Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
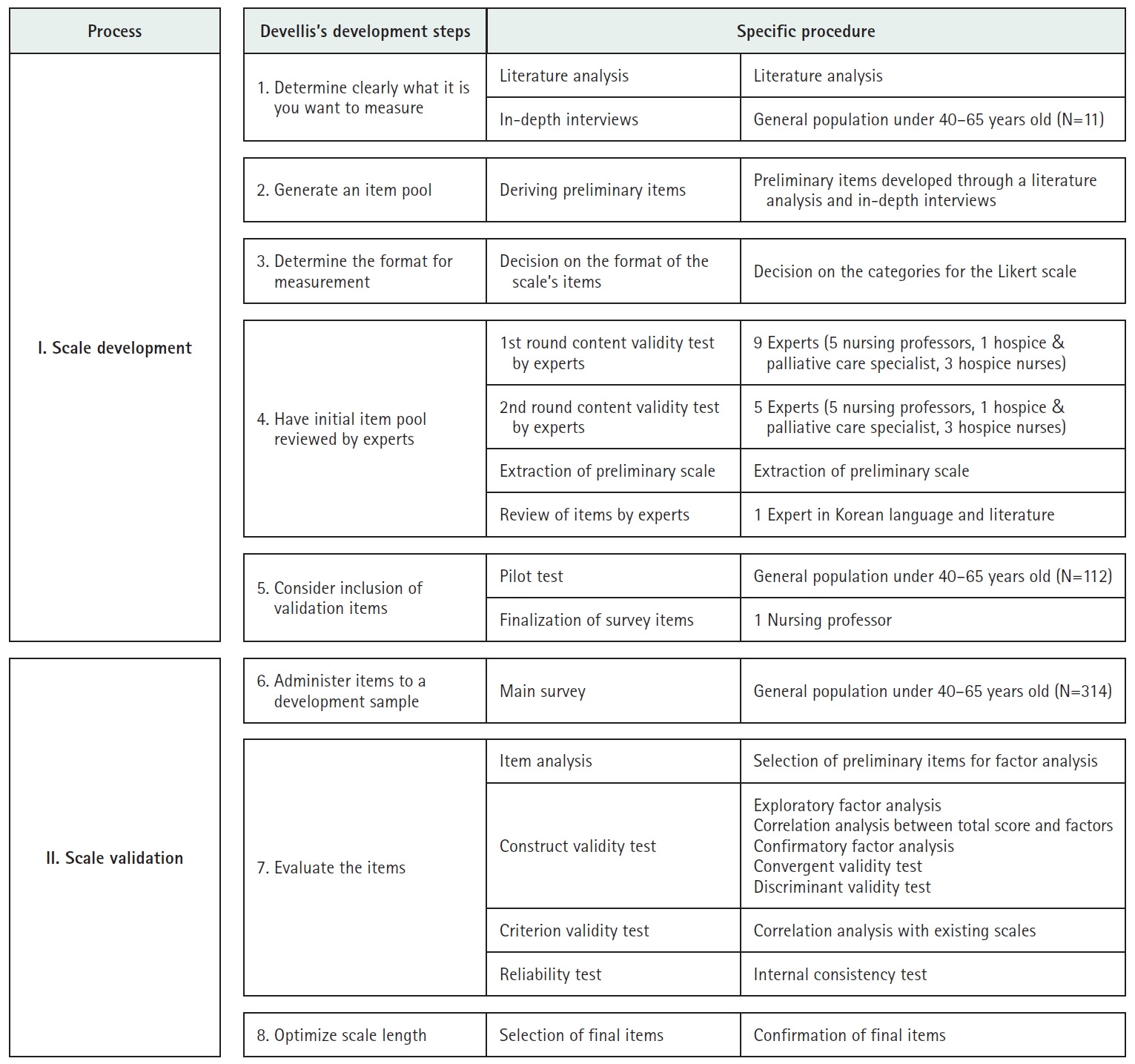
- Development of a well-dying awareness scale for middle-aged adults in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Yu Jin Jung, Eun Joung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):285-300. Published online March 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a valid and reliable tool to measure awareness of well-dying among middle-aged adults.
Methods
A mixed-methods approach was adopted, consisting of a qualitative phase to identify the characteristics of well-dying and a quantitative phase to validate the instrument with middle-aged participants. Initially, 76 items were generated through a literature review and in-depth interviews, and these were reduced to 35 items through expert validation. A pilot survey was conducted with 112 individuals aged 40–65, selected via quota sampling from 17 administrative regions in South Korea. Based on the pilot survey results, the instrument was refined to 32 items for the main survey. The main survey included 314 participants recruited through quota sampling in Busan and Ulsan Metropolitan Cities and Gyeongsang Region. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA), confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), and reliability testing were performed to validate the instrument.
Results
The final scale comprised 23 items across six factors. EFA demonstrated an explanatory power of 69.1%, with factor loadings ranging from 0.53 to 0.88. CFA confirmed the instrument’s validity, and reliability was established with a Cronbach’s α of .93.
Conclusion
This instrument is a validated and reliable tool for measuring middle-aged individuals’ awareness of well-dying. It can serve as an effective resource for evaluating and assessing well-dying awareness in the middle-aged population.
- 2,912 View
- 200 Download

- The Notion of Death and Caring Behaviors in one Community
- Sung Hee Ko, Young Hee Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(3):688-699. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.3.688
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was to find out the perception of toward death and caring behavior of lay parsons in one community : One Island in Pusan County, Chonbuk. The methodology of this study was ethnography. For this study, The fieldwork was conducted from October 1997 to July 1998. Data collected by in-depth interview and participant observations. The participants consisted of were 17 persons of both sexes. The key informants were four specific people. The result of this study is as follows; The people perceived two different kinds of death. Normal death, which means death from old age. The person was respected as an ancestor God and was believed to exist forever with their offspring. Abnormal death was regarded as negative, many had fears toward this king of death. The causes of abnormal death were supernatural phenomena and had absolute holy meanings. Whether death was good or bad, The death was not personal, but collective events as family or community affairs and was interpreted as death and birth for their offsprings. Funeral rites were family-centered and/or community-centered. The did normal procedures for normal deaths for abnormal deaths, there were many protective ceremonies(BuJungmagi : the prevention of the taboo of uncleanliness) for the remaining people. These ceremonies combined confucism and shamanism. Caring behavior for dying persons was ruled as community-centered, reciprocal and reality-centered principles.
