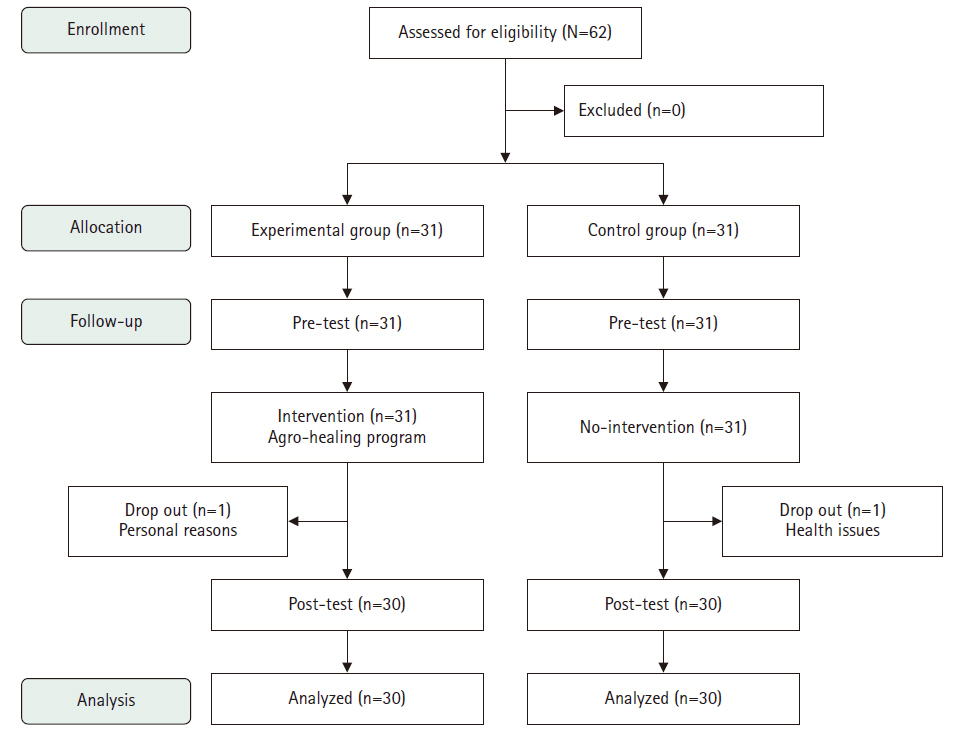
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of an agro-healing program on depression, stress, and cognitive function in older adults.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pretest–posttest design was used. The study was conducted from July 16 to September 6, 2024. Sixty-two individuals aged 65 or older residing in Gimcheon, Gyeongsangbuk-do, were recruited according to the selection criteria (31 in the experimental group and 31 in the control group). The final analysis included 30 participants in each group. The program was delivered by one main instructor (a healing farmer) and three assistants. The pretest assessed general characteristics, the Geriatric Depression Scale Short Form-Korean Version, Stress Response Inventory-Modified Form, and Cognitive Impairment Screening Test. The experimental group participated in the agro-healing program once a week for 90 minutes over 8 weeks. The posttest included the same measurements as the pretest. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0.
Results
The experimental group, which participated in the healing agriculture program, showed reduced depression (F=7.97, p=.007) and stress (F=282.70, p<.001) and improved cognitive function (F=10.12, p=.002) compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that the agro-healing program is an effective intervention for reducing depression and stress and improving cognitive function in older adults. We propose its use to promote health and prevent dementia in this population.
- 2,727 View
- 226 Download

- Development and Effects of a Person-Centered Fall Prevention Program for Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals: For Older Adults with Dementia and Caregivers in LongTerm Care Hospitals
- Jeong Ok Lim, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):341-358. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the effects of a person-centered fall prevention program for older adults with dementia in long-term care hospitals.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The study sample included 42 older adults with dementia (experimental group: 21, control group: 21) and 42 caregivers (experimental group: 21, control group: 21). The program comprised 48 sessions held over 12 weeks and included exercise intervention with resistance and balance, dance walking (45~60 min, three times/week), cognitive and emotional intervention (35~50 min, once per week), and person-centered fall prevention education (10 min, once per week). The program for caregivers consisted of six educational sessions (i.e., fall prevention competency enhancement and person-centered care strategy education, 80 min, once per week) for six weeks. Data were collected before participation and 12 weeks after program completion from February 18 to May 12, 2019. Data analysis was conducted using the chi-square test, t-test, and Mann―Whitney U test with SPSS/WIN 21.0.
Results
The experimental group of older adults with dementia showed significant improvement in physical and cognitive functions, and a decrease in depression, and behavioral and psychological symptoms, when compared with the control group. caregivers in the experimental group exhibited significant improvement in fall-related knowledge and person-centered care of older adults with dementia compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The study findings indicate that this program was effective as a nursing intervention for fall prevention among older adults with dementia in long-term care hospitals. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Affecting Fall Incidents at Long-term Care Hospitals: Using Data from the Korea Patient Safety Reporting and Learning System
Soojin Chung, Jeongim Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(1): 96. CrossRef - Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
Chengfei Duan, Mo Zhu, Xia Li, Ling Yue
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Trends of Exercise Programs for Improving Cognitive Function in Older Adults
Jae-Hyun Lee, Wooyeon Jo, Jaeho Jin, Yaxiong Zheng, Soyoon Lee, Se-Yeon Jang, Minseo Kim, Young-Jin Moon, Hye Gwang Jeong, Sang Ki Lee
Exercise Science.2024; 33(3): 254. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Dementia Care Competence among Care Staff: A Mixed-Methods Systematic Review Protocol
Jinfeng Zhu, Jing Wang, Bo Zhang, Xi Zhang, Hui Wu
Healthcare.2024; 12(11): 1155. CrossRef - Falls in Patients of Medical Institutions in South Korea: A Literature Review
Jongwon Choi, Woochol Joseph Choi
Physical Therapy Korea.2023; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - A Study on Emotions to Improve the Quality of Life of South Korean Senior Patients Residing in Convalescent Hospitals
Aeju Kim, Yucheon Kim, Jongtae Rhee, Songyi Lee, Youngil Jeong, Jeongeun Lee, Youngeun Yoo, Haechan Kim, Hyeonji So, Junhyeong Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(21): 14480. CrossRef
- Factors Affecting Fall Incidents at Long-term Care Hospitals: Using Data from the Korea Patient Safety Reporting and Learning System
- 2,763 View
- 175 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of Virtual Reality Program for Alleviating Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia Patients
- Seon-Min Park, Seung-Yi Choi, Jung-Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):121-133. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the impact of a virtual reality intervention program based on psychological needs on behavioral and psychological symptoms, apathy, and quality of life (QOL) in patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment living in nursing facilities.
Methods
This study is nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design of quasi-experimental study. The study collected data from November 18, 2020 to July 24, 2021 from patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment (30 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group) at three nursing facilities in G city using self-reporting and caregiver-informant reporting methods. The analysis employed the chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, paired t-test, independent t-test, Wilcoxon signed rank test, Mann–Whitney U, repeated measures ANOVA, GEE, using SPSS/WIN 27.0.
Results
The severity of behavioral and psychological symptoms (Wald χ2 = 2.68, p = .102) and the care burden of caregivers (Wald χ2 = 1.72, p = .190) were not significant and was no significant time and group interaction effect (Wald χ2 = 0.63, p = .426, Wald χ2 = 0.52, p =. 471). The difference in apathy and QOL score were statistically significant for the group-time interaction (F = 43.65, p < .001; F = 4.35, p= .041).
Conclusion
The virtual reality intervention program of this study shows a positive effect on the apathy reduction and QOL of patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment residing in nursing facilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for elderly dementia patients based on virtual reality technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jun Wen, Hong Yan, Siyu Wang, Jialan Xu, Zitong Zhou
Ageing Research Reviews.2024; 93: 102135. CrossRef - Development of the “living well” concept for older people with dementia
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for elderly dementia patients based on virtual reality technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 2,053 View
- 100 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Influence of Self-care on Burnout in Primary Family Caregiver of Person with Dementia
- Jeong Hwa Kwon, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):217-231. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20274
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the influence of self-care on burnout experienced by primary family caregivers of persons with dementia.
Methods
The subjects of the study were 156 primary family caregivers of persons with dementia at home in Korea. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, independent t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient, and hierarchical multiple regression using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 24.0 for Windows.
Results
The mean scores for self-care and burnout were 42.35 and 61.60, respectively. Self-care, subjective health status, living with a person with dementia, and behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia were significant factors affecting burnout in family caregivers. Self-care was identified as the strongest factor affecting burnout, explaining 13.9% of burnout with controlling factors in caregivers and care receivers.
Conclusion
To prevent burnout in primary family caregivers of persons with dementia, self-care of family caregivers should be emphasized. In nursing education, family caregivers should be recognized and approached as nursing clients who are responsible for taking care of their health. In nursing practice and research, digital self-care or self-care improvement intervention programs should be designed to help family caregivers, and further studies on self-care centered on health of family caregivers should be conducted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Tool to Measure Slow Nursing for Older Adults in Long-term Care Hospitals: A Methodological Study
Hyeon Mi Woo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 212. CrossRef - Factors influencing the care burden among family caregivers using dementia care centers for older adults with dementia in Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
Ja Eun Kim, Soo Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(4): 382. CrossRef - Effects of stress on burnout among infection control nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating effects of social support and self-efficacy
Su-jin Lee, Ju-Young Park, Seo-Hyeon Kim
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Survey on Tele-Rehabilitation Therapy Awareness Among Primary Caregivers of Dementia Patients
Ae-Lyeong Kwon, Hye-Jin Jang, Ki-Jeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(6): 190. CrossRef - Time usage analysis according to occupational area and satisfaction level in family caregivers of dementia patients
Woo-Hyuk Jang, Jong-Sik Jang, Jong-Hwi Park
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15178. CrossRef - Self-Care Experiences of Family Members of Mentally Ill Patients
Won Hee Jun, Eun Ju Cho, Eun Joung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(4): 458. CrossRef
- Development of a Tool to Measure Slow Nursing for Older Adults in Long-term Care Hospitals: A Methodological Study
- 3,905 View
- 148 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of Ghrelin on Memory Impairment in a Rat Model of Vascular Dementia
- Jong-Min Park, Youn-Jung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):317-328. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of ghrelin on memory impairment in a rat model of vascular dementia induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
Methods Randomized controlled groups and the posttest design were used. We established the representative animal model of vascular dementia caused by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion and administered 80 μg/kg ghrelin intraperitoneally for 4 weeks. First, behavioral studies were performed to evaluate spatial memory. Second, we used molecular biology techniques to determine whether ghrelin ameliorates the damage to the structure and function of the white matter and hippocampus, which are crucial to learning and memory.
Results Ghrelin improved the spatial memory impairment in the Y-maze and Morris water maze test. In the white matter, demyelination and atrophy of the corpus callosum were significantly decreased in the ghrelin-treated group. In the hippocampus, ghrelin increased the length of hippocampal microvessels and reduced the microvessels pathology. Further, we confirmed angiogenesis enhancement through the fact that ghrelin treatment increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-related protein levels, which are the most powerful mediators of angiogenesis in the hippocampus.
Conclusion We found that ghrelin affected the damaged myelin sheaths and microvessels by increasing angiogenesis, which then led to neuroprotection and improved memory function. We suggest that further studies continue to accumulate evidence of the effect of ghrelin. Further, we believe that the development of therapeutic interventions that increase ghrelin may contribute to memory improvement in patients with vascular dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the mechanism of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves in the treatment of vascular dementia based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation
Jienuo Pan, Jiqin Tang, Jialin Gai, Yilan Jin, Bingshun Tang, Xiaohua Fan
Medicine.2023; 102(21): e33877. CrossRef - Quercetin Alleviates Demyelination Through Regulating Microglial Phenotype Transformation to Mitigate Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Mice with Vascular Dementia
Zihu Tan, Guang Yang, Jing Qiu, Wenjing Yan, Yu Liu, Zhengling Ma, Jia Li, Jing Liu, Nan Shan
Molecular Neurobiology.2022; 59(5): 3140. CrossRef - Effect of Obesity on Cognitive Impairment in Vascular Dementia Rat Model via BDNF-ERK-CREB Pathway
Yoonju Kim, Youn-Jung Kim
Biological Research For Nursing.2021; 23(2): 248. CrossRef - Ghrelin treatment leads to dendritic spine remodeling in hippocampal neurons and increases the expression of specific BDNF-mRNA species
M.L. Perea Vega, M.S. Sanchez, G. Fernández, M.G. Paglini, M. Martin, S.R. de Barioglio
Neurobiology of Learning and Memory.2021; 179: 107409. CrossRef
- Exploring the mechanism of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves in the treatment of vascular dementia based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation
- 1,187 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Reminiscence Therapy on Depressive Symptoms in Older Adults with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Kyungsoo Kim, Jia Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):225-240. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.225
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of reminiscence therapy on depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from January 2000 to January 2018 were searched through Research Information Sharing Service (RISS), Korean Studies Information Service System (KISS), Korean Medical Database (KMbase), KoreaMed, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), and Ovid MEDLINE. Two researchers independently performed the search, selection, and coding. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis 3.0 was used for meta-analysis, and Review Manager program 5.3 was used for quality assessment.
Results Out of the 1,250 retrieved articles, 22 RCTs were selected for analysis. The overall effect size of reminiscence therapy for mitigating depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia was -0.62 (95% Cl: -0.92 to -0.31). The effect size was greater in older adults under 80, those with less disease severity, and those for whom the therapy session lasted less than 40 minutes.
Conclusion Reminiscence therapy is an effective non-pharmacological therapy to improve depressive symptoms in older adults with dementia. Because its effectiveness is also influenced by age, disease severity, and application method, it is necessary to consider treatment designs based on individual characteristics as well as methodological approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Group reminiscence therapy interventions in non-clinical older adults: A systematic review
Ali Eryılmaz, Emre Yıldırım, Hacer Yıldırım Kurtulus, Murat Yıldırım
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 63: 35. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Influence of Garden Therapy on Memory Decline and Depression in Older Adults with Cognitive Impairments
Chohye Youn, Minji Kang, Hyejin Kim, Hyeyoon Kim, Jiyun Choi, Suyeon Lee, Juyoung Lee
Journal of Environmental Science International.2025; 34(3): 125. CrossRef - Mental health and treatment challenges in older adults
Ken Laidlaw, Georgina Charlesworth, Sunil Bhar
Nature Reviews Psychology.2025; 4(11): 737. CrossRef - Effects of reminiscence interventions on depression and anxiety: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Martin Pinquart
Aging & Mental Health.2024; 28(5): 717. CrossRef - Effects of reminiscence therapy on quality of life and life satisfaction of the elderly in the community: a systematic review
Eunyoung Shin, Myeongshin Kim, Seyoon Kim, Sohyune Sok
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcultural Pilot Study of the Efficacy of Reminiscence Therapy for Mexican and Spanish Older Adults with Different Levels of Cognitive Decline
Alba Villasán-Rueda, Antonio Sánchez-Cabaco, Manuel Mejía-Ramírez, Rosa Marina Afonso, Eduardo Castillo-Riedel
Journal of Cross-Cultural Gerontology.2023; 38(4): 371. CrossRef - Cross-cultural effects of reminiscence therapy on life satisfaction and autobiographical memory of older adults: a pilot study across Mexico and Spain
Alba Villasán Rueda, Antonio Sánchez Cabaco, Manuel Alejandro Mejía-Ramírez, Rosa Marina Afonso, Eduardo Castillo-Riedel
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of group reminiscence therapy based on Chinese traditional festival activities (CTFA-GRT) on loneliness and perceived stress of rural older adults living alone in China: a randomized controlled trial
Shasha Li, Yanyan Dai, Yuqiu Zhou, Jiayuan Zhang, Chiteng Zhou
Aging & Mental Health.2022; 26(7): 1377. CrossRef - Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms and Associated Factors in Community-Dwelling Persons at the First Time of Dementia Diagnosis
Gijung Jung, Jia Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 7765. CrossRef
- Group reminiscence therapy interventions in non-clinical older adults: A systematic review
- 2,417 View
- 54 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Communication Behavior Scale for Nurses Caring for People with Dementia
- Jihye Lee, Moonhee Gang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):1-13. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and validate the Communication Behavior Scale for nurses caring for people with Dementia (CBS-D).
Methods Based on communication accommodation theory, the initial items were generated through a literature review and interviews with 20 experts. Content and face validity of the initial items were assessed. Data from 486 nurses caring for people with dementia were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, criterion-related validity, and internal consistency.
Results The final scale consisted of 18 items and four factors (discourse response management, interpersonal control, emotional expression, and interpretability) that explained 57.6% of the variance. Confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the theoretical model with 18 items satisfied all goodness-of-fit parameters. Criterion-related validity was shown by the Global Interpersonal Communication Competence Scale (
r =.506,p <.001). Cronbach's alpha for the total scale was .88.Conclusion The CBS-D can be used to measure the communication behavior of nurses caring for people with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Soo Yeon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(2): 269. CrossRef - The influence of socio-cognitive mindfulness, moral sensitivity and dementia communication behaviors on dementia nursing performance of nurses in long-term care hospitals: a cross-sectional study
Hyun Ju Bong, Mikyoung Lee
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing shared decision-making in long-term care facilities
Da Eun Kim, Min Jung Kim
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing students' experiences as dementia partners in volunteer activities: An inductive content analysis
Dooree Kim, Yunhee Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(2): 146. CrossRef
- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- 2,183 View
- 63 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Shifting of Centricity: Qualitative Meta Synthetic Approach on Caring Experience of Family Members of Patients with Dementia
- Young Mi Ryu, Mi Yu, Seieun Oh, Haeyoung Lee, Haejin Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):601-621. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.601
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to synthesize the caring experiences of Korean family members of patients with dementia through a qualitative meta-synthesis method.
