Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A qualitative exploration of acute stroke patients’ experiences with aphasia in Korea
- Jiyeon Kang, Hyunyoung Heo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):621-633. Published online November 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the lived experiences of patients with acute stroke-related aphasia within the Korean healthcare context.
Methods
A qualitative research design using inductive content analysis was employed, following the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research guidelines. Fourteen adults with acute stroke-related aphasia participated in one-on-one, in-depth interviews conducted between January and May 2025. Participants were recruited through purposive sampling until theoretical saturation was reached. Data were analyzed using an inductive qualitative content analysis approach.
Results
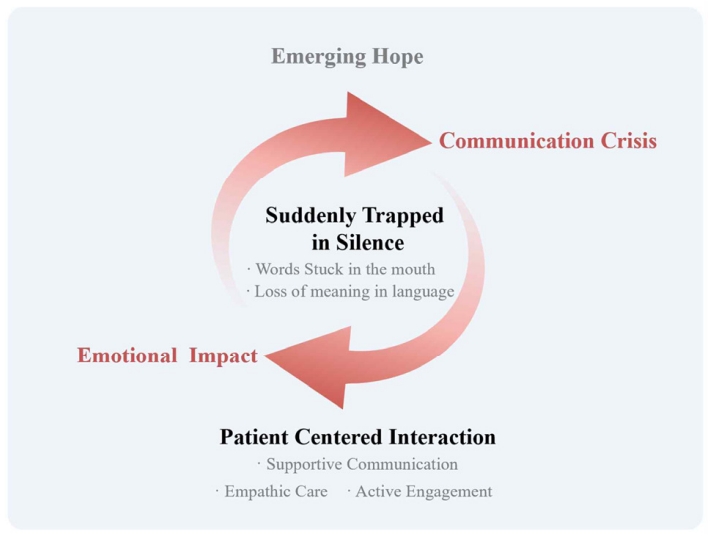
Five main categories emerged: “suddenly trapped in silence” described the abrupt loss of language, including the inability to articulate intended words and understand others; “emotional impact” captured psychological shock and feelings of loss; “communication crisis” encompassed expressive difficulties, exclusion from decision-making, and social withdrawal; “patient-centered interaction” highlighted supportive communication, empathic care, and active engagement by others; and “emerging hope” reflected signs of recovery, self-directed efforts, and anticipation of improvement. These categories converged into the overarching theme, “communication beyond language,” illustrating how patients sought meaningful interaction despite linguistic limitations.
Conclusion
Acute aphasia extends beyond a language disorder to encompass profound emotional and social experiences. Although communication barriers exist, meaningful interaction remains possible through empathetic, person-centered approaches. Healthcare professionals should recognize that patients with aphasia retain cognitive competence despite expressive limitations. These findings underscore the need to integrate emotional sensitivity into clinical care and to develop training programs that enhance person-centered communication skills in stroke rehabilitation settings.
- 1,244 View
- 128 Download

- A review of domestic and international contexts for establishing a communication platform for early-career nurse scientists
- Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Hye Young Kim, Mi Yu, Sun Joo Jang, Yeonsoo Jang, Sangeun Jun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):317-325. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
As nursing continues to advance through digital health, clinical specialization, and interdisciplinary research, early-career nurse scientists are central to advancing innovation. However, Korea lacks a structured platform to support their research, collaboration, and career development. This review aimed to identify the needs of early-career nurse scientists and examine international best practices to guide the creation of an effective communication platform.
Methods
This study involved a secondary analysis of the final report from the project “Establishment of a communication platform for young nursing scientists,” carried out by the Korean Society of Nursing Science. The report comprises data from focus group interviews with domestic graduate students and early-career researchers, a literature review of international communication and support systems, and a global policy analysis related to young nursing scientists. Based on this report, the present review synthesizes key findings and draws implications for the development of a communication platform in Korea.
Results
International examples, such as grant writing programs, mentoring initiatives, and digital collaboration hubs, showed positive outcomes in strengthening research capacity and promoting the professional growth of nurse scientists. Based on these findings, key considerations for platform development include: (1) establishing clear leadership and a participatory governance model; (2) providing demand-driven content such as research guides, mentoring, and mental health resources; (3) implementing mechanisms to ensure sustainability, content quality, and user data protection; and (4) designing an integrated platform that fosters synergy across research, policy development, education, and global networking.
Conclusion
A digital platform for early-career nurse scientists should function not merely as an information portal, but also as dynamic infrastructure for collaboration, mentorship, and growth. It is recommended that the Korean Society of Nursing Science spearhead this initiative, with governmental support, to enhance the research capacity and expand the global engagement of Korean nursing scientists.
- 2,373 View
- 80 Download

- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Soo Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):269-284. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This methodological study was conducted to develop a scale to measure communication self-efficacy in nurses and examine its validity and reliability.
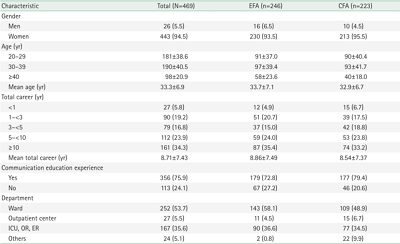
Methods
We selected 54 initial items from literature reviews and interviews with 10 clinical nurses. Thirty-two preliminary items were derived from consultations with 10 experts. To verify the scale’s factor structure, we conducted exploratory factor analysis (EFA), and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) among 469 nurses. Data were analyzed using item analysis, EFA, CFA, discriminant validity, convergent validity, and internal consistency using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 29.0 (IBM Corp.) and IBM SPSS AMOS ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp.).
Results
The scale consisted of 18 items with three factors (ability to apply therapeutic communication skills, crisis management capabilities, and communication competence), which explained 46.1% of the total variance. Convergent validity and discriminant validity were confirmed for the factors. CFA supported the fit of the measurement model comprising three factors (standardized root mean square residual=.04, root mean square error of approximation=.03, goodness of fit index=.92, Tucker-Lewis index=.97, comparative fit index=.98, normed fit index=.89, critical N=216). Internal consistency was confirmed by a Cronbach’s α coefficient of .91.
Conclusion
The communication self-efficacy scale for nurses is expected to measure communication self-efficacy among nurses. It will be useful for improving nurses’ professional communication abilities.
- 3,574 View
- 272 Download

- Development of the Patient Caring Communication Scale
- Myoung Lyun Heo, Sook Bin Im
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.80
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study attempted to develop a scale that measures the level of patients' recognition of the nurses' care, based on Watson's caring theory, and confirmed its reliability and validity.
Methods The items were developed through a literature review and an expert content validity test. The questionnaires were administered to 285 inpatients of internal medicine and surgical units at two general hospitals. Construct validity was tested using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, and reliability was tested using Cronbach's alpha.
Results This process resulted in a preliminary scale composed of 34 items; We used item analysis and five exploratory factor analyses, and consequently selected 14 items composed of three factors (respect, genuineness, and relationality). The confirmatory factor analysis verified the model fit and convergent and discriminant validity of the final items; criterion validity was confirmed with the positive correlation with the measurement scale of the patient-perceived quality of nursing . The overall scale reliability had a Cronbach's alpha of .92, which indicated internal consistency and reliability.
Conclusion The developed scale showed content, construct, and criterion validity, and reliability, as well as convergent validity for each item and discriminant validity between the factors. This makes it suitable for use in a diverse range of future studies on nurse communication using structural equation models.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of the Caring Competence Scale for Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Disorders
Won Hee Jun
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 32(5): 1248. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Therapeutic Communication Scale in Nursing Students
Soolgi Han, Jinhee Yoo, Kyonghwa Kang
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 394. CrossRef - A structural model of nursing students’ performing communication skills
Cho Rong Gil, Kyung Mi Sung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 148. CrossRef - Nurse’s Evaluation on Health Education in Portuguese Pediatric Hospitals and Primary Care for Children/Young and Parents
Anabela Fonseca Pereira, Joaquim Escola, Vitor Rodrigues, Carlos Almeida
Children.2022; 9(4): 486. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Korean version of ComOn coaching for oncology nurses
Myoung Soo Kim, Eun-Jung Bae, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 9(4): 210. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-Item Scale
Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee, So-Young Kim, Nayoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(5): 617. CrossRef - Development of the Nursing Start-up Attitude Scale for Student Nurses
Ji Young Lim, Geun Myun Kim, Eun Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 388. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Watson Caritas Patient Score
SookBin IM, MiKyoung CHO, MyoungLyun HEO
Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 28(2): e80. CrossRef
- Development of the Caring Competence Scale for Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Disorders
- 2,982 View
- 134 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Communication Behavior Scale for Nurses Caring for People with Dementia
- Jihye Lee, Moonhee Gang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):1-13. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and validate the Communication Behavior Scale for nurses caring for people with Dementia (CBS-D).
