Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Research trends in generative artificial intelligence in nursing: a scoping review
- Myung Jin Choi, Myoung Hee Seo, Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):468-487. Published online August 5, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has yet to be comprehensively analyzed in the nursing literature. This study aimed to identify research trends in generative AI within the nursing field through a scoping review and propose strategies for its effective utilization in nursing.
Methods
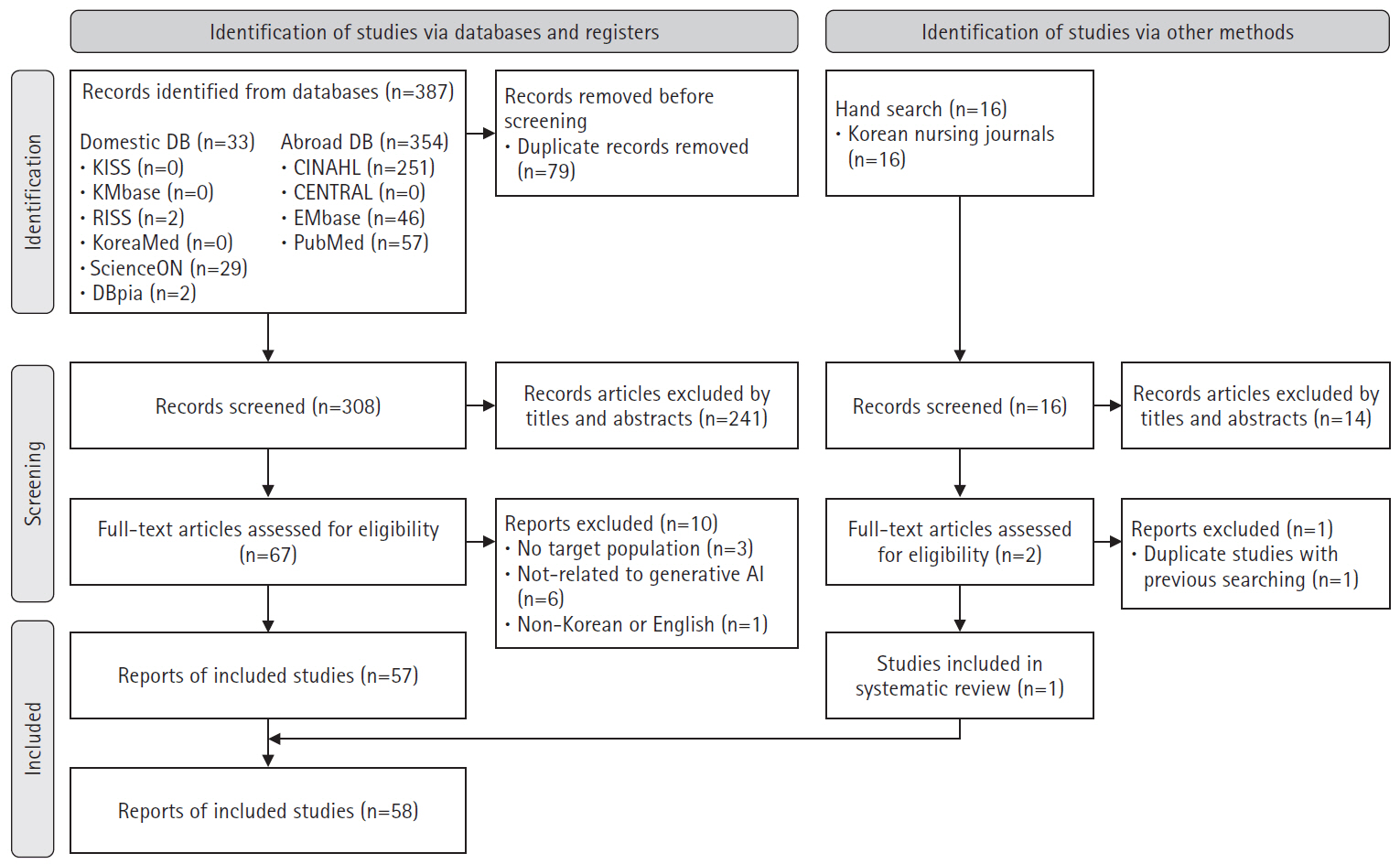
A scoping review was conducted following Arksey and O’Malley’s six-stage framework. The inclusion criteria included: (1) studies conducted in nursing; (2) research related to generative AI; and (3) original research articles, theses, communications, editorials, letters, or commentaries published in academic journals. Database used PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL, CINAHL, KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, DBpia, and 27 nursing-specific journals.