Methods By searching through nine Korean and English databases, we compared 37 qualitative studies on caring experiences of family members of patients with dementia. The selected studies were synthesized through meta-synthesis, proposed by Sandelowski and Barroso (2007).
Results The meta-synthesis elicited four themes: tough life due to care for patients, changes in relationships, adaptation to caregiver's roles, and new perspectives of life through personal growth. Caregivers were shocked when a sudden diagnosis of dementia was made prior to any preparation on their part. They were tied to their patients all the time and their mind and body got exhausted. Their relationship with patients began to change and they looked at them differently. They experienced conflicts with the other non-caring family members and were alienated from them. They were also socially isolated. However, by building their own care strategies and utilizing social resources, they gradually adapted to their caregiver roles. Finally, they experienced personal growth and acquired a new perspective toward life by accepting their roles and finding meaning in their lives. Shifting the caregiver's centricity from themselves to the patient was the process of becoming human beings who actively constructed their realities while giving meaning to their painful lives and interacting with the environment.
Conclusion The results of the study can be useful for nurses in understanding the experiences of caregivers of the patients with dementia and in providing them with practical interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A qualitative meta-synthesis of the essence of patient experiences of dialysis
Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Yoonhee Seok
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 119. CrossRef - Self-care experiences of male spouses of people with dementia: a descriptive phenomenological study
Sua Jung, Jun-Ah Song
Aging & Mental Health.2025; 29(7): 1329. CrossRef - Time Usage and Satisfaction Based on Occupational Area Between Weekdays and Weekends of Family Caregivers and Non-family Caregivers of Dementia Patients
Woo-Hyuk Jang, Jong-Hwi Park
Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology.2024; 27(5): 543. CrossRef - Health and medical experience of migrant workers: qualitative meta-synthesis
Hyun-Jin Cho, Kyoungrim Kang, Kyo-Yeon Park
Archives of Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Time usage analysis according to occupational area and satisfaction level in family caregivers of dementia patients
Woo-Hyuk Jang, Jong-Sik Jang, Jong-Hwi Park
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15178. CrossRef - Factors related to depression in primary caregivers of older adults with dementia in the COVID-19 pandemic era: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Su-In Kim, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(4): 420. CrossRef - Partners' Experience of Informal Caregiving for Patients With Heart Failure
Zequan Wang, Christine Tocchi
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2023; 38(2): E40. CrossRef - Caring Experience of Spouse Caregivers of Persons with Alzheimer's Disease: A Qualitative Study
Jin-Hee Lee, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 257. CrossRef - Korean Family Caregivers' Experiences With Managing Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Keeping Harmony in Daily Life
Jiyeon Kim, Jun-Ah Song, Sua Jung, Hongjin Cheon, Jiyeon Kim
Research in Gerontological Nursing.2022; 15(3): 141. CrossRef - Family Caregiver Suffering in Caring for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Korea
Juyeon Oh, Jung-A Kim, Min Sun Chu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(9): 4937. CrossRef - Relationship between Caring Burden and Caring Behavior among Family Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia in Community-Dwelling: Mediating Effects of Caring Self-Efficacy and Social Support
Young Ju Oh, Myung Ha Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(2): 186. CrossRef - Family Members’ Experience in Caring for Elderly with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals
Eun Kyoung Suh, Hye Ryoung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 335. CrossRef - Caring experiences of family caregivers of patients with heart failure: A meta-ethnographic review of the past 10 years
Eun Young Kim, Seieun Oh, Youn-Jung Son
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2020; 19(6): 473. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Care Burden among Family Caregivers for Elders with Dementia: Focusing on Family Caregivers using a Support Center for Dementia
Kyung Choon Lim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 136. CrossRef
- A qualitative meta-synthesis of the essence of patient experiences of dialysis
- 2,388 View
- 156 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Development and Effects of a Coping Skill Training Program for Caregivers in Feeding Difficulty of Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Facilities
- Hyun Hwa Hong, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):167-181. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose We developed and tested the effects of a coping skill training program for caregivers in feeding difficulty among older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The subjects comprised 34 caregivers (experimental group: 17, control group: 17) and 40 older adults with dementia (experimental group: 20, control group: 20). The developed program was delivered in 4-hour sessions over 6 weeks (including 2 weeks of lectures and lab practice on feeding difficulty coping skills, and 4 weeks of field practice). Data were collected before, immediately after, and 4 weeks after the program (January 3 to April 6, 2016). The data were analyzed using t-test and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results Compared to their counterparts in the control group, caregivers in the experimental group showed a significantly greater improvement in feeding knowledge and feeding behavior, while older adults with dementia showed greater improvements in feeding difficulty and Body Mass Index.
Conclusion The study findings indicate that this coping skill training program for caregivers in feeding difficulty is an effective intervention for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mealtime Support by Direct Care Workers in Long‐Term Care Facilities: Secondary Behavioural Analysis of Videos
Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Soogyung Shin, Dukyoo Jung
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility of a nurse-led online video intervention for mealtime assistance in dementia care: a quasi-experimental mixed-methods study
Dukyoo Jung, Leeho Yoo, Soogyung Shin, Sukyung Byeon, Hyein Seo, Eunju Choi
BMC Geriatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
Chengfei Duan, Mo Zhu, Xia Li, Ling Yue
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting Mealtime Difficulties in Older Adults with Dementia Living in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Multilevel Model Analysis
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C. De Gagne, Hyesoon Lee, Leeho Yoo, Jisung Park, Eunju Choi, Yonggang Zhang
Journal of Nursing Management.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Case-Based Small-Group Learning on Care Workers’ Emergency Coping Abilities
Soon-Ok Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11458. CrossRef - Eating Difficulties among Older Adults with Dementia in South Korean Long-Term Care Facilities: A Scoping Review
Dukyoo Jung, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 470. CrossRef Feasibility of a Mobile Meal Assistance Program for Direct Care Workers in Long-Term Care Facilities in South Korea
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C De Gagne, Minkyung Lee, Hyesoon Lee, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi, Juyoun Chung
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2020; Volume 15: 2019. CrossRef- Informal dementia caregivers’ experiences and perceptions about mealtime care: A qualitative evidence synthesis
Yijing Li, Dan Sun, Xu Zhang, Huanhuan Li, Yingnan Zhao, Dongfei Ma, Zehui Li, Jiao Sun
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2020; 76(12): 3317. CrossRef
- Mealtime Support by Direct Care Workers in Long‐Term Care Facilities: Secondary Behavioural Analysis of Videos
- 976 View
- 19 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Predictors of Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Based on the Model of Multi-Dimensional Behavior
- Jeong Eun Yang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):143-153. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify factors predicting behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) in persons with dementia. Factors including the patient, caregiver, and environment based on the multi-dimensional behavioral model were tested.
Methods The subjects of the study were 139 pairs of persons with dementia and their caregivers selected from four geriatric long-term care facilities located in S city, G province, Korea. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, inverse normal transformations, Pearson correlation coefficients, Spearman's correlation coefficients and hierarchical multiple regression with the SPSS Statistics 22.0 for Windows program.
Results Mean score for BPSD was 40.16. Depression (β=.42,
p <.001), exposure to noise in the evening noise (β=-.20,p =.014), and gender (β=.17,p =.042) were factors predicting BPSD in long-term care facilities, which explained 25.2% of the variance in the model.Conclusion To decrease BPSD in persons with dementia, integrated nursing interventions should consider factors of the patient, caregiver, and environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The influence path of caregivers’ positive aspects, expressed emotion and coping style on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
Shuang Zhang, Xiumei Ying, Shuyan Fang, Wenxia Wang, Xiangning Zhu, Yueyang Dong, Meng He, An Chang, Jiao Sun
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 44: 143. CrossRef
- The influence path of caregivers’ positive aspects, expressed emotion and coping style on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
- 1,095 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Korean Family Caregivers' Perceptions of Care in Dementia Care Units
- Myonghwa Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):967-976. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.967
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the demanding level of care needed for people with dementia, more Korean families are institutionalizing their relatives with dementia. This presents particular concerns for the Korean culture that values family responsibility for elder care. The purpose of this study was to describe Korean family members' perceptions of stress and satisfaction with care, the caregiving role, the family-staff relations. A purposive sample of 94 family members in 10 long-term care dementia care facilities in Korea participated in the study. Family Perceptions of Care Tool and Family Perceptions of Caregiving Role developed by Maas and Buckwalter (1990) were used to investigate Korean family caregivers' perceptions of care. Findings from the study can be summarized as follows: a) family caregivers showed the lowest satisfaction level for staff management effectiveness, especially for facility's resources available for care, and (b) family caregivers showed the highest stress from staff members' control on caregiving, feeling the same responsibilities after placement, and guilt over their placement. The results contribute to the understanding of Korean family caregivers' perceptions of caregiving and the care relationship after institutionalizing their elderly persons with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between guilt feelings, conflicts with staff and satisfaction with care in relatives of nursing home residents with dementia: A longitudinal analysis
Laura Gallego-Alberto, Hanneke JA Smaling, Anneke L Francke, Tim van de Brug, Jenny T van der Steen, Karlijn J Joling
Dementia.2022; 21(1): 5. CrossRef - Predictors of Satisfaction with Care Services among Family Members of Older Adult Residents of Long-Term Care Facilities
Eun-Ok Song, Hye-Young Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3298. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Scale for Partnership in Care—for Family (SPIC-F)
Hye-Young Jang, Eun-Ok Song
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(6): 1882. CrossRef - How do nurses recognize subtle signs of stroke and minimize serious damage in older residents of nursing homes?
Eunyoung Park, Mi So Kim, Ki No Kang, Su Jung Lee, Sung Ok Chang
Collegian.2016; 23(2): 143. CrossRef - Delusions of Korean patients with Alzheimer's disease: Study of drug‐naïve patients
Yong Tae Kwak, YoungSoon Yang, Soon‐Gu Kwak, Min‐Seong Koo
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2013; 13(2): 307. CrossRef - Nursing Staff Stress From Caregiving and Attitudes Toward Family Members of Nursing Home Residents With Dementia in Korea
Myonghwa Park
Asian Nursing Research.2010; 4(3): 130. CrossRef - Residential and Caregiver Preferences of Older Korean Americans
Dong-soo Shin
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2008; 34(6): 48. CrossRef - Interventions for Residents with Dementia and Their Family and Staff Caregivers: Evaluating the Effectiveness of Measures of Outcomes in Long-Term Care
Janet K Pringle Specht, Myonghwa Park, Meridean L Maas, David Reed, Elizabeth Swanson, Kathleen C Buckwalter
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2005; 31(6): 6. CrossRef
- The relationship between guilt feelings, conflicts with staff and satisfaction with care in relatives of nursing home residents with dementia: A longitudinal analysis
- 867 View
- 3 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Review of the Effects of Respite Care for Patients with Dementia and Caregivers
- Jin Sun Kim, Eun Hyun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(6):1077-1087. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.1077
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to analyze the effects of respite care. The analysis was conducted by reviewing published intervention studies on the effects of formal respite care for caregivers of dementia patients, patients with dementia, and the prevented or delayed rate of institutionalization of the patients.
METHOD
Two computerized databases (MEDLINE, CINAHL) were searched to find respite care-related articles published from the year of 1981 to 2000. A total of 49 published articles were identified. Of them, nine studies, which met for the inclusion criteria of this study, were included.
RESULTS
Results revealed that there was little evidence of the effect of respite care on, not only caregivers' burden, stress, depression and well-being, but also the rate of institutionalization of the patients. It was noteworthy that dementia patients reported fewer problems in behavior, although cognitive functioning and activity of daily living abilities continued to decline. However, these findings should be carefully interpreted because of methodological problems, such as non-random sampling, non random group assignment, a small sample size, uncontrolled confounding variables, limited period of services, and no specific types of services.
CONCLUSION
It is recommended to conduct intervention studies of respite care being conducted in Korea with the corrections of methodological problems suggested from this study.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Relevant to Life Satisfaction of Female Caregivers for the Elderly: Focused on Long-Term Care Insurance Settlement
Sang-Nam Jeon, Hak-Gene Shin
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2014; 8(4): 187. CrossRef - An Analysis of the Meaning of Respite for Family Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia
Mi Ryeong Song, Yong-Mi Lee, Suk-Hee Cheon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 482. CrossRef
- Factors Relevant to Life Satisfaction of Female Caregivers for the Elderly: Focused on Long-Term Care Insurance Settlement
- 662 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Study on ADL and Dementia of Aged Person with Medicaid in Korea
- Ho Sihn Ryu
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(1):139-149. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.1.139
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to analyze characteristics related to the activity of Daily Living (ADL) and dementia among the elderly people who have Medicaid. The cross-sectional descriptive survey study was a nationwide randomization sampling among the population of elderly families who have Medicaid. The data were collected during the month of October, 1999 and total sample was 1,027 elderly people. There were major findings according to the studies. In the results of the ADL assessment most of elderly people were within the 24 to 45 point range. Also, 63.3% of elderly people who made 45 points do not need help when performing daily activities according to the 15 areas of activity components, and 4.9% of these people couldn't do their daily activities. The results of the Dementia assessment were 70.6% of elderly people were in the normal range, 21.7% have a mild case, and 2.8% have severe case of dementia. These were found by using instruments for mental states, which simplified to items of detection of early dementia. In the result of these tests, there was a significantly positive correlation between ADL and degree of dementia with the pearson correlation coefficients. As a result of these studies, the author recommend to strengthen function and organization of public health like a visiting nurse center for elderly people who are over 65 years old. In addition, the government should apply early detection and management system for dementia in the community continuously and cost-effectively, especially for elderly people who live alone and are vulnerable elderly as our priority.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Depressive symptoms in individuals with family members requiring ADL assistance
Junhyun Kwon, Eun-Cheol Park, Woorim Kim, Dong-Woo Choi, Sung-In Jang
Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of a Multimodal Interventional Program on Cognitive Function, Instrumental Activities of Daily Living in Patients With Mild Alzheimer’s Disease
Min-Joo Ham, Su-Kyoung Kim, Doo-han Yoo, jae Shin Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2018; 26(1): 91. CrossRef - The Effects of Activity in Rhythem Movement on Depressive Mood, Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms in Elderly with Mild Alzheimer’s Disease
홍혜전
Official Journal of the Koeran Society of Dance Science.2016; 33(2): 97. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Factors Influencing the Life Satisfaction of the Elderly According to their Cognitive Impairment Level
Rah Il Hwang, Ji Young Lim, Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 622. CrossRef - Activity Intolerance and Impaired Physical Mobility in Elders
Hea‐Kung Hur, So‐Mi Park, So‐Sun Kim, Margaret J. Storey, Gi‐Yon Kim
International Journal of Nursing Terminologies and Classifications.2005; 16(3-4): 47. CrossRef
- Depressive symptoms in individuals with family members requiring ADL assistance
- 720 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- The Experience of Nursing Staff on the Dementia Patients' Aggressive Behavior
- Jin Joo Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):293-306. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.293
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Providing care to the dementia elderly with behavioral problem is a major issue in nursing homes today. This study was aimed to explore the nursing staffs' response to aggressive dementia patients, and the effect that the aggressive behavior had on Nsgstaff. The interviews used a semi-structured questionnaire are were carried out from May to July, 1999. The subjects were 23 nursing personnel working in the nursing homes for dementia elderly. The result are as follows; 1. The types of aggressive behavior cited by the subjects was "physical", "linguistic", and "sexual". 2. The factors that caused the behavior were "symptoms of disease", "under- conditioning", "context of nursing care", "unsatisfied need", "relationship to other patients", "change of outer environment", and "invasion of one's own privacy". 3. The response of the subjects were "unhappiness", "stress", "anger", "exaggeration", "anxiety", and "fear". 4. The management strategies listed by nursing personnel used to alleviate aggressive behavior were "ignorance" "patience" "leaving the area" "soothing sounds" "verbal punishment" "restriction and isolation" and "various management skill appliance" "adaptation". 5. The effect that aggressive behavior and were "disturbance of relationship to elderly" "decline in the amount and quality of nursing care" "interruption of task performance" "job exhaustion" "desire to leave the job" "physical impact" "stress on the cognition of others" "anxiety about health and one own future" "interference to family life'. The findings of this study will be useful in understanding the difficulties of nursing personnel when confronting the aggressive behavior of dementia partients. It also is useful as basic data in preparing efficient intervention program for these difficulties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors related to aggressive behaviors among older adults in nursing homes of Korea: A cross-sectional survey study
Hyoungshim Choi, Young-Il Jung, Hongsoo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2018; 88: 9. CrossRef - Extraction and Analysis of Risk Elements for Korean Homecare Patients with Senile Dementia
Mi-Hyun Choi, Hyung-Sik Kim, BoSeong Kim, Jung-Chul Lee, Sung-Jun Park, Ul-Ho Jeong, Ji-Hye Baek, Hyun-Jun Kim, Dae-Woon Lim, Soon-Cheol Chung
The Journal of Behavioral Health Services & Research.2016; 43(1): 116. CrossRef - Coping with dementia related behavior problems of the elderly and care providers
Dong Young Lim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(7): 4805. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Job Satisfaction of Nurses Working in Long-term Care Hospitals: Focused on Burnout and Burden for Caring Problematic Behaviors in Dementia
Ji Won Park, Eun Joung Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7403. CrossRef - Agitation in Home-dwelling Persons with Dementia and Coping Behaviors in Primary Care-givers to the Agitation
Hye Suk Kim, Heeok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(3): 256. CrossRef - Effects of an Educational Program for the Reduction of Physical Restraint Use by Caregivers in Geriatric Hospitals