Methods Based on communication accommodation theory, the initial items were generated through a literature review and interviews with 20 experts. Content and face validity of the initial items were assessed. Data from 486 nurses caring for people with dementia were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, criterion-related validity, and internal consistency.
Results The final scale consisted of 18 items and four factors (discourse response management, interpersonal control, emotional expression, and interpretability) that explained 57.6% of the variance. Confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the theoretical model with 18 items satisfied all goodness-of-fit parameters. Criterion-related validity was shown by the Global Interpersonal Communication Competence Scale (
r =.506,p <.001). Cronbach's alpha for the total scale was .88.Conclusion The CBS-D can be used to measure the communication behavior of nurses caring for people with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Soo Yeon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(2): 269. CrossRef - The influence of socio-cognitive mindfulness, moral sensitivity and dementia communication behaviors on dementia nursing performance of nurses in long-term care hospitals: a cross-sectional study
Hyun Ju Bong, Mikyoung Lee
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing shared decision-making in long-term care facilities
Da Eun Kim, Min Jung Kim
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing students' experiences as dementia partners in volunteer activities: An inductive content analysis
Dooree Kim, Yunhee Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(2): 146. CrossRef
- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- 2,261 View
- 65 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Prediction Modeling on Family Life Satisfaction of Old Adults Living at Home
- Young Mi Huh, Sohyune Sok
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):534-544. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.534
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to construct and test a structural model on family life satisfaction of aged individuals living at home. The conceptual model was based on Bandura's self-efficacy and social cognitive theories (1977; 1986) and Bowen's (1976) family systems theory.
Methods From January 25 to March 5, 2016, 227 older adults living at home completed a structured questionnaire. Data were analyzed to calculate the direct and indirect effects of factors affecting family life satisfaction. SPSS WIN 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 were used.
Results The hypothetical model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were χ2=78.05, χ2/df=1.35, RMSR=.02, GFI=.98, AGFI=.96, NFI=.94, CFI=.98, and RMSEA=. 05. Family life satisfaction was positively affected by perceived collective family efficacy, status of physical health, family communication, and family support. Depression resulted in a significant negative effect. Family differentiation had a significant indirect effect on family life satisfaction. The model explained 76% of variance in family life satisfaction.
Conclusion Perceived collective family efficacy, status of physical health, depression, family differentiation, family communication, and family support were significant factors explaining family life satisfaction among older adults staying at home. Further research should be conducted to seek intervention strategies to improve family life satisfaction among older adults living at home by focusing on the respective contributing factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between family support and life satisfaction in hypertensive patients: the multiple mediating roles of self-esteem and self-care
Han Wu, Haijun Zhang, Congzhi Wang, Tian Pan, Yue Zhao, Xiang Chen, Lin Zhang
Geriatric Nursing.2026; 69: 103799. CrossRef - The Effect of Pain Catastrophizing on Depression among Older Korean Adults with Chronic Pain: The Mediating Role of Chronic Pain Interference and Sleep Quality
Kyoung-eun Lee, Hyunju Ryu, Sun Ju Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 8716. CrossRef
- The relationship between family support and life satisfaction in hypertensive patients: the multiple mediating roles of self-esteem and self-care
- 1,115 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of Communication Empowerment Program Based on Situated Learning Theory for Nursing Students
- Soo Jin Kim, Boyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):708-719. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.708
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to examine the effects of a communication empowerment program based on situated learning theory for nursing students.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The study participants were 61 nursing students (31 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group) from G city. Data were collected from November 3, 2015 to December 10, 2015. The experimental group received eight sessions of the program, which were scheduled twice a week, with each session lasting two hours. The data were analyzed using chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, and an independent t-test using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results There were significant increases in self-efficacy for communication (t=2.62,
p =.011), emotional intelligence (t=2.66,p =.010), and interpersonal communication competence (t=2.87,p =.006) in the experimental group compared to the control group.Conclusion Based on the findings, our study suggests a need to include content from communication curricula or clinical communication training programs for improving undergraduate nursing students’ communication skills in practice settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Virtual reality education for preventing safety incidents in pediatric hospital settings: Quasi-experimental design pre-post-testing
Raim Hyeon, Won-Oak Oh
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 80: 56. CrossRef - Gamification as a Tool for Understanding Mental Disorders in Nursing Students: Qualitative Study
Pablo Del Pozo-Herce, Alberto Tovar-Reinoso, Eva García Carpintero-Blas, Ana Casaux Huertas, Regina Ruiz de Viñaspre-Hernández, Antonio Martínez-Sabater, Elena Chover-Sierra, Marta Rodríguez-García, Raul Juarez-Vela
JMIR Nursing.2025; 8: e71921. CrossRef - Therapeutic Communication Using Mirroring Interventions in Nursing Education: A Mixed Methods Study
Seung Hee Lee, Hye Jin Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(5): 435. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of Patient-Centered Care Tool: For Outpatients
Yeo Ju Kim, Gunjeong Lee, Sunyeob Choi
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1525. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a neonatal intensive care unit medication safety simulation for nursing students in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study
Mi Seon Son, Minyoung Yim, Eun Sun Ji
Child Health Nursing Research.2022; 28(4): 259. CrossRef - Patient handover education programme based on situated learning theory for nursing students in clinical practice
Jung Hee Kim, Jong Mi Lim, Eun Man Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Situation-Based Flipped Learning and Gamification as Combined Methodologies in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Haeran Kim, Boyoung Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 644. CrossRef - Cyberbullying in the University Setting. Relationship With Emotional Problems and Adaptation to the University
María Carmen Martínez-Monteagudo, Beatriz Delgado, José Manuel García-Fernández, Cecilia Ruíz-Esteban
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Virtual reality education for preventing safety incidents in pediatric hospital settings: Quasi-experimental design pre-post-testing
- 2,039 View
- 31 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- A Study about the Human Communication between Clinical Nurse and Patient
- Myung Hee Jun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(4):841-854. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.4.841
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study tried to the answer to the question : "How does the human communication happen between clinical nurse and patient?" To answer that, a micro-ethnographic research method was used and I performed field work at the orthopedic ward in one Korean metropolitan city. After analysis of interview data, observational data and field notes, I could understand that clinical nurse-patient communication performed for clinical decision making, providing patient education and emotional support. Prepared nurse communicate with patient more effectively, eventually can establish more trust relationship with patient. Conclusively I discussed about the way of nurse's skill acquisition, need of collaborative conference with doctor and nurse, and curriculum development to promote nurses's understanding of human.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Interpersonal Attitude on Communication Competence in Care Workers for Frail Elderly
Seung Joo Lim, Yeo-Jin Yi
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(2): 112. CrossRef
- Influence of Interpersonal Attitude on Communication Competence in Care Workers for Frail Elderly
- 620 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of the Group Commuication Program on the Dysfunctional Communication, Self-Esteem and Depression : In the Group of Mothers with Children of Mental Disorder
- Gil Za Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):801-809. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.801
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was carried out the group communication program which I had composed of using the Satir's communication family theory and skills. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects on the dysfunctional communication self-esteem and depression, executed this program for the mothers group with caring the mental disorders, and then for the test of some hypotheses it was divided two groups ; the experimental group(n= 20) and control group(n=25). In the control group they were learned two session family education program in the psychiatric of Pusan National University Hospital and it the experimental group they had experienced during the 10 session by the group communication program. In the methods of the statistics on this data, it was to statistics x2-test for the comparison between the experimental group and control group with general characteristics. The effect of the Group Communication Program was analyse ANCOVA between pre-post test on the dysfunctional communication, self-esteem and depression in the control group and experimental group. The conclusions were derived from the results and test of hypothesis as followings : 1) The results were tested the differentiation between the experimental and control group, and the pre-post test in the experimental group with dysfunctional communication self-esteem and depression. Some hypothesis were tested and supported as following: It was supported that the level of dysfunctional communication of the experimental group would be lower than the control group(hypothesis 1). It was supported that the level of self-esteem of the experimental group would be lower than the control group(Hypothesis 2) It was supported that the level of depression of the experimental group would be lower than the control group(Hypothesis 3) 2) The relation of the dysfunctional communication with the self-esteem was presented negative correlation and with the depression was not correlation. The relation of the dysfunctional communication with the self-esteem was presented negative correlation. The relation of the sacrificuny pattern of dysfunctional communication with the self-esteem was presented negative correlation and with the depression positive correlation.
