Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Successful aging among the elderly with mild cognitive impairment facing the crisis of old age: a grounded theory study
- Haeyun Shin, Suhye Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):301-316. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Methods
The participants were 15 older adults with mild cognitive impairment who had experienced successful aging. Data were collected from January to October 2021 through individual deep, unstructured interviews. Data analysis was performed using Charmaz’s grounded theory method. In addition, the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research checklist was used to ensure the quality of the study.
Results
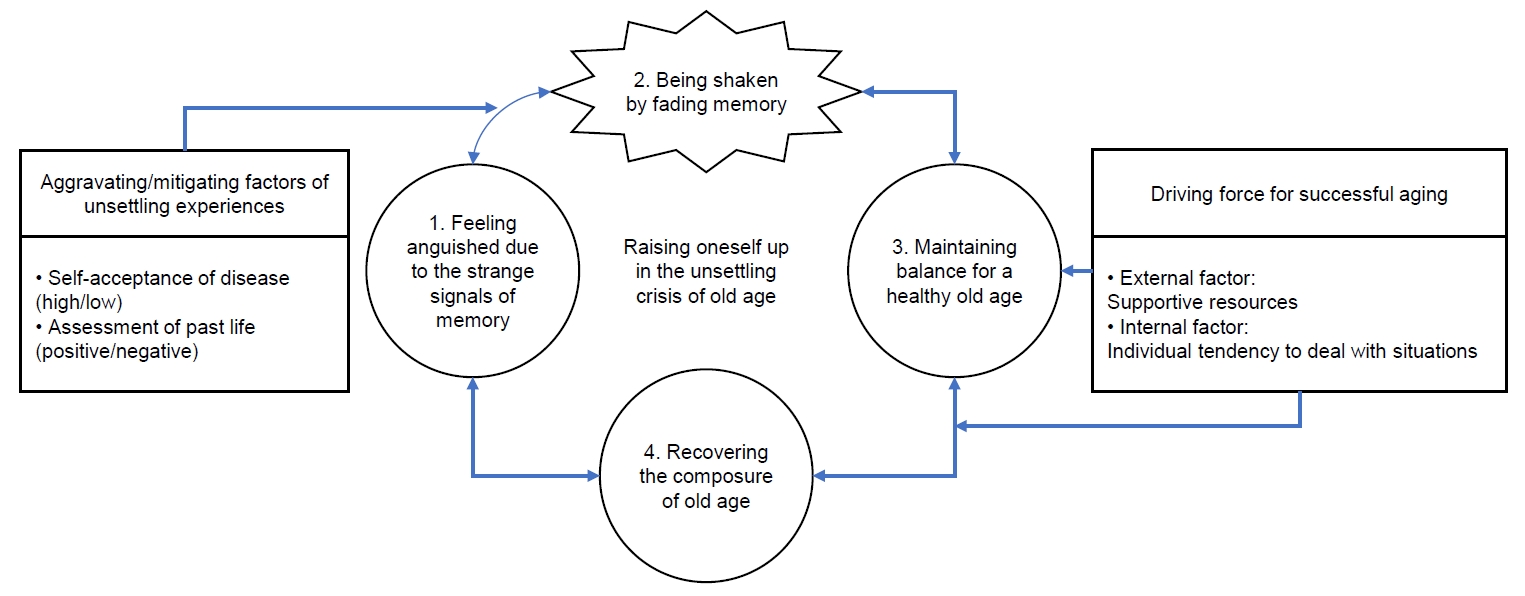
The key category representing experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment was “raising oneself up in the unsettling crisis of old age.” Four stages were derived: “feeling anguished due to the strange signals of memory,” “being shaken by fading memory,” “maintaining balance for a healthy old age,” and “recovering the composure of old age.”
Conclusion
Participants tried to successfully achieve aging while implementing their own plans and strategies in the midst of the challenges of old age, when the mind and body were unsettled by mild cognitive impairment. The results of this study provide a deep understanding of experiences of successful aging in older adults with mild cognitive impairment, potentially contributing to the development and implement of nursing intervention programs to promote the successful pursuit of aging in this population.
- 2,257 View
- 113 Download

- Nomogram for predicting changes in cognitive function in community dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment based on Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data: a retrospective study
- Hyuk Joon Kim, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):50-63. Published online February 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify factors associated with normal cognitive reversion and progression to dementia in older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) residing in the community and to develop a nomogram.