- 401 View
- 0 Download

- Development of an Education Program for Hospice Care and Its Performance
- Boon Han Kim, Moon Sil Kim, Hung Kyu Kim, Tae Joon Jeong, Young Ran Tak, Hye Ryoung Kim, Mi Young Chon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(3):576-584. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.3.576
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to develop an education program for hospice care and to examine the effect of program. The education program for hospice care was developed based on the philosophy and principle of Hospice and integrated with various professional areas related to the problems with witch terminal patients and their family might be associated. The program was continued for 16 weeks and consisted of lectures and practices. The courses of this program were The Concept and Principle of Hospice, The Role of the Hospice Nurse, The Characteristics of Terminal Disease, Physical Care in Terminal Patients, Death Orientation, Psychological care for Terminal Patients, Spiritual care for Terminal Patients, and Care for the Family. To identify the effect of the education program for hospice care, the difference in death orientation of subjects between the pre and post performance of the education program was examined using the t-test. The finding of this statistic indicated that this education program for hospice care was effective in terms of changing the death orientation of subjects with positive direction. The education program for hospice care was performed several times at Kwangrim Hospice Missionary, Chungbuk University Hospital, and Wooam Church. Case studies were reported for a description after the performance of education. put this at the beginning 8 the sentence. In conclusion, the education program for hospice care was developed effectively. Therefore, this program should be used to educate and activate the subjects in community to be participants in hospice care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of an End-of-Life Care Education Program Among Korean Nurses
Kae-Hwa Jo, Ardith Z. Doorenbos, Gyeong Ju An
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2009; 11(4): 230. CrossRef - Cognition and Needs for Hospice Care among Parents of Children with Cancer
Hyun Young Koo, Sun Hee Choi, Ho Ran Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2009; 15(3): 325. CrossRef - Hospice and Hospice Care in Korea: Evolution, Current Status, and Challenges
Bok Yae Chung, Yu Xu, Chanyeong Kwak
Home Health Care Management & Practice.2005; 18(1): 73. CrossRef
- Effect of an End-of-Life Care Education Program Among Korean Nurses
- 655 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- How People Understand Death: a Coorientational Look
- Eun Ja Yeun, Hung Kyu Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):270-279. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Since death is an extremely subjective and unique experience, if we take into account the lack of understanding about death due to the difficulty in methodology, it is very important to try to understand the subjectivity of death. In this respect, Q-methodology that explains and shows the respondents' subjectivity by objectifying his subjectivity is employed as a solution to the questions in this study. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to provide data on how medical personnel should treat their patients, when, it comes to death ; by finding out the opinions of those who are being treated, namely the patients, and those who are providing the treatment, namely the medical personnel. It also by examined the characteristics and relationships between these two groups on attitudes to death. The results of this study show that medical personnel have two(fate-recipient, reality-oriented) types of response and patients have three(religion-dependent, science-adherent, sardonist) types. Medical personnel saw patients as having three(life-attached, traditionalist, death-rejector) types of response and to patients saw medical personnel as having two(rationalist, humanist)types. The relationship between the above-mentioned types will be examined in a coorientation model, the subjectivity of the medical personnel and the patient toward death indicates a relatively high understanding between the two groups under the great proposition of 'death'. Therefore, in their relationship with people who are facing death, the provider of care, namely the medical personnel, should identify the subjectivity of the patient before approaching them. By doing this, they can minimize the conflicts they might experience in establishing a therapeutic relationship, reduce suffering, and help the patient in greeting a more comfortable death. Throughout the study, Q-methodology expands out understanding of coorientation model that has only been approached with R-methodology. This study confirmed Q's potentiality and its validity in human subjective matters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Journal of Targeted at the general public for the Modeling of Well-dying Program Development
Kwang-Hwan Kim, Yong-Ha Kim, Sang-Yoon Ahn, Chong Hyung Lee, Moo-Sik Lee, Moon-Joon Kim, Arma Park, Hye-Jeong Hwang, Moon-Sook Shim, Hyeon-Dong Song
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(8): 369. CrossRef - Attitudes of elderly Korean patients toward death and dying: an application of Q-methodology
Eunja Yeun
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2005; 42(8): 871. CrossRef
- The Journal of Targeted at the general public for the Modeling of Well-dying Program Development
- 922 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Development and Application of Online Education on Death
- Kae Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee, Yun Ju Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(4):442-452. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.4.442
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an online education on death, ‘successful life, and beautiful death’ for university students and to evaluate students' changes regarding perception of self and death.
Method A quasi-experimental design was used with one experimental group pre-post test. Subjects were 154 students who enrolled for online education about death for 16 weeks. SPSS/WIN 12 was used for analyzing data.