- 383 View
- 1 Download

- Conversation Analysis for Improving Nursing Communication
- Myungsun Yi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):772-780. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.772
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Nursing communication has become more important than ever before because quality of nursing services largely depends on the quality of communication in a very competitive health care environment. This article was to introduce ways to improve nursing communication using conversation analysis.
Methods This was a review study on conversation analysis, critically examining previous studies in nursing communication and interpersonal relationships.
Results This study provided theoretical backgrounds and basic assumptions of conversation analysis which was influenced by ethnomethodology, phenomenology, and sociolinguistic. In addition, the characteristics and analysis methods of conversation analysis were illustrated in detail. Lastly, how conversation analysis could help improve communication was shown, by examining researches using conversation analysis not only for ordinary conversations but also for extraordinary or difficult conversations such as conversations between patients with dementia and their professional nurses.
Conclusion Conversation analysis can help in improving nursing communication by providing various structures and patterns as well as prototypes of conversation, and by suggesting specific problems and problem-solving strategies in communication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of nurses’ communication styles, nurse-mother partnerships, and mothers’ anxiety on coping of hospitalized children’s mothers
Yonghee Kim, Areum Choi, Insun Jang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 170. CrossRef - The Validity and Reliability of Nursing Assessment Communication-Competence Scale for Clinical Nurses
Hyojin Kim, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 78. CrossRef - Influence of Communication Competence and Communication Style on the Nurse-Parent Partnership in Pediatric Nurses
Hyun Jin Cho, Hyoung Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(2): 170. CrossRef - Effects of Customer Orientation, Belief of Patient Activation and Professional Self-concept on Caring Behaviors of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Units
Ji Eun Jeon, Eun Hee Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 344. CrossRef - Educational Needs of Communication among Nursing Students
Min Young Jung, Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(1): 91. CrossRef - The Relation between Interpersonal Attitude and Communication Competence of New Visiting Nurses in Community Health Center
Seung Joo Lim, Eun A Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Perceived Nurse's Communication Style on Admitted Children Mother's Stress and Coping
In Sook Park, Jaewoo Oh, Yang-Sin Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(6): 365. CrossRef - Occupational Health Nurses' Role Experiences
Kyung-Ja June, Hea-Ju Joo, Young-Mi Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 250. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nurses' Competency in Nurse-Patient Communication about Medications: Conversational Analysis Approach
Haeng-Mi Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Conversation between Elderly Patients with Dementia and Nurses: Focusing on Structure and Sequential Patterns
Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 166. CrossRef
- The effects of nurses’ communication styles, nurse-mother partnerships, and mothers’ anxiety on coping of hospitalized children’s mothers
- 919 View
- 10 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The Persuasive Effects according to Types of Exercise Promotion Advertisements for Obesity Prevention in Elementary School Students
- Gyeong Ju An, Myoung Ae Choe, Byoung Hee Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(5):817-828. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.5.817
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to identify the persuasive effects of exercise promotion advertisements for obesity prevention according to the source types(ordinary people, experts, celebrity endorsers) and advertising message types(slices of life, testimonials).
Method Gender, height, body weight, BMI, attitude toward obesity(Aob) and exercise(Aex), and intention to exercise(Iex) were collected from 626 elementary school students in a pretest. After 2 months, six advertisements type attached to a questionnaire were provided for 20 minutes and then Aob, Aex, Iex, source credibility and attitude toward advertisements(Aad) were collected in posttest.
Result 1) In posttest the Iex of 6 the groups increased significantly compared with that of the pretest, 2) Source credibility of the Ordinary+Testimonial group was lower than the Celebrity+Testimonial, Celebrity+Slice of life, Ordinary+Slice of life, and Expert+Testimonial groups. Aad of the Celebrity+Testimonial group was higher than the Ordinary+ Testimonial group. 3) The Main effect and interaction effect of source types and advertising message types were significant in source credibility and Aad.
Conclusion Persuasive effects of exercise promotion advertisements in elementary school students was found to be the most effective in Celebrity+Testimonial. This study suggests that selection of health education advertisements according to demographic characteristics is important to promote persuasive effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Hepatitis Education Program according to Message Frames
Ju-Young Park, Chung-Hee Woo
Journal of muscle and joint health.2014; 21(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparison of the Effects between Positive Message and Negative Message in Diabetes Mellitus Education
Bong Jo Lee, Mee Ock Gu
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(4): 344. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Hepatitis Education Program according to Message Frames
- 666 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Development and Effects of a Comprehensive Communication Course for Nursing Students
- Sunah Kim, Jung Hwa Park, Hyun Hwa Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(3):412-420. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.3.412
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to: (a) develop a comprehensive communication course combined with a group program for improving communication skills; and (b) examine the effects of the comprehensive communication course on interpersonal communication, relationship change, self-esteem, and depression in nursing students.
Method The experimental group consisted of 82 nursing students, and the control group, 108 nursing students. Both groups each took communication courses from March to June, 2002 and 2003. A group program for improving communication skills was conducted for each 8 subgroups of the experimental group for 90 minutes once a week during the 6 weeks, while the existing communication lecture was conducted for the control group. Both groups were post-tested after the intervention for verifying the difference of variables between the two groups, and the experimental group was also pre-tested for verifying the difference between before and after the treatment.
Result & Conclusion Interpersonal communication score of the post-test in the experimental group was significantly higher than in the control group and the depression score of the post-test in the experimental group was significantly lower than in the control group. Interpersonal communication, relationship change and self-esteem scores were significantly increased and the depression score was significantly decreased in experimental group after the treatment. In conclusion, the comprehensive communication course that was developed in this study had positive effects on communication skills in nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Communication-related Educational Needs for Optometry Students
Se-Jin Kim, Ji-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Ophthalmic Optics Society.2022; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - The mediating effect of self-efficacy on the relationship between social anxiety and communication ability in nursing students
Mi-Jin You, Hye-Sook Han
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 298. CrossRef - Educational Needs of Communication among Nursing Students
Min Young Jung, Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(1): 91. CrossRef - The Effect of an Empathy Education Program on Nursing Students' Empathy Ability, Interpersonal Ability, and Caring
Jin Ok Jeong, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 344. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Motivational Interviewing Based Communication Training to Promote Communication Competency for Nursing Students
Hee-Jung Kim
Stress.2018; 26(4): 268. CrossRef - Effects of Communication Empowerment Program Based on Situated Learning Theory for Nursing Students
Soo Jin Kim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 708. CrossRef - The Relationship of Communication Skill, Communication Self-Efficacy and Communication Related Educational Needs
In-Young Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(4): 2593. CrossRef - Curriculum Integration of Communication Simulation to Community Health Nursing Course for Nursing Students: Pilot Study
Yi-Kyung Ha
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(4): 2329. CrossRef - Development and Application of Integrated Nursing Practice Program preceded Role-play related to Clinical Communication Situation
Seo-Young Kang, You-Jin Lim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(5): 3037. CrossRef - Needs and perception of medical communication course in the dental hygiene students
Da-Young Ryu, Hyun-Suk Yang, Yong-Keum Choi
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2014; 14(5): 623. CrossRef - Changes in Communication and Relationship Pattern for Undergraduate Nursing Students After 'Satir Communication Education'
Seung Joo Lim, Eun Young Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(2): 151. CrossRef - Influence of Interpersonal Attitude on Communication Competence in Care Workers for Frail Elderly
Seung Joo Lim, Yeo-Jin Yi
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(2): 112. CrossRef - Nursing Activities Identified through Pediatric Nursing Simulation.
Hyun Sook Shin, Ka Ka Shim, Yu Na Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(2): 111. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Medical Communication Skill of Medical Students, through an Emphasis on Role Play
Ho Seob Lihm, Heung Yeol Kim, Jong Soon Choi
Kosin Medical Journal.2012; 27(2): 151. CrossRef - Application and Evaluation of Small Group and Music Activity in a Communication Course
Sunah Kim, Narae Han, Jeong Hwa Park, Minjeong Kim, Hyun Lye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(3): 307. CrossRef
- Communication-related Educational Needs for Optometry Students
- 888 View
- 5 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Developing a Home Care Nursing Information System by utilizing Wire-Wireless Network and Mobile Computing System
- Jung Ho Park, Sung Ae Park, Soon Nyoung Yoon, Sung Rye Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):290-296. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a home care nursing network system for operating home care effectively and efficiently by utilizing a wire-wireless network and mobile computing in order to record and send patients' data in real time, and by combining the headquarter office and the local offices with home care nurses over the Internet. It complements the preceding research from1999 by adding home care nursing standard guidelines and upgrading the PDA program.
