Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 41(6); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Predictors of Maternal Identity of Korean Primiparas
- Hyun-Ju Chae, Ju-Eun Song, Sue Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(6):733-741.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.6.733
Published online: December 31, 2011
1Part-time Lecturer, College of Nursing, Sungshin Women's University, Seoul, Korea.
2Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
3Associate Professor, College of Nursing, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Song, Ju-Eun. Department of Nursing, Dankook University, Anseo-dong, Dongnam-gu, Cheonan 330-714, Korea. Tel: +82-41-550-3987, Fax: +82-41-550-3888, songje@dankook.ac.kr, songje72@hanmail.net
© 2011 Korean Society of Nursing Science
- 203 Views
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing maternal identity of Korean primiparas.
-
Methods
- The data were collected by a self-report questionnaire in 2006. The participants were 210 healthy primiparous women who delivered at one of three medical centers and revisited the outpatient department for follow up between 4 to 6 weeks after childbirth. Data were analyzed using the SPSS WIN 17.0 program with descriptive statistics, t-test, one way ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient, and stepwise multiple regression.
-
Results
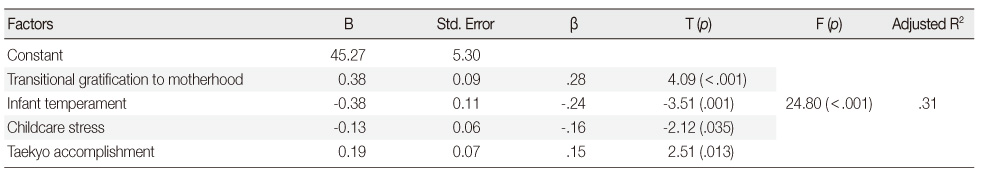
- Maternal identity was significantly correlated with Taekyo accomplishment, the culturally based prenatal preparation (p<.001). Transitional gratification to motherhood (p<.001), postpartum depression (p<.001), childcare stress (p<.001), infant temperament (p<.001), and social support (p<.001) were also significantly correlated with maternal identity. The stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that maternal identity was significantly predicted by transitional gratification to motherhood, infant temperament, childcare stress, and Taekyo accomplishment. These variables explained 31.0% of the variance of maternal identity.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study suggest that postpartum nursing interventions to promote maternal identity should focus on reinforcing education and support for reducing childcare stress and infant difficulty, and increasing transitional gratification to motherhood. Also, prenatal encouragement and education for improving Taekyo accomplishment may be helpful to promote maternal identity after birth.
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSION
- 1. Bae JY. Construction of postpartum depression model. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2002;11:572–587.
- 2. Barr JA. Postpartum depression, delayed maternal adaptation, and mechanical infant caring: A phenomenological hermeneutic study. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2008;45:362–369. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2006.10.002.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Chae HJ, Kim S. Effects of maternal role practice education on becoming a mother. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2011;17:52–63. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2011.17.1.52.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Chang SB, Kim KY, Kim ES. Changes of maternal-infant attachment and self efficacy for delivery after the Taekyo-perspective prenatal class. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2001;7:1–17.
- 5. Choi YS, Kim HO. A survey on the practice of Taekyo among childbearing couples. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 1995;1:153–173.ArticlePDF
- 6. Chun CA. The effect of postpartum stress and social network on the postpartum depression. 1990;Seoul, Korea University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 7. Fontenot HB. Transition and adaptation to adoptive motherhood. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 2007;36:175–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6909.2007.00134.x.Article
- 8. Fowles ER. The relationship between maternal role attainment and postpartum depression. Health Care for Women International. 1998;19:83–94.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Hassall R, Rose J, McDonald J. Parenting stress in mothers of children with an intellectual disability: The effects of parental cognitions in relation to child characteristics and family support. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research. 2005;49:405–418.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Hong EJ, Lee JY. The effects of the 'Taegyo' program using art therapy techniques in the anxiety, postpartum depression and maternal identity of pregnant women. The Korean Journal of Human Development. 2006;13(1):97–115.
- 11. Kim HS, Oh KS, Shin YH, Kim TI, Yoo HN, Sim MK, et al. Factors influencing parenting stress in primiparas. Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing. 2005;11:290–300.
- 12. Koh HJ. The relationship between role strain and identity in first-time mothers with regard to employment status. 1996;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 13. Kowk S, Wong D. Mental health of parents with young children in Hong Kong: The roles of parenting stress and parenting self-efficacy. Child and Family Social Work. 2000;5:57–65.ArticlePDF
- 14. Kwon JH. A test of a vulnerability-stress model of postpartum depression. Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology. 1997;16(2):55–66.
- 15. Lee ES. Maternal role attainment of primiparous during the postpartum period. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 1992;2:5–20.
- 16. Lee SN, Long A, Boore J. Taiwanese women's experience of becoming a mother to a very-low-birth-weight preterm infant: A grounded theory study. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2009;46:326–336.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Lee TG, Lee JH. Literature review of postpartum depression. The Journal of Oriental Gynecology. 2000;13(1):518–530.
- 18. Logsdon MC, Wisner KL, Pinto-Foltz MD. The impact of postpartum depression on mothering. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 2006;35:652–658. doi: 10.1111/J.1552-6909.2006.00087.x.Article
- 19. Mantymaa M, Puura K, Luoma I, Salmelin RK, Tamminen T. Mother's early perception of her infant's difficult temperament, parenting stress and early mother-infant interaction. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry. 2006;60:379–386. doi: 10.1080/08039480600937280.ArticlePubMed
- 20. McGrath JM, Records K, Rice M. Maternal depression and infant temperament characteristics. Infant Behavior & Development. 2008;31:71–80. doi: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2007.07.001.Article
- 21. Mercer RT. Becoming a mother versus maternal role attainment. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2004;36:226–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2004.04042.x.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Mercer RT. Nursing support of the process of becoming a mother. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 2006;35:649–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6909.2006.00086.x.Article
- 23. Mercer RT, Walker LO. A review of nursing interventions to foster becoming a mother. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 2006;35:568–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6909.2006.00080.x.Article
- 24. Munro BH, Page EB. Statistical methods for health care research. 1993;2nd ed.Philadelpia, J.B. Lippincott, USA.
