Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy Scale for Nurses
- Youngrye Park, Sunah Park, Hee Ran Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):633-644. Published online November 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24094
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the occupational coping self-efficacy for nurses (K-OCSE-N) scale.
Methods The English version of the OCSE-N scale was translated into Korean using a translation and back-translation process. Data were gathered from 213 nurses employed in a general hospital in South Korea. The content validity was assessed using the content validity index. The construct validity was verified through exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Criterion validity was assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients with the job stress coping and general self-efficacy scales. Reliability was examined using item-total score correlation and Cronbach’s α coefficient for internal consistency.
Results The exploratory factor analysis identified two factors that explained 61.8% of the cumulative variance: occupational burden and relational difficulty. In confirmatory factor analysis, the model exhibited adequate fit (
χ 2/df = 2.07, GFI = .95, SRMR = .04, RMSEA = .07, CFI = .97, and TLI = .95), with both convergent and discriminant validity deemed acceptable. The criterion validity presented a positive correlation of the K-OCSE-N with both job stress coping (r = .72,p < .001) and general self-efficacy (r = .72,p < .001). The internal consistency of the scale using Cronbach’s α for the total items was .89.Conclusion The K-OCSE-N scale is a valid and reliable tool for measuring nurses’ occupational coping self-efficacy. This study suggests that various intervention studies can use the scale to assess and strengthen nurses’ occupational coping self-efficacy in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
Hyun Suk Gwag, Jin Ah Kim
Healthcare.2026; 14(2): 270. CrossRef
- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
- 7,175 View
- 407 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Experiences of Patients and Their Families Receiving Medical Services Provided by Advanced Practice Nurses at Tertiary General Hospitals
- Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Su Jung Choi, Ji Eun Han, Eun Kyung Kwon, Jeong Hee Park, Jeong Hye Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):594-606. Published online November 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to understand and describe the experiences of patients and their families who have received medical services from advanced practice nurses in tertiary general hospitals in Korea.
Methods Data were collected through four focus group interviews with 20 patients and their families who had received medical services from advanced practice nurses for more than six months at four tertiary hospitals from November 29 to December 28, 2023. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using qualitative content analysis.
Results The four themes extracted from the experiences of patients and their families were as follows: unfamiliar medical personnel encountered during the treatment process, healthcare professionals who exhibited excellence, companions to light my way through the tunnel of illness, and an advanced practice nurse system that must be activated urgently.
Conclusion The study’s findings indicate that patients and their families view the care provided by advanced practice nurses as excellent, reliable, and holistic. Research suggests that advanced practice nurses are valuable healthcare professionals in team-based care. The findings suggest that hospitals should utilize an advanced practice nurse system to improve patient outcomes and ensure the quality of care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