Keumbong Choi, Jinsun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 769. CrossRef - Wandering behaviour of persons with dementia in Korea: Investigation of related factors
Jun-Ah Song, Young Mi Lim, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Aging & Mental Health.2008; 12(3): 366. CrossRef
- Factors related to aggressive behaviors among older adults in nursing homes of Korea: A cross-sectional survey study
- 739 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The Effect of Reminiscence with Audio-Visual Stimulation on Senile Dementia
- Nam Cho Kim, Yang Sook Yoo, Sook Won Hahn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(1):98-109. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.1.98
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify the effect on improvement of the Activity of Daily Living (ADL) and decrease the cognitive function and agitation behaviors by reminiscence with audio-visual stimulation for senile dementia. The quasi-experimental design was used in this study. Subjects were 26 with mild senile dementia who were cared for at a Day Care Center for Dementia in Seoul. The data were collected from March to July, 1999. Subjects were divided into three groups: Control I group with 10 subjects, reminiscence group(Control II group with 8 subjects), and reminiscence with audio-visual stimulation group(experimental group with 8 subjects). The Control I group got routine care as usual. Control II group participated in reminiscence sessions for one hour a day, five times a week, for a period of 4 weeks. The experimental group participated in reminiscence with audio-visual stimulation sessions for one hour a day, five times a week, for a period of 4 weeks. Instruments of this study were color photography with sound that was developed through an open questionnaire about events, objects, humans in action and animals that 100 Korean elderly over 60 would like to memorize. This was referred from the Sensory Stimuli Package by Namazi and Haynes(1994). The effects of treatment was evaluated through MMSE-K by Kwon & Park(1989). Also the Brief Cognitive Rating Scale(BCRS) by Reisberg et al(1983) for the cognitive function, through Agitation Inventory by Cohen- Mansfield and Colleague(1989) for behavioral response and through the Rapid Disability Rating Scale-2(RDRS-2) by Linn & Linn(1982) for the activity of daily living respectively. Data analysis was done using SPSS for X2-test, ANOVA, repeated measures ANOVA. The results were as follows : 1. Reminiscence with audio-visual stimulation did not improve cognitive function for senile dementia, but significantly improved verbal expression, the subscale of cognitive function. 2. Reminiscence with audio-visual stimulation reduced agitation behavior of experimental group significantly, but there was no significant difference between groups. 3. Reminiscence with audio-visual stimulation did not significantly effect the activity of daily living after treatment. In conclusion, it was shown that the reminiscence with audio-visual stimulation was an effective therapy to improve verbal expression and to reduce agitation behaviors of senile dementia. Further research with more indepth approach is needed, considering characteristic and level individualized for each senile dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of an educational tooth-brushing program using priming in an elderly population with dementia residing in nursing homes
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Jung-Soo Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(3): 149. CrossRef - Effects of individual reminiscence therapy for older women living alone
S.R. Sok
International Nursing Review.2015; 62(4): 517. CrossRef - Effects of a Short-term Life Review on Spiritual Well-being, Depression, and Anxiety in Terminally Ill Cancer Patients
Sung Hee Ahn, Young Lan An, Yang Sook Yoo, Michiyo Ando, Soo Jin Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 28. CrossRef - Agitation in Home-dwelling Persons with Dementia and Coping Behaviors in Primary Care-givers to the Agitation
Hye Suk Kim, Heeok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(3): 256. CrossRef
- Effect of an educational tooth-brushing program using priming in an elderly population with dementia residing in nursing homes
- 755 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- A Critical Review and Visim of Family Caregiving Research on the Demented Elderly's in Republic of Korea
- Jin Sun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1419-1433. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1419
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Little is known about the impact of family caregiving for the demented elderly in Korea. The purpose of this study was to identify the current state of development of family caregiving research for the demented elderly in Korea and to identify correlates of caregiver or health problems and burdens within the socio-political contexts of Korea. A critical review of 17 family caregivers was carried out. The review revealed that various caregiving impacts and correlates of caregiver burden or health problems have been studied in relation to demented elderly family caregiving. Family caregiving for the demented elderly is a very complex phenomenon and various factors were related to caregiver burden, or their emotional and physical health. Findings from studies reviewed have shown inconsistent, inconclusive, and contradictory results. Furthermore, several conceptual and methodological problems were identified in the studies reviewed: restricted conceptualization, unrepresentative study samples, inadequate sample size, inappropriate study design, absence of comparison groups, inappropriate psychometric properties, and uncontrolled confounding factors. More research, as well as directions for further research, is recommended to identify family caregiving the impact of for the demented elderly, and to clarify the factors that explain results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Overcoming Experiences of Family Members Caring for Elderly Patients with Dementia at Home
Mi Ra Sung, Myungsun Yi, Dong Young Lee, Hye Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(3): 389. CrossRef
- Overcoming Experiences of Family Members Caring for Elderly Patients with Dementia at Home
- 656 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Lives of Daughters-in-Law Who Care for Parents with Dementia
- Hyun Sook Kang, Keum Ja Go, Won Ock Kim, Eun Sim Kim, Soon Yong Khim, Hyun Li Kim, Soon Ok Shin, Sang Eun Oh, Jeong Sook Won, Chun Yu Li, Min Jung, Nam Hee Choe
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1233-1243. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1233
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to investigate the lives of the daughters- in- law caring for parents with dementia and participate in their lives through having quality time with them. Data were collected by depth interviews and interpreted through the hermeneutic circle as follows. These daughters-in-law have conflict between social custom and subjective self. They had ambivalence toward their demented partents-in- law and were fighting a battle between rationality and emotions in their mind. These daughters-in law and mothers-in- law did not get along and the parents' dementia aggravated the relationships. They were alienated from their family by the parents with dementia. The indifference of their family especially their husbands, made these subjects live in misery. They cared for the demented mother-in-law with hatred. Even though they had this yoke, there daughters- in-law were not able to throw off the shackles of convention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between dementia caregivers and quality of life in South Korean populations
Sujin Lee, Jae Ho Chung
Medicine.2024; 103(25): e38605. CrossRef - Association between Living with Patients with Dementia and Family Caregivers’ Depressive Symptoms—Living with Dementia Patients and Family Caregivers’ Depressive Symptoms
Minah Park, Fatima Nari, Soo Hyun Kang, Sung-In Jang, Eun-Cheol Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4372. CrossRef - The Experience of Adult Korean Children Caring for Parents Institutionalized with Dementia
Suhye Kwon, Young-Sook Tae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(1): 41. CrossRef - Overcoming Experiences of Family Members Caring for Elderly Patients with Dementia at Home
Mi Ra Sung, Myungsun Yi, Dong Young Lee, Hye Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(3): 389. CrossRef - The Relationship among Perceived Entrapment, Depression and Subjective Well-being of Women as Family Caregivers Caring for Dementia Elderly
Suk-Hee Cheon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 285. CrossRef - Family Caregiver Burden by Relationship to Care Recipient with Dementia in Korea
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Hyojeong Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2008; 29(4): 267. CrossRef - Daughters‐in‐law in Korean caregiving families
Jin‐Sun Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2001; 36(3): 399. CrossRef
- The relationship between dementia caregivers and quality of life in South Korean populations
- 683 View
- 0 Download
- 7 Crossref

- A Study on the Burdens and Depressive Reactions on Families who Cared for Patients Suffering from Senile Dementia
- Young Ja Kim, Pyoung Sook Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):766-779. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.766
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between the burdent on families who live with an elderly person suffering from senile dementia, and the degree of their depression. There were 400 participants in this study, staying in the Seoul and Kyonggi areas from August, 1, 1997 to February 28, 1998. Among the group, 100 participants took care of their patients at home, and another 300 participants left 100 patients at a day-care center, 100 sanatorium for senile dementia(asylum for helpless elderly people), 100 an infirmary for elderly people. Eventually 242 subjects out of the 400 were selected for the data analysis. The Zarit(1980) tool was employed to measure the degree of burden and Zung's(1965) "Self-Rating Depression Scale" was employed for the data analysis. The data was analyzed, and the percentage, t-test, ANOVA, and Pearson's Correlation Coefficient were calculated. The results are as follows. 1. The average degree of burden that care-giving families felt was 49.13, which is somewhat high. 2. The average degree of depression that-giving families felt was 51.95, which is relatively high. 3. The degree of burden was directly affected by the relation with the patient(F=2.48, P<.05), and the socio-economic status of the family(F=5.17, P<.05). It's also affected by the patient's educational status(F=2.17, P<.05). 4. The degree of depression of the family was significantly dependent on sex(t=-2.05, P<.05), age(F=2.99, P<.05), the relationship with the patient(F=3.65, P<.01), socio-economic status(F=7.74, P<.001), occupation(t=2.82, P<.01), health status(F=4.42, P<.01), and the place of residence(F=4.30, P<.01). The patient characteristics was significantly dependent on his/her educational status(F=3.85, P<.01), the period of suffering from senile dementia(F=2.47, P<.05), and smoking habit(F=6.17, P<.001). 5. The relationship between the degree of burden and that of depression reads r=0.43, which is statistically positive correlation in the high significant level. Upon analyzing the entire summation, most care-giver for elderly patients suffering from senile dementia lack time in caring for themselves. They also experience chronic fatigue and mental discomfort caused by the isolation from society, curtailment of certain activities, a sense of responsibility of certain activities, a sense of responsibility for their patients, and limits of their endurance in taking care of their patients over time. In conclusion, this study emphasizes the necessity for the following propositions : 1. In order to measure the degree of burden that Korean care-giving families undergo, a new tool must be developed on the basis of Korean culture. 2. An educational program based on the demands that care-giving families undergo must e developed, and its clinical effect also has to be examined.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the Quality of Life among Family Caregivers of the Elderly with Dementia
Hwasoon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 500. CrossRef - Review of studies on spousal caregivers of frail spouses in South Korea
Youngsam Oh, Eunyoung Han
International Social Work.2019; 62(2): 529. CrossRef - The Burden of Aged Parents Caring for Adult Children with Disabilities
Min-Hyun Suk, Eunhye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 439. CrossRef - Comparison in Care Burden, Fatigue, and Life Contentment of Caregivers by Gender Relationship with Demented Elders
Young Whee Lee, In Sook Cho, Hwa Soon Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(3): 196. CrossRef - Family Caregiver Burden by Relationship to Care Recipient with Dementia in Korea
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Hyojeong Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2008; 29(4): 267. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Burden of Family Caregivers of Community-Dwelling Ambulatory Elders with Dementia in Korea
Young Mi Lim, Gwi-Ryung Son, Jun-Ah Song, Elizabeth Beattie
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2008; 22(4): 226. CrossRef - A thematic analysis of Korean family caregivers' experiences in making the decision to place a family member with dementia in a long‐term care facility
Myonghwa Park, Howard Karl Butcher, Meridean L. Maas
Research in Nursing & Health.2004; 27(5): 345. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the Quality of Life among Family Caregivers of the Elderly with Dementia
- 683 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of Gerontological Nursing Practicum on Attitudes toward Elders with Dementia and General Elders among Korean Nursing Students
- Jung Hee Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(4):645-651. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.4.645
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study investigated changes in attitudes toward elders in general and elders with dementia after students finished a gerontological nursing practicum.
Methods Questionnaires developed for Asian cultures were administered pre practicum, immediately post practicum, and at 8-months follow up to 31 senior students in a baccalaureate nursing program. The 1-week practicum occurred at two adult day care centers: a center for elders with dementia and a center for elders with stroke. Repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni correction procedures were used to analyze data.
Results Students' evaluation of elder vitality and flexibility increased significantly at post practicum, however this increase was not sustained at follow up. Score of generosity of elders, the only positively evaluated dimension for elders in general, improved partly at post practicum. Students evaluated flexibility and generosity of elders with dementia more negatively than general elders. All of the decreased attitudes at follow up were not significantly different from those at pre practicum.
Conclusions Students had more negative attitudes toward elders with dementia. Attitudes of students in direct contact with elders with dementia were improved through the practicum regarding generosity and flexibility. However the sustainability of the immediate effect was not observed at follow up.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Educational interventions to improve student nurses’ knowledge, attitudes, or willingness to work with older people: a systematic review of quantitative findings
Xingjuan Tao, Margaret MacAndrew, Sherry Dahlke, Jeffrey I. Butler, Jo Rayner, Deirdre Fetherstonhaugh, Christina Parker
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing Students' Knowledge and Attitudes Toward Alzheimer's Disease in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jazi S Alotaibi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An analysis of nursing and medical students’ attitudes towards and knowledge of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
Asem Abdalrahim, Mohammed ALBashtawy, Abdullah Alkhawaldeh, Rasmieh M. Al-amer, Ahmad Bani Salameh, Sa’d ALBashtawy, Abdallah Abu Khait, Zaid ALBashtawy
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and Attitudes toward Dementia among Undergraduate Health Professional Students in China: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Anhong Dong, Guilan Gong, Elizabeth Reifsnider, Sha Huang, Zeyu Zhang, Jing Mao
Teaching and Learning in Medicine.2022; 34(5): 455. CrossRef - Teaching and learning about dementia care among undergraduate nursing students: A scoping review
Susana Cariñanos-Ayala, Marta Arrue, Jagoba Zarandona
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 61: 103326. CrossRef - Nursing Staff’s Knowledge and Attitudes toward Dementia: A Pilot Study from an Indian Perspective
Benedicte Sørensen Strøm, Knut Engedal, Lasse Andreassen
Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders Extra.2019; 9(3): 352. CrossRef - Student participation in a dementia-outreach research project as community-based experiential learning
Sora Choi, Myonghwa Park
Educational Gerontology.2017; 43(4): 186. CrossRef - Living as a nursing college students in Korea
Jung-ae Kim
The International Journal of Advanced Culture Technology.2016; 4(3): 20. CrossRef - Knowledge and attitudes of undergraduate nursing students toward dementia: An Indian perspective
Vijayalakshmi Poreddi, Brian D Carpenter, Sailaxmi Gandhi, Rama Chandra, Suresh BadaMath
Investigación y Educación en Enfermería.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Geriatric Nursing Education for Nursing Students' Attitude, Perception toward Dementia and Dementia Policy
Su-jin Park, Kyung-sook Park, Young-Ji Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(7): 4467. CrossRef - Nursing students' knowledge and attitudes towards dementia — A questionnaire survey
Anthony Scerri, Charles Scerri
Nurse Education Today.2013; 33(9): 962. CrossRef - The Effect of Dementia Education Program on Nursing Students
Hee-Young Kang, Myeong-Jeong Chae, Hee-Suk Seo, Kyung-Mi Yang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(1): 69. CrossRef - Student experiences in learning person‐centred care of patients with Alzheimer’s disease as perceived by nursing students and supervising nurses
Mari W Skaalvik, Hans Ketil Normann, Nils Henriksen
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2010; 19(17-18): 2639. CrossRef
- Educational interventions to improve student nurses’ knowledge, attitudes, or willingness to work with older people: a systematic review of quantitative findings
- 761 View
- 7 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Development and Analysis of the Effects of Caregiver Training Program on Aggressive Behavior in Elders with Cognitive Impairment
- Heeyoung Oh, Myung Haeng Hur, Miran Eom
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(4):745-753. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.4.745
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose The purposes of this study were to 1) describe the type and frequency of aggressive behavior of cognitively impaired nursing home resident, 2) develop a caregiver training program on prevention and management of aggressive behavior, 3) examine the effects of caregiver training program on the incidence of aggressive behavior of cognitively impaired nursing home resident, and 4) examine the effects of caregiver training program on nursing staff's aggressive behavior management skills.
Methods One-group, time series, quasi-experimental design with a pre-test and two post-tests was used. Data were collected from cognitively impaired home residents (N=32) and nursing staff (N=36) in a proprietary nursing home using Ryden Aggression Scale I, II, and Aggressive Behavior Management Scale. Data were entered and analyzed by descriptive statistics and repeated measures ANOVA.
Results Incidence of aggressive behavior was high with a mean score of 3.09 (SD=3.11) at baseline. Caregiver training program was developed based on Progressively Lowered Stress Threshold (PLST) model and gerontological and psychiatric literature. The mean scores of aggressive behavior at baseline, Post I, and II did not differ significantly although the difference approached to the significant level (F=2.925, p=.066). Nursing staff's aggressive behavior management skills increased at Post I, and at Post II when compared to baseline, and the difference was significant (F=12.736, p=<.001).
Conclusion Caregiver training program showed potential impact on reduction of aggressive behavior in elders with cognitive impairment and was effective in increasing nursing staff's aggressive behavior management skills.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Staff Training for Assisted Living Residences protocol for caregivers of older adults with dementia: A pilot study in the Brazilian population
Larissa da Silva Serelli, Ramon Castro Reis, Jerson Laks, Analuiza Camozzato de Pádua, Cássio MC Bottino, Paulo Caramelli
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2017; 17(3): 449. CrossRef - Coping with dementia related behavior problems of the elderly and care providers
Dong Young Lim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(7): 4805. CrossRef - “The educating nursing staff effectively (TENSE) study”: design of a cluster randomized controlled trial
Theo J G M Hazelhof, Debby L Gerritsen, Lisette Schoonhoven, Raymond T C M Koopmans
BMC Nursing.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Patterns of Antecedents of Catastrophic Reactions in Nursing Home Residents With Dementia in the United States
Hye-A Yeom, Nancy M. Watson
Asian Nursing Research.2009; 3(3): 99. CrossRef
- Effects of the Staff Training for Assisted Living Residences protocol for caregivers of older adults with dementia: A pilot study in the Brazilian population
- 749 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Effect of Lavender Aromatherapy on Cognitive Function, Emotion, and Aggressive Behavior of Elderly with Demenita
- Sun Young Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(2):303-312. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.2.303
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to develop an aromatherapy hand massage program, and to evaluate the effects of lavender aromatherapy on cognitive function, emotion, and aggressive behavior of elderly with dementia of the Alzheimer's type.
