Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(3); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Multi-level Analysis of Factors related to Quality of Services in Long-term Care Hospitals
- Seon-heui Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(3):409-421.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.409
Published online: June 29, 2009
General Manager, Health Technology Assessment Team, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, Seon-heui. Health Technology Assessment Department, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, 1451-34 Seocho 3-dong, Seocho-gu, Seoul 137-706, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2182-2620, Fax: 82-2-585-7160, sunarea68@hiramail.net
• Received: January 13, 2009 • Accepted: May 28, 2009
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- In this research multi-level analysis was done to identify factors related to quality of services. Patient characteristics and organizational factors were considered.
-
Methods
- The data were collected from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) data base. The sample was selected from 17,234 patients who had been admitted between January 2007 and May 2008 to one of 253 long-term care hospitals located in Seoul, six other metropolitan cities or nine provinces The data were analyzed with SAS 9.1 using multi-level analysis.
-
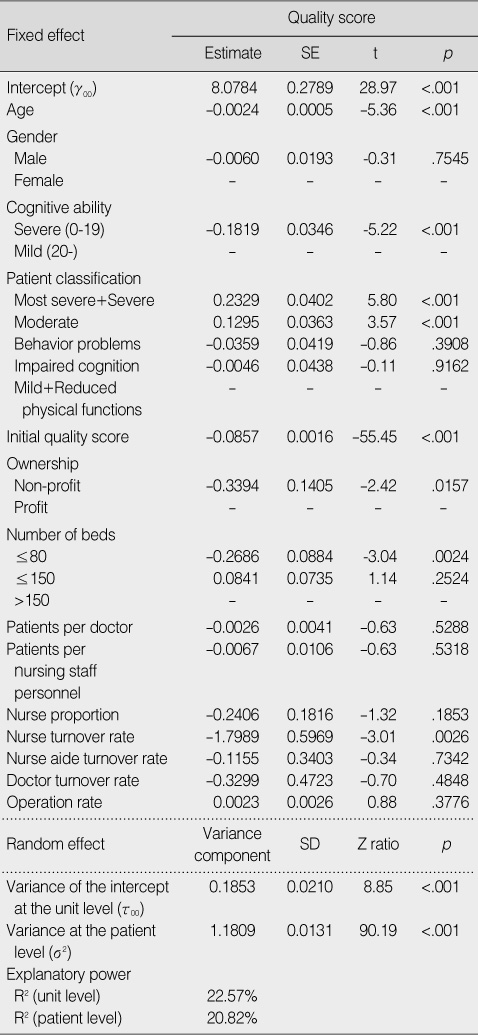
Results
- The results indicated that individual level variables related to quality of service were age, cognitive ability, patient classification, and initial quality scores. The organizational level variables related to quality of service were ownership, number of beds, and turnover rate. The explanatory power of variables related to organizational level variances in quality of service was 23.72%.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study indicate that differences in the quality of services were related to organizational factors. It is necessary to consider not only individual factors but also higher-level organizational factors such as nurse' welfare and facility standards if quality of service in long term care hospitals is to be improved.
- 1. Aaronson WE, Zinn JS, Rosko MD. Do for-profit and not-for-profit nursing homes behave differently? Gerontologist. 1994;34:775–786.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Aiken LH, Havens DS, Sloane DM. The magnet nursing services recognition program: A comparison of two groups of magnet hospitals. American Journal of Nursing. 2000;100:26–36.Article
- 3. Aiken LH, Clarke SP, Cheung RB, Sloane DM, Silber JH. Educational levels of hospital nurses and surgical patient mortality. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2003;24:1617–1623.
- 4. Arling G, Karon SL, Sainfort F, Zimmerman DR, Ross R. Risk adjustment of nursing home quality indicators. Gerontologist. 1997;37:757–766.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Bang EJ. Multilple Analysis of relationship between socioeconomic factor and health. 2005;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 6. Bernabei R, Gambassi G, Lapane K, Landi F, Gatsonis C, Dunlop R, et al. Management of pain in elderly patients with cancer. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1998;17:1877–1882.
- 7. Bliesmer MM, Smayling M, Kane RL, Shannon I. The relationship between nursing staffing levels and nursing home outcomes. Journal of Aging and Health. 1998;10:351–371.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Bravo G, De WP, Dubois M, Charpentier M. Correlates of care quality in long-term care facilities: A multilevel analysis. Journals of Gerontology. 1999;54B:180–188.
