Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
- Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):557-567. Published online November 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
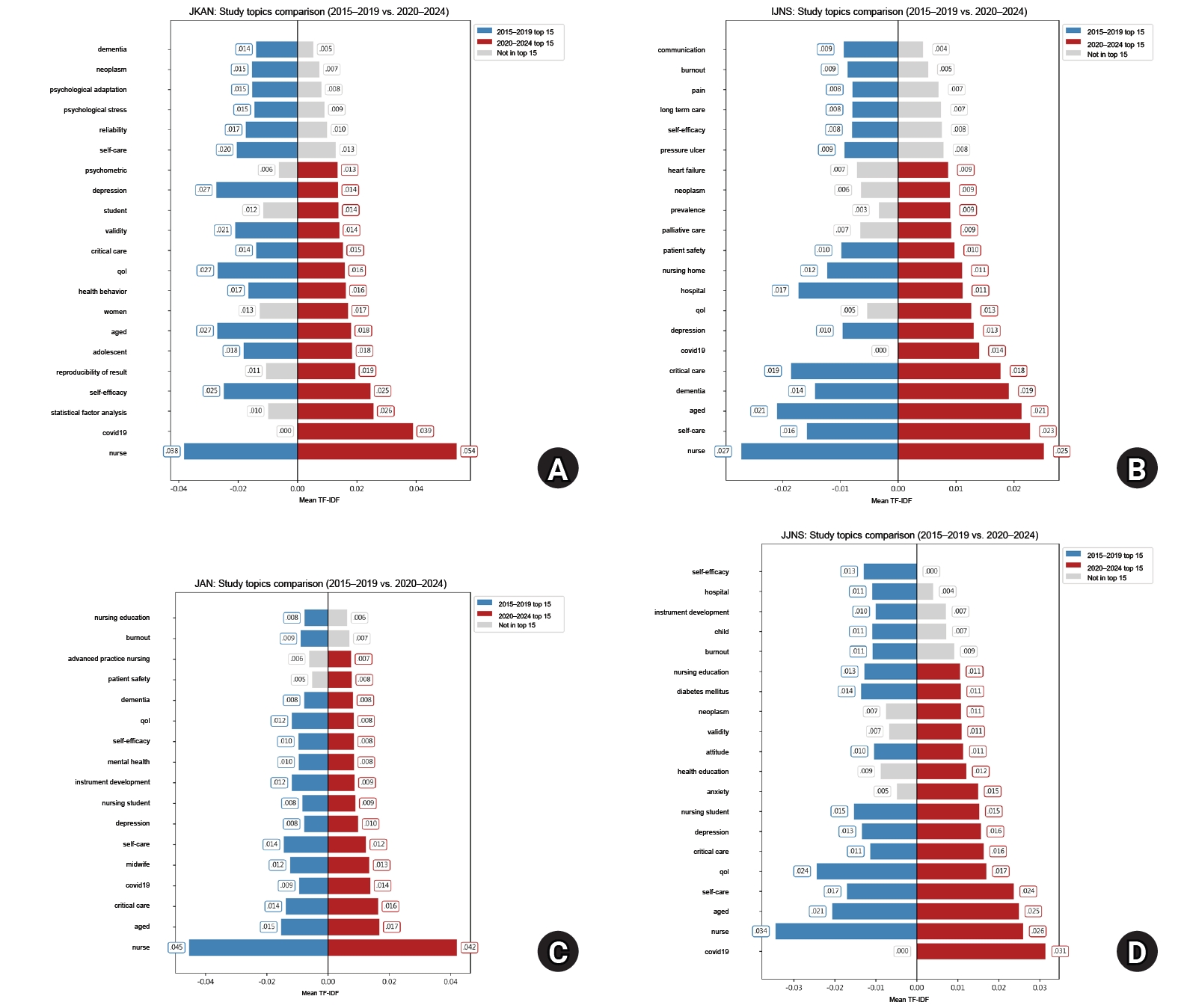
This study compared trends in research designs and keywords by analyzing the abstracts of four major nursing journals over the past decade, focusing on the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing (JKAN) in comparison with the International Journal of Nursing Studies (IJNS), Journal of Advanced Nursing (JAN), and Japan Journal of Nursing Science (JJNS).