Methods The Research design was a nonequivalent control group non-synchronized quasiexperimental study. Lavender aromatherapy was administrated to experimental group I for 2 weeks, jojoba oil massage was administrated to experimental group II for 2 weeks, and no treatment was administrated to the control group for 2 weeks. Data was analyzed using the chi-square-test, ANOVA, repeated measures of ANCOVA and ANCOVA in the SPSS program package.
Result 1. Experimental group I did not show significant differences in cognitive function in relation to the experimental group II and control group. 2. Experimental group I showed significant differences in emotion and aggressive behavior in relation to the experimental group II and control group.
Conclusion A Lavender aromatherapy hand massage program is effective on emotions and aggressive behavior of elderly with dementia of the Alzheimer's type.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of aromatherapy on agitation and aggression in cognitive impairment: A meta‐analysis
Shudan Xiao, Ying Wang, Shumin Duan, Bo Li
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(12): 4974. CrossRef - Nursing strategies for enhancing calm in older Arabs with dementia: integrating Snoezelen methods, aromatherapy, and personal items to reduce agitation
Abeer Nuwayfi Alruwaili, Majed Mowanes Alruwaili, Osama Mohamed Elsayed Ramadan, Sayed Ibrahim Ali, Mostafa Shaban
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 59: 379. CrossRef - Aromatherapy in Nursing and Midwifery Practice: A Scoping Review of Published Studies Since 2005
Wendy Maddocks
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2023; 41(1): 62. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Safety of Aromatherapy in Managing Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: A Mixed-Methods Systematic Review
Becky Siu Yin Li, Carmen Wing Han Chan, Minjie Li, Irene Kit Yee Wong, Yvonne Hoi Un Yu
Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders Extra.2021; 11(3): 273. CrossRef - Convergence Study on the Relation between Cognition, Depression and Aggression in the Elderly
Myoung-Jin Kwon
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2015; 6(6): 171. CrossRef - Effect of Laugher Therapy on Pain, Depression and Sleep with Elderly Patients in Long Term Care Facility
Kyeong-Im Lee, Young Eun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2011; 18(1): 28. CrossRef
- Effects of aromatherapy on agitation and aggression in cognitive impairment: A meta‐analysis
- 1,467 View
- 57 Download
- 6 Crossref

- A Study on Aggressive Behavior Among Nursing Home Residents with Cognitive Impairment
- Heeyoung Oh, Miran Eom, Yunjung Kwon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(8):1451-1459. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.8.1451
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose With a sample of cognitively impaired nursing home residents and nursing staff, the following were examined 1) the proportion and nature of aggressive behavior, 2) the frequency and types of aggressive behavior, 3) the difference between the residents who demonstrate aggressive behavior and those who do not demonstrate aggressive behavior (age, mental status, functional status, and pain, length of nursing home stay), and 4) nursing staff responses to aggressive behavior by residents.
Methods A cross-sectional descriptive study design was used. Data were collected from cognitively impaired nursing home residents (N=205) and nursing staff (N=60) at two nursing homes using Ryden Aggression Scale I and II, Mini-Mental State Exam, Modified Barthel Index, Verbal Descriptor Scale, and aggressive behavior management questionnaire. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics including t-test.
Results About 62.9% residents were found to be aggressive and 38.5% were both physically and verbally aggressive. Pushing, making threatening gestures, hitting, slapping, cursing/obscene/vulgar languages, making verbal threats were occurred frequently. Aggressive residents were significantly older, had more cognitive impairment, had more pain, and stayed longer in the nursing home when compared with non-aggressive residents. Considerable proportion of nursing staff responded to aggressive behaviors inadequately.
Conclusion Aggressive behavior among cognitively impaired nursing home residents is prevalent thus needs to be prevented and reduced. Along with environmental modification, educational programs for nursing staff and family caregivers need to be developed and implemented so that they can have extensive knowledge and skills to manage aggressive behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Psychological Aggression at the Workplace on Employees’ Health: A Systematic Review of Personal Outcomes and Prevention Strategies
Emelda C. R. L. Pacheco, Ana Bártolo, Fabiana Rodrigues, Anabela Pereira, João C. Duarte, Carlos F. Silva
Psychological Reports.2021; 124(3): 929. CrossRef - Care workers health in Swiss nursing homes and its association with psychosocial work environment: A cross-sectional study
Suzanne R. Dhaini, Franziska Zúñiga, Dietmar Ausserhofer, Michael Simon, Regina Kunz, Sabina De Geest, Rene Schwendimann
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2016; 53: 105. CrossRef - Do Sound Levels and Space Contribute to Agitation in Nursing Home Residents with Dementia?
Laura L. Joosse
Research in Gerontological Nursing.2012; 5(3): 174. CrossRef - Patterns of Antecedents of Catastrophic Reactions in Nursing Home Residents With Dementia in the United States
Hye-A Yeom, Nancy M. Watson
Asian Nursing Research.2009; 3(3): 99. CrossRef
- Impact of Psychological Aggression at the Workplace on Employees’ Health: A Systematic Review of Personal Outcomes and Prevention Strategies
- 728 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Self-Care in Elders with Dementia: A Concept Analysis
- Hye A Yeom
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(8):1402-1408. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.8.1402
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the concept of self-care in elders with dementia through a review of nursing literature and to provide more understanding of the definition and perspectives of the concept of self-care notion in elders with dementia.
Methods The technique developed by Walker and Avant was used as a guide in analyzing the concept of selfcare.
Results Attributes of self-care in dementia may include a single or group of actions needed for sustaining life, a personal effort to maintain functional independence while minimizing other's assistance, an outcome behavior from the person's interaction with inter-personal and/or contextual environment, and a functional ability that may decline in parallel to cognitive impairment. Antecedents of self-care in dementia may include at least presence of a certain degree of cognitive appraisal for the self-care needs, self-willingness for the selfcare action, spatial and visual orientation, cultural pre-conception of the self-care behavior, presence of environmental context/equipment available for self-care, and sufficient time available. The consequences may include sustaining of life, feel of satisfaction, achieving independence, extended life expectancy, increased self-confidence, decreased caregiver distress and/or burden, savings in health care costs.
Discussion Defining attributes and antecedents and consequences of self-care in dementia identified in this study provided empirical ground of a middle-range theory of self-care for a clinical population with dementia and generated possible hypotheses to be tested in future studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- 940 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Women Caregivers' Experiences in Caring at Home for a Family Member with Dementia: A Feminist Approach
- Bong Sook Yih, Chun Mi Kim, Myung Sun Yi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(5):881-890. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.5.881
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore women caregivers' lived experiences in caring at home for a family member with dementia and to identify conditions that oppress women in the context of family caregiving.
Method This study was conducted within the feminist perspectives using qualitative secondary data. Ten secondary data conveying self reflective contents were selected from the 25 original data obtained in 1999 to 2000.
Result Six themes that emerged from the qualitative thematic content analysis were; androcentric view of family caregiving, undervalued family caregiving by the family members, Self rationalization in the context of family caregiving, family-centric care mechanism, exemplary caring within the family context, and inter-familial relationships among women.
Conclusion The main focus of feminist research is to provide empowerment for the women research participants and to bring about social change of oppressive constraint through some actions. On the basis of the research findings, therefore, action strategies from feminist perspectives were suggested in some aspects of health care delivery sectors, nursing education and research sectors, and administrative sectors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Do Young Adults Become Socially Isolated?
Juyeon Ryu, Kiok Seong, Soojin Kim
Journal of Social Science.2023; 34(3): 47. CrossRef - Time usage analysis according to occupational area and satisfaction level in family caregivers of dementia patients
Woo-Hyuk Jang, Jong-Sik Jang, Jong-Hwi Park
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15178. CrossRef - Changes in Family Dynamics in Caregiving for People With Dementia in South Korea: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Seieun Oh, Mi Yu, Young Mi Ryu, Haejin Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Qualitative Health Research.2020; 30(1): 60. CrossRef - A Content Analysis of the Experience of Participation in Community Leisure Programs among Older Adults
Insuk Rho, Sunhee Cho
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2016; 22(2): 138. CrossRef - The Barriers and Solution of Providing Long-term Care Services at Home for the Beneficiaries with Mild Dementia: A Focus Group Interview
Mi Sook Song, Kyung Sook Lim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 259. CrossRef - Overcoming Experiences of Family Members Caring for Elderly Patients with Dementia at Home
Mi Ra Sung, Myungsun Yi, Dong Young Lee, Hye Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(3): 389. CrossRef - Nurses' Experiences of Caring with Demented Oder Persons
Chun-Gill Kim, Young Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(5): 454. CrossRef - An Analysis of the Meaning of Respite for Family Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia
Mi Ryeong Song, Yong-Mi Lee, Suk-Hee Cheon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 482. CrossRef
- How Do Young Adults Become Socially Isolated?
- 696 View
- 6 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Predictors of Depression among Family Caregivers of Older Adults with Dementia
- Hae Jung Lee, Young Sook Kim, Ki Ryeon Kim, Ju Sung Kim, Ji Min Seo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(7):936-944. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.7.936
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to identify important predictors of depression among characteristics of caregiving situation and utilized resources in order to provide basic information for effective nursing interventions to reduce depression experienced by family caregivers of older adults with dementia.
Method Seventy one family caregivers were identified from community service centers and face-to-face interviewed using structured questionnaires. Data were analyzed with descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation and hierarchical multiple regression using SPSS WIN 10.0 program.
Result Family caregivers reported high levels of depression, moderate levels of social support, and moderate utilization of coping strategies. Female caregivers who (β=.22) utilized ‘negative’ coping strategies more often (β=.48) and ‘cognitive reconstructuring’ coping strategies less often (β=-.23) were more likely to report higher depression (R2=0.63).
Conclusion Nursing interventions increasing family caregivers' utilization of positive coping strategies such as problem solving, existential growth, and help seeking and decreasing their utilization of negative coping strategies such as self-blaming are needed to decrease their depression levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Problem-Solving Program on Problem-Solving Ability, Self-Esteem, and Depression for Middle School Girls
Hwa-Yoon Um, Haejung Lee, Yeonjung Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(3): 318. CrossRef - Comparison in Care Burden, Fatigue, and Life Contentment of Caregivers by Gender Relationship with Demented Elders
Young Whee Lee, In Sook Cho, Hwa Soon Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(3): 196. CrossRef - Family Caregiver Burden by Relationship to Care Recipient with Dementia in Korea
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Hyojeong Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2008; 29(4): 267. CrossRef
- Effects of a Problem-Solving Program on Problem-Solving Ability, Self-Esteem, and Depression for Middle School Girls
- 657 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Care Dependency in Patients with Dementia
- Eun Joo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(6):705-712. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.6.705
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore factors that influence care dependency of institutionalized patients with dementia.
Method This study utilized descriptive correlational design. The convenience sample was composed of 110 residents with dementia of two long-term care facilities in Korea. Stepwise multiple regression was used to identify significant factors influencing care dependency in patients with dementia. Care dependency was measured using the Care Dependency Scale, Korean version(CDS-K). Cognition was measured by the MMSE-K. Functional disability was measured by the PULSES Profile. Behavioral dysfunction was measured by the modified E-BEHAVE AD.
Result Care dependency was significantly influenced by cognition, functional disability, behavioral dysfunction, and duration of dementia. This regression model explained 61% of the variances in care dependency. Cognition explained 37% of the variances, and functional disability explained 21% of the variances.
Conclusion Results of this study suggest that professional caregivers intervene more effectively in caring for their patients with dementia by recognizing the patients cognitive, functional, behavioral disability, and its periodic change. Individually, remaining abilities-focused intervention should be applied to enhance patient to be dependent and to prevent unnecessary independency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of care dependency in nursing home residents with moderate to severe dementia: A cross-sectional study
Marinda Henskens, Ilse M. Nauta, Katja T. Drost, Maarten V. Milders, Erik J.A. Scherder
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2019; 92: 47. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Care Burden among Family Caregivers for Elders with Dementia: Focusing on Family Caregivers using a Support Center for Dementia
Kyung Choon Lim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Perceptions regarding Purpose in Life and Good Death on Caring Behaviors of Formal Caregivers of Community-dwelling Older Adults with Dementia
Chun-Gill Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(2): 57. CrossRef - Perceived oral health awareness in dementia and dementia-suspected depending on KMME
Eun Sook Kim, Min-Hee Hong
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2015; 15(2): 217. CrossRef - The Long-term Care Utilization of the Elderly with Dementia, Stroke, and Multimorbidity in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Soonman Kwon, Hongsoo Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(1): 90. CrossRef - Relationships Among Cognition, Activities of Daily Living and Depression in Persons With Decreased Memory
Min Suk Kim, Soon Young Yoon, Eun Young Oh
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(3): 404. CrossRef
- Predictors of care dependency in nursing home residents with moderate to severe dementia: A cross-sectional study
- 780 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Prevalence of Cognitive Impairment and Related Factors Among the Elderly in Rural Communities of Jeju Province
- Keumja Ko, Min Jung, Sungchul Hong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(4):503-509. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.4.503
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to survey the prevalence rate of cognitive impairments and to identify the factors influencing cognitive impairment in the elderly in rural communities of Jeju Province..
Methods 590 elderly in 6 rural communities of Jeju Province were interviewed, using a questionnaire consisting of sociodemographic characteristics, health behavior, quality of life, and MMSE-K
Results Prevalence of cognitive impairment was 33.1% (39.1% of females, 16.76% of males). Prevalence of dementia was 12.4% (16.3% of females, 2.87% of males). Factors related to cognitive impairment were age, sex, education, standard of living, employment status, and subjective health state.
Conclusions In community health care for the elderly, factors relating to cognitive impairment have to be considered. When planning community health care, priority should be given to the elderly; who need care but live alone; who lack social support; who have a low standard of living; who experience discomfort in the activities of daily living; who believe they are not in a good state of health; or whose life satisfaction is low.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of the Major Mental Disorders among the Korean Elderly
Maeng Je Cho, Jun Young Lee, Byung-Soo Kim, Hae Woo Lee, Jee Hoon Sohn
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2011; 26(1): 1. CrossRef
- Prevalence of the Major Mental Disorders among the Korean Elderly
- 661 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Screening for High Risk Population of Dementia and Development of the Preventive Program Using Web
- Jung Soon Kim, Ihn Sook Jeong, Yoon Jin Kim, Sun Kyung Hwang, Byung Chul Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(2):236-245. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.2.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to develop a screening model for identifying a high risk group of dementia and to develop and evaluate the web-based prevention program.
Method It was conducted in 5 phases. 1) Data were collected from dementia patients and non-dementia patients in a community. 2) A screening model of the high risk population was constructed. 3) The validity test was performed and the model was confirmed. 4) Four weeks-prevention program was developed. 5) The program was administered, and evaluated the effects.
Result The model consisted of age, illiteracy, history of stroke and hypercholesterolemia. The program was designed with 12 sessions, group health education using web-based individual instruction program, and 12 sessions of low-intensity physical exercise program. After the completion, their self-efficacy, and health behaviors in experimental group were significantly improved over those in the control group. The perceived barrier in the treatment group is significantly decreased.
Conclusion The screening model developed is very simple and can be utilized in diverse community settings. And the web based prevention program will encourage individual learning and timely feedback, therefore it can facilitate their active participation and promote health management behaviors at home.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Among Health Insurance Type, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and the Risk of Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Korea
So-Hyun Moon, Hyun-Ju Seo, Dong Young Lee, Seong Min Kim, Jeong Min Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(14): 2616. CrossRef - The Effects of Computer - based Attention Program on Cognition and Executive Function in Elderly with Vascular Dementia
Hyojeong Lee, Kyoungok Hwang
Journal of The Korean Society of Integrative Medicine.2014; 2(2): 13. CrossRef - Analysis of Nutrition and Antioxidants of Yak-Kong Chungkukjang Powder Added Black Foods
Hyun-Joo Kong, Heyun-Sook Park, Tae-Hoon Kim, Seung-Ryeul Shin, Ju-Yeon Hong, Kyung-Mi Yang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(11): 1727. CrossRef - Comorbidity and Health Habits of Seoul City Elders with Dementia
Yoon Kyoung Lee, Mi Ra Sung, Dong Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(3): 411. CrossRef - Effects of an Exercise Program on Frontal Lobe Cognitive Function in Elders
Mee-Kyung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 107. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Factors Influencing the Life Satisfaction of the Elderly According to their Cognitive Impairment Level
Rah Il Hwang, Ji Young Lim, Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 622. CrossRef
- Associations Among Health Insurance Type, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and the Risk of Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Korea
- 614 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on Caring Experience of Spouses of Elderly People with Dementia at Home
- Hye-Young Jang, Myungsun Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):367-379. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.367
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to understand and describe the caring experiences of spouses of elderly people with dementia.