Results
In total, 403 studies were initially identified, and 58 were included in the final analysis. In the care domain, strengths included rapid information retrieval and improved nurse-patient communication, while limitations included the irreplaceable human element and low reliability. The administration domain had no relevant studies. In the research domain, generative AI exhibited strengths such as enhanced efficiency in the paper writing process and improved dissemination speed, but its weaknesses included lack of ethical and legal accountability and a risk of inaccurate or biased information. In the education domain, generative AI was effective in saving time in educational design and implementation, as well as supporting content creation, but challenges included algorithmic bias and risks of plagiarism.
Conclusion
This study identified potential benefits and limitations of generative AI across nursing domains. For effective application, it is essential to develop comprehensive guidelines and policies, provide user education and support, and create opportunities for nurses, educators, and students to learn about strengths and risks of generative AI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Sukyung Son, Eunyoung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(Special Is): 9. CrossRef
- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
- 6,989 View
- 516 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and evaluation of a question-answering chatbot to provide information for patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention
- Geunhee Lee, Yun Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):153-164. Published online May 13, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a question-answering chatbot that provides accurate and consistent answers to questions that may arise during the recovery process of patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention, and to evaluate the chatbot.
Methods
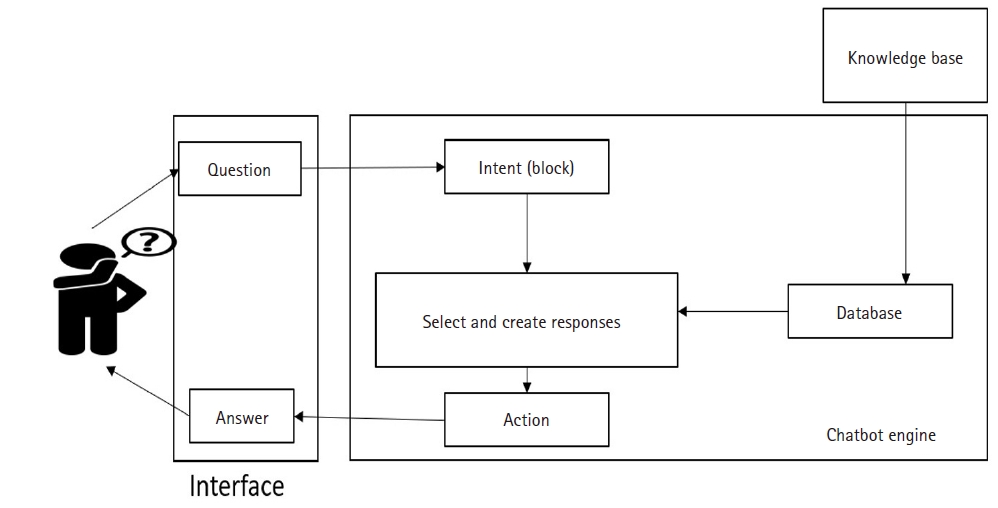
The chatbot was developed through the stages of analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation. It was evaluated by five experts, and the user experience was evaluated by 27 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Furthermore, chatbot utilization was analyzed based on user experience logs.
Results
The chatbot was constructed as a question-answering database that included three categories: coronary artery disease, percutaneous coronary intervention, and post-intervention management. The question-answering chatbot, referred to as the “Cardiovascular Strong” channel, has been launched and implemented. An expert evaluation of the chatbot revealed no usability issues or necessary modifications. The overall result of the user experience evaluation was 4.26 points. Based on the user experience log, the question-answer accuracy was 84.6%, and medications during post-intervention management were the most frequently searched topic, accounting for 110 cases (20.8%) out of a total of 528.