- 25. Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH. Psychometric theory. 1994;3rd ed.New York, McGraw-Hill, USA.
- 26. Oh HE. The relationship among maternal identity, role attainment and postpartum depression. Journal of the Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health. 2001;5:255–266.
- 27. Rubin R. Maternal identity and the maternal experience. 1984;New York, Springer.
- 28. Walker LO, Crain H, Thompson E. Maternal role attainment and identity in the postpartum period: Stability and change. Nursing Research. 1986;35:68–71.PubMed
- 29. Leahy Warren P. First time mother: Social support and confidence in infant care. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2005;50:479–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03425.x.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Yee YH. Patterns of infant-father attachment in the strange situation. Journal of Korean Home Management Association. 1993;11(2):40–54.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Effects of stress, depression, and spousal and familial support on maternal identity in pregnant women
Hye-Jung Seo, Ju-Eun Song, Youngjin Lee, Jeong-Ah Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 84. CrossRef - The Influence of Ego-identity, Parenting Efficacy and Stress Coping Style on Depression in Mothers of Toddlers
Hyun-Yi Chai, Mi-Young Choi
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(2): 196. CrossRef - The pregnancy experience of Korean mothers with a prenatal fetal diagnosis of congenital heart disease
Yu-Mi Im, Tae-Jin Yun, Il-Young Yoo, Sanghee Kim, Juhye Jin, Sue Kim
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
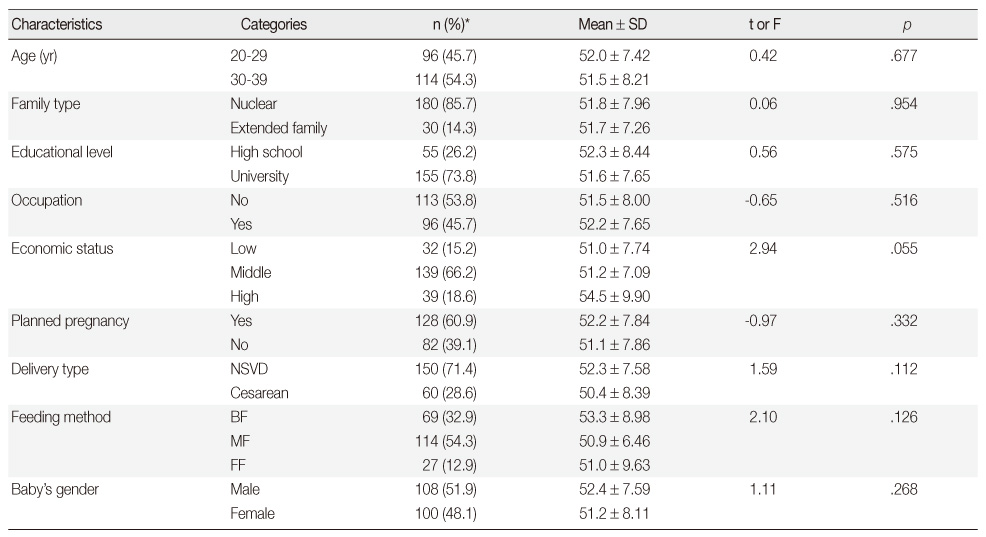
General Characteristics and Differences in Maternal Identity (N=210)
*Valid percent.
NSVD=Normal spontaneous vaginal delivery; BF=Breast feeding; MF=Mixed feeding; FF=Formula feeding.
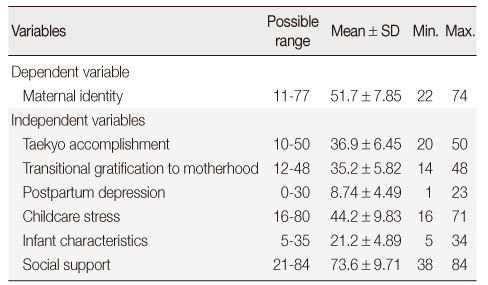
Descriptive Statistics of the Study Variables (N=210)
Min.=Minimum; Max.=Maximum.
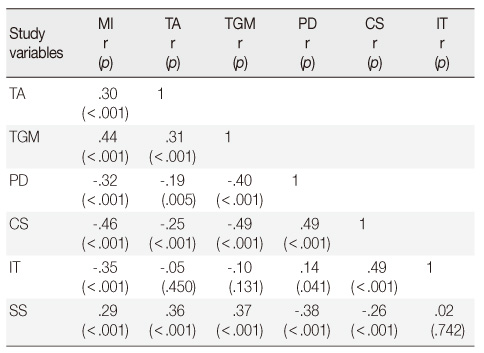
Correlation Coefficients among Study Variables (N=210)
TA=Taekyo accomplishment; TGM=Transitional gratification to motherhood; PD=Postpartum depression; CS=Childcare stress; IT=Infant temperament; SS=Social support.
Predicting Factors of Maternal Identity (N=210)
*Valid percent. NSVD=Normal spontaneous vaginal delivery; BF=Breast feeding; MF=Mixed feeding; FF=Formula feeding.
Min.=Minimum; Max.=Maximum.
TA=Taekyo accomplishment; TGM=Transitional gratification to motherhood; PD=Postpartum depression; CS=Childcare stress; IT=Infant temperament; SS=Social support.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

