-
Effects of an agro-healing program on depression, stress, and cognitive function in older adults: a quasi-experimental study
-
Gyu Yeon Park, Kwang Ok Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):342-352. Published online August 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25058
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
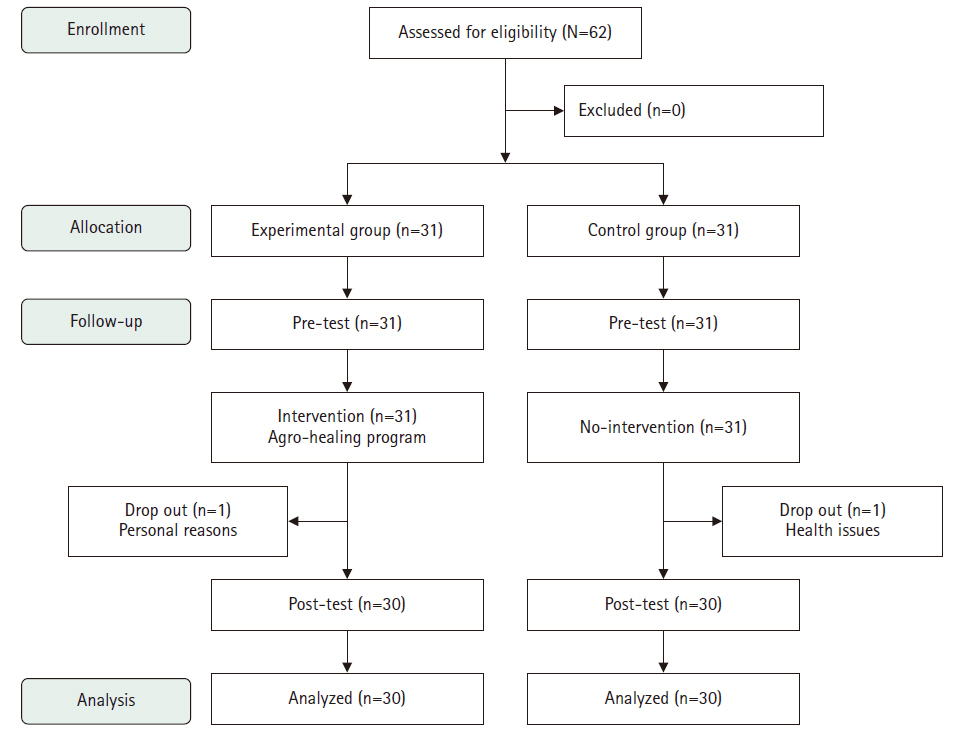
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of an agro-healing program on depression, stress, and cognitive function in older adults.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pretest–posttest design was used. The study was conducted from July 16 to September 6, 2024. Sixty-two individuals aged 65 or older residing in Gimcheon, Gyeongsangbuk-do, were recruited according to the selection criteria (31 in the experimental group and 31 in the control group). The final analysis included 30 participants in each group. The program was delivered by one main instructor (a healing farmer) and three assistants. The pretest assessed general characteristics, the Geriatric Depression Scale Short Form-Korean Version, Stress Response Inventory-Modified Form, and Cognitive Impairment Screening Test. The experimental group participated in the agro-healing program once a week for 90 minutes over 8 weeks. The posttest included the same measurements as the pretest. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0.
Results
The experimental group, which participated in the healing agriculture program, showed reduced depression (F=7.97, p=.007) and stress (F=282.70, p<.001) and improved cognitive function (F=10.12, p=.002) compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that the agro-healing program is an effective intervention for reducing depression and stress and improving cognitive function in older adults. We propose its use to promote health and prevent dementia in this population.
-
Violent Experiences and Coping among Home Visiting Health Care Workers in Korea
-
In Sook Lee, Kwang Ok Lee, Hee Sun Kang, Yeon-Hwan Park
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(1):66-75. Published online February 29, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.1.66
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to explore violent experiences of home visiting health care workers in Korea.
Methods
This study was a cross-sectional survey. Data were collected using self-report questionnaires from 1,640 health care workers. Data collection was done between September 1, 2009 and June 30, 2010.
Results
Of the respondents, 70.6% had experienced work-related violence. Shouting (51.9%) was the most common verbal violence, followed by verbalizing sexual remarks to the health care workers (19.0%) and touching the hands (16.5%), the most common acts relating to sexual harassment. Of the respondents who had experienced violence, 50.9% told their peers about the incidents. However, the major reasons why they did not report these incidents was due to the fact that they felt it was useless to file reports and that they expected such incidents to occur as part of their job. The majority of the respondents (86.4%) wanted education on how to deal with such violence at work.
