Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(3); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of Abdominal Breathing on State Anxiety, Stress, and Tocolytic Dosage for Pregnant Women in Preterm Labor
- Woo-Jeong Yu, Ju-Eun Song
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(3):442-452.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.442
Published online: June 30, 2010
1Registered Nurse, Department of Nursing, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
2Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Song, Ju-Eun. Department of Nursing, Dankook University, Anseo-dong, Cheonan 330-714, Korea. Tel: 82-41-550-3987, Fax: 82-41-550-3888, songje@dankook.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of abdominal breathing on state anxiety, stress and tocolytic dosage for pregnant women in preterm labor.
-
Methods
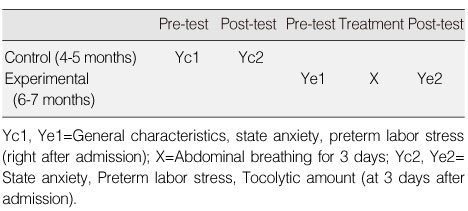
- The participants were 60 pregnant women in preterm labor who were hospitalized from April to July, 2009. Thirty participants were assigned to the experimental group and 30 to the control group. None of them had any other complications except preterm labor. The modified Mason's breathing technique was used with the experimental group 3 times a day for 3 days. Data were collected using a self-report questionnaire and chart review, and analyzed with the SPSS 13.0 WIN program.
-
Results
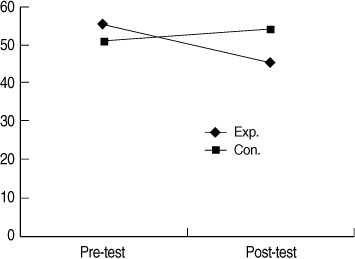
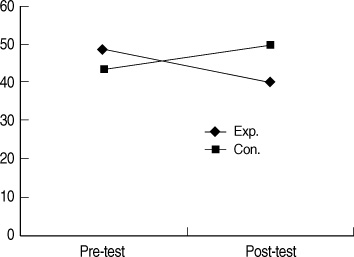
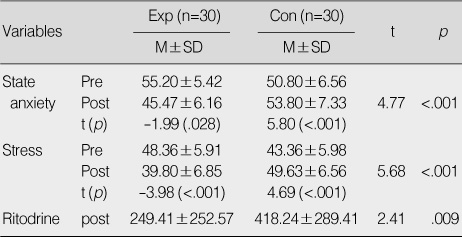
- "State anxiety of the experimental group will be lower than that of the control group" was supported. "Stress of the experimental group will be lower than that of the control group" was supported. "The Ritodrine dosage for the experimental group will be lower than that of the control group" was supported. "The Atosiban dosage for the experimental group will be lower than that of the control group" was supported.
-
Conclusion
- These results indicate that abdominal breathing is an effective nursing intervention for pregnant women in preterm labor.
- 1. An JD. The effect of Taekwondo players' stress decrease on abdominal breathing and meditation program. Journal of Korean Society for the Study of Physical Education. 2004;8:172–187.
- 2. An SE. Effects of abdominal breathing on anxiety and labor time in primipara women. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2008;14:196–204.ArticlePDF
- 3. Bastani F, Hidarnia A, Kazemnejad A, Vafaei M, Kashanian M. A randomized controlled trial of the effects of applied relaxation training on reducing anxiety and perceived stress in pregnant women. Journal of Midwifery and Women's Health. 2005;50:36–40.
- 4. Chang SB, Kim HS, Ko YH, Bae CH, An SE. Effects of abdominal breathing on anxiety, blood pressure, peripheral skin temperature and saturation oxygen of pregnant women in preterm labor. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2009;15:32–43.Article
- 5. Chang SB, Park HJ, Bae CH, Shim JO. The effects of abdominal breathing on preterm labor anxiety and frequency of uterine contraction. Clinical Nursing Research. 2007;13(3):31–41.
- 6. Cunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom S, Hauth JC. Williams obstetrics. 2009;23rd ed. New York, NY, McGraw-Hill.
- 7. Debra PJ. The nursing management of women experiencing preterm labor: Clinical guidelines and why they are needed. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Neonatal Nursing. 1996;26:569–573.