Result The results of the study clearly indicated this class had positive effects on students' perception of death-related concepts, attitudes toward death, and self-concept, showing statistically significant higher scores in post-tests than in pre-tests. In addition, the result of class evaluations showed a positive response,
Conclusion Findings suggested that this online education about death was effective to change students' perceptions of death related knowledge, attitude toward death, and self-concept. Recommendations for further studies were provided.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Adaptation Processes of Family with Sudden Bereavement
Hee Hyen Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(2): 143. CrossRef - The Effects of Hospice Unit Practice Education on Spiritual Well-being, Attitude to Death, and Hospice Awareness of Nursing Students
Gyung Duck Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(4): 176. CrossRef - Convergence Analysis of Factors Influencing the End-of-life Care Attitude in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Seung Ae Yang
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(4): 141. CrossRef - Effects of a Well-dying Program on Nursing Students
Hyunjung Moon, Sunkyung Cha, Sungwon Jung
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2015; 18(3): 188. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Death Education Program for Nursing Students*
Soon-Hee Kim, Dong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(3): 277. CrossRef - Types of Attitudes of Nursing Students in Korea Toward Bucket Lists Q-Methodological Approach
Hong Seon Lee, Kae Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 129. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ First Clinical Experiences of Death
Hyoung Sook Park, Youngju Jee, Soon Hee Kim, Yoon-ji Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(3): 161. CrossRef - Effect of Death Education Program for University Students
Eun Min Hyun
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(7): 4220. CrossRef - Effects of Death Education Program on Family Caregivers of Disabled Individuals
Bock-Ryn Kim, Ok-Hee Cho, Yang-Sook Yoo
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2011; 14(1): 20. CrossRef - Effects of a Death Education Program on Life Satisfaction and Attitude toward Death in College Students
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 1. CrossRef
- The Adaptation Processes of Family with Sudden Bereavement
- 776 View
- 1 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Types of Students' Death Attitudes Majoring in Human Service Area: Q-Methodological Approach
- Kae Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee, Yun Ju Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(5):829-841. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.5.829
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze death attitudes of students majoring in the human service area, such as nursing science, education, and social welfare.
Method The Q-methodology which provides a method of analyzing the subjectivity of each item was used. The 38 selected Q-statements from each of 42 subjects were classified into a shape of normal distribution using a 9 point scale. The collected data was analyzed using a QUANL PC program.
Result Four types of death attitudes for research subjects in nursing, education, and social welfare areas were identified. Type I is fatalistic admission, Type II is pursuit of existential life, Type III is uncertainty of life after death, and Type IV is separation-connection between life and death.
Conclusion The results of the study indicate that different approaches of death educational programs are recommended based on the four types of death attitudes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Convergence Analysis of Factors Influencing the End-of-life Care Attitude in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Seung Ae Yang
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(4): 141. CrossRef - Factors influencing the attitude toward death in college nursing student
Jong Gun Kim, Su Min Oh, Eui Young Cheon, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 676. CrossRef - Paramedic students' awareness and attitude toward a do-not-resuscitate (DNR) order and death
Bo-Ram Choi, Dong-Ok Kim
The Korean Journal of Emergency Medical Services.2015; 19(2): 71. CrossRef - Subjectivity toward Death among HIV-Positive Men
Eun-Ju Lee
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(3): 142. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ First Clinical Experiences of Death
Hyoung Sook Park, Youngju Jee, Soon Hee Kim, Yoon-ji Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(3): 161. CrossRef - An Analysis of Factors about Nursing Students' Attitudes Toward the Perception of Death : Q-sort method
Yong-Sook Eo, Young-Hee Kim, Kyong-Ri Lee
Journal of Fisheries and Marine Sciences Education.2013; 25(6): 1294. CrossRef - Death Metaphors in Korean Undergraduate Nursing Students
Kae-Hwa Jo, Gyeong-Ju An
Holistic Nursing Practice.2012; 26(2): 79. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Dignified Dying Scale for Korean Adults
Kae-Hwa Jo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(3): 313. CrossRef - Effect of an End-of-Life Care Education Program Among Korean Nurses
Kae-Hwa Jo, Ardith Z. Doorenbos, Gyeong Ju An
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2009; 11(4): 230. CrossRef - Relationship between Self-efficacy, Depression, Level of Satisfaction and Death Attitude of College Students
Kae-Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 229. CrossRef - The Perception of Good Death Among Human Service Students in South Korea: A Q-Methodological Approach
Hyun Ji Lee, Kae Hwa Jo, Kyong Hee Chee, Yun Ju Lee
Death Studies.2008; 32(9): 870. CrossRef
- Convergence Analysis of Factors Influencing the End-of-life Care Attitude in Undergraduate Nursing Students
- 772 View
- 2 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of a Self-Reflection Program for Intensive Care Unit Nurses Who Have Experienced the Death of Pediatric Patients
- Hyun-Ju Kang, Kyung-Sook Bang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):392-405. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.392
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aims to develop a self-reflection program for nurses who have experienced the death of pediatric patients in the intensive care unit and to evaluate its effectiveness.
Methods The self-reflection program was developed by means of the following four steps: establishment of the goal through investigation of an initial request, drawing up the program, preliminary research, and implementation and improvement of the program. The study employed a methodological triangulation to evaluate the effectiveness of the program. Participants were 38 nurses who had experienced the death of pediatric patients (experimental group=15, control group=23); they were recruited using convenience sampling. The self-reflection program was provided over 6 weeks (6 sessions). Data were collected from April to August, 2014 and analyzed using t-tests and content analysis.