Method Method/1 and Prototyping were adopted to develop the main network system.
Result The detailed research process is as follows : 1)home care nursing standard guidelines for Diabetes, cancer and peritoneal-dialysis were added in 12 domains of nursing problem fields with nursing assessment/intervention algorithms. 2) complementing the PDA program was done by omitting and integrating the home care nursing algorhythm path which is unnecessary and duplicated. Also, upgrading the PDA system was done by utilizing the machinery and tools where the PDA and the data transmission modem are integrated, CDMX-1X base construction, in order to reduce a transmission error or transmission failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of a Web-based Expert System using Artificial Intelligence for Management of Mental Health by Korean Emigrants
Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(2): 203. CrossRef - Developing an Electronic Nursing Record System for Clinical Care and Nursing Effectiveness Research in a Korean Home Healthcare Setting
EUN JOO LEE, MIKYOUNG LEE, SUE MOORHEAD
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2009; 27(4): 234. CrossRef
- Development and Application of a Web-based Expert System using Artificial Intelligence for Management of Mental Health by Korean Emigrants
- 703 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Comparative Study of Consistent and Inconsistent Contraceptive Users on Partner Communication, Perceived Contraceptive Control, and Sexual Autonomy
- Mi Jong Kim, Hee Sun Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(6):784-791. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.6.784
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study is to investigate the influencing factors in the consistent use of contraception methods by comparing consistent and inconsistent users on partner communication, contraceptive control perception, and sexual autonomy among married Korean women.
Method This study consists of 243 married women living in Korea. A convenient sampling technique was used and data were collected by self report questionnaires from September 14, 2000 to October 20, 2000.
Result Only 41.6% of women were using contraception methods consistently and the rest of them were using contraception methods inconsistently. Between the two groups, statistical significances were noted in sexual communication(t=-2.5, p=.01), perceived contraceptive control(t=-7.5, p=.00) and sexual autonomy(t=-3.1, p=.00). As for general communication, it was not statistically significant(t=-1.0, p=.31).
Conclusion Family planning program advisors should recognize that intervention programs for the promotion of consistent contraceptive behavior should focus on the sexual communication, perceived contraceptive control, and sexual autonomy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting reproductive health promotion behavior among late-adolescent girls in South Korea: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Minji Je, Hyeon Ok Ju, Jaeyoung Lee
Children and Youth Services Review.2020; 118: 105347. CrossRef - Effects of Birth Control Empowerment Program for Married Immigrant Vietnamese Women in South Korea
Jihyun Kim, Nam Cho Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Self-Efficacy and Sexual Autonomy among University Students
Kyung-Won Kim, Kyeong-Hwa Kang, Geum-Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(1): 51. CrossRef - Contraceptive Knowledge and Contraceptive Attitude of Female Nursing Students of a College
Inn-Sook Lee, A-Young Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(7): 3102. CrossRef - Contraceptive Knowledge and Practice among Married Immigrant Women
Tae Im Kim, Ji-Young Kim, Gye-Hyun Jung, Sun-Mi Choi
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(4): 290. CrossRef - Contraception Behavior and Related Factors in Unmarried Female and Male
Shin Woo Hwang, Chae Weon Chung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(1): 77. CrossRef
- Factors affecting reproductive health promotion behavior among late-adolescent girls in South Korea: A cross-sectional descriptive study
- 703 View
- 0 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Semantic Network Analysis of Online News and Social Media Text Related to Comprehensive Nursing Care Service
- Minji Kim, Mona Choi, Yoosik Youm
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):806-816. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.806
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose As comprehensive nursing care service has gradually expanded, it has become necessary to explore the various opinions about it. The purpose of this study is to explore the large amount of text data regarding comprehensive nursing care service extracted from online news and social media by applying a semantic network analysis.
Methods The web pages of the Korean Nurses Association (KNA) News, major daily newspapers, and Twitter were crawled by searching the keyword ‘comprehensive nursing care service’ using Python. A morphological analysis was performed using KoNLPy. Nodes on a ‘comprehensive nursing care service’ cluster were selected, and frequency, edge weight, and degree centrality were calculated and visualized with Gephi for the semantic network.
Results A total of 536 news pages and 464 tweets were analyzed. In the KNA News and major daily newspapers, ‘nursing workforce’ and ‘nursing service’ were highly rated in frequency, edge weight, and degree centrality. On Twitter, the most frequent nodes were ‘National Health Insurance Service’ and ‘comprehensive nursing care service hospital.’ The nodes with the highest edge weight were ‘national health insurance,’ ‘wards without caregiver presence,’ and ‘caregiving costs.’ ‘National Health Insurance Service’ was highest in degree centrality.
Conclusion This study provides an example of how to use atypical big data for a nursing issue through semantic network analysis to explore diverse perspectives surrounding the nursing community through various media sources. Applying semantic network analysis to online big data to gather information regarding various nursing issues would help to explore opinions for formulating and implementing nursing policies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Public Perception Before and After COVID-19 Vaccine Pass for the Unvaccinated to Eat Alone: Social Media Data Analytics
Sun Ok Jung, Yoon Hee Son
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influences of Emotional Labor and Work-Life Balance on Organizational Commitment among Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Wards
Young-Yi Yoon, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(2): 100. CrossRef - Developing a COVID-19 Crisis Management Strategy Using News Media and Social Media in Big Data Analytics
Young-Eun Park
Social Science Computer Review.2022; 40(6): 1358. CrossRef - Research evidence for reshaping global energy strategy based on trend-based approach of big data analytics in the corona era
Young-Eun Park
Energy Strategy Reviews.2022; 41: 100835. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Policy for Facilitating of Health Behaviors Related to Particulate Matter: Using Topic and Semantic Network Analysis of Media Text
Hye Min Byun, You Jin Park, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 68. CrossRef - A data-driven approach for discovery of the latest research trends in higher education for business by leveraging advanced technology and big data
Young-Eun Park
Journal of Education for Business.2021; 96(5): 291. CrossRef - Perceptions Related to Nursing and Nursing Staff in Long-Term Care Settings during the COVID-19 Pandemic Era: Using Social Networking Service
Juhhyun Shin, Sunok Jung, Hyeonyoung Park, Yaena Lee, Yukyeong Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(14): 7398. CrossRef - Topic Modeling and Keyword Network Analysis of News Articles Related to Nurses before and after “the Thanks to You Challenge” during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Eun Kyoung Yun, Jung Ok Kim, Hye Min Byun, Guk Geun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(4): 442. CrossRef - Identification of the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors’ Return to Work and Quality of Life: A Text Network Analysis
Kisook Kim, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9368. CrossRef - Family nursing with the assistance of network improves clinical outcome and life quality in patients underwent coronary artery bypass grafting
Liying Jin, Ruijin Pan, Lihua Huang, Haixia Zhang, Mi Jiang, Hao Zhao
Medicine.2020; 99(50): e23488. CrossRef - Uncovering trend-based research insights on teaching and learning in big data
Young-Eun Park
Journal of Big Data.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Analysis of Trends in Domestic Nursing Research on Integrated Nursing Care Service
Hyun Ju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(5): 510. CrossRef - Hospitalization Experience of Patients Admitted to Nursing Care Integrated Service Wards in Small and Medium-size General Hospitals
Hyun Ju Choi, A Leum Han, Young Mi Park, JI Hyeon Lee, Young Sook Tae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 396. CrossRef - Exploring Research Topics and Trends in Nursing-related Communication in Intensive Care Units Using Social Network Analysis
Youn-Jung Son, Soo-Kyoung Lee, SeJin Nam, Jae Lan Shim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(8): 383. CrossRef
- Public Perception Before and After COVID-19 Vaccine Pass for the Unvaccinated to Eat Alone: Social Media Data Analytics
- 1,469 View
- 13 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Emotional Intelligence Program for Undergraduate Nursing Students: Mixed Methods Research
- Oi Sun Lee, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(6):682-696. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.682
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop and test the effects of an emotional intelligence program for undergraduate nursing students.