Su Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 69. CrossRef - Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 568. CrossRef - Nurses' Patient Care Experiences in a Changing Healthcare Environment Following One Year of Healthcare Policy Conflict - A Focus Group Interview
Eun Hee Kang, Yunhyung Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 280. CrossRef
- Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
- 4,481 View
- 266 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Clinical Nurses’ Perception of Structural and Content Career Plateau
- Ji Hye Kim, Ji Yun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):534-546. Published online October 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24002
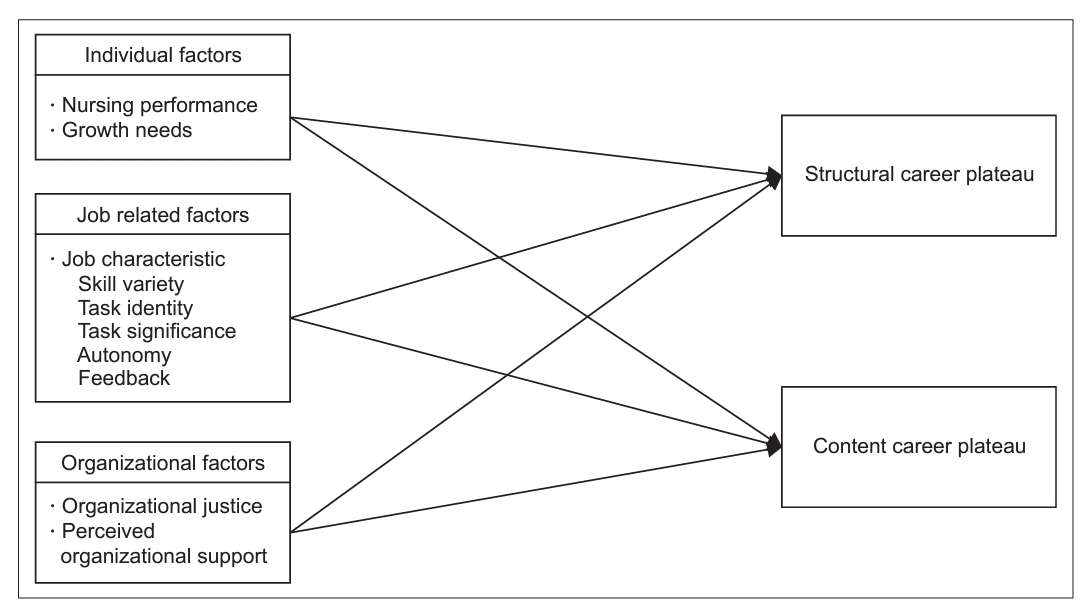
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study was intended to provide basic data for reducing the career plateaus of clinical nurses.
Methods The participants were 288 clinical nurses who worked at five hospitals, general hospitals, and tertiary hospitals in Seoul, Gyeonggi, and Chungcheong provinces and had more than one year of clinical experience. The research data were collected from December 26, 2022, to April 7, 2023, using structured questionnaires and analyzed using SPSS software. The study conducted mean, standard deviation, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson‘s correlation coefficient, and hierarchical regression analysis.
Results Perceived organizational support was identified as the factor influencing structural career plateaus. Factors influencing content career plateaus included growth needs, skill variety, organizational justice, and perceived organizational support.
Conclusion The above research results suggest that to increase the motivation of clinical nurses and reduce career plateaus, it is necessary to improve awareness and systems of human resource management at the organizational level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing managers’ perceptions of clinical nurses’ self-management in professional title promotion: a qualitative user persona study
Xiang Gao, Xuemei Wang
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Nursing managers’ perceptions of clinical nurses’ self-management in professional title promotion: a qualitative user persona study
- 2,425 View
- 171 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Predictive Model on Patient-Centered Care of Hospital Nurses in Korea
- Hyun Jeong, Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):191-202. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Patient-centered care is a widely utilized concept in nursing and health care. However, the key components of patient-centered nursing have not yet been reported. Moreover, previous studies on patient-centered care have mostly focused on components of nursing rather than organizational factors. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of influential factors of patient-centered care is required.
Methods The purpose of this study was to develop a theoretical model based on person-centered care theory, and the relevant literature and to test the developed model with covariance structure analysis in order to determine the causal paths among the variables.
Results The model fit indices for the hypothetical model were suitable for the recommended level (goodness of fit index=.87, standardized root mean residual=.01, root mean square error of approximation=.06, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.92, parsimonious normed fit index=.75). In this study, five of the six paths established in the initial hypothetical model were supported. The variables of teamwork, self-leadership, and empathy accounted for 56.4% of hospital nurses' patient-centered care. Among these, empathy was the strongest predictor of patient-centered care.