Conclusion
The results of this study indicate that efforts should be made to increase awareness and to minimize violence in the workplace. Also, educational programs should be designed to improve knowledge and to prevent workplace violence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Improving Local Government Performance Through the Use of Contract Workers: A Case From South Korea
Naon Min, Jongseong Lee
Review of Public Personnel Administration.2025; 45(1): 172. CrossRef - Classifying Studies on Workplace Violence for Visiting Nurses Using the Social-Ecological Model: A Scoping Review
Eunjoo Kim, Juna Lee
Journal of Community Health Nursing.2024; 41(2): 96. CrossRef - Workplace Violence Experienced by Personal Care Workers in a District in Seoul, Republic of Korea: A Comparison Study with Office and Service Workers
Mi-Suk Cho, Kyoung-Bok Min, Jin-Young Min
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 320. CrossRef - Needs assessment of a home-visit safety management training program for visiting nurses
Eunjoo Kim, Hyori Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 138. CrossRef - Prevalence of workplace violence against registered nurses and their perceptions of relevant management systems in acute care hospitals
Seungmi Park, Eunju Kwak, Ye-Won Lee, Eun-Jun Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 319. CrossRef - Experience of Violence and Factors Influencing Response to Violence Among Emergency Nurses in South Korea: Perspectives on Stress-Coping Theory
Seung-Yi Choi, Hyunlye Kim, Kwang-Hi Park
Journal of Emergency Nursing.2022; 48(1): 74. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Psychological States on Work Performance of Visiting Nurses According to COVID-19 Workplace Quarantine Measures: A Multi-Group Path Analysis Study
Jee-Hyun Hwang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 19(1): 444. CrossRef - Difficulties and Coping Experienced by Advanced Practice Nurses in Home Health Nursing Field
Moon-Sook Hwang, Hak Young Park, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 143. CrossRef - Who Cares for Visiting Nurses? Workplace Violence against Home Visiting Nurses from Public Health Centers in Korea
Eunjoo Kim, Heeseung Choi, Ju Young Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4222. CrossRef - Workplace Bullying, Job Stress, Intent to Leave, and Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety in South Korean Hospitals
Hyunjin Oh, Dong-choon Uhm, Young Joo Yoon
Nursing Research.2016; 65(5): 380. CrossRef - The Relation between Interpersonal Attitude and Communication Competence of New Visiting Nurses in Community Health Center
Seung Joo Lim, Eun A Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 115. CrossRef
-
1,242
View
-
11
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
A Study on the Risk Factors for Maternal and Child Health Care Program with Emphasis on Developing the Risk Score System
-
Kwang OK Lee
-
Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1983;13(1):7-21. Published online April 3, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1983.13.1.7
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
For the flexible and rational distribution of limited existing health resources based on measurements of individual risk, the socalled Risk Approach is being proposed by the World Health Organization as a managerial tool in maternal and child health care program. This approach, in principle, puts us under the necessity of developing a technique by which we will be able to measure the degree of risk or to discriminate the future outcomes of pregnancy on the basis of prior information obtainable at prenatal care delivery settings. Numerous recent studies have focussed on the identification of relevant risk factors as the Prior infor mation and on defining the adverse outcomes of pregnancy to be dicriminated, and also have tried on how to develope scoring system of risk factors for the quantitative assessment of the factors as the determinant of pregnancy outcomes. Once the scoring system is established the technique of classifying the patients into with normal and with adverse outcomes will be easily de veloped. The scoring system Should be developed to meet the following four basic requirements. 1) Easy to construct 2) Easy to use 3) To be theoretically sound 4) To be valid In searching for a feasible methodology which will meet these requirements, the author has attempted to apply the "Likelihood Method", one of the well known principles in statistical anlysis, to develop such scoring system according to the process as follows. Step 1. Classify the patients into four groups: Group AI: With adverse outcomes on fetal (neonatal) side only. Group A2: With adverse outcomes on maternal side only. Group A3: With adverse outcome on both maternal and fetal (neonatal) sides. Group B: With normal outcomes. Step 2. Construct the marginal tabulation on the distribution of risk factors for each group.
Step 3. For the calculation of risk score, take logarithmic transformation of relative proportions of the distribution and round them off to integers.