Methods The study design was a mixed method research. Participants were 36 nursing students (intervention group: 17, control group: 19). The emotional intelligence program was provided for 4 weeks (8 sessions, 20 hours). Data were collected between August 6 and October 4, 2013. Quantitative data were analyzed using Chi-square, Fisher's exact test, t-test, repeated measure ANOVA, and paired t-test with SPSS/WIN 18.0. Qualitative data were analyzed using content analysis.
Results Quantitative results showed that emotional intelligence, communication skills, resilience, stress coping strategy, and clinical competence were significantly better in the experimental group compared to the control group. According to the qualitative results, the nursing students experienced improvement in emotional intelligence, interpersonal relationships, and empowerment, as well as a reduction in clinical practice stress after participation in the emotional intelligence program.
Conclusion Study findings indicate that the emotional intelligence program for undergraduate nursing students is effective and can be recommended as an intervention for improving the clinical competence of undergraduate students in a nursing curriculum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research trends and effectiveness analysis of social and emotional learning programs for adult learners: A scoping review
Yoon-ju Lee, Insook Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(3): 299. CrossRef - Emotional Intelligence, Academic Motivation, and Achievement among Health Science Students in Saudi Arabia: A Self-Deterministic Approach
Rasha Mohammed Mahrous, Bussma Ahmed Bugis, Samiha Hamdi Sayed
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 571. CrossRef - A Literature Review of Simulation-Based Nursing Education in Korea
Sumee Oh, Jungmin Park
Nursing Reports.2023; 13(1): 506. CrossRef - The Effects of a Non-Technical Skills Training Program on Emotional Intelligence and Resilience in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Diana Jiménez-Rodríguez, María del Mar Molero Jurado, María del Carmen Pérez-Fuentes, Oscar Arrogante, Nieves Fátima Oropesa-Ruiz, José Jesús Gázquez-Linares
Healthcare.2022; 10(5): 866. CrossRef - Development and effects of a high-risk pregnancy emotive role-play program for nursing students: a quasi-experimental study
Bo Gyeong Lee, Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 317. CrossRef - The development and effects of an emotional competency promotion program for nursing students: A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design
Hyewon Kang, Jeongyee Bae
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 369. CrossRef - Understanding the relationships among emotional exhaustion, job satisfaction, and emotional intelligence of hotel front desk employees
Kwang-Hi Park, Dae-Kwan Kim
Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research.2021; 26(5): 504. CrossRef - The assessment of emotional intelligence in social care and healthcare student selection: a qualitative descriptive study
Anne Pienimaa, Kirsi Talman, Elina Haavisto
Educational Research.2021; 63(3): 302. CrossRef - Social–Emotional Competence and Academic Achievement of Nursing Students: A Canonical Correlation Analysis
Sun-Hee Kim, Sujin Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1752. CrossRef - The Influences of Nursing Professionalism and Emotional Intelligence on the Clinical Performance Ability in Nursing Students
Hyo-Won Kim, Myung-Sook Yoo
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2020; 14(2): 41. CrossRef - Impact of emotional development intervention program on subjective well-being of university students
Konstanze Schoeps, Usue de la Barrera, Inmaculada Montoya-Castilla
Higher Education.2020; 79(4): 711. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale (K-WLEIS)
Harim Jeong, Heejung Choi, Myungsook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 611. CrossRef - Influence of Metacognition and Emotional Intelligence on Self-leadership in Nursing Students
Myoung Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(2): 146. CrossRef - The Effect of an Empathy Education Program on Nursing Students' Empathy Ability, Interpersonal Ability, and Caring
Jin Ok Jeong, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 344. CrossRef - The Effects of Emotional Labor on Job Satisfaction of Hotel Employees: Analyzing Moderating Effects of Emotional Intelligence
Kwang-Hi Park
Stress.2018; 26(3): 166. CrossRef - Effects of Communication Empowerment Program Based on Situated Learning Theory for Nursing Students
Soo Jin Kim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 708. CrossRef - The level of emotional intelligence in undergraduate students of nursing
Ľudmila Majerníková, Andrea Obročníková
Pielegniarstwo XXI wieku / Nursing in the 21st Century.2017; 16(1): 25. CrossRef - Relationships between Personal Traits, Emotional Intelligence, Internal Marketing, Service Management, and Customer Orientation in Korean Outpatient Department Nurses
Bogyun Kim, Jia Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 18. CrossRef - Vocational Identity and Ego Identity Status in Korean Nursing Students
Hyun-Young Koo, Eun-Jung Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 68. CrossRef - Effects of Discipline-based Career Course on Nursing Students' Career Search Self-efficacy, Career Preparation Behavior, and Perceptions of Career Barriers
Soonjoo Park
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 259. CrossRef - Influence of Emotional Intelligence and Ego Resilience on Interpersonal Relationship of Nurses
Oi Sun Lee, Mee Ock Gu, Mi Jung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 3902. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Stress on Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Burnout among Nursing College Students
Chung Mee Ko
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2015; 28(3): 239. CrossRef
- Research trends and effectiveness analysis of social and emotional learning programs for adult learners: A scoping review
- 1,642 View
- 43 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Comparison of Boys' and Girls' Families for Actor and Partner Effect of Stress, Depression and Parent-Adolescent Communication on Middle School Students' Suicidal Ideation: Triadic Data Analysis
- Sung Hee Shin, Suk Jeong Ko, Yu Jeong Yang, Hyun Su Oh, Mi Young Jang, Joong Myung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(3):317-327. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.3.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to compare families of boys or of girls for actor and partner effect of stress, depression and parent-adolescent communication as perceived by mother, father and adolescent on adolescents' suicidal ideation.
Methods Participants were 183 families (104 boys' families, 79 girls' families) who met eligibility criteria. All measures were self-administered. Data were analyzed using SPSS 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 program.
Results In boys' families, boys' depression and communication with father showed actor effect on boys' suicidal ideation. Boys' stress showed indirect effect on boys' suicidal ideation through communication with father and boys' depression. Mothers' depression showed indirect partner effect on boys' suicidal ideation through boys' depression. In families of girls, girls' depression and stress showed actor effects on girls' suicidal ideation. Girls' communication with mother showed indirect effects through girls' depression. Also girls' stress showed indirect effect through girls' depression. Stress in mothers and/or fathers showed partner effect on girls' suicidal ideation.
Conclusion To intervene in adolescents' suicidal ideation and promote adolescents' mental health, programs should be developed differently according to gender and based on parent's psychological states.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations between Suicidal Ideation and Relatives’ Physical and Mental Health among Community Residents: Differences between Family Members and Lineal Consanguinity
Caifeng Li, Zhen Wei, Yifan Wang, Long Sun
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15997. CrossRef - Actor-Partner Effects of Mother-Adolescent Communication and Conflict on Psychological Well-Being for Mothers and Male/Female Adolescents
Yeon Soo Cho, Sae-Young Han
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2021; 42(5): 565. CrossRef - Parents’ Perceptions and Responses to Parent-adolescent Conflict Situations: A Mixed Methods Approach
Heeseung Choi, Sumi Kim, Heesung Ko
Stress.2020; 28(3): 142. CrossRef - The Effects of Depression, Anxiety, and Parents’ Support on Suicide Ideation and Attempts by Gender among Korean Adolescents
Joowon Jung, So Yeon Cho
Journal of Child and Family Studies.2020; 29(5): 1458. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of depression among Korean adolescents
Je-Yeon Yun, Halin Chung, Jin-ah Sim, Young Ho Yun, Kwaku Oppong Asante
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(10): e0223176. CrossRef - Association of temporomandibular disorder and high frequency of suicide ideation in Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional survey
Hyun A. Heo, Suhyun Park, Sung Woon Pyo
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2018; 76(5): 374. CrossRef - The Differences in Obesity Rates According to Status of Co-Residence with Their Parents in Korean Adolescents: The Implication of the Gender of Single Parent Living with Adolescents
Nahee Kim, Young Gyu Cho, Jae-Heon Kang, Hyun Ah Park, Kyoungwoo Kim, Yang-Im Hur, Duho Kwon
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(4): 177. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Suicide Ideation Among Adolescents: Five-Year National Data Analysis
Yeojin Im, Won-Oak Oh, Minhyun Suk
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2017; 31(3): 282. CrossRef
- Associations between Suicidal Ideation and Relatives’ Physical and Mental Health among Community Residents: Differences between Family Members and Lineal Consanguinity
- 1,156 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of 「Hospice Smart Patient」 Service Program
- Chai-Soon Park, Yang-Sook Yoo, Dong-Won Choi, Hyun-Jeong Park, Ji-In Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(1):9-17. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and implement the Hospice Smart Patient Program and to evaluate its effectiveness.