Methods
A bibliometric analysis was conducted, encompassing 5,522 abstracts published between 2015 and 2024. Research designs were first classified as “quantitative,” “qualitative,” or “other,” and then further sub-classified based on international evidence-based frameworks. Text preprocessing was also conducted, and term frequency–inverse document frequency was applied to evaluate keyword importance. The 2015–2019 and 2020–2024 periods were compared to examine changes in both research designs and keyword importance.
Results
Compared to IJNS, JAN, and JJNS, JKAN published more instrument development and analytic studies but fewer randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews. Over time, the number of instrument development and mixed-methods studies in JKAN increased, while high-evidence designs remained scarce. Keyword analysis showed JKAN’s emphasis on psychosocial themes such as self-efficacy, quality of life, and depression, whereas the other journals more often highlighted policy- and institution-related topics. Across journals, COVID-19 and patient safety emerged as important themes after 2020.
Conclusion
JKAN demonstrates strengths in methodological diversity within quantitative research and in digital health–related analytics. However, high-evidence study designs and policy-oriented keywords are underrepresented in JKAN. Strategic expansion toward randomized controlled trials, systematic review, global and digital health, and policy-relevant research is recommended to strengthen JKAN’s international competitiveness.
- 826 View
- 87 Download

- Structural Topic Modeling Analysis of Patient Safety Interest among Health Consumers in Social Media
- Nari Kim, Nam-Ju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):266-278. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate healthcare consumers’ interest in patient safety on social media using structural topic modeling (STM) and to identify changes in interest over time.
Methods
Analyzing 105,727 posts from Naver news comments, blogs, internet cafés, and Twitter between 2010 and 2022, this study deployed a Python script for data collection and preprocessing. STM analysis was conducted using R, with the documents’ publication years serving as metadata to trace the evolution of discussions on patient safety.
Results
The analysis identified a total of 13 distinct topics, organized into three primary communities: (1) “Demand for systemic improvement of medical accidents,” underscoring the need for legal and regulatory reform to enhance accountability; (2) “Efforts of the government and organizations for safety management,” highlighting proactive risk mitigation strategies; and (3) “Medical accidents exposed in the media,” reflecting widespread concerns over medical negligence and its repercussions. These findings indicate pervasive concerns regarding medical accountability and transparency among healthcare consumers.
Conclusion
The findings emphasize the importance of transparent healthcare policies and practices that openly address patient safety incidents. There is clear advocacy for policy reforms aimed at increasing the accountability and transparency of healthcare providers. Moreover, this study highlights the significance of educational and engagement initiatives involving healthcare consumers in fostering a culture of patient safety. Integrating consumer perspectives into patient safety strategies is crucial for developing a robust safety culture in healthcare. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- From Posts to Protection: Understanding User-Generated Safety Content on Reddit
Mashael Yousef Almoqbel
International Journal of Computational and Experimental Science and Engineering.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- From Posts to Protection: Understanding User-Generated Safety Content on Reddit
- 2,097 View
- 68 Download
- 1 Crossref

- National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
- HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):635-651. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the main keyword, network structure, and main topics of the national petition related to “nursing” in South Korea.
Methods
Data were gathered from petitions related to the national petition in Korea Blue House related to the topic “nursing” or “nurse” from August 17, 2017, to May 9, 2022. A total of 5,154 petitions were searched, and 995 were selected for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were analyzed using the Netminer 4.5.0 program.