Methods The hermeneutic phenomenological method was used and participants were 12 spouses aged 65 and over who were taking care of their husbands or wives with dementia at home. Data were collected from individual in-depth interviews on participants’ actual caring experiences. Additionally, novels, movies, and memoirs on elderly couples with partner who had dementia were included as data for the analysis. The qualitative data analysis software program was used to manage and process the collected qualitative data. Data were analyzed using hermeneutic phenomenological analysis based on four fundamental existentials including lived body, lived space, lived time, and lived others.
Results Five essential themes emerged from the analysis: 1) body moving like an old machine, 2) swamp of despair filling with hope, 3) sweet time after bitterness, 4) disappointed elderly couple in the empty nest, and 5) unappreciation vs. empathetic feelings. These essential themes were comprehensively summarized as “the road leading to the maturation of life with dedication and hope while bearing the weight of caring based on the couple's relationship.”
Conclusion The findings indicate that the nature of the caring experience of spouses of elderly individuals with dementia is filled with many dynamic and paradoxical dimensions. Thus, results of the study would help with developing interventions tailored specifically for elderly spouse caregivers to support their role adaptation and ultimately improving their quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between anxiety and fatigue in dementia family caregivers: hope as a mediator
Jiin-Ling Jiang, Shing-Ling Chang, Ke-chieh Wang, Yu-Chin Ma
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-care experiences of male spouses of people with dementia: a descriptive phenomenological study
Sua Jung, Jun-Ah Song
Aging & Mental Health.2025; 29(7): 1329. CrossRef - Development of a Bayesian nomogram for predicting depression in family caregivers for dementia patients at home in South Korea
Haewon Byeon
Medicine.2025; 104(44): e45164. CrossRef - A web-based care assistant for caregivers of the elderly: Development and pilot study
Hwawoo Jeon, Yong Suk Choi, Yoonseob Lim
DIGITAL HEALTH.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Sleep Quality in Spouse Caregivers of Community-Dwelling People With Dementia Using Propensity Score Matching Analysis
Hyeon Sik CHU, Hye-Young JANG
Journal of Nursing Research.2023; 31(6): e299. CrossRef - Barriers to Social Inclusion among Older Adults with Disabilities in Imo State, Nigeria: A Descriptive Phenomenological Inquiry
Anthony Iwuagwu, Paulinus Okah, Chinwe Nnama-Okechukwu, Ngozi Chukwu, Agha Agha, Nkemdili Anazonwu, Chinyere Onalu, Uzoma Okoye
Scandinavian Journal of Disability Research.2023; 25(1): 132. CrossRef - Caring Experience of Spouse Caregivers of Persons with Alzheimer's Disease: A Qualitative Study
Jin-Hee Lee, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 257. CrossRef - Safety Accidents and Coping Experiences among Family Caregivers Caring for Community-Dwelling Persons Living with Dementia
Ji Yeon Lee, Ha Rim Lee, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 352. CrossRef - Dementia: How does spouse perceive it?
Anung Ahadi Pradana, Junaiti Sahar, Henny Permatasari
Enfermería Clínica.2021; 31: S16. CrossRef - Predictors of Satisfaction with Care Services among Family Members of Older Adult Residents of Long-Term Care Facilities
Eun-Ok Song, Hye-Young Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3298. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Scale for Partnership in Care—for Family (SPIC-F)
Hye-Young Jang, Eun-Ok Song
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(6): 1882. CrossRef - Family Members’ Experience in Caring for Elderly with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals
Eun Kyoung Suh, Hye Ryoung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 335. CrossRef - Partnership between staff and family in long-term care facility: a hybrid concept analysis
Hye-Young Jang
International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being.2020; 15(1): 1801179. CrossRef - Predictors of Health-related Quality of Life among Spouses of Older Adults with Dementia in the Community-dwelling
Hye-Young Jang, Song Yi Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(4): 518. CrossRef - Empathy in Family Caregivers for Persons with Dementia: A Q Methodology Study
Kim Hyojin, Song Jun-Ah
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(3): 214. CrossRef
- Relationship between anxiety and fatigue in dementia family caregivers: hope as a mediator
- 2,121 View
- 18 Download
- 15 Crossref

- A Prediction Model for Unmet Needs of Elders with Dementia and Caregiving Experiences of Family Caregivers
- Sora Choi, Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(5):663-674. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.5.663
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to develop and test a prediction model for caregiving experiences including caregiving satisfaction and burden in dementia family caregivers.
Methods The stress process model and a two factor model were used as the conceptual frameworks. Secondary data analysis was done with 320 family caregivers who were selected from the Seoul Dementia Management Survey (2014) data set. In the hypothesis model, the exogenous variable was patient symptomatology which included cognitive impairment, behavioral problems, dependency in activity of daily living and in instrumental activity of daily living. Endogenous variables were caregiver's perception of dementia patient's unmet needs, caregiving satisfaction and caregiving burden. Data were analysed using SPSS/WINdows and AMOS program.
Results Caregiving burden was explained by patient symptomatology and caregiving satisfaction indicating significant direct effects and significant indirect effect from unmet needs. The proposed model explained 37.8% of the variance. Caregiving satisfaction was explained by patient symptomatology and unmet needs. Mediating effect of unmet needs was significant in the relationship between patient symptomatology and caregiving satisfaction.
Conclusion Results indicate that interventions focusing on relieving caregiving burden and enhancing caregiver satisfaction should be provided to caregivers with high levels of dementia patients' unmet needs and low level of caregiving satisfaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences of Family Caregivers Utilizing Care Support of Dementia Center
Chun-Gill Kim, Myung Soon Kwon, Young Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(3): 314. CrossRef
- Experiences of Family Caregivers Utilizing Care Support of Dementia Center
- 947 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Stimulation-Oriented Interventions for Behavioral Problems among People with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Eun Young Kim, Sung-Dong Hwang, Eun Joo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(4):475-489. Published online August 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.4.475
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate the effects of stimulation-oriented interventions for behavioral problems among people with dementia.
Methods Based on the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA), a literature search was conducted using seven electronic databases, gray literature, and other sources. Methodological quality was assessed using the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) for randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Data were analyzed using R with the ‘meta’ package and the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA 2.0) program.
Results Sixteen studies were included for meta-analysis to investigate the effect of stimulation-oriented interventions. The quality of individual studies was rated as ‘++’ for eight studies and ‘+’ for the rest. The effect sizes were analyzed according to three subgroups of interventions (light, music, and others); Hedges’ g=0.04 (95% CI: -0.38~0.46), -0.23 (95% CI: -0.56~0.10), -0.34 (95% CI: -0.34~0.00), respectively. To explore the possible causes of heterogeneity (I2=62.8%), meta-regression was conducted with covariates of sample size, number of sessions, and length of session (time). No moderating effects were found for sample size or number of sessions, but session time showed a significant effect (Z=1.96, 95% CI: 0.00~0.01). Finally, a funnel plot along with Egger's regression test was performed to check for publication bias, but no significant bias was detected.
Conclusion Based on these findings, stimulation-oriented interventions seem to have a small effect for behavioral problems among people with dementia. Further research is needed to identify optimum time of the interventions for behavioral problems among dementia patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Horticultural Therapy on Korean Elderly with Dementia: A Meta-analysis
Kyung Ja Kang, Mi-Jung Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(4): 352. CrossRef - Effect of aquatic exercise on gait in persons with chronic stroke: a meta-analysis study in Korea
Dong-Jin Lee, Sung-Hyoun Cho
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2019; 8(2): 112. CrossRef
- Effects of Horticultural Therapy on Korean Elderly with Dementia: A Meta-analysis
- 1,394 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of Family Support Programs for Caregivers of People with Dementia - Caregiving Burden, Depression, and Stress: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Seyeon Park, Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):627-640. Published online October 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.627
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The objective of this systematic review was to assess the effects of family support programs on caregiving burden, depression, and stress in family caregivers of people with dementia.
Methods A literature search was conducted of electronic databases to identify randomized controlled studies with family support programs done between 2000 and 2014. Studies published in English and/or Korean were included for the analysis with search strategies adapted from the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group. Studies were rated for quality assessment by two independent reviewers using the appraisal checklist developed by Cochrane Reviews and Dissemination. Of 8,334 articles identified in the literature search, full texts of 76 articles that met the inclusion criteria were reviewed and 38 were found to include relevant outcomes.
Results Results from selected studies were pooled in statistical meta-analysis using Review Manager Software and heterogeneity between combined studies was assessed using the Chi-square test. Meta-analysis showed that the effect sizes of family caregiver support programs were small to medium for categories of caregiving burden (Hedge's g= - 0.17, 95% CI= - 0.30~ - 0.04), depression (Hedge's g= - 0.30, 95% CI= - 0.40~ - 0.20), and stress (Hedge's g= - 0.39, 95% CI= - 0.52~ - 0.25).
Conclusion The review results indicate that a support programs can assist family care-givers in reducing their psycho-emotional distress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the presence of a family member with dementia on the prevalence of depression: a comparison based on household income level
Min Hui Moon, Suk Woong Kang, Min Hyeok Choi
International Journal for Equity in Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Reitman Centre CARERS program for supporting dementia family caregivers: a pre–post intervention study
Joel Sadavoy, Sima Sajedinejad, Mary Chiu
International Psychogeriatrics.2022; 34(9): 827. CrossRef - Caregiver Burden among Caregivers of Patients with Mental Illness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Choy Qing Cham, Norhayati Ibrahim, Ching Sin Siau, Clarisse Roswini Kalaman, Meng Chuan Ho, Amira Najiha Yahya, Uma Visvalingam, Samsilah Roslan, Fairuz Nazri Abd Rahman, Kai Wei Lee
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2423. CrossRef - Evaluating the Effectiveness of Community-Based Dementia Caregiver Intervention on Caregiving Burden, Depression, and Attitude Toward Dementia: A Quasi‐experimental Study
Su Jung Lee, Hyun-Ju Seo, IL Han Choo, Seong Min Kim, Jeong Min Park, Eun-Young Yang, Yu Mi Choi
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2022; Volume 17: 937. CrossRef - Loss and Grief in the Context of Dementia Caregiving
Olimpia Paun, Dimitra Loukissa, Marianne G. Chirica, Horace M. Nowell
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2022; 60(10): 7. CrossRef - Korean Family Caregivers' Experiences With Managing Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Keeping Harmony in Daily Life
Jiyeon Kim, Jun-Ah Song, Sua Jung, Hongjin Cheon, Jiyeon Kim
Research in Gerontological Nursing.2022; 15(3): 141. CrossRef - Health Promotion Behavior among Older Korean Family Caregivers of People with Dementia
Aram Cho, Chiyoung Cha
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4123. CrossRef - A systematic review of interventions for family caregivers of the elderly with dementia in Korea
Seonghee Jeong, Jeonghae Hwang, Doonam Oh
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 306. CrossRef - An empowerment program for family caregivers of people with dementia
Heun Keung Yoon, Gwang Suk Kim
Public Health Nursing.2020; 37(2): 222. CrossRef - Horticultural Therapy Programs Enhancing Quality of Life and Reducing Depression and Burden for Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia
Yong Hyun Kim, Chul Soo Park, Hwa-Ok Bae, Eun Ji Lim, Kyung Heui Kang, Euy Sun Lee, Su Hyeon Jo, Moo Ryong Huh
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2020; 23(3): 305. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study of the Research on Caregiver Depression: Using Bibliometrics and LDA Topic Modeling
Soyoung Choi, JooYoung Seo
Issues in Mental Health Nursing.2020; 41(7): 592. CrossRef - The Effects of a Support Program for Family Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia on Empowerment and Attitudes toward Dementia
So Yoon Kim, Seonghee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 103. CrossRef - Behavioural Changes in Dementia and their Impact on Professional Caregivers: A Grounded Theory Approach
Katie Appleton, Antonina Pereira
Dementia.2019; 18(4): 1479. CrossRef - The Effects of Group Occupational Therapy Including Education Programs on Depression, Anxiety, and Participation of Activities in People With Dementia
Min-Joo Ham, Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2018; 26(4): 97. CrossRef - Shifting of Centricity: Qualitative Meta Synthetic Approach on Caring Experience of Family Members of Patients with Dementia
Young Mi Ryu, Mi Yu, Seieun Oh, Haeyoung Lee, Haejin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 601. CrossRef - Effects of a Dementia Family Education Program for Dementia Recognition, Burden, and Depression in Caregivers of Elders with Dementia
Sun-A Lee, Hee-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(1): 14. CrossRef - Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on Caring Experience of Spouses of Elderly People with Dementia at Home
Hye-Young Jang, Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 367. CrossRef - The voices of family caregivers of seniors with chronic conditions: a window into their experience using a qualitative design
Suzette Brémault-Phillips, Jasneet Parmar, Melissa Johnson, Arlene Huhn, Anna Mann, Victoria Tian, Lori-Ann R. Sacrey
SpringerPlus.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Conceptualization of an evidence-based smartphone innovation for caregivers and persons living with dementia
Melvyn W.B. Zhang, Sally Chan, Olivia Wynne, Sarah Jeong, Sharyn Hunter, Amada Wilson, Roger C.M. Ho
Technology and Health Care.2016; 24(5): 769. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Caregiving Satisfaction among Family Caregivers of Patients with Dementia
Yunhee Lee, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2016; 18(3): 117. CrossRef
- Impact of the presence of a family member with dementia on the prevalence of depression: a comparison based on household income level
- 2,078 View
- 34 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Implementing Evidence into Practice for Best Dementia Care
- Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):495-500. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.495
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this paper was to discuss the need for translation studies in dementia care and current translational endeavors, and to provide recommendations for evolving evidence-based dementia care.
Methods A literature review yielded current evidence and translational efforts.
Results Dementia care interventions need to be implemented at various service levels. Barriers to translation include evidence gaps, lack of the use of a conceptual framework to explain the implementation process, and unsupportive funding mechanisms for applying innovations.
Conclusion There is clear evidence of the need for and benefits of evidence-based dementia care for patients with dementia, family caregivers, and care professionals. The urgent need now is finding ways to advance translational activities and facilitate future research into translation science.
- 1,052 View
- 6 Download

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Pain Assessment Checklist for Seniors with Limited Ability to Communicate
- Eun-Kyung Kim, Se Young Kim, Mi Ran Eom, Hyun Sook Kim, Eunpyo Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):398-406. Published online August 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.398
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop and test the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Pain Assessment Checklist for Seniors with Limited Ability to Communicate (PACSLAC-K) in assessing pain of elders with dementia living in long-term care facilities.
Methods The PACSLAC-K was developed through forward-backward translation techniques. Survey data were collected from 307 elders with dementia living in 5 long-term care facilities in Korea. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, Spearman's rho, paired t-test, ROC (receiver operation characteristic) curve with the SPSS/WIN (20.0) program.
Results The PACSLAC-K showed high internal consistency (.90), inter-rater reliability (.86), intra-rater reliability (.93), and high concurrent validity (.74) in paired t-test with PAINAD. Discriminant validity also showed a significant difference compared with no pain. The PACSLAC-K showed a sensitivity of .93, specificity of .88, and Area Under the Curve of .95 in the ROC curve.
Conclusion The findings of this study demonstrate that PACSLAC-K is useful in assessing pain for elders with dementia living in long-term care facilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quality of Assessment Tools for Aphasia: A Systematic Review
Francescaroberta Panuccio, Giulia Rossi, Anita Di Nuzzo, Ilaria Ruotolo, Giada Cianfriglia, Rachele Simeon, Giovanni Sellitto, Anna Berardi, Giovanni Galeoto
Brain Sciences.2025; 15(3): 271. CrossRef - Feasibility of Using the EuroQol-5 Dimensions to Identify Masticatory Discomfort in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Han-Nah Kim, Nam-Hee Kim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(3): 237. CrossRef - Implementation and evaluation of a pain assessment app and novel community platform for long-term care health professionals
Vivian Tran, Emily Winters, Eleni Stroulia, Thomas Hadjistavropoulos
Aging & Mental Health.2024; 28(4): 611. CrossRef - Measuring Pain in Aphasia: Validity and Reliability of the PACSLAC-D
Neeltje J. de Vries, Jenny T. van der Steen, Wilco P. Achterberg, Hanneke J.A. Smaling
Pain Management Nursing.2023; 24(4): e68. CrossRef - Development of the Korean Version of the Pain Assessment Tool in Impaired Cognition (KPAIC-15) for Patients with Dementia: A Scale Development
Sun Young Lim, Su Jung Lee, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(2): 218. CrossRef - Reliability and Feasibility of the Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia Scale–Korean Version (PAINAD-K)
So-Hi Kwon, Yeon-Su Cho, Hyunsim Kim
Pain Management Nursing.2021; 22(5): 660. CrossRef - Validation of Pain Assessment Checklist for Seniors with Limited Ability to Communicate‐II (PACSLAC‐II) in Iranian older adults with dementia living in nursing homes
Marjan Haghi, Reza Fadayevatan, Mahtab Alizadeh‐khoei, Bijan Kaboudi, Mahshid Foroughan, Behrouz Mahdavi
Psychogeriatrics.2020; 20(3): 278. CrossRef - Development and Effect of Evidence-based Nursing Practice Guidelines for Pain Management in Patients with Dementia
Young Seun Ryu, Jeong Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(2): 176. CrossRef - Protocolos de gestión del dolor en demencia avanzada
Mercedes Montoro-Lorite, Montserrat Canalias-Reverter
Enfermería Clínica.2018; 28(3): 194. CrossRef - Advanced dementia pain management protocols
Mercedes Montoro-Lorite, Montserrat Canalias-Reverter
Enfermería Clínica (English Edition).2018; 28(3): 194. CrossRef - Pain assessment in elderly with dementia: Brazilian validation of the PACSLAC scale
Karol Bezerra Thé, Fernanda Martins Gazoni, Guilherme Liausu Cherpak, Isabel Clasen Lorenzet, Luciana Alves dos Santos, Edlene Maria Nardes, Fânia Cristina dos Santos
Einstein (São Paulo).2016; 14(2): 152. CrossRef - Nonverbal Pain Measurement for Elders: A Literature Review
Kyung Mi Lee, Jun-Ah Song
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2016; 18(3): 147. CrossRef - Factors affecting nurse's pain management for patients with dementia
Young-Seun Ryu, Jeong-Sook Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 253. CrossRef
- Quality of Assessment Tools for Aphasia: A Systematic Review
- 1,213 View
- 10 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Factors Affecting Dementia Prevalence in People Aged 60 or Over: A Community based Cross-sectional Study
- Seong Min Kim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Mi Ra Sung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):391-397. Published online August 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.391
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to examine the association between body mass index (BMI) and any type of clinical dementia.