Methods It was quasi-experimental non-equivalent pre-post study. Breast cancer patients who underwent surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy, or who needed palliative care, participated in the study. Participants were divided into two groups, experimental and control groups based on their preferences. The program was developed after literature review and discussion among experts on hospice and palliative care. Participants who were in the experimental group received either face-to-face or phone 「Hospice Smart Patient」 Service at least once a week for 5 months.
Results There was a significant difference in quality of life and communication skill between the two groups after the service was provided. In addition, participants in experimental group showed improved decision making skills, mastery sense, and understanding of hospice and palliative care, which would be beneficial in improving their quality of life.
Conclusion We have concluded that the 「Hospice Smart Patient」 Program is useful for cancer patients in decision making, improving self-control and choosing hospice care to improve their quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Palliative care in the treatment of women with breast cancer: A scoping review
Romel Jonathan Velasco Yanez, Ana Fátima Carvalho Fernandes, Erilaine de Freitas Corpes, Régia Christina Moura Barbosa Castro, Judith Sixsmith, Luís Carlos Lopes-Júnior
Palliative and Supportive Care.2024; 22(3): 592. CrossRef - Efficacy of a Digital Health Tool on Contraceptive Ideation and Use in Nigeria: Results of a Cluster-Randomized Control Trial
Stella Babalola, Caitlin Loehr, Olamide Oyenubi, Akinsewa Akiode, Allison Mobley
Global Health: Science and Practice.2019; 7(2): 273. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the HIV Self-Management Scale in Patients with HIV
Gwang Suk Kim, Sang Hui Chu, Yunhee Park, Jun Yong Choi, Jeong In Lee, Chang Gi Park, Linda L. McCreary
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(3): 439. CrossRef - Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of home palliative care services for adults with advanced illness and their caregivers
Barbara Gomes, Natalia Calanzani, Vito Curiale, Paul McCrone, Irene J Higginson, Maja de Brito
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- Palliative care in the treatment of women with breast cancer: A scoping review
- 1,155 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Actor Effect and the Partner Effect of Self-esteem and Mother-Adolescent Communication on Depression in Mothers and Adolescents in Kirogi Families according to Adolescent' Development Stage
- Eun Kyung Yun, Sung Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(5):620-630. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.5.620
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to compare the level of depression, self-esteem and mother-adolescent (M-A) communication perceived by both mothers and adolescents between the early adolescent (E-A) group and the late adolescent (L-A) group; and to examine the actor effect and the partner effect of self-esteem and M-A communication on depression in mothers and adolescents.
Methods Participants were 107 Kirogi families who resided in the Midwest region of the U. S. Data were collected from September, 2008 to March, 2009 using the scales of Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D), Self-esteem and Parent-Adolescent Communication Inventory.
Results Mothers in E-A group reported higher scores on depression than mothers in L-A group. Adolescents in L-A group reported higher scores on depression and lower scores on self-esteem than adolescents in E-A group. In the E-A group, mothers' self-esteem had big actor effect on mothers' depression and partner effect on adolescents' depression. In the L-A group, self-esteem of mothers and adolescents had actor effect on their depression respectively without partner effect. M-A communication of mothers influences mothers' depression negatively and adolescents' depression positively. In both group, M-A communication influences their depression with mediating effect of self-esteem.
Conclusion To promote Kirogi families' mental health, programs for mothers and adolescents should be developed differently according to adolescents' development stage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Navigating motherhood across borders: An integrative review of role transformation and emotional challenges among Korean
kirogi
mothers
Boram Lee
Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Testing of the factor structure of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale 10 in a sample of Korean “geese” mothers
Boram Lee
Health Care for Women International.2019; 40(5): 539. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-esteem and Family Stress on Depression of Middle-aged Couples: Analysis of Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Yu Jeong Yang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 60. CrossRef - The mental health of Korean transnational mothers: A scoping review
Jaemin Kim, Branka Agic, Kwame McKenzie
International Journal of Social Psychiatry.2014; 60(8): 783. CrossRef
-
Navigating motherhood across borders: An integrative review of role transformation and emotional challenges among Korean
kirogi
mothers
- 892 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effects on Couples' Communication, Intimacy, Conflict and Quality of Life by Foot Massage between Immigrants
- Dong-choon Uhm
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(4):493-502. Published online August 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.4.493
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects on immigrant couples' communication, intimacy, conflict and quality of life when using foot massage.
Methods The research design consisted of pre-and-post test consecutive experimental design through a nonequivalent control group. Data were collected July 6, 2009 to February 27, 2010. The 36 couples were divided into two groups, experimental and control with 18 couples in each group. Foot massage was applied twice a week for 6 weeks by the couples in the experimental group.
Results There were statistically significant increases in communication (
p =.011), intimacy (p <.001), quality of life (p =.017) between the couples in the experimental group compared to the control group. There was also a statistically significant decrease in conflict (p =.003) between the couples in the experimental group compared to the control group.Conclusion Foot massage can be applied as a nursing intervention for improvement of marital relationship in immigrant couples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Immigrant Vietnamese women’s adaptation to culture and society in rural areas of Korea
Misoon Jeon, Okhee Ahn, Minjeong An, Shang E. Ha
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(2): e0212265. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience to Family of Immigrant Women in Multicultural Families
Jin-Hyang Yang, Hyun-Joo Park, Song-Soon Kim, Eun-Jeong Kang, Sang-Hee Byun, Ji-Soo Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 36. CrossRef - Comparison of Marital Satisfaction and Quality of Life in International Married Woman Migrants and Korean Man
Yoon-Ji Park, Myunghee Jun
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2012; 18(3): 383. CrossRef - Effects of a Marital Relationship Enrichment Program on Communication, Conflict Resolution, and Marital Satisfaction in Multicultural Couples
Young-Ran Yeun, Soo Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(3): 250. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience to Family of Immigrant Women in Multicultural Families
Jin-Hyang Yang, Hyun-Joo Park, Song-Soon Kim, Eun-Jeong Kang, Sang-Hee Byun, Ji-Soo Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 36. CrossRef
- Immigrant Vietnamese women’s adaptation to culture and society in rural areas of Korea
- 1,130 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Evaluation of Nurses' Competency in Nurse-Patient Communication about Medications: Conversational Analysis Approach
- Haeng-Mi Son
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(1):1-13. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop evaluation criteria for conversations about medication and to demonstrate conversational analysis with actual dialogues on medication as examples.
Methods This study was a secondary analysis of qualitative research using conversational analysis which showed functional phases and patterns of dialogue about medication (greeting, identifying the patient, medicating, finishing). Nurse-patient conversations were videotaped and transcribed and 75 conversations were used for analysis.
Results Not all functional phases were showed in the conversations about medication. Therefore, conversations about medication can be considered as incomplete dialogues. The evaluation-criteria were represented in terms of the structure and content of the dialogues. Structural evaluation-criteria were the same as the functional phases, as functional stage is the standard for evaluation. The criteria of evaluation for content suggested 3 domains, content, expression, and interaction with 20 items scored on a Likert-type scale of 5-points. Finally, analysis of actual conversations about medication according to the evaluative criteria were provided.
Conclusion The results provide the basic data to develop educational programs and strategies to improve nurses' competency in conversation about medication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An investigation into health professionals’ perception of the appropriateness of elderspeak in a Korean hospital setting
Miseon Lee, Jeong Youn Lee
Journal of Pragmatics.2021; 172: 181. CrossRef
- An investigation into health professionals’ perception of the appropriateness of elderspeak in a Korean hospital setting
- 1,012 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Analysis of Conversation between Elderly Patients with Dementia and Nurses: Focusing on Structure and Sequential Patterns
- Myungsun Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(2):166-176. Published online April 28, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.166
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to identify functional structure and patterns of dialogue sequence in conversations between elderly patients with dementia and nurses in a long-term care facility.
Methods Conversation analysis was used to analyze the data which were collected using video-camera to capture non-verbal as well as verbal behaviors. Data collection was done during February 2005.