Methods
This longitudinal study used secondary data from the Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data (2006–2018). The study included 1,262 participants aged 60 or older, with initial Mini-Mental State Examination scores ranging from 18 to 23. Data were analyzed using the Rao-Scott chi-square test, panel binary logistic regression, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve in Stata ver. 17.0 (Stata Corp.).
Results
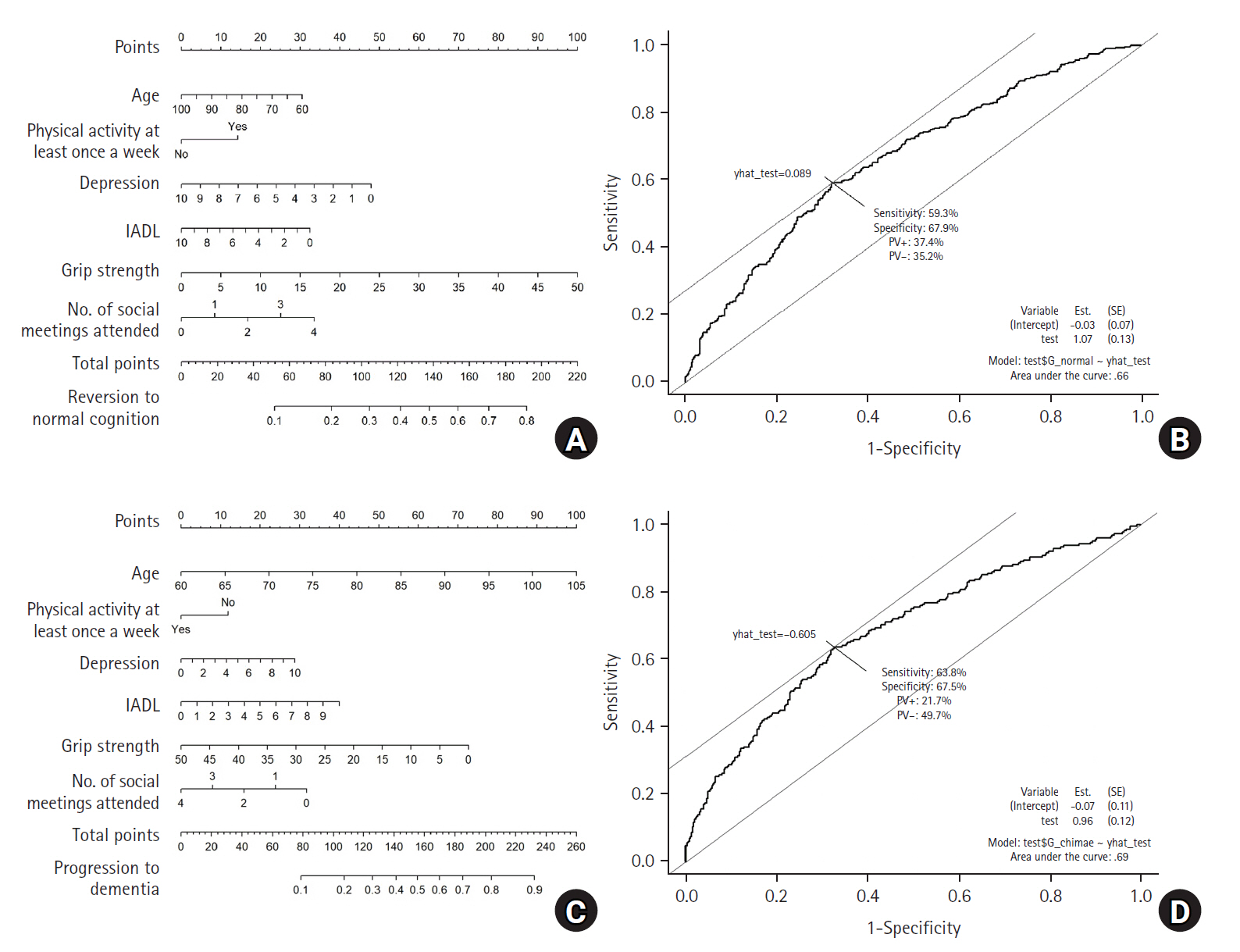
The rate of reversion from MCI to normal cognition was 37.0% after 2 years and 32.9% after 12 years. The rate of progression to dementia was 18.0% after 2 years and 30.2% after 12 years. In the nomogram for reversion to normal cognition, the most significant influences were grip strength, depression, number of meetings, age, and regular exercise, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of .66. In contrast, in the nomogram for progression to dementia, the most significant influences were age, grip strength, instrumental activities of daily living, number of social meetings attended, depression, and regular exercise, with an AUC of .69.