- 8. Jacobson E. Progressive relaxation: A physiological and clinical investigation of muscular states and their significance in psychology and medical practice. 1974;2nd ed. Chicago, IL, University of Chicago Press.
- 9. Jang MS, Ha YS, Jeong JS, Yu BH. The effect of biofeedback-assisted relaxation on the clinical symptoms and stress responses in patients with chronic headache. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2004;43:697–705.
- 10. Janke J. The effect of relaxation therapy on preterm labor outcome. Journal of Obstetric Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing. 1999;28:255–263.
- 11. Joyce AM, Brady EH, Paul DS, Stephanie JV, Fay M, Martha LM, et al. Final data for 2003, National Vital Statistics Reports. 2005;Hyattsville, National Center for Health Statistics.
- 12. Kim HK. Stress and copying style of women with preterm labor. 2003;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 13. Kim JT, Shin DK. A study based on the standardization of the STAI for Korea. New Medical Journal. 1978;21:1220–1223.
- 14. Kim KS, Lee SW, Choe MA, Yi MS, Choi S, Kwon SH. Effects of abdominal breathing training using biofeedback on stress, immune response and quality of life in patients with a mastectomy for breast cancer. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:1295–1303.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Kim MA, Kho HJ, Park KM, Kwon YS, Kim CN, Park YS, et al. Psycho-neuro-immunological effects of health management program for middle-aged women with low back pain. Journal of the Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health. 2001;5:29–42.
- 16. Kim MO. The effect of a mind-body therapeutic program for infertile women repeating IVF treatment on uncertainty, anxiety, and implantation rate. 2008;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 17. Live births by period of pregnancy: Provinces. Korean Statistical Information Service. 2007;Retrieved January 19, 2009. from http://www.kosis.kr.
- 18. Lee PS, Yu EG. A study on the physical and emotional status, and nursing needs of the pregnant women hospitalized by premature labor. Journal of Korean Academy of Women's Health Nursing. 1996;2:76–91.ArticlePDF
- 19. Mason LJ. Guide to stress reduction. 1985;Berkeley, Celestial Arts.
- 20. Moon DH. The comparative study with fatigue, anxiety and stress between full-term and preterm pregnancy. 2006;Daejeon, Chungnam University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 21. Moon H, Park OI. The effect of the Yoga exercise in expectant mothers. The Korean Journal of Community Living Science. 2006;1:96–99.
- 22. Park SH, Lee PS, Han KS. Effect of relaxation therapy on anxiety through meta-Analysis. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental health Nursing. 2004;10:317–323.ArticlePDF
- 23. Satyapriya M, Nagendra HR, Nagarathna R, Padmalatha V. Effect of integrated Yoga on stress and heart rate variability in pregnant women. International Journal of Gynecology. 2009;104:218–222.ArticlePDF
- 24. Shim JO, Chang SB. The effects of abdominal breathing on preterm labor anxiety. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2006;12:106–114.
- 25. Shin IH, Park JW, Kim HK, Kim TY, Kang EG, Lee IH, et al. Solution medical statistics. 2008;Seoul, Kunja.
- 26. Spielberger CD. Anxiety current trends in theory and research. 1972;New York, NY, Academic Press.
- 27. Teixeira J, Martin D, Prendiville O, Glover V. The effects of acute relaxation on indices of anxiety during pregnancy. Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2005;26:271–276.Article
- 28. Yang MS. Experience in daily life related to the preterm labor of mother. Qualitative Research. 2007;6:65–69.
