-
The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience in Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity and Learning Burnout
-
Liu Zhang, Qin Zhang, ShuWen Li, YuHong Li, GuoCui Wu, Ying Chen, YunNa Zhou
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):509-518. Published online November 25, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24044
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study investigated whether professional identity predicts learning burnout among Chinese nursing students, and whether resilience moderates this relationship.
Methods
This cross-sectional study recruited 635 students from a nursing college at a medical university in Hefei, China. Data were collected using the professional identity questionnaire, learning burnout scale for college students, and 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale. Pearson’s correlation analysis was used to investigate the relationships between variables. The mediation effect was evaluated using linear regression and the bootstrap method in SPSS.
Results
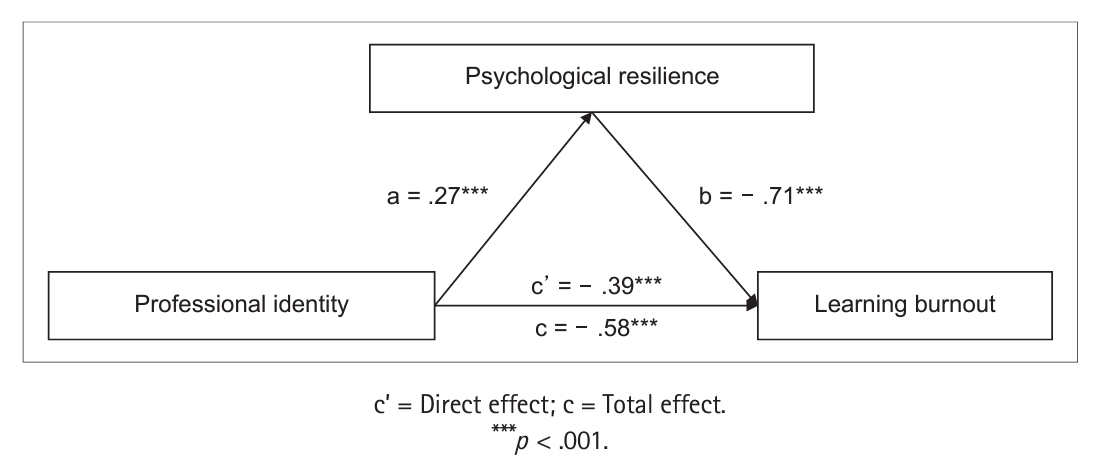
Nursing students exhibited intermediate learning burnout levels (score: 54.95 ± 10.42). Professional identity was positively correlated with psychological resilience (r = .42, p < . 001), whereas learning burnout was negatively correlated with professional identity (r = - .54, p < . 001) and psychological resilience (r = - .57, p < . 001). Psychological resilience mediated the relationship between professional identity and learning burntout to the tune of 32.8%.
Conclusion
Psychological resilience mediates the relationship between professional identity and learning burnout. Thus, nursing educators can mitigate student burnout by developing their students' professional identities and psychological resilience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The impact of creative anxiety on professional identity among master’s nursing students: a chain mediation effect of psychological resilience and achievement motivation
Yao Ding, Xiaolan Guo, Ruifeng Wang, Lu Xu, Shajie Hou, Fengjiao Chang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sense of Coherence and Perceived Academic Stress Among Nursing Students: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
David Ballester-Ferrando, Esther Cáceres-Malagelada, Carolina Rascón-Hernán, Teresa Botigué, Ana Lavedán, Olga Masot, Dolors Burjalés, Luis González-Osorio, Ximena Osorio-Spuler, Eva Serrat-Graboleda, Concepció Fuentes-Pumarola
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(8): 288. CrossRef
-
4,316
View
-
185
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
|