Results
Regarding network characteristics, a density of 0.03, an average degree of 144.483, and an average distance of 1.943 were found. Compared to results of degree centrality and betweenness centrality, keywords such as “work environment,” “nursing university,” “license,” and “education” appeared typically in the eigenvector centrality analysis. Topic modeling derived four topics: (1) “Improving the working environment and dealing with nursing professionals,” (2) “requesting investigation and punishment related to medical accidents,” (3) “requiring clear role regulation and legislation of medical and nonmedical professions,” and (4) “demanding improvement of healthcare-related systems and services.” Conclusion: This is the first study to analyze Korea's national petitions in the field of nursing. This study's results confirmed both the internal needs and external demands for nurses in South Korea. Policies and laws that reflect these results should be developed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hyunjung Ko, Nara Han, Seulki Jeong, Jeong A Jeong, Hye Ryoung Yun, Eun Sil Kim, Young Jun Jang, Eun Ju Choi, Chun Hoe Lim, Min Hee Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Dong Hyu Cho, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 529. CrossRef - A Study on Internet News for Patient Safety Campaigns: Focusing on Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2024; 12(19): 1914. CrossRef
- Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
- 2,703 View
- 42 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Knowledge Structure of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Health Information on HealthRelated Websites and Patients’ Needs in the Literature Using Text Network Analysis
- Ja Yun Choi, Su Yeon Lim, So Young Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):720-731. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21086
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the knowledge structure of health information (HI) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Methods
Keywords or meaningful morphemes from HI presented on five health-related websites (HRWs) of one national HI institute and four hospitals, as well as HI needs among patients presented in nine literature, were reviewed, refined, and analyzed using text network analysis and their co-occurrence matrix was generated. Two networks of 61 and 35 keywords, respectively, were analyzed for degree, closeness, and betweenness centrality, as well as betweenness community analysis.
Results
The most common keywords pertaining to HI on HRWs were lung, inhaler, smoking, dyspnea, and infection, focusing COPD treatment. In contrast, HI needs among patients were lung, medication, support, symptom, and smoking cessation, expanding to disease management. Two common sub-topic groups in HI on HRWs were COPD overview and medication administration, whereas three common sub-topic groups in HI needs among patients in the literature were COPD overview, self-management, and emotional management.
Conclusion
The knowledge structure of HI on HRWs is medically oriented, while patients need supportive information. Thus, the support system for self-management and emotional management on HRWs must be informed according to the structure of patients’ needs for HI. Healthcare providers should consider presenting COPD patient-centered information on HRWs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef - Development of pictogram‐based content of self‐management health information for Korean patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Ja Yun Choi, Eui Jeong Ryu, Xin Jin
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of the feature genes involved in cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19
Bing Yang, Meijun Pan, Kai Feng, Xue Wu, Fang Yang, Peng Yang, Salman Sadullah Usmani
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0296030. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Feedback Journals for New Nurses From Preceptor Nurses Using Text Network Analysis
Shin Hye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(10): 780. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef - A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis of Self-management Experiences of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Euna PARK, Jeong-Soo KIM
THE JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2022; 34(5): 794. CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,737 View
- 14 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- A Topic Modeling Analysis for Online News Article Comments on Nurses' Workplace Bullying
- Jiyeon Kang, Soogyeong Kim, Seungkook Roh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):736-747. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.736
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to explore public opinion on workplace bullying in the nursing field, by analyzing the keywords and topics of online news comments.
Methods This was a text-mining study that collected, processed, and analyzed text data. A total of 89,951 comments on 650 online news articles, reported between January 1, 2013 and July 31, 2018, were collected via web crawling. The collected unstructured text data were preprocessed and keyword analysis and topic modeling were performed using R programming.
Results The 10 most important keywords were “work” (37121.7), “hospital” (25286.0), “patients” (24600.8), “woman” (24015.6), “physician” (20840.6), “trouble” (18539.4), “time” (17896.3), “money” (16379.9), “new nurses” (14056.8), and “salary” (13084.1). The 22,572 preprocessed key words were categorized into four topics: “poor working environment”, “culture among women”, “unfair oppression”, and “society-level solutions”.