Conclusion
These nomograms can serve as an effective intervention tool for preventing dementia in the field of community health care since they can serve as a visual technique for presenting information on risk to individuals with MCI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Functions and Cognitive Functions Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Primary Care
Nan Hu, Wupeng Yin, Rabeya Illyas Noon, Noof Alabdullatif
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(6): 908. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Nomogram Predicting Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Sook Kyoung Park, Hyuk Joo Kim, Young-Me Lee, Hye Young Kim
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Emotional Labor on Burnout in Nurses: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Social Intelligence and Emotional Intelligence
Kyung Ran Lee, Jeoung Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(1): 22. CrossRef
- The Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Functions and Cognitive Functions Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Primary Care
- 3,513 View
- 212 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- An Investigation of the Cumulative Effects of Depressive Symptoms on the Cognitive Function in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging
- Eunmi Kim, Jinkyung Oh, Iksoo Huh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):453-467. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the cumulative effects of depressive symptoms on cognitive function over time in community-dwelling older adults. Methods: Data were investigated from 2,533 community-dwelling older adults who participated in the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA) from the 5th (2014) to the 8th wave (2020). The association between cumulative depressive symptoms and cognitive function was identified through multiple regression analysis. Results: When the multiple regression analysis was conducted from each wave, the current depressive symptoms scores and cognitive function scores were negatively associated, regardless of the waves (B5th = - 0.26, B6th = - 0.26, B7th = - 0.26, and B8th = - 0.27; all p < .001). Further, when all the previous depressive symptoms scores were added as explanatory variables in the 8th wave, the current one (B8th = - 0.09, p < .001) and the previous ones (B5th = - 0.11, B6th = - 0.09, and B7th = - 0.13; all p < .001) were also negatively associated with the cognitive function score. The delta R2 , which indicates the difference between the model’s R2 with and without the depressive symptoms scores, was greater in the model with all the previous and current depressive symptoms scores (6.4%) than in the model with only the current depressive symptoms score (3.6%). Conclusion: Depressive symptoms in older adults have a long-term impact. This results in an accumulated adverse effect on the cognitive function. Therefore, to prevent cognitive decline in older adults, we suggest detecting their depressive symptoms early and providing continuous intervention to reduce exposure to long-term depressive symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic identification and quantification of factors and their interactions with age, sex, and panel wave influencing cognitive function in Korean older adults
Eunmi Kim, Jinkyung Oh, Jungsoo Gim, Iksoo Huh
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Systematic identification and quantification of factors and their interactions with age, sex, and panel wave influencing cognitive function in Korean older adults
- 2,263 View
- 56 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Virtual Reality Program for Alleviating Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia Patients
- Seon-Min Park, Seung-Yi Choi, Jung-Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):121-133. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the impact of a virtual reality intervention program based on psychological needs on behavioral and psychological symptoms, apathy, and quality of life (QOL) in patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment living in nursing facilities.
Methods
This study is nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design of quasi-experimental study. The study collected data from November 18, 2020 to July 24, 2021 from patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment (30 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group) at three nursing facilities in G city using self-reporting and caregiver-informant reporting methods. The analysis employed the chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, paired t-test, independent t-test, Wilcoxon signed rank test, Mann–Whitney U, repeated measures ANOVA, GEE, using SPSS/WIN 27.0.
Results
The severity of behavioral and psychological symptoms (Wald χ2 = 2.68, p = .102) and the care burden of caregivers (Wald χ2 = 1.72, p = .190) were not significant and was no significant time and group interaction effect (Wald χ2 = 0.63, p = .426, Wald χ2 = 0.52, p =. 471). The difference in apathy and QOL score were statistically significant for the group-time interaction (F = 43.65, p < .001; F = 4.35, p= .041).
Conclusion
The virtual reality intervention program of this study shows a positive effect on the apathy reduction and QOL of patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment residing in nursing facilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for elderly dementia patients based on virtual reality technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jun Wen, Hong Yan, Siyu Wang, Jialan Xu, Zitong Zhou
Ageing Research Reviews.2024; 93: 102135. CrossRef - Development of the “living well” concept for older people with dementia
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for elderly dementia patients based on virtual reality technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 2,136 View
- 105 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Influences of Autonomic Function, Salivary Cortisol and Physical Activity on Cognitive Functions in Institutionalized Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: Based on Neurovisceral Integration Model
- Minhee Suh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):294-304. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate objectively measured physical activity (PA) in institutionalized older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and to elucidate the influence of autonomic nervous function, salivary cortisol, and PA on cognitive functions based on neurovisceral integration model.