Results The quantitative results showed that changes in personal growth (t=-6.33,
p <.001) and burnout scores (z=-2.76,p =.005) were better in the experimental group compared to the control group. The qualitative results exhibited two themes, namely “personal growth” and “professional growth”, and ten sub-themes.Conclusion The self-reflection program developed by this study was effective in helping nurses who had experienced the death of pediatric patients to achieve personal growth through self-reflection, and it was confirmed that the program can be applied in a realistic clinical nursing setting. Furthermore, it can be recommended as an intervention program for clinical nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Work–Life Balance and Nursing Reflection on the Nursing Performance of Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital
Yoo Jin Hwang, Won Hee Jun
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses’ perceptions of end-of-life care in neonatal and pediatric intensive care units in Korea: a qualitative descriptive study using thematic analysis
Hyo Jeong Lee, Hyejin Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(4): 272. CrossRef - Improving Intensive End-of-Life Care for Infants and Children: A Scoping Review of Intervention Elements
Elizabeth G. Broden Arciprete, Na Ouyang, Sarah E. Wawrzynski, Ijeoma J. Eche-Ugwu, Janene Batten, Deena K. Costa, Shelli L. Feder, Jennifer M. Snaman
Children.2025; 12(11): 1485. CrossRef - Interventions for Compassion Fatigue in Healthcare Providers—A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials
Sanjay Patole, Dinesh Pawale, Chandra Rath
Healthcare.2024; 12(2): 171. CrossRef - Effectiveness of End-of-Life Care Debriefing for Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Sook Hyun Park, Jung Eun Lee, Yu-Jin Jung, Ha Neul Yoo, Yeon Su Kim, Young Hee Yi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 87. CrossRef - Interventions to reduce burnout among clinical nurses: systematic review and meta-analysis
Miran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a critical reflection competency program for clinical nurse educators: a pilot study
Sujin Shin, Inyoung Lee, Jeonghyun Kim, Eunyoung Oh, Eunmin Hong
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-reflection of a General Ward Nurses on the Experience of End-of-Life Care for a Patient who Decided to Suspend Life-sustaining Treatment: van Manen's Hermeneutic Phenomenological Approach
Hee Jung Hong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(3): 273. CrossRef - Effects of psychological intervention on empathy fatigue in nurses: A meta-analysis
Xiaojuan Chen, Mingdi Chen, Huang Zheng, Chaoyu Wang, Huimin Chen, Qinglan Wu, Huizhao Liao, Jinru Zhu, Junyan Lin, Xudong Ou, Zhihong Zou, Zhiwei Wang, Zhenzhen Zheng, Xianrui Zhuang, Riken Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of posttraumatic growth of intensive care unit nurses in Korea
Ae Kyung Chang, Hyejin Yoon, Ji Hyun Jang
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Burnout and Resilience After a Decade in Palliative Care: What Survivors Have to Teach Us. A Qualitative Study of Palliative Care Clinicians With More Than 10 Years of Experience
Mervyn Y.H. Koh, Allyn Y.M. Hum, Hwee Sing Khoo, Andy H.Y. Ho, Poh Heng Chong, Wah Ying Ong, Joseph Ong, Patricia S.H. Neo, Woon Chai Yong
Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.2020; 59(1): 105. CrossRef - Neonatal ICU Nurses’ Coping with Death of High Risk Newborn
Yu Mi Kim, Hyu Yong Yoon, Yong-Jun Choi, Dong-Soo Shin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(2): 103. CrossRef - Relationship between Job Stress and Compassion Satisfaction, Compassion Fatigue, Burnout for Nurses in Children’s Hospital
Heekang Choi, Jisun Park, Mijeong Park, Bobae Park, Yeseul Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(4): 459. CrossRef
- Impact of Work–Life Balance and Nursing Reflection on the Nursing Performance of Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital
- 1,856 View
- 29 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Nurses' Experiences of the Death of Patients in Geriatric Hospitals
- Mi Joung Yi, Jeong Seop Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):513-522. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.513
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify and understand nurses' experiences of the death of patients in geriatric hospitals.
Methods Van Manen's hermeneutic phenomenological analysis was applied in the interpretation of experiential descriptions of seven nurses who had experienced the death of patients in a geriatric hospital.
Results The essential subjects derived from the experience of the nurses on the death of patients in a geriatric hospital are covered in the following 7 themes. 'Placed in death site', 'Difficult repetition of death and farewell', 'Emotional waves that rushes in after farewell', 'Dilemmas in a place with no preparation to greet expected death', 'Getting dull from continually being struck with sorrow', 'Being together with living death', and 'Showing courtesy for a good farewell and living well'.
Conclusion The results of this research will contribute to the development of policy on all the deaths of patients in geriatric hospitals and suggest basic data that need to be applied in real practice and directions to introduce plans for realistic improvements in nursing care of deathbed patients in geriatric hospitals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- “A Life Slips Through Our Fingers” Experiences of Nurses Working in Pediatric Intensive Care Units About Children’s Death: A Qualitative Study
Musa Özsavran, Aylin Kurt, Tülay Kuzlu Ayyıldız, Zeynep Gül
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2026; 92(4): 2227. CrossRef - Exploring nursing students’ emotional experiences of patient cardiac arrest in the operating room: a descriptive phenomenological study
Fatemeh Hesami, Zahra Yousefi, Mobin Mottahedi, Hossein Bagheri
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Death Perception and Terminal Care Stress on Terminal Care Performance of Nurses Working in Long-Term Care Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ja-Young Kim, Hanyi Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 269. CrossRef - Factors Influencing End-of-Life Care Competency of Long Term Care Hospital Nurses: A Cross Sectional Study
Sookyeon Son, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(2): 174. CrossRef - Knowledge, Experience, and Attitudes of Nurses at Long-Term Care Hospitals regarding Advance Directives
Go Eun Park, Nae Young Lee
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(4): 139. CrossRef - A qualitative study of phenomenology of perspectives of student nurses: experience of death in clinical practice
ShiShuang Zhou, LiZhen Wei, Wei Hua, XiaoChong He, Jia Chen
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ICU Nurses’ Experiences with Patient Care after Death
Ji Young Park, Ki Kyong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(1): 43. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Quality of Life Among the Elderly in Long-Term Care Hospitals
Hee-Kyung CHANG, Cho-Rong GIL, Hye-Jin KIM, Han-Ju BEA
Journal of Nursing Research.2021; 29(1): e134. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experiences on End-of-Life Care for Older Patients in Long-Term Care Hospitals: Focusing on the Process of Practice and Barriers
Iktae Kim, Jun-Ah Song
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(3): 311. CrossRef - Nurses' Experiences of End-of-life Care for Elderly Patients in Long-term Care Hospitals
Chun Yee Lee, Ga Eon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 199. CrossRef - Lived experiences toward moral distress among long-term care hospital nurses: A phenomenological approach
So young Lee, Jung A Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(2): 167. CrossRef - Long-term Care Hospital Nurses' Awareness and Ethical Attitudes toward DNR
Kye Ha Kim, Sun Jin Jeong
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2019; 21(2): 61. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Professionalism and Organizational Communication on Intent to Stay in Geriatric Hospital Nurses
Bi-Joo Kim, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 455. CrossRef - Effects of Empathy and Attitude in Caring for Elders by Nurses in Geriatric Nursing Practice in Long-term Care Hospitals
Young Kyoung Kim, Suhye Kwon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(3): 203. CrossRef - Experience of Life-sustaining Treatment in Patient Care among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: Phenomenological Approach
Su Jeong Lee, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(2): 172. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Nurses’ Acceptance of Patient Deaths
Mi Joung Yi, Jeong Seop Lee
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(1): 34. CrossRef
- “A Life Slips Through Our Fingers” Experiences of Nurses Working in Pediatric Intensive Care Units About Children’s Death: A Qualitative Study
- 1,310 View
- 15 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Effects of Death Anxiety and Meaning of Life on Somatization of Grandparent Raising Grandchildren
- Se-Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(2):262-270. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted in order to examine the effects of death anxiety and meaning of life on somatization of grandparents raising grandchildren.