Conclusion Public interest in workplace bullying among nurses has continued to increase. The public agreed that negative work environment and nursing shortage could cause workplace bullying. They also considered nurse bullying as a problem that should be resolved at a societal level. It is necessary to conduct further research through gender discrimination perspectives on nurse workplace bullying and the social value of nursing work.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Topic Modeling of Nursing Issues in the Media During 4 Emerging Infectious Disease Epidemics in South Korea: Descriptive Analysis
Jungok Kim, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2025; 27: e60446. CrossRef - Exploring research themes in the Journal of Librarianship and Information Science: Insights from topic modelings
Alper Aslan, Özcan Özyurt
Journal of Librarianship and Information Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Forty Years of International Journal of Information Management: A Topic Modeling Approach
Ahmet Ayaz
Bilgi Yönetimi.2025; 8(2): 284. CrossRef - 30-year trends in research on enriching education and training with virtual reality: An innovative study based on machine learning approach
Ozcan Ozyurt, Hacer Ozyurt
Education and Information Technologies.2024; 29(7): 8221. CrossRef - Effectiveness of cognitive rehearsal programs for the prevention of workplace bullying among hospital nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yulliana Jeong, Hye Sun Jung, Eun Mi Baek
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the latest trends of Industry 4.0 based on LDA topic model
Ozcan Ozyurt, Hakan Özköse, Ahmet Ayaz
The Journal of Supercomputing.2024; 80(13): 19003. CrossRef - A Study on Internet News for Patient Safety Campaigns: Focusing on Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2024; 12(19): 1914. CrossRef - Exploring the Evolution of Educational Serious Games Research: A Topic Modeling Perspective
Hacer Ozyurt, Ozcan Ozyurt, Deepti Mishra
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 81827. CrossRef - Post-traumatic responses to workplace violence among nursing professionals: a collaborative and comparative study in South Korea and Hong Kong
Soyun Hong, Sujin Nam, Janet Yuen Ha Wong, Heejung Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Topic Modeling Analysis of Diabetes-Related Health Information during the Coronavirus Disease Pandemic
Soyoon Min, Jeongwon Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(13): 1871. CrossRef - A large-scale study based on topic modeling to determine the research interests and trends on computational thinking
Ozcan Ozyurt, Hacer Ozyurt
Education and Information Technologies.2023; 28(3): 3557. CrossRef - Exploring Gamification Research Trends Using Topic Modeling
Ahmet Ayaz, Ozcan Ozyurt, Waleed Mugahed Al-Rahmi, Said A. Salloum, Anna Shutaleva, Fahad Alblehai, Mohammed Habes
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 119676. CrossRef - Research Topic Trends on Turnover Intention among Korean Registered Nurses: An Analysis Using Topic Modeling
Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1139. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Social Issues Related to ChatGPT: Focusing on News Big Data-based Topic Modeling Analysis
Taejong Kim, Songlee Han
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(6): 1209. CrossRef - Exploring the Online News Trends of the Metaverse in South Korea: A Data-Mining-Driven Semantic Network Analysis
Eun Joung Kim, Jung Yoon Kim
Sustainability.2023; 15(23): 16279. CrossRef - Uncovering the Educational Data Mining Landscape and Future Perspective: A Comprehensive Analysis
Ozcan Ozyurt, Hacer Ozyurt, Deepti Mishra
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 120192. CrossRef - Topic Modeling: Perspectives From a Literature Review
Andres M. Grisales A., Sebastian Robledo, Martha Zuluaga
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 4066. CrossRef - Empirical research of emerging trends and patterns across the flipped classroom studies using topic modeling
Ozcan Ozyurt
Education and Information Technologies.2023; 28(4): 4335. CrossRef - Analysis of News Articles on Urban Agriculture using Text Mining from 2012 to 2021
Yumin Park, Yong-Wook Shin
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2023; 26(2): 105. CrossRef - Management Information Systems Research: A Topic Modeling Based Bibliometric Analysis
Hakan Özköse, Ozcan Ozyurt, Ahmet Ayaz
Journal of Computer Information Systems.2023; 63(5): 1166. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - Analysis of Telephone Counseling of Patients in Chemotherapy Using Text Mining Technique
Seoyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Heiyoung Kang, Jeehye Bae, Kayoung Sim, Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 46. CrossRef - COVID-19 pandemic & cyber security issues: Sentiment analysis and topic modeling approach
Sonal Khandelwal, Aanyaa Chaudhary
Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences and Cryptography.2022; 25(4): 987. CrossRef - Images of Nurses Appeared in Media Reports Before and After Outbreak of COVID-19: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Min Young Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Jee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 291. CrossRef - Comparison of the Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Sildenafil and Tadalafil Using Patient Medication Reviews: Topic Modeling Study
Maryanne Kim, Youran Noh, Akihiko Yamada, Song Hee Hong
JMIR Medical Informatics.2022; 10(2): e32689. CrossRef - Twenty-five years of education and information technologies: Insights from a topic modeling based bibliometric analysis
Ozcan Ozyurt, Ahmet Ayaz
Education and Information Technologies.2022; 27(8): 11025. CrossRef - Analysis of Headline News about Nurses Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic
Su-Mi Baek, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 319. CrossRef - Comparing workplace violence among nurses and other professionals using online articles: A social network analysis
Soyun Hong, Heejung Kim, Myeongseop Cha
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1750. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef - Exploring Nurses' Experience and Grievance: Network Analysis and Topic Modeling using a Social Networking Service
Hyunju Ji, Arum Lim, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(3): 169. CrossRef - The Experience of Clinical Nurses after Korea’s Enactment of Workplace Anti-Bullying Legislation: A Phenomenological Study
Hee-Sun Kim, In-Ok Sim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(11): 5711. CrossRef - Topic Modeling and Keyword Network Analysis of News Articles Related to Nurses before and after “the Thanks to You Challenge” during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Eun Kyoung Yun, Jung Ok Kim, Hye Min Byun, Guk Geun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(4): 442. CrossRef - A Network Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in End-of-Life Care and Nursing
Kisook Kim, Seung Gyeong Jang, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(1): 313. CrossRef - Silent Counterattack: The Impact of Workplace Bullying on Employee Silence
Xiwei Liu, Shenggang Yang, Zhu Yao
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Bullying Measurement in Korean Nurses' Workplace
Hyo-Suk Song, So-Hee Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 478. CrossRef - Relationship of Workplace Violence to Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses: Resilience as a Mediator
Hyun-Jung Kang, Jaeyong Shin, Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 728. CrossRef
- Topic Modeling of Nursing Issues in the Media During 4 Emerging Infectious Disease Epidemics in South Korea: Descriptive Analysis
- 2,657 View
- 27 Download
- 30 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Electronic Health Record Data-Driven Predictive Models for Pressure Ulcers
- Seul Ki Park, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):575-585. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.575
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop predictive models for pressure ulcer incidence using electronic health record (EHR) data and to compare their predictive validity performance indicators with that of the Braden Scale used in the study hospital.
Methods A retrospective case-control study was conducted in a tertiary teaching hospital in Korea. Data of 202 pressure ulcer patients and 14,705 non-pressure ulcer patients admitted between January 2015 and May 2016 were extracted from the EHRs. Three predictive models for pressure ulcer incidence were developed using logistic regression, Cox proportional hazards regression, and decision tree modeling. The predictive validity performance indicators of the three models were compared with those of the Braden Scale.
Results The logistic regression model was most efficient with a high area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC) estimate of 0.97, followed by the decision tree model (AUC 0.95), Cox proportional hazards regression model (AUC 0.95), and the Braden Scale (AUC 0.82). Decreased mobility was the most significant factor in the logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models, and the endotracheal tube was the most important factor in the decision tree model.