Conclusion These results suggest that it is necessary to use strategies to improve self-leadership and empathy. In addition to enhancing the personal factors of nurses, nursing organizations should strive for effective multidisciplinary cooperation with active support for patient-centered care and openness to change.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Clinical Nursing Competency and Nursing Working Environment of Psychiatric Nurses on Person-Centered Care
Pan Heui Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(3): 229. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care Among Psychiatric Nurses in Hospitals
Ji Su Lee, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2024; 12(22): 2269. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Changes in Patient-Centered Care in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Seongkum Heo, Brandy Haley, Patricia Wright, Claudia P. Barone, Michael Anders, Tara Bertulfo, Patricia Troyan
Nursing Education Perspectives.2023; 44(2): 82. CrossRef - Factors associated with the person-centered care competence of nursing students
Ju Young Park, Chung Hee Woo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(1): 48. CrossRef - Listening to patients' voices: Applying the design‐thinking method for teaching person‐centered care to nursing students
Myonghwa Park, Thi‐Thanh‐Tinh Giap, Insook Jang, Miri Jeong, Jahyeon Kim
Nursing Forum.2022; 57(1): 9. CrossRef - Factors influencing mental health nurses in providing person-centered care
Suyoun Ahn, Yeojin Yi
Nursing Ethics.2022; 29(6): 1491. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale*
Seong Eun KIM, Jeong Suk KIM
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2022; 25(2): 137. CrossRef - A Meta-Synthesis Study of Person-Centered Care Experience from the Perspective of Nursing Home Residents
Eun-Young Kim, Sung-Ok Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(14): 8576. CrossRef - Effects of health literacy competencies on patient-centered care among nurses
Yaki Yang
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Person-Centered Care Experience of Nursing Home Workers: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 33. CrossRef - Nurse Spiritual Care Therapeutics Scale
Kyung-Ah Kang, Elizabeth Johnston Taylor, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2022; 24(6): E250. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Hospice Nurses
Sinyoung Kwon, Kyoung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(2): 66. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Person-Centered Fall Prevention Program for Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals: For Older Adults with Dementia and Caregivers in Long-Term Care Hospitals
Jeong Ok Lim, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 341. CrossRef - Role of self‐efficacy in nursing organizational climate: A way to develop nurses' humanistic practice ability
Mengru Bu, Haiqi Ma, Huimin Zhai, Yue Ma, Ningjun Xu
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2107. CrossRef - Effects of Compassionate Competence, Communication Skills, and Nursing Work Environment on Person-centered Care in General Hospital Nurses who Care for Cancer Patients
Mi Jin Han, Seonho Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Performance of Person-centered Care Among Nurses in Designated COVID-19 Hospitals
Hyun-Joung Yun, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(4): 413. CrossRef - Hospital Culture and Healthcare Workers' Provision of Patient-Centered Care: A Moderated Mediation Analysis
Xianhong Huang, Yuan Gao, Hanlin Chen, Hao Zhang, Xiaoting Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Performance of Person-Centered Care among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: An Ecological Perspective
Yein Lee, Yunhee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 522. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Care Workers at Long-term Care Facilities
Geun-Young Kim, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 13. CrossRef - A predictive model of the perceptions of patient-centered care among nurses in long-term care hospitals: A cross-sectional study
Myonghwa Park, Hyun Jeong, Thi-Thanh-Tinh Giap
Geriatric Nursing.2021; 42(3): 687. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Nurses
Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 363. CrossRef - Hospital Nurses’ Experience of Patient-Centered Nursing
Soojin Chung, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2021; 27(1): 26. CrossRef - Inducing a sense of worthiness in patients: the basis of patient-centered palliative care for cancer patients in Iran
Mir Hossein Aghaei, Zohreh Vanaki, Eesa Mohammadi
BMC Palliative Care.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of the Nursing Practice Environment and Self-leadership on Person-centered Care Provided by Oncology Nurses
Sun-Ui Shin, Hyun-E Yeom
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2021; 24(3): 174. CrossRef - The influence of health literacy competencies on patient-centered care among clinical nurses
Minyeon Kim, Jieun Cha
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 132. CrossRef - “Walking in the patient’s shoes”: An innovative training method using storytelling to promote knowledge transfer of patient-centered care in hospital: A quasi-experimental study
Myonghwa Park, Insook Jang, Thi-Thanh-Tinh Giap
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 56: 103199. CrossRef - Factors affecting to the Person-Centered Care among Critical Care Nurses
Seunghye Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(2): 36. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis on Patient-Centered Care in Hospitalized Older Adults with Multimorbidity
Youn-Jung Son, Heun-Keung Yoon
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 61. CrossRef - The Relationship between Person-Centered Nursing and Family Satisfaction in ICUs
Jiyeon Kang, Eun-Ja Shin
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Lateral Violence on Burnout and Empathy with Patients among Nurses: The Moderating Effect of Communication
Soohyun Nam, Boyoung Hwang
Stress.2019; 27(3): 224. CrossRef
- Influence of Clinical Nursing Competency and Nursing Working Environment of Psychiatric Nurses on Person-Centered Care
- 5,104 View
- 185 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref

- Development of the Patient Caring Communication Scale
- Myoung Lyun Heo, Sook Bin Im
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.80
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study attempted to develop a scale that measures the level of patients' recognition of the nurses' care, based on Watson's caring theory, and confirmed its reliability and validity.