Methods A convenience sample of 92 elderly grandparents raising grandchildren was recruited. The study instrument for death anxiety was the 5-point 15 items scale designed by Templer and translated by Ko, Choi, & Lee and for meaning of life, the 7-point 10-items scale by Steger, Frazier, Oishi & Kaler and translated by Won, Kim & Kwon. For somatization, the 5-point 12 items scale designed by Derogatis and translated by Kim, Kim & Won was used. Collected data were analyzed with descriptive statistics, independent t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson Correlation and regression using the SPSS 21.0 program.
Results Average scores were 3.55 for death anxiety, 3.43 for meaning of life, and 2.74 for somatization. Death anxiety had the highest positive correlation with somatization. Meaning of life was negatively correlated with death anxiety and somatization. Death anxiety and health status were shown to influence somatization but meaning of life was not shown to influence somatization.
Conclusion The research results indicate that death anxiety and health status influence somatization in grandparents raising grandchildren. These results also provide basic information on the importance of nursing interventions in which the variables influencing somatization in grandparents raising grandchildren are considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Korean Grandparents Raising Grandchildren: The Influence of Cultural Factors
Youjung Lee, Sok An, Nancy Mendoza
Journal of Intergenerational Relationships.2026; 24(1): 97. CrossRef - Understanding Grandparent Caregiving in Korean and U.S. Culture: An Analysis Using Role Theory
Youjung Lee, Nancy Mendoza, Sok An
The International Journal of Aging and Human Development.2025; 101(4): 399. CrossRef - “Who is going to take care of these grandkids if I go?”: End-of-life planning by caregivers in grandparent-headed households
Jessica D. Freeman, Jessica Elton, Andrea Lambert South
Death Studies.2023; 47(3): 268. CrossRef - “What If You Die?”: Skipped‐Generation Caregivers' Reported Conversations With Their Grandchildren About Death
Jessica D. Freeman, Jessica Elton
Family Relations.2021; 70(2): 374. CrossRef - The Effect of Physical Health Variables on the Depression of the Korean Rural Elderly : with a Focus on a Comparison of Young-old and Old-old
Junggook Go, Jeonghwa Lee, Young eun Oh
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2019; 30(1): 83. CrossRef - Death Anxiety Among New Zealanders: The Predictive Roles of Religion, Spirituality, and Family Connection
Rod MacLeod, Donna M. Wilson, Jackie Crandall, Phil Austin
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2019; 80(1): 3. CrossRef - Correlates of perceived death competence: What role does meaning-in-life and quality-of-life play?
Lauren Miller-Lewis, Jennifer Tieman, Deb Rawlings, Christine Sanderson, Deborah Parker
Palliative and Supportive Care.2019; 17(5): 550. CrossRef - Factors associated with Meaning in Life among Elderly Female Community Dwellers Living Alone
Si Eun Lee, Boon Han Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(3): 221. CrossRef
- Korean Grandparents Raising Grandchildren: The Influence of Cultural Factors
- 1,221 View
- 4 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effect of Family Cohesion, Subjective Happiness and other Factors on Death Anxiety in Korean Elders
- Kae Hwa Jo, Byung Sook Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(5):680-688. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.680
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to explore the effects of family cohesion and subjective happiness on death anxiety of Korean elders and to identify other factors contributing to death anxiety.
Methods The participants were 280 elders who lived in P metropolitan city. Data were collected between November 5, 2011 and January 12, 2012 using the Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire (SPMSQ), Family Cohesion Evaluation Scale, Subjective Happiness Scale, and Fear of Death Scale (FODS). Data were analyzed using the SPSS/WIN 19.0 program.
Results Family cohesion, marital status, religious activity, perceived health status, and subjective happiness were included in the factors affecting death anxiety of Korean elders. These variables explained 50.1% of death anxiety.
Conclusion The results of the study indicate that these variables should be considered in developing nursing intervention programs to decrease death anxiety and increase family cohesion and subjective happiness for life integration in Korean elders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with attitudes toward death and dying in the second half of life: A scoping review
Alana Officer, Matthew Prina, Andreea Badache, Barbara Broers, Sam Gnanapragasam, Sophie Pautex
Death Studies.2026; 50(1): 53. CrossRef - Relationship of Depression, Hopelessness and Life Satisfaction With Death Anxiety in Individuals Who Have Had COVID-19
Neslihan Lok, Zekiye Aydın, Gülten Uzun, Büşra Kayaaslan, Alime Selçuk Tosun
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2025; 92(1): 5. CrossRef - Translation and Validation Study of the Korean Self-Compassion Scale
Si Woo Chae, Jeong Eun Cheon, Janet D. Latner, Young-Hoon Kim
Mindfulness.2024; 15(10): 2697. CrossRef - Impact of Death Anxiety on Psychological Well-Being and Successful Aging of Older Adults With Chronic Illness
Akanksha Bharti, Das Ambika Bharti
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Societal impact of death anxiety and mental health among nurses in India
Monika Srivastava, Anindita Ghosh
Societal Impacts.2024; 4: 100095. CrossRef - Stress-related to COVID-19, anxiety, and protective factors among middle-aged and older adults in the largest outbreak areas in South Korea
Sukyung Yoon, Soochan Choi
Aging & Mental Health.2022; 26(10): 2090. CrossRef - The effect of group logotherapy on spirituality and preoperative anxiety in patients seeking open heart surgery referring to Tehran Heart Center in 2020
Fatemehsadat Alavi, Seyed Hossein Ahmadi Tafti, Farshid Alaeddini, Zainab Ebrahimyan, Atieh Ebrahimyan, Morteza Mansourian
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2022; 11(1): 233. CrossRef - Factors associated with family cohesion and adaptability among Chinese registered nurses
Lei Huang, Ya Wang, Hao Huang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(1-2): 113. CrossRef - The mediating effect of resilience on happiness of advanced lung cancer patients
Sunwha Cho, Eunjung Ryu
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(11): 6217. CrossRef - Patterns of Religiosity, Death Anxiety, and Hope in a Population of Community-Dwelling Palliative Care Patients in New Zealand—What Gives Hope If Religion Can’t?