Methods
Overall cognitive function was evaluated using the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) and executive function was evaluated using semantic verbal fluency test and clock drawing test. Actigraph for PA, HRV and sAA for autonomous function, and the geriatric depression scale for depression were used. Saliva specimens were collected in the morning for sAA and cortisol.
Results
Ninety-eight older adults from four regional geriatric hospitals participated in the study. They took 4,499 steps per day on average. They spent 753.93 minutes and 23.12 minutes on average in sedentary and moderate-to-vigorous activity, respectively. In the multiple regression analysis, lower salivary cortisol level (β = - .33, p = .041) and greater step counts (β = .37, p = .029) significantly improved MMSE score. Greater step count (β = .27, p = .016) also exerted a significant influence on verbal fluency, and greater sAA (β = .35, p = .026) was significantly associated with a better clock drawing test result.
Conclusion
Salivary cortisol, sAA and physical activity were significantly associated with cognitive functions. To prevent older adults from developing dementia, strategies are needed to increase their overall PA amount by decreasing sedentary time and to decrease salivary cortisol for cognitive function, and to maintain their sympathetic nervous activity for executive function. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between physical activity levels, sedentary time, and mild cognitive impairment in older adults
Wei Chen, Lei Zhang, Palida Abulizi, Ting Zou, Xuan Xiang, Ruikai Wu, Xiaohui Zhou
Frontiers in Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Rest-activity circadian rhythm in hospitalized older adults with mild cognitive impairment in Korea and its relationship with salivary alpha amylase: an exploratory study
Minhee Suh, Jihye Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(4): 306. CrossRef - Circadian Rhythm Changes in Healthy Aging and Mild Cognitive Impairment
Ahmadreza Keihani, Ahmad Mayeli, Fabio Ferrarelli
Advanced Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in stress pathways as a possible mechanism of aerobic exercise training on brain health: a scoping review of existing studies
Cristina Molina-Hidalgo, Chelsea M. Stillman, Audrey M. Collins, Daniel Velazquez-Diaz, Hayley S. Ripperger, Jermon A. Drake, Peter J. Gianaros, Anna L. Marsland, Kirk I. Erickson
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between physical activity levels, sedentary time, and mild cognitive impairment in older adults
- 1,719 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Prediction Models of Mild Cognitive Impairment Using the Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing
- Hyojin Park, Juyoung Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):191-199. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to compare sociodemographic characteristics of a normal cognitive group and mild cognitive impairment group, and establish prediction models of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI).
Methods
This study was a secondary data analysis research using data from “the 4th Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing” of the Korea Employment Information Service. A total of 6,405 individuals, including 1,329 individuals with MCI and 5,076 individuals with normal cognitive abilities, were part of the study. Based on the panel survey items, the research used 28 variables. The methods of analysis included a c2-test, logistic regression analysis, decision tree analysis, predicted error rate, and an ROC curve calculated using SPSS 23.0 and SAS 13.2.
Results
In the MCI group, the mean age was 71.4 and 65.8% of the participants was women. There were statistically significant differences in gender, age, and education in both groups. Predictors of MCI determined by using a logistic regression analysis were gender, age, education, instrumental activity of daily living (IADL), perceived health status, participation group, cultural activities, and life satisfaction. Decision tree analysis of predictors of MCI identified education, age, life satisfaction, and IADL as predictors.