Methods The items were developed through a literature review and an expert content validity test. The questionnaires were administered to 285 inpatients of internal medicine and surgical units at two general hospitals. Construct validity was tested using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, and reliability was tested using Cronbach's alpha.
Results This process resulted in a preliminary scale composed of 34 items; We used item analysis and five exploratory factor analyses, and consequently selected 14 items composed of three factors (respect, genuineness, and relationality). The confirmatory factor analysis verified the model fit and convergent and discriminant validity of the final items; criterion validity was confirmed with the positive correlation with the measurement scale of the patient-perceived quality of nursing . The overall scale reliability had a Cronbach's alpha of .92, which indicated internal consistency and reliability.
Conclusion The developed scale showed content, construct, and criterion validity, and reliability, as well as convergent validity for each item and discriminant validity between the factors. This makes it suitable for use in a diverse range of future studies on nurse communication using structural equation models.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of the Caring Competence Scale for Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Disorders
Won Hee Jun
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 32(5): 1248. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Therapeutic Communication Scale in Nursing Students
Soolgi Han, Jinhee Yoo, Kyonghwa Kang
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 394. CrossRef - A structural model of nursing students’ performing communication skills
Cho Rong Gil, Kyung Mi Sung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 148. CrossRef - Nurse’s Evaluation on Health Education in Portuguese Pediatric Hospitals and Primary Care for Children/Young and Parents
Anabela Fonseca Pereira, Joaquim Escola, Vitor Rodrigues, Carlos Almeida
Children.2022; 9(4): 486. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Korean version of ComOn coaching for oncology nurses
Myoung Soo Kim, Eun-Jung Bae, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 9(4): 210. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-Item Scale
Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee, So-Young Kim, Nayoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(5): 617. CrossRef - Development of the Nursing Start-up Attitude Scale for Student Nurses
Ji Young Lim, Geun Myun Kim, Eun Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 388. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Watson Caritas Patient Score
SookBin IM, MiKyoung CHO, MyoungLyun HEO
Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 28(2): e80. CrossRef
- Development of the Caring Competence Scale for Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Disorders
- 2,984 View
- 134 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Structural Equation Model for Sleep Quality of Female Shift Work Nurses
- Ji Yeong Jeong, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):622-635. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.622
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to develop and test a structural model for sleep quality in female shift work nurses. The hypothetical model was constructed on the basis of Spielman's 3P model of insomnia and previous research related to the sleep quality of shift nurses.
Methods This cross-sectional study used structural equation modeling and recruited 285 female shift work nurses from four general and university hospitals with over 300 beds located in C and J cities in Gyeongsangnamdo. Data were collected from September 27 to October 20, 2016, and then analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation, and structural equation modeling. The study used SPSS/Win 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 in processing the data.
Results The final model showed good fit to the empirical data: χ2/df=2.19, SRMR=.07, RMSEA=.07, AGFI=.85, TLI=.91, GFI=.93, GFI=.89, NFI=.87. The factors that influenced sleep quality were sleep hygiene (β=.32), perceived shift work status (β=−.16), stress response (β=.16), shift work experience (β=.15), perceived health status (β=−.14), and circadian rhythm (β=−.13) explaining 36.0% of the variance.