Catherine M. Byrne, Deidre D. Morgan
American Journal of Hospice and Palliative Medicine®.2020; 37(5): 377. CrossRef - Effects of Social Support, Family Support and Repulsion Related Nursing Home Use on the Well-Dying of Elderly
Young Ju Oh, Kyeong In Cha, Young Hee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(3): 235. CrossRef - The Effect of Spiritual Care Program on Death Anxiety of Cardiac Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Jalil Azimian, Mohammad ali Soleimany, Saeed Pahlevan Sharif, Hedyeh Banihashemi
Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care.2019; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Death Anxiety Among New Zealanders: The Predictive Roles of Religion, Spirituality, and Family Connection
Rod MacLeod, Donna M. Wilson, Jackie Crandall, Phil Austin
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2019; 80(1): 3. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Death Anxiety among Rural Elderly
Hyenam Hwang
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(2): 111. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth and Related Factors in Firefighters
Minyeong Kwak, Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(2): 124. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Death Anxiety in Elderly Patients in Long-term Care Hospitals
Mi Suk Lee, Hee Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2016; 18(3): 138. CrossRef - Service improving the subjective happiness in Cancer Patient receiving Radiation Therapy
Mi Soon Song, Hyun Li Kim
Journal of Service Research and Studies.2016; 6(2): 51. CrossRef - A Meta Analysis on Variables related to Death Anxiety of Elderly in Korea
Sinhyang Kim, Kyung Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(2): 156. CrossRef - Study of Death Attitudes by General Characteristics and Death Perceptions of the Severely Diseased Persons in Hospice Facilities -Focus in O City, Gyeonggi-do
Moon-Dol Kim, Sung-Je Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(12): 7148. CrossRef
- Factors associated with attitudes toward death and dying in the second half of life: A scoping review
- 1,228 View
- 6 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of a Dignified Dying Scale for Korean Adults
- Kae-Hwa Jo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(3):313-324. Published online June 13, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.313
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The study was done to develop a dignified dying scale for Korean adults.
Methods The process included construction of a conceptual framework, generation of initial items, verification of content validity, selection of secondary items, preliminary study, and extraction of final items. The participants were 428 adults who lived in one of 3 Korean metropolitan cities: Seoul, Daegu, and Busan. Item analysis, factor analysis, criterion related validity, and internal consistency were used to analyze the data. Data collection was done from March to June 2010.
Results Thirty items were selected for the final scale, and categorized into 5 factors explaining 54.5% of the total variance. The factors were labeled as maintaining emotional comfort (10 items), arranging social relationship (9 items), avoiding suffering (3 items), maintaining autonomous decision making (4 items), and role preservation (4 items). The scores for the scale were significantly correlated with personal meanings of death scale. Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the 30 items was .92.
Conclusion The above findings indicate that the dignified dying scale has a good validity and reliability when used with Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing the completion of advance directives in cancer patients: a descriptive survey
Wonjeong Hwang, Jiyoung Do
BMC Palliative Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors That Influence Attitudes toward Advance Directives among Female Cancer Patients
Aeri Kim, Kisook Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2023; 26(2): 80. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Dignity in Care Scale of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses
Yun Sil Ahn, Pok Ja Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 340. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Advanced Directives Among Hemodialysis Patients
Eunseong SON, Minjeong SEO
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2022; 25(3): 243. CrossRef - The Relationships Between Oncology Nurses’ Attitudes Toward a Dignified Death, Compassion Competence, Resilience, and Occupational Stress in South Korea
Sun-A Park, Hee Jung Park
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2021; 37(3): 151147. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Intention of Signing an Advanced Directives in Cancer Patients
Eun-Ju Ha, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(1): 121. CrossRef - The Effect of Hospice Patients' Pain, Anxiety, Depression, Perception of Dignity, and Spiritual Well-Being on their Attitudes toward Dignified Death
Yun Sil Ahn, Pok Ja Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 212. CrossRef - Factors affecting Elders' Acceptance of Death
Seon Mi Ha, Jung Seop Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(3): 165. CrossRef - Types of Attitudes of Nursing Students in Korea Toward Bucket Lists Q-Methodological Approach
Hong Seon Lee, Kae Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 129. CrossRef - Health Care Professional Factors Influencing Shared Medical Decision Making in Korea
Kae-Hwa Jo, Gyeong-Ju An, Hong Seon Lee
Sage Open.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility Evaluation of Korean Advance Directives (K-AD)
Shin Mi Kim, Sun Woo Hong, Jin Shil Kim, Ki Sook Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(4): 639. CrossRef - Preferences for Care Near the End of Life among Hospital Employees
Jiyeon Kang, Seonyoung Yun, Soo Jeong Kim, So Ra An, Myeong Hee Lee, Shinmi Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(3): 197. CrossRef - The Impact of Nurses’ Attitude toward Dignified Death and Moral Sensitivity on Their End-of-Life Care Performance
Kae Hwa Jo, Yeon Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2013; 16(4): 223. CrossRef - Predictive Factor s for City Dweller s’ Attitudes toward Death with Dignity
Kae Hwa Jo, Gyeong Ju An, Gyun Moo Kim, Yeon Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2012; 15(4): 193. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Shared Medical Decision-Making Scale for End-of-Life Patients in Korea
Kae Hwa Jo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(4): 453. CrossRef
- Factors influencing the completion of advance directives in cancer patients: a descriptive survey
- 1,089 View
- 6 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Effects of a Death Education Program on Life Satisfaction and Attitude toward Death in College Students
- Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(1):1-9. Published online February 28, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this experimental study was to examine the values of a death education program developed to improve life satisfaction and attitude toward death in college students.