Results Introduction, assessment, intervention, and closing phases were identified as functional structure. Essential parts of the conversation were the assessment and intervention phases. In the assessment phase three sequential patterns of nurse-initiated dialogue and four sequential patterns of patient-initiated dialogue were identified. Also four sequential patterns were identified in nurse-initiated and three in patient-initiated dialogues in the intervention phase. In general, "ask question", "advise", and "directive" were the most frequently used utterance by nurses in nurse-initiated dialogue, indicating nurses' domination of the conversation. At the same time, "ask back", "refute", "escape", or "false promise" were used often by nurses to discourage patients from talking when patients were raising questions or demanding.
Conclusion It is important for nurses to encourage patient-initiated dialogue to counterbalance nurse-dominated conversation which results from imbalance between nurses and patients in terms of knowledge and task in health-care institutions for elders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A staff training intervention to improve communication between people living with dementia and health-care professionals in hospital: the VOICE mixed-methods development and evaluation study
Rowan H Harwood, Rebecca O’Brien, Sarah E Goldberg, Rebecca Allwood, Alison Pilnick, Suzanne Beeke, Louise Thomson, Megan Murray, Ruth Parry, Fiona Kearney, Bryn Baxendale, Kate Sartain, Justine Schneider
Health Services and Delivery Research.2018; 6(41): 1. CrossRef
- A staff training intervention to improve communication between people living with dementia and health-care professionals in hospital: the VOICE mixed-methods development and evaluation study
- 1,076 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of a Group Therapy for the Offenders of Family Violence
- Mi-Yeul Hyun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(3):420-427. Published online June 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.3.420
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the contribution of group therapy to the improvement of self-esteem, anger, stress coping and communication of those who were violent in to family.
Methods The research design was a one-group-pretest-posttest design in quasi-experimental research, and the period of this study was from March to October, 2005. Participants were 14 offenders who were ordered to be counseled according to 'the special exemption law for punishing domestic violence.' Group therapy was applied once a week for 8 weeks. Results were collected by using a questionnaire for self-esteem, anger, stress coping and communication. In the data analysis, Wilcoxon signed test with SPSS/WIN 12.0 program was used.
Results The scores of self-esteem and communication showed statistically significant improvement from pre to post therapy. However, the scores of anger and stress coping were not significantly changed from pre to post therapy.
Conclusion This group therapy was effective in improving the self-esteem and communication in offenders of family violence.
- 606 View
- 4 Download

- The Relationship between Eating Disorders and Parent-Adolescent Communication in Middle School Students in Rural Areas
- Kye-Ha Kim, Kyoung-Mi Yang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):55-63. Published online February 28, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between eating disorders and parent-adolescent communication in middle school students.
Methods There were 267 adolescents taken as participants from two middle schools in rural areas. Data were collected from June to July 2005, using the Eating Disorder Inventory-2 questionnaire (23 items) and Parent-Adolescent Communication Inventory (10 items for open family communication, 10 items for problem in family communication). The SPSS Win version 12.0 was used for descriptive analysis, t-test, and partial correlation coefficient.
Results The mean score on the eating disorder was 2.74 (range: 1-6). Meanwhile, the mean scores on the parentadolescent communication was 3.37 (range: 1-5). There were significant differences in eating disorders according to gender, age, negative perception of the participant's body weight, family's perception of obesity, diet experiences, and BMI. Eating disorders showed a significant negative correlation with parent-adolescent communication.
Conclusion In this study, there was a significant negative correlation between eating disorders and parent-adolescent communication. In order to prevent an eating disorder, education and training to enhance communication skills should be provided to adolescents and their parents as well.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Korean Enneagram Program on the Ego-identity, Interpersonal Relationship, and Self-leadership of Nursing College Students
Weon-Gyeong Kim, Hyang-In Cho Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(4): 393. CrossRef - Impact of Sport-related Games on High School Students’ Communication Skills
Ozden Tepekoylu Ozturk, Selhan Ozbey, Hatice Camliyer
Physical Culture and Sport. Studies and Research.2015; 67(1): 53. CrossRef - A study on the effect of emotional intelligence on adjustment to college life in first year nursing college students
Hyun Tae Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(3): 1576. CrossRef - Testing the Biobehavioral Family Model in Understanding the Eating Problems of Adolescent Girls.
Ji Young Park, Su Yon Baek, Hee Soon Kim, Jung Ha Lim, Tae Hyung Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(3): 228. CrossRef - Interpersonal Relations, Hope, Professional Self-concept and Turnover Intention according to Adult Attachment Styles in Early Stage Nurses
Eun Jin Oh, Se Young Lee, Kyung Mi Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 491. CrossRef - A Study on the Correlation between Middle School Students' Eating Disorder Behavior and Scholastic Adjustment
Joo-Yeon Yoo, Yang-Ho Jin, Se-Jeong Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(6): 707. CrossRef - Eating Attitudes, Depression, Parent-child Interaction, and Family Function of Adolescent Girls
Suyon Baek, Jiyoung Park, Heesoon Kim, Taehyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(3): 176. CrossRef - Effects of Child-rearing Attitude and Parent-School Age Communication on Self-Efficacy of School-age Children
Yeon Ran Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 392. CrossRef
- Effects of Korean Enneagram Program on the Ego-identity, Interpersonal Relationship, and Self-leadership of Nursing College Students
- 1,108 View
- 6 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Conversational Analysis about Patient's Discomfort between a Patient with Cancer and a Nurse
- Hwa Jin Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(1):145-155. Published online February 28, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.1.145
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to describe and to analyze real communication about a patient's discomfort between a patient with cancer and a nurse.
Method A dialogue analysis method was utilized. Fifteen patients and 4 nurses who participated in this research gave permission to be videotaped. The data was collected from January, 3 to February 28, 2006.
Results The communication process consisted of 4 functional stages: ‘introduction stage’, ‘assessment stage’, ‘intervention stage’ and ‘final stage’. After trying to analyze pattern reconstruction in the ‘assessment stage’ and ‘intervention stage’, sequential patterns were identified. In the assessment stage, if the nurse lead the communication, the sequential pattern was ‘assessment question-answer’ and if the patient lead the communication, it was ‘complaint-response’. In the intervention stage, the sequential pattern was ‘nursing intervention-acceptance’.
Conclusion This research suggests conversation patterns between patients with cancer and nurses. Therefore, this study will provide insight for nurses in cancer units by better understanding communication behaviors
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determinants of nursing students’ inclination to ethical values: Compassionate love and perceived social support from the family
Neslihan Lok, Gülten Uzun, Alime Selçuk Tosun
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 67: 103556. CrossRef - Nursing Students' Knowledge, Attitudes to Advance Medical Directives and Ethics Values
Hyun-Ju Lee, Jae-Hyun Ha, Jungmi Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(4): 282. CrossRef - Impact of Biomedical Ethics Awareness and Ethical Values in Nursing Student on Their Attitudes towards DNR
Mi Yeon Kim, Mi Yeong Mun
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2018; 21(4): 115. CrossRef - Effects of a Blended Learning Program on Ethical Values in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Sang Dol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(5): 567. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nurses' Competency in Nurse-Patient Communication about Medications: Conversational Analysis Approach
Haeng-Mi Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Conversation between Elderly Patients with Dementia and Nurses: Focusing on Structure and Sequential Patterns
Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 166. CrossRef
- Determinants of nursing students’ inclination to ethical values: Compassionate love and perceived social support from the family
- 789 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Crossref

- A Conversation Analysis of Communication between Patients with Dementia and Their Professional Nurses
- Myungsun Yi, Bong Sook Yih
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(7):1253-1264. Published online December 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.7.1253
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand conversations and to identify typical conversational problems between nurses and patients with dementia.
Method A conversation analysis method was used. The data was collected in a geriatric institutional setting, using a videotape recorder, and transcribed. The transcribed data was analyzed in terms of expressions, contents, and relationships to identify communicative problems and their resolutions.
Results Among a total of 532 episodes, 440(82.7%) were identified as nurse-involved episodes. In addition, 66 of the 440 episodes were selected based on the significance of the conversation. The communicative problems between nurses and patients in terms of expressions were identified as “directive and authoritative expressions”, “emotional and competitive expressions”, “evasive and on-looking expressions”, and “excessive use of title only”, such as calling them granny or grandpa without proper names. In terms of content and relationships, “lack of themes in psychosocial areas” and “nurse-led relations” were identified respectively as communicative problems.
