-
Validity and reliability of the Security Neglect Subscale of the Child Neglect Scale in vulnerable Chinese children: a methodological study
-
Zexi Su
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):613-620. Published online November 27, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25089
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
Security neglect is common among vulnerable children. The Child Neglect Scale (CNS) is widely used to screen children for neglect. However, little is known about the accuracy of the Security Neglect Subscale when administered in isolation. This study aimed to examine the reliability and validity of the Security Neglect Subscale of the CNS among vulnerable children in China.
Methods
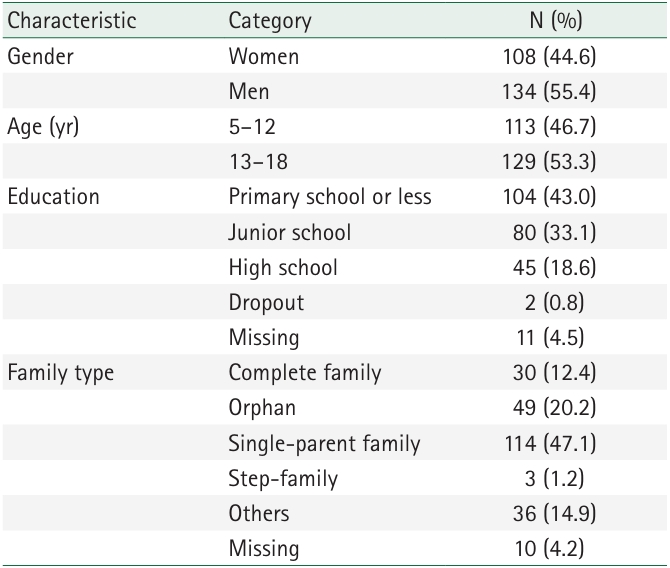
Cluster sampling was used, and 242 vulnerable children participated in the study. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 28.0 and Amos ver. 28.0, and the test construct validity of the CNS Security Neglect Subscale was analyzed through confirmatory factor analysis. In addition, convergent and discriminant validity, as well as reliability, were evaluated.
Results
The construct validity of the nine-item CNS Security Neglect Subscale was confirmed by a two-factor structure. The modified model fit the data well, as shown by a normed chi-square of 2.48, a comparative fit index of .97, a Tucker-Lewis index of .96, and a root mean square error of approximation of .08. The model had acceptable convergent and discriminant validity for each structure. The Cronbach’s α coefficient was .87 overall, and values for the two factors ranged from .78 to .93.
Conclusion
The findings of this study support the satisfactory psychometric properties of the CNS Security Neglect Subscale, indicating its utility in evaluating security neglect in vulnerable children in China.
|