- 29. Yen SC, Jaffe RB. Reproductive endocrinology. 1991;2nd ed. West Washington Square, PA, W. B Saunders.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Examining the potential of a breath pacer as an adjuvant in cognitive behavioral therapy: case studies in digital health for mental well-being
Eva PLEUMEEKERS, Elisabeth HONINX , Hanne LIETEN , Nele JACOBS , Stefanie BROES , Veerle ROSS
Journal of Evidence-Based Psychotherapies.2024; 24(1): 43. CrossRef - Existing Meditation and Breathing Devices for Stress Reduction and Their Incorporated Stimuli: A Systematic Literature Review and Competition Analysis
Elisabeth Honinx, Stefanie Broes, Bente Roekaerts, Isabelle Huys, Rosanne Janssens
Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health.2023; 1(3): 395. CrossRef - Can Yoga, Qigong, and Tai Chi Breathing Work Support the Psycho-Immune Homeostasis during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic? A Narrative Review
Bruno Mendo, Mário Gonçalves, Lara Lopes, Luís Carlos Matos, Jorge Machado
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 1934. CrossRef - Effects of nonpharmacological interventions on the psychological health of high-risk pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hyeji Yoo, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 180. CrossRef - Effects of the Unpleasant Symptom-Relief Program on Preterm Labor Stress, Anxiety, Physical Discomfort, and Situational Discomfort among Hospitalized High-Risk Pregnant Women: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial
Guy Nam Kim, Eun-Young Jun
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2021; 25(4): 269. CrossRef - The Effect of a Breathing Relaxation Therapy for Pregnant Women with Preterm Labor Pain: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Seo-A Park
Keimyung Medical Journal.2021; 40(1): 39. CrossRef - Effects of a supportive program on uncertainty, anxiety, and maternal-fetal attachment in women with high-risk pregnancy
Hyun Jin Kim, Nami Chun
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 180. CrossRef - The effect of rhythmic deep breathing on pain and anxiety in patients with burns
AnjanaRajhamsan Iyer, Suroshree Mitra, Rachana Dabadghav
Indian Journal of Burns.2020; 28(1): 74. CrossRef - Heart Rate Variability of Various Video-Aided Mindful Deep Breathing Durations and Its Impact on Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Symptom Severity
Kok Suen Cheng, Paul E. Croarkin, Poh Foong Lee
Mindfulness.2019; 10(10): 2082. CrossRef - Factors influencing Stress in Spouses of Hospitalized Women Diagnosed with Preterm Labor
Jeong Im Lee, Sehoon Hong
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 459. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Diaphragmatic Breathing Relaxation Training for Reducing Anxiety