- 9. Choi HS. Relationship among the cognitive status, activities daily living and the COPM (canadian occupational performance measure) in cerebral vascular accident. Journal of Dongnam Health University Theses. 2001;29:295–302.
- 10. Chung J. Development and application of nursing service quality indicators in nursing homes. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:401–413.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Cohen JW, Spector WD. The effect of Medicaid reimbursement on quality of care in nursing homes. Journal of Health Economics. 1996;15:23–48.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Copeman J. Promoting nutrition in older people in nursing and residential homes. British Journal of Community Nursing. 2000;5:277–278.Article
- 13. Harrington C, Woolhandler S, Mullan J, Carrillo H, Himmelstein DU. Does investor ownership of nursing homes compromise the quality of care? American Journal of Public Health. 2001;91:1452–1455.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Hay DG. Health care services in 100 superior nursing homes. Long-term Care And Health Services Administration Quarterly. 1977;1:300–313.PubMed
- 15. Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service. Health insurance reimbursement fee. 2008;Seoul, Aramedit.
- 16. Holroyd-Leduc JM, Mehta KM, Covinsky KE. Urinary incontinence and its association with death, nursing home admission, and functional decline. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2004;52:712–718.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Horn SD, Bender SA, Bergstrom N, Cook AS, Ferguson ML, Rimmasch HL, et al. Description of the national pressure ulcer long-term care study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2002;50:1816–1825.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Institute of Medicine. Improving the quality of long-term care. 2001;Washinton DC, National Academy Press.
- 19. Jang SM, Song SH, Kim JH, Kim JY, Lee JY, Lee JY, et al. Demonstration project evaluation report to apply long-term care hospital fee. 2006;Seoul, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service.
- 20. Jiexin L. Assessing the relationship between staffing levels and quality outcomes in nursing facilities. 2003;Minnesota, USA, University of Minnesota. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 21. Kang SJ, Jeon MJ, Chang JH. A comparative analysis on the problem behaviors of academic high school students and vocational high school students-3-level hierachical linear models. Korean Education and Employment panel. 2005;7:145–173.
- 22. Kim EK. Research on the actual condition & operation plan of long-term care hospitals. 2003;Seoul, Korean Health Industry Development Institute.
- 23. Kim KA. Development of an evaluation tool for the quality of nursing care in eldery facility. 2006;Seoul, Chungang University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 24. Ko YK. Identification of factors related to hospital nurses's organizational citizenship behavior using a multilevel analysis. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:287–297.PubMed
- 25. Lee SH. The determinants of nursing home quality indicators: A multilevel analysis. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2006;12:473–481.
- 26. Lee JU, Yoon JY, Jang SR. A study of validity and reliability of a patient assessment instrument for long-term care hospitals. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2008;10:7–19.
- 27. Luke DA. Multilevel Modeling. 2004;Beverly Hills, CA, Sage Publications.
- 28. Moineddin R, Matheson FI, Glazier RH. A simulation study of sample size for multilevel logistic regression models. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2007;7:34–43.PubMedPMC
- 29. Munroe DJ. The influence of registered nursing staffing on the quality of nursing home care. Research in Nursing and Health. 1990;13:263–270.PubMed
- 30. Nyman JA, Bricker DL, Link D. Technical efficiency in nursing homes. Medical Care. 1990;28:541–551.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Porell F, Caro FG. Facility-level outcome performance measures for nursing homes. Gerontologist. 1998;38:665–683.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Robinson JP. Managing urinary incontinence in the nursing home: Residents' perspectives. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2000;31:68–77.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Song JS, Chung HG. National health insurance statistical yearbook. 2008;Seoul, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service.
