-
Effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to reduce internalized stigma in people with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
Soyoung Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Myung-Sun Hyun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):1-18. Published online February 25, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24072
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study systematically reviewed and analyzed the effects of non-pharmacological interventions on internalized stigma among people with severe mental illness.
Methods
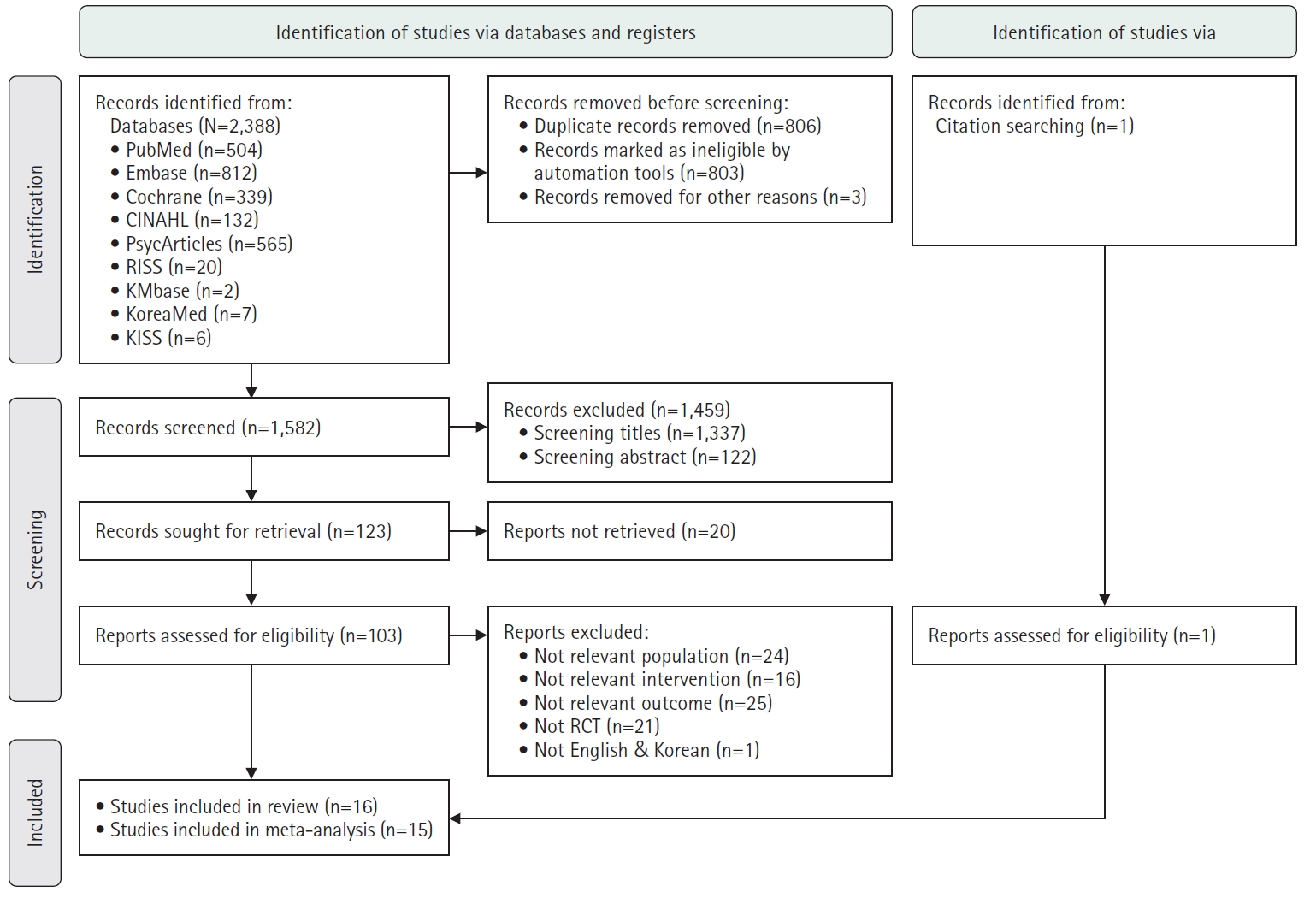
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted following the Cochrane Intervention Research Systematic Review Manual and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis guidelines. This study targeted people with severe mental illness as the population, interventions aimed at reducing internalized stigma, comparisons with control groups, and internalized stigma as the outcome. A literature search was performed across multiple databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycArticles, RISS, KMbase, and KoreaMed. The risk of bias was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool. Effect sizes were computed using Hedges’s g, and subgroup analyses were conducted with Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software version 4.0.
Results
Of 2,388 papers, 15 were included in the meta-analysis. The overall effect size (Hedges’s g) of the intervention was –0.60 (95% confidence interval, –1.01 to –0.19), indicating a statistically significant reduction in internalized stigma (Z=–2.88, p=.004). Subgroup analyses revealed that the intervention type (p=.008) and session length (p=.011) were significant moderators influencing the effectiveness of the interventions.
Conclusion
Tailoring interventions by considering variables such as the intervention type and session length could enhance the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions for reducing internalized stigma among people with severe mental illness (PROSPERO: CRD42023418561).
|