Yu-Fen Chen, Xuan-Yi Huang, Ching-Hui Chien, Jui-Fen Cheng
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2017; 53(4): 329. CrossRef - Effects of Music Therapy on Stress of Preterm Labor and Uterine Contraction in Pregnant Women with Preterm Labor
Hye-Jin Park, Mi-Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(2): 109. CrossRef - The Effect of Diaphragmatic Breathing on Attention, Negative Affect and Stress in Healthy Adults
Xiao Ma, Zi-Qi Yue, Zhu-Qing Gong, Hong Zhang, Nai-Yue Duan, Yu-Tong Shi, Gao-Xia Wei, You-Fa Li
Frontiers in Psychology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Stress, Coping Style and Nursing Needs for Hospitalized Pregnant Women due to Preterm Labor
Su Hyun Kim, Hyang-In Cho Chung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(2): 83. CrossRef - The effects of relaxation breathing on procedural pain and anxiety during burn care
Eunok Park, Hyunjin Oh, Taeim Kim
Burns.2013; 39(6): 1101. CrossRef - Study on Fatigue, Stress and Burnout of Pregnant Nurses
Ja-Sook Kim, Young-Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(3): 208. CrossRef - Relaxation therapy for preventing and treating preterm labour
Bussarin Khianman, Porjai Pattanittum, Jadsada Thinkhamrop, Pisake Lumbiganon
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2012;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Relaxation Therapy on Anxiety and Stress of Pregnant Women with Preterm Labor
Myung Sook Choi, Young Joo Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 336. CrossRef
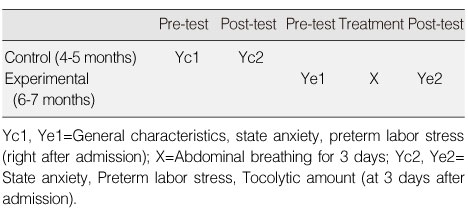
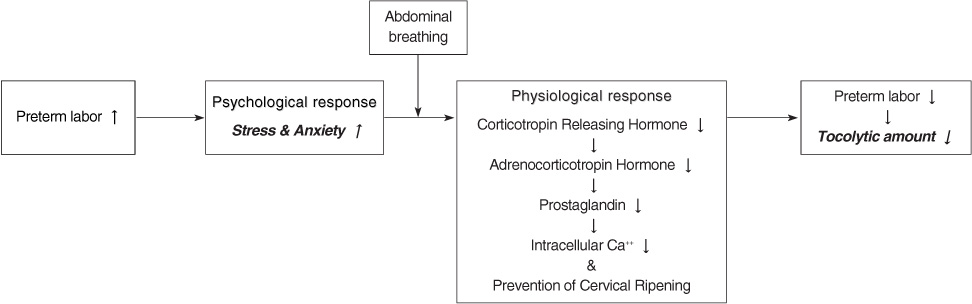
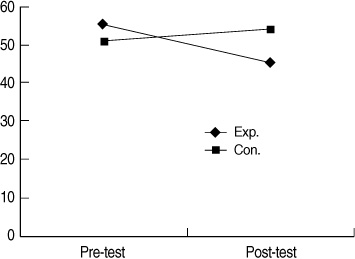
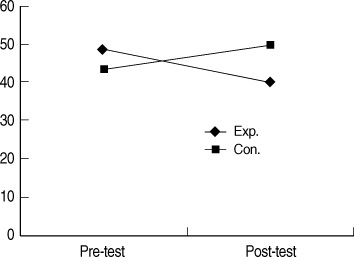
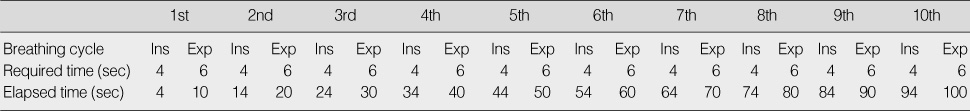
Figure 1
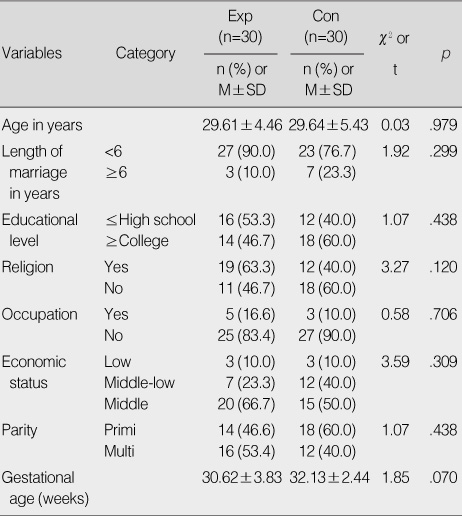
Figure 2
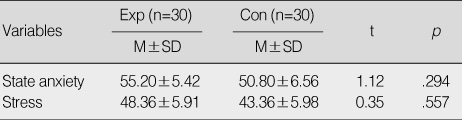
Figure 3
Figure 4
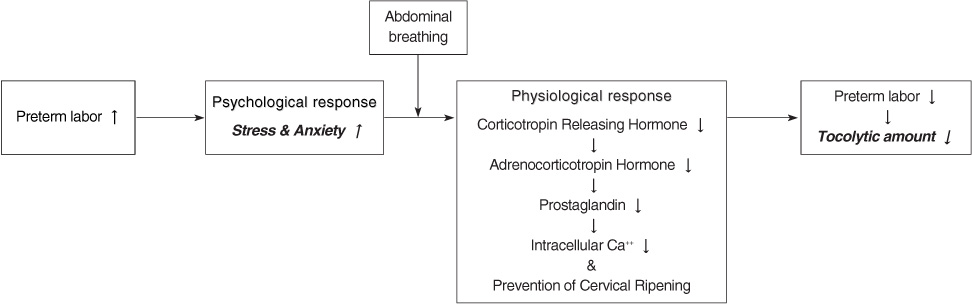
Abdominal Breathing (1 set)
Ins=Inspiration; Exp=Expiration.
Homogeneity Test of General Characteristics between Two Groups (N=60)
Exp=experimental group; Con=control group.
Homogeneity Test of State Anxiety and Stress between Two Groups (N=60)
Exp=experimental group; Con=control group.
Differences in Dependent Variables between Two Groups (N=60)
Exp=experimental group; Con=control group.
Differences in Amount of Atosiban between Two Groups (N=13)
Exp=experimental group; Con=control group.
Ins=Inspiration; Exp=Expiration.
Exp=experimental group; Con=control group.
Exp=experimental group; Con=control group.
Exp=experimental group; Con=control group.
Exp=experimental group; Con=control group.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 Cite
Cite