Conclusion The model of sleep quality of the shift work nurses constructed in this study is recommended as a model to understand and predict the sleep quality of shift work nurses. The results suggest that strategies for improving the sleep quality of shift work nurses should focus on sleep hygiene, perceived health status, stress response, circadian rhythm, perceived shift work status, and shift work experience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Pathways Linking Work and Nonwork Factors to Sleep, Fatigue, and Health in Night Shift Nurses: A Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
Bo Min Jeon, Su Hyun Kim, Juan Gómez-Salgado
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of COVID-19-related resilience on depression, job stress, sleep quality, and burnout among intensive care unit nurses
Sojin Hwang, Jungmin Lee
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Holistic sleep improvement strategies for frontline nurses served during a public health emergency (COVID‐19) in Wuhan, China: A quasi‐experimental study
Yanli Zhang, Manli Tang, Yanrong Zhou
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1471. CrossRef - Associations between the Timing and Nutritional Characteristics of Bedtime Meals and Sleep Quality for Nurses after a Rotating Night Shift: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Jung Hoon Park, Hyuntae Park, Seongryu Bae, Jiyeon Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(2): 1489. CrossRef - Predictors of dropout in university students participating in an 8-week e-mail-based cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia intervention
Hyojin Nam, Jinyoung Chang, Mickey Trockel, Isa Okajima, Chien-Ming Yang, Ngan Yin Chan, Shirley Li, Sooyeon Suh
Sleep and Breathing.2023; 27(1): 345. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Gastrointestinal Symptoms among Rotating Shift Nurses in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sun-Kyung Hwang, Yun-Ji Lee, Min-Eun Cho, Bo-Kyoung Kim, Yea-In Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 9795. CrossRef - Psychosocial factors affecting sleep quality of pre-employed firefighters: a cross-sectional study
MyeongSeob Lim, Solam Lee, Kwanghyun Seo, Hyun-Jeong Oh, Ji-Su Shin, Sung-Kyung Kim, Hee-Tae Kang, Kyeong-Sook Jeong, Sung-Soo Oh, Sang-Baek Koh, Yeon-Soon Ahn
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Secondary Data Analysis on the Quality of Sleep and Related Factors of Novice and Experienced Shift Work Nurses
Minjeong Yu, Smi Choi-Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 646. CrossRef - Sleep quality among shift-work nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jiwon Kang, Wonjung Noh, Youngjin Lee
Applied Nursing Research.2020; 52: 151227. CrossRef - Work-related Characteristics and Sleep Quality of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Units of Small-medium Sized Hospitals
Sujin Shin, Inyoung Lee, Jeonghyun Kim, Sung-Heui Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(4): 260. CrossRef
- Exploring Pathways Linking Work and Nonwork Factors to Sleep, Fatigue, and Health in Night Shift Nurses: A Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
- 2,325 View
- 45 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Chronically Ill Patients' Perception of Hospital Nurses
- Byoung-Sook Lee, Mi-Aie Lee, Yong-Sook Eo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):311-322. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.311
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this qualitative research was to investigate chronically ill patients' perception of hospital nurses.
Methods Individual in-depth interviews and qualitative content analysis were used for data collection and analysis respectively. Participants were 13 chronically ill hospitalized patients or outpatients in three universities hospitals. All interviews were recorded and transcribed verbatim. Data were analyzed using the qualitative content analysis suggested by Graneheim and Lundman (2004).
Results Three themes emerged from the 10 sub-themes, which were categorized from the 21 condensed meaning units by interpreting the underlying meanings. The three themes were “person giving comfort and support by caring”, “person facilitating the process of healing”, and “person taking the initiative in power relations”. Two themes involved positive experiences of patients and the other included negative ones.