Conclusion Predictive validity performance indicators of the Braden Scale were lower than those of the logistic regression, Cox proportional hazards regression, and decision tree models. The models developed in this study can be used to develop a clinical decision support system that automatically assesses risk for pressure ulcers to aid nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of an educational intervention on pressure ulcer documentation among tertiary hospital nurses in Jordan
Emran A Abu Aqoulah, Rosliza Abaul Manaf, Suriani Ismail, Salam Bani Hani, Aya Al-Ali
British Journal of Nursing.2025; 34(12): S30. CrossRef - Application of Air Pillows and Left‐Right Lateral Tilt Position to Prevent Increased Risk of Pressure Injuries in Bedridden Patients in the ICU: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
Nur Chayati, Wantonoro Wantonoro, Mahsuna Alfianti, Tiara Marthias
Health Science Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Pressure Injury Machine Learning Prediction Model and Integration into Clinical Practice: A Prediction Model Development and Validation Study
Ju Hee Lee, Jae Yong Yu, So Yun Shim, Kyung Mi Yeom, Hyun A Ha, Se Yong Jekal, Ki Tae Moon, Joo Hee Park, Sook Hyun Park, Jeong Hee Hong, Mi Ra Song, Won Chul Cha
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 191. CrossRef - Could we prove the nursing outcomes utilising clinical data warehouse? Effectiveness of pressure ulcer intervention in Korean tertiary hospital
Moonsook Kim, Se Yeon Park, Meihua Piao, Earom Lim, Soon Hwa Yoo, Minju Ryu, Hyo Yeon Lee, Hyejin Won
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(1): 201. CrossRef - Data‐driven approach to predicting the risk of pressure injury: A retrospective analysis based on changes in patient conditions
Yinji Jin, Ji‐Sun Back, Sun Ho Im, Jong Hyo Oh, Sun‐Mi Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(19-20): 7273. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Pressure Injury Among Critically Ill Patients in a Coronary Care Unit
Eunji Ko, Seunghye Choi
Advances in Skin & Wound Care.2022; 35(10): 1. CrossRef - Data-Driven Learning Teaching Model of College English Based on Mega Data Analysis
Jie Zhang, Tongguang Ni
Scientific Programming.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Effect of an educational intervention on pressure ulcer documentation among tertiary hospital nurses in Jordan
- 2,089 View
- 54 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Knowledge Discovery in Nursing Minimum Data Set Using Data Mining
- Myonghwa Park, Jeong Sook Park, Chong Nam Kim, Kyung Min Park, Young Sook Kwon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(4):652-661. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.4.652
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to apply data mining tool to nursing specific knowledge discovery process and to identify the utilization of data mining skill for clinical decision making.
Methods Data mining based on rough set model was conducted on a large clinical data set containing NMDS elements. Randomized 1000 patient data were selected from year 1998 database which had at least one of the five most frequently used nursing diagnoses. Patient characteristics and care service characteristics including nursing diagnoses, interventions and outcomes were analyzed to derive the meaningful decision rules.
Results Number of comorbidity, marital status, nursing diagnosis related to risk for infection and nursing intervention related to infection protection, and discharge status were the predictors that could determine the length of stay. Four variables (age, impaired skin integrity, pain, and discharge status) were identified as valuable predictors for nursing outcome, relived pain. Five variables (age, pain, potential for infection, marital status, and primary disease) were identified as important predictors for mortality.
Conclusions This study demonstrated the utilization of data mining method through a large data set with stan-dardized language format to identify the contribution of nursing care to patient's health.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Standardized Nursing Diagnoses in a Surgical Hospital Setting: A Retrospective Study Based on Electronic Health Data
Manuele Cesare, Fabio D’agostino, Massimo Maurici, Maurizio Zega, Valentina Zeffiro, Antonello Cocchieri
SAGE Open Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors for Successful Smoking Cessation in Korean Adults
Young-Ju Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(1): 1. CrossRef
- Standardized Nursing Diagnoses in a Surgical Hospital Setting: A Retrospective Study Based on Electronic Health Data
- 665 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Analysis of the Characteristics of the Older Adults with Depression Using Data Mining Decision Tree Analysis
- Myonghwa Park, Sora Choi, A Mi Shin, Chul Hoi Koo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(1):1-10. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a prediction model for the characteristics of older adults with depression using the decision tree method.
Methods A large dataset from the 2008 Korean Elderly Survey was used and data of 14,970 elderly people were analyzed. Target variable was depression and 53 input variables were general characteristics, family & social relationship, economic status, health status, health behavior, functional status, leisure & social activity, quality of life, and living environment. Data were analyzed by decision tree analysis, a data mining technique using SPSS Window 19.0 and Clementine 12.0 programs.