Methods The death education program was developed and then used with 22 college students for 5 weeks, once a week for 150 min. Before and after the intervention, students responded a questionnaire developed to measure life satisfaction and attitude toward death. t-test, χ2-test, and paired t-test with the SPSS program were used to analyze the data.
Results The death education program significantly improved life satisfaction but had no statistically significant effect on attitude toward death. There was a significant difference in life satisfaction between the experimental and control groups but not in attitude toward death.
Conclusion Based on the above results, it is apparent that the death education program has an affirmative effect on life satisfaction in college students and some impact on attitude toward death. We suggest, therefore, that the death education program should be used with all human beings to help them recognize the values of themselves and their current lives and improve their satisfaction with life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Seeing life through life: Unpacking life education in intergenerational learning in China
Hao Cheng
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experiences of Chinese advanced cancer patients after attending a “four-stage” death education programme: A qualitative study
Bing Wu, Ping Zhu, Tao Wang, Jing-Yu(Benjamin) Tan, Zhenglan Cao, Jing Wan, Suya Wu, Liuliu Zhang, Yihui Xing
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 66: 102361. CrossRef - Death Education for Palliative Psychology: The Impact of a Death Education Course for Italian University Students
Lucia Ronconi, Gianmarco Biancalani, Georgiana Alexandra Medesi, Hod Orkibi, Ines Testoni
Behavioral Sciences.2023; 13(2): 182. CrossRef - Death education and photovoice at school: A workshop with Italian high school students
Melania Raccichini, Gianmarco Biancalani, Luca Franchini, Silvia Varani, Lucia Ronconi, Ines Testoni
Death Studies.2023; 47(3): 279. CrossRef - Exploring Filipinos’ Preferred Funerary Arrangement for Terminal Departure
Lourdes Urbano Agbing
Illness, Crisis & Loss.2022; 30(2): 240. CrossRef - The Collision Between the Classroom Voice(s) and the Voice of the Mainstream Culture on End-of-Life to Cultivate Students' Attitudes Toward Death in China
Ling Meng, Li Yi, Tian Li
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of a Death Preparation Education Program on Death Anxiety, Death Attitudes, and Attitudes toward End-of-Life Care among Nurses in Convalescent Hospitals
Eun-yeong Chu, Sun-hee Jang
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2021; 24(3): 154. CrossRef - Nursing students’ relationships among resilience, life satisfaction, psychological well-being, and attitude to death
Jihyun Kim
Korean Journal of Medical Education.2019; 31(3): 251. CrossRef - Present-orientation and the outcome of contemplating death
Ryo Ishii
Time & Society.2018; 27(3): 312. CrossRef - The Concept of Death and the Growth of Death Awareness Among University Students in Hong Kong
Wai-ying Wong
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2017; 74(3): 304. CrossRef - Effects of Band Therapy Using Music on Grasping Power, Depression, and Personal Relationships in Nursing-Home-Dwelling Elderly Individuals
Eun Kyung Chang, Heeok Park, Miran Jung, Hae Kyeong Lee, Jieun Park, Mijung Park, Minsuk Gang
Open Journal of Nursing.2016; 06(11): 958. CrossRef - Convergence Analysis of Factors Influencing the End-of-life Care Attitude in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Seung Ae Yang
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(4): 141. CrossRef - Effects of Death Preparation Education on Awareness of Hospice Palliative Care and Withdrawing Life Sustaining Treatment in City Dwellers
Pei-Ling Tsung, Yoon Joo Lee, Su Yeon Kim, Seul Ki Kim, Si Ae Kim, Hyeon Ji Kim, Yi Nam, Suk Young Ham, Kyung Ah Kang
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2015; 18(3): 227. CrossRef - Types of Attitudes of Nursing Students in Korea Toward Bucket Lists Q-Methodological Approach
Hong Seon Lee, Kae Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 129. CrossRef - Paramedic students' awareness and attitude toward a do-not-resuscitate (DNR) order and death
Bo-Ram Choi, Dong-Ok Kim
The Korean Journal of Emergency Medical Services.2015; 19(2): 71. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Death Education Program for Nursing Students*
Soon-Hee Kim, Dong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(3): 277. CrossRef - Effects of a Well-dying Program on Nursing Students
Hyunjung Moon, Sunkyung Cha, Sungwon Jung
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2015; 18(3): 188. CrossRef - Nursing Need and Satisfaction of Patients in Hospice Ward
Jung Ah Kim, Kyunghee Kim, Hee Sun Kang, Ji-su Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(4): 248. CrossRef - Patient‐tailored self‐management intervention for older adults with hypertension in a nursing home
Yeon‐Hwan Park, HeeKyung Chang, JinShil Kim, Jin Sang Kwak
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2013; 22(5-6): 710. CrossRef - Readiness for Death and Death Anxiety among Hospitalized Cancer Patients
Hyang-Suk Kwen, In-Sun Suh, Hyun-Kyung Kim
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2013; 13(9): 334. CrossRef - Trends in Home-visit Nursing Care by Agencies' Characteristics under the National Long-term Care Insurance System
Jung Suk Lee, Rah Il Hwang, Eun Jeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(4): 415. CrossRef - Effects of Death Education on College Students' Death Orientation and Suicidal Ideation - With a Focus on College Students majoring in Social Welfare in Daegu, Korea -
Kyung-Eun Chang
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2012; 21(3): 423. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Death Preparation Education for Middle-aged Adults
Kyung-Ah Kang
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2011; 14(4): 204. CrossRef - Effects of Death Education Program on Family Caregivers of Disabled Individuals
Bock-Ryn Kim, Ok-Hee Cho, Yang-Sook Yoo
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2011; 14(1): 20. CrossRef - Comparison of Attitudes of Nursing Students toward Death, Self-esteem and Life Satisfaction according to Clinical Experience
Soon Hee Kim, Dong-Hee Kim, Hyun-Mi Son
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2011; 14(3): 144. CrossRef - Effects of a Hospice and Palliative Care Education Program Including Meaning in Life on Attitudes Toward End-of-Life Care and Meaning in Life Among Nursing College Students
Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Kim, Soon-Ock Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2011; 17(3): 454. CrossRef - Health Needs of the Elderly in Long-term Care Facilities: Using RAI-MDS-FC
Eun-Joo Bang, Soon-Young Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 263. CrossRef
- Seeing life through life: Unpacking life education in intergenerational learning in China
- 1,736 View
- 19 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Relationship between Self-efficacy, Depression, Level of Satisfaction and Death Attitude of College Students
- Kae-Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(2):229-237. Published online April 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.2.229
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship among self-efficacy, depression, life satisfaction and death attitude of college students.