Step 4. Test the validity of the score chart. A total of 2, 282 maternity records registered during the period of January 1, 1982-December 31, 1982 at Ewha Womans University Hospital were used for this study and the "Questionnaire for Maternity Record for Prenatal and Intrapartum High Risk Screening" developed by the Korean Institute for Population and Health was used to rearrange the information on the records into an easy analytic form. The findings of the study are summarized as follows. 1) The risk score chart constructed on the basis of "Likelihood Method" ispresented in Table 4 in the main text. 2) Prom the analysis of the risk score chart it was observed that a total of 24 risk factors could be identified as having significant predicting power for the discrimination of pregnancy outcomes into four groups as defined above. They are: (1) age (2) marital status (3) age at first pregnancy (4) medical insurance (5) number of pregnancies (6) history of Cesarean sections (7). number of living child (8) history of premature infants (9) history of over weighted new born (10) history of congenital anomalies (11) history of multiple pregnancies (12) history of abnormal presentation (13) history of obstetric abnormalities (14) past illness (15) hemoglobin level (16) blood pressure (17) heart status (18) general appearance (19) edema status (20) result of abdominal examination (21) cervix status (22) pelvis status (23) chief complaints (24) Reasons for examination 3) The validity of the score chart turned out to be as follows: a) Sensitivity: Group A1 : 0.75 Group A2: 0.78 Group A3: 0.92 All combined : 0.85 b) Specificity : 0.68 4) The diagnosabilities of the "score chart" for a set of hypothetical prevalence of adverse outcomes were calculated as follows (the sensitivity "for all combined" was used). Hypothetidal Prevalence : 5% 10% 20% 30% _40% 50% 60% Diagnosability : 12% 23% 40% 53% 64% 75% 80%.
-
A Research on Subjective Symptoms of Fatigue of Housewives at Shin: Chon Area in Seoul
-
Kwang Ok Lee, Kong Bum Shin
-
Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1979;9(2):27-38. Published online April 3, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1979.9.2.27
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
This study was undertaken to determine the subjective symptoms of fatigue among the housewives groups. Inquiries into subjective symptoms of fatigue were made by the form designied by the Industrial Fatigue Research Committee of the Japan Society of Industrial Health (1967), Comprising 30 items. These items are classified into 3 groups of 10 items, namely, A) Physical Symptoms, B) Mental Symptoms, C) Neuro Sensory Symptoms (Figure 1). The results of the investigation can be summerized as follows: 1. Within the total items (T), the physical symptoms (A) were the strongest in the effect on the feelings of fatigue, and were followed by (B), and (C). 2. There was a significant difference shown in the distribution of responses by height (X2=236.29, d.f. = 145, p < 0.00001). In the mental category (F = 2.22, d.f. = 4, p = 0.05) and neuro-sensory category (F = 2.64, d.f. = 4, p < 0.001), there was a difference in the responses' complaints by weight. 3. As for the ages, housewives at the age of 50 presented a higher rate than those 30 or 20. 4. Regarding the number of children, respendents have more children showed higher frequency rate of complaints. 5. In the investigation sample, complaints were related to education level (f = 18.34, d.f. = 3, p < 0.0001) nentruation (t = 2.31, p < 0.022), and sleeping hours (F = 6.04, d.f. = 6, p < 0.0001).
-
Study on Needed Professional Knowledge and Understanding of Family Planning Workers in Kyonggi-Do, Korea.
-
Kwang Ok Lee
-
Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1971;2(1):159-174. Published online April 3, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1971.2.1.159
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The Family Planning Program has been intensively implemented in Korea by the national policy since 19 62. However, the desired effective results were not fully obtained by many reasons such as the shortae of qualified workers, lack of eligible women's cooperation and understanding of the importance of family planning etc.. The field family planning workers is classified into two categories along the gouernmental personnel order; the senior field worker and the assistant field worker. The former is qualified licensed nurse and the latter same as the former of a certified nurses-aid. These family planning worker's roles are somewhat in change not only in field education, distribution of contraceptions, administrating mother's class of assistant field workers but also responsible for the senior field workers such as recording, reporting and keeping statistics. Therefor, the desired success of family planning programming in Korea depends on family planning worker's professional abilities and activities in the field. In aiming to study on professional knowledge of the above two kinds of family planning workers, the following results were obtained through a field survey with questionnairs done as of October, 1970 in Kyonggi-Do. 1. Working term of the family planning workers in average were less than two years. The younget the assistant Field workers were, the earlier they left job. 2. The assistant field workers selected their job in order to the superficial rather than implernenting job itself. 3. Most of the workers either in the health center or in the Up-Myun had a better understanding concern- ing with their job; contraceptive methcds, maintenance of equipment and drug keeping, and other admini- strative procedures, etc.. 4. They had relatively better understanding and sufficient knowledge about contraception itself appli- cation of it's methods and side effects in detail too, but less knowledges for the care after. 5. It was hard to Find out any differences in administrative knowledge and demographic understanding. 6. It is fully agreed upon that the lenger the worker have experienced with the program, the more skilful she applied. 7. The worker who had training whether pre-service or inservice are working more effectively than the untrained. 8. The fundamental demographic knowledge is recommended to obtain for the workers in Kyonggi-Do.
|