Conclusion
The accuracy of logistic regression model for MCI is slightly higher than that of decision tree model. The implementation of the prediction model for MCI established in this study may be utilized to identify middle-aged and elderly people with risks of MCI. Therefore, this study may contribute to the prevention and reduction of dementia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nomogram for predicting changes in cognitive function in community dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment based on Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data: a retrospective study
Hyuk Joon Kim, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 50. CrossRef - Development of a neural network-based risk prediction model for mild cognitive impairment in older adults with functional disability
Deyan Liu, Yuge Tian, Min Liu, Shangjian Yang
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding Cognitive Trajectories in Middle-Aged and Older Cancer Survivors: An Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging
Mi Sook Jung, Munkyung Park, Kyeongin Cha, Xirong Cui, Nondumiso Satiso Dlamini, Ah Rim Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 507. CrossRef - Cognitive Dysfunction Prediction Model with Lifelog Dataset based on Random Forest and SHAP
Myeongjin Lee, Jongun Lee, Hanjun Lee
The Journal of Korean Institute of Information Technology.2024; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Sociodemographic Factors Predict Incident Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Brief Review and Empirical Study
Shuyi Jin, Chenxi Li, Jiani Miao, Jingyi Sun, Zhenqing Yang, Xingqi Cao, Kaili Sun, Xiaoting Liu, Lina Ma, Xin Xu, Zuyun Liu
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2023; 24(12): 1959. CrossRef - Characteristics and Factors Associated with Cognitive Decline of Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Eul Hee Roh
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(3): 179. CrossRef - Detection and Intervention of Subjective Cognitive Decline in Pre-Alzheimer’s Disease
雅红 何
International Journal of Psychiatry and Neurology.2022; 11(04): 65. CrossRef - Influencing Factors of Subjective Cognitive Impairment in Middle-Aged and Older Adults
Min Roh, Hyunju Dan, Oksoo Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11488. CrossRef
- Nomogram for predicting changes in cognitive function in community dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment based on Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data: a retrospective study
- 2,861 View
- 40 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients
- Jung Ran Lee, Pok Ja Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):375-385. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.375
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and test a structural model for chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment of breast cancer patients based on a literature review and Hess and Insel's chemotherapy-related cognitive change model.
Methods The Participants consisted of 250 patients who were ≥19 years of age. The assessment tools included the Menopause Rating Scale, Symptom Experience Scale, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Everyday Cognition, and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast Cancer. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs.
Results The modified model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were χ 2=423.18 (
p <.001), χ 2/df=3.38, CFI=.91, NFI=.91, TLI=.89, SRMR=.05, RMSEA=.09, and AIC=515.18. Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment was directly influenced by menopausal symptoms (β=.38,p =.002), depression and anxiety (β=.25,p =.002), and symptom experiences (β=.19,p =.012). These predictors explained 47.7% of the variance in chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety mediated the relations among menopausal symptoms, symptom experiences, and with chemotherapy related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety (β=-.51,p =.001), symptom experiences (β=-.27,p =.001), menopausal symptoms (β=-.22,p =.008), and chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (β=-.15,p =.024) had direct effects on the quality of life and these variables explained 91.3%.Conclusion These results suggest that chemotherapy-related toxicity is highly associated with cognitive decline and quality of life in women with breast cancer. Depression and anxiety increased vulnerability to cognitive impairment after chemotherapy. Nursing intervention is needed to relieve chemotherapy-related toxicity and psychological factor as well as cognitive decline for quality of life in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of social support on cognitive function in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: The chain-mediating role of fatigue and depression
Yuanqi Ding, Qingmei Huang, Fulei Wu, Yang Yang, Ling Wang, Xuqian Zong, Xiaoyan Yu, Changrong Yuan
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100743. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 418. CrossRef - Relationships Between Chemotherapy-Related Cognitive Impairment, Self-Care Ability, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nan Wu, Ze Luan, Zijun Zhou, He Wang, Shiyuan Du, Yulu Chen, Xinxin Wang, Jiong Li, Xin Peng
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2024; 40(5): 151690. CrossRef - Effects of different exercise interventions on chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer: a study protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
Yu Dong, Hao Huang, Aiping Wang
BMJ Open.2024; 14(4): e078934. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Impact of discriminant factors on the comfort-care of nurses caring for trans-arterial chemoembolisation patients
Myoung Soo Kim, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(9): 7773. CrossRef - Brain morphological alterations and their correlation to tumor differentiation and duration in patients with lung cancer after platinum chemotherapy
Pin Lv, Guolin Ma, Wenqian Chen, Renyuan Liu, Xiaoyan Xin, Jiaming Lu, Shu Su, Ming Li, ShangWen Yang, Yiming Ma, Ping Rong, Ningyu Dong, Qian Chen, Xin Zhang, Xiaowei Han, Bing Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Clinical Study
Teresa Paolucci, Aristide Saggino, Francesco Agostini, Marco Paoloni, Andrea Bernetti, Massimiliano Mangone, Valter Santilli, Raoul Saggini, Marco Tommasi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8585. CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,795 View
- 23 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