Methods The subjects consisted of 232 college students. Data were collected by self-reported questionnaires, which were constructed to include self-efficacy, depression, satisfaction with life, and death attitude. Data were analyzed by the SPSS/PC WIN. 12.0 program.
Results Death attitude and life satisfaction of college students were significantly different according to frequency of death ideation. Death attitude for college students correlated with self-efficacy, depression, and life atisfaction. The most significant predictor of death attitude for college students was life satisfaction.
Conclusion The above findings indicate that death attitude for college students is influenced by self-efficacy, depression, and life satisfaction. These findings suggest that a death education program to improve life satisfaction and to give a positive attitude toward death is needed for college students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Death education, communication, and happiness: An unlikely general education triad?
Kurt Wise, Laura Bruns
Policy Futures in Education.2025; 23(5): 880. CrossRef - Death attitudes and good life experience: the mediation and suppression effects of intrinsic and extrinsic goals
Yuanyuan Wang, Fuhua Pei, Yisheng Yang, Junxiu Wang
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the impact of a life education program on the resilience of nursing students
Yao-Mei Chuang, Wei-Hsiang Huang, Mostafa Shaban
PLOS One.2025; 20(4): e0322793. CrossRef - Predictors of Support for Euthanasia and Physician-Assisted Suicide (EPAS) Among Older Adults in Israel
Amit Dolev Nissani, Norm O’Rourke, Sara Carmel, Yaacov G. Bachner
European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education.2025; 15(10): 207. CrossRef - Factors influencing the attitude toward death in college nursing student
Jong Gun Kim, Su Min Oh, Eui Young Cheon, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 676. CrossRef - Convergence Analysis of Factors Influencing the End-of-life Care Attitude in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Seung Ae Yang
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(4): 141. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Death Education Program for Nursing Students*
Soon-Hee Kim, Dong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(3): 277. CrossRef - Types of Attitudes of Nursing Students in Korea Toward Bucket Lists Q-Methodological Approach
Hong Seon Lee, Kae Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 129. CrossRef - Influence of Appearance Stress, Ego-Resilience, Interpersonal Relations and Depression on Eating Attitude in Women Undergraduates
Hae Kyung Chang, Jung Nam Sohn
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(3): 235. CrossRef - Effects of Perceived Death and Self-esteem on Meaning in Life among University Students
Chun-Gill Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(3): 539. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Depression of Korean Female University Students
Kyung-Sook Lee, Chin-Kang Koh, Joo Hyun Kim, Haeng-Mi Son, Mi Ryeong Song, Su Jeong Yu, Kyung Sook Cho
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(2): 112. CrossRef - Relationship of Psychological Separation, Depression and Antidepressive Coping Behaviors in University Students
Hae-Ok Jeon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(6): 2655. CrossRef - A comparative study on the spiritual needs between nursing students and nurses in Busan and Gyeongnam province
Hyun Cho, Eun-Kyung Sim, Young-Chae Kwon, Young-Hee Bae, Young-Ok Woo, Jae-Hoon Ji, Ja-Young Jung
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(5): 2178. CrossRef - Comparison of Attitudes of Nursing Students toward Death, Self-esteem and Life Satisfaction according to Clinical Experience
Soon Hee Kim, Dong-Hee Kim, Hyun-Mi Son
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2011; 14(3): 144. CrossRef - Effects of a Death Education Program on Life Satisfaction and Attitude toward Death in College Students
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 1. CrossRef
- Death education, communication, and happiness: An unlikely general education triad?
- 1,128 View
- 10 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Development of an Evaluation Instrument for Subjects Related to Death
- Kae Hwa Jo, Hyun Ji Lee, Yun Joo Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(1):74-83. Published online February 28, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.1.74
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an evaluation instrument integrated and interdisciplinary death education for the human service areas such as nursing, social welfare, and education and to test the reliability and validity of it.
Method The subjects used to verify the instrument's reliability and validity were 407 students who were enrolled in the departments of nursing, social welfare, and education in universities located in Seoul, Pusan, Daegu, and Daejeon. The data was collected from April to May, 2005, and was analyzed by SPSS/WIN 12.
Result A factor analysis was conducted. Items with over a .40 factor loading and over a 1.0 eigen value were selected. Nine identified factors were learning about death, role of professionals, personal attitudes, hospice care, ethics and legal issues, death and dying, spiritual aspect of death, transcultural aspect of death, and multidisciplinary theory of death. The instrument consisted of 44 items and the reliability was a cronbach's of .953
Conclusion Based on the study results, the content scale developed in this study was identified as a tool with a high degree of reliability and validity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of end-of-life care education using humanistic approach in Korea
Kae-Hwa Jo, Gyeong-Ju An
Collegian.2015; 22(1): 91. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Death Education Program for Nursing Students*
Soon-Hee Kim, Dong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(3): 277. CrossRef - Constructing a Questionnaire on Male Workers' Sobriety Behavior: Based on Ajzen's Theory of Planned Behavior
Inhyae Park, Younkyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 156. CrossRef - Effect of an End-of-Life Care Education Program Among Korean Nurses
Kae-Hwa Jo, Ardith Z. Doorenbos, Gyeong Ju An
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2009; 11(4): 230. CrossRef - The Effects of an Environmental Education with Newspaper in Education (NIE) on the Environmental Concern and Practice
Ki-Wol Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 891. CrossRef
- Effect of end-of-life care education using humanistic approach in Korea
- 710 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