Conclusion The results of this study will provide substantial guidelines for nurses in caring for elderly patients with dementia by deeply understanding linguistic structures and problems of everyday conversations between nurses and patients with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of perceptions of dental hygienists and general public about communication skills of dental hygienists : Empirical test of co-orientation model
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An investigation into health professionals’ perception of the appropriateness of elderspeak in a Korean hospital setting
Miseon Lee, Jeong Youn Lee
Journal of Pragmatics.2021; 172: 181. CrossRef - Dementia screening for elderly in-patients and its association with nursing care satisfaction-an observational study
Li-Kai Huang, Jui-Chen Tsai, Hsun-Hua Lee, Yi-Chun Kuan, Yao-Tung Lee, Chia-Pei Lin, Shu-Ping Chao, Chaur-Jong Hu
Medicine.2020; 99(2): e18741. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Communication Behavior Scale for Nurses Caring for People with Dementia
Jihye Lee, Moonhee Gang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Communication of Dental Hygienist in Oral Hygiene Instruction during Scaling
Su-Kyung Kang, Hyun-Sook Bae, Soon-Ryun Lim
Journal of dental hygiene science.2014; 14(4): 546. CrossRef - Long-term Care Nurses' Communication Difficulties with People Living with Dementia in Taiwan
Jing-Jy Wang, Pei-Fang Hsieh, Chi-Jane Wang
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(3): 99. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nurses' Competency in Nurse-Patient Communication about Medications: Conversational Analysis Approach
Haeng-Mi Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Conversation between Elderly Patients with Dementia and Nurses: Focusing on Structure and Sequential Patterns
Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 166. CrossRef
- Comparison of perceptions of dental hygienists and general public about communication skills of dental hygienists : Empirical test of co-orientation model
- 944 View
- 8 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The Effect of Assertiveness Training on Communication Related Factors and Personnel Turnover Rate among Hospital Nurses
- Myung Ja Kang, Haejung Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(5):681-690. Published online August 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.5.681
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of assertiveness training on nurses' assertive behaviors, interpersonal relations, communication conflicts, conflict management style and personnel turnover rate.
Method A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used in this study. Nurses were assigned into the experimental or control groups, each consisting of 39 nurses. Data was collected between January to March 2004. An ‘Assertiveness Training Program’ for Nurses developed by Park was used for the study. To emphasize assertiveness practice, 5 practice sessions utilizing ABCDE principles were added to Park's program. To examine the effects of the program, differences between the two groups in assertive behaviors, interpersonal relations, communication conflicts, conflict management style and personnel turnover rate were analyzed using ANCOVA.
Results The assertiveness training was effective in improving the nurses' assertiveness behaviors, but was not effective in improving interpersonal relations, reducing the subjects' communication conflicts, changing the conflict management style or reducing their personnel turnover rate.
Conclusion There have been many studies about factors affecting nurses' personnel turnover rates, but few have been done about methods of intervention to reduce the personnel turnover rate. Thus, this study provides a significant contribution in attempting such an intervention from nursing management perspectives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of speak-up training programs for clinical nurses: A scoping review
Eunhee Lee, Jennie C. De Gagne, Paige S. Randall, Hyokyung Kim, Branti Tuttle
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2022; 136: 104375. CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef - Assess the Level of Assertiveness among BSc Nursing Final Year Students in a Selected Nursing College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
C Sumathi, J Van Vagula Devi, V Prathiba Sivakumar
Pondicherry Journal of Nursing.2020; 13(2): 33. CrossRef - The Effect of Assertiveness Program on Clinical Competence of Intensive Care Units Nurses; A Randomized Clinical Trial
Samira Abbasi, Reza Masoudi, Leili Rabiei, Koroush Shahbazi
Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care.2019; 27(5): 293. CrossRef - Effects of SBAR Program on Communication Clarity, Clinical Competence and Self-efficacy for Nurses in Cancer Hospitals
Youn Hwa Kim, Yooun Sook Choi, Hye Young Jun, Myung Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(1): 20. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Communication between Nurses during Preceptorship
Yeon Ok Jeoung, Song Chol Park, Jeong Kun Jin, Joo Young Kim, Ji Uhn Lee, Soon Young Park, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 82. CrossRef - Moral Distress, Moral Sensitivity and Ethical Climate of Nurses Working in Psychiatric Wards
Dabok Noh, Sunah Kim, Sanghee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(4): 307. CrossRef - Turnover intention of graduate nurses in South Korea
Haejung LEE, Yeonjung LIM, Hee Young JUNG, Youn‐Wha SHIN
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2012; 9(1): 63. CrossRef - Work Stress, Turnover Intention and Burnout among Nurses in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(1): 115. CrossRef - Comparison of Anger Expression, Assertive Behavior, and Self-esteem between a Nursing Student Group and an Educational Student Group
Ki-Wol Sung, Oh-Gye Kwag, Won-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on the Experience of Hurt and Forgiveness of Clinical Nurses in Korea after Loss of Employment
Kae-Hwa Jo, Ki-Wol Sung, Yeong-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(4): 561. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of speak-up training programs for clinical nurses: A scoping review
- 1,275 View
- 9 Download
- 11 Crossref

- A Marital-Relationship Enhancement Program for Couples: Randomized Controlled Trial
- Seong Sook Kong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(6):991-1003. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.6.991
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This paper reports a randomized controlled trial to investigate the effects of a Marital-relationship enhancement program(MREP) for marital couples.
Methods Volunteer couples from several well-being centers in Seoul were randomly assigned either to a treatment group (n=36), participating in a MREP based on Gottman's “sound marital house” theory, or to a control group (n=35) receiving no treatment. The content of the MREP was provided to the control group after the research was completed. Data was collected from December 2003 to May 2004 using modified versions of the inventories developed by Gottman on marital satisfaction, positive affect, conflict regulation, and communication barriers.
Results Participants in the experimental group showed significant improvements in marital satisfaction, positive affects, conflict regulation, and communication-barrier scores compared to the control group.
Conclusion The present program for marital-relationship enhancement is helpful in enhancing marital relationships and regulating conflict between marital couples and, ultimately, may be useful to prevent divorce.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improved couple satisfaction and communication with marriage and relationship programs: are there gender differences?—a systematic review and meta-analysis
Zeinab Javadivala, Hamid Allahverdipour, Mohammad Asghari Jafarabadi, Somaye Azimi, Neda Gilani, Vijay Kumar Chattu
Systematic Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting Quality of Life in Patients with Radical Prostatectomy
Hyo Jung Park, Yoonju Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(2): 190. CrossRef - Effects of a Marital Relationship Enrichment Program on Communication, Conflict Resolution, and Marital Satisfaction in Multicultural Couples
Young-Ran Yeun, Soo Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(3): 250. CrossRef
- Improved couple satisfaction and communication with marriage and relationship programs: are there gender differences?—a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 972 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Headache in Children
- Yeon Ran Hong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(6):1183-1189. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.6.1183
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This descriptive study was conducted to examine the degree of stress, coping styles, communication with the mother and depression between headache-suffering children and headache-free children and to explore predicted factors for headache occurrence in children.
Method The subjects of this study consisted of 196 headache-free children and 107 headache-suffering children. They were 4th-6th graders of an elementary school in T city. The instruments in this study were David's stressor of children, Lazarus & Folkman's Stress Coping Style, PACI (Parent-Adolescent Communication Inventory) by Barnes & Olsen and Kovac's CDI (Children's depression inventory). Data were collected from May 2 to July 16, 2004.
Results Total stress(t=-3.76, p=.035), school stress(t=-3.02, p=.001), mass media stress(t=-1.39, p=.029) and depression(t=7.62, p=.001) in headache-suffering children were significantly higher than those of headache-free children. Problem-oriented coping skills (t=1.23, p=.023), and the score of communication with the mother (t=2.32, p=.012) in headache-suffering children were lower than those of headache-free children. Logistic regression analysis (stepwise) showed that the most powerful predictor was stressors in school, followed by depression, stressors in mass media and communication with the mother.
Conclusions This study revealed that important factors such as the degree of school stress, depression, the degree of mass media stress, communication with the mother and problem-oriented coping skills should be controlled for reducing of headaches in children.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Affecting Social Adjustment of Childhood Cancer Survivors.
Su Mi Oh, Hye Jung Lee, Gwang Suk Kim, Kyung Duk Park
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(3): 238. CrossRef
- Factors Affecting Social Adjustment of Childhood Cancer Survivors.
- 709 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