- 34. Spector WD, Takada HA. Characteristics of nursing homes that affect resident outcomes. Journal of Aging & Health. 1991;3:427–454.ArticlePDF
- 35. Wagner C, Klein Ikkink K, van der Wal G, Spreeuwenberg P, de Bakker DH, Groenewegen PP. Quality management systems and clinical outcomes in Dutch nursing homes. Health Policy. 2006;75:230–240.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Zimmerman DR. Improving nursing home quality of care through outcomes data: The MDS quality indicators. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2003;18:250–257.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Zimmerman S, Gruber-Baldini AL, Hebel JR, Sloane PD, Magaziner J. Nursing home facility risk factors for infection and hospitalization: Importance of registered nurse turnover, administration, and social factors. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2002;50:1987–1995.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- The Effects of Long-term Care Hospitals' Nurse Staffing Level on Patient Outcomes: Differences according to Region
Kyung Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 354. CrossRef - Longitudinal associations of nursing staff turnover with patient outcomes in long-term care hospitals in Korea
Yoonseo Kim, Kihye Han
Journal of Nursing Management.2018; 26(5): 518. CrossRef - Person-centered Care and Nursing Service Quality of Nurses in Long-term Care Hospitals
Hae Sagong, Ga Eon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 309. CrossRef - Characteristics and Mortality Risk Factors in Geriatric Hospital Patients visiting One Region-wide Emergency Department
Kyoung Wan Kim, Soongnang Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 327. CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Empowerment in Relationship between Self-leadership and Job Satisfaction for Nurses Working in Long-term Care Hospitals
Kyoungsuk Kim, Heeok Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2016; 18(1): 32. CrossRef - Nursing outcomes of inpatient on level of nursing staffing in long term care hospitals
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(3): 715. CrossRef - Comparing Risk-adjusted In-hospital Mortality for Craniotomies : Logistic Regression versus Multilevel Analysis
Sun-Hee Kim, Kwang-Soo Lee
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(2): 81. CrossRef - Impact of Nurse, Nurses' Aid Staffing and Turnover Rate on Inpatient Health Outcomes in Long Term Care Hospitals
Yunmi Kim, Ji Yun Lee, Hyuncheol Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(1): 21. CrossRef - Association between Efficiency and Quality of Health Care in South Korea Long-term Care Hospitals: Using the Data Envelopment Analysis and Matrix Analysis
Minsung Sohn, Mankyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(4): 418. CrossRef - Perception and Practice of Hospital Infection Control of Nursing Staff depending on the Supplementation of Nurses in Long-term Care Hospitals