Methods Participants were 60,321 people over 60 years of age enrolled in the Seoul Dementia Management Project in 2011. K-MMSE was used to classify participants as having a cognitive impairment and the Clinical Dementia Rating or DSM-IV by psychiatrists or neurologists to determine whether participants were in the dementia group or the non-dementia group. Descriptive statistics, chi-square test, and binary logistic regression analysis were performed.
Results In the univariate analysis, age, education level, living with spouse, BMI, alcohol consumption, and exercise were significantly associated with dementia. In multivariable analysis, increasing age was positively associated with dementia, and educational level was negatively associated with dementia. The exercise group had a lower prevalence of dementia than the non-exercise group. The odds ratio of dementia in the over-weight and obese groups compared to the normal group was 0.85 (95% CI 0.60, 0.98) and 0.64 (95%CI 0.46, 0.75), respectively.
Conclusion Results indicate that dementia is negatively associated with increasing BMI in people aged 60 years or older, but a prospective cohort study is needed to elucidate the causal effect relationship between BMI and dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trajectories of Alzheimer’s Disease Prevalence among National Health Insurance and Medical Aid Beneficiaries from 2010 to 2019
Sanghyun Kim, Changsoo Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Yonsei Medical Journal.2025; 66(9): 590. CrossRef - A comparison of dementia care and policy in five Asian regions: A literature review
Younhee Kang, Dukyoo Jung, Jay Jung Jae Lee, Sumalee Lirtmunlikaporn, Huei-Chuan Sung, Miyae Yamakawa, Yujin Hur, Leeho Yoo
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(2): 174. CrossRef - Associations Among Health Insurance Type, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and the Risk of Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Korea
So-Hyun Moon, Hyun-Ju Seo, Dong Young Lee, Seong Min Kim, Jeong Min Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(14): 2616. CrossRef - Factors affecting aging cognitive function among community‐dwelling older adults
Chun‐Ja Kim, JeeWon Park, Se‐Won Kang, Elizabeth A. Schlenk
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Convergence factors among their physical state, function and activities influencing on the cognition of elderly residents in a community
Jin-Kyoung Park
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2015; 6(6): 153. CrossRef
- Trajectories of Alzheimer’s Disease Prevalence among National Health Insurance and Medical Aid Beneficiaries from 2010 to 2019
- 1,047 View
- 7 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Comparison of Demographic Characteristics, Comorbidity, and Health Habits of Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Older Adults with Normal Cognitive Function
- Myonghwa Park, Mi Ra Sung, Sun Kyung Kim, Dong Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):351-360. Published online August 15, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.351
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was done to compare demographic characteristics, comorbidity, and health habits of elders with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and elders with cognitively normal function (CNF).
Methods Secondary data analysis was conducted using data from the Database of the Seoul Dementia Management Project for 5,773 adults age 60 and above.
Results The MCI group showed an older age distribution, but there was no significant education difference between the two groups. Elders with MCI had more diabetes and stroke than elders with CNF. In subgroups, the same findings were observed in women, but not in men. While more men with MCI had hypertension compared to men with CNF, there was no significant difference in hypertension between the two groups for women. Elders with MCI, men in particular, had a lower prevalence of obesity than men with CNF. MCI individuals did less exercise compared to individuals with CNF. While there were no significant differences in alcohol consumption and smoking between MCI and CNF groups, the over 80's subgroup with MCI reported more alcohol consumption.
Conclusion Findings from this study could be helpful in designing community-based dementia prevention programs and health policies to reduce the prevalence of dementia or related cognitive impairments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimized Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761®: boosted therapeutic benefits with minimized CYP enzyme interference
Sunbeom Kwon, Suji Jeong, Seulah Lee
Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A radiomics model predicts progression from mild cognitive impairment to alzheimer’s disease using structural MRI
Yifei Li, Pengcheng Yi, Mingmin Jin, Yifan Li, Wei Chen
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Manchmal trink ich auch Wasser… – Alkoholkonsum von
Menschen mit leichter kognitiver Beeinträchtigung
Carolin Donath, Elmar Gräßel, Julia-Sophia Scheuermann, Sophia Bösl, Petra Scheerbaum
Psychiatrische Praxis.2024; 51(01): 39. CrossRef - Development of an Internet of things-based treatment adherence program among older adults with mild cognitive impairment using Intervention Mapping: A developmental study
Jinhee Shin, Eunhee Cho, Gwang Suk Kim, Heejung Kim, Byoung Seok Ye, Chang-Gi Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(3): 217. CrossRef - Characteristics and Factors Associated with Cognitive Decline of Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Eul Hee Roh
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(3): 179. CrossRef - Potential genetic biomarkers are found to be associated with both cognitive function and blood pressure: A bivariate genome-wide association analysis
Liming Zhang, Weijing Wang, Chunsheng Xu, Haiping Duan, Xiaocao Tian, Dongfeng Zhang
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development.2022; 204: 111671. CrossRef - Examining the effects of multiple chronic conditions on cognitive decline and potential moderators among older Koreans: Findings from the Korean Longitudinal Study of Ageing 2006–2016
Yura Lee, Chi C. Cho
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2021; 95: 104424. CrossRef - Correlation between Sleep, Depression, Metabolic Syndrome and Cognition in Community Dwelling Elderly
Joohee Shim, Jihyun Baek
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(2): 212. CrossRef - Differential Deficits of Nouns and Verbs in a Generative Naming Task for Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Sujin Choi, Jee Eun Sung, Jee Hyang Jeong
Communication Sciences & Disorders.2020; 25(1): 50. CrossRef - Correlates of cognitive impairment in patients with chronic kidney failure on haemodialysis: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
HyunSoo Oh, JinA Mo, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2019; 75(5): 962. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Participation in National Health Screening Program among Korean Older Adults by Cognitive Function Level
Song Yi Han, Young Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(4): 508. CrossRef - Causal Relationships Between Modifiable Risk Factors of Cognitive Impairment, Cognitive Function, Self-Management, and Quality of Life in Patients With Rheumatic Diseases
JiSuk Park, HyunSoo Oh, Won Park, SeongRyul Kwon, OkKyung Ham, YeonOk Suh, HyeSun Jeong, WhaSook Seo
Orthopaedic Nursing.2018; 37(5): 305. CrossRef - Factors affecting cognitive function according to gender in community-dwelling elderly individuals
Miwon Kim, Jeong-Mo Park
Epidemiology and Health.2017; 39: e2017054. CrossRef - The Effects of a Functional Game (Rejuvenescent Village) for Older Koreans' Cognitive Function, Instrumental Activities of Daily Living, Depression, and Life Satisfaction
Kyung Choon Lim, Min Ho Chun
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2016; 18(4): 296. CrossRef - Effect of an educational tooth-brushing program using priming in an elderly population with dementia residing in nursing homes
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Jung-Soo Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(3): 149. CrossRef - Correlates of Cognitive Impairment of Rheumatic Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
JinA Mo, JiSuk Park, HyunSoo Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 1. CrossRef - Reversion to Normal Cognition and Its Correlates among the Community-dwelling Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment: the Longitudinal Cohort Study
Younhee Kang, Sun A Whang, Kuemju Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(6): 656. CrossRef
- Optimized Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761®: boosted therapeutic benefits with minimized CYP enzyme interference
- 1,152 View
- 8 Download
- 17 Crossref

- The Experience of Adult Korean Children Caring for Parents Institutionalized with Dementia
- Suhye Kwon, Young-Sook Tae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):41-54. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to explore and describe the experience of adult Korean children who are caregivers for parents institutionalized with dementia.
Methods Participants were fourteen adult children caregivers of elders institutionalized with dementia. Data were collected through in-depth unstructured interviews with individual participants from August to November, 2012. Theoretical sampling was used to the point of theoretical saturation. Data were analyzed using Strauss and Corbin's Grounded Theory Method.
Results From open coding, 67 concepts, 29 sub-categories, and 14 categories were identified. Analysis revealed that the core category of the experience of adult children caring for their parents institutionalized with dementia was 'enduring the role of a prop' consisting of four phases: initial turmoil, exploration, role adjustment, and acclimation. To manage the role of a prop, participants utilized various action/interactional strategies such as overcoming the unfamiliarity, overseeing the nursing home care, and counterbalancing the caring roles. As a result, participants experienced ambivalence towards the existence of parents with dementia, changes in family relationships, altered viewpoint towards nursing homes, and restructuring of life.
Conclusion In-depth understanding of the experience will guide nurses to promote effective interventions in order to better support the Korean family caregivers of parents institutionalized with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Association Between Cohabitation With Dementia Patients and Family Mental Health
Yoo J. Lee, In C. Hwang, Hong Y. Ahn
Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders.2025; 39(4): 328. CrossRef - Development of the Care Burden Scale for Family of Elderly in Nursing Facilities
Eun Jeong Kim, Kyung Mi Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(1): 80. CrossRef - A web-based care assistant for caregivers of the elderly: Development and pilot study
Hwawoo Jeon, Yong Suk Choi, Yoonseob Lim
DIGITAL HEALTH.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Time in the State of Dementia Caregiving in South Korea: When Care Becomes (Non-)Waiting
Jieun Lee
Culture, Medicine, and Psychiatry.2023; 47(4): 898. CrossRef - Depression, anxiety, and sleep quality of caregivers of children with spinal muscular atrophy
Almala Pinar Ergenekon, Zeynep Gümüş, Cansu Yilmaz Yegit, Muruvvet Cenk, Aynur Gulieva, Mine Kalyoncu, Merve Selcuk, Seyda Karabulut, Gulten Ozturk, Ela Erdem Eralp, Olcay Unver, Bulent Karadag, Yasemin Gokdemir
Pediatric Pulmonology.2023; 58(6): 1697. CrossRef - Empathy and perceived burden in caregivers of patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders
Rosaria Di Lorenzo, Anna Girone, Nunzio Panzera, Gianluca Fiore, Margherita Pinelli, Giulia Venturi, Federica Magarini, Paola Ferri
BMC Health Services Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Family Members’ Experience in Caring for Elderly with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals
Eun Kyoung Suh, Hye Ryoung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 335. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Scale for Partnership in Care—for Family (SPIC-F)
Hye-Young Jang, Eun-Ok Song
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(6): 1882. CrossRef - Partnership between staff and family in long-term care facility: a hybrid concept analysis
Hye-Young Jang
International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being.2020; 15(1): 1801179. CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Evaluation of a Fear of Dementia Scale for Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Minkyung LEE, Dukyoo JUNG
Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 28(3): e94. CrossRef - Predictors of Satisfaction with Care Services among Family Members of Older Adult Residents of Long-Term Care Facilities
Eun-Ok Song, Hye-Young Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3298. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis of Fear of Dementia
Minkyung Lee, Dukyoo Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(2): 206. CrossRef - Caregiver burden and prevalence of depression, anxiety and sleep disturbances in Alzheimer's disease caregivers in China
Shuai Liu, Chonghui Li, Zhihong Shi, Xiaodan Wang, Yuying Zhou, Shuling Liu, Jing Liu, Tao Yu, Yong Ji
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2017; 26(9-10): 1291. CrossRef - The Effect of Post-Stroke Depression on Rehabilitation Outcome and the Impact of Caregiver Type as a Factor of Post-Stroke Depression
Dong-Heun Ahn, Yung-Jin Lee, Ji-Hun Jeong, Yong-Rok Kim, Jong-Bum Park
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2015; 39(1): 74. CrossRef
- The Association Between Cohabitation With Dementia Patients and Family Mental Health
- 1,132 View
- 8 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Overcoming Experiences of Family Members Caring for Elderly Patients with Dementia at Home
- Mi Ra Sung, Myungsun Yi, Dong Young Lee, Hye Young Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(3):389-398. Published online June 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.389
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to understand and describe the overcoming experiences of family members caring for elderly patients with dementia at home.
Methods Data came from autobiographies on the overcoming experiences of caregiving from 31 participants, who had submitted the autobiographies to a public contest held by the Seoul Metropolitan Center for Dementia in 2012. Data were analyzed using qualitative content analysis.
Results Four overcoming stages emerged from the analysis: confronting stage; challenging stage; integrating stage; and transcendental stage, representing transformation of experiences from frustration and suffering to happiness and new hope in life. The confronting stage illustrates severe negative feelings and exhaustion occurring after the diagnosis of dementia. The challenging stage signifies major driving forces in taking good care of their patients. It includes tender loving memories about the patients as well as family and social supports. The integrating stage shows genuine empathy for the patients' situation and the happiness of 'here and now', while the transcendental stage represents new hope in the future.
Conclusion Health professionals need to support caregivers to find true meaning of caring and happiness in everyday life, while providing specific information on dementia care and relieving various negative feelings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing the care burden among family caregivers using dementia care centers for older adults with dementia in Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
Ja Eun Kim, Soo Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(4): 382. CrossRef - Experiences of Family Caregivers of Older Adults With Dementia in Korea During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Analysis
Eun Same Joh, Yun-Jung Choi
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2024; 50(10): 42. CrossRef - Characteristics of Early Onset Dementia and Caring Experiences and Service Needs of Family Caregivers: A Mixed Methods Study
Jin Ha Kim, Gyungjoo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(2): 101. CrossRef - Time usage analysis according to occupational area and satisfaction level in family caregivers of dementia patients
Woo-Hyuk Jang, Jong-Sik Jang, Jong-Hwi Park
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15178. CrossRef - Experience of family caregivers using dementia management programs for patients with dementia during COVID-19: Based on focus group interviews
Doonam Oh, Jeonghae Hwang, Seonghee Jeong
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(5): 101. CrossRef - Safety Accidents and Coping Experiences among Family Caregivers Caring for Community-Dwelling Persons Living with Dementia
Ji Yeon Lee, Ha Rim Lee, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 352. CrossRef - Health Promotion Behavior among Older Korean Family Caregivers of People with Dementia
Aram Cho, Chiyoung Cha
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4123. CrossRef - Changes in Family Dynamics in Caregiving for People With Dementia in South Korea: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Seieun Oh, Mi Yu, Young Mi Ryu, Haejin Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Qualitative Health Research.2020; 30(1): 60. CrossRef - Family Members’ Experience in Caring for Elderly with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals
Eun Kyoung Suh, Hye Ryoung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 335. CrossRef - Factors associated with Burden of Family Caregivers of Home-dwelling Elderly People with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Eun Kyung Kim, Heeok Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(4): 351. CrossRef - Patient and Caregiver Interplay in Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Family Caregiver’s Experience
Jun-Ah Song, Myonghwa Park, Jaewon Park, Hong Jin Cheon, Mihyun Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2018; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Experience of a Special Rating Dementia Service for Family Caregivers of Elderly People with Dementia
Hee Kyung Cho, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(2): 231. CrossRef - Experiences of Family Caregivers Utilizing Care Support of Dementia Center
Chun-Gill Kim, Myung Soon Kwon, Young Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(3): 314. CrossRef - Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on Caring Experience of Nurses Working in a Chemotherapy Ward in Korea
Ji Young Seo, Myungsun Yi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(1): 55. CrossRef - A Prediction Model for Unmet Needs of Elders with Dementia and Caregiving Experiences of Family Caregivers
Sora Choi, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 663. CrossRef - Knowledge about dementia in South Korean nursing students: a cross-sectional survey
Jung Ha Shin, Hyun-Ju Seo, Kye Ha Kim, Kyoung-Hoon Kim, Youngjin Lee
BMC Nursing.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Compassion Fatigue within Dementia Nursing Practice: A Concept Analysis
Ju Young Ha, So Young Jeon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2015; 17(1): 48. CrossRef - Experience of Treatment Adherence in Korean Patients with HIV
Yunhee Park, Min Jeong Seo, Sanghee Kim, Soon-Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(4): 407. CrossRef - Cognitive Function, Behavioral Problems, and Physical Function in Long‐Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries with Dementia in South Korea: Comparison of Home Care and Institutional Care Services
Tae Wha Lee, Eunsil Yim, Eunhee Cho, Jane Chung
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2014; 62(8): 1467. CrossRef
- Factors influencing the care burden among family caregivers using dementia care centers for older adults with dementia in Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
- 1,247 View
- 7 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Depression and Suicidal Ideation in Elders with Dementia
- Jong Pil Kim, Mi-Yeul Hyun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(2):296-303. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.296
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the prevalence of depression and suicidal ideation in elders with dementia and to identify factors influencing their suicidal ideation.
Methods A descriptive and cross-sectional study was conducted from February to March, 2011. The participants were 298 older adults whose MMSE-KC score was 15 to 23. Collected Data were analyzed using t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression.