Conclusion The results showed that the participants perceived the hospital nurses as devoted to caring for patients and facilitating treatments, but authoritative in performing their duty. Based on these results, it is recommended that hospital nurses improve their nursing knowledge, skills and humanistic attitude.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Significado de la cronicidad para el cuidador y la persona cuidada: una revisión integrativa
Claudia Andrea Ramírez-Perdomo, Claudia Patricia Cantillo-Medina, Alix Yaneth Perdomo-Romero , María Elena Rodríguez-Vélez, Lili Andrea Buitrago Malaver, Ana Ligia Escobar Tobón
Avances en Enfermería.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Person-Centered Care Experience of Nursing Home Workers: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 33. CrossRef - The Effect of Nursing Competence on Patient-Centered Care among Nurses Caring for Patients with Chronic Disease: The Mediating Effect of Burnout and the Moderating Effect of Nursing Work Environment
Jin-Yeong Ahn, Young Eun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(2): 134. CrossRef - Perceptions Related to Nursing and Nursing Staff in Long-Term Care Settings during the COVID-19 Pandemic Era: Using Social Networking Service
Juhhyun Shin, Sunok Jung, Hyeonyoung Park, Yaena Lee, Yukyeong Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(14): 7398. CrossRef
- Significado de la cronicidad para el cuidador y la persona cuidada: una revisión integrativa
- 1,504 View
- 13 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Patterns and Influential Factors of Inter-Regional Migration of New and Experienced Nurses in 2011~2015
- Bohyun Park, Se Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):676-688. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.676
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the migration patterns of new nurses and experienced nurses and to identify the factors influencing inter-regional migration for solving regional imbalances of clinical nurses in South Korea.
Methods This study involved a secondary analysis of data from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results New nurses tended to migrate from Kyunggi to Seoul. However, experienced nurses tended to migrate from Seoul and Chungchung to Kyunggi. Significant predictors of inter-regional migration among new nurses were location and nurse staffing grade of hospitals. Significant predictors of inter-regional migration among experienced nurses were location, hospital type, nurse staffing grade, ownership of hospitals and age of nurses.
Conclusion Inter-regional migration occupied a small portion of total hospital movement among clinical nurses. The regional imbalances of nurses were not caused by the migration from non-metropolitan areas to Seoul. Nurse shortage problems in the small and medium hospitals of the non-metropolitan area can be solved only through improvement of work environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ideation Model for Healthcare Workforce Management in the Philippine Context
Jose Abantao, Jose Marlon Refuncion, Marife Lacaba
Journal of Interdisciplinary Perspectives.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Turnover Rates and Factors Associated With Turnover: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Retention Period of Clinical Nurses in Korea Using National Data
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice.2024; 25(2): 83. CrossRef - A Study on the Outflow Intention of Nursing Students in Non-Metropolitan Area: Honam Region
Purum Kang, A Young Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 234. CrossRef - Impact evaluation of nurse staffing policy reform in Korea: A quasi‐experimental study
Jinseon Yi, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 3457. CrossRef - Re-employment Hospital Types of Early Career Nurses and Changes in Work-Life Balance
Eun-Young Kim, Yun-Kyung Oh
STRESS.2022; 30(3): 163. CrossRef - Retention Rates and the Associated Risk Factors of Turnover among Newly Hired Nurses at South Korean Hospitals: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10013. CrossRef - Emotional Labor Strategies, Stress, and Burnout Among Hospital Nurses: A Path Analysis
Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2020; 52(1): 105. CrossRef - Nursing stress factors affecting turnover intention among hospital nurses
Eun‐Kyoung Lee, Ji‐Soo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Organizational Justice, Organizational Culture and Emotional Intelligence on Intention of Retention in Reemployed Nurses
Yu Ri Jung, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 501. CrossRef - Intention to leave among staff nurses in small‐ and medium‐sized hospitals
Jeong Hye Park, Min Jung Park, Hye Young Hwang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2019; 28(9-10): 1856. CrossRef - Why newly graduated nurses in South Korea leave their first job in a short time? A survival analysis
Eunhee Lee
Human Resources for Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Students' Choices of a Place of Employment
Sun Ju You, Jong Kyung Kim, Myun Sook Jung, Se Young Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(4): 184. CrossRef
- Ideation Model for Healthcare Workforce Management in the Philippine Context
- 1,640 View
- 13 Download
- 12 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