Conclusion
The chatbot that was developed to provide information via real-time answers to questions after the intervention can be easily accessed in clinical settings with no time or space constraints. It also will contribute to providing accurate disease-related information via the familiar KakaoTalk platform. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
Adrianna L. Watson, Carmel Bond, Helen Aveyard, Graeme D. Smith, Debra Jackson
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
- 2,394 View
- 250 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Keyword Network Analysis and Topic Modeling of News Articles Related to Artificial Intelligence and Nursing
- Ju-Young Ha, Hyo-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):55-68. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the main keywords, network properties, and main topics of news articles related to artificial intelligence technology in the field of nursing.
Methods
After collecting artificial intelligence-and nursing-related news articles published between January 1, 1991, and July 24, 2022, keywords were extracted via preprocessing. A total of 3,267 articles were searched, and 2,996 were used for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were performed using NetMiner 4.4.
Results
As a result of analyzing the frequency of appearance, the keywords used most frequently were education, medical robot, telecom, dementia, and the older adults living alone. Keyword network analysis revealed the following results: a density of 0.002, an average degree of 8.79, and an average distance of 2.43; the central keywords identified were ’education,’ ‘medical robot,’ and ‘fourth industry.’ Five topics were derived from news articles related to artificial intelligence and nursing: ‘Artificial intelligence nursing research and development in the health and medical field,’ ‘Education using artificial intelligence for children and youth care,’ ‘Nursing robot for older adults care,’ ‘Community care policy and artificial intelligence,’ and ‘Smart care technology in an aging society.’ Conclusion: The use of artificial intelligence may be helpful among the local community, older adult, children, and adolescents. In particular, health management using artificial intelligence is indispensable now that we are facing a super-aging society. In the future, studies on nursing intervention and development of nursing programs using artificial intelligence should be conducted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mapping the Landscape of AI-Driven Human Resource Management: A Social Network Analysis of Research Collaboration
Mehrdad Maghsoudi, Motahareh Kamrani Shahri, Mehrdad Agha Mohammad Ali Kermani, Rahim Khanizad
IEEE Access.2025; 13: 3090. CrossRef - Characteristics of Online Articles Related to Youth Drug Use: An Analysis Using Keyword Network Analysis
Ji-Min Kim
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(11): 3087. CrossRef - The Impact of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Learning on Nursing Students' Ethical Decision-making and Clinical Reasoning in Pediatric Care
Hyewon Shin, Jennie C. De Gagne, Sang Suk Kim, Minjoo Hong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(10): 704. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef
- Mapping the Landscape of AI-Driven Human Resource Management: A Social Network Analysis of Research Collaboration
- 6,818 View
- 175 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Development of a Nursing Diagnosis System Using a Neural Network Model
- Eun Ok Lee, Mi Soon Song, Myung Ki Kim, Hyeoun Ae Park
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(2):281-289. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.2.281
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Neural networks have recently attracted considerable attention in the field of classification and other areas. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate an experiment using back-propagation neural network model applied to nursing diagnosis. The network's structure has three layers; one input layer for representing signs and symptoms and one output layer for nursing diagnosis as well as one hidden layer. The first prototype of a nursing diagnosis systern for patients with stomach cancer was developed with 254 nodes for the input layer and 20 nodes for the output layer of 20 nursing diagnoses, by utilizing learning data set collected from 118 patients with stomach cancer. It showed a hitting ratio of .93 when the model was developed with 20,000 times of learning, 6 nodes of hidden layer, 0.5 of momentum and 0.5 of learning coefficient. The system was primarily designed to be an aid in the clinical reasoning process. It was intended to simplify the use of nursing diagnoses for clinical practitioners. In order to validate the developed model, a set of test data from 20 patients with stomach cancer was applied to the diagnosis system. The data for 17 patients were concurrent with the result produced from the nursing diagnosis system which shows the hitting ratio of 85%. Future research is needed to develop a system with more nursing diagnoses and an evaluation process, and to expand the system to be applicable to other groups of patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in women’s health nursing
Geum Hee Jeong
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 5. CrossRef - A Study on Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions, Outcomes Frequently Used and Linkage to NANDA-NOC-NIC in Major Nursing Departments
Jong Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(2): 121. CrossRef
- Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in women’s health nursing
- 938 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