Results The decision trees were classified into five different rules to define the characteristics of older adults with depression. Classification & Regression Tree (C&RT) showed the best prediction with an accuracy of 80.81% among data mining models. Factors in the rules were life satisfaction, nutritional status, daily activity difficulty due to pain, functional limitation for basic or instrumental daily activities, number of chronic diseases and daily activity difficulty due to disease.
Conclusion The different rules classified by the decision tree model in this study should contribute as baseline data for discovering informative knowledge and developing interventions tailored to these individual characteristics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Attribution analysis and forecast of salinity intrusion in the Modaomen estuary of the Pearl River Delta
Qingqing Tian, Hang Gao, Yu Tian, Qiongyao Wang, Lei Guo, Qihui Chai
Frontiers in Marine Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A prediction model for adolescents’ skipping breakfast using the CART algorithm for decision trees: 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun A Choi, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 300. CrossRef - Development of a prediction model for the depression level of the elderly in low-income households: using decision trees, logistic regression, neural networks, and random forest
Kyu-Min Kim, Jae-Hak Kim, Hyun-Sill Rhee, Bo-Young Youn
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Predictive Model of Ischemic Heart Disease in Middle-Aged and Older Women Using Data Mining Technique
Jihye Lim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(4): 663. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Predictive Factors for Passing the National Physical Therapy Examination using Logistic Regression Analysis and Decision Tree Analysis
So Hyun Kim, Sung Hyoun Cho
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2022; 11(3): 285. CrossRef - Occupational accident prediction modeling and analysis using SHAP
Hyung-Rok Oh, Ae-Lin Son, ZoonKy Lee
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2021; 22(7): 1115. CrossRef - FACTORS DETERMINING THE EXTENT OF GDPR IMPLEMENTATION WITHIN ORGANIZATIONS: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM CZECH REPUBLIC
Adam Faifr, Martin Januška
Journal of Business Economics and Management.2021; 22(5): 1124. CrossRef - Evaluation of Food Labeling Policy in Korea: Analyzing the Community Health Survey 2014–2017
Heui Sug Jo, Su Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depression in Middle Aged Women: Focused on Quality of life on Menopause
Jung Nam Sohn
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(2): 148. CrossRef - Song-Induced Autobiographical Memory of Patients With Early Alzheimer's Dementia
Seung Ah Han
Journal of Music and Human Behavior.2016; 13(2): 49. CrossRef - Factors Affecting on Life Satisfaction of Elderly after Total Knee Arthroplasty
You-Jin Park, Eun-Hee Park
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(9): 563. CrossRef - Application of big data analysis with decision tree for the foot disorder
Jung-Kyu Choi, Keun-Hwan Jeon, Yonggwan Won, Jung-Ja Kim
Cluster Computing.2015; 18(4): 1399. CrossRef - A Study on Comparison of Classification and Regression Tree and Multiple Regression for Predicting of Soldiers' Depression
Chung Hee Woo, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(4): 268. CrossRef - Knowledge Discovery in a Community Data Set: Malnutrition among the Elderly
Myonghwa Park, Hyeyoung Kim, Sun Kyung Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2014; 20(1): 30. CrossRef - The predictability of dentoskeletal factors for soft-tissue chin strain during lip closure
Yun-Hee Yu, Yae-Jin Kim, Dong-Yul Lee, Yong-Kyu Lim
The Korean Journal of Orthodontics.2013; 43(6): 279. CrossRef - Some fixed point theorems in locally p-convex spaces
Leila Gholizadeh, Erdal Karapınar, Mehdi Roohi
Fixed Point Theory and Applications.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Depressive Symptoms in Community Dwelling Older People
Jung Nam Sohn
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(2): 107. CrossRef
- Attribution analysis and forecast of salinity intrusion in the Modaomen estuary of the Pearl River Delta
- 1,353 View
- 5 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Predictive Bayesian Network Model Using Electronic Patient Records for Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Pressure Ulcers
- In Sook Cho, Eunja Chung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(3):423-431. Published online June 13, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.423
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The study was designed to determine the discriminating ability of a Bayesian network (BN) for predicting risk for pressure ulcers.