Results According to the Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) classification criteria, 86.2% of the elders in this study exhibited depression (GDS=5), and 31.5% manifested severe depression. The mean score of suicidal ideation was 5.70 (range 0-20). The risk factors for suicidal ideation were depression, suicidal attempt experience, present location for care, and activities of daily living.
Conclusion The results of this study can be utilized in the development of suicide prevention programs for older adults with dementia. In particular, depression should be screened and managed to reduce suicidal ideation of older adults with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determinants of suicidal behavior in dementia: A Swedish national register-based study
Khedidja Hedna, Robert Sigström, Kristina Johnell, Margda Waern
International Psychogeriatrics.2024; 36(5): 415. CrossRef - Understanding Suicide Risk in People with Dementia and Family Caregivers in South Korea: A Systematic Review
Jung Won Kong, Ji Young Park
Behavioral Sciences.2022; 12(4): 97. CrossRef - Suicide prevention strategies for older persons—An integrative review of empirical and theoretical papers
Anne Lise Holm, Elin Salemonsen, Elisabeth Severinsson
Nursing Open.2021; 8(5): 2175. CrossRef - Suicide risk within 1 year of dementia diagnosis in older adults: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Jae Woo Choi, Kang Soo Lee, Euna Han
Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience.2021; 46(1): E119. CrossRef - Effects of Fumanet exercise on Korean older adults with mild dementia
Sun Mi Lee, Jaewon Joung, Sung Hee Shin
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of Suicide and the Psychiatric Perspective
Silke Bachmann
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2018; 15(7): 1425. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a community-based program for suicide prevention among elders with early-stage dementia: A controlled observational study
Jong-Pill Kim, Jinhyang Yang
Geriatric Nursing.2017; 38(2): 97. CrossRef - Suicide and assisted dying in dementia: what we know and what we need to know. A narrative literature review
J. Diehl-Schmid, R. Jox, S. Gauthier, S. Belleville, E. Racine, C. Schüle, G. Turecki, S. Richard-Devantoy
International Psychogeriatrics.2017; 29(8): 1247. CrossRef - Depression and suicidal ideation in community-dwelling older adults in Korea
So-Hi Kwon, Myungji Sohn
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2014; 25(3): 655. CrossRef - The Correlation between Problematic Behaviors and Activities of Daily Living of Elderly People with Dementia in Patients in a Geriatric Hospital
Joong San Wang, Ju Hwan Lee, Ki Mai Um
Journal of International Academy of Physical Therapy Research.2013; 4(2): 545. CrossRef
- Determinants of suicidal behavior in dementia: A Swedish national register-based study
- 1,153 View
- 2 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of Dementia Knowledge, Self-Efficacy and Depression on Dementia Preventive Behavior in Elderly Couples: Dyadic Data Analysis
- Suk Jeong Ko, Sung Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(2):276-286. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to examine actor and partner effect of dementia knowledge, self-efficacy and depression on dementia preventive behavior in elderly couples.
Methods Participants were 115 couples aged 60 years or over who met eligibility criteria. All measures were self-administered. Data were analyzed using SPSS 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 program.
Results Dementia knowledge in elderly couples showed actor and partner effect on dementia preventive behavior. Self-efficacy in the wife did not have direct effects on dementia preventive behavior, but showed indirect effects through dementia knowledge. Self-efficacy in the husband showed direct effects on dementia preventive behavior and indirect effects through dementia knowledge. Wife's depression had direct actor effect on dementia preventive behavior and indirect effect through self-efficacy and dementia knowledge. Husband's depression did not have direct actor effect on dementia preventive behavior, but indirect effect through self-efficacy and dementia knowledge. Effect size of wives' dementia knowledge, self-efficacy and depression on dementia preventive behavior was larger than that of husbands'. Dementia preventive behavior, dementia knowledge and depression had a mutual effect.
Conclusion Results indicate that to promote dementia preventive activity in elderly couples, programs should be conducted for both of the couple, but focused differently for wife and husband.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expanding the health belief model on dementia knowledge, fear, and preventive behaviors among older adults in Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
Jeong Eui Yun, Suyoung Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 60. CrossRef - Factors Related to Dementia Attitudes Among Dementia Care Providers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jong-Mi Lim, OK-Hee Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 159. CrossRef - Effects of the dual-task training program for Korean older adults with mild cognitive impairment in community
Eunyoung Shin, Hyun Jin Roh, Sohyune Sok
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 60: 5. CrossRef - Determinants of Dementia-Preventive Behaviors: A Scoping Review Based on the PRECEDE Model
So Im Ryu, Min Hye Lee, Yeon-Hwan Park
Sage Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between dementia education and preventive behaviors: The mediation of fear and knowledge of dementia
Jina Han
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(2): 55. CrossRef - Factors associated dementia preventive behavior of older adults in a local community: Application of the information-motivation-behavioral skills model: A cross-sectional study
Eun Hye Ha, Mi Yang Jeon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 34. CrossRef - The development and evaluation of a self-efficacy enhancement program for older adults with mild cognitive impairment
Jungeun Lee, Eunhee Cho, Heejung Kim, Kyung Hee Lee, Eosu Kim, Byoung Seok Ye
Applied Nursing Research.2023; 73: 151726. CrossRef - Development of the Korean Health Behavior for Dementia Prevention Scale for Older Adults
Hyukjoon Kim, Moonjoo Oh, Hyangsuk Kwon, Seohee Jeong, Hyangsoon Cho, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(3): 363. CrossRef - Factors influencing dementia prevention behaviors in older Koreans enrolled in senior welfare centers
Kyung-Choon Lim, Myoungsuk Kim, Hana Ko
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(1): 39. CrossRef - Factors associated with Burden of Family Caregivers of Home-dwelling Elderly People with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Eun Kyung Kim, Heeok Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(4): 351. CrossRef - Actor and Partner Effects of Health Status, Marital Satisfaction and Self Efficacy on Retirement Preparation of Middle Aged Couples: Actor-Partner Interdependence Model Analysis
Eun Hee Jung, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(2): 154. CrossRef - Testing the stress-buffering hypothesis of social support in couples coping with early-stage dementia
Paul Gellert, Andreas Häusler, Ralf Suhr, Maryam Gholami, Michael Rapp, Adelheid Kuhlmey, Johanna Nordheim, Horacio Firmino
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(1): e0189849. CrossRef - Effects of a Memory and Visual-Motor Integration Program for Older Adults Based on Self-Efficacy Theory
Eun-Hwi Kim, Soon-Rim Suh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 431. CrossRef - The Dementia Knowledge, Attitude and Preventive Behavior of the Elderly Lived in the Urban-Rural Complex City
Koung-Me Kim, Young-Ok Yang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 485. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Alzheimer's Disease Knowledge Scale-Korean Version
Eun Joo Kim, Ji-young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 107. CrossRef - Dyadic Effects of Individual and Friend on Physical Activity in College Students
Gwang Suk Kim, Chung Yul Lee, In Sook Kim, Tae Hwa Lee, Eunhee Cho, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Linda L. McCreary, Su Hee Kim
Public Health Nursing.2015; 32(5): 430. CrossRef - Does Pain Mediate or Moderate the Effect of Cognitive Impairment on Aggression in Nursing Home Residents with Dementia?
Hyochol Ahn, Ann Horgas
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(2): 105. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-esteem and Family Stress on Depression of Middle-aged Couples: Analysis of Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Yu Jeong Yang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 60. CrossRef
- Expanding the health belief model on dementia knowledge, fear, and preventive behaviors among older adults in Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
- 1,038 View
- 10 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Characteristics of Eating Behavior in Elders with Dementia residing in Long-Term Care Facilities
- Kyoung Min Lee, Jun-Ah Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(4):466-476. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.466
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore characteristics of eating behavior according to level of functional status of elders with dementia (EWD), and to examine feeding time, change in food intake and body mass index (BMI) according to eating behavior.
Methods Participants were 149 EWD residing in long-term care facilities located in Seoul or Gyeonggi province and evaluated using the Mini-Mental State Exam-Korean version, Korean version-Activities of Daily Living, and Eating Behavior Scale (EBS). Feeding time, change in food intake, and BMI were also measured. Data were analyzed using SPSS 17.0, specifically descriptive statistics, ANOVA, and Chi-square test.
Results Participants' mean EBS score was 10.43±6.01 and half of them (54.4%) needed moderate or total assistance while eating. The EBS score was significantly lower for elders with severe dementia compared to those with mild or moderate dementia; and elders with severe ADL dependence compared to those with mild or moderate ADL dependence. Lower EBS scores were related to longer feeding time, a greater the rate of participants with decreased food intake and 'underweight' BMI.
Conclusion Nursing intervention programs which are designed for EWD are needed to maintain functional eating skills and prevent negative consequences in this population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of mealtime difficulty scale for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities
Dukyoo Jung, Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Hyesoon Lee
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with eating performance in older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities: a cross-sectional study
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C. De Gagne, Hyesoon Lee, Minkyung Lee
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Eating Difficulties among Older Adults with Dementia in South Korean Long-Term Care Facilities: A Scoping Review
Dukyoo Jung, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 470. CrossRef Feasibility of a Mobile Meal Assistance Program for Direct Care Workers in Long-Term Care Facilities in South Korea
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C De Gagne, Minkyung Lee, Hyesoon Lee, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi, Juyoun Chung
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2020; Volume 15: 2019. CrossRef- High feeding dependence prevalence in residents living in Italian nursing homes requires new policies: Findings from a regionally based cross-sectional study
Alvisa Palese, Luca Grassetti, Davide Bandera, Ranieri Zuttion, Barbara Ferrario, Sandra Ponta, Mark Hayter, Roger Watson
Health Policy.2018; 122(3): 301. CrossRef - Factors associated with Feeding Difficulty in Long-term Care Facility Older Adults with Dementia
Jeong Lee, Se Ang Ryu
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Feeding Difficulty and its influencing factors of Elders with Dementia in Long-term Care Facilities
Hyun-Hwa Hong, Mee-Ock Gu
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(2): 1240. CrossRef
- Development of mealtime difficulty scale for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities
- 920 View
- 5 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of Multisensory Stimulation Using Familiarity: Persons with Dementia in Long-term Care Facility in Korea
- Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(4):528-538. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.528
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to examine the effects of multisensory stimulation (MSS) using familiarity on persons with dementia (PWDs) residing in nursing homes in Korea.
Methods A nonequivalent control group with pre and posttests was used. Fifty one PWDs were included if they: 1) were over 65 yr old, 2) were diagnosed with dementia, 3) had no visual or speech impairments, 4) were able to communicate, and 5) had spent more than one month in a nursing home. The experimental group (n=25) received a 55 min MSS program twice a week for 10 weeks. The outcome variables included were cognition, activities of daily living, grip strength, depression, wandering, and aggressive behaviors. Repeated ANOVA was used for data analysis.
Results There were no significant differences in demographics or the main variables at pretest. Cognition, depression, wandering, and aggressive behaviors were significant over time between the two groups. Grip strength was only significant when accounting for interaction between group and time.
Conclusion An intervention of MSS using familiarity was marginally effective in improving cognition, depression, wandering, and aggression. Future study is suggested with a larger sample and longer treatment to retest the effects of MSS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of multisensory environment/stimulation therapy on adults with cognitive impairment and/or special needs: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Meret Helbling, Marie‐Laure Grandjean, Murali Srinivasan
Special Care in Dentistry.2024; 44(2): 381. CrossRef - Personally tailored activities for improving psychosocial outcomes for people with dementia in long-term care
Ralph Möhler, Stella Calo, Anna Renom, Helena Renom, Gabriele Meyer
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomization controlled and nonrandomized controlled studies on nurse‐led nonpharmacological interventions to improve cognition in people with dementia
Yujin Suh, Sumi Lee, Go‐Eun Kim, JuHee Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3155. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological Intervention for Wandering Behavior in Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Yoojin Kim, Eunhee Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 321. CrossRef - A pragmatic trial testing a tailored non pharmacologic therapies on nocturnal behavioral and psychological symptoms associated with dementia
Thierry Bautrant, Caroline Franqui, Hossein Clément, Maurice Rabault, Faima Masseboeuf, Manon Pastore, Magali Pardo, Yannick Brandi, Nicolas Drouin, Anne-Daphnée Brice, Michel Grino
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 43: 85. CrossRef - The Development of Wholeness Program for Effects Dementia-Buffering Testing of the Demented Elderly
Hye-Jeon Hong
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(1): 405. CrossRef - Personally tailored activities for improving psychosocial outcomes for people with dementia in long-term care
Ralph Möhler, Anna Renom, Helena Renom, Gabriele Meyer
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of an educational tooth-brushing program using priming in an elderly population with dementia residing in nursing homes
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Jung-Soo Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(3): 149. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological interventions for agitation in dementia: systematic review of randomised controlled trials
Gill Livingston, Lynsey Kelly, Elanor Lewis-Holmes, Gianluca Baio, Stephen Morris, Nishma Patel, Rumana Z. Omar, Cornelius Katona, Claudia Cooper
British Journal of Psychiatry.2014; 205(6): 436. CrossRef
- Effects of multisensory environment/stimulation therapy on adults with cognitive impairment and/or special needs: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- 1,256 View
- 29 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Comorbidity and Health Habits of Seoul City Elders with Dementia
- Yoon Kyoung Lee, Mi Ra Sung, Dong Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(3):411-422. Published online June 13, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.411
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to clarify the actual condition of elders with dementia who were registered in the Seoul Dementia Management Project.
Methods Data were collected from 5,312 elderly patients with dementia. Demographic included characteristics, comorbidity, and healthy lifestyle habits; data from the Seoul Dementia Management Project.
Results First, demographic characteristics were as follows; mean age at the time of definite diagnosis was 78.0 yr. There were slightly more women (69.3%), and 4.55 yr was the average length of education with 41.4% being illiterate or uneducated patients. Second, there were several comorbidities including hypertension (61.7%), diabetes mellitus (31.8%), hypercholesterolemia (10.2%), heart disease (11.1%), obesity (4.2%), and stroke (21.4%). Third, alcoholic history was found in 11.8% of the patients, and smoking in 9.8%. Regular exercise was done by only 29.1% of the patients with dementia. Finally, significant differences between men and women were found for the following; age, education, medical security, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, stroke, alcoholic consumption, smoking, and regular exercise.
Conclusion Authors expect that the present data will be used for establishment of dementia associated projects and policies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Dementia in Korea by Socioeconomic Status between Medical Aid Beneficiaries and National Health Insurance Beneficiaries
Sanghyun Kim, Yoon Jung Choi, Changsoo Kim
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2023; 3(2): 205. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Participation in National Health Screening Program among Korean Older Adults by Cognitive Function Level
Song Yi Han, Young Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(4): 508. CrossRef - Associations Among Health Insurance Type, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and the Risk of Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Korea
So-Hyun Moon, Hyun-Ju Seo, Dong Young Lee, Seong Min Kim, Jeong Min Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(14): 2616. CrossRef - Public knowledge about dementia in South Korea: a community-based cross-sectional survey
Hyun-Ju Seo, Dong Young Lee, Mi Ra Sung
International Psychogeriatrics.2015; 27(3): 463. CrossRef - Comparison of Demographic Characteristics, Comorbidity, and Health Habits of Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Older Adults with Normal Cognitive Function
Myonghwa Park, Mi Ra Sung, Sun Kyung Kim, Dong Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(4): 351. CrossRef - The Common Patterns of Multimorbidity and Its Impact on Healthcare Cost in Korea
Chang-Hoon Kim, Inkyung Hwang, Weon-Seob Yoo
Health Policy and Management.2014; 24(3): 219. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Dementia Prevalence in People Aged 60 or Over: A Community based Cross-sectional Study
Seong Min Kim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Mi Ra Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(4): 391. CrossRef - Application Technologies of Smart Phone for Emotional Satisfaction and Mental Health-care of the Elderly
Myeon-Gyun Cho, Shik Kim
IEMEK Journal of Embedded Systems and Applications.2013; 8(1): 31. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Dementia in Korea by Socioeconomic Status between Medical Aid Beneficiaries and National Health Insurance Beneficiaries
- 990 View
- 1 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Development of Dementia Care Standards
- Ju Young Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(5):631-641. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.5.631
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop standards for dementia care as a baseline for professional nurses to provide a framework for dementia care evaluation.
Methods The dementia care standards were developed through a literature review and focus group discussions. According to the Delphi method, the data analysis was conducted using the Content Validity Index (CVI).
Results The final set of 18 standards on dementia care was developed through one round of CVI. The standards included four structural standards: 'Organization of nursing system', 'Operating system', 'Management of human resources', 'Management of material resources', 13 procedural standards: 'Advanced assessment', 'Nursing diagnosis', 'Nursing plan', 'Advanced nursing implementation', 'Evaluation', 'Education', 'Research', 'Consultation', 'Counseling and cooperation', 'Development of specialty', 'Utilizing resources', 'Nursing quality assurance', 'Ethics', and one standard concerning outcome ('Evaluation of nursing tasks in care of patients with dementia'). The final set of 55 criteria on care of patients with dementia was confirmed through two rounds of CVI. The final 171 indicators were confirmed through four rounds of CVI.
Conclusion These dementia care standards provides a framework that allows registered nurses to clarify their roles and tasks in the care of patients with dementia and provides evaluation criteria.
- 880 View
- 8 Download

- An Analysis of the Meaning of Respite for Family Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia
- Mi Ryeong Song, Yong-Mi Lee, Suk-Hee Cheon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(4):482-492. Published online August 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.4.482
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was a qualitative research study in which focus group interviews were used to collect data on the meaning of respite for family caregivers who are taking care of elders with dementia.