Ji-Hyean Lee, Ga Eon Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2012; 21(3): 308. CrossRef - Improving Service Quality in Long-term Care Hospitals: National Evaluation on Long-term Care Hospitals and Employees Perception of Quality Dimensions
Jinkyung Kim, Woosok Han
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2012; 3(2): 94. CrossRef - Multilevel Analysis of Health Care Service Utilization among Medical Aid Beneficiaries in Korea
Yang Heui Ahn, Ok Kyung Ham, Soo Hyun Kim, Chang Gi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 928. CrossRef - Importance and Performance of Dietitian's Task at Long Term Care Hospital Foodservice in Busan · Kyungnam Area
Mal-Sook Park, Eun-Soon Lyu
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(5): 602. CrossRef - The Effects of Medical Staffing Level on Length of Stay
Hanju Lee, Yu Kyung Ko, Mi-Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(3): 327. CrossRef - Factors Impacting the Physical Function of Older Adults in Korean Long-Term Care Hospitals
Ji-Yun Lee, Eun-Young Kim, Eunhee Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(6): 780. CrossRef - Development of Outcome Indicators of Urinary Incontinence for Quality Evaluation in Long Term Care Hospitals
Ju Young Yoon, Ji Yun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 110. CrossRef - The Comparison of Functional Status and the Level of Health Care Needs in Elderly Koreans in Health Care Institutions
Hyun-Sil Kim, Young-Mi Jung, Hung-Sa Lee, Yoo-Hyang Cho, In-Young Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 386. CrossRef
Multi-level Analysis of Factors related to Quality of Services in Long-term Care Hospitals
Multi-level Analysis of Factors related to Quality of Services in Long-term Care Hospitals
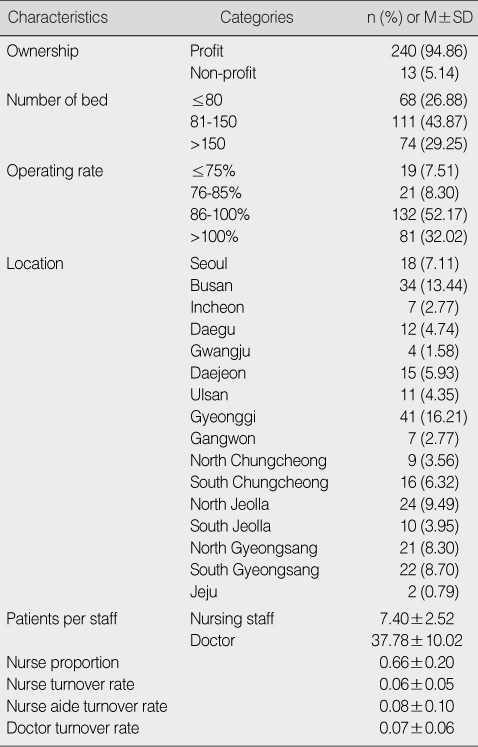
Characteristics of Organizational Factors (N=253)
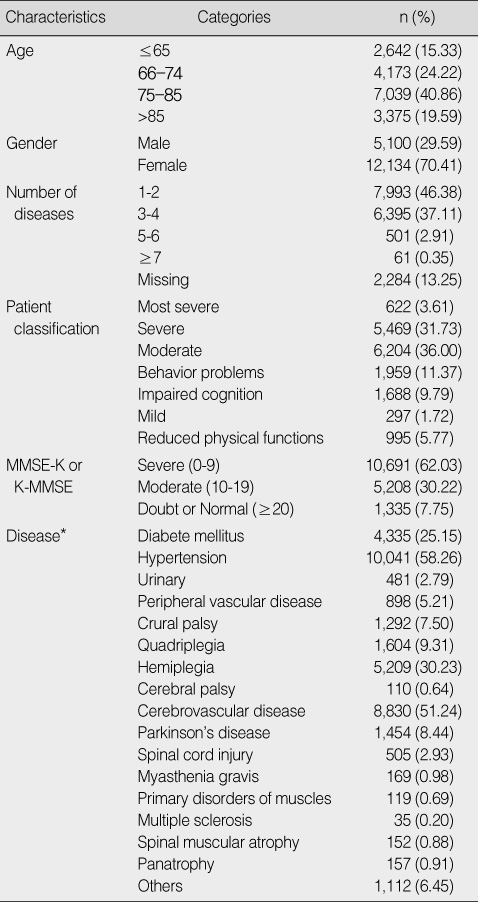
Characteristics of Patients (N=17,234)
*Multiple responses.
MMSE-K=Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination; K-MMSE=Korean Mini-Mental State Examination.
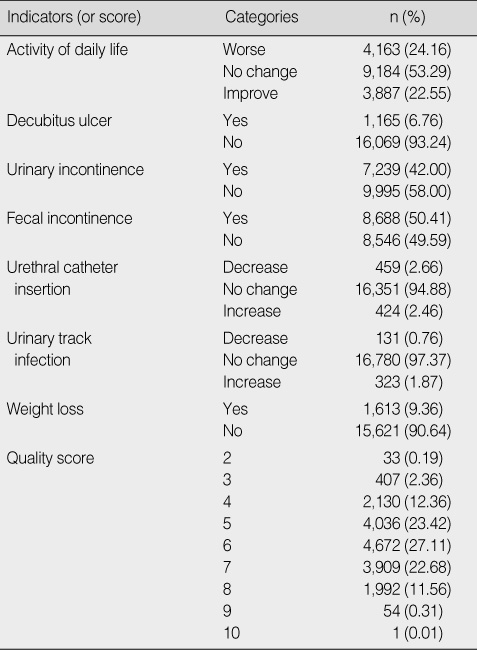
Frequency of Quality Indicators (or score) (N=17,234)
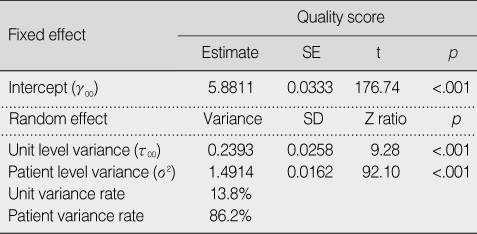
Multilevel Analysis (Empty Model)
Mutilevel Analysis (Patient Level and Unit Level)
Table 1
Characteristics of Organizational Factors (N=253)
Table 2
Characteristics of Patients (N=17,234)
*Multiple responses. MMSE-K=Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination; K-MMSE=Korean Mini-Mental State Examination.
Table 3
Frequency of Quality Indicators (or score) (N=17,234)
Table 4
Multilevel Analysis (Empty Model)
Table 5
Mutilevel Analysis (Patient Level and Unit Level)
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