Methods Analysis was done using a retrospective cohort, nursing records representing 21,114 hospital days, 3,348 patients at risk for ulcers, admitted to the intensive care unit of a tertiary teaching hospital between January 2004 and January 2007. A BN model and two logistic regression (LR) versions, model-I and -II, were compared, varying the nature, number and quality of input variables. Classification competence and case coverage of the models were tested and compared using a threefold cross validation method.
Results Average incidence of ulcers was 6.12%. Of the two LR models, model-I demonstrated better indexes of statistical model fits. The BN model had a sensitivity of 81.95%, specificity of 75.63%, positive and negative predictive values of 35.62% and 96.22% respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) was 85.01% implying moderate to good overall performance, which was similar to LR model-I. However, regarding case coverage, the BN model was 100% compared to 15.88% of LR.
Conclusion Discriminating ability of the BN model was found to be acceptable and case coverage proved to be excellent for clinical use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the risk prediction model of pressure injuries in hospitalized patient: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Yuxia Ma, Xiang He, Tingting Yang, Yifang Yang, Ziyan Yang, Tian Gao, Fanghong Yan, Boling Yan, Juan Wang, Lin Han
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(6): 2117. CrossRef - Using nursing data for machine learning-based prediction modeling in intensive care units: A scoping review
Yesol Kim, Mihui Kim, Yeonju Kim, Mona Choi
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2025; 169: 105133. CrossRef - Development of a Pressure Injury Machine Learning Prediction Model and Integration into Clinical Practice: A Prediction Model Development and Validation Study
Ju Hee Lee, Jae Yong Yu, So Yun Shim, Kyung Mi Yeom, Hyun A Ha, Se Yong Jekal, Ki Tae Moon, Joo Hee Park, Sook Hyun Park, Jeong Hee Hong, Mi Ra Song, Won Chul Cha
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 191. CrossRef - The predictive effect of different machine learning algorithms for pressure injuries in hospitalized patients: A network meta-analyses
Chaoran Qu, Weixiang Luo, Zhixiong Zeng, Xiaoxu Lin, Xuemei Gong, Xiujuan Wang, Yu Zhang, Yun Li
Heliyon.2022; 8(11): e11361. CrossRef - Predictive Modeling of Pressure Injury Risk in Patients Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit
Mireia Ladios-Martin, José Fernández-de-Maya, Francisco-Javier Ballesta-López, Adrián Belso-Garzas, Manuel Mas-Asencio, María José Cabañero-Martínez
American Journal of Critical Care.2020; 29(4): e70. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Electronic Health Record Data-Driven Predictive Models for Pressure Ulcers
Seul Ki Park, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 575. CrossRef - Development and Comparison of Predictive Models for Pressure Injuries in Surgical Patients
Seul Ki Park, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(4): 291. CrossRef - Automated Pressure Injury Risk Assessment System Incorporated Into an Electronic Health Record System
Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Nursing Research.2017; 66(6): 462. CrossRef - Recommendation of Personalized Surveillance Interval of Colonoscopy via Survival Analysis
Jayeon Gu, Eun Sun Kim, Seoung Bum Kim
Journal of Korean Institute of Industrial Engineers.2016; 42(2): 129. CrossRef - Medical Data Based Clinical Pathway Analysis and Automatic Ganeration System
Hanna Park, In Ho Bae, Yong Oock Kim
The Journal of Korea Information and Communications Society.2014; 39C(6): 497. CrossRef - Reusability of EMR Data for Applying Cubbin and Jackson Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Scale in Critical Care Patients
Eunkyung Kim, Mona Choi, JuHee Lee, Young Ah Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2013; 19(4): 261. CrossRef - Using EHR data to predict hospital-acquired pressure ulcers: A prospective study of a Bayesian Network model
Insook Cho, Ihnsook Park, Eunman Kim, Eunjoon Lee, David W. Bates
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2013; 82(11): 1059. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the risk prediction model of pressure injuries in hospitalized patient: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- 1,059 View
- 13 Download
- 12 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