Methods The focus group interviews and participants consisted of 2 family caregiver groups, for a total of 8 people taking care of their elders and 5 professional caregivers working in a geriatrics hospital or social welfare institutions. Content analysis was used and debriefing notes were referred in order to analyze the data.
Results The meaning of respite in this research was measured using 4 main categories: 'Temporary break from routine', 'direct help', 'psychological comfort', 'valuables which cannot be taken easily' and 9 subcategories: 'Temporary diversion of attention', 'temporarily free from my duty', 'taking care of oneself', 'receiving economic help', 'empathize with others', 'comfort based on trust', 'resting together with the elder', 'no time to rest', 'cannot get out of one's obligatory duty'.
Conclusion The findings of the study show that rest means not only a temporary relief from caretaking, but also a real respite based on the patients' stable state and comfort. These results indicate a new meaning for respite, that the first step of respite program has to begin even when the caregivers do not recognize the need for respite.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Self-care on Burnout in Primary Family Caregiver of Person with Dementia
Jeong Hwa Kwon, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 217. CrossRef - Changes in Family Dynamics in Caregiving for People With Dementia in South Korea: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Seieun Oh, Mi Yu, Young Mi Ryu, Haejin Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Qualitative Health Research.2020; 30(1): 60. CrossRef - Recognition Study on Usage Motivation and Dissatisfaction Factor at Short Stay Service -Focus on User’s Caregiver
김영태
Korean Journal of Gerontological Social Welfare.2018; 73(1): 235. CrossRef - Experience of a Special Rating Dementia Service for Family Caregivers of Elderly People with Dementia
Hee Kyung Cho, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(2): 231. CrossRef - The Postnatal Care Experiences among First Time Chinese Immigrant Mothers Living in Korea
Ju-Eun Song, So Mi Park, Eun Ha Roh
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(1): 48. CrossRef - Overcoming Experiences of Family Members Caring for Elderly Patients with Dementia at Home
Mi Ra Sung, Myungsun Yi, Dong Young Lee, Hye Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(3): 389. CrossRef - Respite Care for Family Caregivers of Elders with Dementia : Concept Clarification
Sung-Ok Chang, Mi-Ryeong Song, Gye-Soon Kong, Suk-Hee Choen
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 23. CrossRef
- Influence of Self-care on Burnout in Primary Family Caregiver of Person with Dementia
- 1,048 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of a Robot Pet-assisted Program for Elderly People with Dementia
- Jung Hee Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(4):562-573. Published online August 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.562
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effects on the cognitive function, Activities of Daily Living (ADL), mood, social behaviors, and problematic behaviors of robot pet-assisted program for elderly people with dementia.
Methods This study was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants were 32 elders with dementia. Seventeen were assigned to the experimental group and 15 to the control group. The intervention was conducted twice a week for 6 weeks.
Results 1) After the program, cognitive function, ADL, and social behaviors did not show significant differences. 2) After the program, mood of experimental group was significantly better than that of the control group. 3) After the program, problematic behaviors of the experimental group were significantly more diminished than those of control group. 4) As a result of analyzing the response, robot pet-assisted program was effective such as inducing a positive emotional state and increasing communication and interaction.
Conclusion The robot pet-assisted program was effective in changing the mood and diminishing problematic behaviors and had positive effects such as increasing communication and interaction for elders with dementia. Therefore, this program should be considered as a positive program for physical and emotional support for elders with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital interventions to reduce social isolation and loneliness in older adults: An evidence and gap map
Vivian Welch, Elizabeth T. Ghogomu, Victoria I. Barbeau, Sierra Dowling, Rebecca Doyle, Ella Beveridge, Elisabeth Boulton, Payaam Desai, Jimmy Huang, Nour Elmestekawy, Tarannum Hussain, Arpana Wadhwani, Sabrina Boutin, Niobe Haitas, Dylan Kneale, Douglas
Campbell Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital healthcare for dementia and cognitive impairment: A scoping review
Minsung Sohn, JungYeon Yang, Junyoung Sohn, Jun-Hyup Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2023; 140: 104413. CrossRef - Systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomization controlled and nonrandomized controlled studies on nurse‐led nonpharmacological interventions to improve cognition in people with dementia
Yujin Suh, Sumi Lee, Go‐Eun Kim, JuHee Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3155. CrossRef - The use of technology for social interaction by people with dementia: A scoping review
Merryn Anderson, Rachel Menon, Katy Oak, Louise Allan, Matthew Chua Chin Heng
PLOS Digital Health.2022; 1(6): e0000053. CrossRef - Socially assistive robots for people with dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of feasibility, acceptability and the effect on cognition, neuropsychiatric symptoms and quality of life
Clare Yu, Andrew Sommerlad, Lena Sakure, Gill Livingston
Ageing Research Reviews.2022; 78: 101633. CrossRef - Can Use of Digital Technologies by People with Dementia Improve Self-Management and Social Participation? A Systematic Review of Effect Studies
David Neal, Floor van den Berg, Caroline Planting, Teake Ettema, Karin Dijkstra, Evelyn Finnema, Rose-Marie Dröes
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(4): 604. CrossRef - Pet-Assisted Therapy for Delirium and Agitation in Hospitalized Patients with Neurocognitive Impairment: A Review of Literature
Abu Baker Sheikh, Nismat Javed, Katarina Leyba, Ali Hamza Khair, Zainab Ijaz, Aimen Asim Dar, Hamza Hanif, Asif Farooq, Rahul Shekhar
Geriatrics.2021; 6(4): 96. CrossRef - Factors related to the effectiveness in the use of an ICT-based toy robot for the in-home care of community dwelling elderly
Heui Sug Jo, Ji Hee Kim, Saerom Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(5): 43. CrossRef - Effects of Intervention Using PARO on the Cognition, Emotion, Problem Behavior, and Social Interaction of Elderly People with Dementia
In Soon Koh, Hee Sun Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 300. CrossRef - Prospects of Geriatric Nursing Application Based on Robot Technology
Jin Hwan Oh
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(Suppl 1): 127. CrossRef - Interaction of robot with humans by communicating simulated emotional states through expressive movements
Sara Baber Sial, Muhammad Baber Sial, Yasar Ayaz, Syed Irtiza Ali Shah, Aleksandar Zivanovic
Intelligent Service Robotics.2016; 9(3): 231. CrossRef - Effects of Silver-Care-Robot Program on Cognitive Function, Depression, and Activities of Daily Living for Institutionalized Elderly People
Jin-Hwan Oh, Yeo-Jin Yi, Chul-Jin Shin, Cheonshu Park, Sangseung Kang, Jaehong Kim, In-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(3): 388. CrossRef - Care robots for the supermarket shelf: a product gap in assistive technologies
TIM BLACKMAN
Ageing and Society.2013; 33(5): 763. CrossRef - Effects of Multisensory Stimulation Using Familiarity: Persons with Dementia in Long-term Care Facility in Korea
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 528. CrossRef
- Digital interventions to reduce social isolation and loneliness in older adults: An evidence and gap map
- 1,490 View
- 37 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Analysis of Conversation between Elderly Patients with Dementia and Nurses: Focusing on Structure and Sequential Patterns
- Myungsun Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(2):166-176. Published online April 28, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.166
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to identify functional structure and patterns of dialogue sequence in conversations between elderly patients with dementia and nurses in a long-term care facility.
Methods Conversation analysis was used to analyze the data which were collected using video-camera to capture non-verbal as well as verbal behaviors. Data collection was done during February 2005.
Results Introduction, assessment, intervention, and closing phases were identified as functional structure. Essential parts of the conversation were the assessment and intervention phases. In the assessment phase three sequential patterns of nurse-initiated dialogue and four sequential patterns of patient-initiated dialogue were identified. Also four sequential patterns were identified in nurse-initiated and three in patient-initiated dialogues in the intervention phase. In general, "ask question", "advise", and "directive" were the most frequently used utterance by nurses in nurse-initiated dialogue, indicating nurses' domination of the conversation. At the same time, "ask back", "refute", "escape", or "false promise" were used often by nurses to discourage patients from talking when patients were raising questions or demanding.
Conclusion It is important for nurses to encourage patient-initiated dialogue to counterbalance nurse-dominated conversation which results from imbalance between nurses and patients in terms of knowledge and task in health-care institutions for elders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A staff training intervention to improve communication between people living with dementia and health-care professionals in hospital: the VOICE mixed-methods development and evaluation study
Rowan H Harwood, Rebecca O’Brien, Sarah E Goldberg, Rebecca Allwood, Alison Pilnick, Suzanne Beeke, Louise Thomson, Megan Murray, Ruth Parry, Fiona Kearney, Bryn Baxendale, Kate Sartain, Justine Schneider
Health Services and Delivery Research.2018; 6(41): 1. CrossRef
- A staff training intervention to improve communication between people living with dementia and health-care professionals in hospital: the VOICE mixed-methods development and evaluation study
- 1,006 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Wandering Behavior in Korean Elders with Dementia Residing in Nursing Homes
- Jun-Ah Song, Young Mi Lim, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):29-28. Published online February 28, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study investigated various factors relatied to wandering behavior of Korean elders with dementia (KED).
Methods A sample of 160 ambulatory residents with dementia from 14 long term care facilities was used to examine demographic, individual, cognitive, physical health, and environmental characteristics by comparing wanderers (N=108) to nonwanders (N=52). Subjects were evaluated by Korean versions of the Mini-mental State Exam (K-MMSE), the Physical and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (K-PIADL), and the Revised Algase Wandering Scale Nursing Home version (KRAWS-NH) along its six dimensions. Demographic and environmental data were also obtained. Independent sample t-tests, Chi-square test, Fisher's Exact tests, and ANCOVAs were used to examine differences between wanderers and nonwanders.
Results Wanderers were significantly (p<.05) older and had more limitations in K-PADL and K-IADL. The degree of overall wandering and certain features of wandering were significantly different (p<.05) by total number of residents in the facility, type of bedroom (i.e., "Ondol"), and color of bedroom and living-room walls (i.e., sky blue).
Conclusion Findings of this study may be useful in understanding wandering behavior of KEDs and thus developing more culturally specific management strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors Associated with Missing Incidents among Persons Living with Dementia: A Scoping Review
Hector Perez, Antonio Miguel Cruz, Noelannah Neubauer, Christine Daum, Aidan K. Comeau, Samantha Dawn Marshall, Elyse Letts, Lili Liu
Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement.2024; 43(3): 370. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological Intervention for Wandering Behavior in Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Yoojin Kim, Eunhee Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 321. CrossRef - A Relationship between Depression and Wandering in Community-Dwelling Elders with Dementia
Jae Gwon Jeong, Jun Ah Song, Kun Woo Park
Dementia and Neurocognitive Disorders.2016; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Validation of the Measure of Unmet Need For Dementia Family Caregivers For Korean Sample
Kyeonga Yoon, 손의성
Korean Journal of Gerontological Social Welfare.2015; null(70): 197. CrossRef - The Long-term Care Utilization of the Elderly with Dementia, Stroke, and Multimorbidity in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Soonman Kwon, Hongsoo Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(1): 90. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Dysphagia Assessment Tool and an Intervention Program for the Elderly in the Long-Term Care Facilities
Chi-Young Kim, Young-Mi Lee, Eun-Ho Ha
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(2): 685. CrossRef - Relationship between familiar environment and wandering behaviour among Korean elders with dementia
Gwi‐Ryung Son Hong, Jun‐Ah Song
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2009; 18(9): 1365. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Observable Indicators of Nursing Home Care Quality Evaluation Instrument
Jia Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 474. CrossRef
- Risk Factors Associated with Missing Incidents among Persons Living with Dementia: A Scoping Review
- 1,085 View
- 8 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Conversation Analysis of Communication between Patients with Dementia and Their Professional Nurses
- Myungsun Yi, Bong Sook Yih
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(7):1253-1264. Published online December 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.7.1253
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand conversations and to identify typical conversational problems between nurses and patients with dementia.
Method A conversation analysis method was used. The data was collected in a geriatric institutional setting, using a videotape recorder, and transcribed. The transcribed data was analyzed in terms of expressions, contents, and relationships to identify communicative problems and their resolutions.
Results Among a total of 532 episodes, 440(82.7%) were identified as nurse-involved episodes. In addition, 66 of the 440 episodes were selected based on the significance of the conversation. The communicative problems between nurses and patients in terms of expressions were identified as “directive and authoritative expressions”, “emotional and competitive expressions”, “evasive and on-looking expressions”, and “excessive use of title only”, such as calling them granny or grandpa without proper names. In terms of content and relationships, “lack of themes in psychosocial areas” and “nurse-led relations” were identified respectively as communicative problems.
Conclusion The results of this study will provide substantial guidelines for nurses in caring for elderly patients with dementia by deeply understanding linguistic structures and problems of everyday conversations between nurses and patients with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of perceptions of dental hygienists and general public about communication skills of dental hygienists : Empirical test of co-orientation model
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An investigation into health professionals’ perception of the appropriateness of elderspeak in a Korean hospital setting
Miseon Lee, Jeong Youn Lee
Journal of Pragmatics.2021; 172: 181. CrossRef - Dementia screening for elderly in-patients and its association with nursing care satisfaction-an observational study
Li-Kai Huang, Jui-Chen Tsai, Hsun-Hua Lee, Yi-Chun Kuan, Yao-Tung Lee, Chia-Pei Lin, Shu-Ping Chao, Chaur-Jong Hu
Medicine.2020; 99(2): e18741. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Communication Behavior Scale for Nurses Caring for People with Dementia
Jihye Lee, Moonhee Gang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Communication of Dental Hygienist in Oral Hygiene Instruction during Scaling
Su-Kyung Kang, Hyun-Sook Bae, Soon-Ryun Lim
Journal of dental hygiene science.2014; 14(4): 546. CrossRef - Long-term Care Nurses' Communication Difficulties with People Living with Dementia in Taiwan
Jing-Jy Wang, Pei-Fang Hsieh, Chi-Jane Wang
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(3): 99. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nurses' Competency in Nurse-Patient Communication about Medications: Conversational Analysis Approach
Haeng-Mi Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Conversation between Elderly Patients with Dementia and Nurses: Focusing on Structure and Sequential Patterns
Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 166. CrossRef
- Comparison of perceptions of dental hygienists and general public about communication skills of dental hygienists : Empirical test of co-orientation model
- 862 View
- 6 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The Effects of a Folk Play Program on Cognition, ADL, and Problematic Behavior in the Elderly with Dementia
- Jung Soon Kim, Jeong Sim Jung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(6):1153-1162. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.6.1153
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to develop and evaluate a folk play program as a nursing intervention for the elderly with dementia.
Method First, a folk play program was developed through a careful study of literature review and field-work. Second, a nonequivalent control group pre-post test was designed. The subjects of the study were the elderly with dementia staying in nursing homes; 15 were in an experimental group adopting a folk play program developed through this study, 18 in the control group on a gymnastics and walking program which is generally used. The 40 min. intervention was conducted 5 times a week for 4 weeks.
Result The folk play program improved the cognition(t=6.12, p<.001) and ADL(t=2.92, p=.014) and diminished the frequency of problematic behaviors significantly(t=-6.39, p<.001). There was a significant difference of cognition, ADL, and problematic behaviors between the control and the experimental group before and after the experiment(t=3.38, p=.002; t=2.05, p=.046; t=-7.74, p<.001).
Conclusion Compared with the gymnastics and walking program, the folk play program proved to be much more effective in the elderly with dementia in improving their cognition and ADL, as well as in diminishing their problematic behaviors. Therefore, a folk play program should be appliedas an effective and practical Korean nursing intervention for the elderly with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Dance Sports Program on Physical Function, Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life in Rural Elderly Women
Yun-Hee An, Nam-Soo Hong, Hee-Jung Yoon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2020; 45(4): 385. CrossRef - Effects of experience-based group therapy on cognitive and physical functions and psychological symptoms of elderly people with mild dementia
Hwan-hee Kim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2015; 27(7): 2069. CrossRef - The Effects of an Individual Cognitive Improvement Program on the Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairments
Inhyae Park, In-Hee Choi, Seo Young Kang, Younkyoung Kim, Chong Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors associated with Cognitive Decline in the Elderly in Community
Young-Sook Kwon, Kyung-Shin Paek
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(2): 587. CrossRef - Effects of Multisensory Stimulation Using Familiarity: Persons with Dementia in Long-term Care Facility in Korea
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 528. CrossRef - An Integrated Dementia Intervention for Korean Older Adults
Hee-Young Kang, Yeong-Suk Bae, Eun-Hee Kim, Kap-Soon Lee, Myeong-Jeong Chae, Ree-Aie Ju
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2010; 48(12): 42. CrossRef - The Effects of a Cognitive Enhancement Group Training Program for Community-dwelling Elders
Young Ran Han, Mi Sook Song, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 724. CrossRef - Effects of a Robot Pet-assisted Program for Elderly People with Dementia
Jung Hee Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 562. CrossRef - Rest-Activity Patterns in Institutionalized Korean Older Adults with Dementia: A Pilot Study
Yeonsu Song, Glenna A. Dowling, Margaret I. Wallhagen, Kathryn A. Lee, William J. Strawbridge, Erin M. Hubbard
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2009; 35(12): 20. CrossRef - Effects of an Exercise Program on Frontal Lobe Cognitive Function in Elders
Mee-Kyung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 107. CrossRef - Effects of an Exercise Program on Frontal Lobe Cognitive Function in Elders
Mee-Kyung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 107. CrossRef
- The Effect of Dance Sports Program on Physical Function, Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life in Rural Elderly Women
- 940 View
- 8 Download
- 11 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


